biochem unit 3
1/600
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
601 Terms
for bacteria we dont have
introns
bacteria has a _____ structure
polycistronic mRNA
eukaryotic mrna requires splicing and
polyadenylation
prokaryotic ribosomes are ____ compared to eukaryotic
smaller and consist of distinct subunits.
rRNAS can be separated by
gel electrophoresis
the three components of nucleotides
heterocyclic nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and phosphate
dna is the ____ of genetic information and ____ is central to its expression
repository; RNA
nucleotides are essential _____ in virtually all cellular metabolism
intermediates
nitrogenous bases derive from
purines and pyrimidines
pyrimidines are
single six membered rings with two nitrogen atoms
purines are
fused rings resembling pyrimidine and imidazole
nitrogenous bases are relatively insoluble due to
pronounced aromatic character
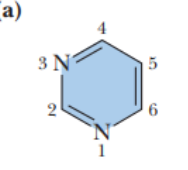
pyrimidine ring
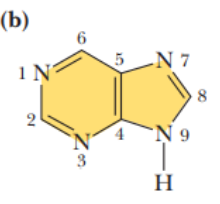
purine ring system
cytosine uracil and thymine are
pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine for dna) and cytosine and uracil for rna
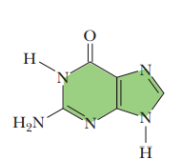
guanine
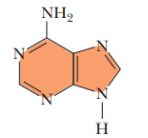
adenine
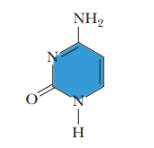
cytosine
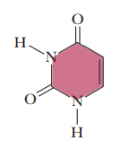
uracil
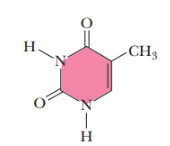
thymine
purine bases for dna and rna
Adenine and guanine for dna and rna
nitrogenous bases undergo ____ shifts
keto-enol
bases have the ____ form at neutral ph
keto tautomer
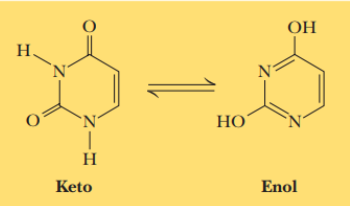
this is an example of
keto-enol tautomerization
tautomeric form determines ______ possibilities which are key to nucleic acid function
H-bonding possibilities
bases strongly absorb UV light around 260 nm this is useful for ______
quantitative and qualitative analysis
nucleosides link a base to a pentose sugar in the ____ form
furanose
nucleoside bases and pentose form what linkage
beta-configuration glycosidic bond
after nucleosides form from bases and pentose the new names are
“idine” for pyrimidines and “osine” for purines
in naming nucleosides of deoxyribose
we use the prefix deoxy - ex, deoxyadenosine
describe adenosine
local hormone and neuromodulator
regulates heartbreak, blood vessel dilation, sleepiness
caffeine blocks receptors
low levels after sleep, high levels when being awake for long
a nucleotide is formed when phosphoric acid is ____ usually at the 5’ of the sugar
esterified
due to the ____ group nucleotides are strong acids
phosphate
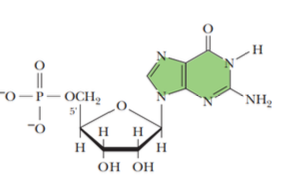
this is an example of
a formed nucleotide
nucleoside diphosphate (NDPs) and triphosphate (NTOs) contain additional phosphates linked by ______ linkages
phosphoric anhydride
nucleoside diphosphate are indispensable carriers of
chemical energy
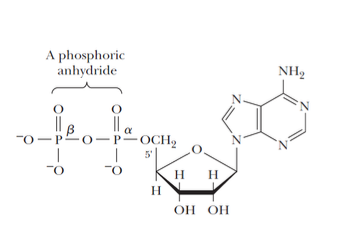
ADP
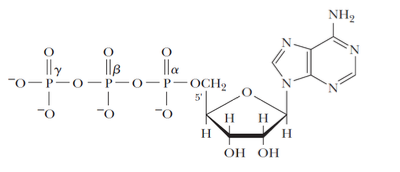
ATP
transfer of ________ groups drive biological work
phosphoric, pyrophosphoryl or nucleotide (NMP)
in high energy nucleotides the different bases (AGCU) Chanel energy into _____ pathways
different metabolic
cyclic nucleotides are cyclic
phosphodiesters
examples of cyclic nucleotides
3’,5’ cyclic amp (camp) and 3’,5’ cyclic GMP c(GMP)
the importance of cyclic and regulatory nucleotides
important regulators of cellular metabolism
cGAMP is a cyclic
dinucleotide
cGAMP is synthesized by
cyclic GMP-AMO synthase (cGAS) when dsDNA is sensed in the cytosol
rising levels of cGAMP levels trigger ______
STING and an immune response
glucagon signaling leads to the activation of the enzyme _____ which converts ATP to cAMP
adenylate cyclase
triphosphate energy intermediates
carriers of metabolic intermediates
chemical signaling aka secondary messengers
These are functions of what
Nucleotides
example of triphosphate as energy intermediates
triphosphate = major energy currency
GTP involved in driving protein synthesis
examples of nucleotides being carriers of metabolic intermediates
UDP in sugar metabolism, CDP in lipid, NAD and CoA are ADP intermediates
example of nucleotides in chemical signaling as secondary messengers
cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP
nucleic acids are polynucleotides formed by nucleotides linked ____ via ____ bridges
3’ to 5’, phosphodiester
what forms a directional sugar phosphate backbone
polynucleotides structure
the sequence of nucleic acids is read from which direction
5’ to 3’
the unique nucleic acid identity is determined solely by
sequence of bases
DNAs singular role
preserving the information for all functional macromolecules
DNA consists of
two antiparallel polynucleotide strands wound together in a double helix
DNA strands are held together by
interchain hydrogen bonds aka base pairing
chargaffs rules
A=T and T=G, purines=pyrimidines
who discovered that A=T and C=G
watson and crick
The A : T and G : C pairs form units, giving the helix uniform dimensions
spatially equivalent
the complementary relationship in DNA means information is conserved in _____
the opposing strand
base pairing ensures
replication
dna encodes information using four bases
A C G T
Eukaryotic DNA is condensed by
wrapping around histone proteins to form nucleosomes
cellular RNA is usually ___ but forms double stranded regions through _____ base pairing
single stranded, intra-stand
mRNA
carries gene information for protein synthesis
Eukaryotic mRNA requires
intron removal (splicing) and polyadenylation
rRNA is the structural and function core of _____ playing a crucial role in _____
ribosomes, protein synthesis.
tRNA transports
amino acids
exons are protein coding regions that must be joined by removing
introns
rRNA has complex secondary structure due to many
intrastrand hydrogen bonds
rRNAs can be separated by
electrophoresis
all tRNAs possess the 3’ terminal sequence ____ where the amino acid attaches
C C A
small nuclear RNAs form complexes with proteins (snRNPs) that mediate splicing of
hnRNA into mRNA
mRNA function
encodes proteins
tRNA functions
acts as adaptor between mRNA and amino acids
rRNA function
forms ribosome
rnRNA function
various processes (gene splicing)
snoRNA
facilitates chemical modification of RNAs
miRNA
regulates gene expression
siRNA
silences gene expression
IncRNA
regulates gene expression
how dna differs chemically from rna
deoxyribose instead of ribose
thymine instead of uracil
in DNA which is “long lived” compared to RNA, the deamination of cytosine to uridine occurs spontaeously at a ____ rate
low
As DNA contains Thymine instead of Uracil, the DNA repair recognition/repair system substitutes the wrong base (Uracil) for the right base ______, thereby correcting the sequence
(Cytosine)
The absence of the 2'-OH group in DNA confers greater resistance to _____
alkaline hydrolysis
alkali liable means
readily hydrolyzed by hydroxide ions
RNA is alkali labile because
the 2’ OH group promotes nucleophilic cleavage at the phosphodiester bond
DNA is acid labile meaning
purine glycosidic bonds hydrolyze in dilute acid
nucleases are enzymes called _____ that hydrolyze phosphodiester bonds
phosphodiesterase
cleavage in phosphodiesterase are categorized as either
internal - endo or terminal - exo
cleavage in nucleases is labeled as ___ side or ___ of the phosphodiester bridge
a 3’ or b' 5’
nucleases exhibit specificity for
single vs double strands
______ are bacterial enzymes that cleave dsDNA at specific recognition sequences, typically four or six nucleotides long
Type II restriction endonucleases
in type II restriction endonucleases recognition sites often have ____ symmetry
twofold
EcoRI cleaves ____ leaving single stranded sticky ends
staggered
the sticky ends from EcoRI cleavage allow for ____. they are essential tools for manipulating DNA and restriction mapping
recombinant DNA formation
how many rotational degrees of freedom give rise to nucleic acid structures
7