biotech part 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
when is the population predicted to become 9 billion
2100
what is the difference between micronutrients and macronutrients? what is the world daily calories?
micronutrients: vitamins and nutrients
macronutrients: water, proteins, carbohydrates and fats
2870 calories
what was impact of the green revolution on chronic hunger of the world?
reduced from 40% to 20%, but 800 million people still undernourished
why is micropropagation sterile?
cause the meristem is sterile
what is molecular breeding and why is it useful?
find DNA marker closely linked to fruit character→ follow it in progeny of cross→ use the marker to identify the seedlings that bear red fruit
so don’t need to wait for fruiting plant to see which ones to grow
how do we find markers from molecular breeding?
generate a fingerprint of parent via using random DNA markers (e.g. single nucleotide polymorphisms from genome sequencing)
find markers linked to the phenotype
check the linkage is close
use markers to identify in seedling stage
how can different species plants be crossed? e.g. wheat and rye
-treat plant tissue w enzymes to remove cell wall
-creates protoplasts
-fuse protoplasts from different genotypes
-use polyethylene glycol or electric pulse
what are some barriers to reproduction between different species?
pre fertilisation: asynchrony of flowering, floral morphology, self-incompatibility
post fertilisation: hybrid weakness
what are some ways of overcoming barriers to cross species breeding?
-embryo rescue: culture embryos that otherwise die
what are the steps in using plants as factories e.g for perfumes, flavours, drugs/dyes
understand the biochemistry→ find the genes → express them in plant cells → harvest the chemicals
what are some problems with using plant cells as factories?
de-differentiaion alters genes expressed, enzymes produced, metabolites produced
what % of the 252 drugs considered basic and essential by the WHO are exclusively of flowering plant origin?
11%
what does taxol do? where is it from?
anti-cancer drug, binds MT, stops cell division
from Pacific Yew tree T. brevifolia
what does a gene in the Tu plasmid code for? causes mass of undifferentiated cells
cytokinin, u can relace the genes that cause the crown gall w transgenes
what are the steps of regeneration of plants from tissue culture?
incubate leaf discs w Agrobacterium
balance cytokinin and auxin to induce callus growth
add more cytokinin to induce shoot growth
add more auxin to induce root growth
transfer to soil and gradually reduce humidity
where are somatic vs autonomic nervous system nerves going to?
somatic- to skeletal muscle
autonomic-visceral organs (also includes sympathetic & parasympathetic)
what are the characteristics of the endocrine system?
-wireless
-specificity of target cell binding
-hormones carried in the blood to long distance
-slow and long-lasting response
-controls long lasting activities (e.g. growth)
-involuntary
-influences CNS output
what are the characteristics of the nervous system?
-wired system
-anatomical connection w target cells
-neurotransmitters diffuse through short distances
-rapid and brief response
-coordinates fast and precise response
-voluntary/ involuntary
-influences endocrine output
-other non-regulatory functions
how fast is endocrine vs nervous system response?
endocrine is sec to hours
nervous is msec to sec
what is characteristic of the human cortex and all primates, not all mammals?
undergone gyrification
what is gray matter and white matter?
gray- primarily cell bodies
white- myelinated neurites projecting from neurons
in the PNS, how many pairs are there of cranial nerves, spinal nerves?
cranial: 12 pairs
spinal: 31 pairs
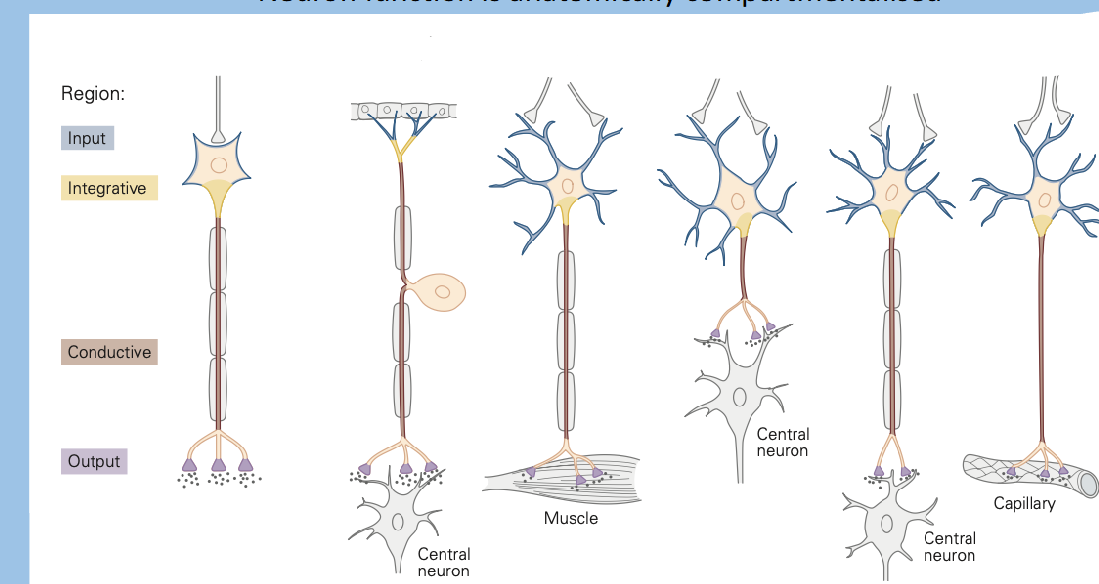
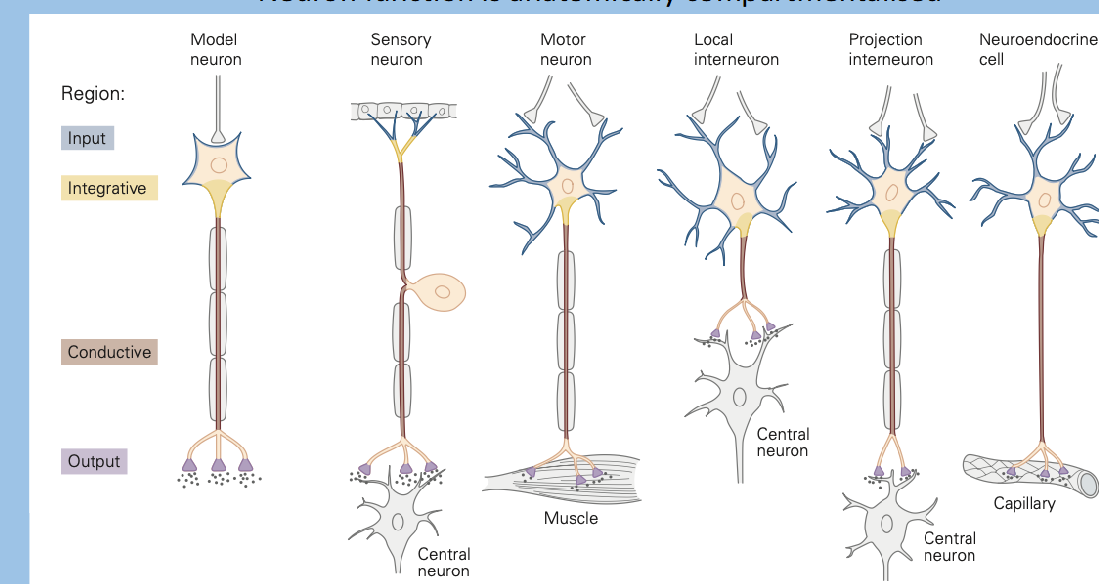
what are the estimates of the ratio of neurones to glia
1:1 to 1:50
what do astrocytes do?
delivery of molecules to/from the vasculature, activate in response to injury, neuroinflammation/ degeneration
what are the differences between non-reactive and reactive astrocytes?
non-reactive- trophic support of neurons, synapse formation and maintenance, clearance or neurotransmitters
reactive- damage neurons, activate microglia, some phagocytic activity
what do microglia do
-survey for damaged material and pathogens
-important roles in development & pruning excess synapses
-inflamed in response to pathogens, injury, and neurodegeneration
how do microglia change when activated?
increased motility, phagocytosis, and release of immune factors (cytokines)
what do Oligodendrocytes & Schwann cells do?
oligodendrocytes- myelinate multiple axons
Schwann cells- myelinate single axons
all motor neurons are myelinated, and some sensory
what are the different cell culture models?
stable cell lines- easily grown, derived from tumours
primary neuronal cultures- derived from model organisms
human stem cell derived- from skin cells of living patients
how can behavioural responses manipulated?
pharmacologically
genetically
e.g. in models of of developmental disorders and neurodegenerative disease
what are some examples of excitable cells?
-muscle (myocytes, cardiomyocytes)
-endocrine cells
-neuronal cells
what are some mb properties of excitable cells?
-hydrophobic lipids
-channels/ pumps facilitate cross mb transport of ions and molecules
-channels/ pumps are selective, based on size, charge and solubility of substrates
how do you measure the electrophysiological activity of a neuron?
use an intracellular electrode to measure internal voltage, extracellular electrode, measure the difference in voltage
what is resting potential in excitable cells?
the point at which difference in ion concentrations are stable across a mb
-permeable to passive diffusion by K+, Na+ (via ATP pump) and Cl- (leaky channels)
-impermeable to intracellular large anions
what does the Na+ -K+ pump work?
3 intracellular Na+ for 2 extracellular K+
why are further K+ not diffusing out?
negative intracellular electrostatic force prevents it
membrane potential is mostly due to potassium. what other ions have an impact?
sodium- have low permeability (ENa= +55mV)
chloride- passively distributed and dependent on Na+ and K+ distribution (ECl= -60mV)
what are the stages of APs?
depolarisation: rapid positive change in mb potential from -70mV to +30mV
repolarisation: rapid negative change in potential (depolarisation-repolarisation spike ~1ms)
hyperpolarisation: mb potential becomes more negative than resting potential
afterpolarisation: mb potential returns to resting potential state
what is threshold stimulus typically
~15mV higher than resting potential
what is the difference between the absolute refractory period and relative refractory period?
absolute refractory- neurone cant be stimulated during a spike
relative- during hyperpolarisation, after polarisation, a suprathreshold stimulus is required to trigger an AP
what are refractory periods important for?
unidirectionality of AP
an upper limit on firing rate
how do APs move along an axon?
differences in membrane induce a local circuit
current spreads from the negative active zone to positively charged surrounding membrane
refractory period blocks travel in reverse direction
where in a neuron are APs triggered?
hillock (voltage gated sodium channels are enriched within the hillock region)
what occurs during the depolarisation phase?
-voltage gated Na+ channels open, Na+ enters cell
voltage gated K+ ion channels slowly open
Na+ channels can be closed but capable of opening, open, or closed and incapable of opening (inactivated)
what occurs during the repolarisation phase?
Na+ channels close slowly
voltage gated K+ channels continue to open (K+ leaves the cell)
K+ can be closed or open (no inactivation)
what occurs during the hyperpolarisation phase?
K+ continues to enter the cell, K+ channels close slowly
what occurs during the after polarisation phase?
K+ and Na+ AT, return to resting potential
how much faster is an unmyelinated axon vs a myelinated?
unmyelinated: 0.5-2.0m/s
myelinated: 80-120m/s
where are sodium channels concentrated?
within nodes