CHEM CH8 - Solids, Liquids & Gasses
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Intramolecular bonds
Bonds within the molecules ex: ionic and covalent bonding
Intermolecular Forces of Attraction
Between the molecules (dipole-dipole, hydrogen, and dispersion / london forces of attraction)
types of bond from strongest to weakest
ionic
covalent
dipole-dipole
hydrogen
london FOA
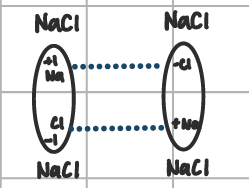
dipole-dipole forces of attraction
when oppositely charged poles of different molecules are attracted to each other
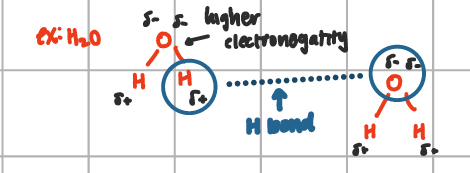
hydrogen bond
exists between the positively charged H+ atom of one molecules & a highly electronegative atom such as O, N, or F atom of another (two molecules needed)
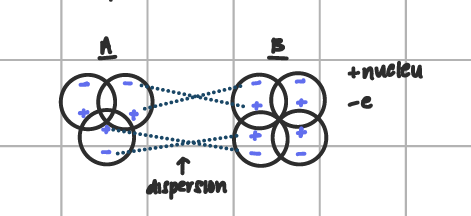
dispersion or london FOA
weakest bond; attraction occurs between the positive charges nucleus of one atom and the negative electrons of another atom of a another molecule
types of solids
crystals (smooth edges / columns)
amorphous solid (does not have sharp edges) ex: glass or plastic
chunky solids (ex: zinc)
powder solids (ex: zinc)
granulated solids (ex: granulated sugar)
wire (ex: Cu, Fe wire)
sheets (ex: Cu, Fe sheets)
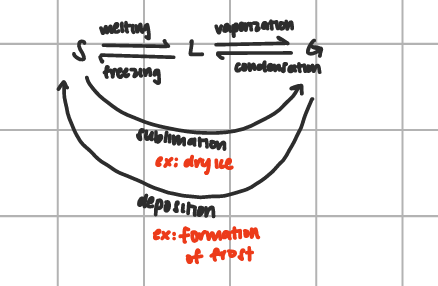
Liquids triple point characteristic
at 0°C, H2O can exist as a solid, liquid of gas
gas
has the largest amount of energy compared to S and L
moves around randomly, in different direction via gentle collision w/ each other and the container around it
creates gaseous pressure
Boyles Law
at constant temperature, volume is inversely proportionate to pressure
P1V1 = P2V2
1 atm = 760 mmHg = 14.7 psi
1 atm = 760 mmHg = 14.7 psi
Charle’s Law
at constant pressure the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (K)
V1/T1 = V2/T2
Gay - Lussac’s Law
at constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (K).
P1/T1 = P2/T2
Combined Gas Law
It relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas, combining Charles's and Gay-Lussac's laws.
The formula is P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2.
Avogadro’s Law
at constant temperature and pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas.
V1/n1 = V2/n2
Ideal Gas Law
describes the relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas, combining all the gas laws into one equation.
Pv = nrt (HAS TO BE CONVERTED TO L, ATM, K AND MOLE)
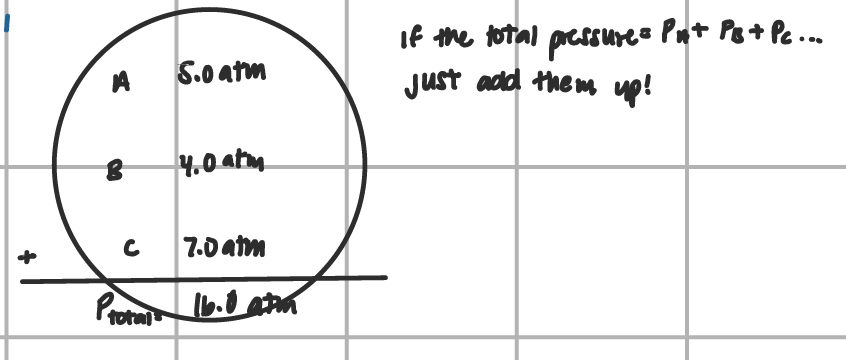
Daltons Gas Law of Partial Pressure
states that the total pressure of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture.
Daltons Gas Law of Partial Pressure (scenario 1)
add total pressures up
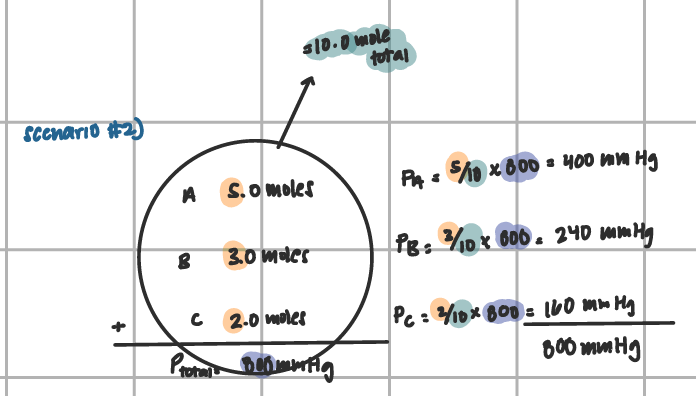
Daltons Gas Law of Partial Pressure (scenario 2)
add moles, then divide by total and mult. by ptotal given
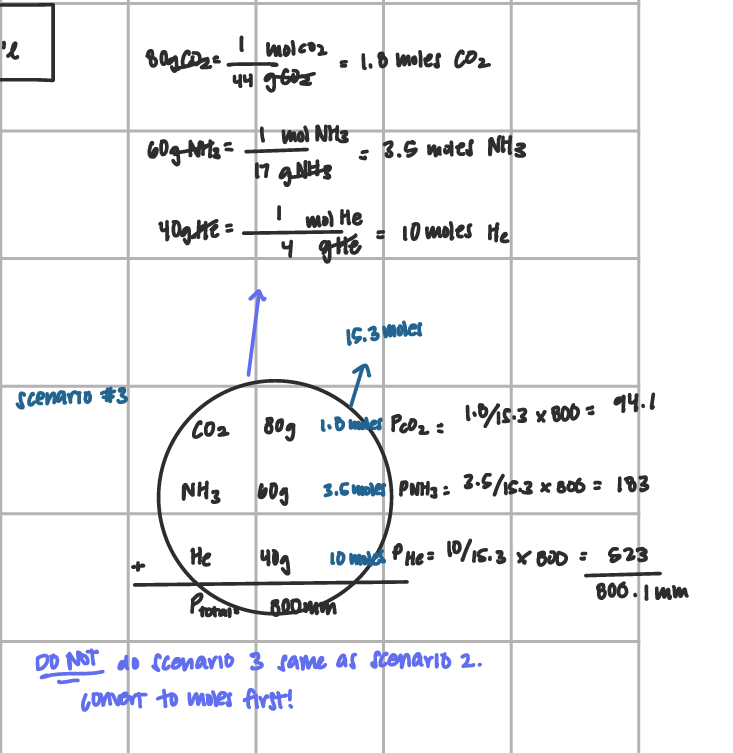
Daltons Gas Law of Partial Pressure (scenario 3)
find the molar mass for the compounds
add together
divide grams/total mm
mult by ptotal