DNA Replication and Transcription in Prokaryotes
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
INITIATION
The first step in DNA replication where the process begins.
ELONGATION
The stage in DNA replication where new DNA strands are synthesized.
TERMINATION
The final step in DNA replication where the process is completed.
Ori-C
The origin/start of replication in bacterial DNA.
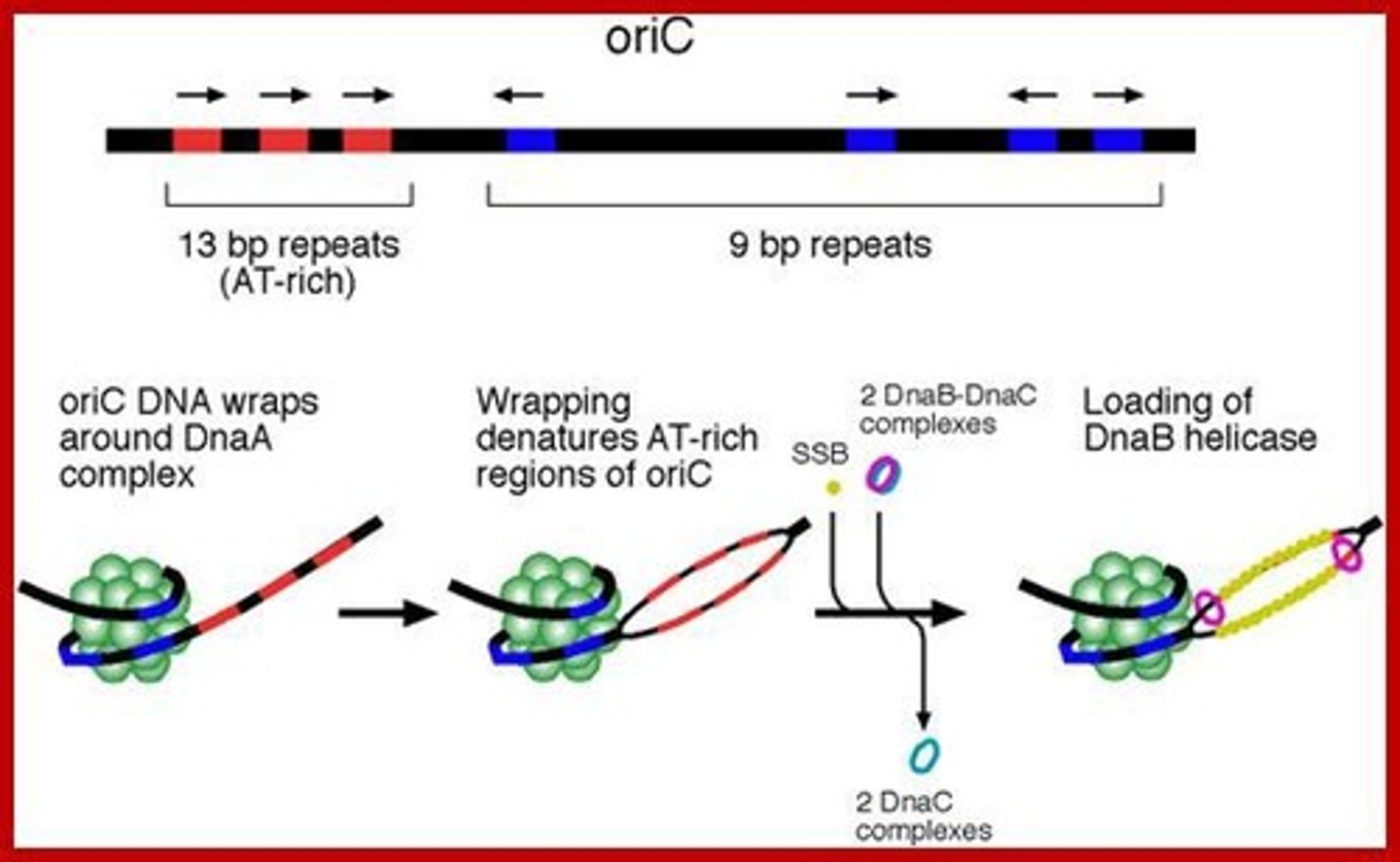
DnaA
A protein that initiates DNA replication.
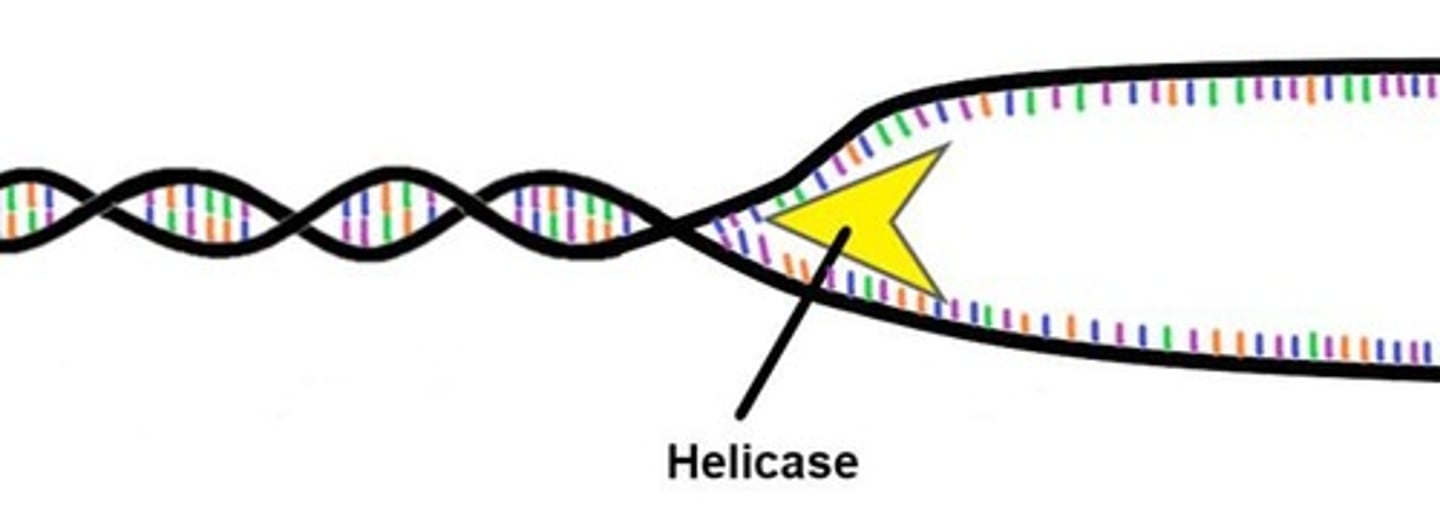
DnaB
Helicase that unzips DNA during replication.
DnaC
Helicase loader that assists DnaB.
Dna gyrase
An enzyme that releases pressure on DNA, functioning as a topoisomerase.
SSB
Single-strand binding protein that prevents reannealing of DNA strands.
DnaG
Primase that adds RNA primers to the DNA strands.
Dna Pol III
The main DNA polymerase that synthesizes new DNA by adding nucleotides from the 5' to 3' end.
Dna Pol I & II
DNA polymerases involved in DNA repair.
Rnase H
An enzyme that removes RNA primers from the newly synthesized DNA.
DNA ligase
An enzyme that ligates pieces of DNA together.
Tus
A protein that forms a complex with the ter site to stop DNA replication.
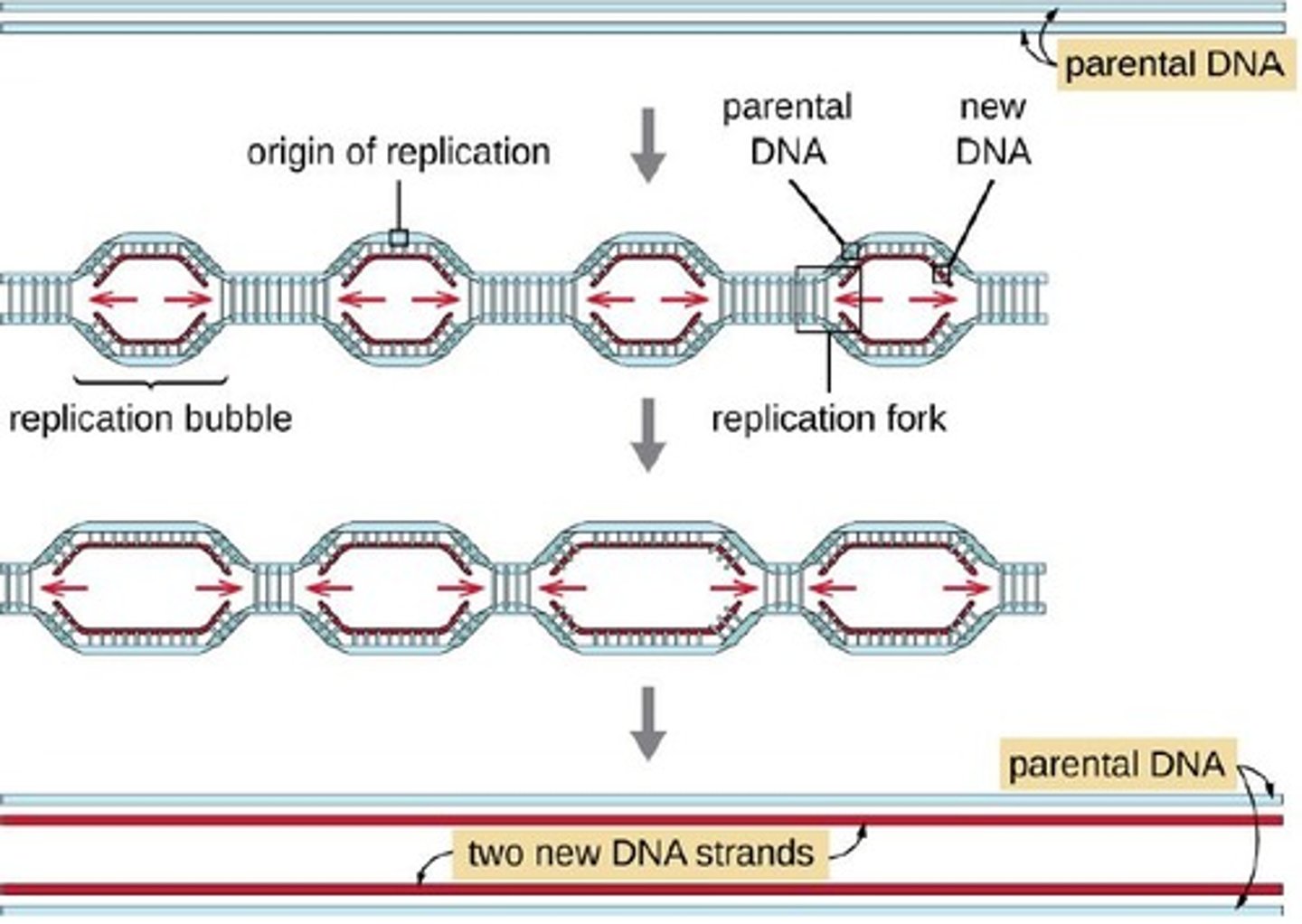
Bidirectional replication
A type of DNA replication where two replication forks move in opposite directions.
Semiconservative replication
A method of DNA replication where each new DNA molecule consists of one old strand and one new strand.
DnaA-ATP complexes
: Complexes that bind to 9-bp repeats in oriC to initiate DNA replication.
Replication bubble
A structure that forms after initiation of replication, containing two replication forks.
Leading strand
The strand of DNA that is synthesized continuously during replication.
Lagging strand
The strand of DNA that is synthesized discontinuously during replication.
Catenane link
A structure formed when replisomes meet and fall apart at the end of replication.
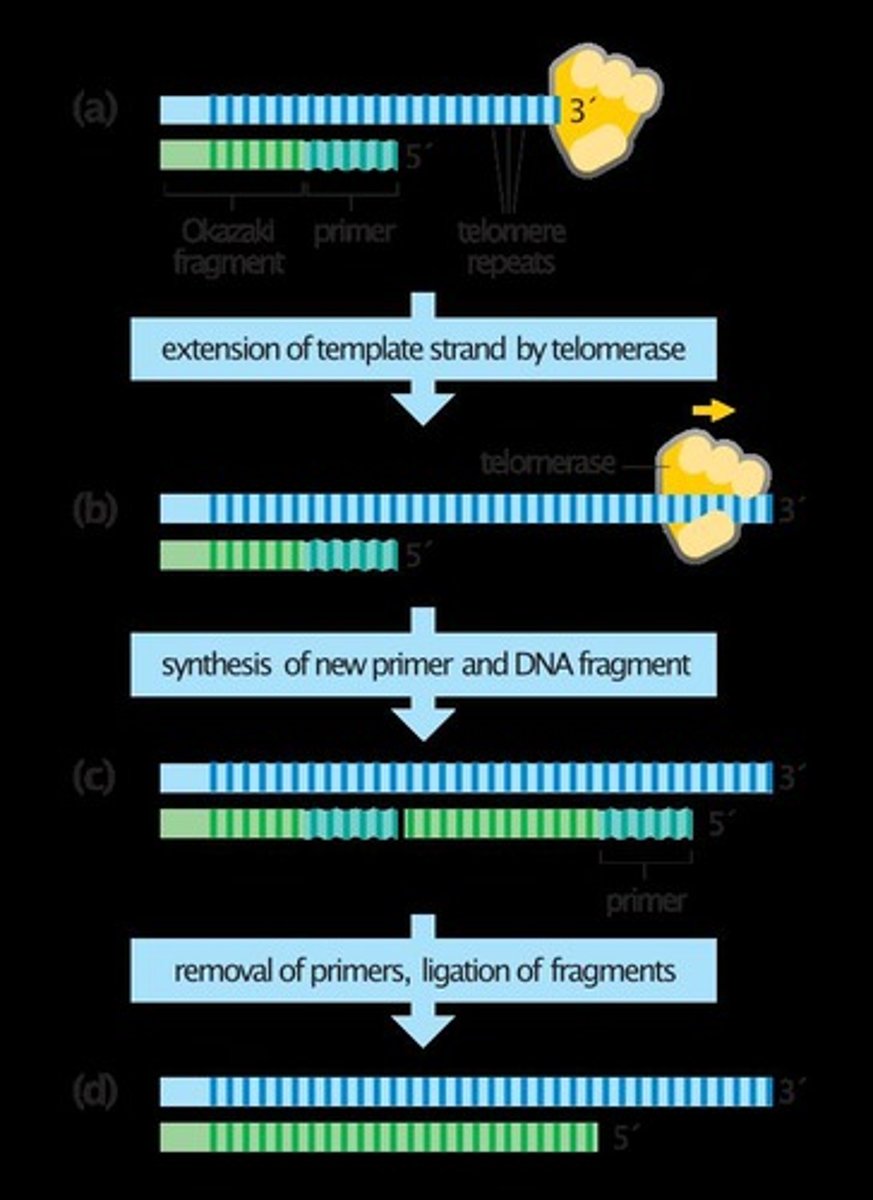
End-replication problem
The issue that arises in linear chromosomes where the lagging strand cannot be fully replicated.
Telomere
The end of a linear chromosome that protects it from deterioration.
Telomerase
An enzyme that extends the 3' end of a chromosome to allow primase to add a primer.
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an individual organism
Phenotype
The set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment.
Nucleoid
The region in a prokaryotic cell where the genetic material is located.
Cell receptors
Proteins that can detect necessary extracellular molecules (ligands).
Cistron
A DNA segment that codes for a single polypeptide.
Operon
A polycistronic unit of gene expression that includes multiple genes under the control of a single promoter.
Regulon
A collection of operons and genes with a unified biochemical purpose under control of a regulatory protein/regulator.
Monocistronic
A type of mRNA that codes for a single protein.
Polycistronic
A type of mRNA that codes for multiple proteins.
Transcription
The process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
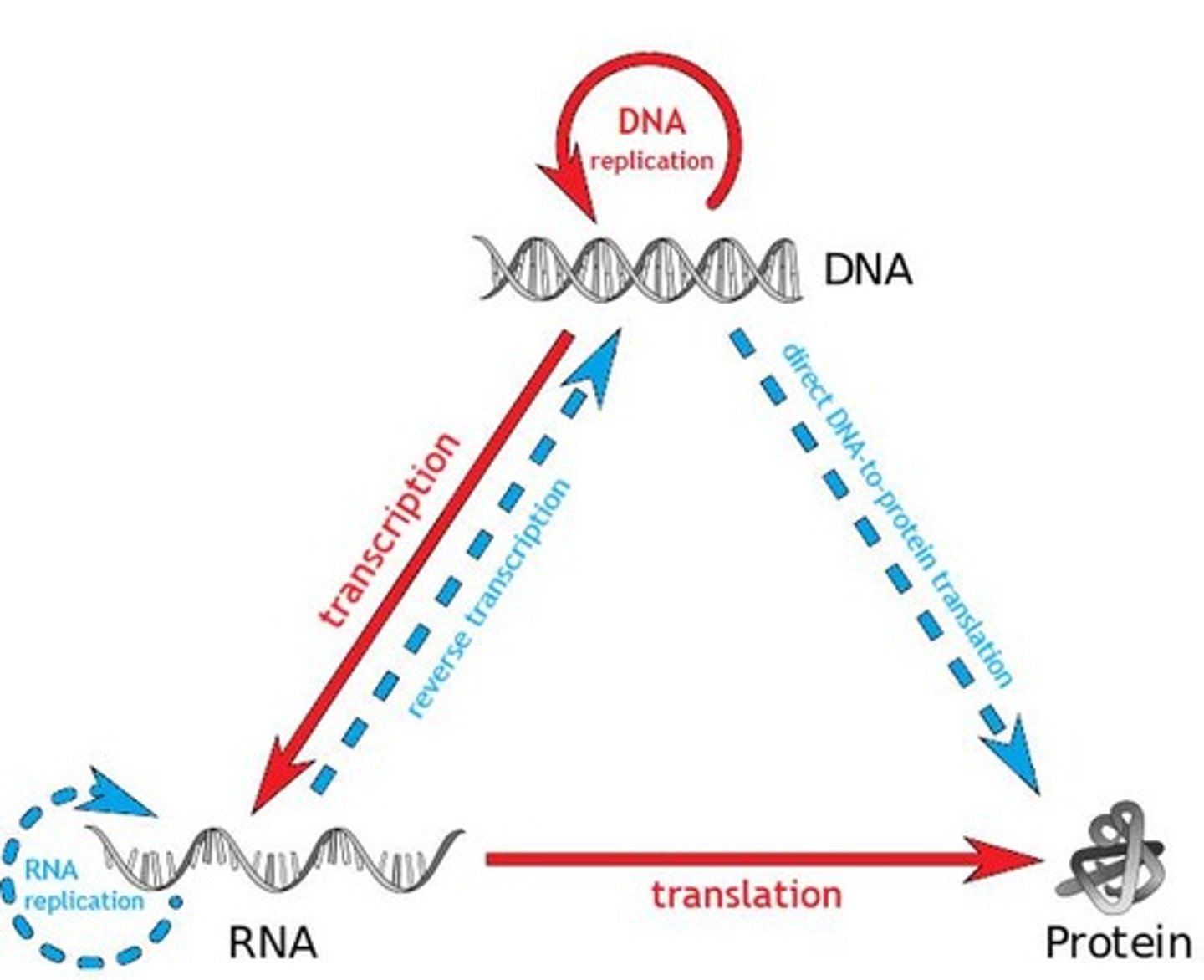
Translation
The process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
Promoter
A sequence of DNA where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
Sigma factor
A protein that binds to specific promoters to assist RNA polymerase in initiating transcription.
Template strand
The strand of DNA that RNA polymerase uses to synthesize mRNA.
Coding strand
The DNA strand that has the same sequence as the mRNA (except for thymine being replaced by uracil).
Transcription bubble
The region where the DNA strands are unwound and RNA synthesis occurs.
Rho-independent termination
A type of transcription termination that occurs without the aid of the rho protein.
Rho-dependent termination
A type of transcription termination that requires the rho protein to dissociate RNA polymerase from the DNA.
Downstream
Nucleotides after a specific site in DNA.
Upstream
Nucleotides before a specific site in DNA.
Protein synthesis from mRNA
The process by which proteins are synthesized from messenger RNA.
Reading frame
Each codon after the start is translated in a systematic fashion until a stop codon.
Codon
3 ribonucleotides that correspond to 1 amino acid.
Stop codons
3 different codons that signal the ribosome to stop translation.
Start codon
The codon that initiates translation.
Ribosome
The molecular machine that synthesizes proteins by reading mRNA.
30S subunit
The ribosomal subunit that binds the Shine-Dalgarno sequence during initiation of translation.
Polycistronic mRNA
An mRNA that encodes multiple proteins and forms a polyribosome structure.
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs)
Molecules that bind codons via an anticodon and add the corresponding amino acid to the polypeptide chain.
Release factor
A protein that recognizes the stop codon and facilitates the termination of translation.
RNA Polymerases
Three types of RNA polymerases (RNA Pol I, II & III) involved in transcription.
5' cap
A modified guanine nucleotide added to the 5' end of mRNA, signaling for exportation.
3' poly-A tail
A string of adenine nucleotides added to the 3' end of mRNA, providing degradation protection.
Pre-mRNA
The initial transcript that contains both exons and introns.
Exons
Segments of pre-mRNA that encode for functional polypeptides.
Introns
Segments of pre-mRNA that do not encode for functional polypeptides.
RNA splicing
The process of removing introns from pre-mRNA.
Alternative splicing
A process where some introns are kept and some exons are removed.
Kozak sequence
A sequence found in most eukaryotic transcripts that includes the start codon.
Shine-Dalgarno sequence
A ribosomal binding site in bacterial mRNA that helps initiate translation.