Psychoactive Substances - Substance Abuse
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Substance abuse and behavioral treatments
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What type of reinforcement initiates drug use?
Positive reinforcement
What type of reinforcement maintains drug use?
Negative reinforcement
Define positive reinforcement
an appetitive stimulus activates the reinforcement mechanism that increases the likelihood that the most recent behavior will be expressed
What is an example for positive reinforcement with inhaling nicotine?
Smoking makes you feel more alert; you will smoke more in the future
What would IMPEDE addiction potential?
a delay in drug effects
What would ENHANCE addiction potential?
immediate and robust positive reinforcement
What is positive reinforcement’s role in drug abuse?
reinforcement effects are greatest if it occurs immediately after a response
heroin is more addictive than morphine because it has more rapid effects (heroin is more lipid-soluble)
up regulation of cocaine with AMPA receptors occurs after ONE time with the brain learning that cocaine is good
What are the neural mechanisms of positive reinforcement?
addictive drugs trigger the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens
necessary but not sufficient for positive reinforcement
drug “hijack” normal mechanism
increased activation of other brain regions
synaptic changes that are responsible for compulsive behaviors occur within the dorsal striatum after continued use
What are the long-term changes produced by positive reinforcement
drugs increase the strength of excitatory synapses on dopaminergic neurons in the VTA
leads to increased activation in regions that receive dopaminergic input from the VTA
What brain regions have increased activation during positive reinforcement?
first changes appear in the ventral tegmental area (VTA)
insertions of AMPA receptors into the postsynaptic membrane of dopamine neurons
changes last a few days after a single injection of an addictive drug
Define negative reinforcement
a behavior that reduces/turns off an aversive stimulus will be reinforced
What is an example for negative reinforcement with inhaling nicotine?
smoking makes your craving for a cigarette go away; you will smoke more in the future
True or false; negative reinforcement is the same as punishment
false; a responsive action makes the unpleasant stimulus appear
Describe tolerance in relation to negative reinforcement
decrease sensitivity to a drug
body’s attempt to compensate for having the drug present
Describe withdrawal symptoms in relation to negative reinforcement
primarily the opposite effect of the drug itself
taking drugs prevents the unwanted withdrawal and could provide negative reinforcement
could explain addiction to drugs that reduce anxiety
What are the components of addiction?
self-administered maintenance
increased consumption over time to combat tolerance
abstinence
during this period, individuals are most vulnerable for relapse due to craving and withdrawal symptoms
relapse
Describe therapeutic interventions
must be supported by research as effective treatment
successful treatment is challenging
40 to 60% are abstinent one year after a substance abuse intervention
Describe the role of the prefrontal cortex in relation to craving and relapse
activity of this area was lower than controls during abstinence
people with a long history of abuse have deficits on tasks involving this area and have structural abnormalities here
can’t tell if abnormalities in the PFC predispose people to addiction or are caused by addiction
nature AND nurture
high comorbidity of schizophrenia and substance abuse
Describe the comorbidity of schizophrenia and substance abuse
up to half os schizophrenics have a substance abuse disorder
70 to 90% of schizophrenics are nicotine dependent
all have reduced prefrontal gray matter volume, suggesting a common factor
they also have hypofrontality (low impulse control)
Does the medial prefrontal cortex decrease or increase in activity in individuals abusing substances?
Decrease
What brain region is most involved in craving and relapse?
medial prefrontal cortex
Describe the lower activation of the medial prefrontal cortex during craving/relapse?
deficits on tasks and structural abnormalities
less gray matter (less myelinated cell axons)
hypofrontality (low activation of the MPFC)
involved in the extinction of conditioned emotional responses
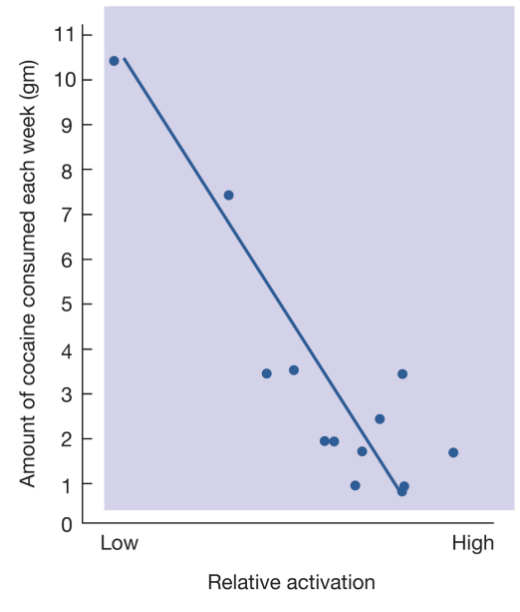
What is the relationship between cocaine intake and the medial prefrontal cortex?
negative correlation (inverse relationship)
less cocaine consumption = more medial prefrontal cortex activation
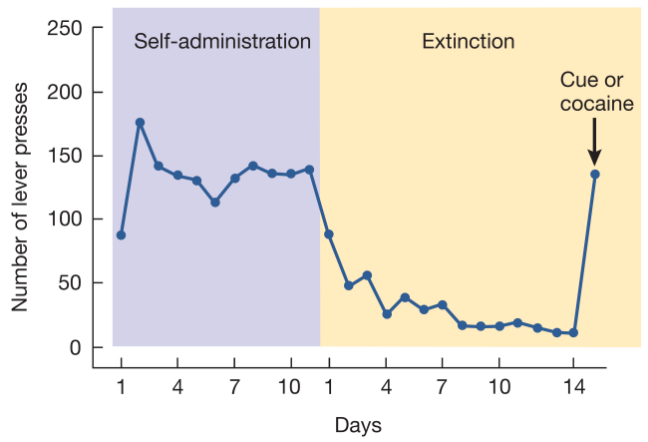
Describe the reinstatement model in relation to craving and relapse
animal trained to respond to stimulus with drug
behavior is extinguished
“free” drug is given
responding behavior returns
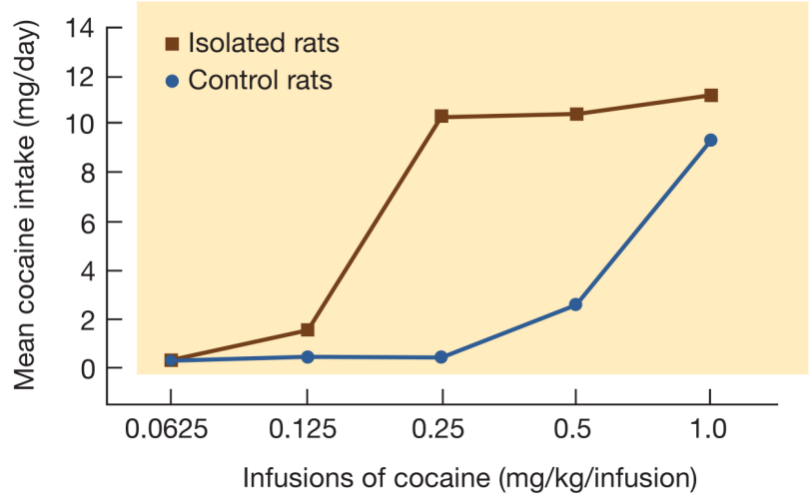
How do you get from abstinence to relapse?
being within the drug environment/context/queues
being in a non-enriching environment
environmental stressors
How can stress trigger a relapse?
stress-induced release of CRH (cortical-releasing hormones)
CRH caused an enhanced activation of dopaminergic neurons in the VTA, heightens dopamine release, enhancing positive reinforcement
Opiates increases what neurotransmitter in what brain area?
Dopamine in the VTA
What receptors do opiates stimulate?
mu receptors
Where do rats NOT self-administer opiates into?
Medial prefrontal cortex
What is NOT an example of a stimulant?
Nicotine
What is the mechanism of action for cocaine?
deactivates dopamine transporters
What is the mechanism of action for amphetamine?
inhibits reuptake and stimulates the release of dopamine
How do stimulants increase dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens?
dopamine antagonists into the NAC block cocaine’s reinforcing effects
destruction of dopaminergic terminals in the NAC interferes with the reinforcing effects of cocaine and amphetamine
Describe methamphetamine
more potent version of amphetamines
inhibits reuptake and stimulates the release of dopmaine
What commonly abused substance is methadone used for?
opiates
Describe methadone maintenance for opiates
full agonist that binds to the mu receptor that has a lower affinity
oral administration prevents high
increases the opiate level in the brain slowly
injecting heroin has little effect if treatment drug present
not effective, they just switch addiction from heroin
Describe the lower affinity aspect of methadone
methadone provides some of the opiate action but doesn’t provide the full opiate experience; decreases withdrawal symptoms
Is methadone a full or partial agonist of the mu receptor?
full agonist
define full agonist
opens the ion channel completely (a lot of ions will flow into the cell)
define partial agonist
the ion channel is only slightly opened
What commonly abused substance is buprenorphine used for?
opiates
Describe buprenorphine for opiates
partial agonist for the mu-receptor
blocks the effects of opiates and produces a weak opiate effect
leads to a longer length of abstinence (compared to methadone), but they still relapse long-term
can be used in an office-based treatment setting
no abuse potential (unlike methadone)
Is bupreneorphrine a full or partial agonist?
partial agonist
describe suboxone for opiates
combination of buprenorphine (partial agonist) and naloxone (full antagonist)
shows more promise than buprenorphrine but still doesn’t prevent long-term relapse
What commonly abused substance is suboxone used for?
opiates
What commonly abused substance is ibogaine used for?
opiates
Describe ibogaine for opiates
psychoactive alkaloid extracted from the iboga plant (ibogaine is the main psychoactive compound)
being heavily researched but not FDA approved yet
has almost immediate effects after 1 treatment but the detox lasts days
Describe the neurological effects of ibogaine
similar to other psychedelics, they have similar chemical structures to serotonin and work on the 2A receptor site (agonist and antagonist in different brain regions)
default mode network (DMN) is involved in self-referential, identity, ego
gets excited when you think about oneself
identity foreclosure
made of the tract between the anterior and posterior cingulate cortex
pschadelics DISRUPTS the connection between the ACC and PCC
How does ibogaine and other psychodelics affects the default mode network?
DISRUPTS (changes the firing pattern) the connection between the anterior cingulate cortex (PCC) and posterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
no matter how rigid you are in your identity, this network is willing to change/adapt
temporary rewiring
What is facilitating the new connections between the PCC and ACC within the default mode network while on psychadelics?
BDNF and GDNF are proteins that are essential for neurogenesis and synaptic-genesis
psychedelics increase BDNF and GDNF
BDNF = brain derived neurotrophic factor
GDNF = glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor
Describe immunization for cocaine
vaccines that prevent cocaine molecules from crossing the blood-brain barrier
drug molecules are tagged with a hapten molecule making it too large to pass through the BBB
patient will receive no reward from the drug so they are less likely to take it again
BUT, individuals still experience withdrawal symptoms
while vaccinated, your body will see it as a virus and make antibodies to attack the drug molecules
What are the issues with using traditional pharmaceutic treatments for cocaine?
because cocaine and amphetamines work directly on the reward pathway, there are no PDA prescriptions
why would you give a dopamine agonist to somone who is addicted to a dopamine agonist"?
why can’t you give a dopamine antagonist to someone?
absolutely no pleasure for the patient
Describe the reinforcing effects of nicotine
activation of nicotinic receptors in the VTA
Describe the maintenance program for nicotine
ineffective when used alone
most effective if combined with counseling program
fails to provide non-nicotine components of smoking
ex: nicotine gum, transdermal patches, etc.
What commonly abused substance is rimanobant used for?
nicotine
Describe rimonabant for nicotine
CB1 receptor antagonist
if you target the CB1 receptor, you can indirectly modulate dopamine release in the presence of a stimulator
if you block the CB1 receptor, the dopaminergic receptor is being repressed because this receptor is a heteroreceptor
effective at smoking cessation but not FDA approved due to its side effects (anxiety and depression)
What commonly abused substance is bupropion used for?
nicotine
Describe bupropion for nicotine
antidepressant
serves as a catecholamine reuptake inhibitor
mimics nicotine’s effects
less activation of medial prefrontal cortex and reduced craving in response to cigarette cues
doesn’t support longer term abstinence
What commonly abused substance is varenicline used for?
nicotine
Describe varenicline for nicotine
partial agonist for nicotinic ACh receptor but doesn’t support longer term abstinence
What commonly abused substance is deep brain treatment (DBT) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) used for?
nicotine
Describe deep brain treatment (DBT) for nicotine
invasive because it involves neurosurgery
putting electrodes in places associated in nicotine addiction
long been used to treat movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease
EXCLUSIVE for nicotine
electrodes are place in the insula because it has a high concentration of nicontinic acetylcholine receptors
this is unlike treatment for other drug addictions
Where are electrodes placed during DBT?
in the insula because it has a high concentration of nicontinic acetylcholine receptors
What areas are targeted/changed from deep brain treatment?
ventral tegmental area
substantria nigra in limbic system
medial prefrontal cortex to enhance activation so they have the neural hardware to ignore craving
Describe transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) for nicotine
repetitive treatments but non-invasive
uses magnetic waves at different frequencies to affect neural firing events
can target brain regions associated with addiction causing synaptic genesis (plasticity)
What brain regions are targeted during transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)?
right inferior frontal gyrus AKA medial prefrontal cortex
associated with impulse control, craving, and emotional regulation
dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex
associated with decision making
reward pathway can be restored without drug involvement
Which treatment is more invasive?
deep brain treatment (DBT)
Describe the neural mechanisms of alcohol
indirect antagonist at NMDA receptors
indirect agonist at GABAA receptors
indirect agonist for mu receptors
opiate endogenous receptor site (site for reinforcing alcohol/when someone is trying to abstain indirect agonist for endorphins)
How does alcohol produce both negative and positive reinforcing effects?
release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens
ability to trigger the release of endogenous opioids
effects of alcohol withdrawal are serious and can be fatal
What commonly abused substance is naltrexone used for?
alcohol
Describe naltrexone for alcohol
opiate antagonist
blocks opiate mu receptor to a lesser degree
individuals with blocked opiate receptors report high levels of craving events
decreases the reinforcing value of alcohol
What commonly abused substance is rimanobant used for?
potentially all abused drugs
What commonly abused substance is amcamprosate used for?
alcohol
Describe acamprosate for alcohol
NMDA receptor antagonist
glutamate antagonist
reduces the likelihood of drinking
What is addiction?
Learning a maladaptive response to feel safe
What are some problems with treatment?
pharmacotherapies result in little to no long-term success
need to focus on both neurological and enviornmental contingencies
What is the best way to help sustain long-term abstinence?
combining treatment medications with behavioral therapy
How does behavioral treatment work?
provide incentives to remain abstinent
teach important life skills that will help support abstinence in the presence of stressors or other environmental cues that may trigger intense craving for drugs
LEARNING abstinence
Describe Contingency Management
re-arrange the drug user’s environment to that drug abstinence is positively reinforced and drug use results in an immediate loss of reinforcement
uses both positive and negative consequences
need to met a set/pre-determined criteria to receive reward
individual learns that they CAN be abstinent based on their environment
What are the strengths of contingency management?
increase in the duration of abstinence
increased number of clients who fulfilled specified periods of abstinence
acceptance of therapy
uses both reinforcement and punishment strategies
What are the limitations of contingency management?
abstinence is only promoted when the contingency is in place
needs to be generalized in natural settings
cost of vouchers add up
increase cost of voucher with increased length of abstinence
Describe how contingency management gives individuals robust, non-pharmacological rewards
no negatives associated with positive enrichment (can outweigh drug reinforcing effects)
creates behavioral contrast where when you have the choice between a drug and reward, you choose the reward
What does contingency management build to?
environmental enrichment
What is the definition of Environmental Enrichment
Non-contingent procedures that presents a choice between drug and other types of alternative natural rewards (e.g. food, social interaction, exercise, etc.) so that the organism can learn that another choice is concurrently avaliable besides relapse
Describe aspects of environmental enrichment
potential rewards include career enrichment in their dream field so they can maintain the extravagent lifestyle of their “perfect/unlimited reward”
addiction has almost all negative reinforcements
environmental enrichment has almost all positive reinforcements
even if the individual consumes the drug, it is NOT taken away because the reinforcement of EE is more robust
Describe the research behind environmental enrichment
if animals have the choice between a drug and other types of rewards, they will typically prefer the alternative rewards over the drug
as they learn enrichment, they slowly reduce drug intake
maximize reinforcement opportunities to reach behavioral bliss
in humans, whether or not environmental enrichment can sustain long-term abstinence is relatively unknown
What if you maximize behavioral bliss through environmental enrichment?
you’re reward pathway cannot maintain the amount of dopamine release
you need a hedonic reset
a period where you decrease the amount of pleasurable stimuli to recalibrate the brain's reward system
AKA when you are overstimulated because you have maximized hedonism
What is the final goal of self enrichment?
understanding that you are enough within yourself without any external factors
Describe hypnosis
cognitive approach (rather than behavioral)
“meditation with a goal”
real altered state of consciousness so they are heightened for repeatability
suggest sobriety while in this state
related to different adaptive patterns so they are not “identifying” as an addict
Why must one be in an altered state for hypnosis?
if an individual is in a non-altered state, they are non-receptive to anything that is counterintuitive to their maladaptive behaviors
hypnosis exposes the internal maladaptive behaviors and suggest adaptive treatments
What are post hypnotic suggestions?
strategies used to remain in abstinence
What is hypnosis similar to?
psychedelic treatment (ex: ibogaine)