Mental Status Examination and Cranial Nerves Overview
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Mental Status Examination (MSE)
A structured assessment of a person's cognitive, emotional, and psychological functioning.
Attention Span
An example assessment where a person is asked to spell the word WORLD backwards or recite the months of the year backwards.
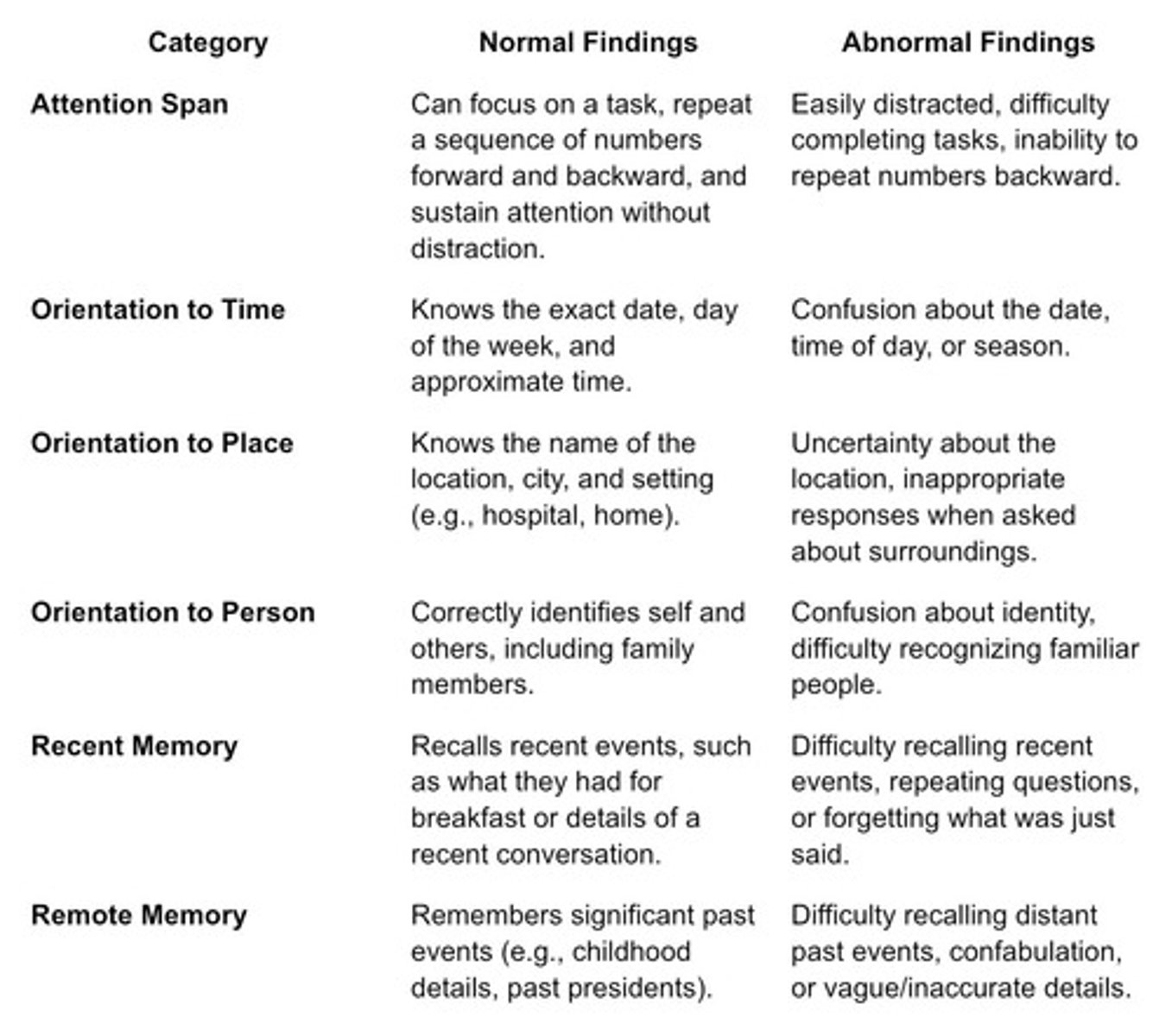
Orientation to Time, Space, and Person
An assessment where a person is asked questions such as who was with them during breakfast, where they are currently, and what day and time it is.
Cranial Nerve VII (Facial Nerve)
Innervates every other movement that the face can make, except for the mandible and eyelid elevation.
Memory (Recent and Remote)
An assessment where recent memory is tested by asking a person to repeat three words (RED, BALL, KEY) and remote memory is tested by asking about past events like their last birthday or high school graduation.
Normal and Abnormal Findings of Facial Nerve
Includes controlling and protecting facial apertures and dampening excessive movement of the ossicles by stapedius muscle contraction.
Hyperacusis
A symptom where ordinary sounds may seem uncomfortably loud, often due to stapedius paralysis.
Functions of Cranial Nerve VII
Includes tasting from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, snotting to the nasal mucosa, tearing to the lacrimal gland, and salivating via the submandibular ganglion.
Complete Interruption of Cranial Nerve VII
Causes ipsilateral facial paralysis, xerophthalmia, loss of nasal secretions, loss of taste, xerostomia, and hyperacusis.
Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) Lesion
Results in contralateral paralysis of the lower face with forehead sparing, often caused by stroke or cortical lesions.
Lower Motor Neuron (LMN) Lesion
Results in ipsilateral paralysis of the upper and lower face, commonly seen in Bell's palsy, along with loss of lacrimation, taste, and hyperacusis.
Cranial Nerve VIII (Vestibulocochlear Nerve)
Conveys afferents from the cochlear apparatus for detecting sound and the vestibular apparatus for detecting motion and gravity.
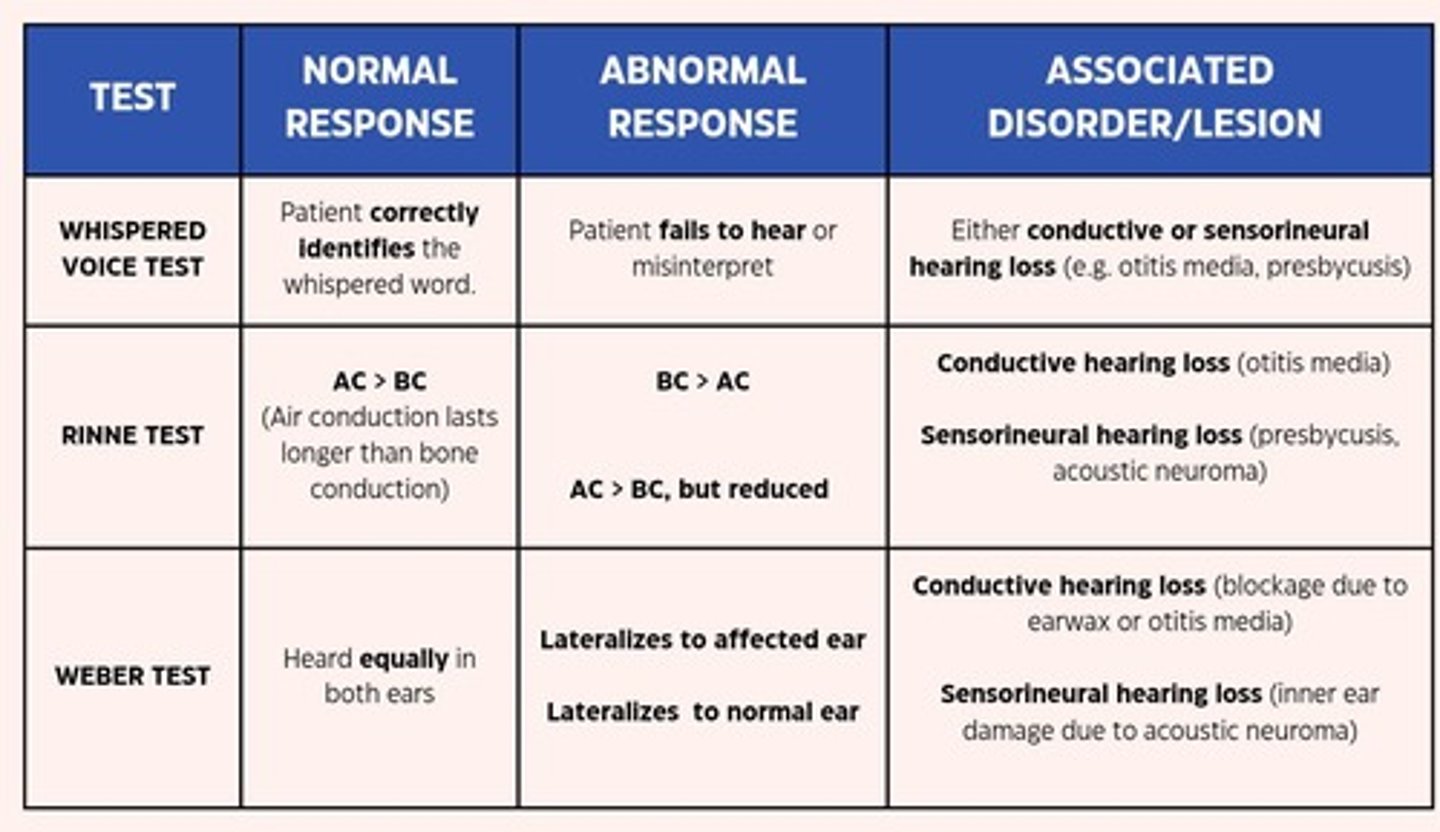
Cochlear Function Tests
Includes the whispered voice test, Rinne test, and Weber test.
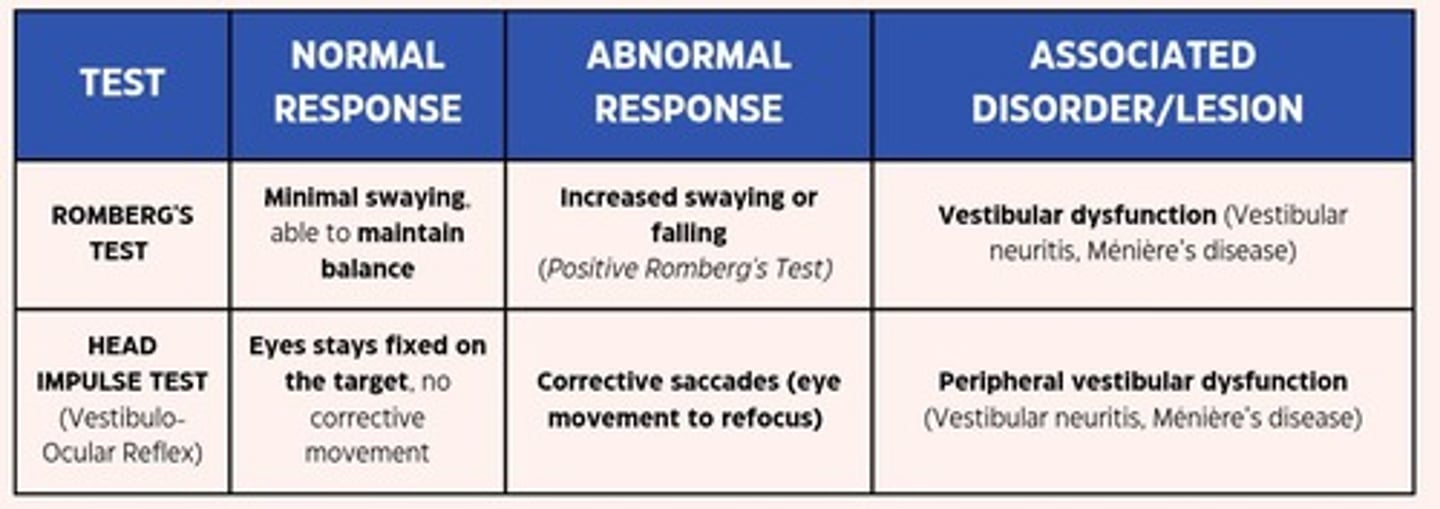
Vestibular Function Tests
Includes the Romberg test and head impulse test.
Cranial Nerve VIII Histology
Of the three special sensory cranial nerves, only VIII has typical peripheral nerve histology.
Motor Function Tests for Cranial Nerve VII
Includes testing the ability to wrinkle the forehead using the frontalis muscle.
Facial Movements
Involves expression of emotions such as frowning and smiling, and actions like whistling, blowing, and spitting.
Compression of Lips
Involved in labial sounds of speech, swallowing, and other feeding actions.
Tasting
Involves taste sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue via the geniculate ganglion.
Snotting
Refers to the parasympathetic axons to the nasal mucosa via the pterygopalatine ganglion.
Tearing
Refers to the parasympathetic axons to the lacrimal gland via the pterygopalatine ganglion.
Salivating
Refers to the parasympathetic axons via the submandibular ganglion.
Facial Apertures
Includes the palpebral fissures, oral fissure, nares, lips, and external auditory canals.
Hearing (Cochlear Division)
It transmits sound signals from the inner ear (cochlea) to the brain, allowing for auditory perception.
Balance and Equilibrium (Vestibular Division)
It carries information from the vestibular system in the inner ear to the brain to help maintain balance, spatial orientation, and coordination of head and eye movements.
Auditory Acuity Test
Rub your fingers lightly near each ear.
Whisper Test
Whisper a combination of 3 numbers and letters; use a different combination for the other ear.
Weber Test (Lateralization)
Place a vibrating tuning fork on the middle of the head.
Rinne Test (Comparing AC and BC)
Place the base of the vibrating tuning fork on the mastoid, behind the ear at level with the canal.
Corneal Reflex
Lightly touch the cornea (limbal junction) with a fine cotton wisp.
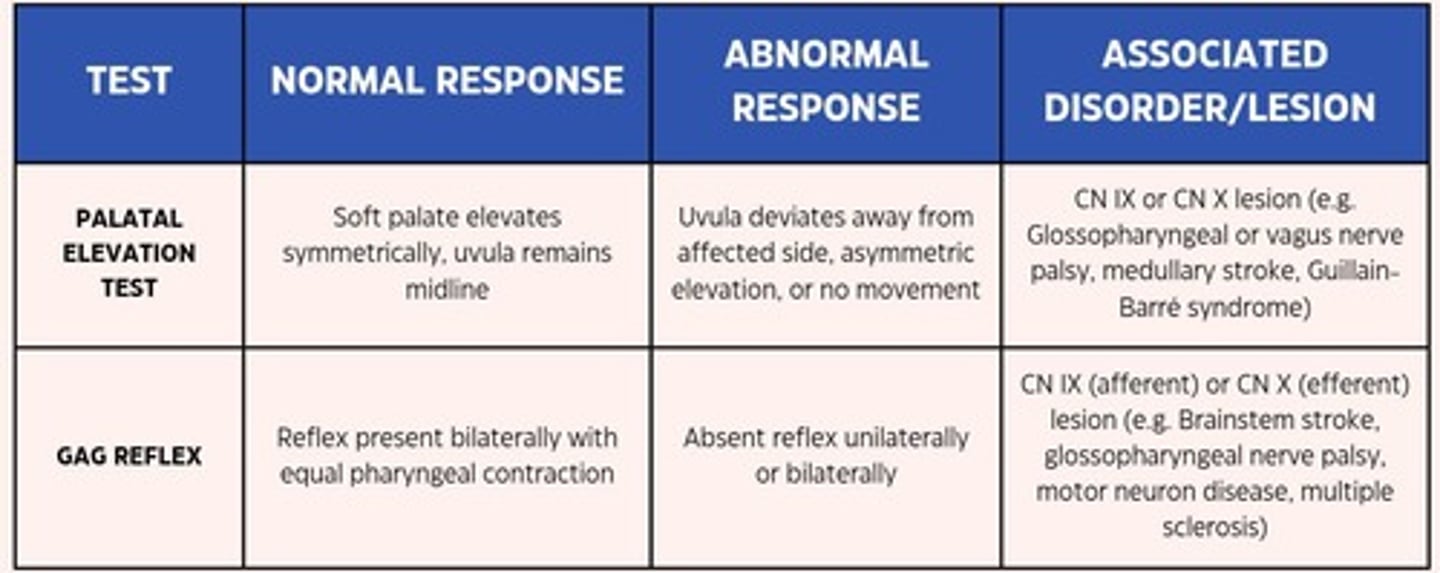
Gag Reflex
Check the integrity of your gag reflex with the use of a tongue depressor.
Cranial IX (Glossopharyngeal Nerve)
It supplies taste fibers to the tongue and activates the pharynx during swallowing.
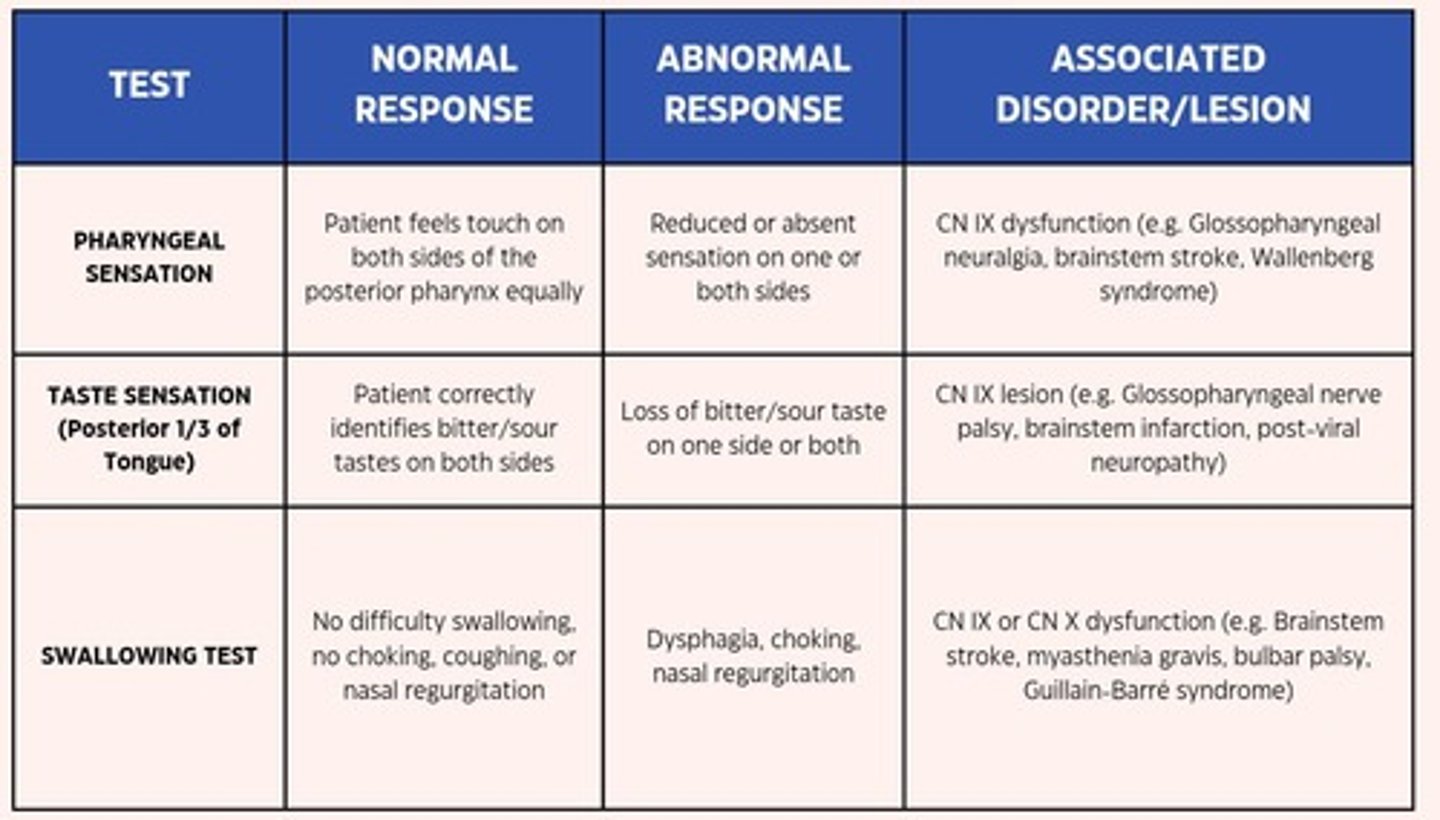
Taste Sensation
Taste sensation from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue.
General Sensation
General sensation from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue, pharynx, tonsils, soft palate, and middle ear.
Visceral Sensory
Visceral sensory from the carotid body and carotid sinus (involved in blood pressure and oxygen level regulation).
Pharyngeal Sensation
Use a cotton swab or tongue depressor to lightly touch the posterior pharyngeal wall (avoiding the tongue).
Motor Function of Cranial IX
Controls the stylopharyngeus muscle, which helps elevate the pharynx during swallowing and speech.
Swallowing Test
Ask the patient to swallow a small sip of water.
Palatal Elevation Test
Inspect the mouth cavity while the patient is saying 'aaaah'.
Afferent Limb of Gag Reflex
Afferent limb of the gag reflex (with the vagus nerve as the efferent limb).
Afferent Limb of Carotid Sinus Reflex
Afferent limb of the carotid sinus reflex, which helps regulate blood pressure.
Tearing
Lacrimal glands via pterygopalatine ganglion.
Salivating
Submandibular ganglion.
Snotting
Nasal mucosa via pterygopalatine ganglion.
Auditory Acuity Frown Test
Frown - Mentalis.
Auditory Acuity Smile Test
Smile - Zygomaticus Major.
Auditory Acuity Show Teeth Test
Show both upper and lower teeth - Risorius.
Auditory Acuity Puff Cheeks Test
Puff out cheeks - Buccinator.
Auditory Acuity Use Ticking Watch Test
Use a ticking watch.