Ch 1 fundamentals of data science
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
querying and reporting
you know exactly what you are looking for
(no modeling or pattern finding)
OLAP : online analytical processing
is a scale up of querying
GUI to query large data collections in real-time
pre-programmed dimensions of analysis
summary level
→ no modeling or pattern finding
(still predetermined what you are looking for)
data science
a set of fundamental principles that guide extraction of knowedge from data
data mining
the extraction of knowledge from data, via technologies that incorporate the principles of data science
→ you don’t know what you are looking for/ want to find new intricate patterns in the (big) data
big data
dtaa that is so large that traditional data storage and processng systems are unable to deal with it
velocity, volume and variety
techniques that allow machines to display intelligent behavior
artificial intelligence
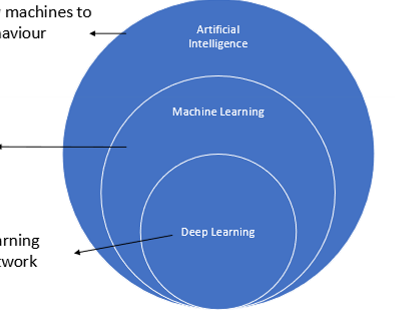
machine learning
subset of AI technioques that improve with data
= learning by doing
deep learning
subset of machine learning which uses neural network technology
data
= raw stream of facts
structured or unstructured
can sometimes be ‘big’= information / knowledge
a model
an (abstract) representation of (a part) of reality
how is a model learned / trained
by machine learning algorithm, based on data
prediction
the estimation of an unknown value
types of machine learning
supervised learning
unsupervised learning
reinforcement learning
supervised learning
learning a mapping X→ Y or f(x) = y
y is the outcome / target / label
dependent on the type of y
- classification (discrete) or regression (continuous)
prediction := estimation of an unknown value
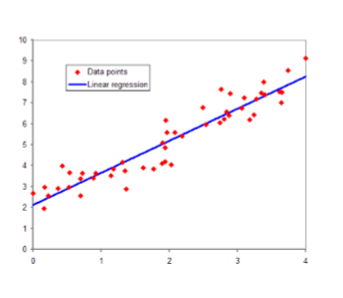
supervised learning : regression
continuous target variable
eg ; linear regression
supervised learning : classification
binary categorical target varable
binary classification
binary outcome
categorical target variable : - multiclass classification
output can also be a probability of class membership
unsuppervised learning
no “Y” target
clustering
anomaly detection
generative models
unsupervised learning : clustering
assigning similar observations to clusters Ie groups of similar obsevations
unsupervised learning : anomaly detection
detecting anaomalous os-bservations
ex
identification of fraudulent transactions
unsupervised learning : generative models
generation of realistic new observations
reinforcement learning
no data set
learning through interaction with the environment (exploration, exploitatiion)
learning a policy that optimizes, a reward
why so few reinforcement learning in the industry
long tails (ex self-driving cars)
expensive exploration
immense dimensionality of problems, need many trials, no simulators
instability : catastrophic forgetting
trust
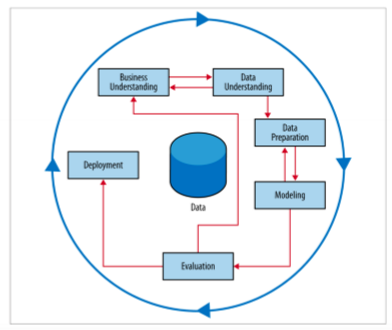
CRISP - DM
cross industry standard process for data minijng
structured process of problem to solution (iterative)
bsuiness understanding
data understanding
data preparation
modeling
evaluation
deployment