Lecture 4 - Psychoanalysis: Its history and early theorists
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
How did Sigmund Freud influence the way Hysteria was understood/used in diagnoses?
Hysteria was a term used before Sigmund Freud that encompassed all sorts of issues and many thought it was due to women’s reproductive organs doing weird stuff.
However, Sigmund Freud helped shift the perception of the causes of Hysteria from that to a repression of trauma.
Define hysteria.
A broad diagnosis typically given to women exhibiting a wide variety of symptoms.
Who was the first person Freud diagnosed with hysteria?
Anna O
Define psychoanalysis.
A system of psychotherapy that focuses on uncovering the unconscious material responsible for a patient’s disorder.
What were the techniques Freud used to conduct psychoanalysis?
free association
dream interpretation
language and symbolic behaviour
Define free association.
It is when patients are encouraged to speak freely about anything that comes to mind, without judgment or self-editing, allowing unconscious material to surface.
What are the assumptions made in the psychoanalytic approach?
Psychic determinism/causality and the unconscious
Internal structure and psychic conflict
mental energy
importance of early experiences
Define psychic determinism.
The idea that all mental events, whether conscious or unconscious, are not random but are caused by prior experiences (ie. past trauma).
Define internal structure and psychic conflict.
The internal clash of things in someone’s mind which can lead to psychological distress.
Define mental energy.
The idea that we can only do so much before we lose our drive.
What does the ‘importance of early experiences’ mean?
It’s talking about how our childhood and relationships with our caregivers shape our personality.
What were Sigmund Freud’s main thoughts about dreams?
Dreams were a wish fulfilment
Objects in dreams are symbols
Why did Freud think dreams were a wish fulfilment?
Freud examined a woman named Urma and he did not know how to help her, which made him feel extremely guilty. However, one night he dreamt that she was neurotic due to a dirty syringe from her doctor.
This dream helped relieve some of his guilt even though IRL he still didn’t know how to help her.
Explain Freud’s psychosexual development theory.
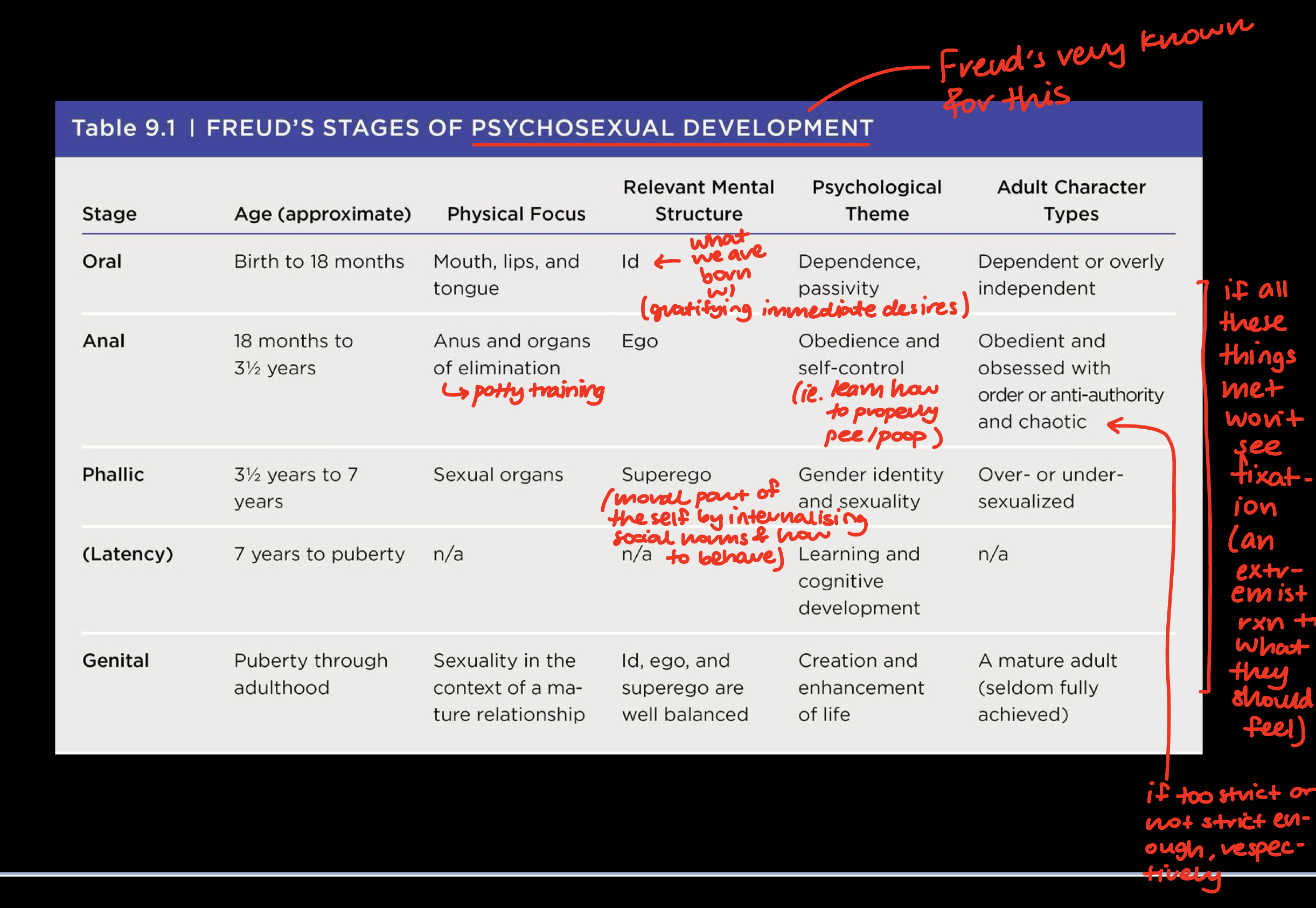
What are the 2 categories of our instincts?
Libido
Thanatos
*aka. pleasure vs reality principle
Define libido.
The idea that we are driven by our sexual instincts.
Define thanatos.
The idea that we have a drive towards death, which manifests in aggressive behaviour.
Why did Freud say that there are only 2 instincts?
He said that there are only 2 instincts because the opposing drives of libido and thanatos create the balance we need in our life. Therefore, the middle of the opposing drives being what we should aim for.
What was the name of Freud’s model of the mind? What did it consist of?
Topographical.
It consisted of these processes:
unconscious
preconscious
conscious
Define the Id.
Actions based on the pleasure principle and wish fulfilment (when we do what we want to do).
Define the Ego.
The thing that satisfies the Id’s impulses, but takes social norms into consideration.
Define the Superego.
Represents societies values and standards (ie. the things we’ve internalised about moral values).
strong supergo = not care enough about yourself
light supergo = not care enough about others
What are the defense mechanisms we use to protect us?
Repression
Sublimation
Displacement
Denial
Reaction formation
Intellectualisation
Projection
Define repression.
Active effort by the ego to push threatening material out of our consciousness.
Define sublimation.
Channeling threatening unconscious impulses into socially acceptable actions.
ie. if you get an unfair grade, you don’t go hit your prof but instead go to the gym and release some of that pent up energy
Define displacement.
Channeling impulses to nonthreatening target.
ie. rather than getting mad at the person who actually made you mad, you lash out on your safe person.
Define denial.
Refusal to accept that certain facts exist.
Define reaction formation.
When people act in a way that is opposite to what they truly feel.
Define intellectualisation.
The removal of emotional content from the thought. Therefore, helping bring difficult thoughts into consciousness without feeling of anxiety.
Define projection.
When people attribute unconscious impulses onto other people.
What’s an example of projecting?
Let’s say deep down you have very low self-esteem and you are ‘seeing it in everyone’ but not acknowledging it in yourself.
What did Carl Jung do?
He established analytic psychology.
Define archetypes.
Images in our collective unconscious that prepare us to respond to the world.
Define the personal unconscious.
Unconscious material of the person.
Define the collective unconscious.
Unconscious material common to all human beings.
Define anima.
The feminine side of the male.
Define animus.
The masculine side of the female.
Define persona.
The part of ourselves that we present to the world.
Define shadow.
The negative side of one’s personality.
What did Jung say were the basic functions of consciousness?
Sensation
Intuition
Feeling
Thinking
*SIFT
What are the 4 dimensions of the Myers-Briggs Personality test?
Extroversion-introversion
Sense-intuition
Thinking-feeling
Judging-perceiving
*SIFT + extroversion, introversion, judging and perceiving
Why has the Myers'-Briggs Personality test been heavily criticised?
poor-test-retest reliability
poor predictive validity
putting people into ‘types’ is problematic
no proper measures for detecting social response bias
Define social response bias.
A bias that influences a participant to deny undesirable traits, and ascribe to themselves traits that are socially desirable.
In essence, it is a bias that drives an individual to answer in a way that makes them look more favorable to the experimenter.
What did Alfred Adler discuss?
will to power
organ inferiority
Define organ inferiority.
The idea people are motivated to attain equality or superiority over other people to compensate for what they felt in childhood was their weakest aspect.
How did Adler see people?
He saw people as whole unified beings (not a collection of separate parts).
Who was Viktor Frankl and what did he discuss?
He was a survivor from the Nazi concentration camps and talked a lot about the will to meaning (logo-therapy).
Define logo-therapy.
The idea that the primary motivation in life is the search for meaning.
Define the existential vacuum.
A a feeling of meaninglessness that manifests from a state of boredom.
Existential frustration.
The feeling of being unable to find or act on meaningful goals due to the absence of meaning in life.
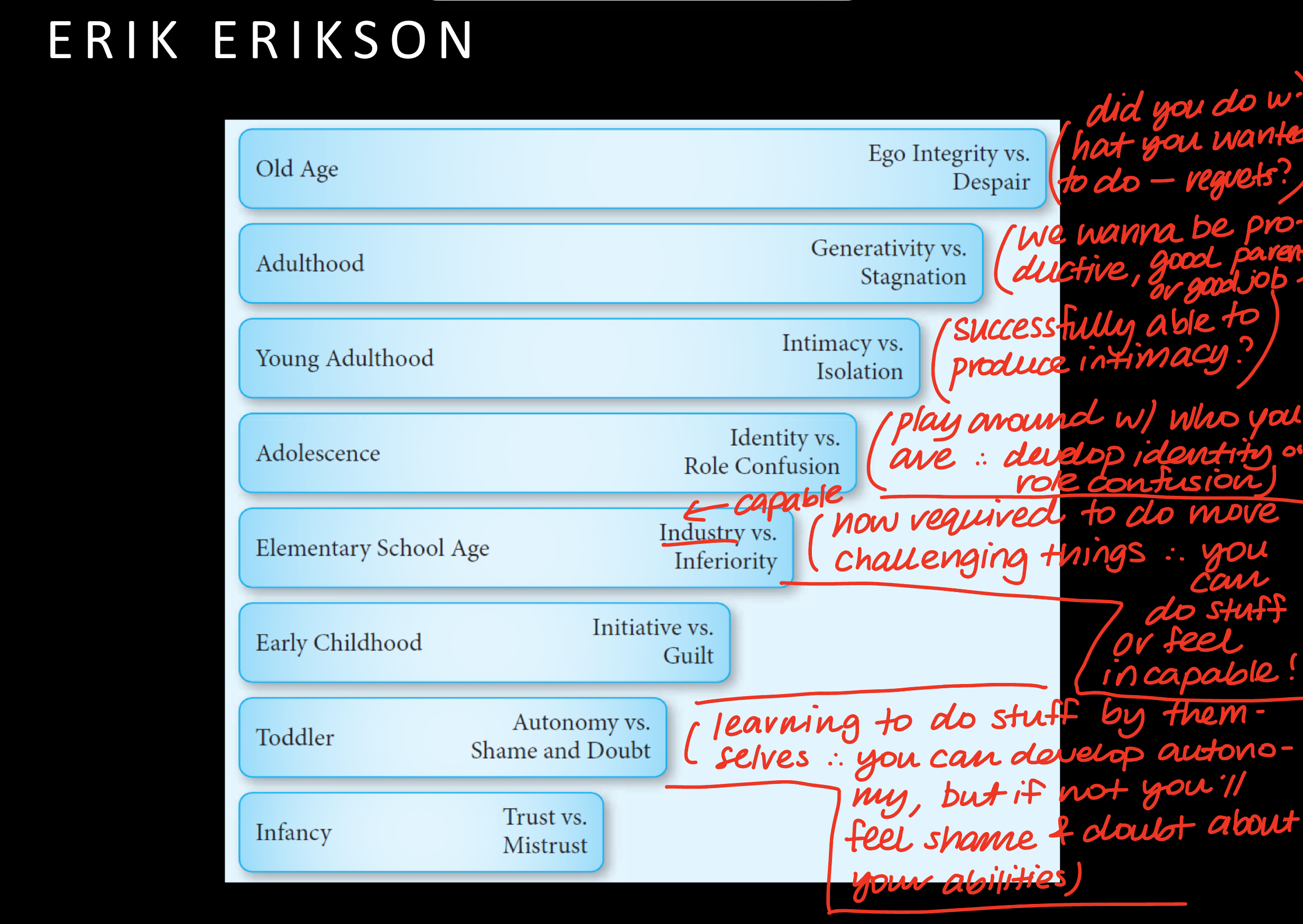
What did Erik Erikson say was the function of the Ego?
He said that function of the ego was to establish and maintain a sense of identity.
*hence, if you don’t do it well you will have an identity crisis.
Erik Erikson’s sum of what he thought:
What did Karen Horney talk about?
She argued that social and environmental factors, rather than biological instincts, were what shaped our personality.
Define neurotic.
People who are trapped in a self-defeating interpersonal style.
What are the things neurotics do to avoid anxiety-provoking experiences?
Moving toward people (ie. needing to make people happy and the desire to be close to others)
Moving against people (ie. using people to get something from them and not caring if you harm them in the process)
Moving away from people (ie. needing perfection and distancing yourself from others)
Explain womb envy. Who came up with the term?
Karen Horney.
The idea that men are jealous of women because they cannot bear children and therefore cannot make something into the world. Hence, they put all their energy into making something in this world to fill that biological void.
What are the theories that try to explain what dreams mean?
Activation-synthesis hypothesis
Information processing theories
Threat simulation theory
Define activation-synthesis hypothesis.
Dreams do not mean anything, it’s just REM sleep where our brain has a lot of randomness occurring so our brain tries to apply those random thoughts to what’s happening IRL.
Define information processing theories.
Dreams help us transfer what we experienced from the day into our memories.
Define threat simulation theory.
The idea that dreams provide an evolutionary advantage as they allow us to simulate threats and improve techniques for threat perception and avoidance while in safety.
What does research tell us about dreams?
vivid and emotional dreams are linked to an activation in parts of the amygdala and hippocampus
REM sleep influences our ability to understand complex emotions IRL
People are more likely to remember their dreams if they are woken up directly after REM sleep. This is because, brain activity related to memory retrieval when we are awake is comparable to brain activity in those that remembered their dream.