JMU Bio 140 Exam 3
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
Acetyl-CoA enters into what?
citric acid cycle
What do all cells require?
-a way to encode/transmit information
-a membrane separating inside from out
-energy
What does Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) do?
provides energy in a form that all cells can readily use to perform the work of the cell
Where does the molecule ATP contain energy?
in its chemical bonds
What part of ATP has high energy potential?
phosphate group
All organisms are split into what two basic categories?
-phototrophs
-chemotrophs
Phototrophs get energy from where?
sunlight
Chemotrophs get energy from what?
chemical compounds
What are the two types of ways organisms receive carbon?
-autotrophs
-heterotrophs
Autotrophs receive carbon from where?
inorganic sources
Heterotrophs receive carbon from where?
organic compounds
Define metabolism
building up and breaking down of carbon sources
What are the two types of metabolism?
-catabolism
-anabolism
Does catabolism produce or require ATP?
produces
Does anabolism produce or require ATP?
requires
What are examples of work which metabolism helps with in the cell?
-synthesizing DNA, RNA, and proteins
-moving vesicles in a cell
-pumping substances across membranes
Define kinetic energy
energy in motion
What are forms of kinetic energy?
-movement
-light
-electricity
-thermal energy
Define potential energy
stored energy
Potential energy depends on what two things?
structure and position
Potential energy can be released when what happens?
structure or position is changed
Chemical energy is a form of what type of energy?
potential
Strong bonds have ________ potential energy than weak bonds.
less
Why are phosphate bonds so weak?
the negatively charged oxygens repel one another
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
energy is neither created nor destroyed, it simply changes from one form to another
How would you calculate the kinetic energy of a ball which rolled down the steps?
potential energy at the top minus the potential energy at the bottom of the stairs
How is energy released in electrons?
heat or lights
Define the second law of thermodynamic
the amount of disorder (entropy) increases when energy is transformed -> some energy is unable to do work
Define entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness (energy not available to do work)
In the universe, the degree of disorder can only _________?
increase
Define gibbs free energy
energy available to do work
∆G= what
G products-G reactants
If the products have more free energy than the reactants the ∆G is what?
positive
Endergonic reaction graph
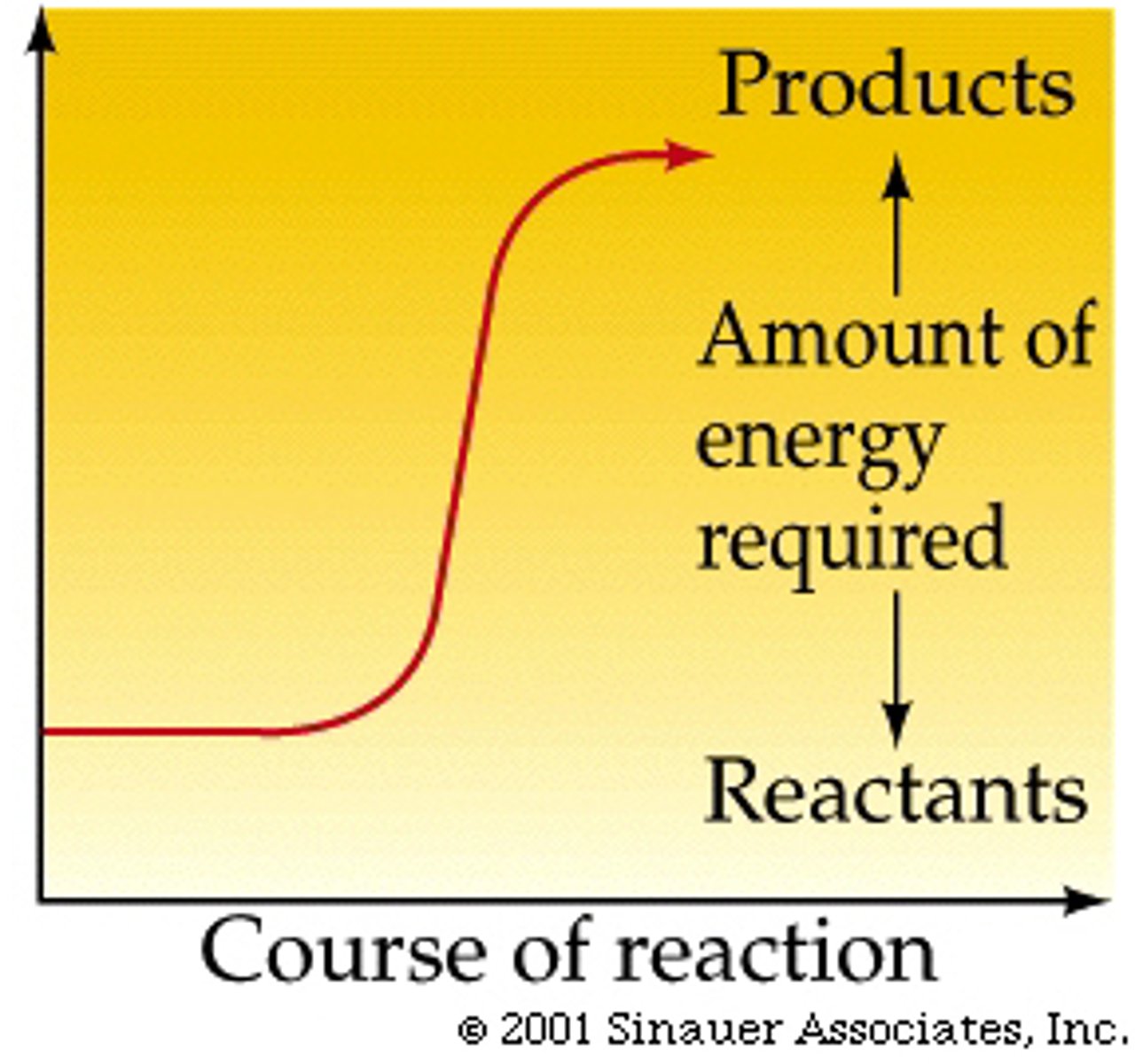
If the products have lesfree energy than the reactants the ∆G is what?
negative
Exergonic reaction graph
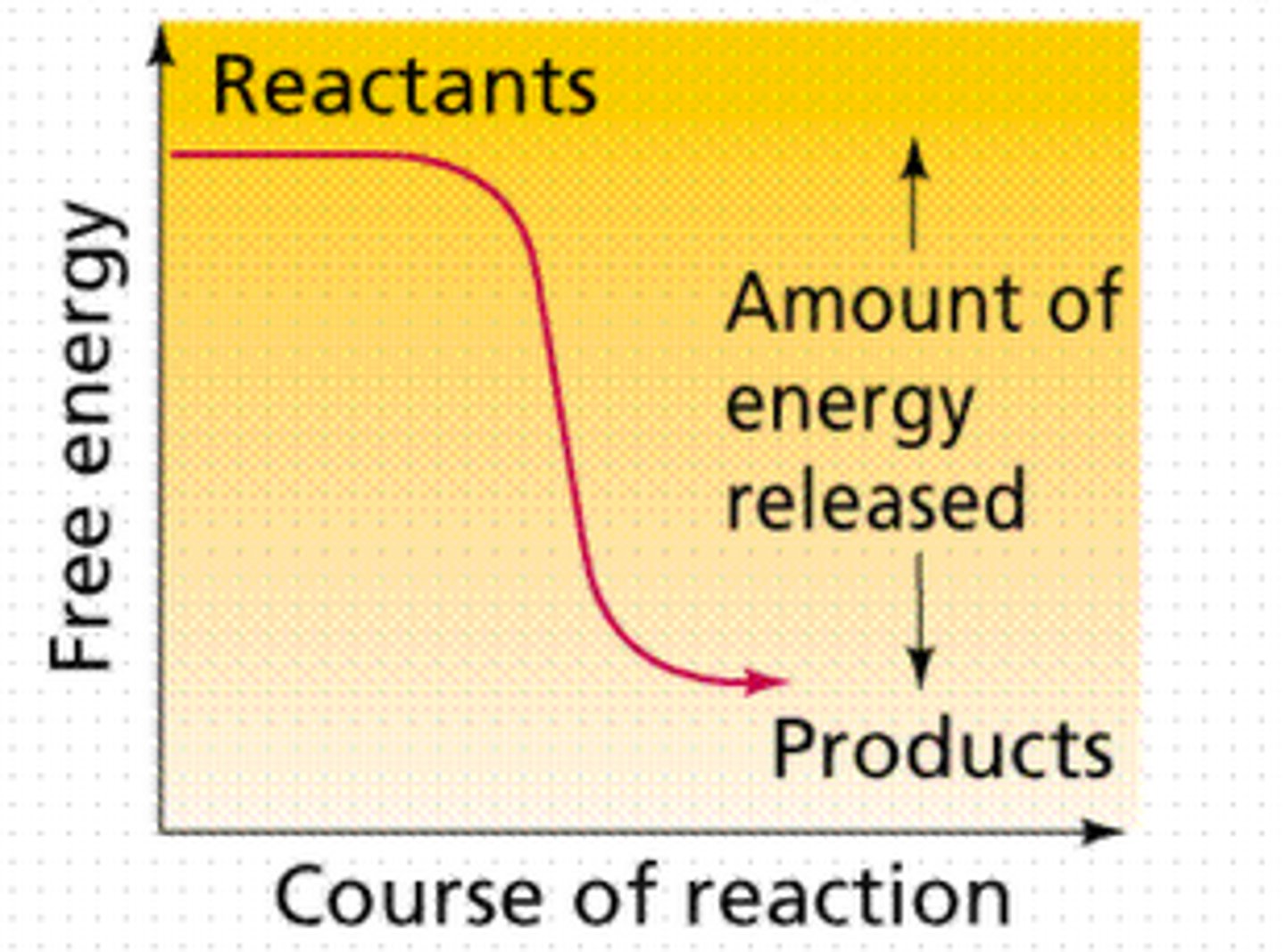
Define ∆H
enthalpy - chemical energy in bonds
Define ∆S
entropy
What is the equation for ∆ change in a system?
∆H=∆G - T∆S
Is an endergonic reaction spontaneous or not?
non-spontaneous
Is an exergonic reaction spontaneous or not?
spontaneous
If your ∆G is positive what is your ∆S and ∆H?
-∆S and ∆H
If your ∆G is negative what is your ∆S and ∆H?
+∆S and -∆H
Is ∆G positive or negative in an anabolic reaction?
positive
Is ∆G positive or negative in an catabolic reaction?
negative
What type of reaction is hydrolysis?
exergonic
Define energetic coupling
spontaneous reaction drives a non-spontaneous reaction
Hydrolysis of what can drive the synthesis of ATP?
phosphoenolpyruvate
What are the two things enzymes do?
-speed up reactions
-selects which reaction will occur
What can enzymes not do?
make a non-spontaneous reaction spontaneous
What are the ways which enzymes lower activation energy?
-align substrates making a reaction possible
-alter ionic structure of substances
-put physical stress on substrates, forcing to transition state
An active site of an enzyme binds to what?
substrate
How are substrate interactions of an enzyme stabilized?
non-covenant interactions
Define activators
increase activity of enzyme
Define inhibitors
decrease activity of enzymes
What are the two types of enzyme inhibitors
-irreversible inhibitors
-reversible inhibitors
What are the two types of reversible inhibitors?
competitive and non-competitive
Where do competitive inhibitors bind
the active site
Where do non-competitive inhibitors bind
second (allosteric) site
How does an non-competitive inhibitory inhibit?
changes the shape of the enzyme
Define feedback inhibition
product from end of pathway turns off enzyme at start of pathway
Feedback inhibition will trigger what type of change?
confirmational change
What is the goal of cellular respiration?
-breakdown of organic molecules
-convert energy into ATP
What is the cell respiration formula?
C₆H₁₂O₆ -> 6CO₂ + 6H₂O +ATP
About how many ATP are make from a single molecule of glucose?
32 ATP
What percent of energy is harnessed in cellular respiration?
34%
What are the two ways which ATP is made in the cell?
-substrate-level phosphorylation
-oxidative phosphorylation
Define substrate-level phosphorylation
two coupled reactions carried out by a single enzyme -> phosphate group is added to ADP from an enzyme's substrate
Substrate-level phosphorylation produces what percent of ATP in cellular respiration?
12%
Define oxidative phosphorylation
a series of redox reactions store chemical energy in the form a proton gradient which is used to drive phosphorylation of ADP. Oxygen is the final election accept
Oxidative phosphorylation produces what percent of ATP in cellular respiration?
88%
The loss of electron is what?
oxidation
The gain of electron is what?
reduction
What are the important molecules for cellular respiration?
NAD+, NADP+, FAD
What is the reduced form of NAD+?
NADH
What is the reduced form of NADP+?
NADPH
What is the reduced form of FAD?
FADH₂
The more carbon or hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon the more ________ that carbon is.
reduced
The more oxygen atoms bonded to carbon, the more _______ that carbon is.
oxidized
What is oxidized in the cellular respiration reaction?
C₆H₁₂O₆
What is reduced in the cellular respiration reaction
O₂
What are the four stages of cellular respiration?
-glycolysis
-pyruvate oxidation
-citric acid cycle
-oxidative phosphorylation
What are other names for the citric acid cycle?
TCA or Krebs cycle
What occurs in the first two stages of cellular respiration?
fuel molecules are partially broken down, producing ATP and electron carriers
What occurs in stage 3 of cellular respiration?
fuel molecules are fully broken down to CO₂, producing ATP and electron carriers
What occurs in stage 4 of cellular respiration?
electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, leading to the synthesis of ATP
Where does glycolysis occur in the cell?
cytosol
Where does the pyruvate oxidation occur in the cell?
matrix of mitochondria
Where does the citric acid cycle occur in the cell?
matrix of mitochondria
Where does the oxidative phosphorulation occur in the cell?
inner mitochondrial membrane
How many reactions occur in the three stages of glycolysis?
10
What are the three stages of glycolysis?
-initial investment of ATP
-cleavage of 6-carbon sugar in half
-energy generation
How many ATPs are invested into glycolysis?
2
What occurs in stage 1 of glycolysis?
-consumes 2 ATP
-making molecules less stable, trapping in the cell
What occurs in stage 2 of glycolysis?
split molecules into two halves rearrange one
What occurs in stage 3 of glycolysis?
-NADH producing reaction
-First ATP producing reaction
-Second ATP producing reaction
What is the net yield of glycolysis?
2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 puruvate
What are the two ways which pyruvate and NADH are metabolized?
fermentation & TCA cycle
Reactions in the mitochondria require what?
O₂
Pyruvate is oxidized to what?
Acetyl CoA