Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: Muscle System
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Muscle Functions
Initiate and resist movement
Generate heat
Skeletal muscle
Striated (parallel), multinucleate cells attached to the skeleton
Helps with strength and mobility
Types of Muscle movement
Synergistic: muscles working together to create the same movement
Anterior deltoids and triceps help move chest
Antagonistic: muscles opposing each other
Biceps flex forearms, triceps extend forearms
Muscle Ends
Origin: end of muscle attached to bone that doesn’t move during contraction
Insertion: end of muscle attached to bone across a joint
Example: origins not moving on top of shoulder, but bicep insertions connect and move near elbow
Fascicles
Bundle of muscle cells
Fascia
Sheath of connective tissue that surrounds fascicles
Myofibrils
Long, cylindrical, parallel structures in a muscle cell
Comprise the interior
Several myofibrils make up a fascicle, several fascia sheaths comprise a muscle
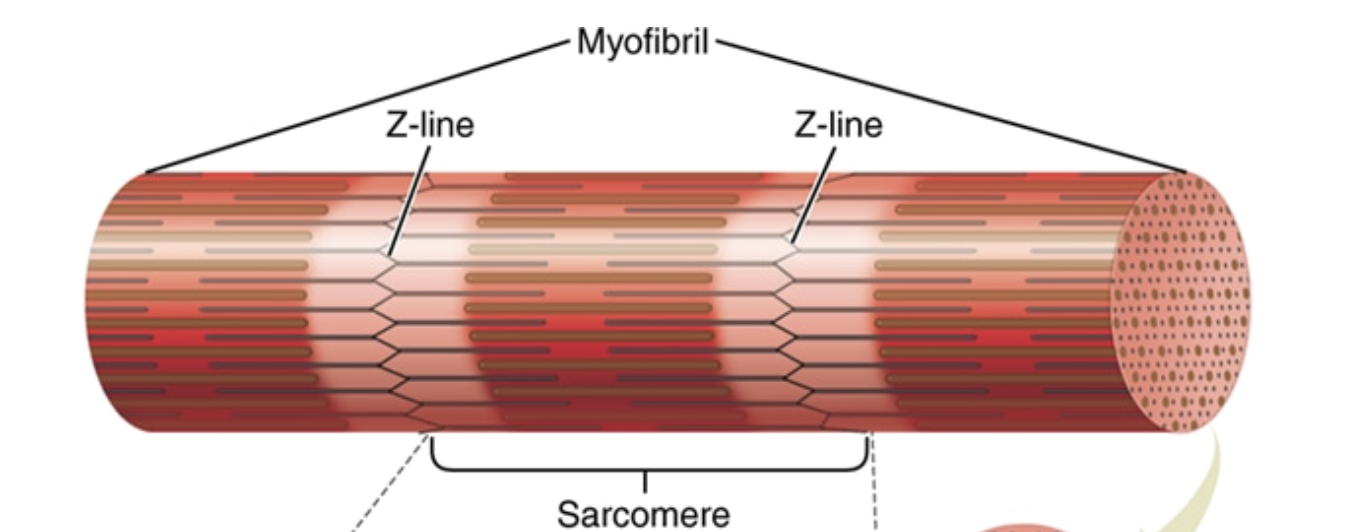
Types of protein filaments
Myosin: contractile protein- thicker filaments
Actin: contractile protein- thinner filaments
Sarcomere (measure from Z-line to Z-line) contracts when the filaments slide closer together
Muscle Contraction Process
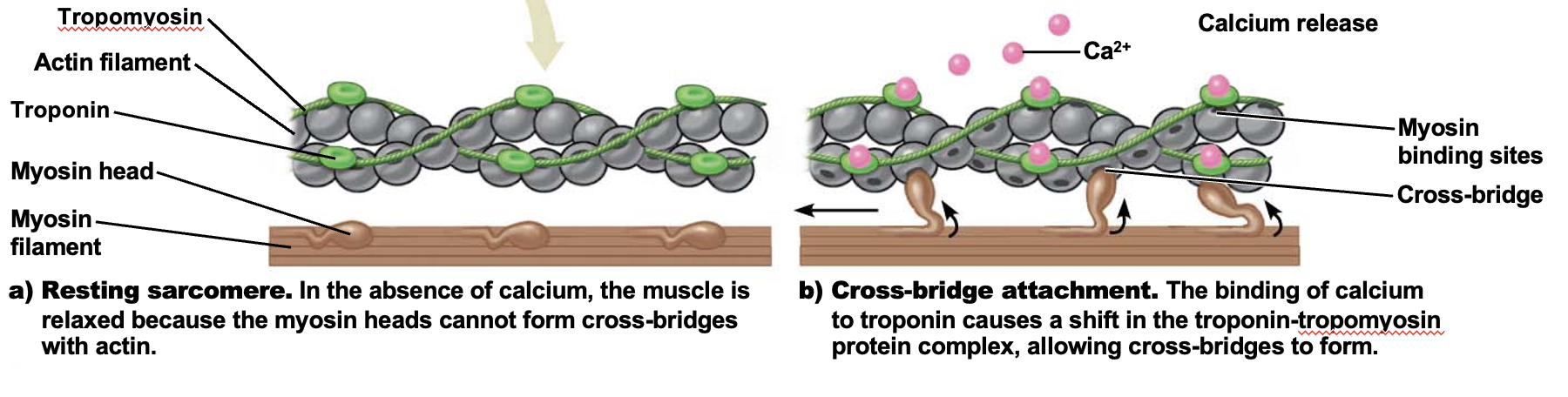
Electrical impulse arrives at the neuromuscular junction, where motor neurons and muscle cells meet
Acetylcholine is released, diffusing across the space and binding to the muscle cell membrane
Acetylcholine binding generates an electrical impulse that travels across all parts of the cell, past the T tubules and into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Sarcoplasmic reticulum: stores calcium ions
T tubules: carry electrical impulse
Calcium ions in the sarcoplasmic reticulum are released
Calcium binds to troponin and tropomyosin, shifting the protein complex, initiating the sliding filament mechanism, where myosin heads make contact with actin filaments, contracting the muscle
Muscle energy
Stored ATP: stored in small quantities, used at first quickly
Stored creatine phosphate: stored three to five times more than ATP, converted quickly to make ATP
Stored glycogen: stored in varying quantities, primarily used in the first 3-5 minutes of exercise
Yields two ATP without oxygen in anaerobic metabolism
36 with aerobic metabolism (yields most ATP of any energy source this way)
Types of muscle contractions
Isotonic contractions: muscles and skeleton move
ie. lifting something
Isometric contractions: muscles contract, skeleton does not
Pushing against an object too heavy to move
Motor unit
Neuron and all muscle cells it controls
All or nothing principle: muscle cells never contract on their own, under complete control of the motor neuron
Muscle tension
Force exerted by contracting muscles
Twitch
Complete cycle of contraction and relaxation in a muscle cell
Slow-twitch fibers: break down ATP and contract slowly
Endurance
Fast-twitch fibers: contract quicker
Short bursts of energy
Use ATP, but also creatine phosphate and anaerobic metabolis
Recruitment
Increasing of a muscle’s force by activating additional motor units
Cardiac muscle
Involuntary
Striated
Have gap junctions at intercalated discs that allow electrical impulses to travel
Contract without nerve signals, but respond to nerve activity
Contracts slower than skeletal muscle, but faster than smooth muscle
Smooth muscle
Involuntary
Not striated
Myosin and actin are not in sarcomeres
Gap junctions allow cells to activate each other, coordinating contraction
Contract without nerve signals, but respond to nerve activity
Contracts more slowly than skeletal and cardiac muscle
Found in blood vessel walls, digestive tract, uterus, and ureter
Muscular dystrophy
Means abnormal growth, several subtypes
Duchenne: a single defective gene causes a lack of a muscle cell protein
Lack of dystrophin protein causes an overflow of calcium into muscle cells, causing damage
Tetanus
Puncture wound to a muscle leads to a bacterial infection
Overproduction of muscle-stimulating toxin, causes lasting contractions
Especially affects jaw and neck muscles, can cause respiratory failure
Cramps
Dehydration and ion imbalances during exercise
Pulled muscles
Excessive stretching of a muscle can cause fibers to tear apart, causing internal bleeding and swelling
Fasciitis
Inflammation of fascia, caused by a strain or tear
Masseter muscle group
Located near cheek
Closes jaw
Orbicularis oris
Located near the front of mouth
Closes lips
Pectoralis major
Top of chest
Draws arm forward and toward the body
Serratus anterior
Below the pec, near the upper abs
Helps raise arm and push
Biceps brachii
Upper arm
Bends forearms at elbow
Rectus abdominus
Ab muscles
Compresses abdomen
External oblique
Next to abs, above hips
Helps lateral rotation of the trunk (side-to-side)
Abductor longus
Upper thigh
Flexes thigh and rotates it laterally
Sartorius
Extends from upper thigh to knee
Bends lower leg at the knee
Quadriceps group
Located just above the knee
Extends leg at the knee
Tibialis anterior
Front of leg, below the knee
Flexes foot toward the knee
Daltoid
Upper shoulder
Raises arm
Trapezius
Middle of upper back
Draws head back
Triceps brachii
Back of upper arm
Straightens forearm at elbow
Latissimus dorsi
Lower back
Draws arm backward and toward body
Gluteus Maximus
Extends thigh
Hamstring group
Bends knee
Back of upper leg
Gastrocnemius
Back of lower leg
Bends foot away from knee
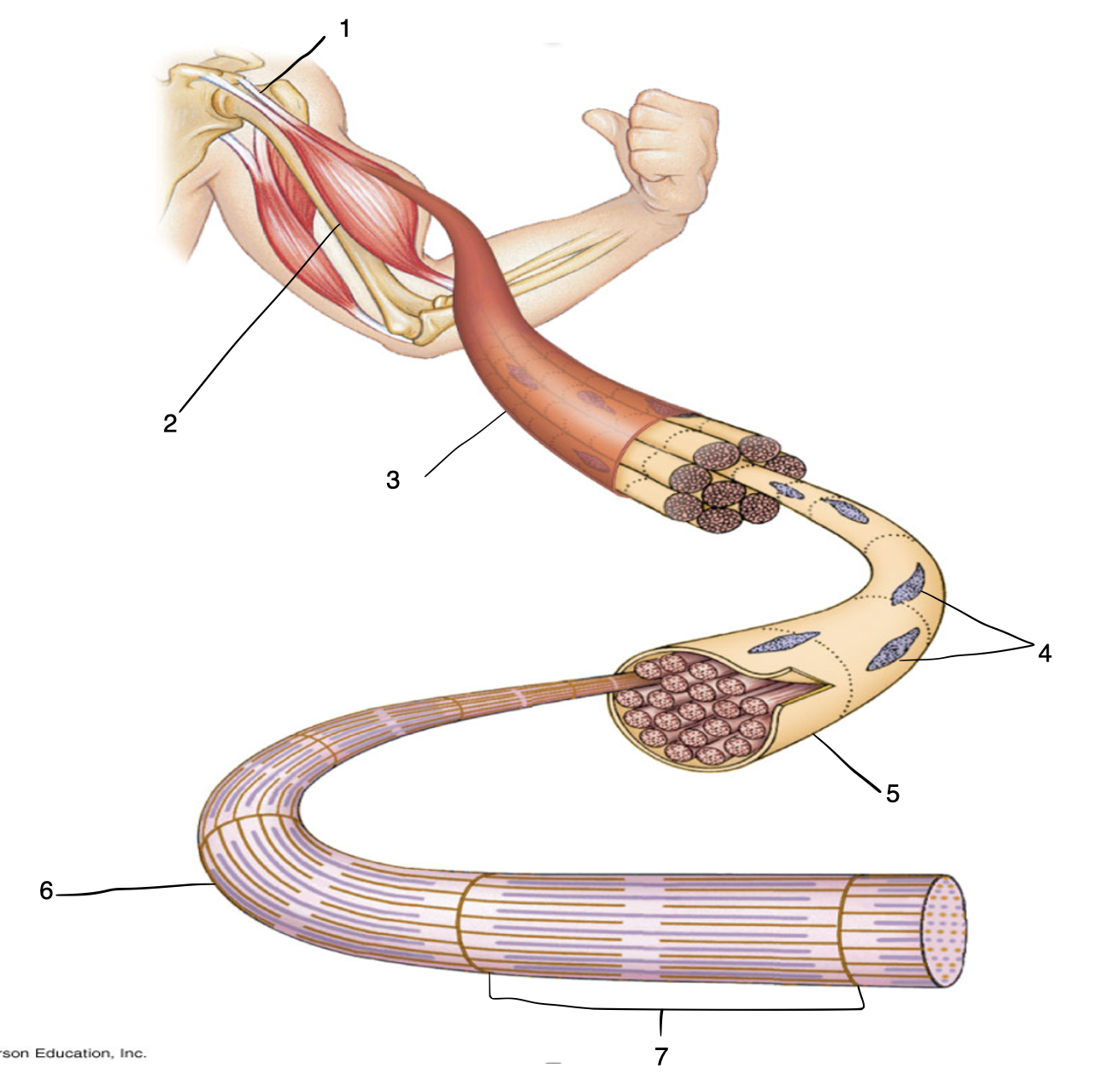
Label
Tendon
Muscle
Muscle cell
Nuclei
Fascia
Myofibril
Sarcomere