AP Calc Exam
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Removable discontinuity
Point discontinuity: limits are approaching the same value, but there is a hole at that point and the function value is in a different location
Non-removable discontinuity
Infinite discontinuity: limits are forever approaching different values
Jump discontinuity: one limit approaches a hole, the other approaches the function value from above or below the hole
MVT theorem (derivatives)
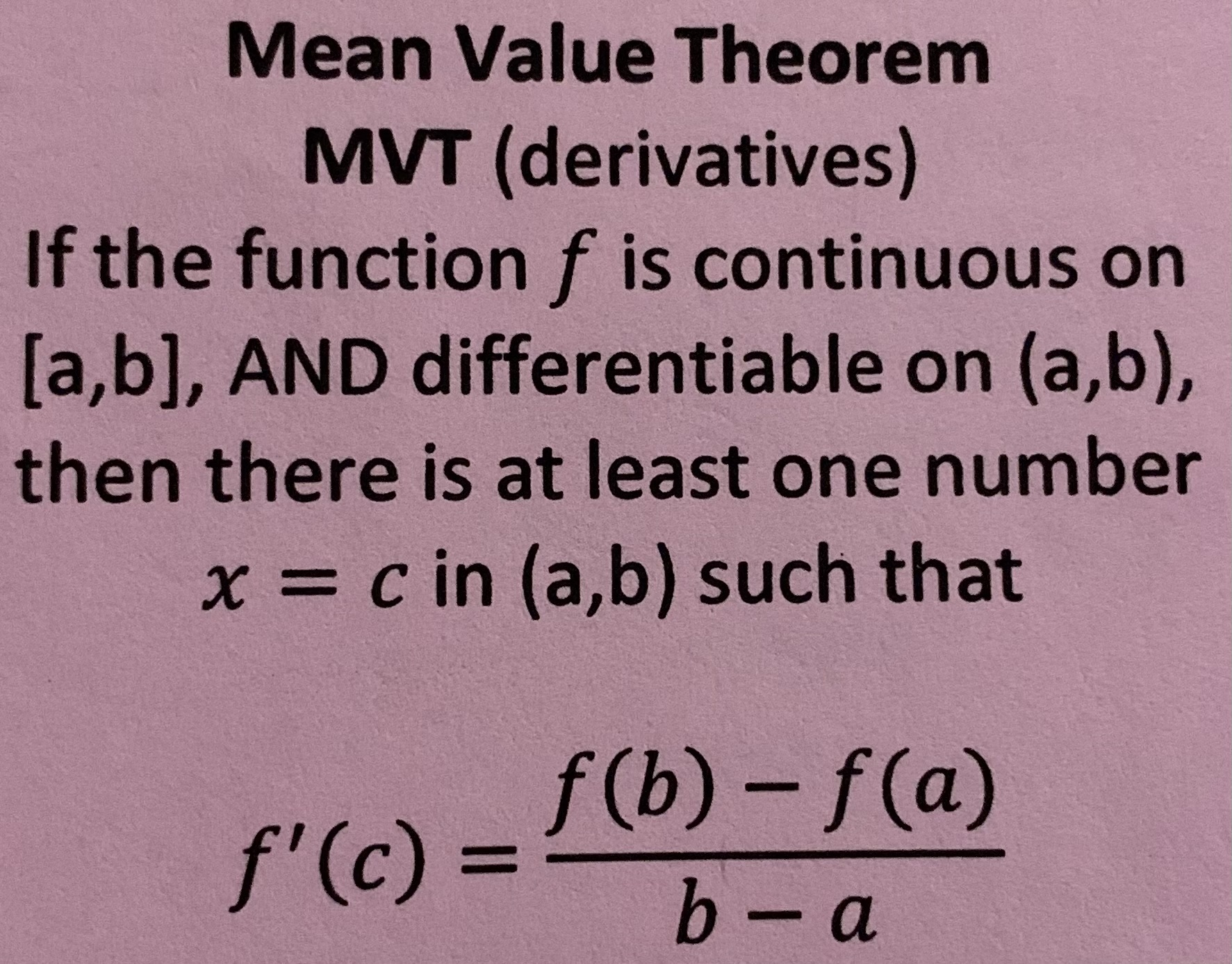
MVT theorem (integrals)

EVT theorem

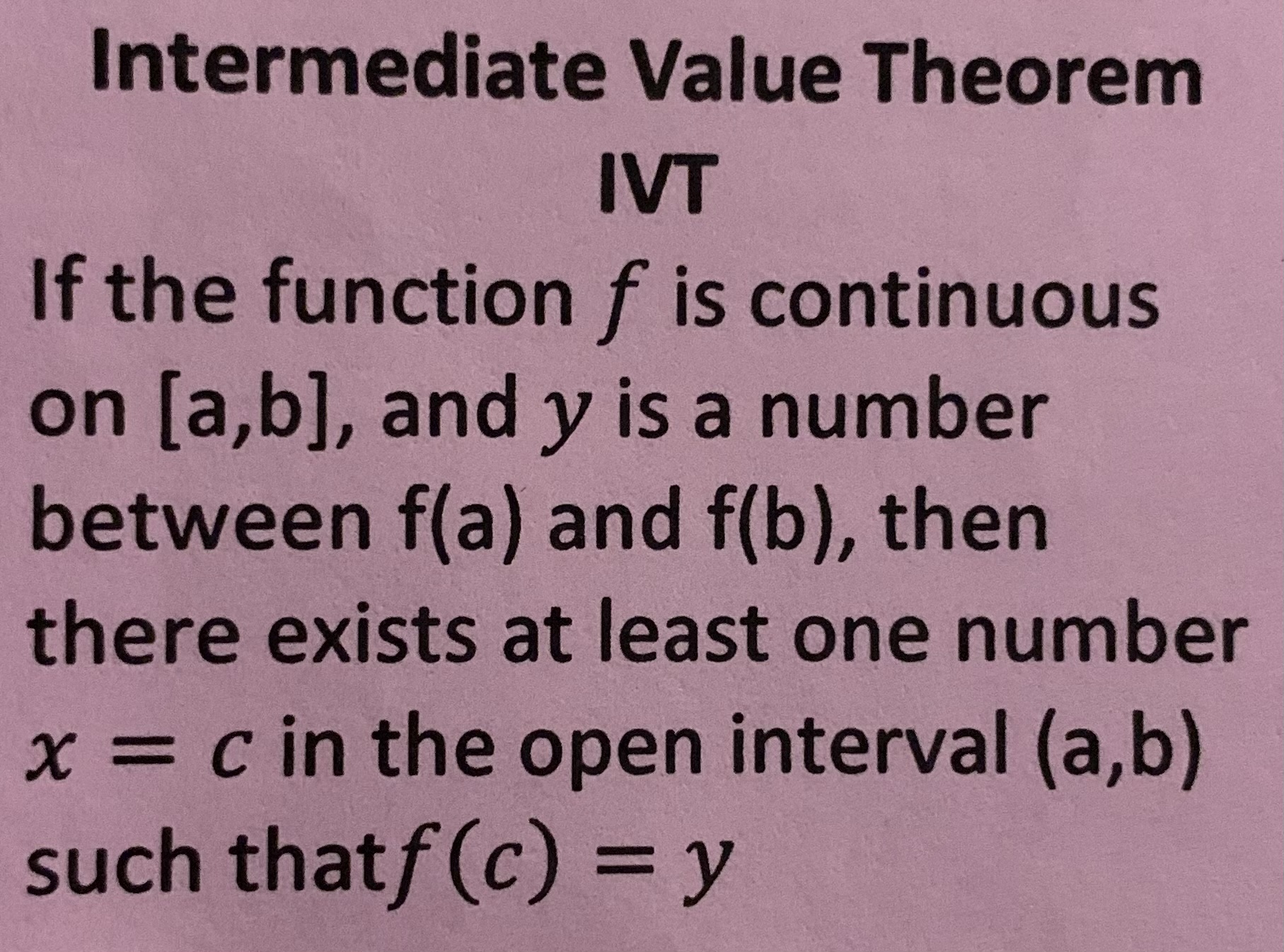
IVT theorem
When is ‘+C’ included
Include ‘+C’ when integrating a function that does not have limits (the a and b values that are plugged in after integration)
How is continuity evaluated
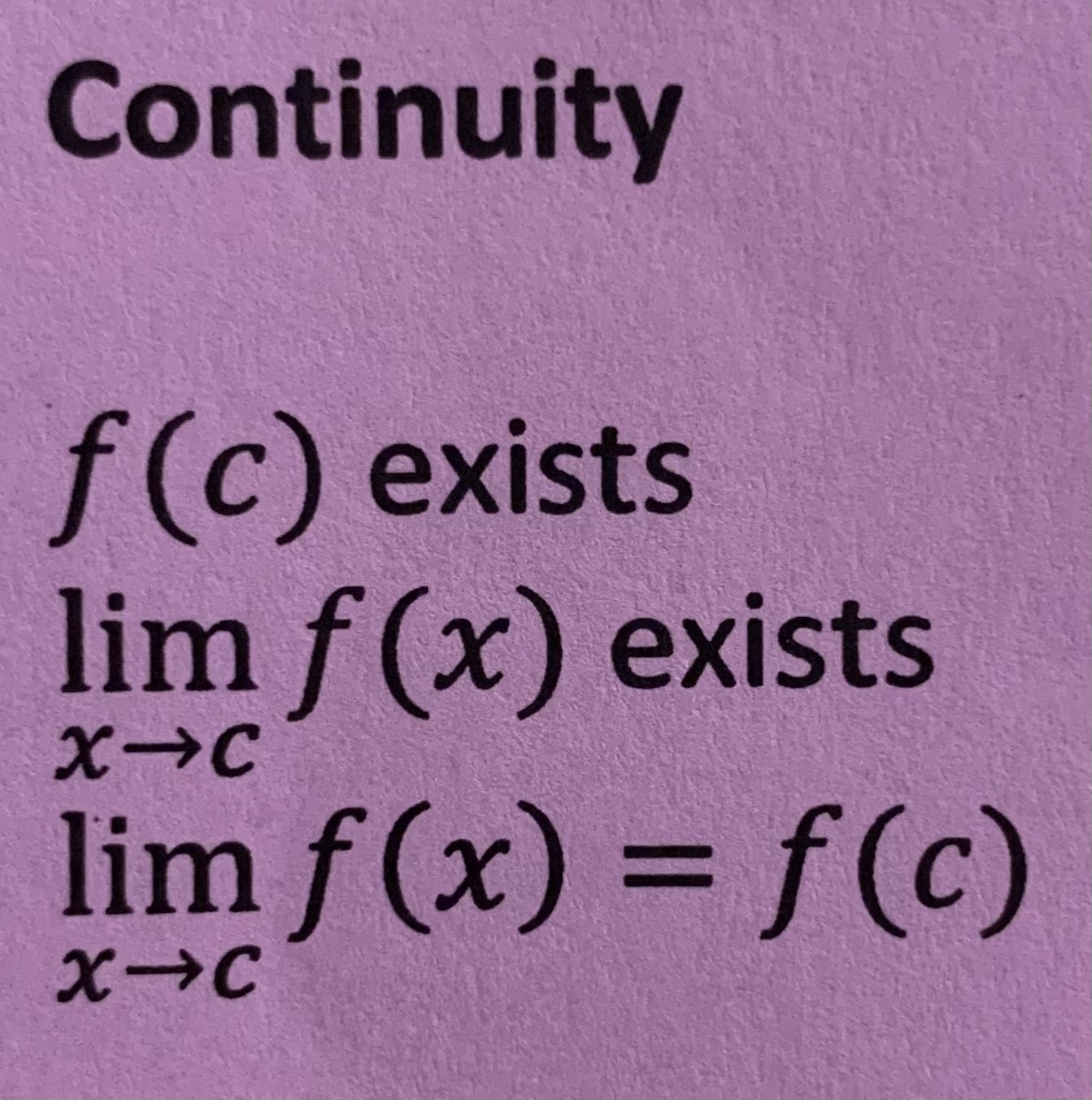
Area of semicircle cross sections formula
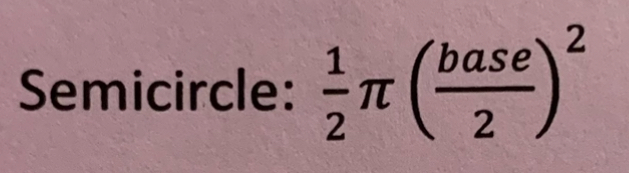
Area of equilateral triangle cross sections formula
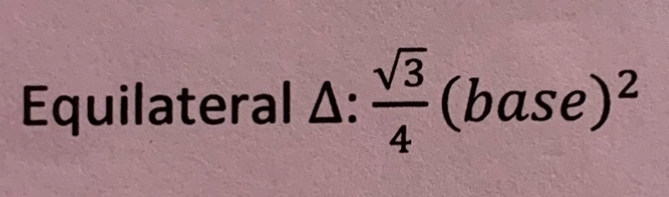
Area of isosceles right triangle cross sections formula
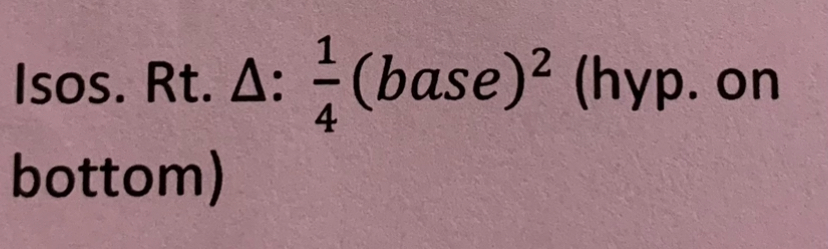
Finding the area between 2 curves:
Finding the volume of a disk or washer:
Finding the volume of a shape with cross sections:

Completing the square
1) trinomial equation
2) take b, divide by 2 and square
3) slide c over, put in the number from step 2, and undo the number from step 2
Example: x²+12x+32 → x²+12x+36-36+32
4) separate the first 3 terms from the last two and factor the trinomial, combine the other two numbers
Example: x²+12x+36-36+32 → (x+6)² -4
5) set equal to zero and solve
RRAM formula
Difference between x0 and x1, multiply that by the y value at the right-hand value, in this case the y value at x1
LRAM formula
Difference between x0 and x1, multiply that by the y value at the left-hand value, in this case the y value at x0
MRAM formula
Take the value of each interval (b-a) and multiply that by the fist x value (x0) plus the second x value (x1) divided by 2
Example: b[f((x+x)/2)+ …]
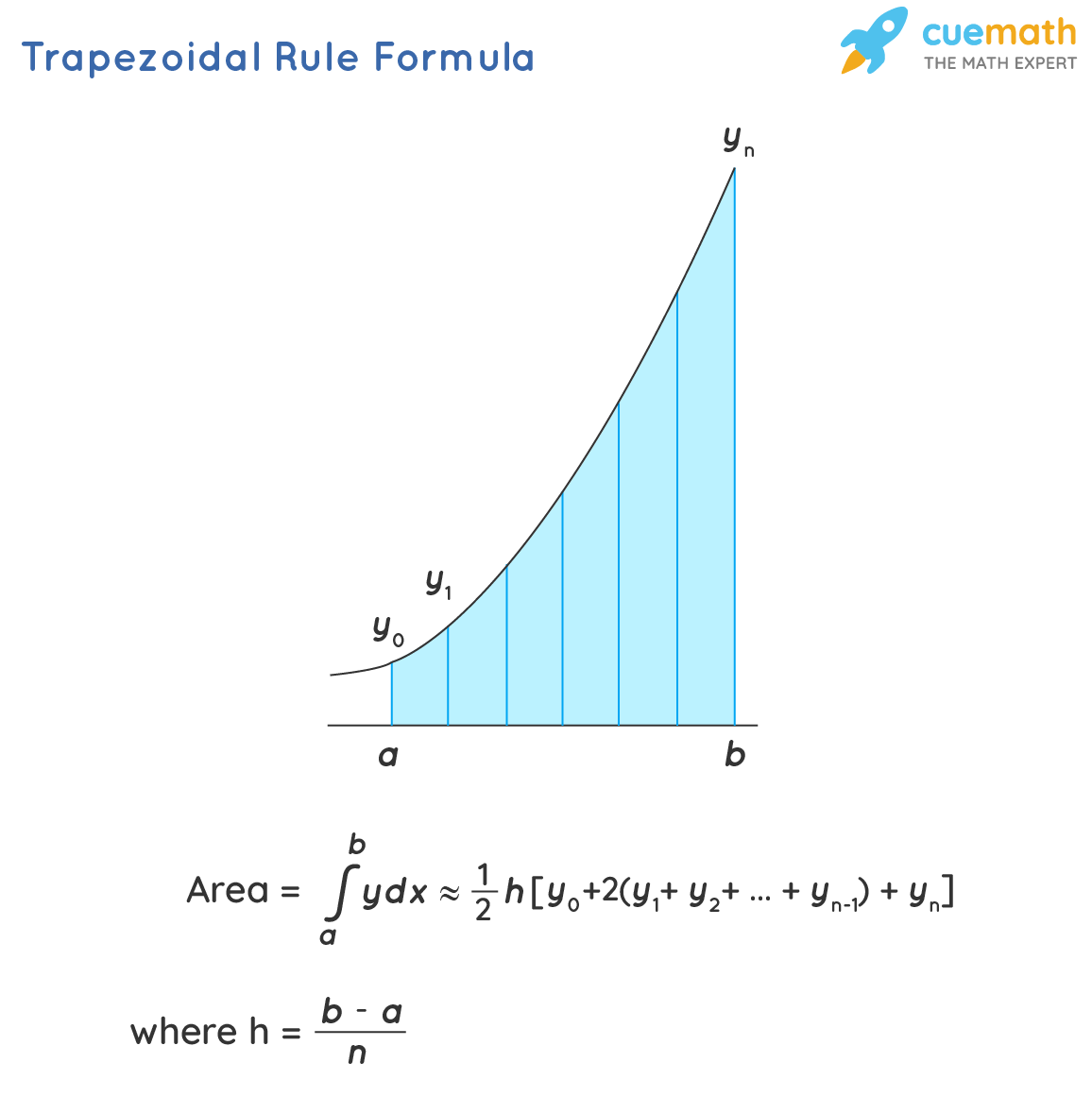
TRAP formula
Basic trig derivatives
Sin(x)= cos(x)
Cos(x)= -sin(x)
Tan(x)= sec2x
Csc(x)= -csc(x)cot(x)
Sec(x)= sec(x)tan(x)
Cot(x)= -csc2x
AROC
(X1,X2) (Y1, Y2) → (Y2-Y1)/(X2-X1)
Basically, AROC is the average velocity over a short period of time.
IROC
IROC is the more specific version of AROC. Find the AROC of the values leading up to the value you are looking for the IROC at, and the value that those are approaching will tell the specific point that is being solved for.