4.2: Lipid Metabolism (Di Foggia)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Only one of these statements is false. Explain all answers.
a) The reducing power for fatty acid biosynthesis is obtained by glucose oxidation
b) All carbon atoms of glucose will be found in palmitic acid
c) Fatty acid biosynthesis is stimulated by insulin
d) Acetyl-CoA carboxylase may be phosphorylated
e) Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is activated by citrate
b) All carbon atoms of glucose will be found in palmitic acid
a) True. NADH from glycolysis; NADPH from pentose phosphate pathway (the oxidative part)
b) False. 4 glucose + 4 O2 + 12 H+ → palmitate + 8 CO2 + 14 H2O
c) True. Insulin signals the body to store (glycogen) or use excess glucose (glycolysis; fatty acid biosynthesis)
d) True. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase:
glucagon → cAMP → phosphorylation = inactive
insulin → dephosphorylation = active
e) True
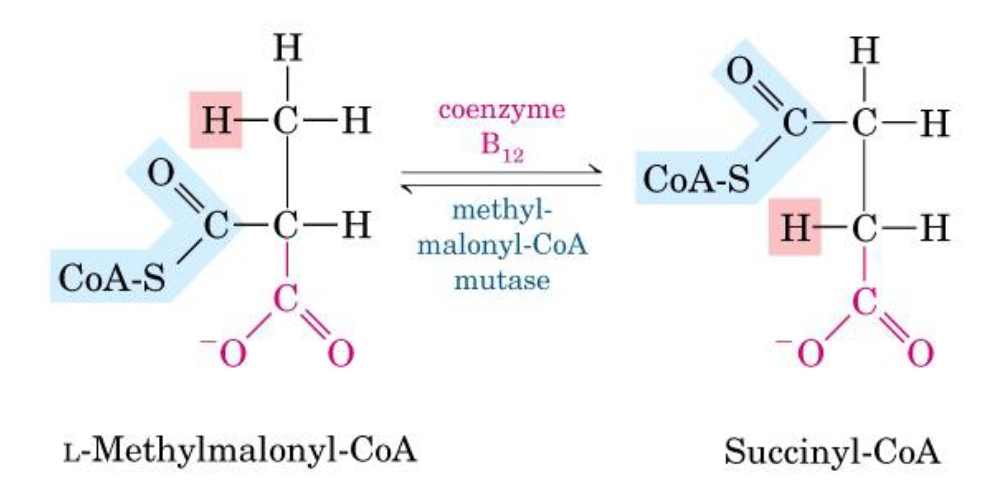
Concerning methylmalonyl-CoA
a) It is involved in cholesterol biosynthesis
b) It is formed from propionyl CoA in a B12-dependent reaction
c) It is converted into succinyl CoA
d) It is an intermediate of fatty acid biosynthesis
e) It is ketogenic
c) It is converted into succinyl CoA
a) False. It is involved in odd-chain fatty acids catabolism; mevalonate is involved in cholesterol biosynthesis
b) False. Biotin is the prosthetic group of propionyl-CoA carboxylase. The transformation of methylmalonyl-CoA into succinyl-CoA need coenzyme B12
c) True
d) False. It is an intermediate of odd-chain fatty chain catabolism
e) False. It can be considered glucogenic because it is converted into succinyl-CoA that can enter the TCA cycle and form oxaloacetate and then pyruvate
Which of the following compounds will NOT be decreased by a genetic defect of HMG-CoA reductase?
a) Cholesterol
b) Acetoacetate
c) Coenzyme Q
d) Vitamin D3
e) Farnesyl pyrophosphate
b) Acetoacetate
It is the only molecule not involved in cholesterol biosynthesis.
In fact, Vitamin D3 is a cholesterol derivative; farnesyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate of cholesterol biosynthesis; the isoprenoid tail of coenzyme Q is synthesised from isopentenyl pyrophosphate, an intermediate of cholesterol biosynthesis
In a well-fed individual
a) The activity of liver glucose-6-phosphatase is high
b) The blood levels of acetoacetate are low
c) The activity of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate phosphatase is high
d) Fatty acid biosynthesis is decreased
e) The secretion of cortisol is increased
b) The blood levels of acetoacetate are low
a) False. In a well-fed individual, the activity of liver glucose-6-phosphatase is typically low. Glucose-6-phosphatase is an enzyme involved in gluconeogenesis
b) True. Acetoacetate is a ketone body produced during fasting periods
c) False. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate phosphatase is involved in also involved in gluconeogenesis
d) False. If carbohydrates and insulin levels are elevated, the body tends to prioritise storing excess energy as fats
e) Insulin levels are elevated
Only one statement is false
a) The nitrogen of sphingosine derives from serine
b) glycolipids (i.e., cerebrosides) contain sphingosine
c) Biosynthesis of cholesterol esters requires activation of cholesterol with ATP
d) Cardiolipin contains 4 fatty acids
e) Biosynthesis of phosphatidyl inositol proceeds through a CDP diacylglycerol intermediate
c) Biosynthesis of cholesterol esters requires activation of cholesterol with ATP
a) True. palmityl-CoA + serine → → → ceramide (containing sphingosine)
b) True. Cerebroside derives from ceramide which contains sphingosine
c) False. Acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) does not need ATP activation
d) True
e) True. Biosynthesis of phosphatidyl inositol proceeds through a CDP-diacylglycerol intermediate
Only one answer is wrong. HMG-CoA reductase
a) in mitochondria is involved in ketone body synthesis
b) may be inhibited by phosphorylation
c) is involved in the synthesis of Coenzyme Q
d) catalyzes two consecutive reductions
e) is a cytosolic enzyme
a) in mitochondria is involved in ketone body synthesis
a) False. It is involved in the mevalonate pathway in the cytosol, where it catalyses the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, a precursor in cholesterol biosynthesis. In mitochondrial ketogenesis, the enzyme is HMG-CoA synthase
Only one answer is wrong. Concerning VLDL
a) They are very rich in triacylglycerols
b) They are synthesised in the liver
c) Their lipids are hydrolysed by lipoprotein lipase
d) Their deficit is the cause of familial hypercholesterolemia
e) They are larger than HDL
d) Their deficit is the cause of familial hypercholesterolemia
It is primarily caused by mutations in the LDL receptor gene, leading to impaired clearance of LDL from the bloodstream
Concerning fatty acid biosynthesis
a) Acetyl CoA carboxylase requires ATP
b) In mammals fatty acid synthase is a complex of 7 distinct enzyme proteins
c) Excess acetyl CoA inhibits fatty acid biosynthesis
d) Fatty acid synthase may synthesise C16:0, C18:0, C20:0
e) The carbon atom of CO2 used for acetyl CoA carboxylase will be incorporated into palmitic acid
a) Acetyl CoA carboxylase requires ATP
d) Fatty acid synthase may synthesise C16:0, C18:0, C20:0
a) True
b) False. It’s a single polypeptide chain with 7 different domains
c) False. Acetyl-CoA is its main substrate
d) True. Elongation can occur in the ER or in the mitochondria
e) False.
Chylomicrons
a) are carried to the liver by portal circulation
b) contains free fatty acids deriving from digestion
c) undergo triglyceride hydrolysis by lipoprotein lipase
d) release glycerol into adipocytes to be used for triacylglycerol re-synthesis
e) are the only lipoproteins that do not contain phospholipids
c) undergo triglyceride hydrolysis by lipoprotein lipase
d) release glycerol into adipocytes to be used for triacylglycerol re-synthesis
a) False. They are carried to adipose tissue
b) False. They contain triacylglycerols
c) True
d) True
e) False. While chylomicrons have a lower proportion of phospholipids compared to other lipoproteins like HDL, LDL and VLDL, they do contain phospholipids as part of their structure
Acetoacetate
a) In skeletal muscle is largely reduced to β-hydroxybutyrate
b) is produced by the reaction catalysed by HMG reductase
c) is a good energetic substrate for muscle mitochondria
d) Is an intermediate of cholesterol biosynthesis
e) Is a good precursor for gluconeogenesis
c) is a good energetic substrate for muscle mitochondria
a) False. Acetoacetate is reduced to β-hydroxybutyrate in liver during ketogenesis by β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. In fasting, muscle may use the opposite reaction to obtain acetyl-CoA
b) False. The reaction is catalysed by HMG-CoA lyase. HMG-CoA reductase converts HMG-CoA into mevalonate
c) True. It can be converted into acetyl-CoA in muscle mitochondria
d) False. Acetoacetyl-CoA is an intermediate of cholesterol synthesis (first reaction)
e) Acetoacetate can be converted into acetyl-CoA, which cannot be converted into pyruvate, the starting point of gluconeogenesis because the opposite reaction, catalysed by pyruvate dehydrogenase is irreversible