Chemistry Chapter 3
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Atomic Theory
The scientific theory that matter is composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms
______ cannot be created, divided, or destroyed (Dalton's Atomic Theory)
Atoms
Atoms combine in whole-number ratios to form _____ (Dalton's Atomic Theory)
compounds
_______ involve the rearrangement of atoms (Dalton's Atomic Theory)
Chemical reactions
Atoms are ______ (contain protons, neutrons, and electrons) (How has Dalton's theory been modified)
divisible
Atoms of the same element can have different _____ (isotopes). (How has Dalton's theory been modified)
masses
Atoms can change in ______ (How has Dalton's theory been modified)
nuclear reactions
Law of Conservation of Mass
Matter cannot be created or destroyed in chemical reactions; atoms are simply rearranged
Law of Definite Proportions
A compound always has the same elements in the same mass ratio
Law of Multiple Proportions
When two elements form multiple compounds, their mass ratios are simple whole numbers
Proton
+1 charge, in nucleus, mass = 1 amu
Electron
-1 charge, in electron cloud, mass ~ 1/1836 amu
Neutron
0 charge, in nucleus, mass = 1 amu
Atomic Number
The number of protons in an atom, which determines the element
Atomic Mass
The weighted average mass of an element's isotopes
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
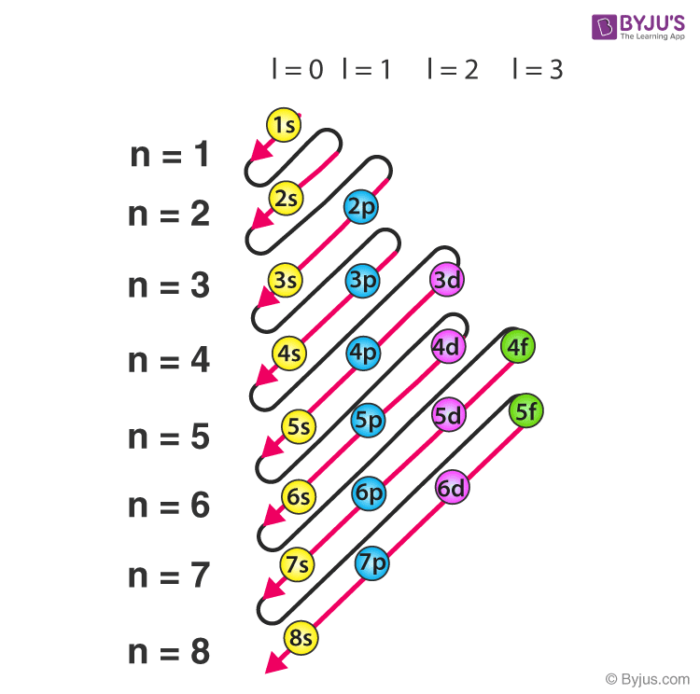
Aufbau Principle
Electrons fill lowest-energy orbitals first
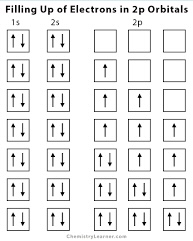
Hund's Rule
Electrons fill orbitals singly before pairing up
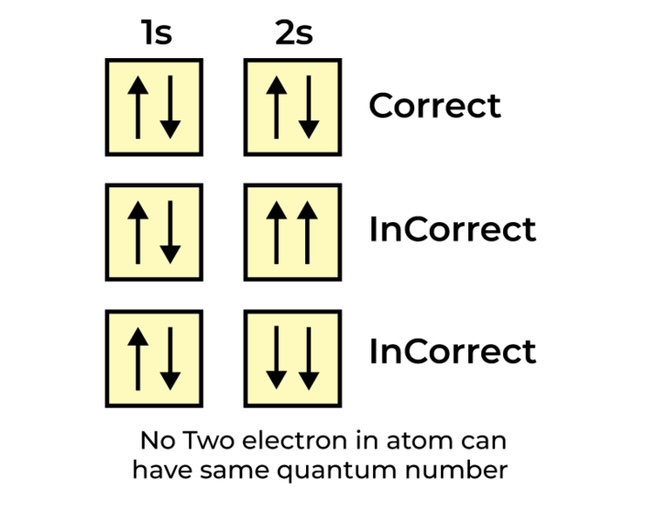
Pauli Exclusion Principle
No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers
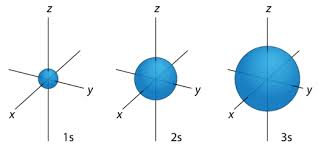
s-orbital
Spherical
p-orbital
Dumbbell-shaped

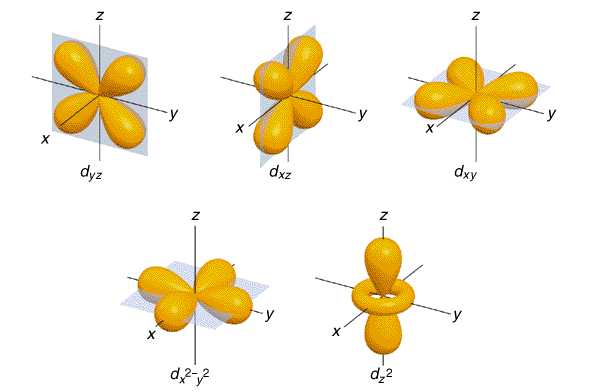
d-orbital
Cloverleaf-shaped
f-orbital
Complex shape
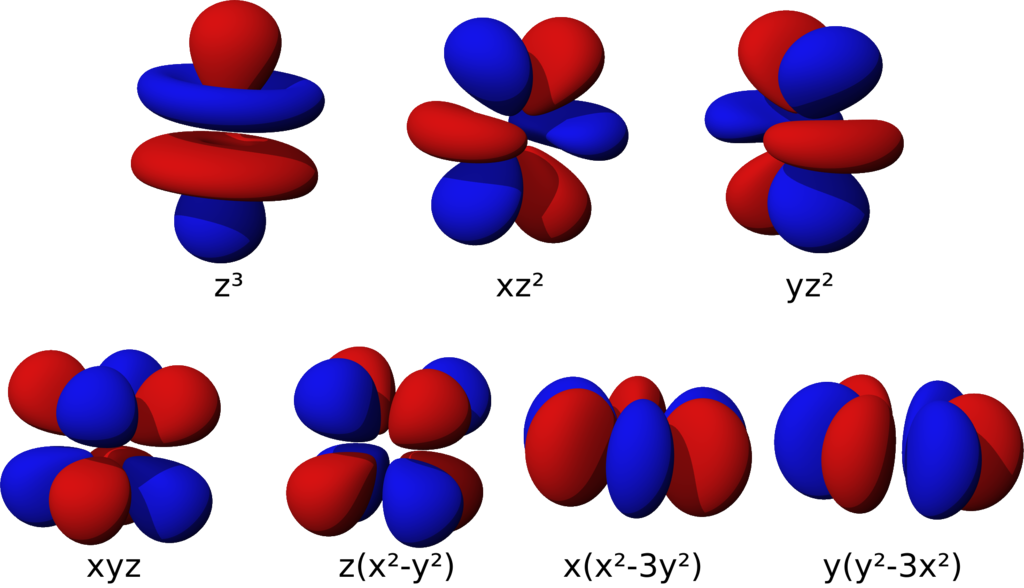
Groups (columns)
Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties
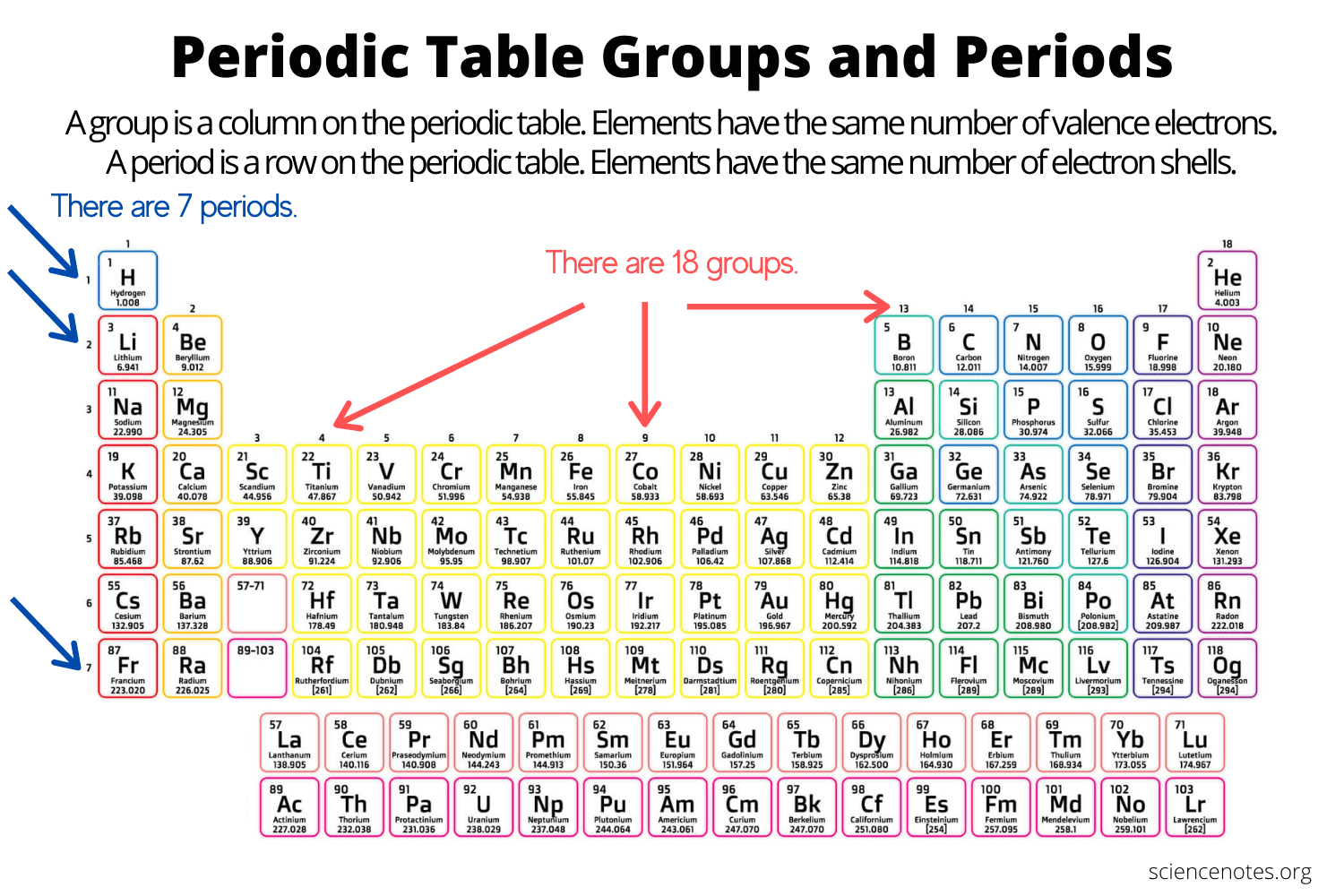
Periods (rows)
Elements in the same period have increasing atomic number
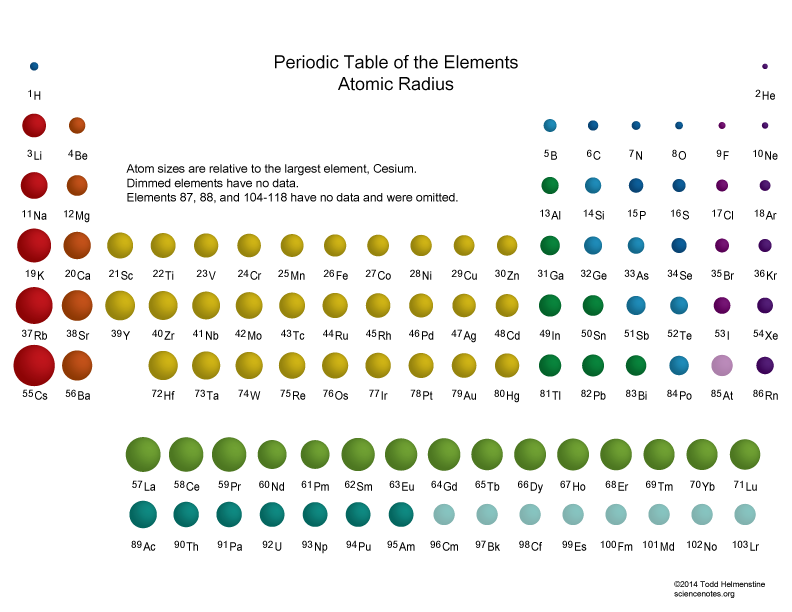
Atomic Radius
Increases down a group, decreases across a period (Average bonding radii when bound to another atom)
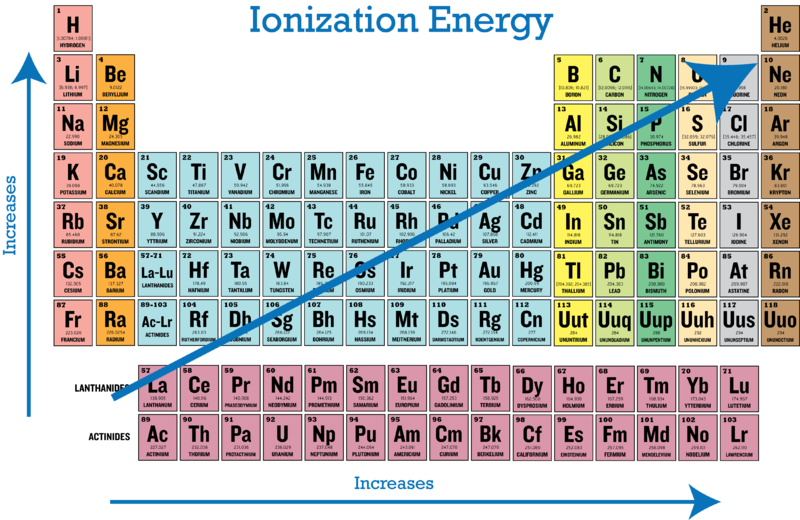
lonization Energy
Increases across a row, decreases down column
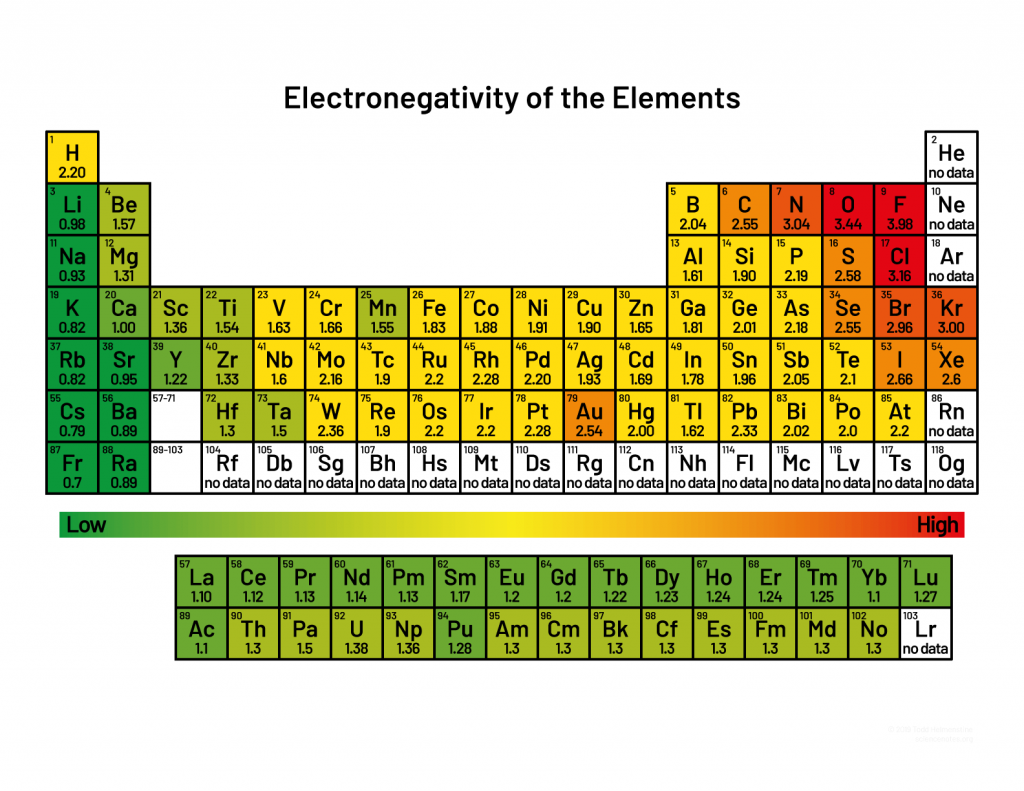
Electronegativity
Increases across a period, decreases down a group
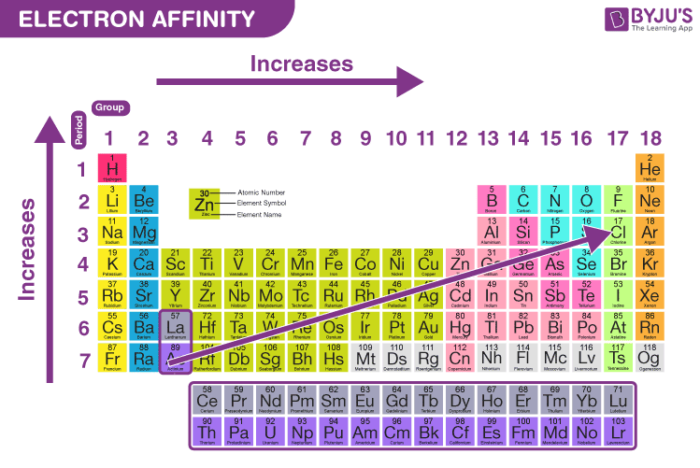
Electron Affinity
Follows a similar trend as electronegativity
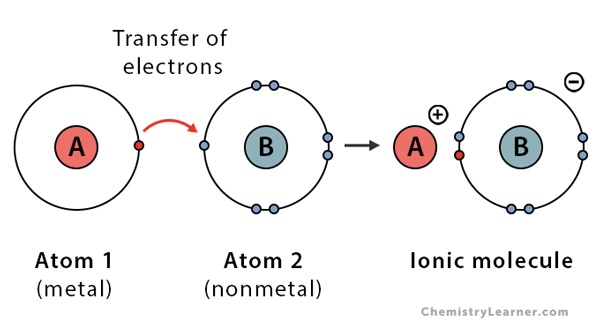
Ionic Bond
Transfer of electrons (metal to nonmetal)
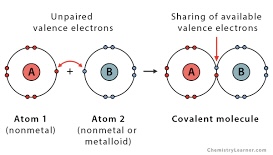
Covalent Bond
Sharing of electrons (nonmetal to nonmetal)
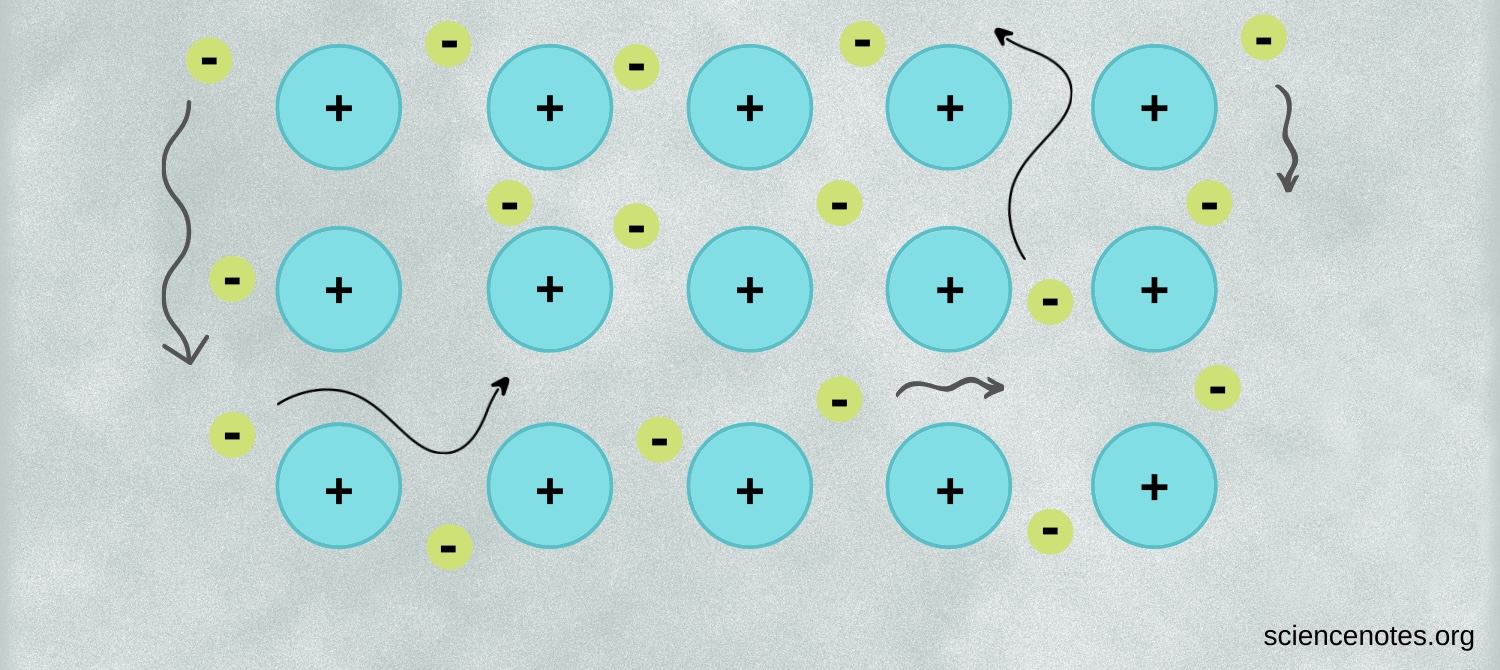
Metallic Bond
Delocalized electrons moving in a metal lattice
What are the three types of chemical bonds?
Ionic, Covalent, Metallic
What are the major types of chemical reactions?
Synthesis (Combination), Decomposition, Single Replacement, Double Replacement, Combustion
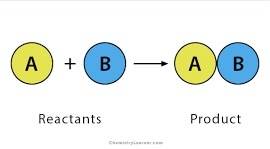
Synthesis (Combination)
A + B → AB
Decomposition
AB → A + B
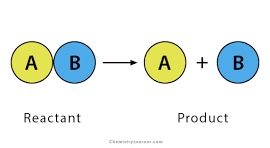
Single Replacement
A +ВС → AC + В
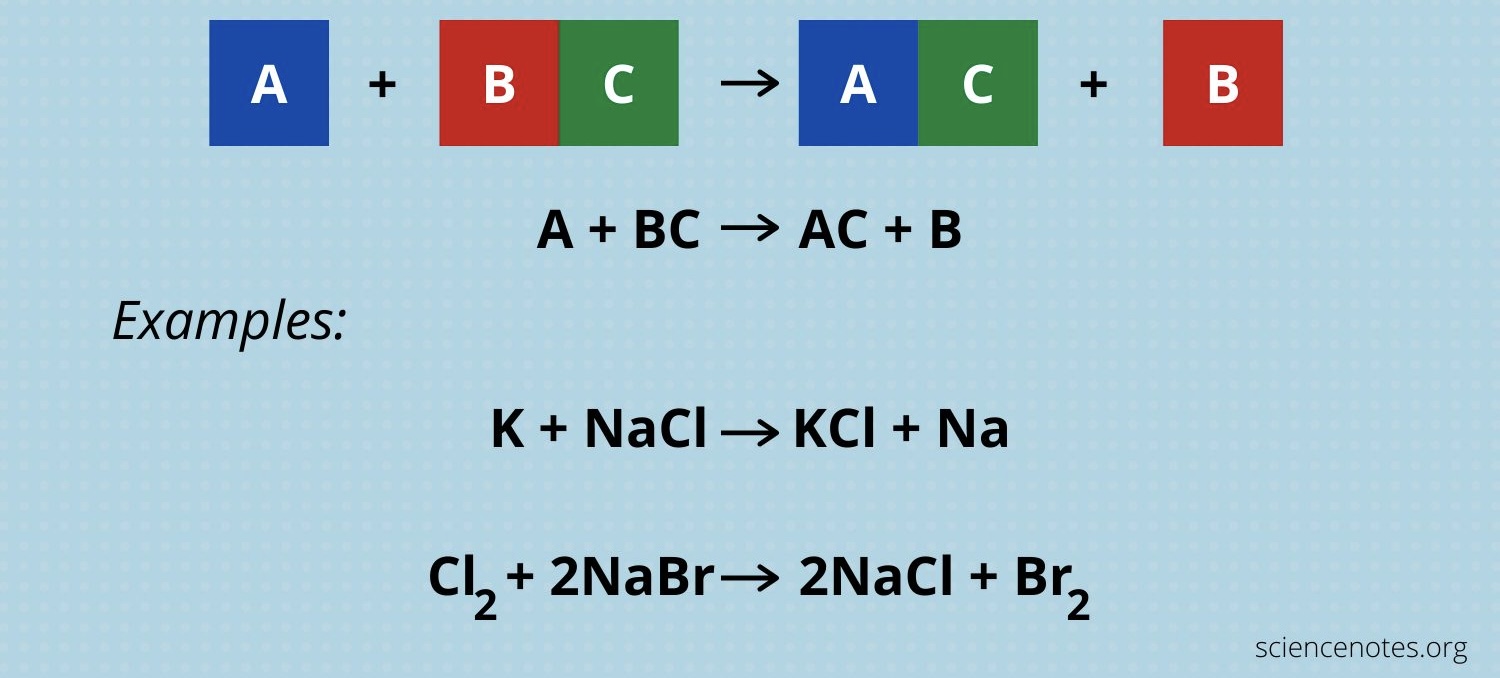
Double Replacement
AB + CD → AD + СВ
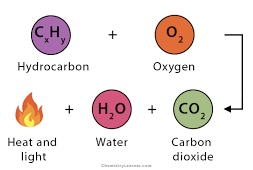
Combustion
Hydrocarbon + 02 → CO2 + H20
Stoichiometry
The study of quantitative relationships in chemical reactions
Mole Concept
1 mole = 6.022 × 1023 particles (Avogadro's number)
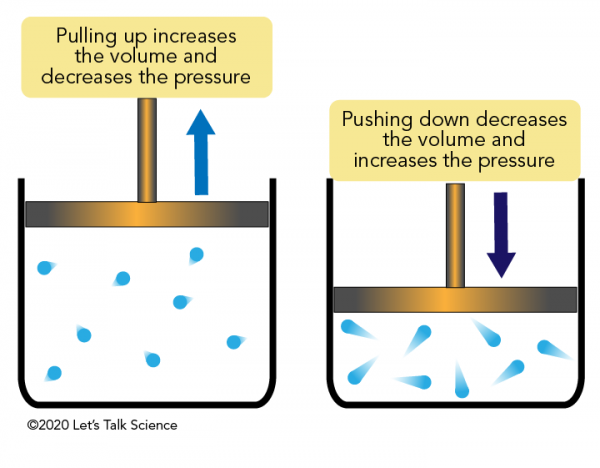
Boyle's Law
P1V1 = P2V2 (Pressure-Volume, inversely related)
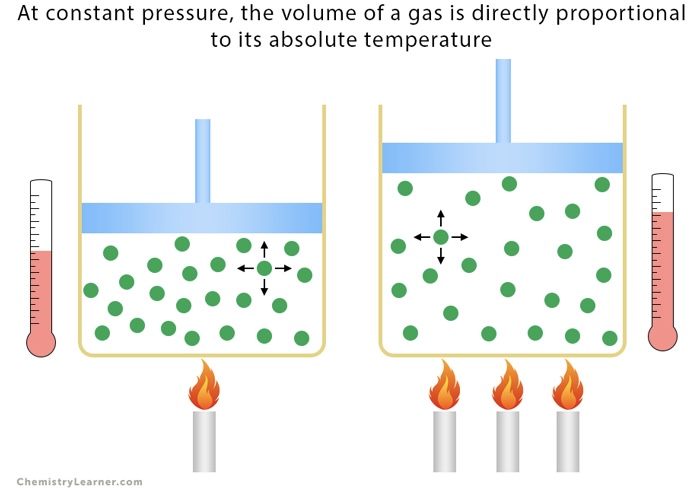
Charles's Law
V1/T1 = V2/T2 (Volume-Temperature, directly related)
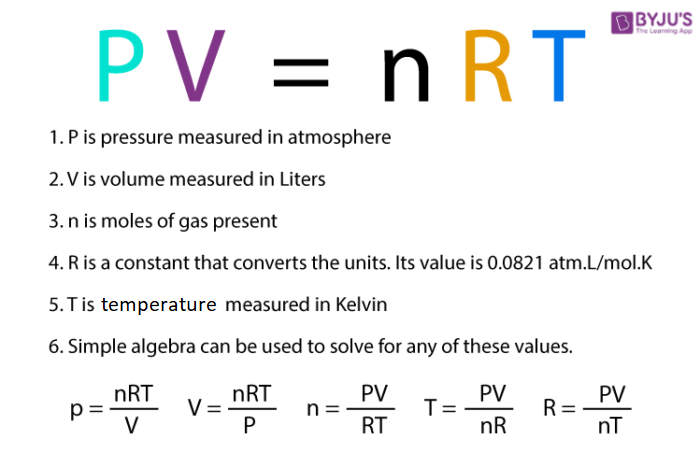
Ideal Gas Law
Pv = nRT
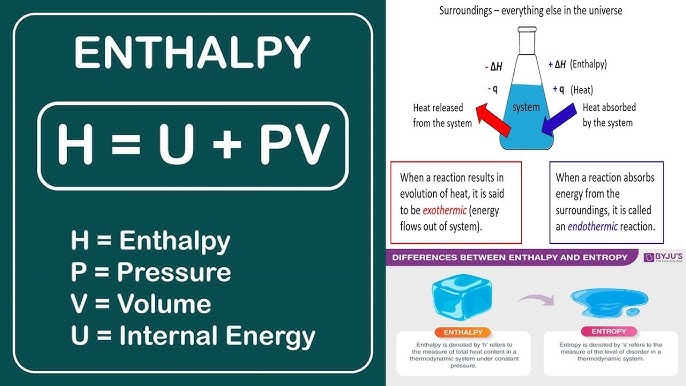
Enthalpy (ДН)
The heat change in a reaction
Periodic Law
The elements are arranged in order of increasing mass, certain sets of properties recur periodically
Electron Configurations
Shows the particular orbitals that electrons occupy for the atom
The farther a principle level is from a nucleus _______
Gets larger, holds more electrons, electrons have higher energies
Sub shells
Angular Momentum Quantum Number (s, p, d, and f)
s
Shell: 1, # of orbitals: 1, Electron Capacity: 2, e- in orbital: 2
s,p
Shell: 2, # of Orbitals: 1,3, Electron Capacity: 8, e- in orbitals: 2,6
s,p,d
Shell: 3, # of Orbitals: 1,3,5, Electron Capacity: 18, e- in orbitals: 2,6,10
s,p,d,f
Shell: 4, # of orbitals: 1,3,5,7, Electron Capacity: 32, e- in orbital: 2,6,10,14
Electron Configuration
Shows the particular orbitals that electrons occupy for the atom
________ describes the attractions and repulsion’s between charged particles. The strength of the interaction increases as the size of the charges increase
Coulomb’s Law
_____ an electron from the full effects of the nuclear charge by repulsion of other electrons
Shielding
______ of the electron cloud by an electron now feels the full effects of the nuclear charge
Penetration
Electrons occupy the ____
lowest energy orbitals available
The group number of a main group element is _______
equal to the number of valance electrons for that element
The row number of a main group element is _____
equal to the highest principle quantum number of that element
Why do elements in a given group of the periodic table have similar properties?
Similar electron configurations in their valance shells- the outermost principle energy level
Valance Shell
Outermost electron shell of an atom
Valance Electron
An electron in the valance shell of an atom
Core electron
an electron that is not part of the valance shell
Metals
Conduct heat and electricity, Form cations in solution, loses electrons in reactions- oxidized
Nonmetals
Electrical and thermal insulators, form anions and polyatomic anions, gain electrons in reactions- reduced
Paramagnetic
contains unpaired e- and attracted to magnetic field
Diamagnetic
Contains paired e- and is not attracted to magnetic field
Octet Rule
Elements undergo reactions to get 8 valance electrons
Electron Affinity (Definition)
The energy released on adding an electron to a single atom in the gaseous state
Ionization Energy (Def)
The energy required to remove one electron from a single atom in the gaseous state
Ionic Solids
Ions are attached by ionic bonds to their nearest neighbors. Compounds of this type are referred to as ionic compounds
The group numbers from 1A through 8A give the numbers of valance electrons for the elements in _____ (Group 1A, 1 Valance Electron, ns1)
each main group
Transition Metals Valance electrons include the ____ (Group 4b, 4 Valance Electrons, ns2nd2)
d electrons
Effective Nuclear Charge
The charge that the valance e- feel from the nucleus
Compounds are composed of atoms held together by chemical _____
Bonds
_____ form because they lower the potential energy of the charged particles (the electrons and protons) that compose atoms
Chemical Bonds
Chemical Bonds are Classified Into two main types
Ionic, Covalent
Ionic
Metals+Nonmetals, Transfer e-, Cation+Anion
Covalent
2 or more nonmetals, share e-, atom+atom
When a metal interacts with a nonmetal, it can transfer one or more of its electrons to the nonmetal. The metal atom then becomes a ______. The nonmetal atom becomes a _____
cation, anion
Molecular Compound
compound that consists of molecules rather than ions
Bond Length
The optimum distance between nuclei in a covalent bond
Chemical Formula
Indicates the elements that are present in the compound and the relative number of atoms or ions
Empirical Formula
Gives the relative # of atoms of each element in a compound (Hydrogen Peroxide-HO)
Molecular Formula
A formula that shows the # and kinds of atoms in one molecule of a compound (H2O2)
Structural Formula
A molecular representation that shows the connections among atoms by using lines to represent covalent bonds (H-O-O-H)
Molecular Model
More accurate and complete way to specify a compound
Ball and Stick molecular model
Represents atoms as balls and chemical bonds as sticks.x how the two connect reflects a molecules shape
Space Filling Molecular Model
Atoms fill the space between each other to more closely represent our best estimates for how a molecule might appear if scaled to visible size
Lewis structures focus on valence electrons because ______ involves the transfer or sharing of valance electrons between two or more atoms
Chemical bonding
Lattice Energy (Always Exothermic)
-E associated with the formation of a crystalline lattice of alternating ± ions in gaseous state
Born-Haber Cycle
Lattice energy generally negative, large amount of heat released when ions coalesce to form a crystalline lattice
Ionic compounds are ____. Cation and Anions combine to cancel charges
Neutral
______ bond almost exclusively covalently
Carbon Atoms
Formula Mass
= Number of atoms of 1st element in chemical formula X atomic mass of 1st element) + (Number of atoms of 2nd element in chemical formula X Atomic Mass of 2nd Element)
When two different elements combine, they form a _____
Binary compound, metals are always written before nonmetals
Coordinate covalent bond
Covalent bond that forms when both electrons are donated by the same atom
Polyatomic Ions
Composed of two or more atoms with a particular charge
Oxyanions
Anions containing oxygen and another element