fetal doppler, multiples, & 3D/4D
1/229
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
230 Terms
Fetal doppler has not been universally accepted for screening ____ risk populations.
Low
Doppler has proven advantages with the evaluation of ____ risk pregnancies.
High
Fetal doppler can be used to identify which 2 pathologies?
SGA VS. IUGR
Fetal anemia
What does ‘SGA’ stand for?
Small for gestational age
Doppler on the uterine artery can help identify those at risk for adverse outcomes, leading to increased _________.
Surveillance
List the 4 factors that can affect the waveform of the uterine artery.
Patient position
Fetal/Maternal breathing
Fetal cardiac arrhythmias
Some medications taken by the mother
Doppler of the uterine artery is performed to help predict (1)_________ disorders and (2)_______ outcomes with the fetus.
Hypertensive
Adverse
Where should the sampling location be for doppler of the uterine artery?
What should always be utilized?
Where it meets the internal iliac artery
Angle correction
Which 2 types of uterine arteries will normally display a high resistance waveform?
Non-gravid
1st trimester
With a non-gravid and 1st trimester uterine artery, what waveform should be displayed?
High resistance
With doppler of the uterine artery, it is normal to see a (1)_____________ until about (2)___ weeks.
Diastolic notch
26
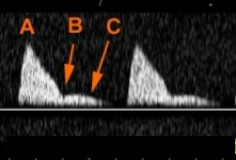
Based on this waveform, what can be assumed about what type of patient this is? This is a Doppler of the uterine artery.
What is seen at letters ‘B’ and ‘C’?
The patient is either not pregnant or in their 1st trimester
Diastolic notch

What vessels are seen here?
Uterine artery
Internal iliac artery
Iliac vein

Label the vessels on the image.
Ovarian artery
Uterine artery
Internal iliac artery
Vaginal arteries
Which 2 types of uterine arteries will normally display a low resistance waveform?
2nd trimester
3rd trimester
With a 2nd trimester and 3rd trimester uterine artery, what waveform should be displayed?
Low resistance
When is it abnormal to see a diastolic notch or a high resistance waveform for the uterine arteries?
After 26 weeks
What 2 sonographic findings on a uterine artery doppler can indicate placental insufficiency or IUGR?
Diastolic notch after 26 weeks
High resistance waveform after 26 weeks
Finding a diastolic notch or a high resistance waveform after 26 weeks on a uterine artery doppler can be an indication of what 2 pathologies?
Placental insufficiency
IUGR
A decreased maternal blood supply to the uterus will have the uterine artery S/D ratio measuring (1)______ than (2)____.
More
2.6
A uterine artery S/D ratio measuring greater than 2.6 can be an indication for what?
Decreased maternal blood supply to the fetus
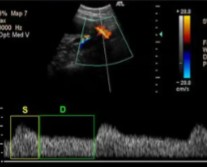
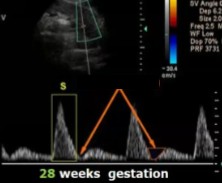
The patient dopplered on is at 28 weeks’ gestation. This is the uterine artery.
Is this waveform normal for how far they are?
If not, what could this indicate?
Yes
Normal
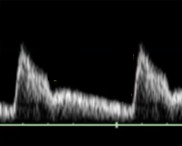
The patient dopplered on is at 32 weeks’ gestation. This is the uterine artery.
Is this waveform normal for how far they are?
If not, what could this indicate?
No
Placenta insufficiency OR IUGR
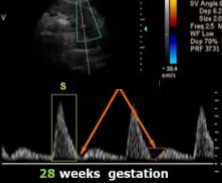
The patient dopplered on is at 28 weeks’ gestation. This is the uterine artery.
Is this waveform normal for how far they are?
If not, what 2 pathologies could this indicate?
No
Placenta insufficiency OR IUGR
This is the uterine artery.
Is this waveform normal or abnormal based on the gestational age?
If abnormal, when would this be considered normal?
Abnormal
First trimester
Where should the sampling location be for doppler of the umbilical vein?
Free floating cord
What does the normal waveform of the umbilical vein look like after 20 weeks?
What can be normal to see prior to 20 weeks?
Constant, non-pulsatile
Pulsatility
What kind of waveform is abnormal to see on the umbilical vein after 20 weeks?
Pulsatility
Pulsatile venous flow is observed in…
Fetuses with _______ restriction
__________ hydrops
Growth
Non-immune
Pulsatile flow after 20 weeks on the umbilical vein is considered to be a late and ominous sign of…
Fetal compromise

Which vessel is dopplered at the top of the baseline?
Bottom?
Is this normal or abnormal if it was dopplored at 18 weeks?
Umbilical artery
Umbilical vein
Abnormal

Which vessel is dopplered at the top of the baseline?
Bottom?
Is this normal or abnormal if it was dopplored at 27 weeks?
Umbilical artery
Umbilical vein
Abnormal
What are some of the different sampling locations of the umbilical artery? (3)
At the fetal cord insert
Placental insert
Mid-section of the umbilical artery
What does the normal waveform of the umbilical artery look like? (2)
Low resistance
Above the baseline
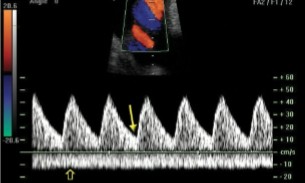
If we are dopplering at the umbilical artery, would this image indicate normalcy or abnormality?
Normal
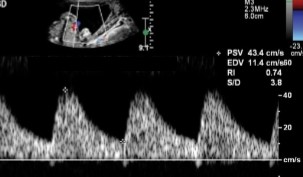
If we are dopplering at the umbilical artery, would this image indicate normalcy or abnormality?
Normal
What does the abnormal waveform of the umbilical artery look like? (2)
High resistance
Little to no end diastalic flow
What does a severely abnormal waveform of the umbilical artery look like?
Absent or reversed diastolic flow
A sonographer is dopplering the umbilical artery and sees that diastolic flow is reversed. What should be done?
Report immediately, ominous sign
An abnormal S/D ratio of the umbilical artery will be (1)________ than (2)___ after (3)___ weeks. It will also be demonstrated with a high resistance waveform.
Greater
3
30
Abnormal umbilical artery waveforms are associated with what 3 pathologies?
Early delivery
IUGR
Death
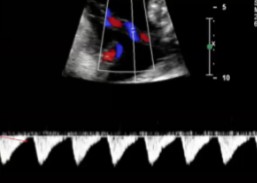
A sonographer dopplered the umbilical artery and this doppler waveform was seen.
Describe the waveform.
Based on the findings, would this be normal or abnormal?
High resistance with little to no end diastolic flow
Abnormal
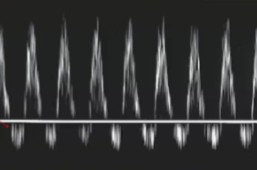
A sonographer dopplered the umbilical artery and this doppler waveform was seen.
Describe the waveform.
Based on the findings, would this be normal or abnormal?
High resistance with flow reversal
Severely abnormal
List the stages of severity associated with the umbilical artery. From normal to severe.
Normal
High resistance waveform
Absent diastolic flow
Reversed diastolic flow
A normal low resistance waveform of the umbilical artery will have _____ diastolic flow.
High
An abnormal low resistance waveform of the umbilical artery will have diastolic flow appear in what three ways?
Losing diastolic flow
Absent diastolic flow
Reversed diastolic flow
Reversed diastolic flow seen at the umbilical artery can be associated with ______ most often.
Death
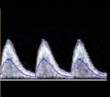
When dopplering the umbilical artery, what flow type is considered normal?
Low resistance

This is a doppler at the umbilical artery.
What waveform is seen here?
Is it normal or abnormal?
Low resistance
Normal
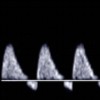
This is a doppler at the umbilical artery.
What waveform is seen here?
Is it normal or abnormal?
High resistance with losing diastolic flow
Abnormal

This is a doppler at the umbilical artery.
What waveform is seen here?
Is it normal or abnormal?
High resistance with no diastolic flow
Abnormal
This is a doppler at the umbilical artery.
What waveform is seen here?
Is it normal or abnormal?
High resistance with reversed diastolic flow
Abnormal
Doppler of the MCA should always show a _____ resistance waveform.
High
Doppler of the MCA is performed on fetuses suspected to have what 2 pathologies?
Anemia
IUGR
Doppler of the MCA is done just below the (1)____ plane and anterior to the (2)________. At the circle of (3)______.
BPD
Thalamus
Willis
List the 3 tips to keep in mind when dopplering the MCA.
0-degree angle
Doppler sample as close to origin from the ICA
Zoom in
If a low resistance waveform is seen at the MCA, what can that be an indication of?
Why would diastolic flow be increasing?
Fetus is not growing well
Because it’s increasing blood flow to the brain to preserve it
What is the term for when blood flow increases to the brain to preserve it?
Brain sparring
Define brain sparring.
Blood flow increasing to the brain to preserve it
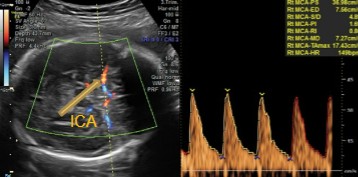
What is being dopplered here?
Is the waveform considered normal or abnormal for this vessel?
MCA
Normal
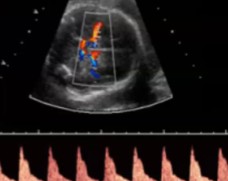
What is being dopplered here?
Is the waveform considered normal or abnormal for this vessel?
MCA
Normal
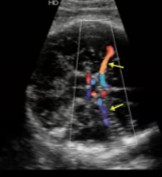
What vessel is seen at the arrows?
Middle cerebral artery (MCA)
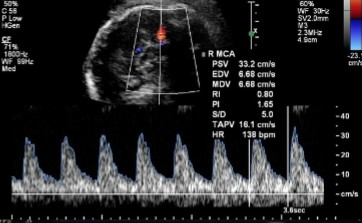
Doppler of the MCA was done and this was seen.
Is this waveform normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology can it be indicative of?
Normal
Normal
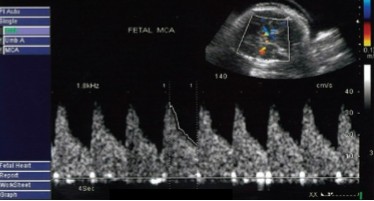
Doppler of the MCA was done and this was seen.
Is this waveform normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology can it be indicative of?
Abnormal
Anemia OR IUGR
The ductus venosus is a vessel that transports the majority of oxygenated blood from the (1)____________ to the (2)____.
Umbilical vein
IVC
The ductus venosus is considered a…
Fetal adaptation
Some evaluate the ductus venosus between weeks __-__ and __ days.
Others will in the __ and __ trimesters.
11 - 13, 6
2nd and 3rd
Dopplering the ductus venosus in the 2nd and 3rd trimester is done to look for which 2 pathologies?
IUGR
Hydrops
An abnormal ductus venosus can be an indication for what?
Down syndrome
A thickened nuchal translucency and an abnormal ductus venosus can be an indication for what?
Congenital heart defects
A normal ductus venosus will have a (1)_________ waveform with positive flow during (2)_________ contraction.
All flow should be (3)________ baseline.
Triphasic
Atrial
Above
When finding the ductus venosus…
What view should be obtained?
The connection should be seen coming off what vessel? Where would that vessel go into?
Transverse view of fetal abdomen (AC)
Umbilical vein, IVC
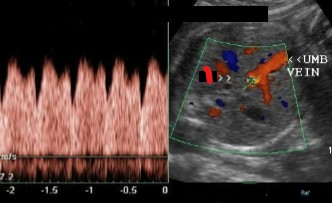
Which vessel is seen coming off the umbilical vein?
Does the doppler of this vessel look normal or abnormal?
Ductus venosus
Normal
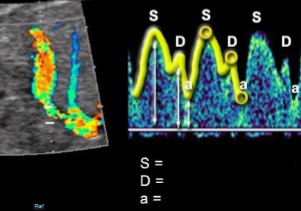
The ductus venosus was dopplered, label what the SDa stands for on the waveform.
S = Ventricular systole
D = Early diastole
a = Atrial contraction
How will a normal ductus venosus waveform appear at 25 weeks gestation?
Triphasic
Positive atrial contraction flow
What would make a ductus venosus waveform abnormal?
What would be done if it was abnormal?
Absent or reversed A-wave
Delivery ASAP
What does an A-wave represent?
Forward flow of blood during fetal atrial contraction of the heart
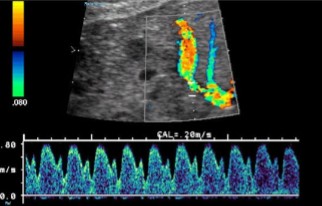
What vessel is being dopplered here?
Is this waveform normal or abnormal?
Ductus venosus
Normal
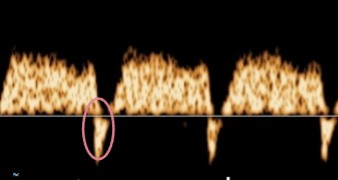
This is a doppler waveform of the ductus venosus.
Does it look normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what about it is?
Abnormal
Reversed A-wave
Mothers with multiple gestations are at an increased risk for what 4 complications?
HTN
Pre-eclampsia
Preterm labor
Placenta abruption
Fetus’ that share the same sac are at an increased risk for what 4 complications?
Umbilical cord problems
Congenital anomalies
IUGR
Twin to twin transfusion
Fetus’ in multiple gestations are at an increased risk for umbilical cord problems. List the 3 umbilical cord problems involved.
Entanglement
Compression
Prolapse knots
Will MS-AFP be higher or lower with multiple gestations?
Explain why.
Higher
More ‘livers,’ means more AFP is produced
Will the uterus be smaller or larger in size with multiple gestations?
Larger
Will the hCG be higher or lower with multiple gestations?
Higher
With multiple gestations, how should fetuses be labeled?
Why are they labeled?
Typically, by alphabetical letter
To consistently identify them in follow up exams
In a multiple gestation pregnancy, how is it determined which fetus is labeled A?
By the fetus directly over the internal Os
Other fetus’/sacs not over the internal os can be labeled what 3 other ways?
Placental location
Being closer to left or right side of uterus
By the next letter of the alphabet (ex. ‘B’)
What is the ideal time for when to label which fetus twin A, twin B, or so on?
10 - 14 weeks
Identifying which fetus is which with a multiple gestation pregnancy between weeks 10-14 is so that the sonographer can help identify which 2 factors?
Chorionicity
Amnionicty
Define chorionicity.
How many chorions there are
Define amnionicity.
How many amnions there are
Is the yolk sac in the chorion or amnion?
Chorion
Is the fetus in the chorion or amnion?
Amnion
At what day will the formation of the chorion occur?
4
At what days will the formation of the yolk sac occur?
6 - 8
At what days will the formation of the amnion occur?
8 - 9
The chorion has a direct relationship with the…
What does that mean?
Placenta
1 chorion = 1 placenta, 2 chorions = 2 placentas
The amnion has a direct relationship with the…
What does that mean?
Amniotic sacs and yolk sacs
1 amnion = 1 yolk sac, 2 amnions = 2 yolk sacs
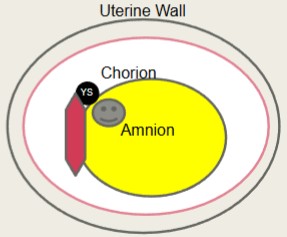
The number of placentas will be determinate with the number of…
The number of yolk sacs will be determinate with the number of…
Chorions
Amnions