Biology Study Material: Chapter 21 - DNA Sequencing Terminology and Techniques
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
DNA sequencing
Determining the exact order of the base pairs in a segment of DNA.
--------------------------------
HISTORY
- developed by Allan Maxam, Walter Gilbert, and Frederick Sanger (1970s)
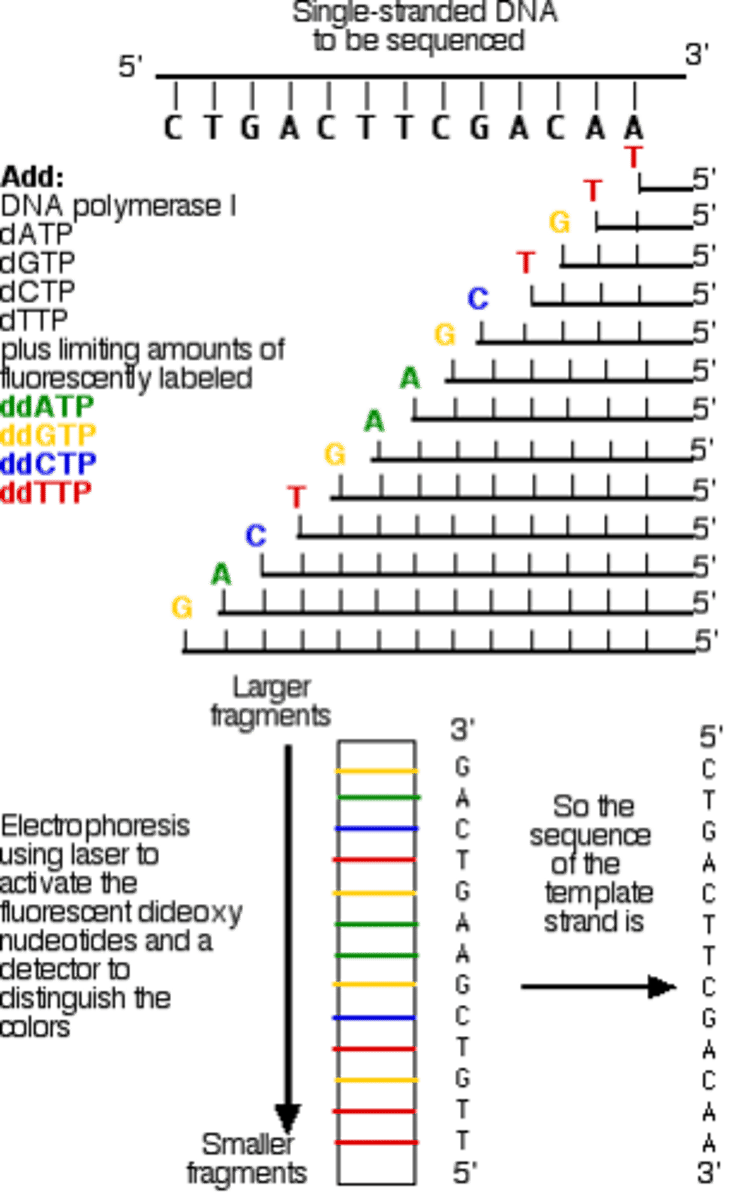
dideoxy sequencing
AKA Chain formation
- a method of DNA sequencing that uses deoxyribonucleotides to terminate the growth of DNA strands
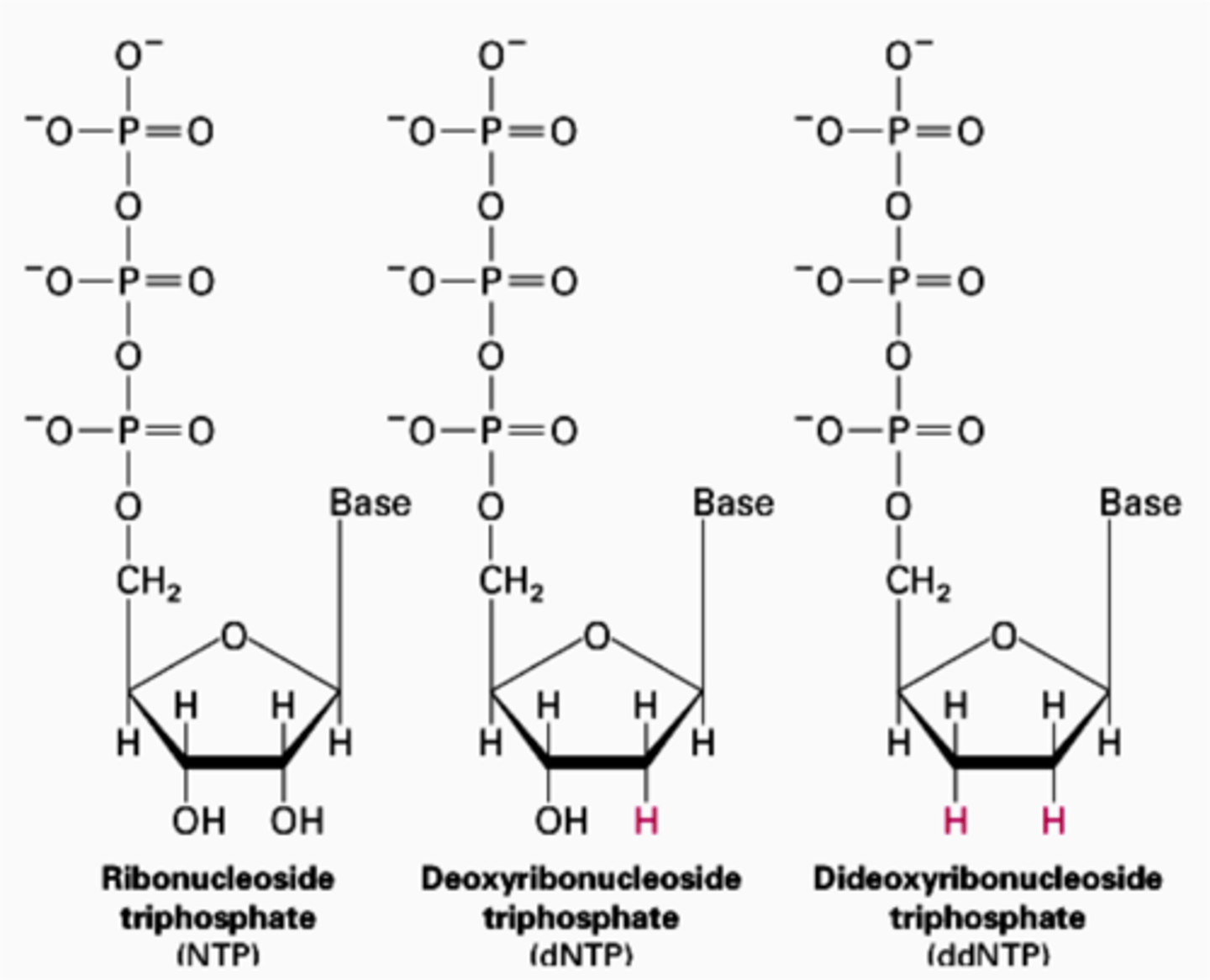
dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (ddNTP)
BASIC SUMMARY
- contains a prefix di-
- 3' on lewis structure contains a H (instead of OH for normal lewis structure)
- 3' is the "chain terminator"
--------------------------------
MAIN IMPORTANCE:
- ddNTP's stop DNA replication
(replication stops COMPLETLY)
chain termination
the stoppage of growth of a DNA strand, RNA strand, or polypeptide sequence from a ddNTP
--------------------------------
RECAP: 3' contains a "H" instead of "OH" which stops elongation of DNA strand
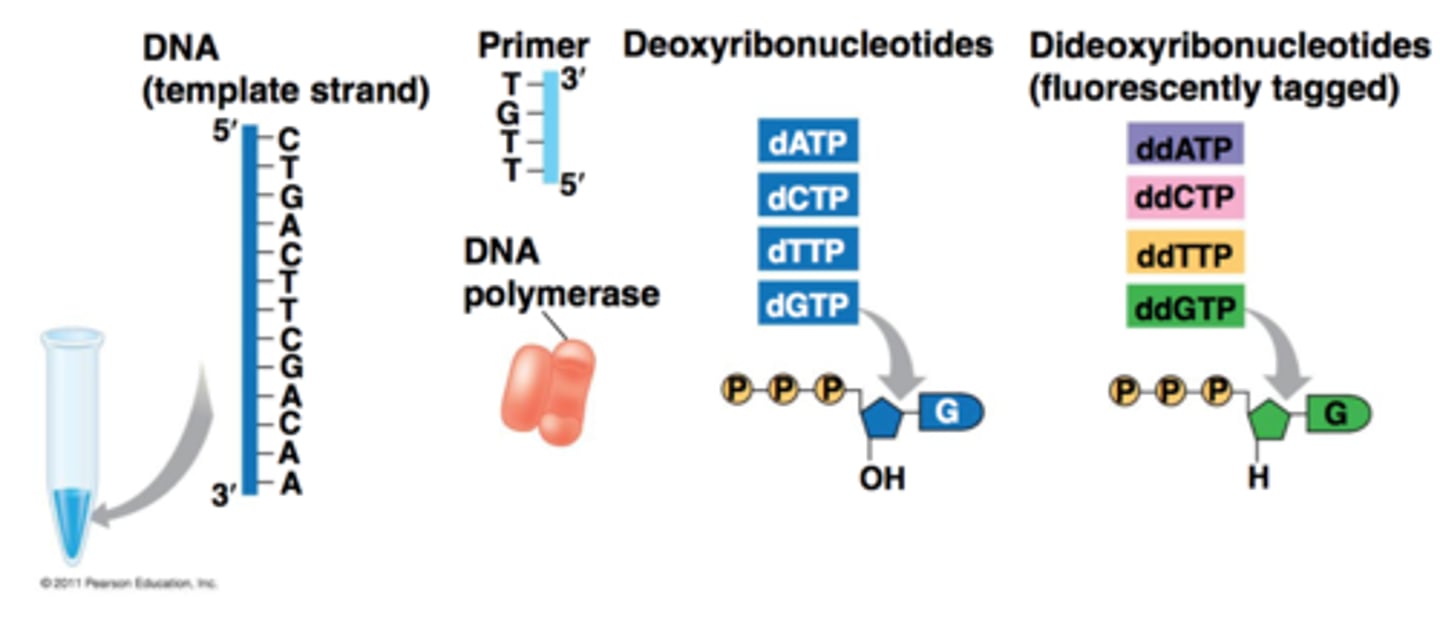
Types of ddNTP's
adenine = ddATP
thymine = ddTTP
cytosine = ddCTP
guanine = ddGTP
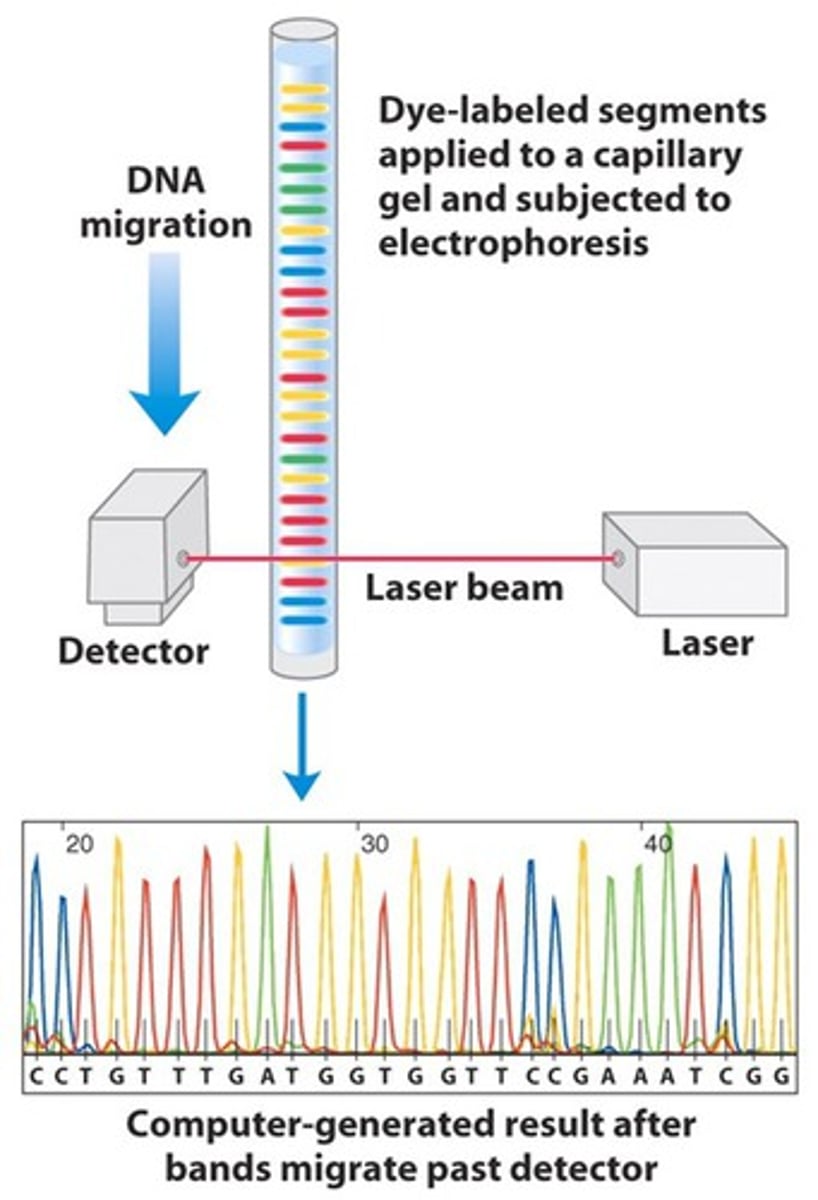
Automated DNA sequencing
the use of fluorescently labeled ddNTP's and a fluorescence detector to sequence DNA
- each type of ddNTP's has a different colored fluorecent that indicates the last base in each strand
site-directed mutagenesis (SDM)
the creation of a mutant from a protein by altering a single site on the protein
- is done by mutating a single amino acid
- done in vitro (outside the cell
- done with DNA inside the plasmid
--------------------------------
ADVANTAGES
- allows for the alteration of a DNA sequence in a specific way
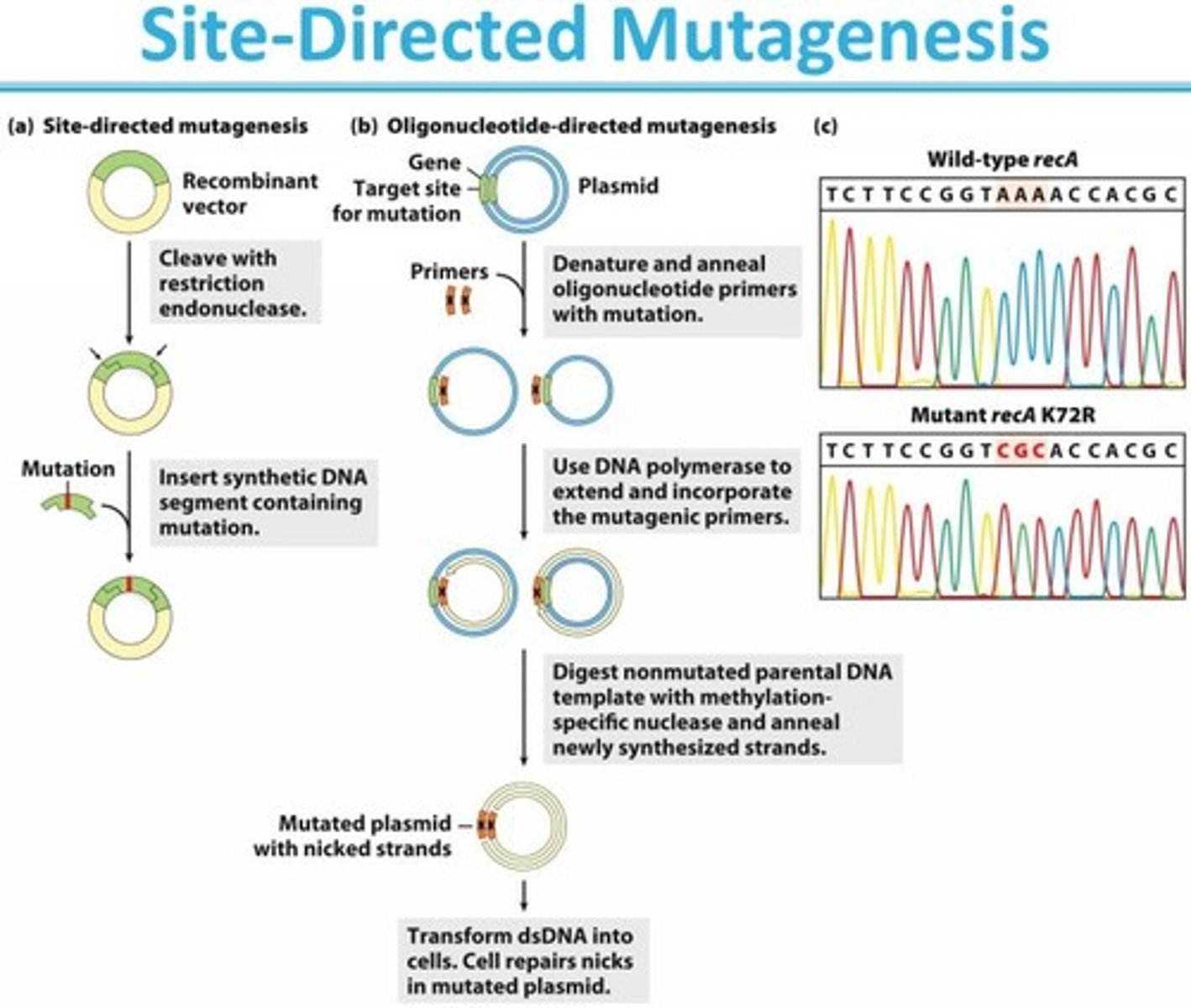
SDM restrictions
A mismatch is created:
- depending on which base is replaced, the mutant or original sequence is produced
- mutant can be identified by DNA sequencing
Why is SDM performed?
allows researchers to see how mutation affects
- the expression of the gene
- the function of a protein
- the phenotype of an organism
Blotting techniques
- Northern blotting (RNA)
- Southern blotting (DNA)
- Western blotting (Protein)
--------------------------------
KEY FEATURES:
- all are quantitative
- uses electrophoresis
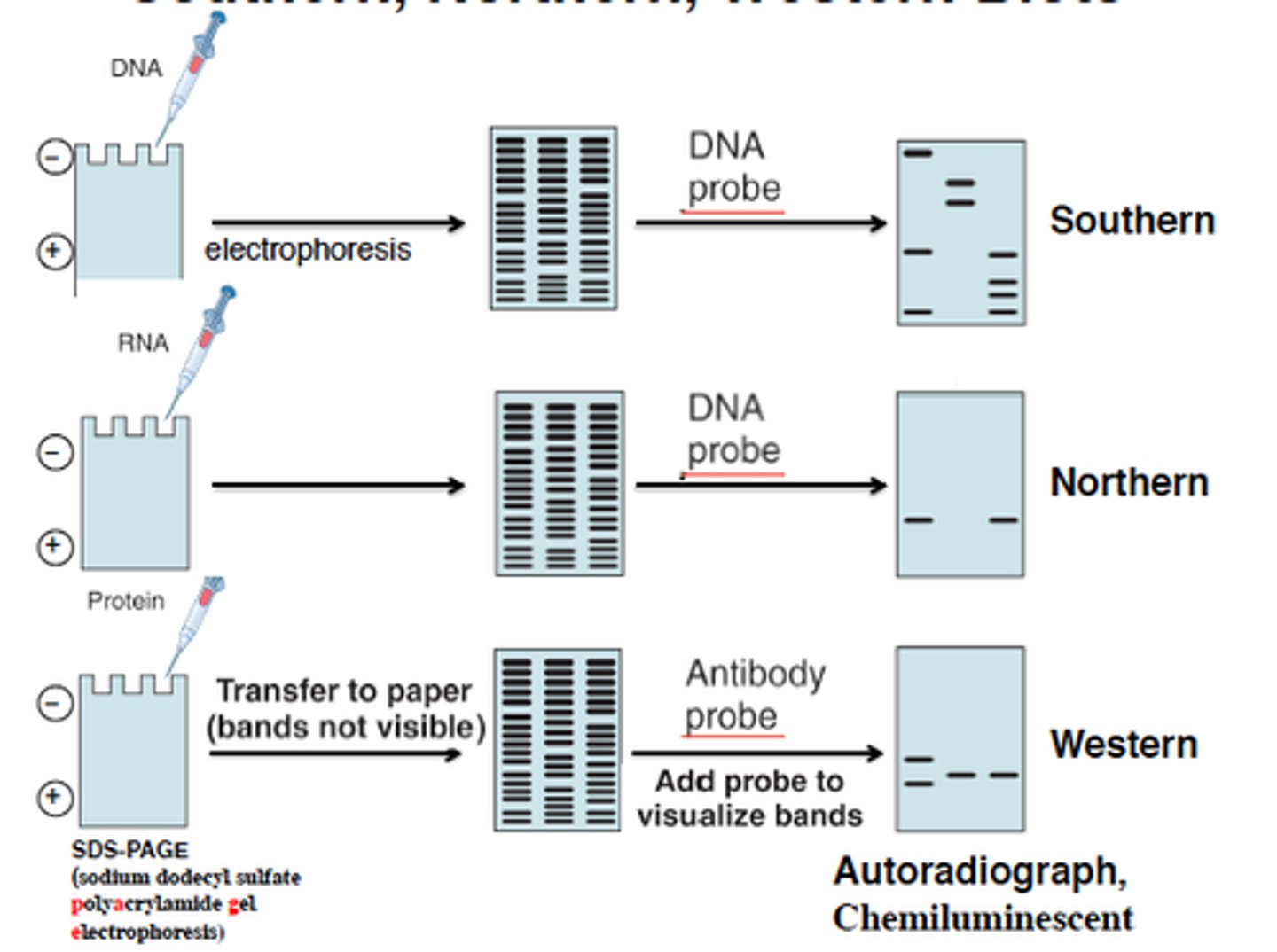
What are blotting techniques used for?
- is used to detect mRNA and proteins
--------------------------------
HOW IS IT VISUALIZED?
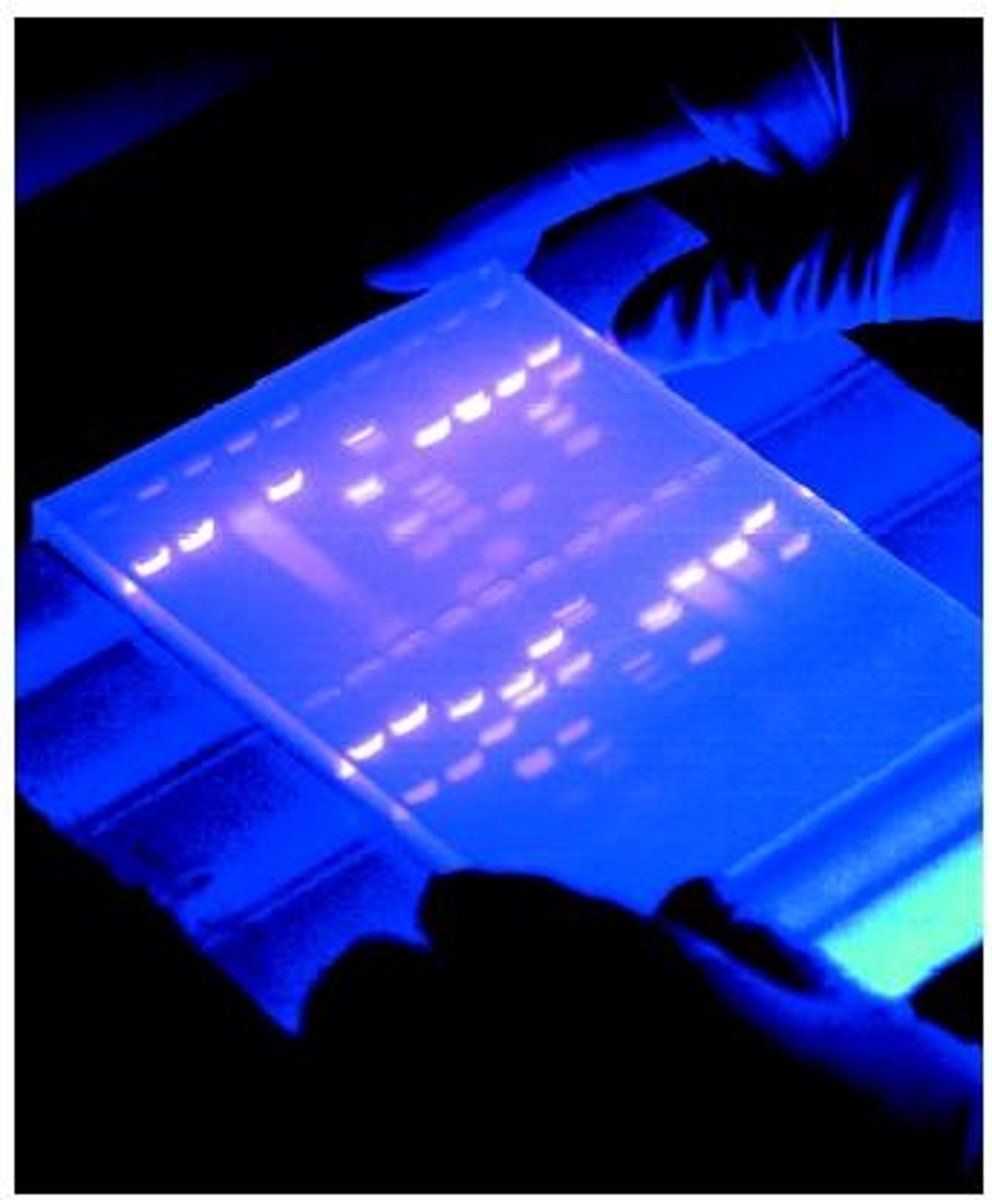
- ETBR
EtBr (ethidium bromide)
planer molecule that intercalates with DNA and makes them visible in orange after being exposed to UV light.
Northern blotting (RNA)
- used to identify specific RNA within a mixture of many RNA molecules
--------------------------------
FEATURES:
- uses RNA for electrophoresis
- uses agarose gel the contains formaldehyde
- uses radioactive sscDNA probes
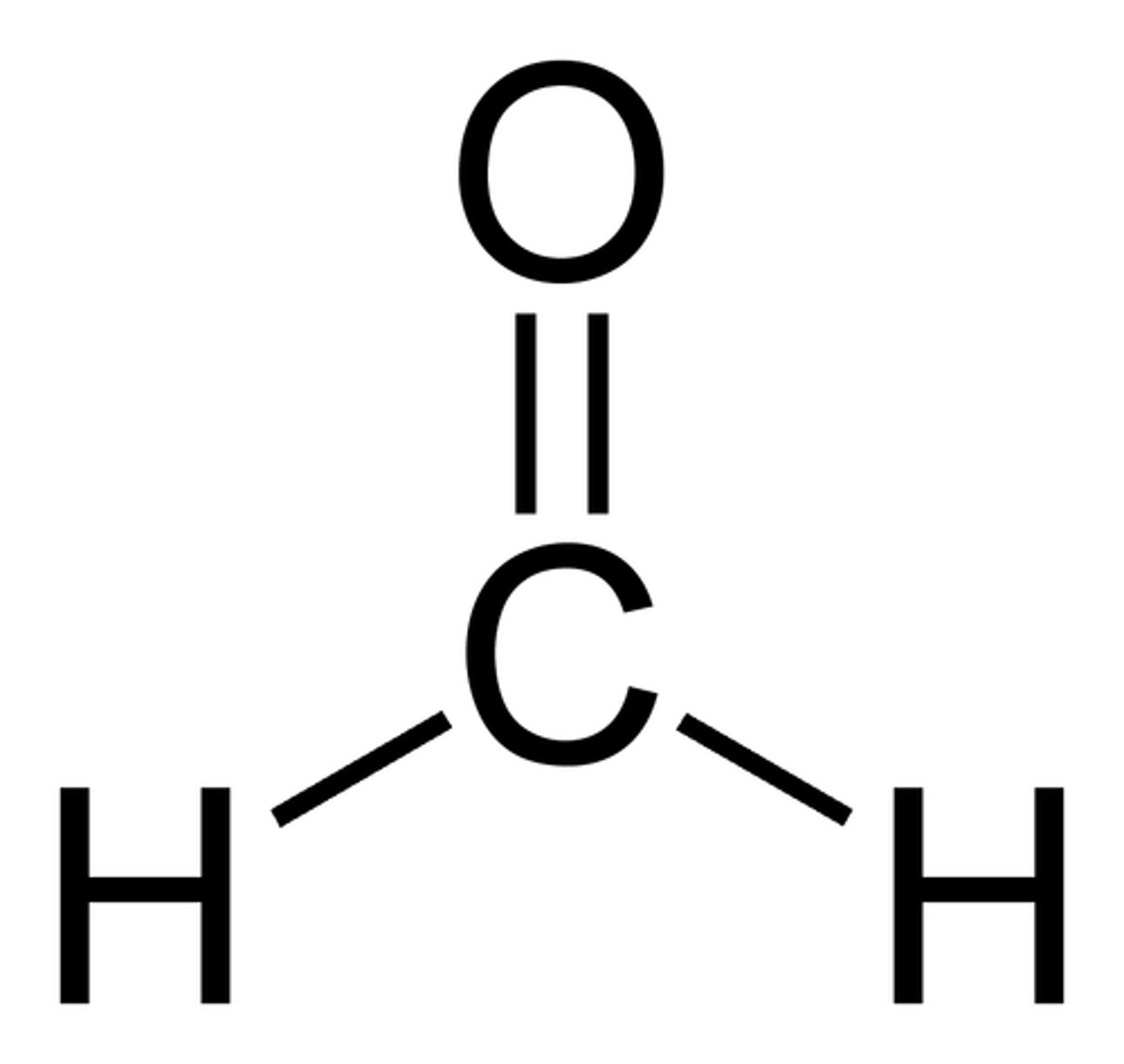
Formaldehyde
the chemical used to break down hydrogen bonds in RNA strands
What can Northern Blotting determine?
- if a specific gene is transcribed in a particular cell type or is in a specific stage of development
- it can reveal if a pre-mRNA is spliced
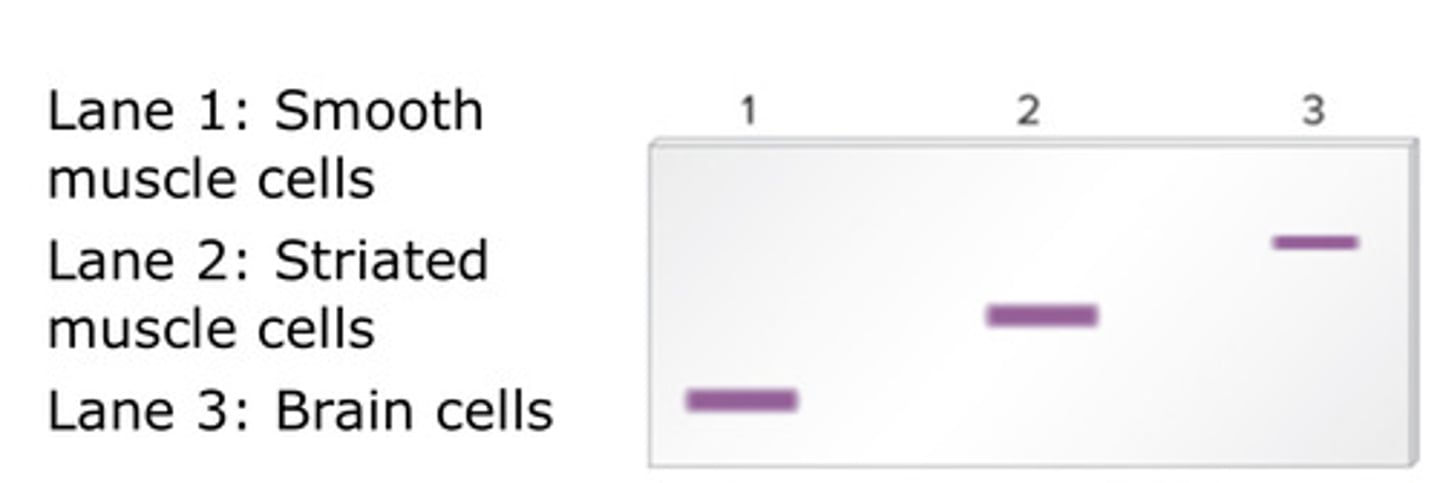
how is Northern Blotting similar/different to RT-qPCR?
Similar:
- both are used to quantify the amount of RNA is spresent for a specific gene of mRNA
--------------------------------
Difference:
- RT-qPCR works for both RNA and DNA
- Northern blotting uses its length instead of its amount to transcribe a gene
Northern Blotting Procedure
1. RNA is extracted from the cells and is then purified
--------------------------------
2. its then separated by gel electro.
--------------------------------
3. its bottled onto nitrocellulose or nylon filters
--------------------------------
4. Filters are placed into a solution containing a radioactive probe
--------------------------------
5. Filters are then exposed to x-ray film
where they can be detected as complementary radiolabeled probe/ dark bands on
spliced
process of removing intron in the nucleus of the cell
--------------------------------
WHAT DOES IT MEAN ON AN AGE MACHINE?
- the bands are separated on one lane
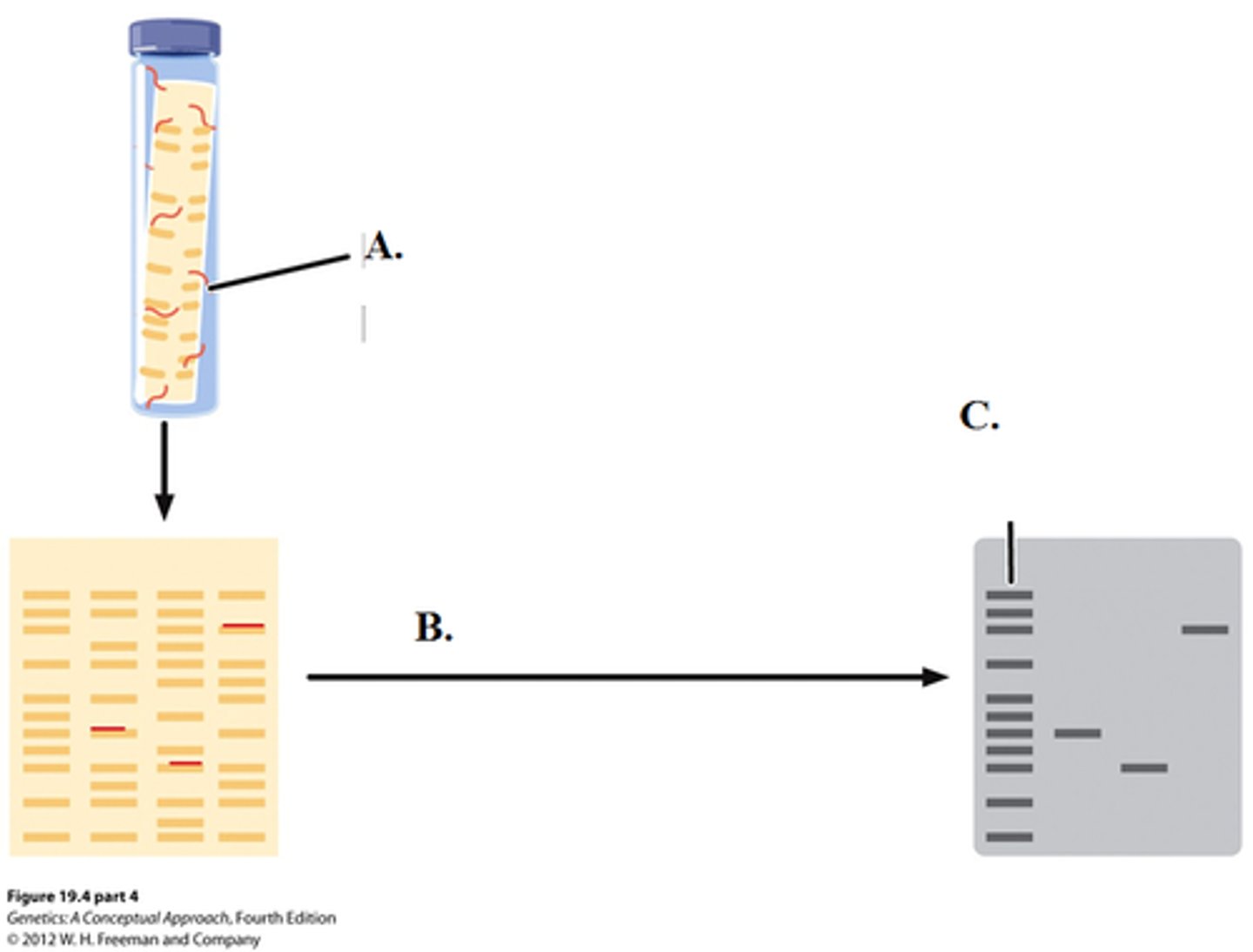
Southern Blotting (DNA)
separating DNA molecules based on size
--------------------------------
FEATURES:
- electrophoresis uses dsDNA
- uses agarose gel (by seeing multiple smears)
- uses a radioactive sscDNA probes
smears
indicates that there is a variety of possibilities of different fragment sizes
What does Southern Blotting determine?
- main use is to identify a specific gene or fragment of DNA
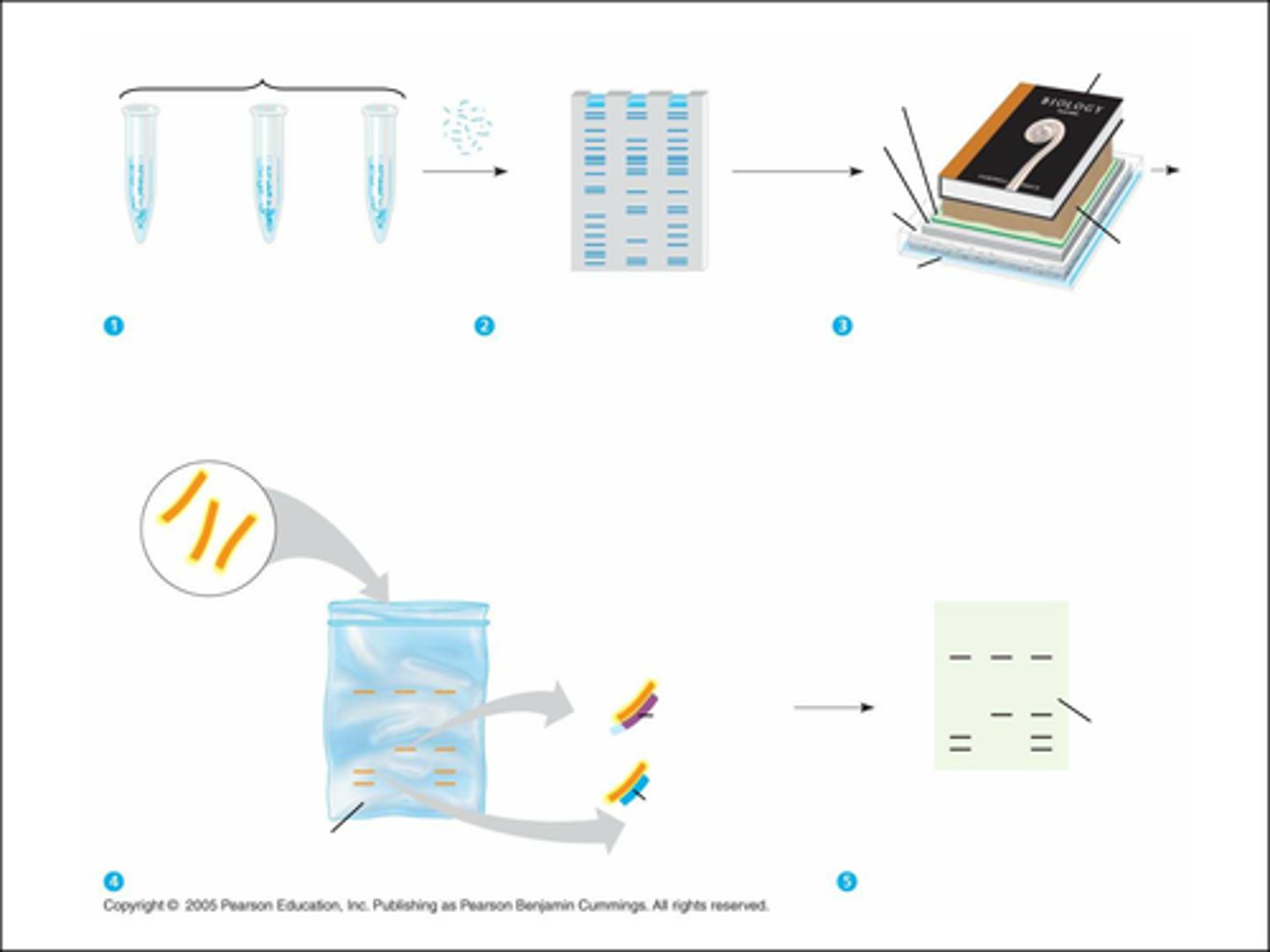
Southern Blotting Procedure?
BASED ON NOTES:
--------------------------------
1. Extract and purify DNA from cells
--------------------------------
2. cut DNA into different sized fragments using restriction endonucleases
--------------------------------
3. Perform gel electrophoresis (to allow the DNA fragments to separate)
--------------------------------
4. Denature the DNA
--------------------------------
5. transfer to nitrocellulose paper (where blotting will occur)
--------------------------------
6. add labeled probe for hybridization to take place
--------------------------------
7. wash off unbound/excess probe
--------------------------------
8. autoradiograph the sample
Restriction endonucleases (enzymes)
RECAP:
molecular scissors that can cut DNA in specific locations
Nitrocellulose
a modified cellulose molecule used to make paper membrane for blots of nucleic acids and proteins
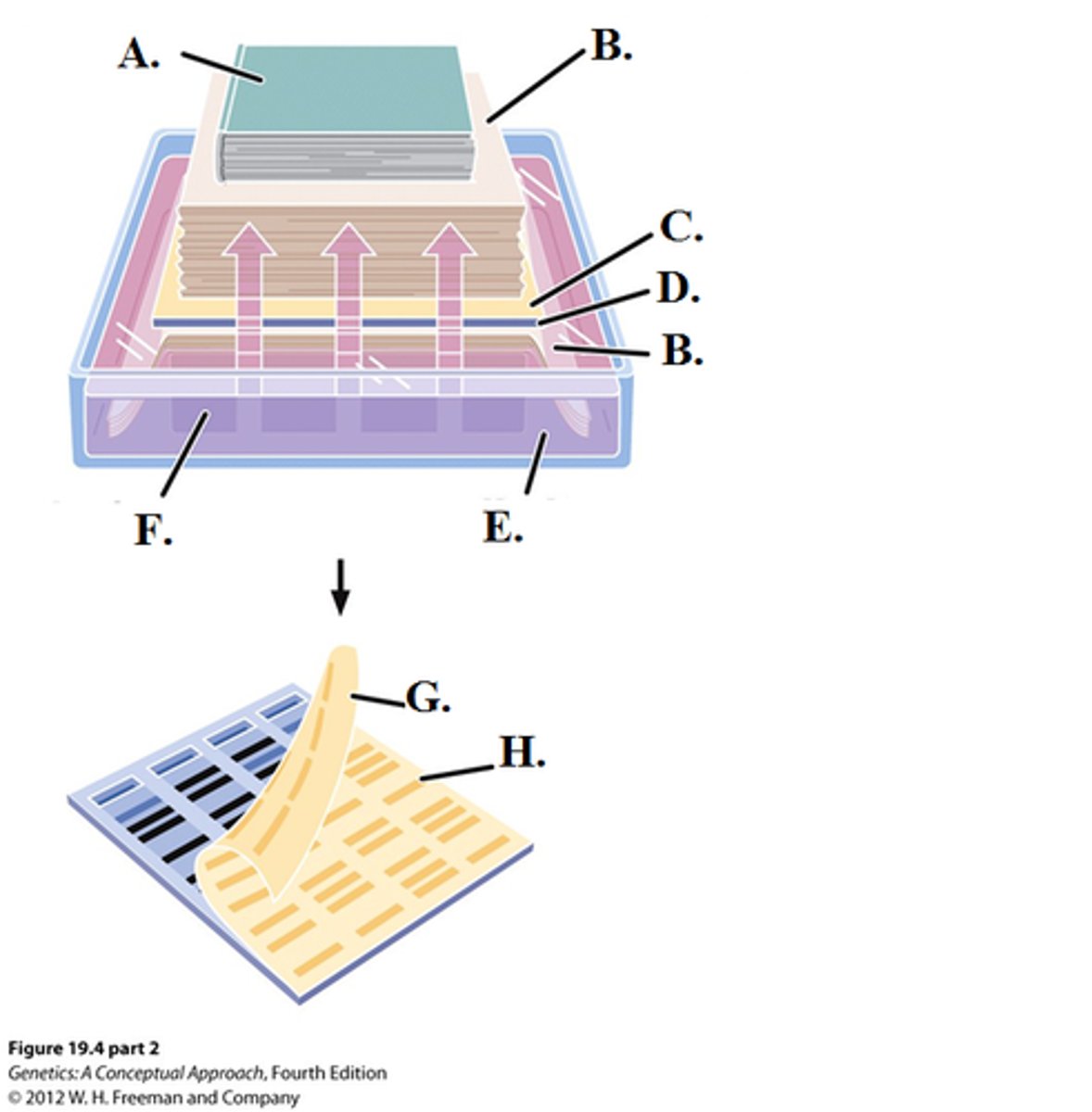
Autoradiography
a procedure that locates radioactive substances in a slice of tissue
--------------------------------
the radiation exposes a photographic emulsion or a piece of film that covers the tissue
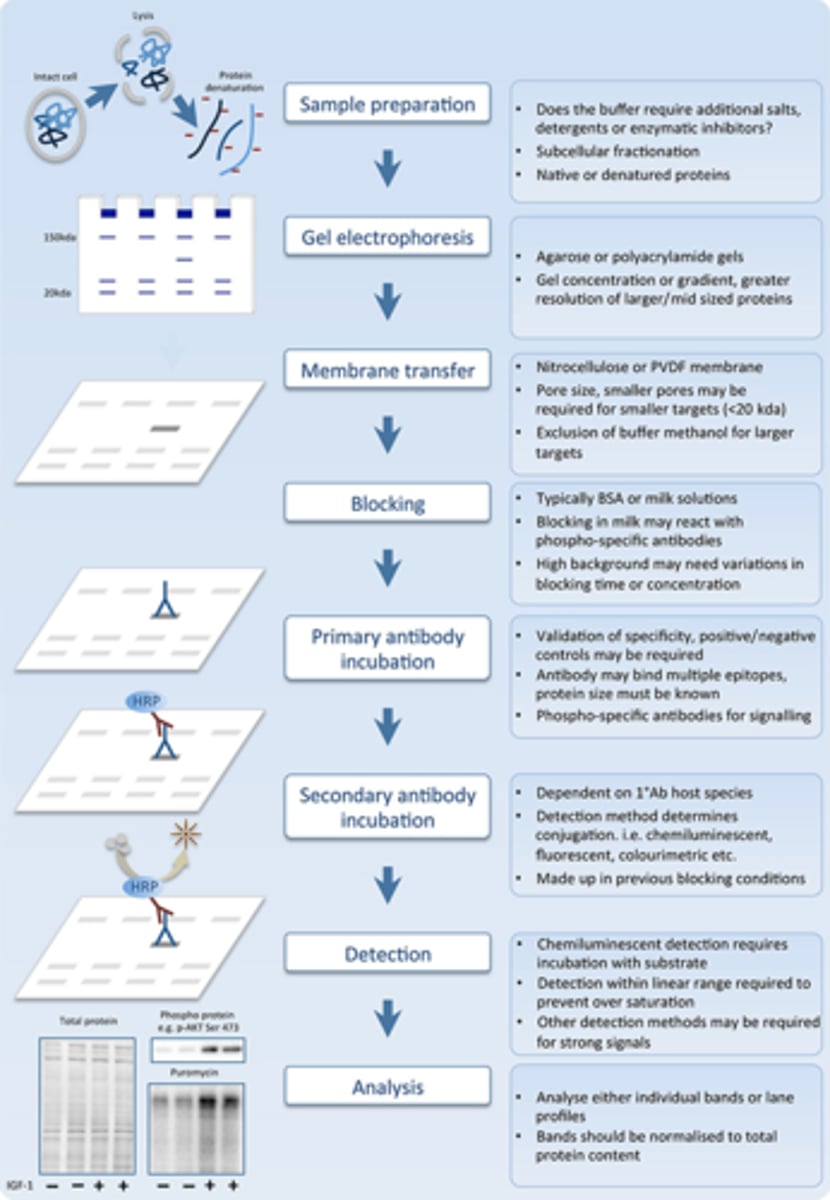
Western blotting (Proteins)
- used to identify a specific protein within a mixture of many protein molecules
--------------------------------
FEATURES:
- electrophoresis uses protein
- gel is polyacrylamide
- uses either folded or denatured proteins
- uses antibodies as its probe
polyacrylamide
A polymer used as a gel material in vertical electrophoresis
--------------------------------
is used to used to separate small proteins apart
what can western blotting determine?
it can determine if:
- a specific protein is made in a particular cell type or is in a particular stage of development (similar to Northern blotting)
Western blotting procedure
BASED ON NOTES:
1. dissolve detergent sodium dodecyl sulfate
--------------------------------
2. separate the "-" charge proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
--------------------------------
3. place sample onto nitrocellulose or nylon filters
--------------------------------
4. place the filter in a solution containing the primary antibody
--------------------------------
5. then place filter in a solution containing a secondary antibody
--------------------------------
6. add colorless XP to the sample to allow an appearance of dark bands on electrophoresis
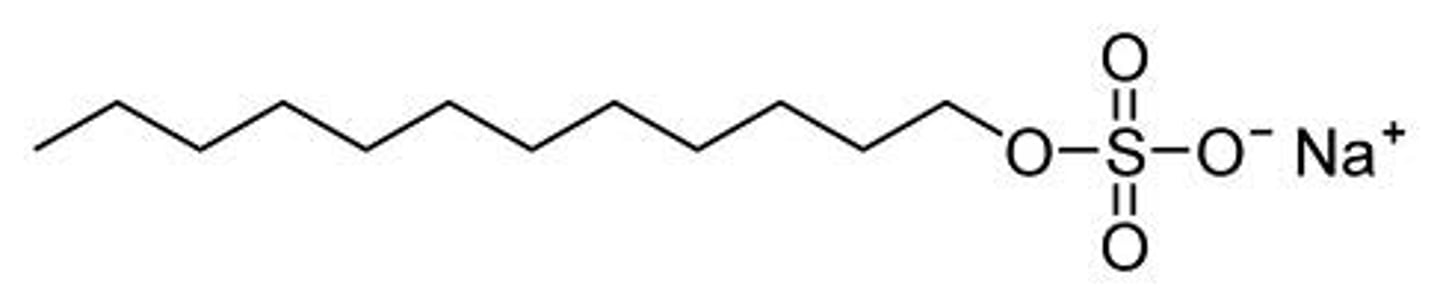
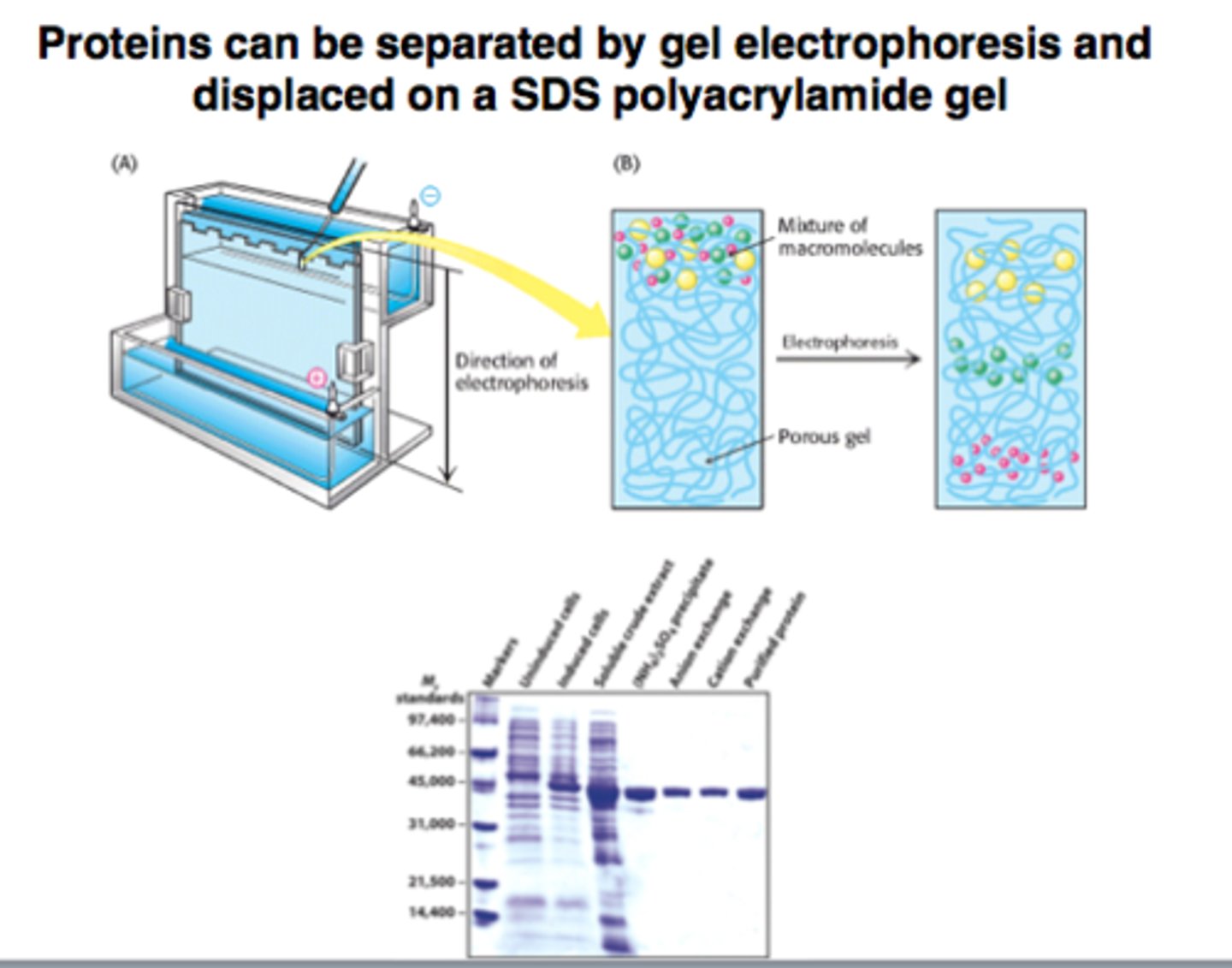
sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
detergent that denatures proteins and coats them with a negative charge
--------------------------------
prefix dode- = 12
Polyarcylamide gel electrophoresis
method of separating proteins depending on:
- size
- structure
- molecular weight
primary antibody
Antibody that recognizes protein of interest
secondary antibody
antibody that is conjugated to alkaline phosphatase
- recognizes the constant region of the primary antibody
methods for analyzing DNA and RNA binding proteins
- electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- DNAse I footprinting
--------------------------------
PURPOSE?
- both methods find what protein is involved in transcription factors
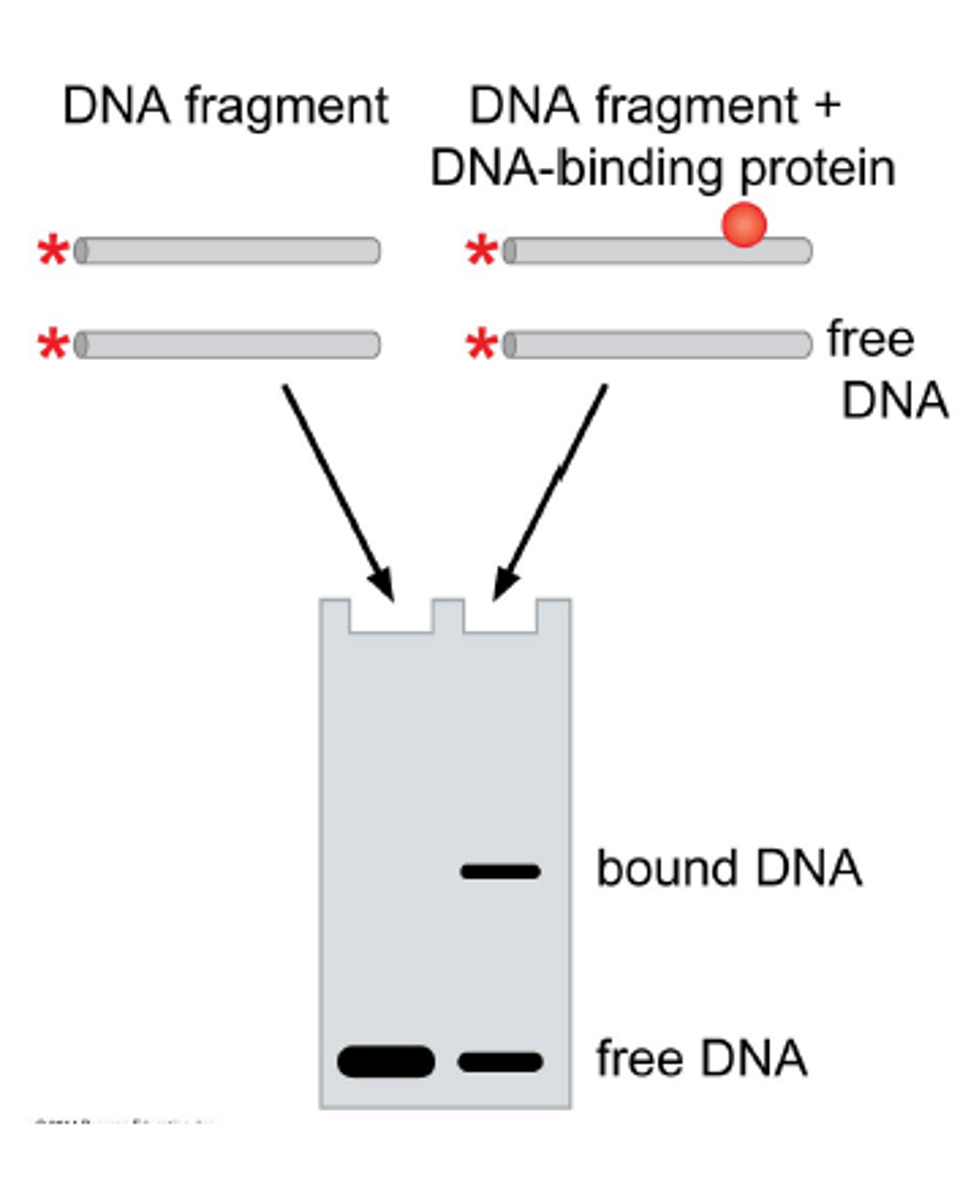
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
AKA: gel shift assay / gel retardation assay
--------------------------------
WHAT DOES IT DETERMINE?
- if a protein binds to a specific DNA fragment or RNA molecule
--------------------------------
FEATURES:
- is ran under native gels
- uses a radioactive dsDNA probe
- commonly looks at 20 base pairs per run
native gels
Polyacrylamide gels:
- acrylamide gels with no SDS
--------------------------------
Agarose gels:
- agarose gels with no denaturing techniques
EMSA restrictions (No denaturing techniques)
must be performed under non-denaturing conditions
--------------------------------
- buffer and gel should not cause the unfolding of the proteins nor the separation of the DNA double helix
how does EMSA work
1. DNA and protein molecules migrate through a gel matrix at different rates
--------------------------------
2. Small DNA oligomers will run quickly through a gel
--------------------------------
3. proteins migrate more slowly
--------------------------------
4. DNA protein complexes are larger than either - we see a shift in migration
--------------------------------
5. monitor the migration of free DNA to protein-bound DNA
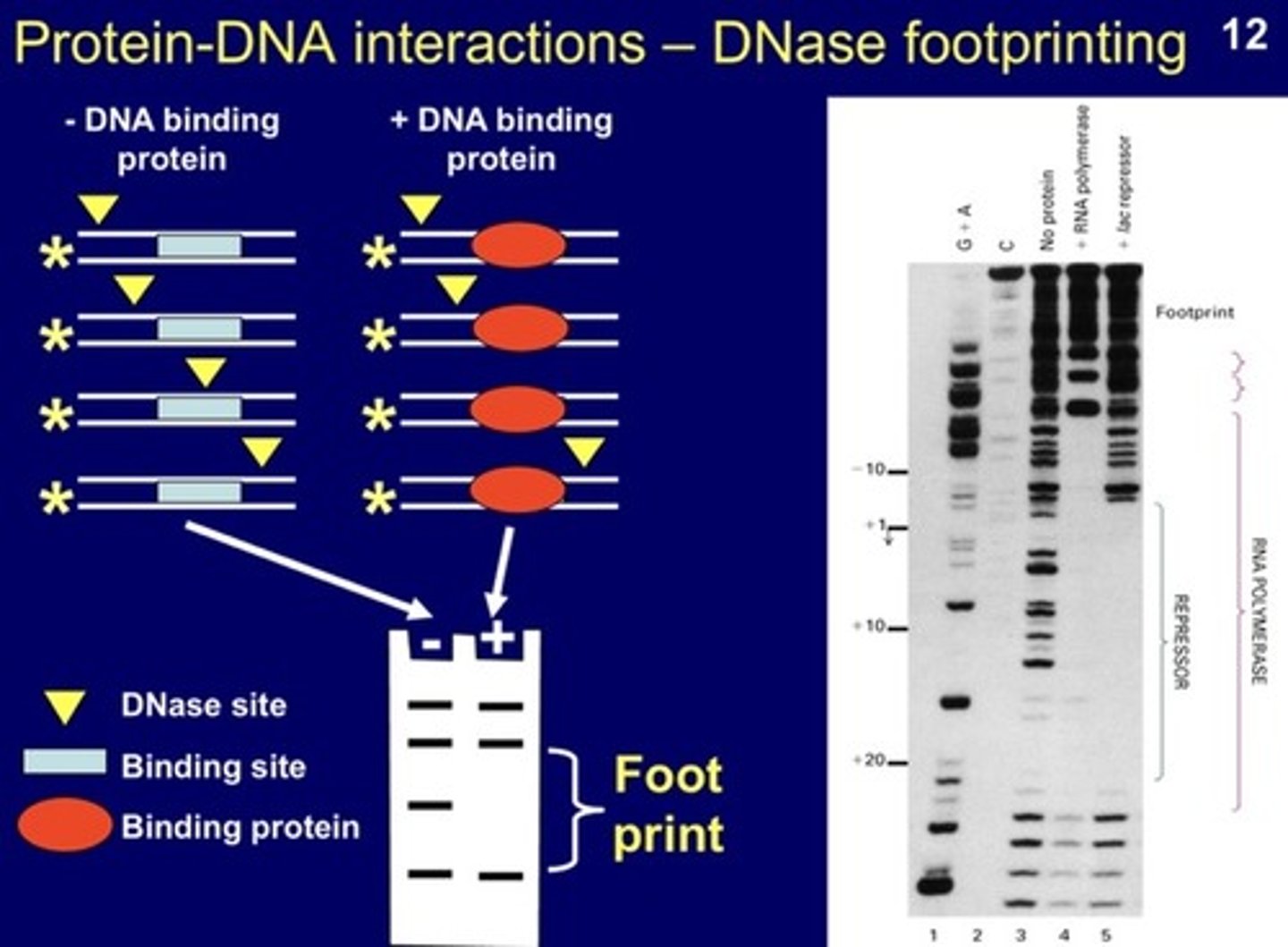
DNase I footprinting assay
AKA: DNA footprinting / DNase footprinting
--------------------------------
WHAT DOES IT DETERMINE?
- a harder assay that shows detailed interactions between a protein and DNA
--------------------------------
FEATURES:
-DNA fragment used is typically around 300 base pairs (BP)
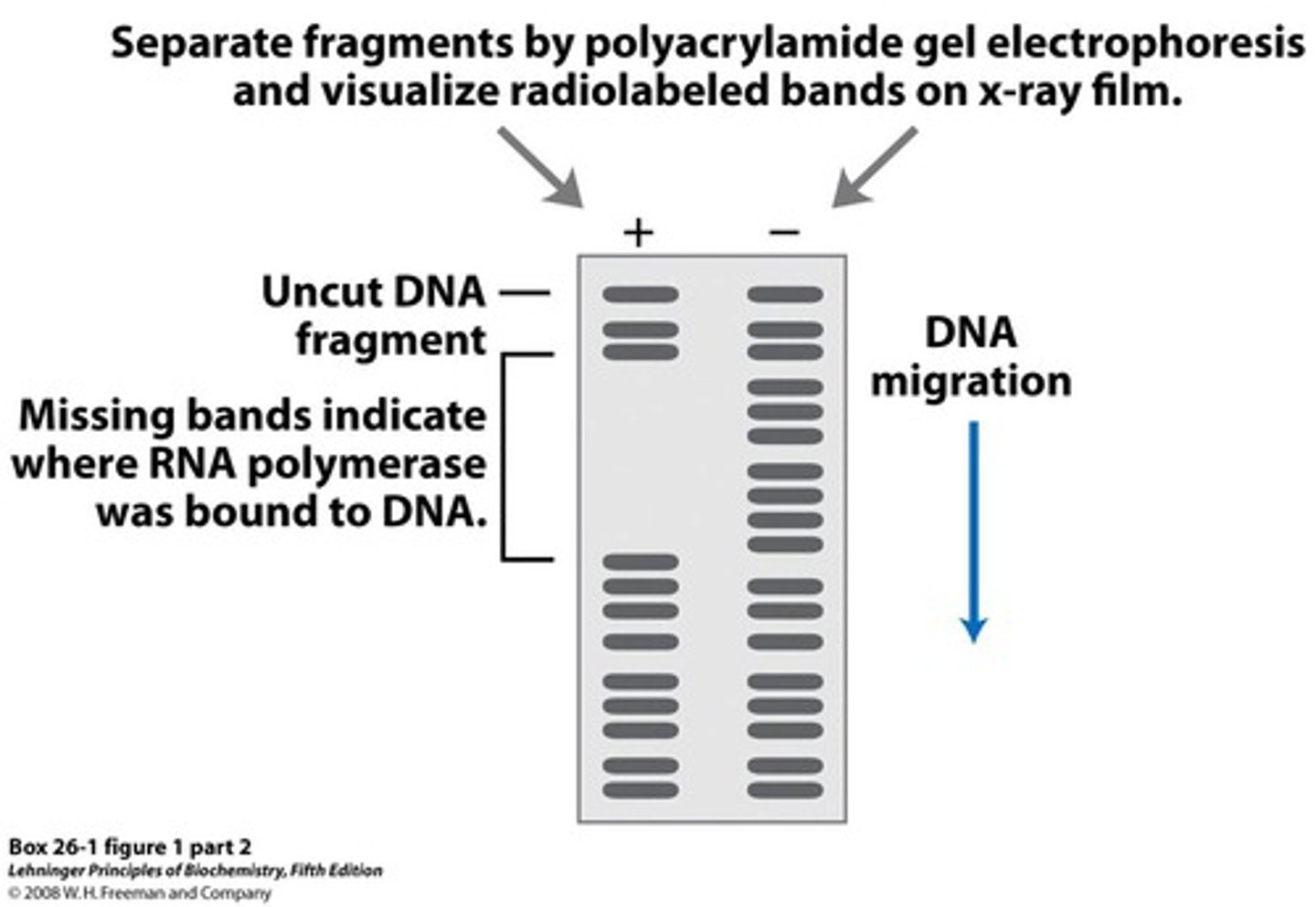
How does DNase I footprinting work?
1. probe with 300 BP is incubated with NL solution
--------------------------------
2. add DNase I to make a single cut on each probe
--------------------------------
3. rub it on a polyacrylamide gel (to denature urea)
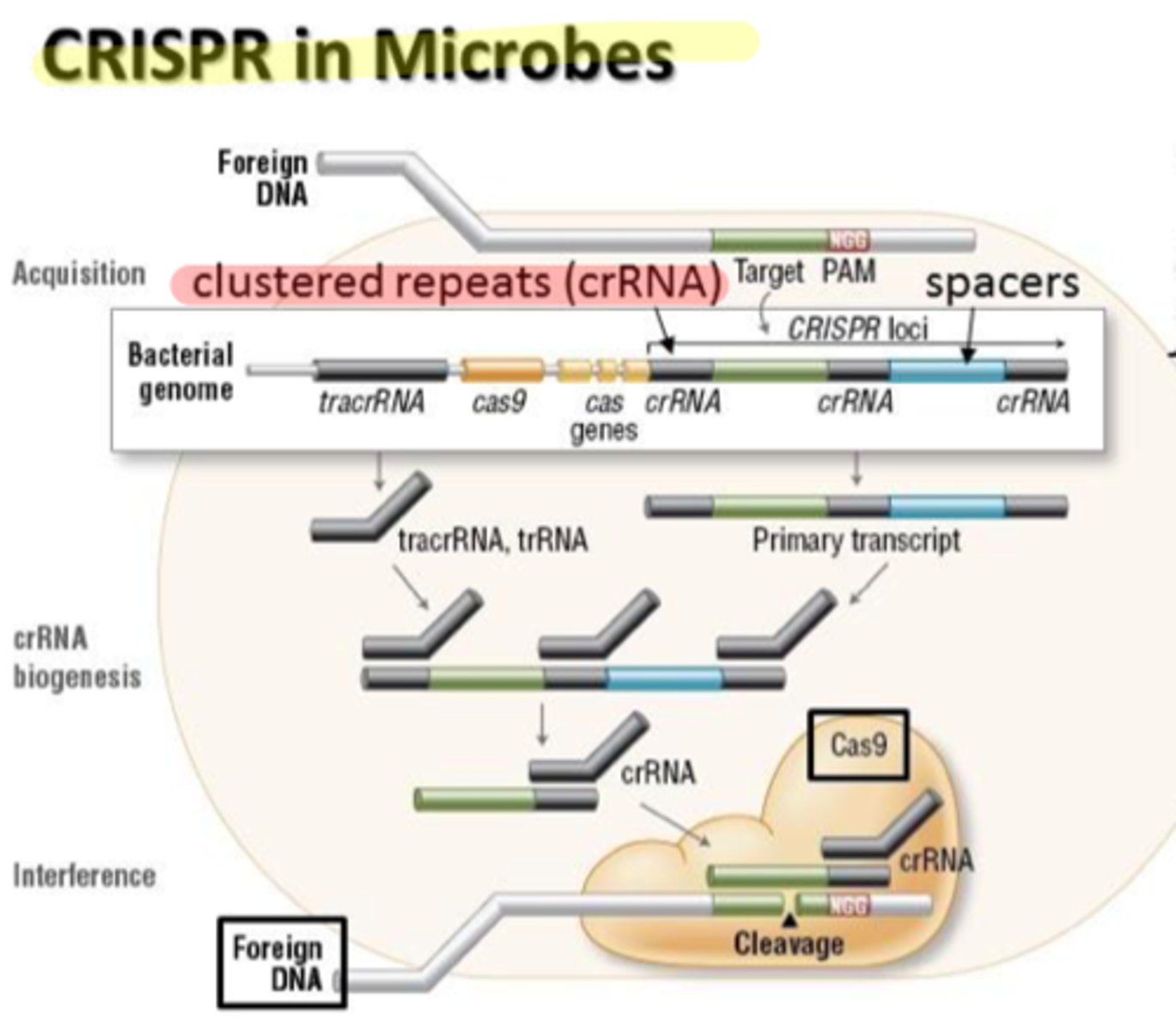
CRISPR-Cas technology
WHAT DOES IT DO?
- allows you to make/insert genes in a living cell
- targets restriction enzymes to create fragments
--------------------------------
ADVANTAGES:
- uses a noncoding RNA from a microbe that doesn't have a specific RNA sequence
types of non coding RNA's
- tracrRNA
- crRNA
tracrRNA
RNA needed to associate with crRNA and Cas9 for function of the enzyme (crRNA binds to Cas9)
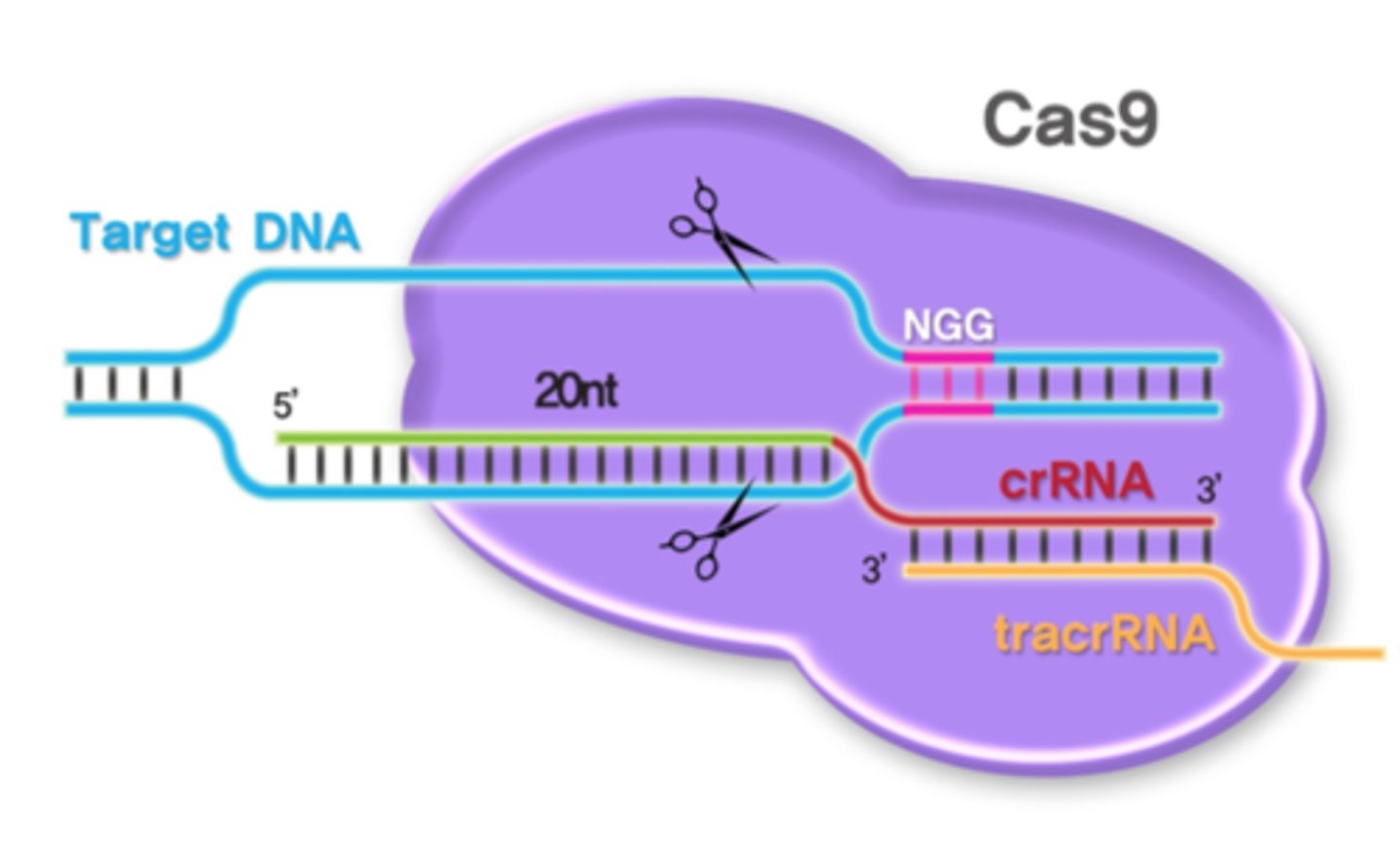
Cas9
RNA-guided DNA endonuclease enzyme associated with the CRISPR
--------------------------------
MAIN FUNCTION:
- produce a ssDNA
- can cut target DNA
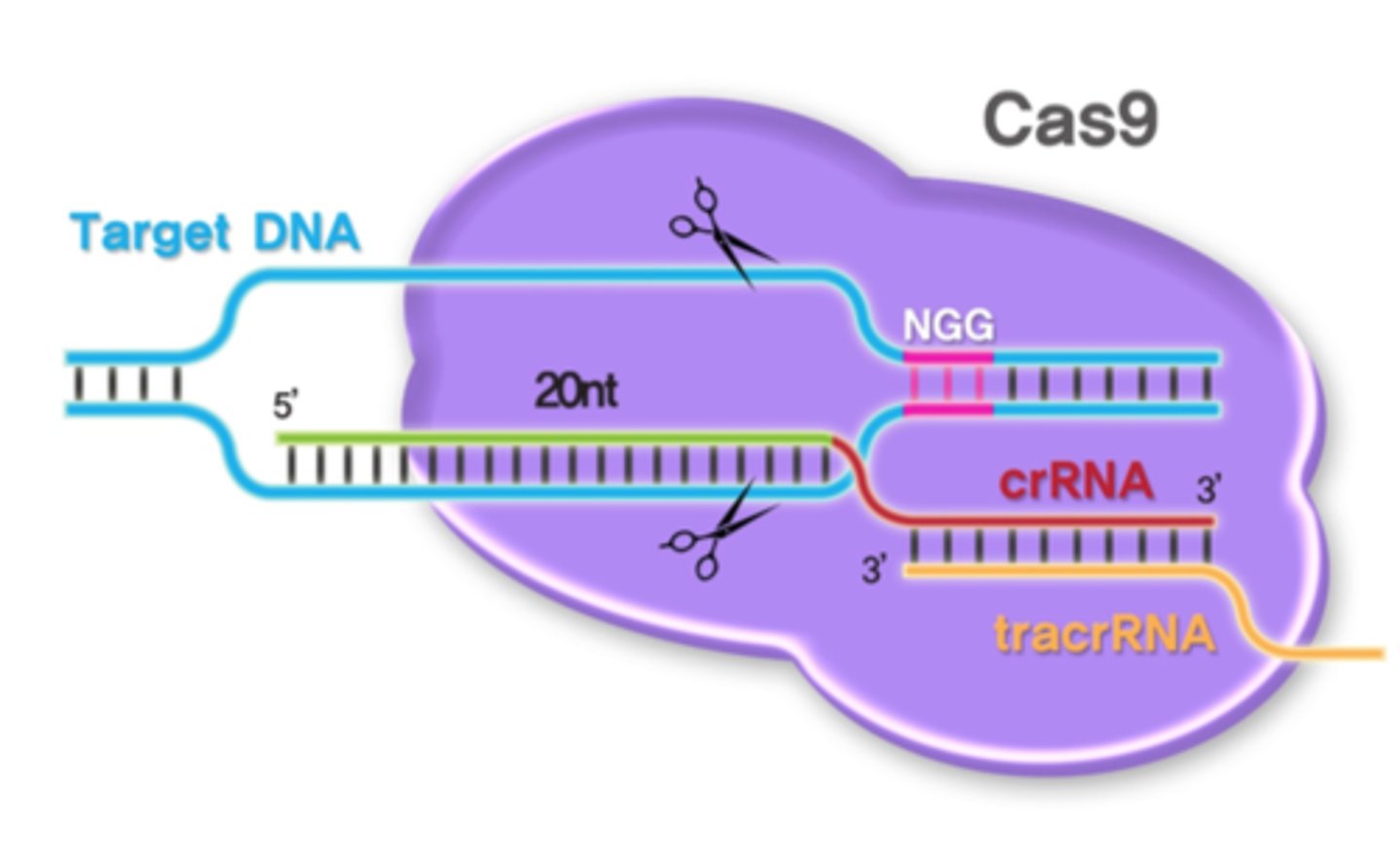
crRNA
RNA transcribed from CRISPR tech. that binds to a target DNA
--------------------------------
MAIN FUNCTION:
- its a protein complex that degrades complementary invading viral nucleic acid
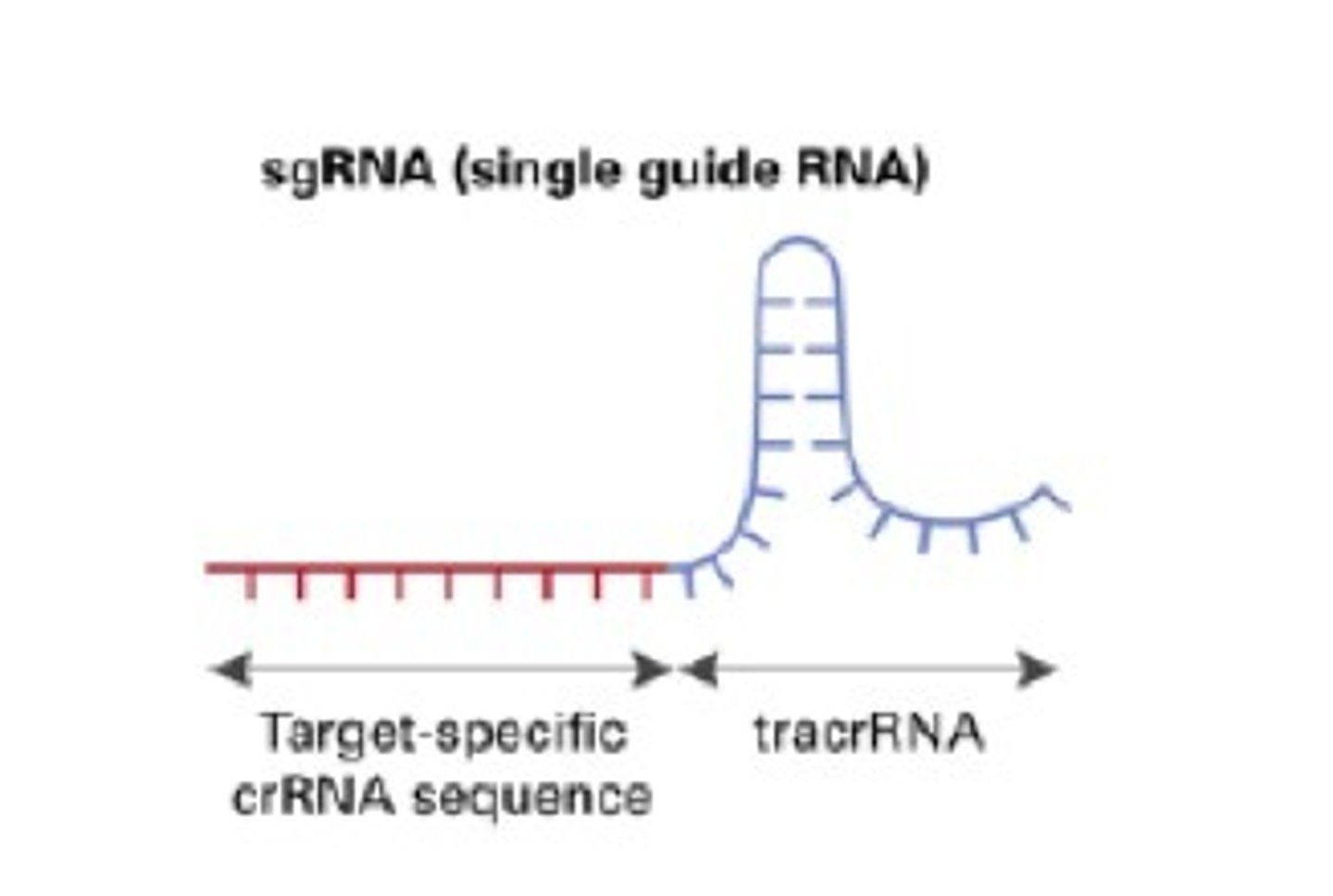
sgRNA (single guide RNA)
a synthetically engineered binding site that links/binds Cas9 to a gene of interest
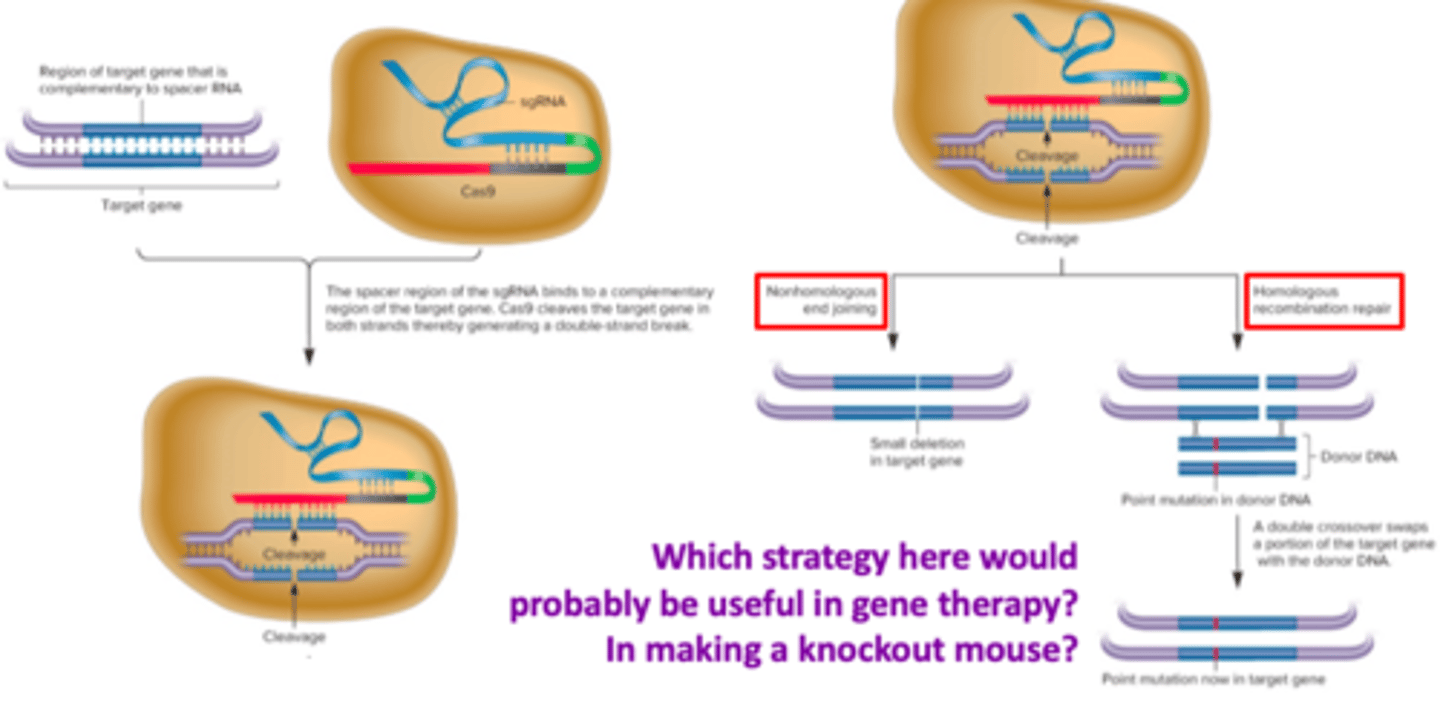
cas9 repair events
- nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ)
- Homologous recombination repair (HRR)
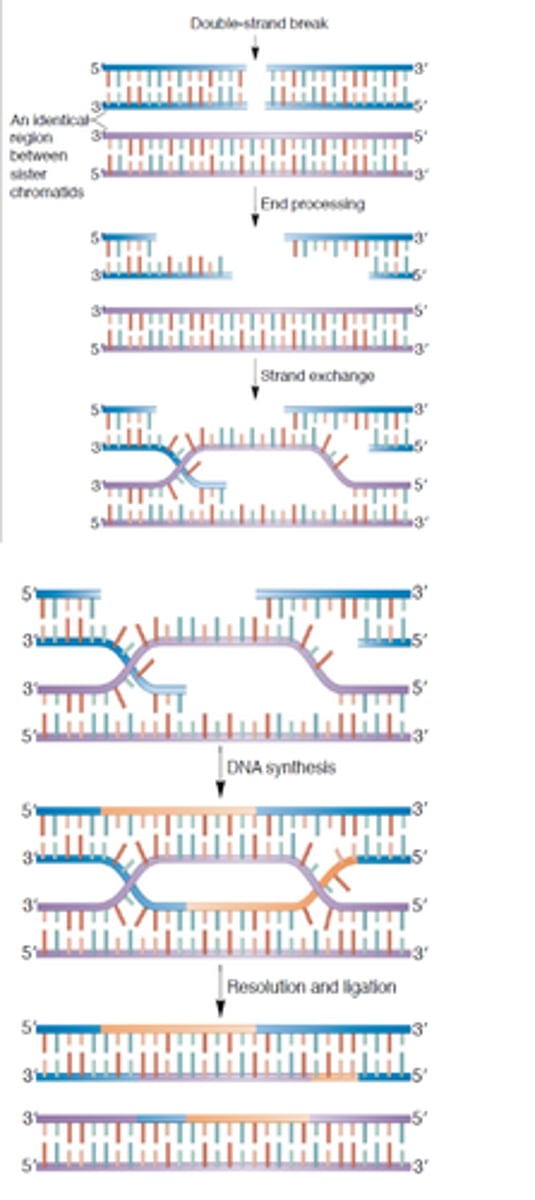
Nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ)
the region that may incur a small deletion that inactivates the gene
- loses information
- cripples/breaks a gene
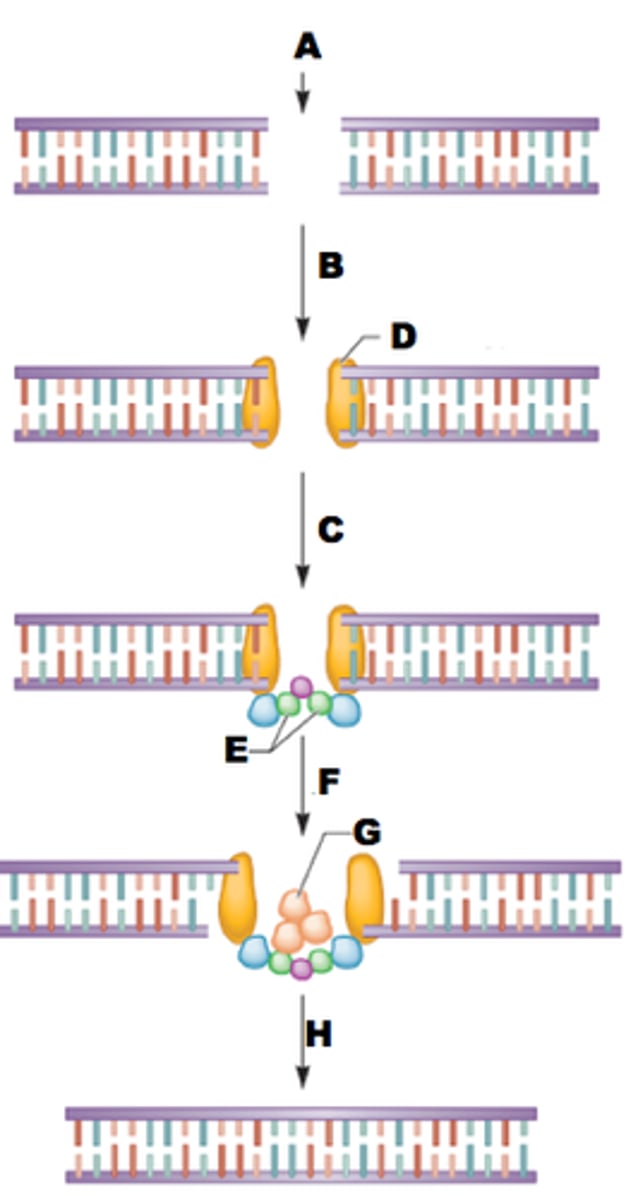
homologous recombination repair (HRR)
a repairing of double-strands that occurs when the DNA strands from a sister chromatid are used to repair a lesion in the other sister chromatid