Body Systems EOC Study
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Cohort Patient
The patient for whom students create a physical therapy and wellness plan.
Cohort Patient Partner
A pair of students who work together to discuss the same cohort patient, gather and document information on their Cohort Patient Chart, develop a physical therapy and wellness plan, and build anatomy
PT Cohort
A group of five students, all with different cohort patients.
Cohort Patient Chart
A document students use to record medical information, sketches, and a care and rehabilitation plan for their cohort patient.
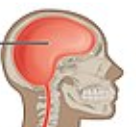
Cranial Cavity
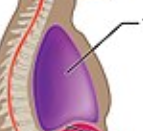
Thoracic Cavity
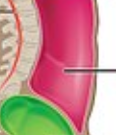
Abdominal Cavity
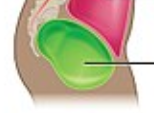
Pelvic Cavity
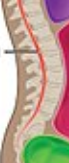
Vertebral Cavity
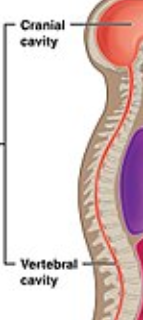
Dorsal body Cavity
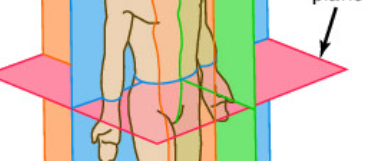
Transverse Plane
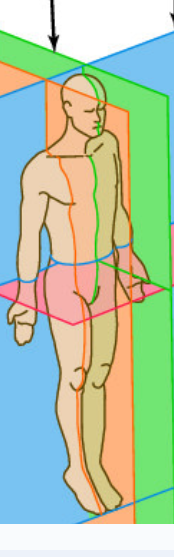
Median Plane
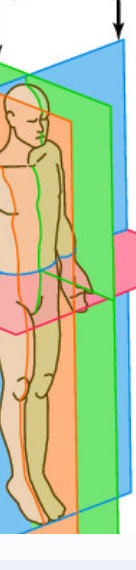
Frontal Plane
Tissue Type: Nervous
Communicating; receiving and responding to signals (Nerves, Spinal cord, Brain)
Tissue Type: Epithelial
Absorbing, secreting, protecting, and sensing (Surface of all organs and blood vessels, mouth & skin)
Tissue Type: Muscle
Contracting, moving (All muscles: striated=attached to bones, smooth=organ walls, cardiac=wall of heart)
Tissue Type: Connective
Supporting and connecting other tissue types, holding organs in place, attaching muscles to bones, linking bones with joints, and enabling other tissues to stretch (Attached to and between other tissue types, Adipose tissue (fat) is a type of connective tissue.)
Type of Bone: Flat
A layer of spongy bone between two thin layers of compact bone containing marrow, but no marrow cavity. (ex. Frontal, Parietal, Occipital)
Type of Bone: Long
A shaft with two ends, more long than wide, and a marrow-filled cavity. (ex. Humerus, Femur, Radius)
Type of Bone: Short
Roughly cubic in shape, consisting mostly of spongy bone. (ex. Carpals, Tarsals)
Type of Bone: Irregular
Thin layers of spongy bone surrounded by compact bone, in atypical shapes. (ex. Vertebrae, Sacrum, Maxilla)
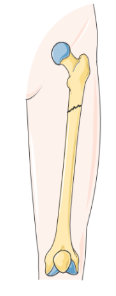
Oblique fracture
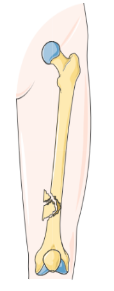
Comminuted fracture
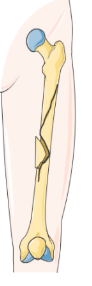
Spiral fracture
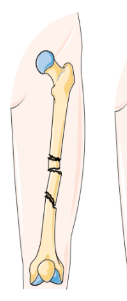
Segmental fracture
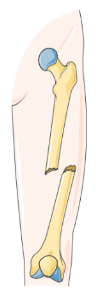
Compound fracture
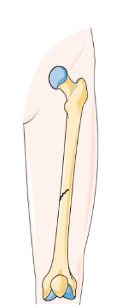
Greenstick fracture
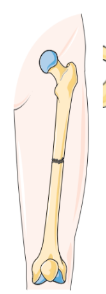
Transverse Fracture
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts form new bone tissue, to replace those reabsorbed by osteoclasts. Produce osteoid
Osteoclasts
Break down and reabsorb bone tissue. Release minerals and other stored materials.
Fracture Healing Step 1
Inflammation: formation of a hematoma at the break (3-5 days)
Fracture Healing Step 2
formation of a fibrocartilaginous (soft) callus (4 days-3 weeks)
Fracture Healing Step 3
formation of a bony (hard) callus (2 weeks- 6-12 months)
Fracture Healing Step 4
remodeling and addition of compact bone (6-12 weeks+)
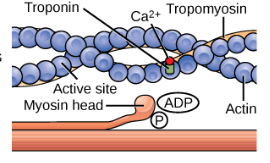
Muscle Contraction: Step 1
The active site on actin is exposed as Ca2+ binds triponin.

Muscle Contraction: Step 2
The myosin head forms a cross-bridge with actin.
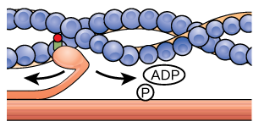
Muscle Contraction: Step 3
During the power stroke, the myosin head bends, and ADP and phosphate are released.
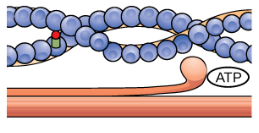
Muscle Contraction: Step 4
A new molecule of ATP attaches to the myosin head, causing the cross-bridge to detach

Muscle Contraction: Step 5
ATP hydrolyzes to ADP and phosphate, which returns the myosin to the “cocked” position
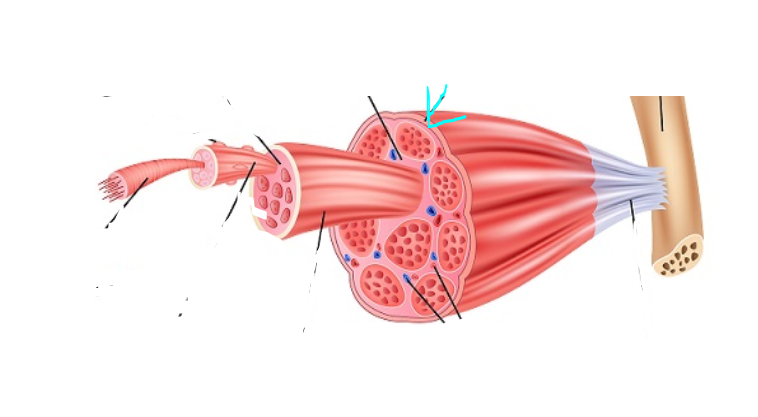
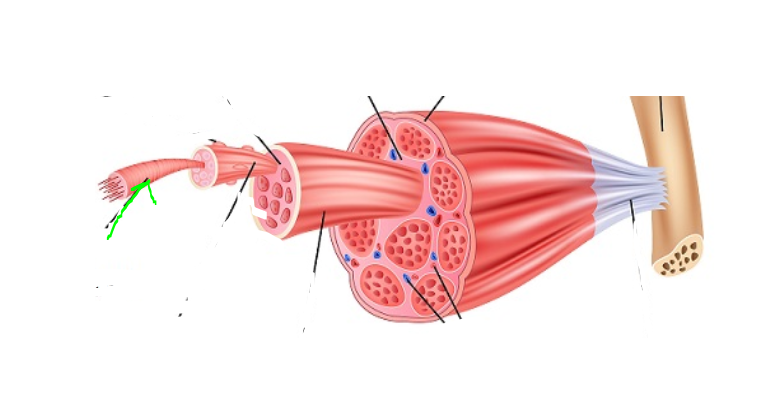
Epimysium
(SkelMusc) (“upon muscle”) outermost layer of connective tissue
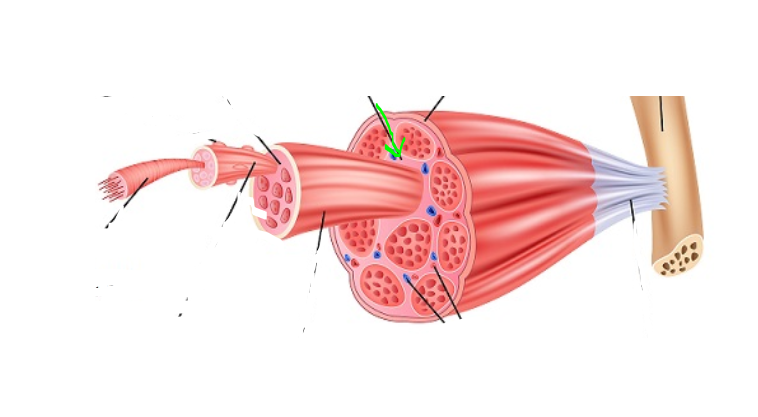
Perimysium
(SkelMusc) (“around muscle”) made of connective tissue and forms casings for bundles of muscle fibers

Endomysium
(SkelMusc) (“within muscle‖) connective tissue surrounding each individual muscle fiber
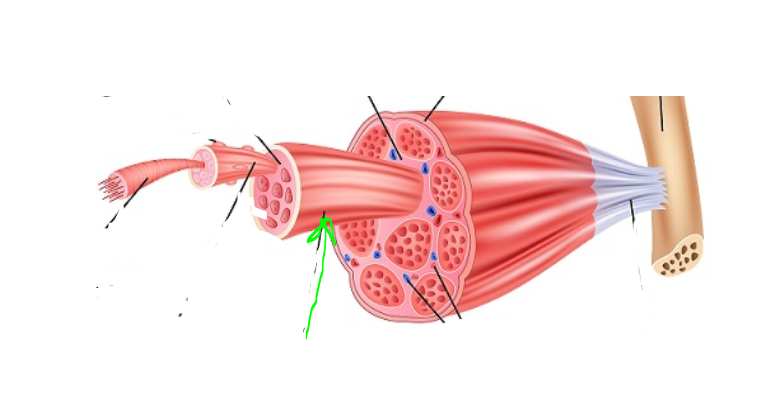
Fascicle
(SkelMusc) a small cluster of muscle fibers, with endomysium between the individual fibers
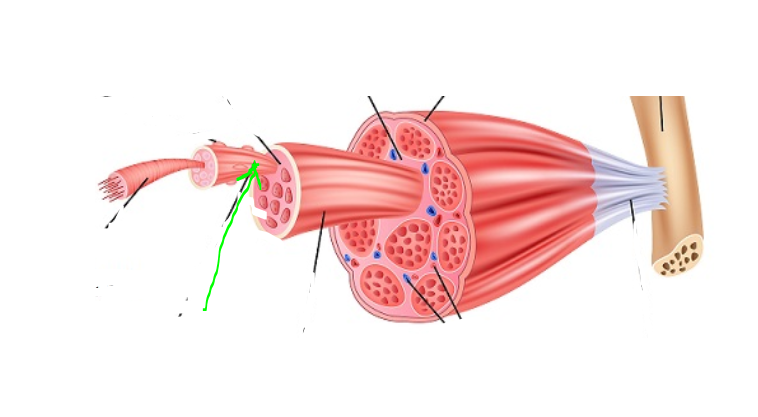
Sarcolemma
(SkelMusc) Surrounds muscle cells. Regulates ion movement across the cell
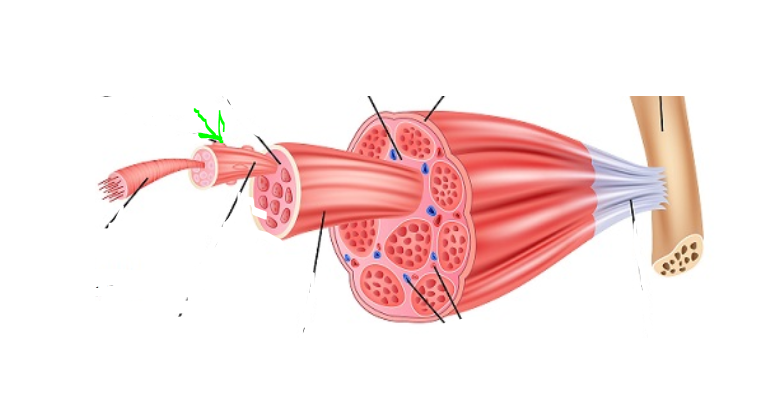
Nuclei
(SkelMusc) Attached to the sarcolemma
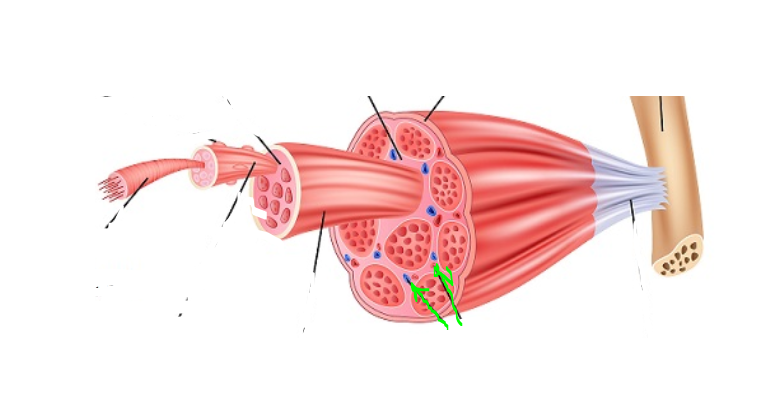
Myofibril
(SkelMusc) Rod-like organalle of a muscle cell. Contain sacromeres and help in muscle contraction.
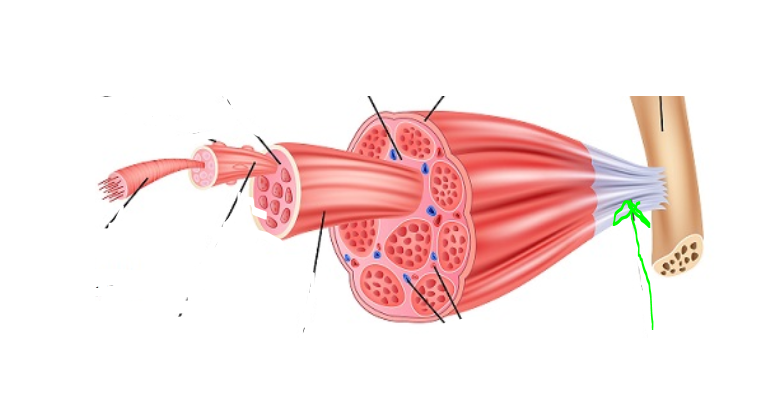
(SkelMusc) Blood Vessel
(SkelMusc) between the fascicles, bringing the tissue nutrients & removing waste
Tendon
(SkelMusc) Attaches to bone
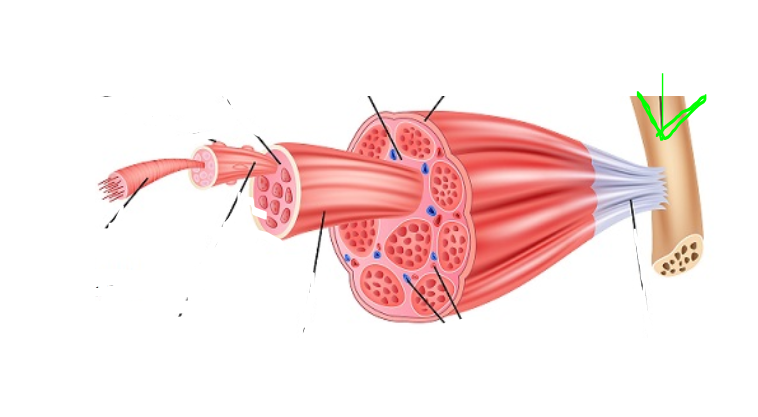
Bone
(SkelMusc) What tendons are attached to
Plexus
(SkelMusc) network of nerves and blood vessels
Muscle Classification: Name
Trapezius is shaped like a trapezoid. Rhomboid minor is shaped like a rhombus.
Muscle Classification: Size
Gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the group. Gluteus minimus is the smallest.
Muscle Classification: Location
Frontalis is on the frontal bone of the skull. Temporalis is on the temporal bone of the skull.
Muscle Classification: Direction of fibers
Fibers in orbicularis oculi form a circle. Fibers in transverse abdominis “traverse” or go across the abdomen.
Muscle Classification: Action
Flexor carpi ulnaris flexes the hand at the wrist. Extensor digitorum longus extends the foot and toes upward.
Muscle Classification: Origin and insertion
Sternocleidomastoid has origins on the breastbone (sternum) and the collar bone (clavicle or “cleido”) and insertions on the mastoid process of the skull’s temporal bone. Brachioradialus has an origin on the brachium or arm and an insertion on the radius.
Muscle Classification: Number of origins
Biceps brachii has two origins on the scapula. Triceps brachii has three origins on the scapula and humerus.
Chest Muscles: Pectoralis Minor
Origin: Anterior surface of ribs 3–5
Insertion: Coracoid process of the scapula
Action: Rotates the shoulder forward
Chest Muscles: Abdominal head of the pectoralis major
Origin: Ribs 5–7 (fascia of the abdominal muscles)
Insertion: Lateral edge of the most proximal part of the humerus
Action: Pulls the arm down; is used during a volleyball spike
Chest Muscles: Sternal head of the pectoralis major
Origin: Ribs 1–5 on the lateral edge of the sternum
Insertion: Lateral edge of the humerus
Action: Adducts the arm across the chest; is used during a sidearm pitch in baseball
Chest Muscles: Clavicular head of the pectoralis major
Origin: Medial half of the inferior edge of the clavicle
Insertion: Lateral edge of the proximal humerus
Action: Allows underhand motions; is used in bowling
Fibrous joint
A fixed, or immovable, joint that connects bones. It is made primarily of collagen.
Cartilaginous joint
A joint that has some motion to it with hyaline cartilage present, in the space between articulating bones.
Synovial joint
A moveable joint that contains synovial fluid in the space around it to reduce friction; the most common type of joint in the body.
(ROM) Rotation
Moving around the longitudinal axis of the bone either toward the midline or away from the midline.
(ROM) Circumduction
Moving in a circular motion.
(ROM) Abduction
Moving away from the axis, or midline, of the body.
(ROM) Adduction
Moving toward the axis, or midline, of the body.
(ROM) Elevation
Moving in an upward direction.
(ROM) Depression
Moving in a downward direction.
(ROM) Flexion
Bending of a joint that decreases the angle between bones.
(ROM) Extension (and Hyperextension)
Straightening of a joint that increases the angle between bones. Hyperextension is excessive straightening beyond the normal range of motion.
(ROM) Plantar flexion
Bending the ankle pointing toes toward the ground.
(ROM) Dorsiflexion
Bending at the ankle to lift the toes toward the knee.