Gen-Bio 2nd Qrt (Yawa kau)
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Kendz's note: Watch vids from yt abt parts of mitosis and just read L09 about the Disorder and Diseases if u wanna learn more about the diseases (diko na sinali ung in-depth description nila :))*Tinatamad nako*
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
The cell cycle
is the process by which cells grow, Replicate their DNA, and divide.
Stages of DNA and Cell Replication
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, M phase
G1 phase
when the cell prepares for division with metabolic changes.
S phase
when the DNA and genetic material of the cell are duplicated, forming two sister chromatids.
G2 phase
when cytoplasmic materials needed for division are gathered with metabolic changes.
M phase
when the genetic material and the cell divide.
S phase
The actual DNA replication occurs during _____ , when two copies of the original cell DNA are produced, each containing one original and one new strand of DNA
G1 phase

S Phase

S Phase
DNA Synthesis
G2 Phase

M Phase

Cytokinesis

Variations in Cell Cycle Duration

Control Mechanisms of the Cell Cycle

Cancer
group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell growth
Mutations
can occur due to replication errors or environmental factors
Interphase

Mitotic Phase

Mitosis (M phase)
is the part of the cell cycle in which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells, which are genetically identical to each other as well as the "mother" cell.
Importance of the Cell Cycle

The Cell Cycle
is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and nuclear and cytoplasmic division that ultimately produces two identical (clone) cells.
Interphase and the Mitotic phase
The cell cycle has two major phases
Interphase
During ______, the cell grows and the nuclear DNA is duplicated.
Mitotic phase
During the ______, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei.
Two genetically identical daughter cells
Following mitosis, the cytoplasm is usually divided as well by cytokinesis, resulting in .
G1 phase
During this phase, a cell grows rapidly and carries out its routine functions. It occupies the major portion of the cell’s life for mostly organisms. In this phase, the cell that are not divided will remain. Most muscle and nerve cells, never divide and if these cells die, the body cannot replace them.
S phase
During this phase, a cell’s DNA is copied. At the end of this phase each chromosome has two chromatids at the centromere
G2 phase
This is the preparation for the nucleus to divide. The microtubules is a hollow protein fibers that are rearranged during _____ for preparation for mitosis.
Mitosis
Is a multistep process during which the duplicated chromosomes are aligned, separated, and move into two new, identical daughter cells
Cytokinesis
is sometimes viewed as the second main stage of the mitotic phase, during which cell division is completed via the physical separation of the cytoplasmic components into two daughter cells.
Prophase

Prometaphase

Metaphase

Anaphase

Telophase

Cytokinesis

Cancer
comprises many different diseases caused by a common mechanism: uncontrolled cell growth.
Meiosis
Sexually reproducing species create their sperm, eggs, and sex cells through a process called _____
Germ Cell
A specialized cell called a _______divides during meiosis to create four new sex cells, each of which has half as many chromosomes as the original ______
Gametes
are created during meiosis, which is necessary for sexual reproduction.
True
The number of chromosomes is reduced from two sets to one set during meiosis.
False
The number of chromosomes is reduced from two sets to one set during mitosis.
Mitosis
guarantees that the quantity of the parent cell's chromosomes are identical to those of its two daughter cells.
Mitosis
_____ generates new cells and replaces injured, destroyed, or aging ones. Skin cells, blood cells, bone cells, connective tissues, structural cells in plants, and fungi are a few examples of body cells that go through _____
Inherited Disorders
can arise when chromosomes behave abnormally during meiosis.
abnormalities in chromosome number and chromosome structural rearrangements
Chromosome disorders can be divided into two categories
Abnormalities in Chromosome Number
These occur when there is an incorrect number of chromosomes in a cell.
Abnormalities in Chromosome Number
Ex:
a. trisomies (such as Down syndrome, where there is an extra copy of chromosome 21) b. monosomies (such as Turner syndrome, where one X chromosome is missing)
Abnormalities in Chromosome Number
These abnormalities arise from nondisjunction, the failure of chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis.
Chromosome Structural Rearrangements
These occur when chromosome segments are altered through duplications, deletions, inversions, or translocations. _______ changes can disrupt multiple genes within affected segments, leading to significant health problems.
Chromosome Structural Rearrangements
Ex:
a deletion of part of chromosome 5 causes Cri du Chat syndrome, which affects development and intellectual abilities.
Karyotype
is the number and appearance of chromosomes, including their length, banding pattern, and centromere position.
Karyogram
To obtain a view of an individual’s karyotype, cytologists photograph the chromosomes and then cut and paste each chromosome into a _______
Cytogenetics
is the study of chromosome structure and number, is essential for detecting chromosomal abnormalities that lead to genetic disorders.
Karyotype
represents the full set of an individual’s chromosomes, organized by
a. number,
b. length,
c. banding patterns,
and d. centromere positions.
Nondisjunctions, Duplications, and Deletions
Of all the chromosomal disorders, abnormalities in chromosome number are the most easily identifiable from a karyogram. Disorders of chromosome number include the duplication or loss of entire chromosomes, as well as changes in the number of complete sets of chromosomes.
Nondisjunction
They are caused by _______, which occurs when pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis.
Nondisjunction
occurs when chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis (in the formation of gametes) or mitosis.
Nondisjunction
Process: During meiosis, chromosomes are supposed to split so that each gamete receives only one chromosome from each pair. When ________happens, both chromosomes go to one gamete, while the other receives none.
Results: This can lead to aneuploidy, a condition in which cells have an abnormal number of chromosomes.

Down Syndrome
Caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21).
Turner Syndrome
Occurs when an individual has only one X chromosome (45, X).
Klinefelter Syndrome
Occurs in males with an extra X chromosome (47, XXY)
Duplication
occurs when a section of a chromosome is copied, resulting in multiple copies of that segment within the chromosome.
Duplication
Process: _______can occur due to errors during DNA replication or as a result of unequal crossing-over during meiosis, where homologous chromosomes exchange unequal lengths of DNA.
Results: This can lead to genetic imbalances, where too much of certain proteins or enzymes are produced, potentially affecting development and cellular functions.

Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 1A
Caused by a duplication on chromosome 17, affecting peripheral nerve function.
Pallister-Killian Syndrome
A rare disorder that results from the duplication of material from chromosome 12 and causes developmental and intellectual disabilities
Deletion
occurs when a segment of a chromosome is missing or deleted.
Deletion
Process: ______can occur through errors in DNA replication, exposure to harmful environmental agents (e.g., radiation), or incorrect chromosome separation.
Results: ______ can lead to a loss of important genes, resulting in various developmental abnormalities or diseases, depending on the size and location of the deleted segment.

Cri du Chat Syndrome
Caused by a deletion on the short arm of chromosome 5, leading to intellectual disability and distinctive facial features.
Williams Syndrome
Caused by a deletion of approximately 26-28 genes on chromosome 7, affecting physical and cognitive development.
chromosome inversion
is the detachment, 180° rotation, and reinsertion of part of a chromosome.
Duplication
• Extra copies of chromosome segments
• Can lead to overexpression of genes
Deletion
• Loss of chromosome segments
• May result in loss of important genetic information
Inversion
• Chromosome segment is flipped 180 degrees
• Can disrupt gene function or regulation
Mitosis
is the process of cell division that creates diploid cells. It plays a vital role in cell growth and repairing damaged tissue. Mitosis is divided into four main stages:
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Karyokinesis
another term for Mitosis
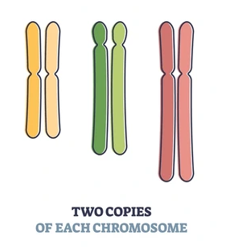
Diploid Cells
These cells have two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. In humans, _____ cells have 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs. _____cells make up most of the body's tissues and are involved in growth and repair. They divide through a process called mitosis.
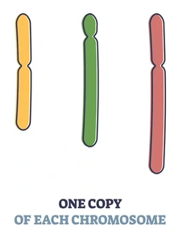
Haploid cells
These cells have only one set of chromosomes. In humans,________ cells contain 23 chromosomes. _________are the reproductive cells (sperm and eggs) and are involved in sexual reproduction. They are produced through a process called meiosis.
Diploid
Two sets of chromosomes (46 total in humans); found in body cells.
Haploid
One set of chromosomes (23 total in humans); found in gametes (sperm and eggs).
Diploid
Haploid
Prophase
is the first phase of mitosis.
-The nuclear envelope breaks down, and organelles like the Golgi and ER disperse.
-The nucleolus disappears, and centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell.
-Microtubules form the mitotic spindle, pushing the centrosomes apart.
-The sister chromatids coil tightly and become visible under a microscope.
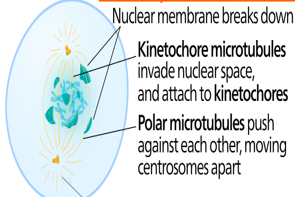
Prometaphase
the nuclear envelope breaks down further, and the mitotic spindle grows.
-Chromosomes condense more, and each sister chromatid forms a kinetochore that attaches to spindle microtubules.
-These microtubules align the chromosomes, pulling them towards opposite poles.
-Polar microtubules help elongate the cell, while astral microtubules assist in spindle orientation.
Metaphase
all chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, forming the metaphase plate.
-The sister chromatids remain attached by cohesin proteins, and the chromosomes are fully condensed.
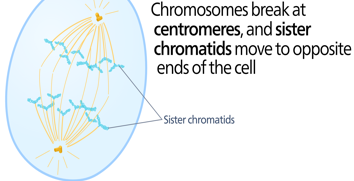
Anaphase
cohesin proteins break down, and sister chromatids separate.
Each chromatid, now a chromosome, is pulled toward opposite poles.
The cell elongates as polar microtubules slide against each other.
Prometaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
During this phase, the chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and start to unwind, transforming back into a relaxed form called chromatin.
The structures that helped separate the chromosomes, known as mitotic spindles, break down into smaller units called tubulin monomers.
These units will be reused to build the cytoskeleton for each new daughter cell.
New nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, and nucleosomes(the basic units of DNA packaging) begin to appear in the newly formed nuclei.
Meiosis

During this phase, the chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and start to unwind, transforming back into a relaxed form called chromatin.
The structures that helped separate the chromosomes, known as mitotic spindles, break down into smaller units called tubulin monomers. These units will be reused to build the cytoskeleton for each new daughter cell. New nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, and nucleosomes(the basic units of DNA packaging) begin to appear in the newly formed nuclei. Early in this stage, the chromosomes become clearly visible under a microscope. As the nuclear envelope starts to break down, proteins help bring homologous chromosomes (the same type of chromosome from each parent) close together. This close pairing is called synapsis. During synapsis, the genes on the chromatids of these paired chromosomes align perfectly with each other. It's important to note that synapsis does not happen during mitosis.
Synapsis
the genes on the chromatids of these paired chromosomes align perfectly with each other. It's important to note that _______ does not happen during mitosis.
Leptotene
The chromosomes start to condense and become visible
Zygotene
The chromosomes begin to pair up. These pairs are called homologous chromosomes. When they are paired together, they form structures known as tetrads, which consist of four chromatids.
Pachytene
This is the stage where crossing over occurs. During crossing over, sections of DNA are exchanged between homologous chromosomes. For example, if one sister chromatid has a gene for eye color labeled (A) and the other has (a) or (B) and (b), they may swap segments. This exchange point is called a chiasma. After crossing over, the sister chromatids may no longer be identical.
Diplotene
The chromosomes start to uncoil, becoming less tightly packed.
Diakinesis
The homologous chromosomes continue to separate further in preparation for the next stages of meiosis.
Five Substages of Prophase I:

Metaphase I
