CVM - Lecture 7: Haemodynamics and Blood Pressure Regulation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
The physical factors that govern bloodflow
Define haemodynamics?
Amount of blood flowing per unit of time
Define blood flow
HR x SV - the amount of blood which circulates in 1 minute
Define cardiac output
1. 0.7
2. 0.2
3. 1.35
4. 1.0
5. 1.05
6. 0.25
7. 0.45
Fill the blanks
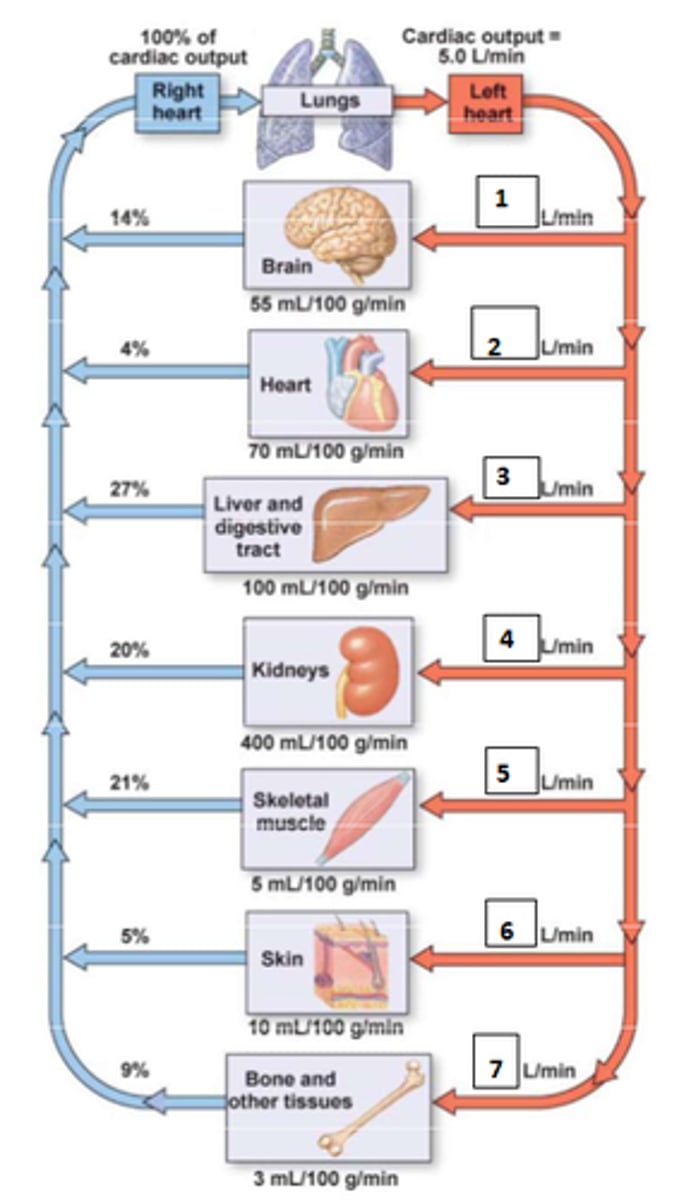
- pressure
- resistance
What are the two major determinants of blood flow?
1. cardiac output
2. peripheral vascular resistance (PVR)
3. blood volume
(BP = CO x PVR)
What are the determining factors of blood pressure?
>10%
At which volume of blood loss do compensatory mechanisms fail to normalise blood pressure?
Friction: vessel diameter (most adjustable), blood viscosity and vessel length
Which physical mechanisms is mostly responsible for resistance and which factors further make it up?
Arterioles
Which area of the vascular system contributes to most of the peripheral vascular resistance?
Cells, particularly red cell due to their high number
Which blood constituent contributes most to blood viscosity?
Q = ∆P/R
Give Ohm's law for blood flow/Q
They are inversely proportional
What is the mathematical relationship between blood flow and resistance?
blood flow is proportional to radius to the fourth power
What does Poiseuille's law state?
Laminar flow refers to smooth, steady blood movement where blood flows fastest in the center of the vessel and slower near the walls. This happens because friction between the blood and vessel walls reduces the speed of flow at the edges.
Describe laminar flow
256 (4^4)
At a given radius of 4, what is the blood flow?
F = flow
∆P = the difference in pressure between two areas of the cardiovascular system
r = radius
η = viscosity
l = length
What do the variables stand for?
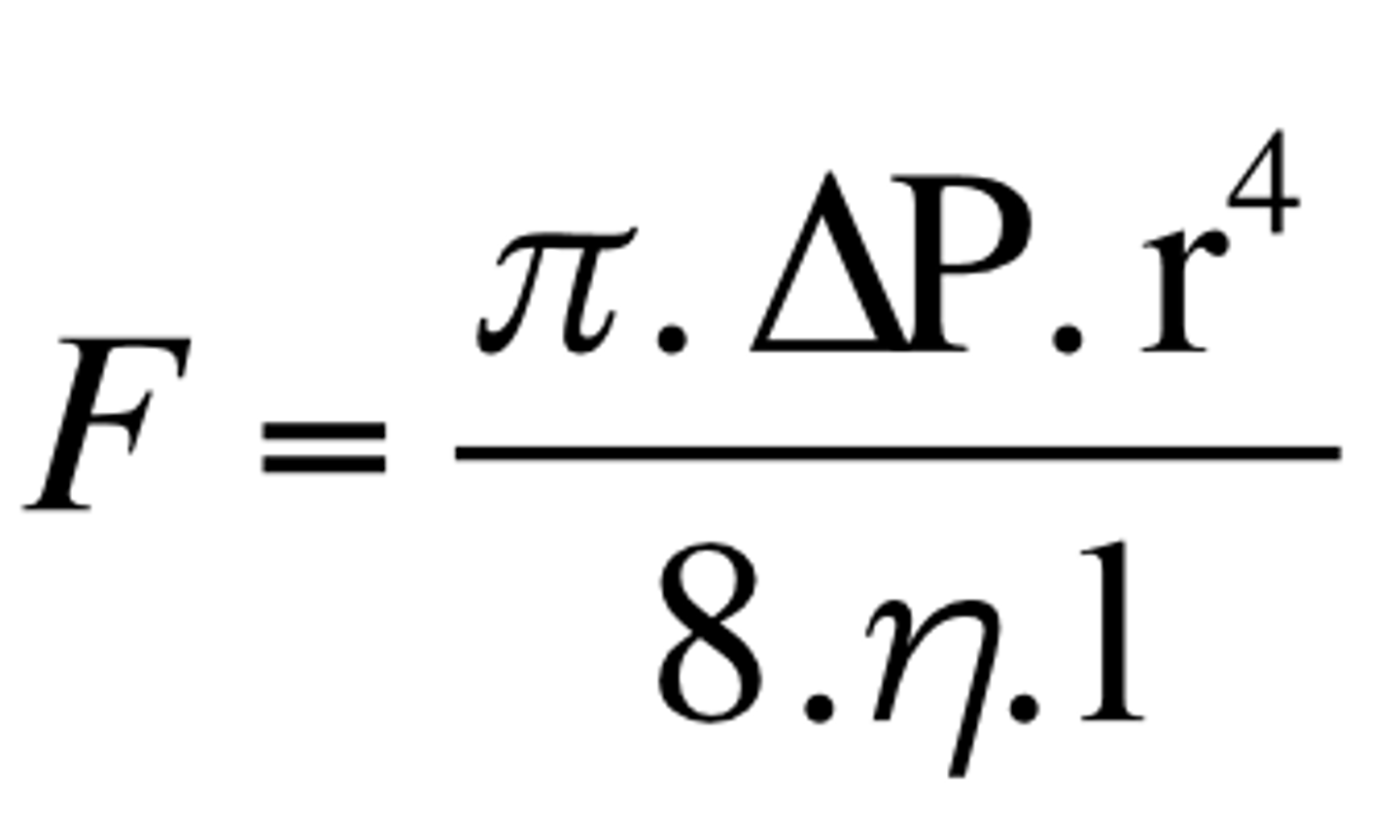
Peak arterial pressure following LV ejection
Define systolic pressure (SP)
minimum arterial pressure prior to next LV ejection
Define diastolic pressure (DP)
SP-DP (eg: 120-80=40)
Define pulse pressure (PP)
MAP = DP + (PP/3)
Define mean arterial pressure (MAP)
1. Blood volume (fluid intake and output)
2. Effectiveness of the heart as a pump ie CO
3. Resistance of the system to blood flow (viscosity, vessel diameter etc)
4. Relative distribution of blood between arterial and venous pressures (diameter of veins)
Give 4 major regulating mechanisms/factors that regulate MAP
1. auto-regulation
2. neural mechanisms
3. endocrine mechanisms
Give the 3 broad regulatory mechanisms that regulate perfusion and blood flow
- myogenic mechanisms
- metabolic factors
What are the two main mechanisms of auto-regulations of vessel diameter?
dilate:
- decreased pH
- decreased O2
- increased CO2
- increased K+
- increased prostaglandins
- increased adenosine
- increased nitric oxide
constrict:
- endothelins
- reverse of the above
Give some examples of metabolic controls that increase and decrease vessel diameter
- increased sympathetic tone can dilate or constrict vessels depending on location
How does nervous input affect blood vessel diameter?
- constriction at alpha adrenergic receptors
- dilation at beta adrenergic receptors
How does epinephrine and norepinephrine affect blood vessels?
ATII is a potent vasoconstrictor
How does angiotensin II affect blood vessel diameter?
ANP causes vasodilation
How does ANP affect blood vessel diameter?
ADH causes vasoconstriction
How does ADH affect blood vessel diameter?
- high blood pressure sensed by aortic and carotid bodies causing increased firing
- signals to medullary cardiovascular control centre
- decreased sympathetic output: vasodilation at arteries, decreased force of contraction and cardiac myocytes, decreased firing rate at SA node
- increased parasympathetic tone: increased muscarinic stimulation causing lower firing rate at SA node and negative dromotropic change
- all factors decrease PVR and CO
- blood pressure drops as a result of lower PVR and CO
Describe how high blood pressure would be reduced through neural mechanisms
- cardioaccelatory centre
- cardioinhibitory centre
- vasomotor centre
- respiratory centre
Which brain centres are stimulated by chemoreceptors?
These are not proportional. Vasodilation may increase blood flow but decrease velocity, both through increased diameter
What is the relationship between blood velocity and blood flow?
Blood velocity is greater in the great arteries, decreasing in arterioles, capillaries and venules and then increasing again in the greater veins and vena cavae
Describe blood velocity throughout the circulation