Chapter 21
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Enolates
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is an enol?
A tautomer of ketones

What conditions does an enol form under?
Acidic Conditions
When are enolates formed?
Under basic conditions by depornatntion of the alpha hydrogen of a carbonyl compound.
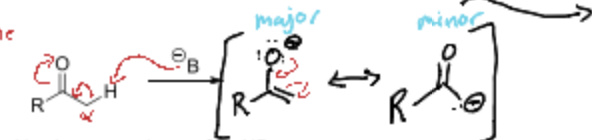
Why do wecare about the major versus minor product in enolates?
The major product in enolate reactions is often more stable due to thermodynamic factors, while the minor product may form more quickly through kinetic control. Understanding the distinction helps predict reaction outcomes.
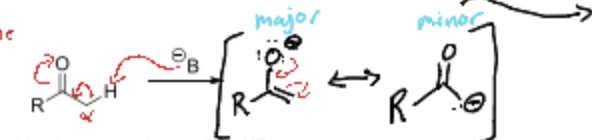
The minor product of an enolate is what?
A better nucleophile
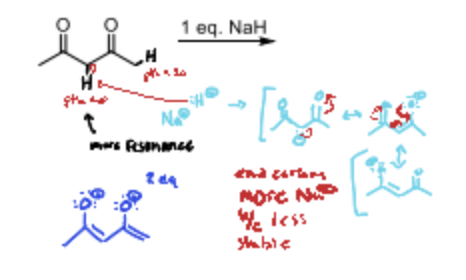
In a diketone where does the base deprotonate with one equivalent present?
The alpha carbon between the two carbonyl groups.
When is an enol favored over the ketone?
A phenol groupis present, or under conditions of increased acidity or steric hindrance that stabilize the enol form.
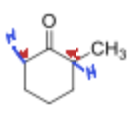
Where does kintetic deprotonation occur in the following compound and why?
The less hindered alpha position because it is faster to get to.
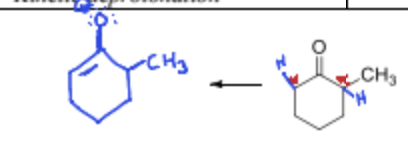
Where does the thermodynamic deprotonation occur in the following compound and why?
More strerically hindered and more stable, making it slower.
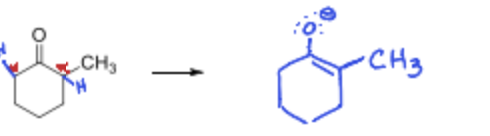
What bases are used to get the kinetic product and what is a common one?
Strong Aprotic bases such as LDA
What temperature does a kinetic deprotonation occur at?
Typically at low temperatures to favor the kinetic product.
What solvent is used for a thermodynamic deprotonation?
The base must match the solvent such as KOtBu in a polar protic solvent.
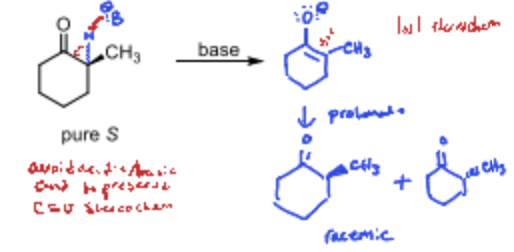
What is the problem with an acidic alpha proton?
The resulting reaction can cause a racemic mixture
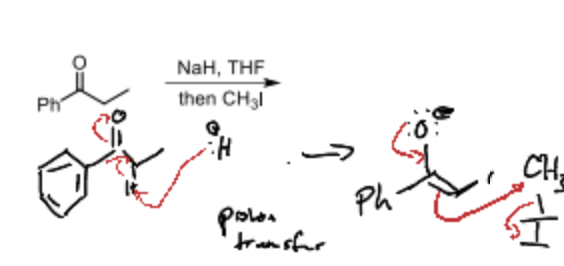
What is the first step fo alkylation at the alpha carbon?
Proton Transfer
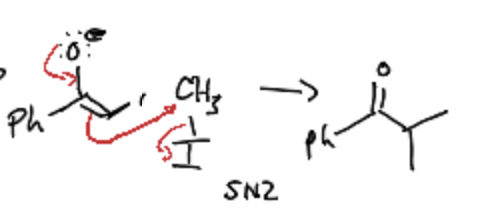
What is the second step of alkylation at the alpha carbon?
SN2
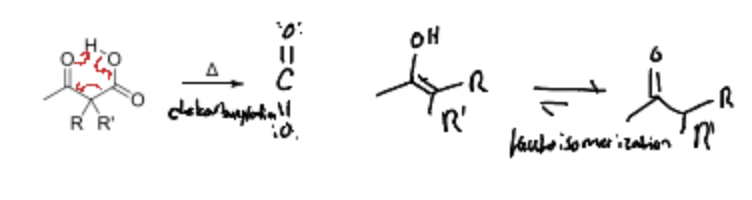
When does decarboxylation occur in enolates?
Only if adjacent EWG
For Halogenation at the alpha-carbon position of a ketone what are the results in acid?
A monohalogenation via enol formation
For Halogenation at the alpha carbon position of a ketone what are the results in base?
Overhalogenation via enolate formation.
Complete the statement:
If methyl ketone is present, then …
perform the haloform reaction
What are the steps of the Halogenation of an alpha carbon position of a ketone in acid?
Ketone-Enol tautoisomerization
Enol Halogenation
What is the reaction of an alpha-halocarbonyl in base?
An Elimination reaction
What is the reaction of an alpha-halocarbonyl with a good nucleophile?
An SN2
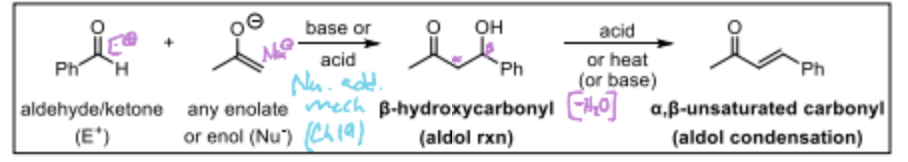
Which of the following are the aldol condensation reaction?
A chemical reaction where two aldehydes or ketones react in the presence of a base to form a β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone, also known as an aldol. This process can lead to further reactions, resulting in larger carbon skeletons. The aldol condensation reaction involves a dehydration step that converts the β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone into an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde or ketone.
What is a crossed aldol?
An aldol condensation reaction between two different carbonyl compounds, typically an aldehyde and a ketone, resulting in a β-hydroxy carbonyl compound.
What is a directed aldol?
An aldol condensation reaction involving one carbonyl compound that acts as a nucleophile and another carbonyl compound as an electrophile, allowing for controlled formation of the β-hydroxy carbonyl product.
What problem arises and how is it solved that stems from a crossed aldol?
The main problem with crossed aldol reactions is the formation of multiple products due to different possible combinations of carbonyl compounds. This issue can be solved by using a specific carbonyl compound as a nucleophile and the other as an electrophile, ensuring a more controlled product formation.
In order to perform an aldol condensation what is required?
Heat
What is the first step of aldol condensation?
Make the enol/enolate
What is the second step of aldol condensation?
Nucleophilic addition
What is the third step of Aldol Condensation?
Dehydration in the presence of heat.
What is the Claisen Condensation
It is a reaction between two esters or an ester and a carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in the formation of a β-keto ester or a β-dicarbonyl compound.
What is the Dieckmann condensation?
A reaction between two esters that leads to the formation of a cyclic β-keto ester in the presence of a strong base.
What is the first step of the Claisen Condensation?
Make the enol/enolate
What is the second step of the Claisen Condensation
Nucleophilic Acyl Substiution
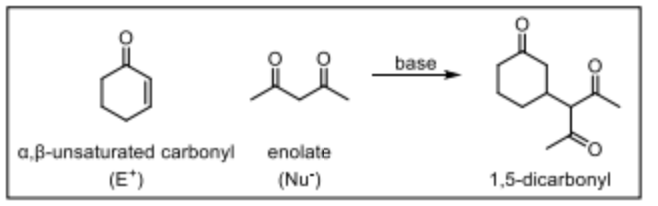
What is the Michael Addition?
The coversion of an alpha-beta-unsaturate carbonyl with an enolate in base that yields a 1,5-dicarbonyl.
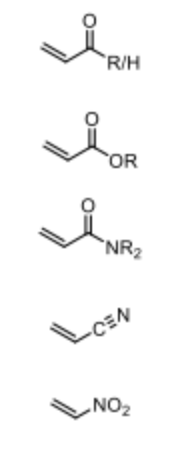
What are the typical Michael Acceptors?
alpha-beta-unsaturated with EWG to activate alkene
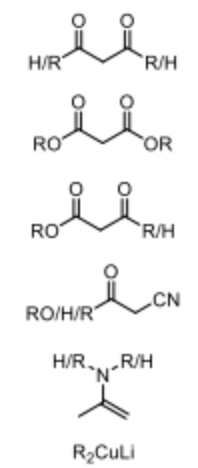
What are the typical Michael Donors?
Stablizied enolates, cuprates, enamines.
What is Robinson Annulation?
A combination of a Michael addition followed by an intramolecular aldol condensation that forms a cyclohexenone.
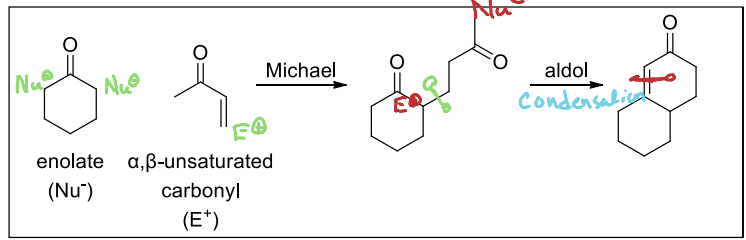
In the Robinson Annulation Reaction, what happens to the nucleophile and electrophile in the Michael addition portion of the reaction in preparation for the aldol condensation?
The nucleophile and electrophiles switch.
If predicting the product or reagent of the Robinson annulation, then the first step is …
identify the micheal and aldol reaction bonds
If predicting the product or reagent of the Robinson annulation, then the second` step is …
Find the nucelophile and electrophile for each step.