MSK2_ELBOW FOR DUMMIES
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SHAKABOOM
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Functional Range of elbow?
30° - 130° flex & extend, 100° of forearm rotation,
equally divided between pronation and supination.
Type of Joint → Humeroulnar
FLEX & EXT
modified hinge
Convex : trochlea
Concave: ulna
Type of Joint → Humeroradial?
flex,ext, pronate & supinate
Modified hinge pivot
Convex : capitulum
Concave: radial head
Provides medial support to the elbow against valgus stresses and limiting end- range elbow extension.
Medial Collateral Ligament
Provides stability to the lateral aspect of the elbow against varus and supination forces
Lateral Collateral Ligament
prevents posterior translation of radial head
Type of Joint → Proximal RadioUlnar Jt?
pronate & supinate
Uniaxial Pivot
Convex : radial notch
Concave: radial head
This generates the greatest force of all the muscles that cross the elbow and its sole function is flexion of the elbow.
Brachialis
Brachialis MOINA
Origin | Distal half of anterior surface of humerus |
Insertion | Coronoid process of the ulna; Tuberosity of ulna |
Innervation | Musculocutaneous nerve (C5,C6); Radial nerve (C7) |
Acts as supinator of forearm & most effective flexor of elbow at 80°-100° of flex
Biceps Brachii
Primary elbow flexor especially during rapid movements against high resistance and acts as a pronator when the forearm
Brachioradialis
3 Muscle Supinators
Supinator
Biceps Brachii ( at 90°)
Brachioradialis
3 Muscle Pronators
Pronator Teres
Pronator Quadratus ( most active)
Most common sites for compression of the ulnar nerve in the elbow
Cubital tunnel & 2 heads of FCU
Most common sites for compression of the radial nerve in the elbow
under ECRB , Arcade of Froshe & distal edge of the supinator muscle
Most common sites for compression of the medial nerve in the elbow
between heads of pronator teres
under ligament of Struthers
Bicipital aponeurosis/deep to FDS
Joint Hypomobility: Nonoperative Management →
RA
JRA
Degenerative Jt Disease
acute joint reactions after trauma,
Dislocations
Fractures
Joint Hypomobility: Nonoperative Management
Acute Stage
(+) joint effusion
muscle spasm
Pain restrict elbow & Shoulder motion
No pain at rest.
Identify which is wrong
+) joint effusion
muscle guarding
pain restrict elbow motion
pain at rest.
Joint Hypomobility: Nonoperative Management
Subacute & Chronic
(+) capsular pattern
Elbow extension > flexion
Bony end feel & INC joint play
pronation and supination restricted in OA
Pain on overpressure at the PRU jt (Arthritis)
Identify which is wrong
(+) capsular pattern
Elbow flexion > extension
firm end feel & DEC joint play
pronation and supination restricted in Arthritis
Pain on overpressure at the DRU jt (Arthritis)
Common Activity Limitations & Participation Restrictions
Difficulty turning a doorknob or key in the ignition
Difficulty or pain with pushing and pulling activities, such as opening and closing doors
Restricted hand-to-mouth activities for eating and drink-ing and hand-to-head activities for personal grooming and using a telephone
Difficulty or pain when pushing up from a chair s Inability to carry objects with a straight arm
Limited reach
Joint Hypomobility: Protection Phase ( READ)
Educate pt
inform length of signs & symptoms
teach methods of jt protection & modify ADLs
avoid excessive fatigue
Reduce effect of immobilization
Frequent periods of controlled movement within pain free range should be performed
complete immob can lead to joint hypomobility, contractures, and limited motion.
Gentle Gr 1-2 joint oscillation/ distraction to inhibit pain & move synovial fluid for nutrition
Maintain Soft Tissue & Joint Mobility
PROM/AAROM within limits of pain including flex/ext & pro/sup
Multiple angle Isoms for all elbow muscles motion in pain free position
Maintain Integrity & Function of related areas
Shoulder,wrist, & hand ROM should be done with tolerance
if edema develops, elevate arm above heart level
Consider retrograde massage
Joint Hypomobility: Protection Phase
6 Things You should do in this phase:
Educate
Gentle Gr 1-2 joint oscillation/ distraction
PROM/AAROM within limits of pain (all motions)
Multiple angle Isoms within limits of pain (all motions)
Shoulder,wrist, & hand ROM
Elevate arm if (+) edema
retrograde massage
Precautions following Traumatic Injury to Elbow
Heterotopic ossification
(+) inflammation
Malunion can happen , preventing full ROM
A bony block end feel → refer to doc
X ray a must
No Stretching or Joint Mob
Alam mo na yan
Joint Hypomobility: Controlled Motion Phase
How to Reduce a pushed elbow?
Apply a distal traction to the radius to reposition the radial head.
If chronic, repetitive stretching with sustained grade III distal traction to the radius is necessary
Pushed Elbow
MOI:
radial head is pushed proximally in the annular ligament and impinges against the capitulum
Accompanied by: ____ fx or _____ fx
Limited elbow _______(3) & wrist ___
MOI: FOOSH
radial head is pushed proximally in the annular ligament and impinges against the capitulum
Colles’ fracture or scaphoid fx
Limited elbow ext/flex/pronation & wrist flex
Pulled Elbow
______ subluxation of the radius
forceful ___ on the hand
Head of the radius is unable to glide proximally in the annular ligament when supination is attempted = restricted _____
(+) patient guarding
Distal subluxation of the radius
forceful pull on the hand
restricted pronation
(+) patient guarding
Joint Hypomobility: Controlled Motion Phase
How to Reduce a pulled elbow?
High-velocity thrust of the radial head with supination
Joint Hypomobility: Controlled Motion Phase
Increase Soft Tissue and Joint Mobility
Passive joint mobilization techniques
Manipulate Pushed Elbow
Manipulate Pulled Elbow
Manual & Self Stretching
Light cuff weight placed on distal forearm with a low-intensity, long-duration stretch (alternative)
Improve Joint Tracking of the Elbow
radial glide in pain free elbow flex/ext or grip
Improve Muscle Performance and Functional Abilities
Initiate active and low-load resistance exercises in open- and closed-chain
Improves muscle endurance,strength
progress toward functional activities
Joint Hypomobility: Controlled Motion Phase
5 Things You should do in this phase:
Passive joint mobilization techniques.
Manipulation reducing pushed/pulled elbow (optional)
Manual stretching and self-stretching
MWM
Initiate active and low-load resistance exercises in open → closed-chain
Joint Hypomobility: Return to Function Phase
Improve Muscle Performance
Progress strengthening exercises
Restore Functional Mobility of Joints and Soft Tissues
Use manual or mechanical stretching and joint mobilization techniques.
Promote Joint Protection
Modify high-load activities to minimize deforming stresses on the involved joints.
:))))))
Joint Hypomobility: Return to Function Phase
4 Things to do
Resistance Exercises Progression
Manual or Mechanical stretching
Vigorous Joint mobilization techniques.
Modify High-load activities/ Teach proper body mechanics
Progression of Resistance Exercises
Setting → Isometrics → Isotonics → Eccentrics
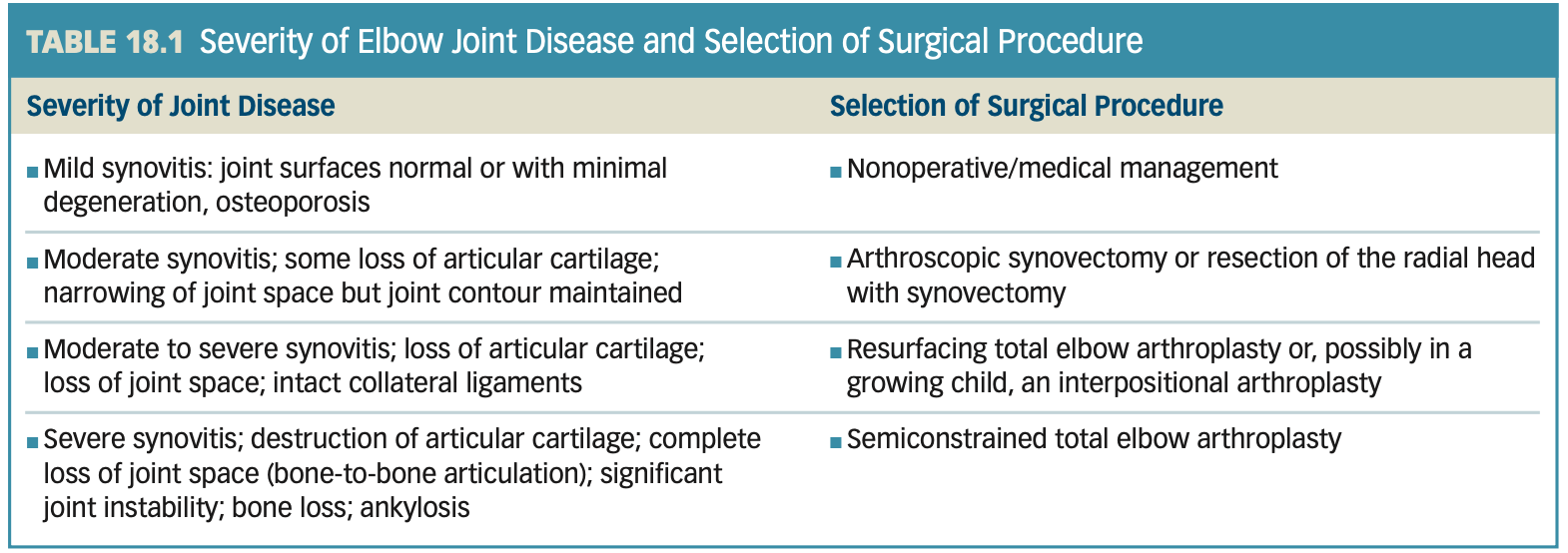
Joint Surgery and Postoperative Management
Most common fracture in the elbow region is
fracture of the head and neck of the radius.
FOOSH c forearm pronated
Joint Surgery and Postoperative Management
basahin mo na lang gg talaga
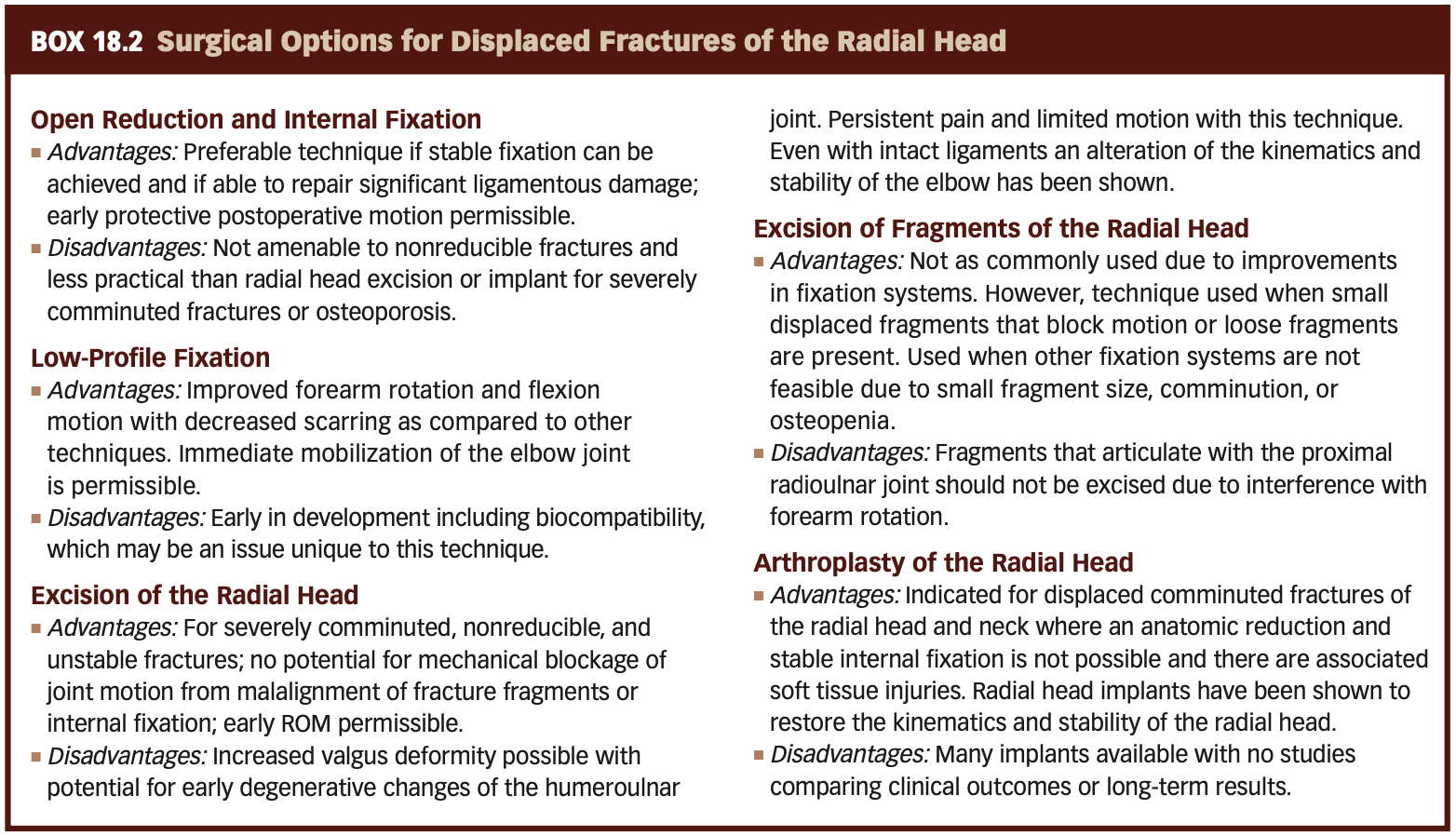
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty
Indications:
Severely comminuted fracture or fracture-dislocations of the head or neck of the radius that cannot be reconstructed
Chronic synovitis and mild deterioration of the articular surfaces associated with arthritis of the HR and proximal RU joints
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty
This approach divides the radial collateral and annular ligaments while preserving the radial ulnar collateral ligament.
Extensor digitorum splitting approach
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty
Approach that expose the joint between the ECU and anconeus muscles
Kocher aproach/ posterolateral
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty
Approach where there is incision between the extensor digitorum and the extensor carpi radialis bravis
Kaplan
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty
Muscle Graft used?
Palmaris Longus
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty Complications
Damage to what nerve?
Post Op complications?
posterior interosseous nerve
Delayed wound closure, infection, limited ROM of the elbow and/or forearm, radial tunnel syndrome, cubital laxity, persistent pain, and a sense of instability.
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty: Immobilization
Arm is immobilized in a long arm orthosis or a hinged protective orthosis with an extension block for _____ wks
Arm positioned at _____ ° with forearm in _____ and the wrist in _____
Non hinged orthosis may be removed during ROM exercises but ibabalik sa gabi
Immobilized in an orthosis with an extension block for up to 3 weeks
positioned at 45° to 90° with the forearm in mid pronation and the wrist in neutral
Non hinged orthosis may be removed during ROM exercises but ibabalik sa gabi
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty: Max Protect Phase
Focus on pt education
Manage Edema
elevate arm above heart & wear compression sleeve
wrist above the elbow; elbow above the shoulder
Mobility of Uninvolved Jts
AROM of the shoulder, wrist, and hand immediately after surgery.
Mobility of Elbow & Forearm
Initiate gentle protected ROM within 2 to 3 days postoperatively.
Self ROM within pain free limits
Active ROM is generally allowed within 1 week postoperatively and begins no longer than 3 weeks
Minimize Atrophy
Submaximal, pain-free, multiple- angle isometric exercises of elbow and forearm musculature.
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty: Max Protect Phase
Inflammatory Phase extends for first ______
2-3 wks after surgery
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty: Max Protect Phase
5 Things to do?
PT educ (wound care)
Manage Edema
wrist above elbow; elbow above shoulder
AROM of the shoulder, wrist, and hand immediately after surgery.
Gentle protected ROM within 2 to 3 days postoperatively within pain free limits
AROM after 1-3 wks
Submaximal, pain-free, multiple- angle isometric exercises of elbow & Forearm
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty: Mod & Min Protect Phase
Wound healing should be satisfactory & Elbow AROM is pain free ~ ________
restore functional ROM or nearly full ROM
2-3 wks until 8 wks
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty: Mod & Min Protect Phase
INC ROM
Gentle (low-intensity, prolonged stretch) manual stretch-
ing, hold-relax techniques, or self-stretching
Grade II joint mobilization techniques → grade III mobilizations once healing has occured
Improve functional strength and muscular endurance.
Low-load (pain-free) resistance exercises (maximum
1 to 2 lb), emphasizing high repetitions
Initiate grip and pinch resistance exercises
Use of the postsurgical upper extremity for light activi-
ties of daily living (ADLs)
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty: Mod & Min Protect Phase
Things to do?
Gentle (low-intensity, prolonged stretch) manual stretching, hold-relax techniques, or self-stretching
Grade II joint mobilization techniques → grade III mobilizations
Low-load (pain-free) 1-2lb resistance exercises only
Initiate grip and pinch resistance exercises
Use of the postsurgical upper extremity for light ADLs
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty: Min - No Protect Phase
Ranges from how many months
2-6 months
Radial Head Excision or Arthroplasty: Min - No Protect Phase
5 Things to do
Grade 3 → 4 joint mob c manual stretching and hold-relax
techniques at end ROM.
Employ radial (lateral) and ulnar (medial) gapping
techniques
Orthotic intervention by 8 wks
Progress to Mechanical Resistance Exercise for the whole UE
Patient educ on return to functional activities
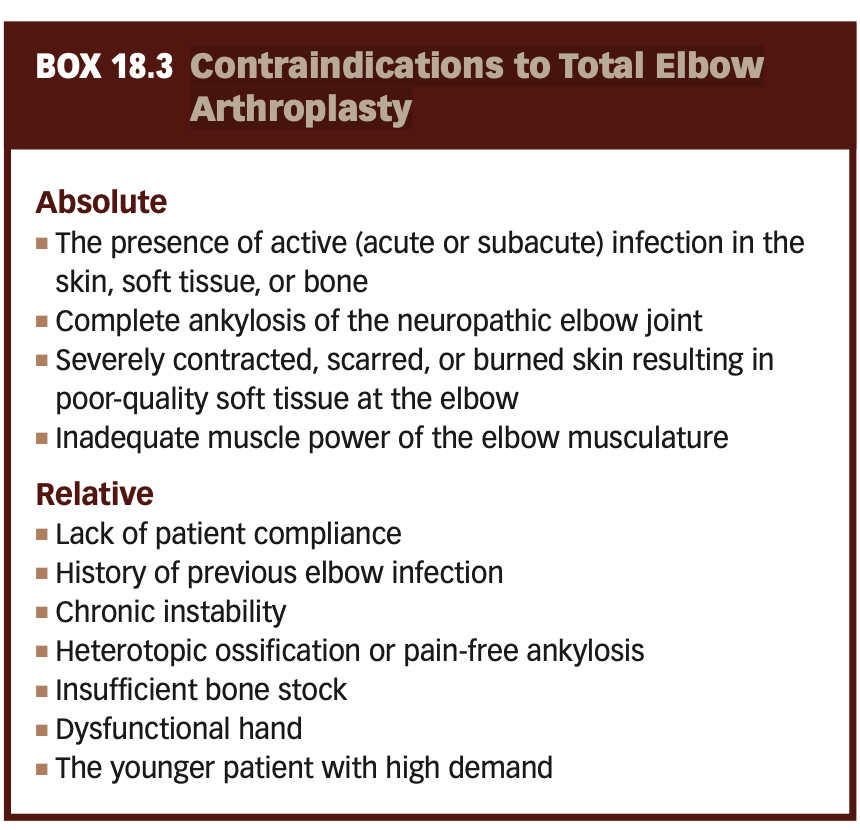
Contraindications to Total Elbow Arthroplasty
LEL
Total Elbow Arthroplasty
linked (articulated)
Linked designs derive inherent stability from one or two pins, which couple the humeral and ulnar components
Unlinked (nonarticulated)
artificial humeral and ulnar components of the joint are not mechanically connected to each other
Triceps Reflecting approach
distal attachment of the triceps is detached and reflected laterally
Triceps Sparing approach
preserves the attachment of the triceps tendon on the olecranon but makes insertion of the implants more technically challenging
Postoperative Management: TEA
Immobilization
triceps-reflecting approach: full or almost full elbow extension
extended position is also indicated if symptoms of ulnar neuropathy are present
Duration
1-2 days only unless several weeks if may RA
If delayed wound healing → maintain in extension for 10 to 14 days postoperatively
Exercise Progression
rehabilitation is RAPID when triceps-sparing approach is used to insert a linked replacement
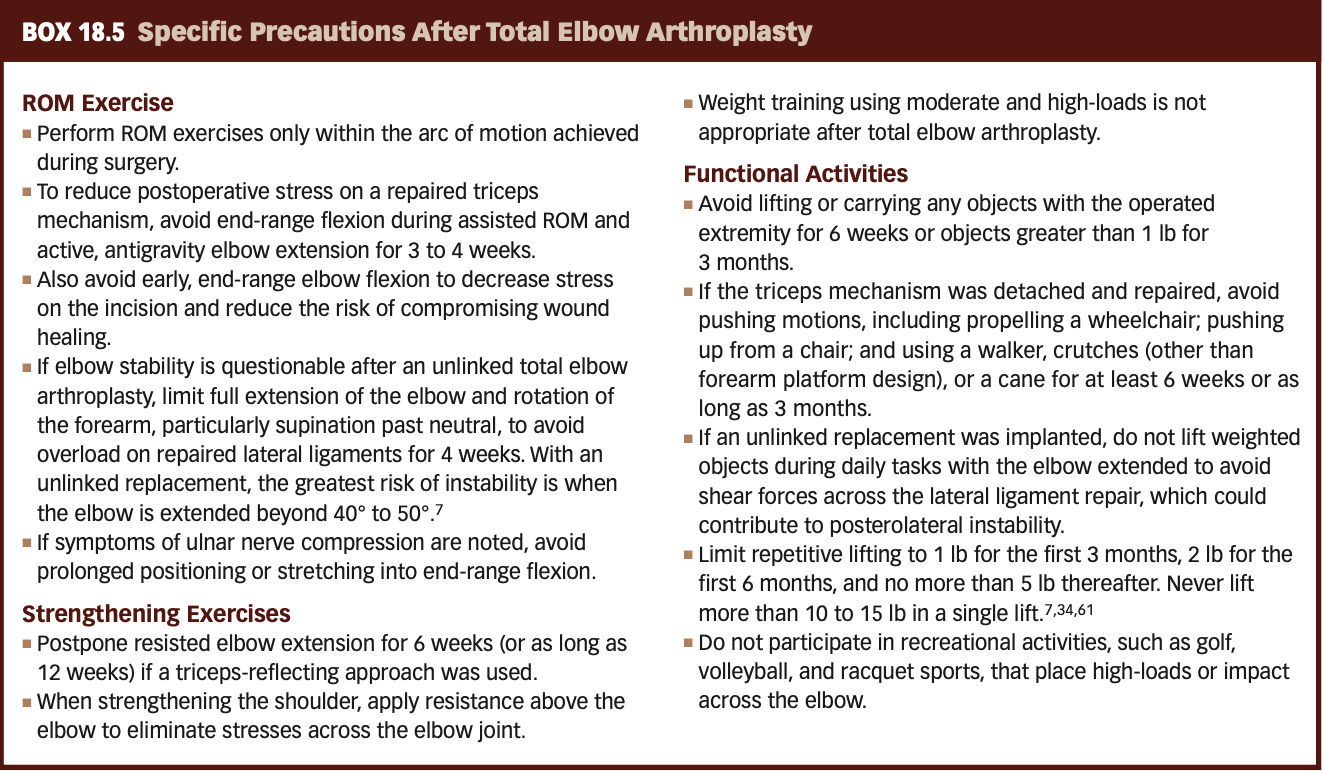
Specific Precautions After Total Elbow Arthroplasty
Analysis of Three Potential Complications After Total Elbow Arthroplasty
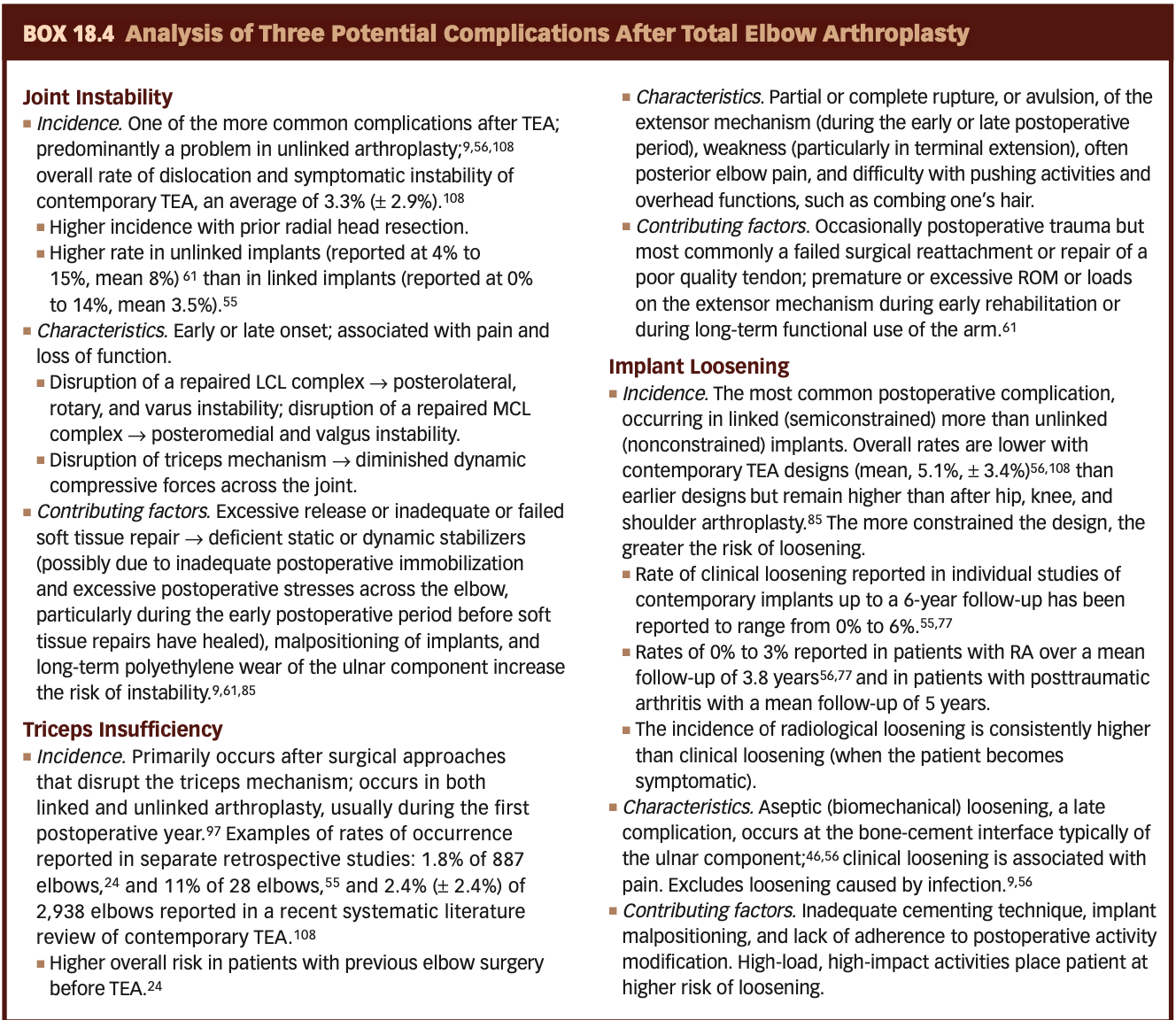
POST OP TEA: Maximum Protection Phase
Extends approx __weeks
AAROM tolerated intiated within ____ days after linked TEA
If significant pre-op instability, ROM is delayed for ____ days
Extends approx 4 weeks
AAROM tolerated intiated within 2-3 days after linked TEA
If significant pre-op instability, ROM is delayed for 7-10days
POST OP TEA: Maximum Protection Phase
5 Things to do:
AROM of shoulder, wrist & hand (Essential for RA/JRA patients)
Gentle self-assisted elbow all motions with the elbow comfortably flexed and the forearm in mid-position → AROM
Gentle, pain-free muscle-setting exercises of elbow
Low-intensity, isometric resistance exercises of the shoulder, wrist, and hand.
Use of the hand for light functional activities as early as 1 to 2 weeks if linked replacement but several weeks if Unlked
POST OP TEA: Maximum Protection Phase
If the triceps mechanism was reflected and repaired, limit assisted flexion to _____ for ___ wks
If the triceps mechanism was reflected and repaired, limit assisted flexion to 90° to 100° for the first 3 to 4 weeks
POST OP TEA: Maximum Protection Phase
Perform active elbow flexion/extension in ________
seated or standing
T/F:
If a linked replacement was implanted using a triceps- sparing approach, AROM in all planes of motion is permissible immediately.
True
POST OP TEA: Maximum Protection Phase
Use of the hand for light functional activities as early as ____ weeks postoperatively if a linked replacement was inserted but _____ weeks later after an unlinked TEA.
1-2 wks if linked
several weeks if unlinked
POST OP TEA: Moderate and Minimum Protection Phases
Starts at ____ weeks postoperatively (sot tissues are healed to withstand increasing stresses)
By ____ weeks, barring complications, only minimum protection is necessary
Full level of activity with ongoing lifting restrictions varies from _ weeks → _to _ months
Starts at 4 to 6 weeks postoperatively (sot tissues are healed to withstand increasing stresses)
By 12 weeks, barring complications, only minimum protection is necessary
Full level of activity with ongoing lifting restrictions varies from 6 weeks to 3 to 4 months
POST OP TEA: Moderate and Minimum Protection Phases
Permanent lifting restriction of _ pounds.
Strength and muscular endurance usually continue to improve up to ____ months
Emphasize end-range _____ before end- range ____ to protect the posterior capsule and the triceps mechanism.
5lb restriction
6-12months
End range extension → end range flexion
POST OP TEA: Moderate and Minimum Protection Phases
5 Things to do:
Low-intensity, manual self-stretching / Low load Long duration orthotic intervention
Resisted, multiple-angle isometric exercises at 5 weeks
Light ADLs (initially <1 lb of weight) performed with the arm positioned along the side of the trunk and the elbow flexed
Lifting excercises & functional activities limited to 1lb → + 1 lb 3mos → single lift <10-15lb
Low-load, closed-chain activities, such as wall push-ups, after 6 weeks or later
POST OP TEA: Moderate and Minimum Protection Phases
Start Resisted, multiple-angle isometric exercises at __ weeks
If a triceps-reflecting approach was used, include elbow ____ activities → elbow _____ → _____ chain motions
5 wks
elbow flexion activities → elbow extension → close chain motions
Myositiis Ossificans is most commonly located at the _______ aspect of the elbow
posteromedial aspect of the elbow
distal brachialis muscle is tender
Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy (Tennis Elbow)
Pain over the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, primarily with gripping activities.
Aggravated by Activities requiring firm wrist stability
backhand stroke in tennis
repetitive work tasks that require repeated wrist extension
computer work or pulling weeds in a garden
Primary Structure involved → ORIGIN OF ECRB AND ED
Do THIS para maalala:
pain with resisted wrist extension performed with the elbow extended,
pain with resisted middle finger extension
pain with passive wrist flexion with the elbow extended and forearm pronated.
Medial Elbow Tendinopathy (Golfer’s Elbow)
Repetitive movements into wrist flexion
swinging a golf club
pitching a ball
work-related grasping and lifting heavy objects.
Concomitant ulnar neuropathy may be associated
DO THIS
pain with resisted wrist flexion performed with the elbow extended
pain with passive wrist extension performed with the elbow extended.
Common Impairments of Structure and Function
Gradually increasing pain in the elbow region after excessive activity of the wrist and hand
Pain when the involved muscle is stretched or when it con- tracts against resistance
Decreased muscle strength and endurance for the demand
Decreased grip strength, limited by pain
Proximal weakness of shoulder and scapular musculature
Decreased mobility of the lower cervical and upper thoracic spine
Tenderness with palpation over the lateral or medial epi-
condyle or tendon origin
Common Activity Limitations and Participation Restrictions
Inability to participate in provoking activities, such as racket sports, throwing, or golf.
Difficulty with repetitive forearm/wrist tasks, such as sort- ing or assembling small parts, typing on a keyboard or using a computer mouse, gripping activities, using a ham- mer, turning a screwdriver, shuffling papers, or playing a percussion instrument.
Nonoperative Management of Overuse Syndromes: Protection Phase
7 Things to do:
Rest/ Immob in wrist extension/ Cryotherapy
Cross Friction Massage/ Massage
Neuromob
Gentle hold-relax techniques to either the wrist extensor or flexor muscles
Passive Stretching for 20-30 secs & few reps
ROM to all joints
Shoulder and scapular stabilization exercises with resistance applied proximal to the elbow.
Nonoperative Management of Overuse Syndromes: Protection Phase
Begin with the muscles in the shortened position with the elbow flexed and wrist either in extension or flexion → lengthening the muscle across the elbow by increasing elbow extension
In short???
Stretch to flexion → extension
Nonoperative Management of Overuse Syndromes: Protection Phase
To stretch the wrist extensors,
extend the elbow
pronate the forearm
flex and ulnarly deviate the wrist
flex the fingers
gently press on the back of the hand until a pain-free stretch is felt in the forearm.
DO IT
To stretch the wrist flexors
extend the elbow
supinate the forearm
extend and radially deviate the wrist
extend the fingers
gently press on the palm of the hand until a pain-free stretch is felt in the forearm.
DO IT
Overuse Syndromes : Controlled Motion and Return to Function Phases
7 Things to do?
Manual stretching ( agonist contract & hold relax)
Self stretch
Massage
MWM & Self MWM
Dynamic Resistance
low intensity c multiple reps
progress to eccentric
Fasters speeds → Higher loads
Pylometrics
Activity Modifications
Overuse Syndromes : Controlled Motion and Return to Function Phases
MWM parameters?
3 sets ; 10 reps (lateral glide always)
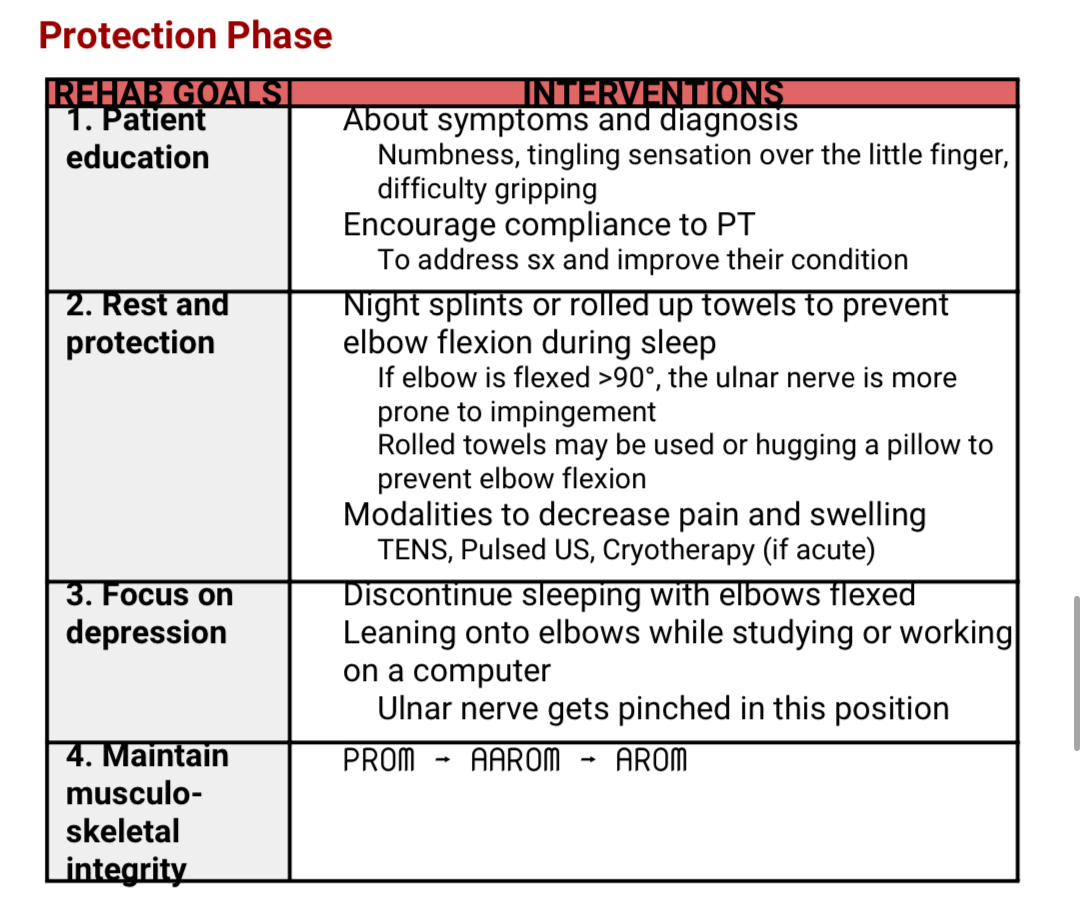
CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME:PROTECT PHASE
CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME: MOD & MIN PHASE
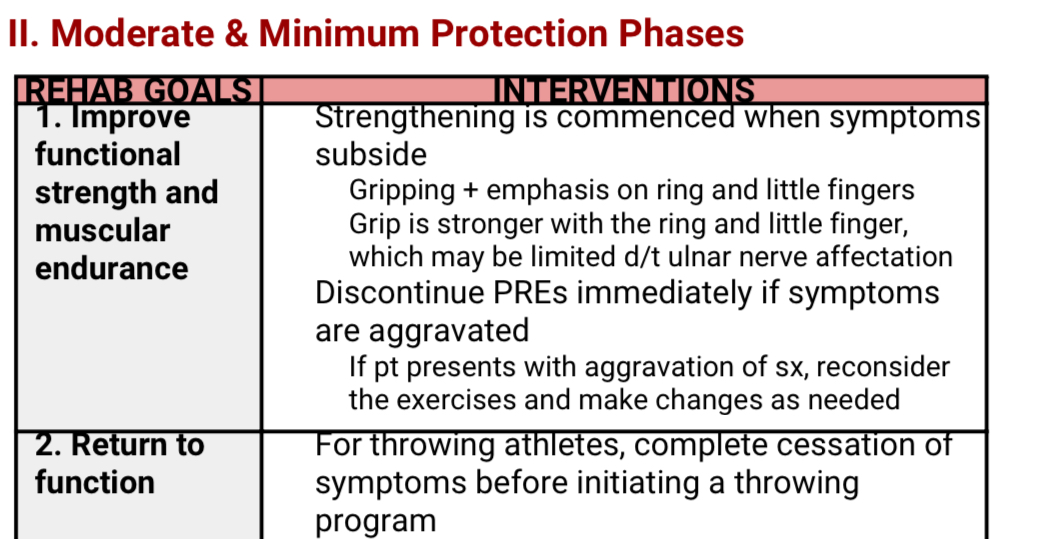

PNI: ACUTE PHASE
PNI: RECOVERY PHASE


PNI: CHRONIC PHASE
PERIPHERAL NERVE MOBILIZATION TECHNIQUES
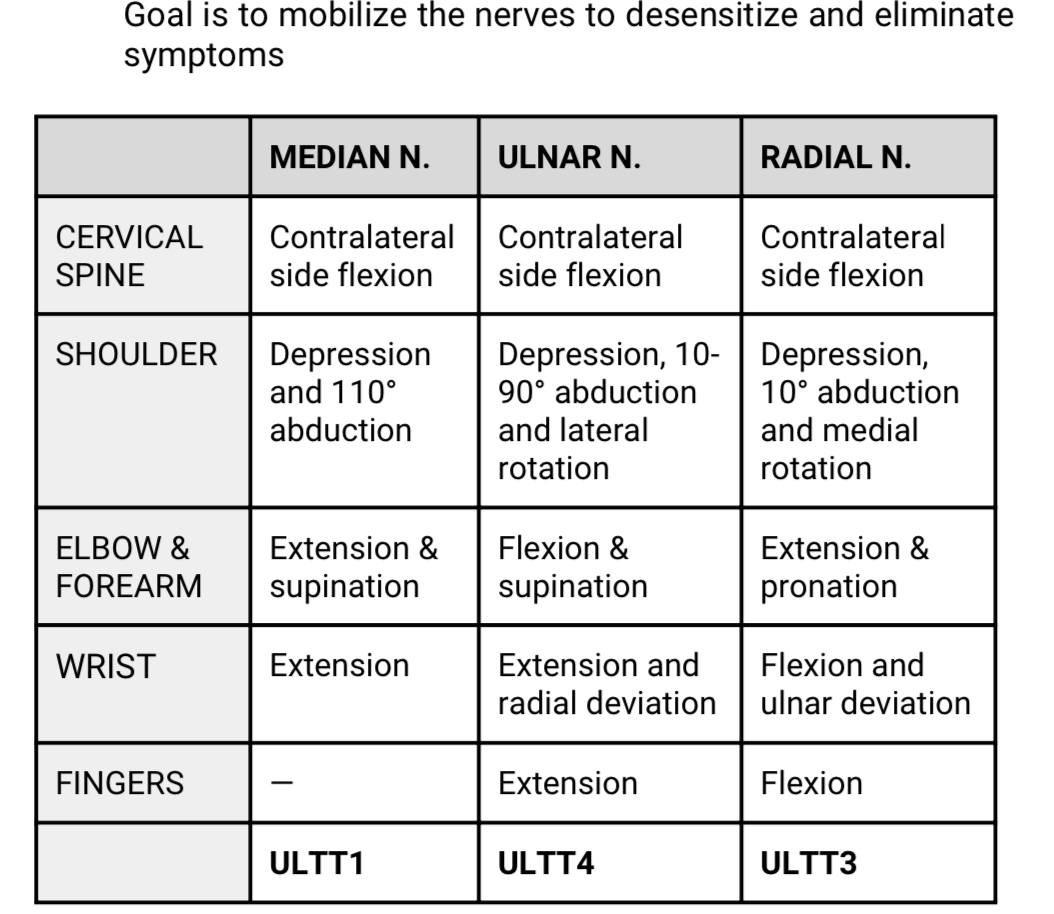
WAZZUP MAH _________?
Sigma boi
