HKS All
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mostly from PSP Y1S1 Revision Session
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
- State the WHO definition of health
A complete state of mental, physical and social well-being, and not purely the absence of disease or infirmity.
- What are the pros and cons of the WHO definition of health?
Pros:
-Recognises that health is not purely a physical, bodily or physiological issue, instead broadening its scope to mental and social domains as well.
-Reinforces that not having a disease does not mean someone is in good health.
Cons:
-‘Complete’ suggests that people with comorbidities or chronic illnesses can never be considered healthy, which can exclude them.
-Subjective in what ‘well-being’ means
- Distinguish between equity and equality
Equity: providing fair opportunities, catering for disadvantages
Equality: providing same opportunities for everyone
- Distinguish between avoidable and unavoidable health disparities/inequalities.
Avoidable: Can be changed e.g. financial status, social status, location (rural, remote, urban), etc…
Unavoidable: Can’t be changed e.g. genetics
- State the WHO definition of equity.
Equity is the absence of avoidable, unfair, or remediable differences among groups of people, whether those groups are defined socially, economically, demographically or geographically or by other means of stratification
- What is a DALY. What is the formula for calculating DALY.
Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALYs): refers to how many years of life are impacted as a result of having disease.
Considers both mortality and morbidity
DALY = YLD + YLL
YLD = Years lived with disability
YLL = years life lost
- List the 4 S’s and distinguish between them.
STAFF: Members of the healthcare team and those involved with the healthcare team, e.g. medical practitioners, nurses, pharmacists, PTs, OTs, technicians, etc
SYSTEMS: Staffing systems, parole systems, softwares in healthcare environments
SPACES: Environments involved in healthcare, e.g. hospitals, clinics, labs, etc
STUFF: Things used by the healthcare team, e.g. medical equipment, sanitary equipment, surgical equipment, technology, imaging machines, etc
- What is managed by the federal government (healthcare)?
National policies
medical
PBS
Regulate private health insurance
Research funding
- What is managed by the state government (healthcare)?
Public hospital management
Private hospital licensing
Ambulance services
Community based and primary health services
Health complaints
- What is managed locally/non-governmental/shared?
Pharmaceutical regulations
Health workforce
Education and training
ATSI funding
Quality control
- What is covered under Medicare?
Free hospital treatment
Low/no cost treatment for those with medicare provider number
- Where do you find info about what is eligible for Medicare?
Medicare benefits schedule (MBS)
- What percentage of the Commonwealth government’s health funding is allocated towards Medicare?
25%
- Where does Medicare get its funding?
-Medicare receives its funding from the Medicare Levy, which is up to 2% of taxable income.
-For people who do NOT use private healthcare insurance, there is an additional surcharge of 1.5%
- What are the objectives of the pharmaceutical benefits scheme (PBS)?
1.Reducing the cost of medication to consumers
2.Regulation of how safe medications are, and their quality. → TGA must approve these drugs.
- What percentage of the cost of medication is covered by the government under the PBS?
87%
- What is the PBS safety net? What are the specific threshold amounts?
However, there is the PBS safety net, which further subsidises/eliminates the cost of prescription medication after reaching the threshold amount.
Concession card holders: $277.20. Prescription medication is free after reaching this value.
General medicare holders: $1694.00. Prescription medication is subsidized after reaching this value
List some structural determinants of health.
Environmental differences: Global warming, environmental influence on agriculture, soil quality, urbanisation
Sociocultural factors: cultural blindness, cultural safety, social determinants
Geopolitical factors: Political issues, displacement (forced relocation/refuge, asylum etc)
Legal/historical factors: Colonial impacts and after-effects, legislation (e.g. health legislation)
- List some social determinants. (As reported by Marmot and Wilson’s WHO report).
Social exclusion
Employment/unemployment
Stress
Access to healthy food
Religion
Socioeconomic status
Access to transport
Early childhood development
Psychological changes
- List some health indicators.
Mortality rates
Neonatal mortality rate
Cause-specific mortality
Infant mortality
Life expectancy
Prevalence of disease/conditions
Admissions to hospital by diseases/conditions
Utilisation of general practice services
Frequency of health risk factors
DALYS
- Distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary healthcare.
Primary Healthcare: Initial interaction with the healthcare system, often through a GP or paramedic, nurse, pharmacist, etc.
Secondary Healthcare: After the primary healthcare encounter, a specialised referral (e.g. paediatrician, hepatologist) or ICU in the emergency dept
Tertiary Healthcare: Care received as a hospital in-patient, from specialists. So not the initial encounter with specialists, but subsequent ones.
- What is the Whitehall study?
Whitehall study are series of research projects that find link between social status and health.
- What are the results of the Whitehall study 1?
Whitehall Study 1:
Increased life expectancy and reduced rates of cardiovascular disease in highly ranked civil servants in comparison to lower ranked ones
Participants: 18,000
Age range: 20-64
- What are the results of the Whitehall study 2?
Whitehall Study 2:
Validated the correlation between health status and employment grade, where this relation was due to social status, perceived control and social support networks available → social determinants are relevant!
This study is still going! It began in 1985 so conveniently about 40 years
The only whitehall study to include female participants
Total participants (male and female): 10,000
- What are the first 10 SDGs?
No poverty
Zero hunger
Good health and well-being
Quality education
Gender Equality
Clean water and sanitation
Affordable and clean energy
Decent work and economic growth
Industry, innovation and infrastructure
Reduced inequalities
- What is structural violence? What does it include?
Systemic ways in which people are subjected to constant disparities in the healthcare system, leading to poorer health outcomes.
Includes:
Significant poverty
Racism and violence
Breach of human rights
- Distinguish between upstream and downstream in the ‘river’ metaphor of healthcare.
Upstream:
Think about how the healthcare system is designed e.g. through legislation, policies, structure. System focused rather than individual focused
Downstream:
Think about how individuals are directly being impacted by the efforts of those higher up in the system.

- How can we improve upstream factors?
Tackle Social and Structural Determinants: Implement changes in legislation, public health policies, and systemic frameworks
Preventive Healthcare: Focus on measures that prevent illness, such as vaccinations, screenings, and lifestyle modifications.
Strengthen Health Systems:
Improve infrastructure, staffing, and resource allocation within healthcare systems.
- How can we improve downstream factors?
Therapeutic interventions: treatment to manage/cure existing health conditions
Access to medicine
Allied health services
Behaviour change initiatives: Develop programs that encourage healthier behaviors, such as quitting smoking, improving diet, and increasing physical activity.
- Define primary healthcare.
Defined as healthcare that is:
Practical, scientifically sound and socially acceptable methods of using technology
Universally accessible to all community members through their full participation
Affordable
Directed towards self reliance and self determination.
- Reforms to primary healthcare are focused on:
Universal coverage
Healthcare service delivery
Public policy
Health leadership
- Compare Aboriginal Australian life expectancy vs non-Aboriginal.
8.8 years lower for males and 8.3 years lower for females when compared to their non-Indigenous counterparts.
- Rheumatic heart disease is how many times higher than non-indigenous in NT, QLD and WA?
Rheumatic heart disease is 37x more common in Indigenous populations than non-Indigenous populations in the Northern Territory, 167x more higher in Queensland and 630x higher in Western Australia
- What are some other diseases with higher occurrence in Indigenous communities?
HepB, HepC, asthma, TB, meningococcal disease, etc
- According to the 2021 census, what percentage of Australia’s population is indigenous? What percentage of them live in major cities?
As per the 2021 census by the AIHW, 3.8% of Australia’s population is Indigenous. However, only 41% of these live in major cities.
- What are 3 requirements to be indigenous?
Be of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander Origin
Identify as of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander
Be accepted as an Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander person by the Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander community they reside in
- What are the 4 time periods in the timeline of Indigenous injustice?
1778: Displacement (Arrival of first fleet)
1837-1937: Segregation
1937-1960s: Assimilation
1960s-Present: Structural discrimination
- When were voting rights given to Indigenous people?
1962 (??)
- Distinguish between vertical and horizontal health equity.
Vertical health equity: People should be treated differently based on their needs to address disparities present.
Horizontal health equity: Equal treatment for people of similar circumstances/health requirements regardless of their ability to pay.
- How much more likely are people living in rural and remote areas to have a mental health disorder?
10%
- Distinguish between the 5 parts of Tanahashi framework.
-Availability: Who are the services designed for and are available to use?
-Accessibility: Can people engage with these services or are there barriers preventing them from doing so, e.g. financial, social, cultural, etc?
-Acceptability: Are people willing to use the service? What is preventing them? E.g. cultural blindness, discrimination, structural violence, etc.
-Contact coverage: Who uses the service (Rather than who is supposed to/encouraged to use it)
-Effectiveness coverage: Care and follow up.
- What are some conditions which refugees and asylum seekers are more prone to include.
Reduced medicare and PBS services
Increased incarceration
Poor mental health
More communicable disease rates
Reduced access to healthcare as a result of linguistic and cultural barriers
- Define refugee
Someone who “owing to well-founded fear of being persecuted for reasons of race, religions, nationality, membership of particular social group or political opinion, is outside the country of their nationality and is unable/unwilling to avail themselves to the protection of the country or return to it
- Define asylum seeker
Someone who has left their home country due to fear of persecution but has not yet been granted legal refugee status
- Define migrant
Someone who chooses to leave their home country and cross an international border, not necessarily for fear of persecution. Umbrella term that can include refugees but also voluntary migrants who are in search of a better life.
- Define internally displaced person (IDP)
Someone who has fled their home but not crossed an international border to seek sanctuary
- ASK guidelines
Country of departure and when they arrived
Languages (interpreter?)
Occupation
Circumstances
Any family present
- SCREEN guidelines
A thorough health assessment.
Screening investigations to detect infectious disease or pre-existing health condition they may be unaware of due to lack of access to healthcare.
Informed consent - must be clear communication→interpreter
- What should everyone be screened for
Hepatitis B, strongyloids, HIV, varicella, NCDs, dental/hearing/visual diseases
- What should people be screened for based on threat
rubella, vitB12
- What should people be screened for depending on country
HepC, malaria, schistoma
- KINDNESS guidelines
Understand the difficult circumstances people may be in
Direct them to support if/when they need it.
What official document contains the international definition of human rights?
United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948)
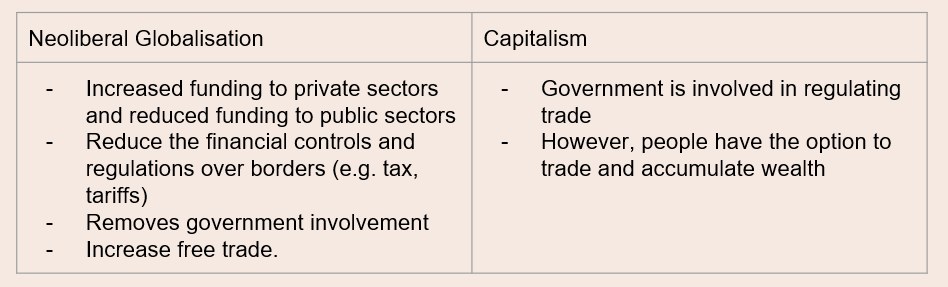
- Distinguish between neoliberal globalization and globalization
- Key features of pharmaceutical patents
Apply to technologies (including medicines) that are new, useful, or non-obvious.
Grant exclusive rights to the owner or manufacturer for making, using, or selling the patented product.
Enable patent holders to set higher prices, often resulting in monopoly-like conditions.
Are territorial—valid only within the country where they are granted. For example, a patent granted in Australia does not apply in Brazil.
Must be registered separately in each country where protection is sought.
Countries that are members of the World Trade Organization (WTO) must adhere to multilateral trade agreements when exporting pharmaceuticals.
- What is a TRIPs agreement?
A key multilateral agreement managed by the WTO.
Sets a minimum of 20 years of patent protection.
Allows governments to bypass patent laws during national emergencies through a "compulsory licence.”
- What is a compulsory license?
A compulsory licence permits another company to produce or sell a patented product without the consent of the patent holder, which breaks the monopoly, encourages competition, and often reduces the original company's profits.