A-Level CIE Biology: 15 Coordination & Control
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
what is a hormone
chemical substance produced by an endocrine gland and carried by the blood.
chemicals which transmit information from one part of the organism to another and bring about a change.
they alter the activity of one or more specific target organs
what do hormones control
functions that don’t need instant responses
what is the endocrine system
endocrine glands that produce hormones in animals collectively
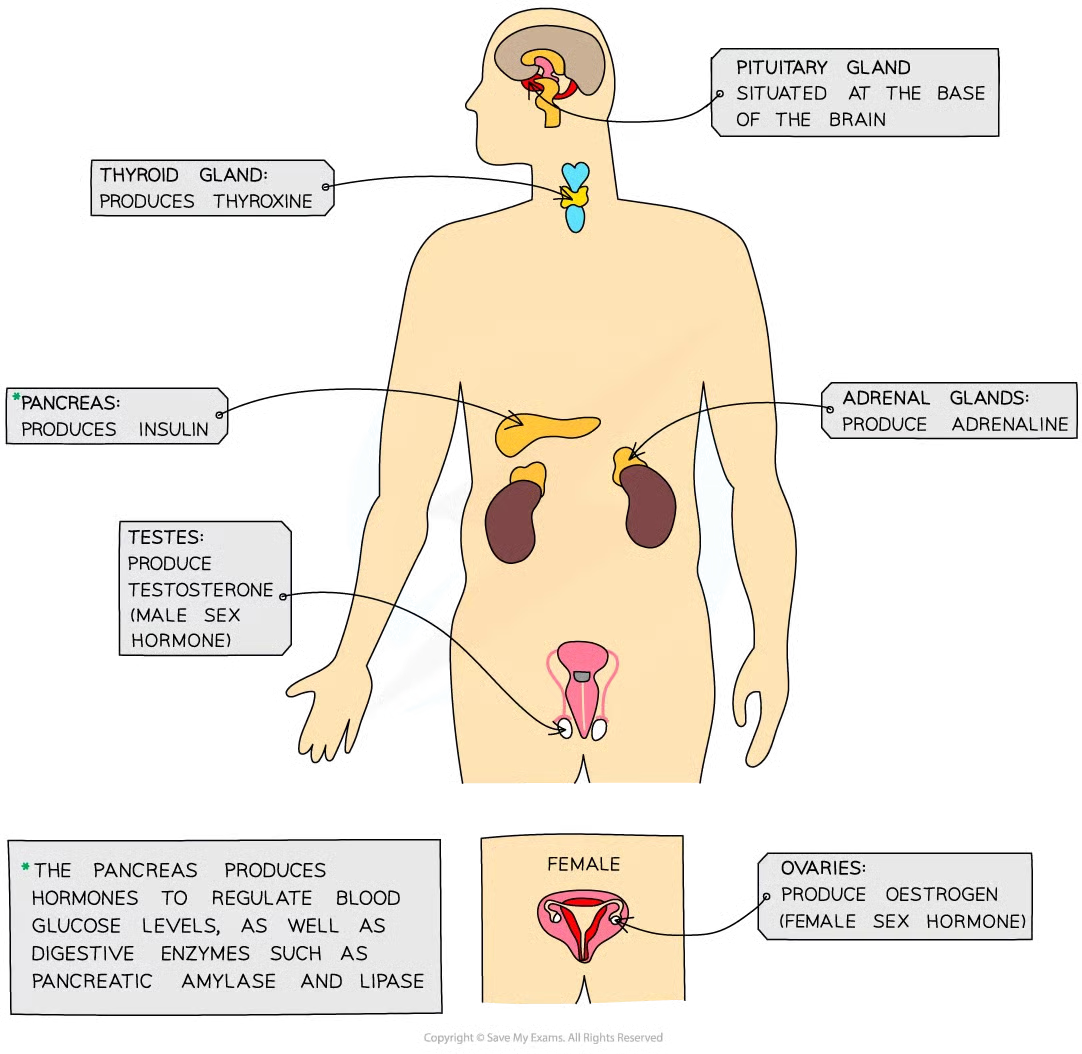
gland
group of cells that produces and releases one or more substances (secretion)
examples of cell-signalling molecules/hormones in blood
insulin
glucagon
ADH
adrenaline
why do endocrine glands have a good blood supply
when they make hormones, they need to get the hormones into the bloodstream/blood plasma asap so they can travel around body to target organs and bring about response
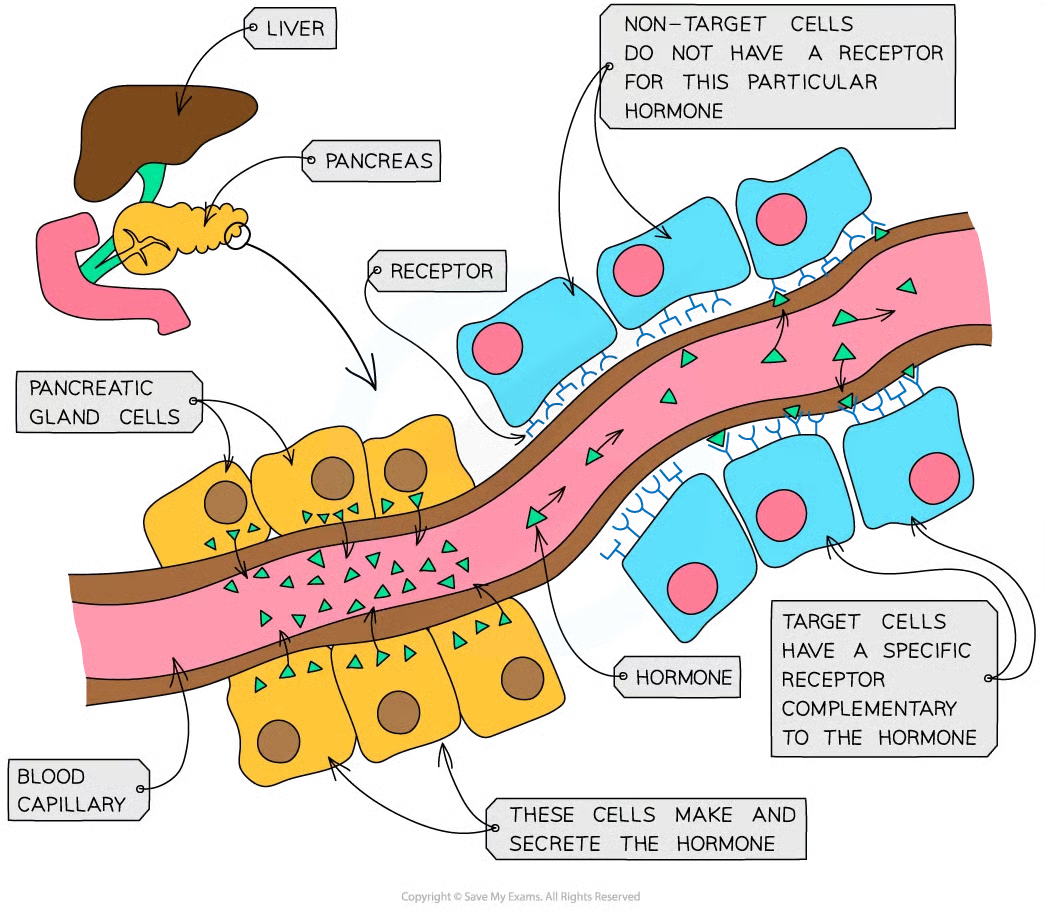
what is needed for hormones
cells with receptors that the hormone can bind to either found on the csm or inside cells. they must be complementary to have an effect
what hormones are peptides
insulin, glucagon and ADH
features of peptide hormones
water-soluble so can’t cross pbl of csm
bind to receptors on csm of target cells which activates second msngers to transfer signal thru cyto
what hormones are steroids
testosterone, oestrogen, and progesterone
features of steroid hormones
lipid-soluble and can cross pbl
bind to receptors in cyto of nucleus of target cells
human nervous system: 2
central nervous system/cns - brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system/pns - all nerves in body
what does the nervous system allow us to do and how
make sense of our surroundings nad respond to them and to coordinate and regulate body functions
info sent thru nervous system as nerve impulses which are electrical signals passing along nerve cells (neurones)
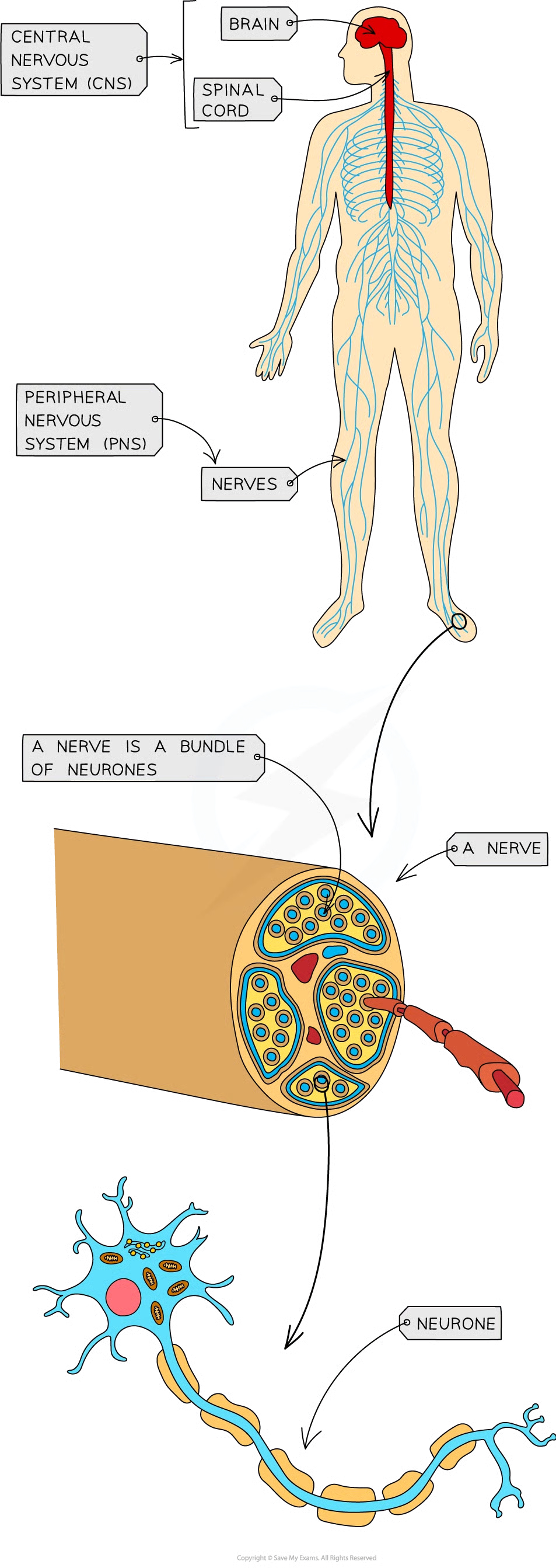
nerve
bundle of neurones
neurones function
coordinate the activity of sensory receptors (e.g. eye), decision making centres in the cns, and effectors such as muscles and glands.
nervous system: parts, message, method, effectors, speed, duration
brains, spinal cord, nerves/neurones
electrical impulse
neurones
muscles or glands
very fast
short until electrical impulses stop
endocrine system: parts, message, method, effectors, speed, duration
glands
chemical/hormone
bloodstream
target cells in specific tissues
slower
longer until hormone broken down
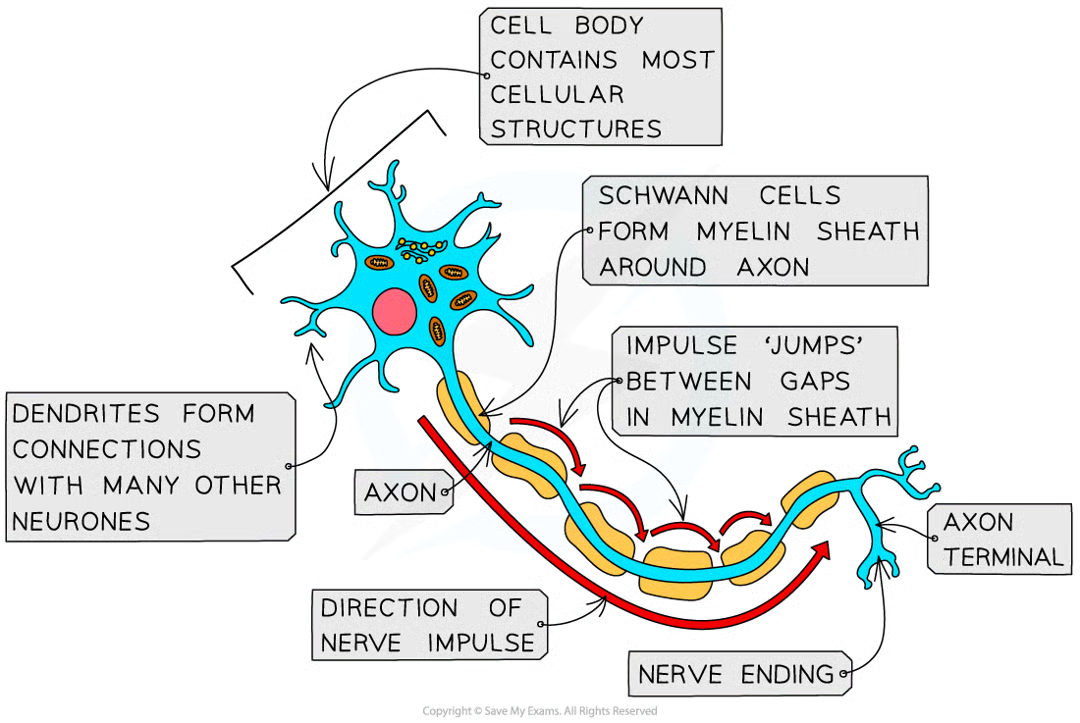
axon
neurone’s long fibre
how is an axon insulated
fatty sheath with small uninsulated sections along its length (nodes of Ranvier)
what is the fatty sheath made of
myelin, substance made by specialised cells (schwann cells) when they wrap themselves around axon along its length
what is the effect of the axon
electrical impulse doesn’t travel down whole axon but jumps from one node to the next
why do electrical impulses jump
less time wasted transferring impulse from one cell to another
dendrites
cell bodies contain many extensions/dendrites that allow them to connect to many other neurones and receive impules from them forming a network for easy communication
3 main types of neurone
sensory, relay, motor
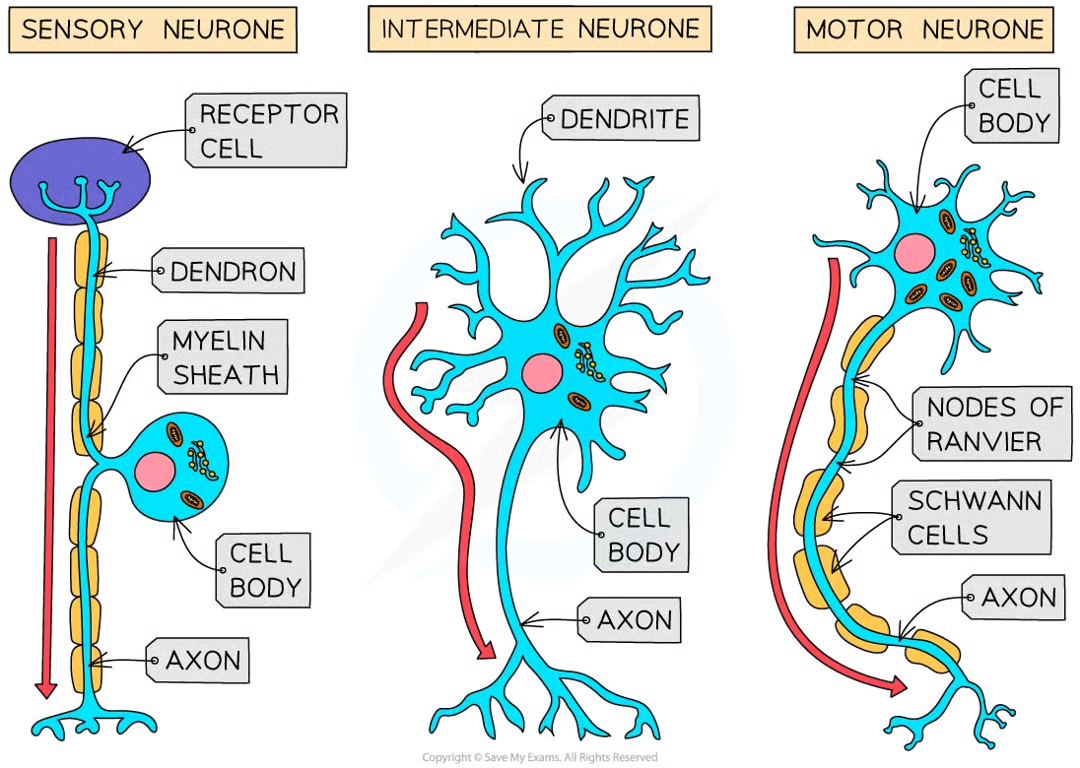
sensory function
carry impulses from receptors to cns/brainorspinalcord
intermediate/relay neurone function
found entirely within cns and connect sensory and motor
motor function
carry impulses from cns to effectors/muscles or glands
are all neurones the same
no, each has slightly diff structure
motor neurone structure: 3
large cell body at one end, that lies within spinal cord or brain
nucleus that is always in its cell body
many highly-branched dendrites extend from cell body, providing large sa for axon terminals of other neurones
sensory neurones structure
same basic as motor but have cell body that branches off in middle of cell = may be near source of stimuli or in swelling of spinal nerve known as ganglion
receptor cell
cell that responds to a stimulus. transducers. convert energy in one form (e.g. light/heat/sound) into energy in electrical impulse within sensory neurone
where are receptor cells found
in sense organs (e.g. light receptor cells found in eye, chemoreceptors in taste buds)
what are some receptors
specialised cells that detect a specific tyep of stimulus and infleunce the elcetrical activity of a sensory neurone (light and chemo eye and tongue)
others (e.g. touch) are just ends of sensory neurones themself
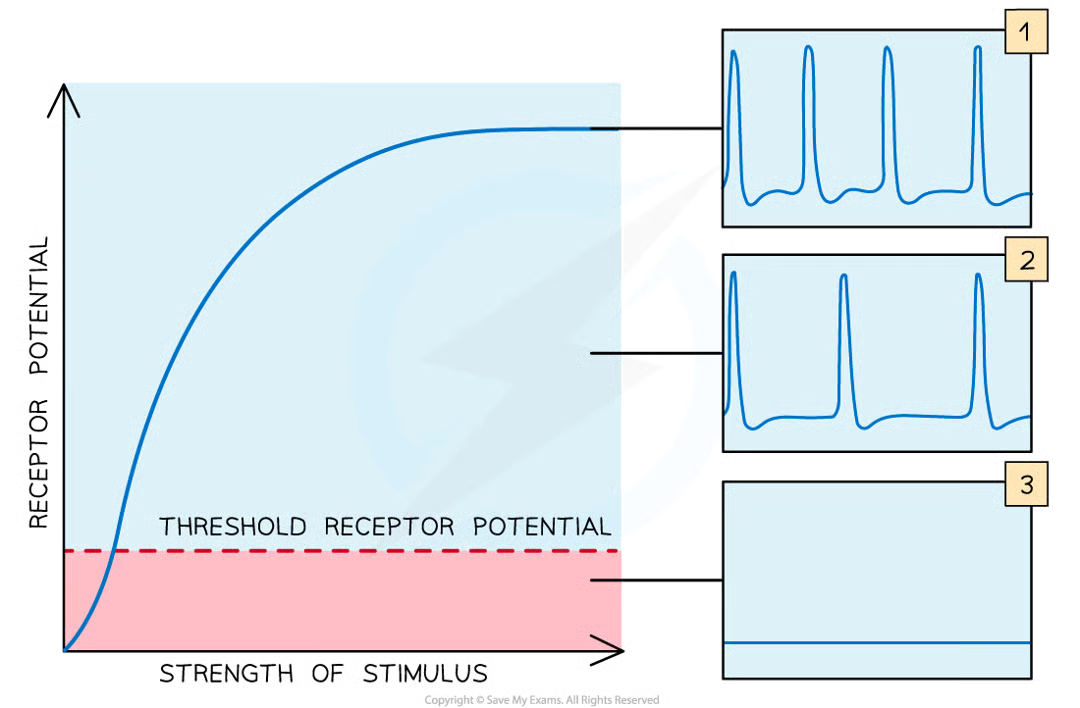
what happens when receptor cells are stimulated. what if its weak/strong
depolarised
weak= not sufficiently depolarised and sensory neurone is not actviated to send impulses
strong=sensory neurone activated and transmits impulses to cns
tongue surface.
many small bumps called papillae covering surface of tongue, each covered in many taste buds which contain many chemoreceptors that are sensitive to chemicals in food and drinks bc covered with receptor proteins to detect diff chemis
what do chemoreceptors in taste buds that detect salt (sodium chloride) respond directly to
sodium ions.
if salt is present in food (dissolved in saliva) being eaten:
na+ diffuse thru highly selective channel proteins in csm of microvilli of chemoreceptor cells
leads to depolarisation of chemoreceptor cell memb
increase in + charge inside cell = receptor potential
if sufficient stimulation by na+ and sufficient depolarisation of membrane, the receptor potential becomes large enough to stimulate voltage-gated calcium ion channel proteins to open
as result, calcium ions enter the cyto of chemoreceptor cell and stimulate exocytosis of vesicles containing neurotransmitters from the basal membrane of the chemoreceptor
neurotransmitter stimulates an action potential in sensory neurone
sensory neurone then transmits an impulse to the brain
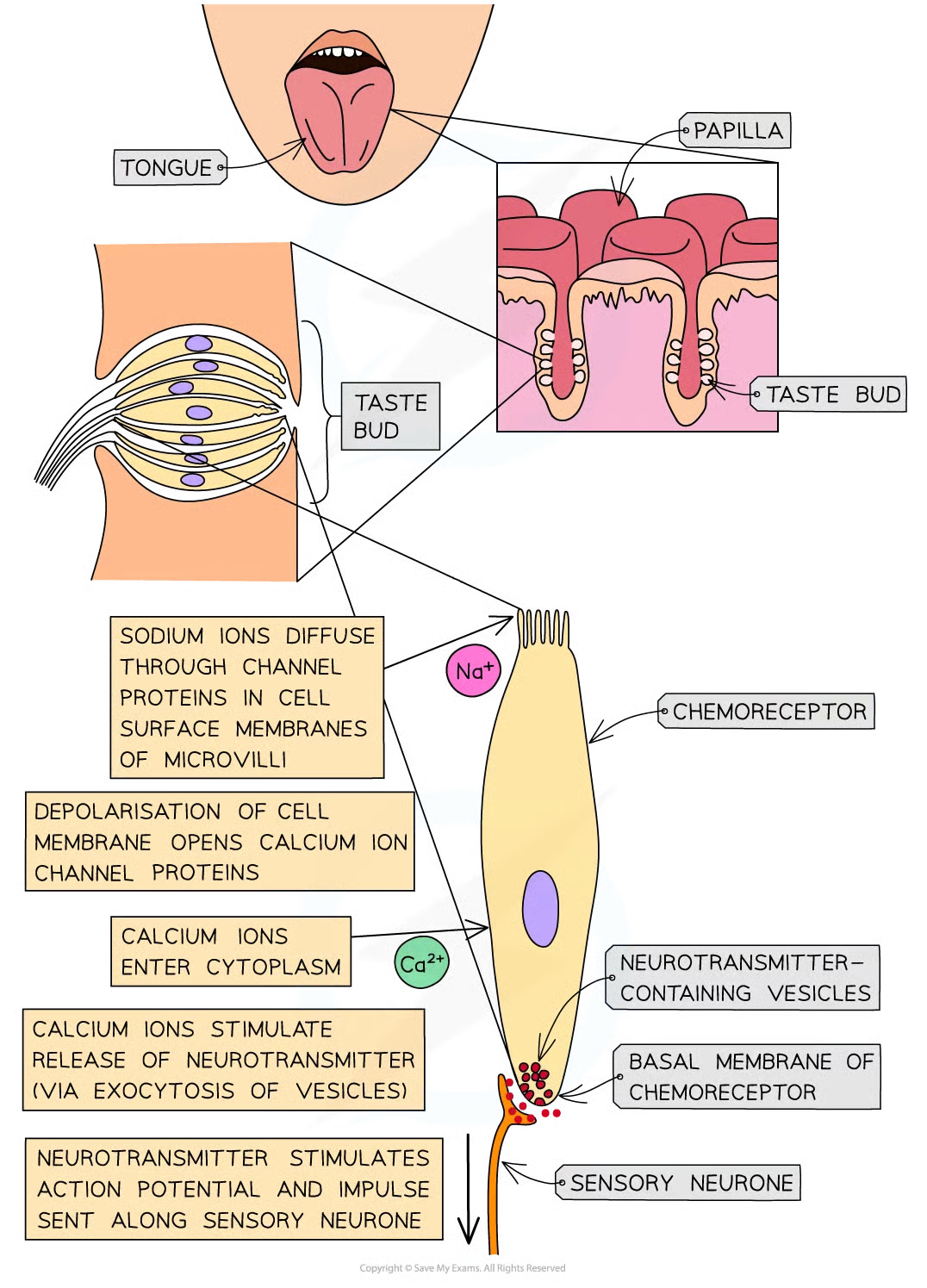
when are receptors depolarised
when they are stimulated
if stimulus is very weak/below certain threshold….
receptor cells wont be sufficiently depolarised and the sensory neurone will not be activated to send impulses
if stimulus is strong enough to increase receptor potential above the threshold potential
then receptor will stimulate sensory neurone to send impulses
all-or-nothing principle
impulse only transmitted if initial stimulus is sufficient to increase membrane potential above threshold potential

with continued stimulation….
threshold levels in receptors often increase so that a greater stimulus is required before impulses sent along sensory neurones
neurones transmit ______ which travel v quickly along __________ from ____ to _____
electrical impulses, neurone cesm, one end to other
are impulses flow of e-
no, they are known as action potentials and occur via very brief changes in distribution of electrical charge across csm.
what are actiona potentials caused by
rapid movement of na+ and potassium ions across the membrane of the axon
what happens in a resting axon (one that isnt transmitting inpulses)
the inside of axon always has slightly negative e- potential cmopared to outside
what is the potential difference
-70mV (inside of axon has electrical potential 70mV lower than outside) ← resting potential
4 factors in maintaining resting potential
sodium-potassium pumps in axon membrane
many large, neg charged mols (anions) inside axon
impermeability of axon membrane to ions
closure of voltage-gated channels (required for action potentials) in axon membrane
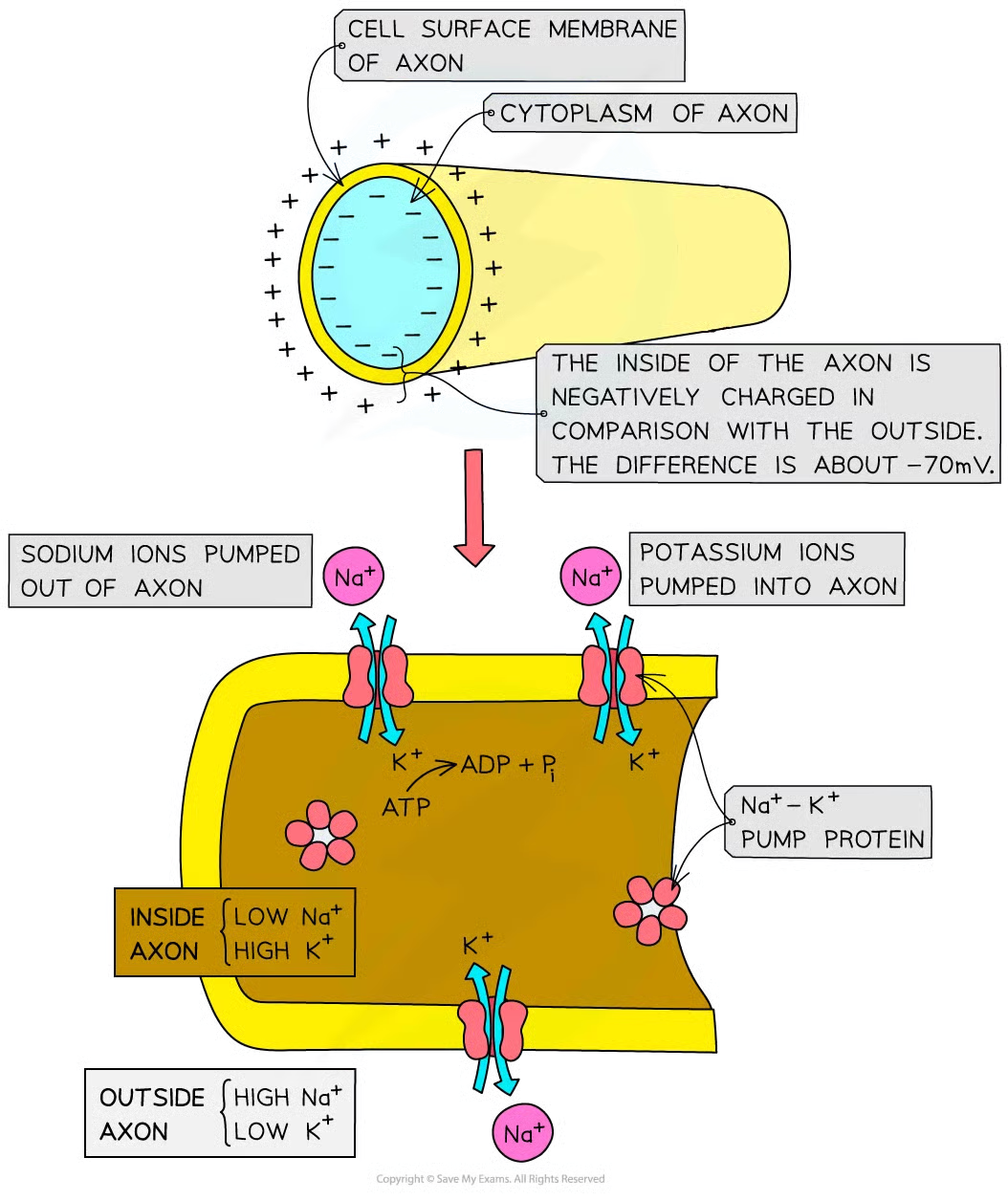
how does sodium-potassium pumps in axon membrane contribute to maintaining RP
pumps move na+ out of axon and k+ into axon
pump proteins use the energy from hydrolysis of ATP to continue moving ions against conc grads
how do many large, neg charged mols (anions) inside axon contribute to maintaining RP
attracts K+ reducing change of them diffusing out of axon
how does impermeability of axon membrane to ions contribute to RP
na+ cant diffuse through axon membrane when neurone is at rest
how does closure of voltage-gated channels (required for action potentials) in axon membrane contribute to RP
stops na and k ions diffusing through axon membrane
why are there channel proteins in axon membrane
allow na+ or k+ to pass through
what does the open and close of the channel proteins depend on
electrical potential/voltage across axon membrane and are known as voltage-gated channel proteins (closed when axon memb at RP)
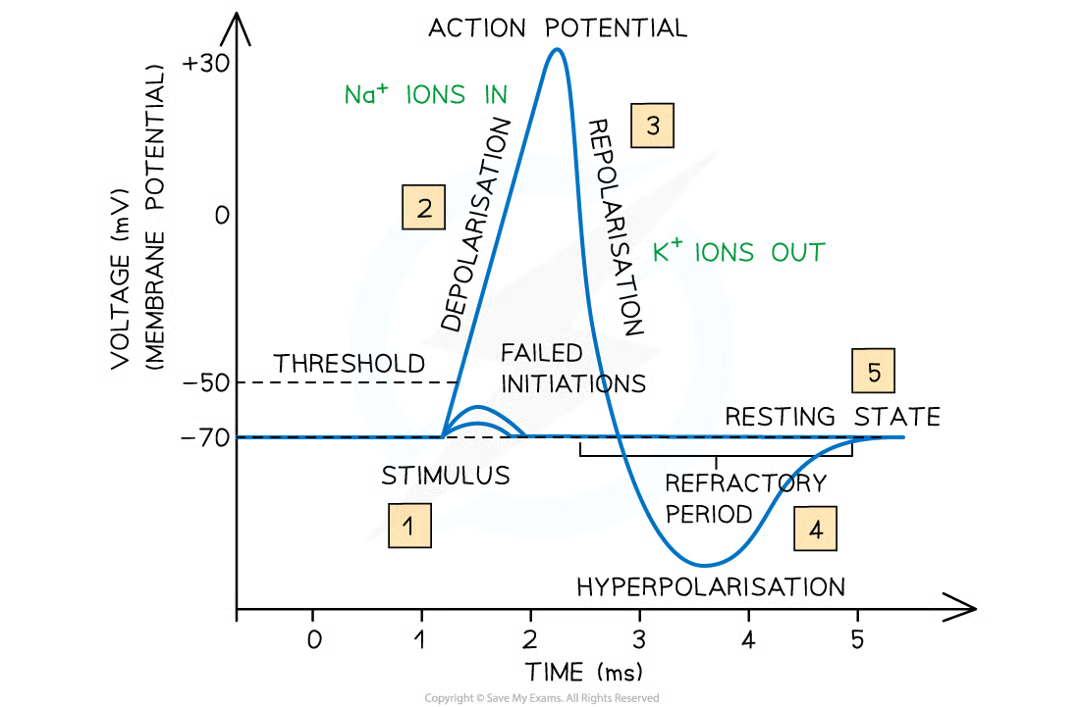
what happens when action potential is stimulated (by receptor) in neurone: 10
na channel proteins in axon membrane open
na+ pass into axon dwon electrochemical gradient (greater conc of na+ outsiide axon than inside. inside of axon neg charged attracting pos charged na+)
reduces potential diff across axon mebrane as inside becomes less negative (depolarisation)
voltage-gated na channels open, allowing more na+ to enter so more depolarisation
positive feedback (small intial depolarisation leads to greater and greater lvls of depolarisation)
if potential diff reaches around -50mV (threshold value) many more channels open and many more na+ enter causing inside of axon to reach potential fo around +30mV
action potential generated
depolarisation of memb at site of first action potential causes current to flow to next section of axon memb, depolarising it and causing na+ voltage-gated hcannel proteins to open
flow of current is caused by diffusion of na+ along axong area of high conc to area of low conc
triggers production of another action potential in section of axon membrane and process continues
allows action potentials to begin at one end of an axon and then pass along entire length of axon membrane
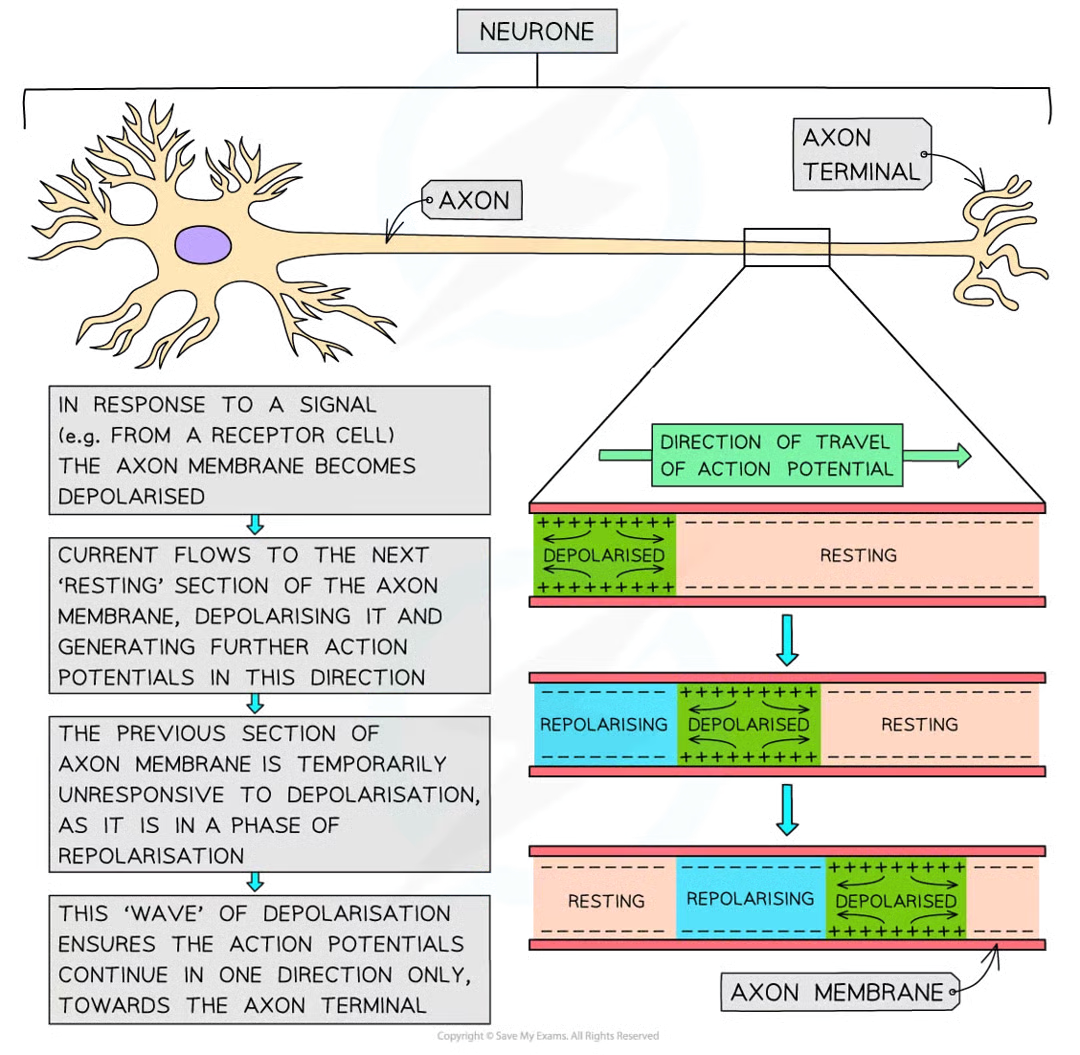
refractory period/repolarisation process 5
very shortly (1ms) after action potential in a section of axon memb is generate, all na+ voltage-gated channel proteins in section close, stopping any further na+ diffusing into axon
k+ voltage-gated channel proteins in this section of axon memb now open, allowing diffusion of k+ out of axon, down their conc grad
returns potential diff to normal (-70mv) a process known as repolarisation
actually short period of hyperpolarisation
potential diff across section of axon membrane briefly becomes more negative than the normal resting potential
once resting potential close to being re-established, k+ ion voltage-gated channel proteins close
K+ ion voltage-gated channel proteins then close and the na+ ion channel proteins in section of memb become responsive to depolarisation again
until occurs, section of the axon membrane is in a period of recovery and unresponsive
add all the drug stuff***
speed of conduction of impulse
how quickly impulse transmitted along neurone
speed of conduction of impulse 2 main factors
presence/absence of myelin (myelin sheath on axon)
diameter of axon
speed of conduction in unmyelinated neurones
very slow
how does presence of myelin increase speed at which action pots can travel along neurone: 6
axon that are surrounded by myelin sheath, depolarisation (and action potentials that this would lead to) cant occur as myelin sheath stops diffusion of na+ and k+
action potentials only occur at nodes of ranvier (small uninsulated sections of axon)
local circuits of current that trigger depolarisation in next sections of axon memb exist between nodes of ranvier
action pots jump from one node to next
saltatory conduction
impulses travel much faster (50x) than unmyelinated axon of same diametr
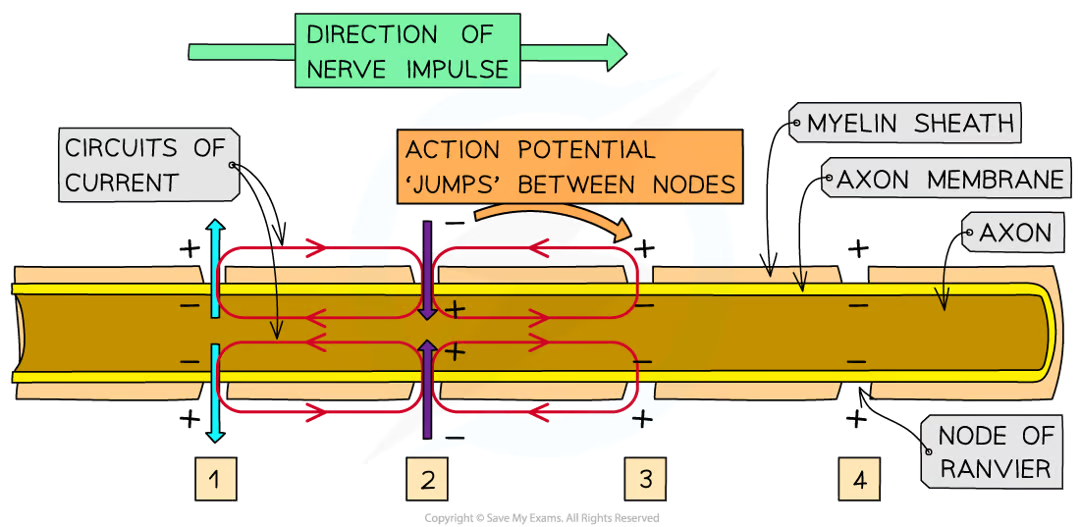
saltatory conduction
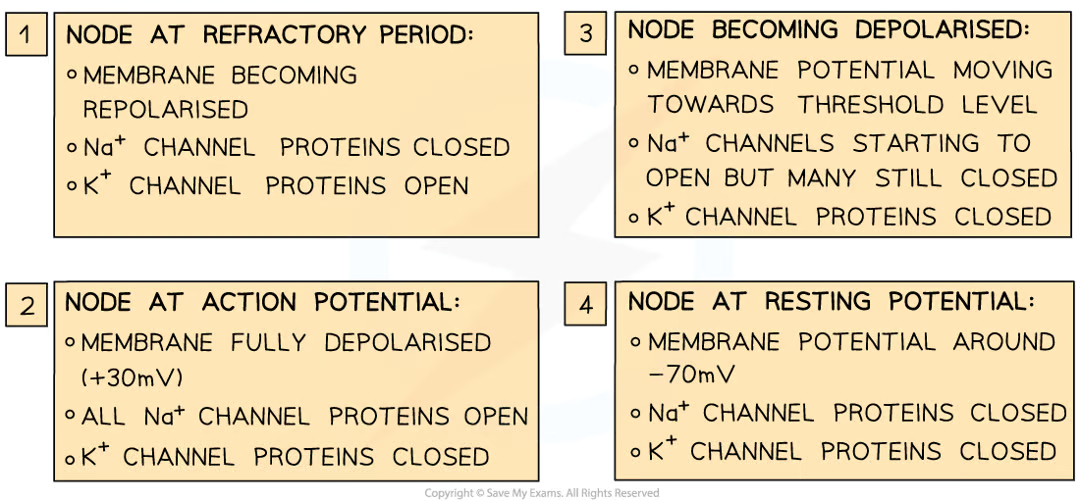
why speed of conduction of impulse along neurones with thicker axons is greater than along those with thinner ones
thicker axons have axon membrane w greater s.a. over which diffusion of ions can occur
increases rate of diffusion of na+ and k+
increases rate at which depolarisation and action potentials can occur
5 reasons why refractory period is important
ensures action potentials are discrete events, stopping them from merging into each other
ensures changes of memb potential are generated ahead (furhter along axon) rather than behind og action depolarisation as region behind is recovering from repolarisation that just occured
impulse can only travel in 1 direction, essential for successdful and efficient transmission of nerve impulses along neurone
minimum time between action potentials occuring at any one place along neurone
length of refractory period is key in determining the maximum frequency at which impulses can be transmitted along neurones between 500-1000 per second
synaptic cleft
when two neurones meet they don;t actually come in physical contact with each other and a very small gap separates them (synaptic cleft)
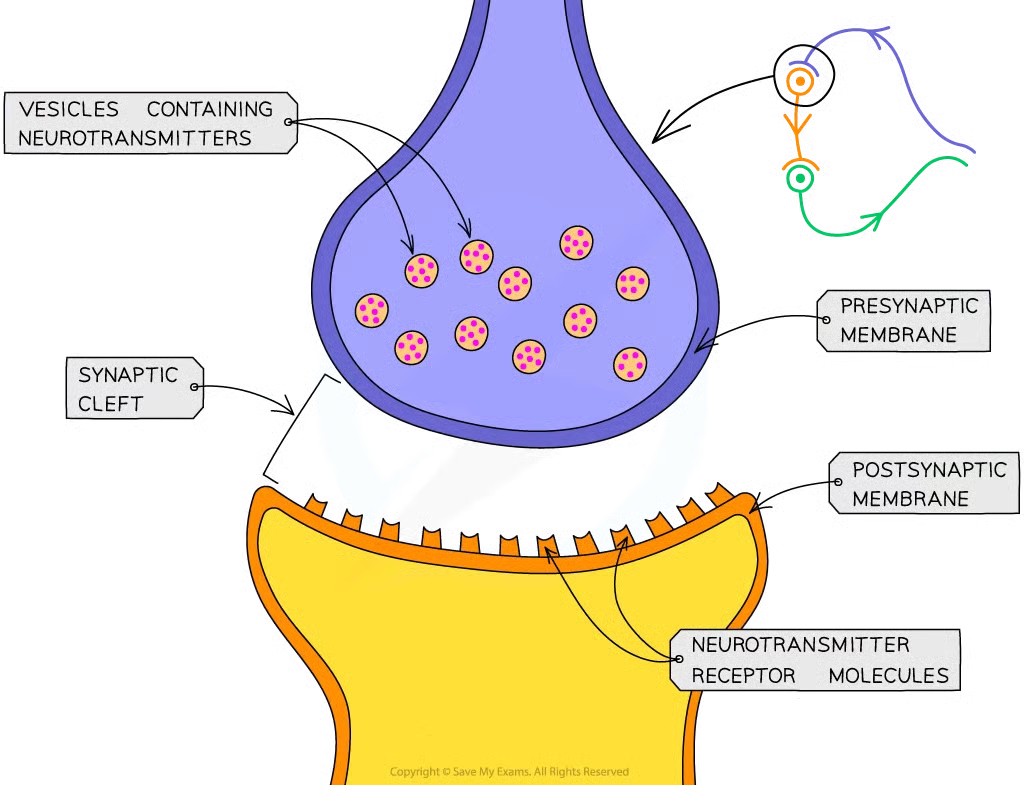
synapse
ends of 2 neurones along synaptic cleft forming synapse
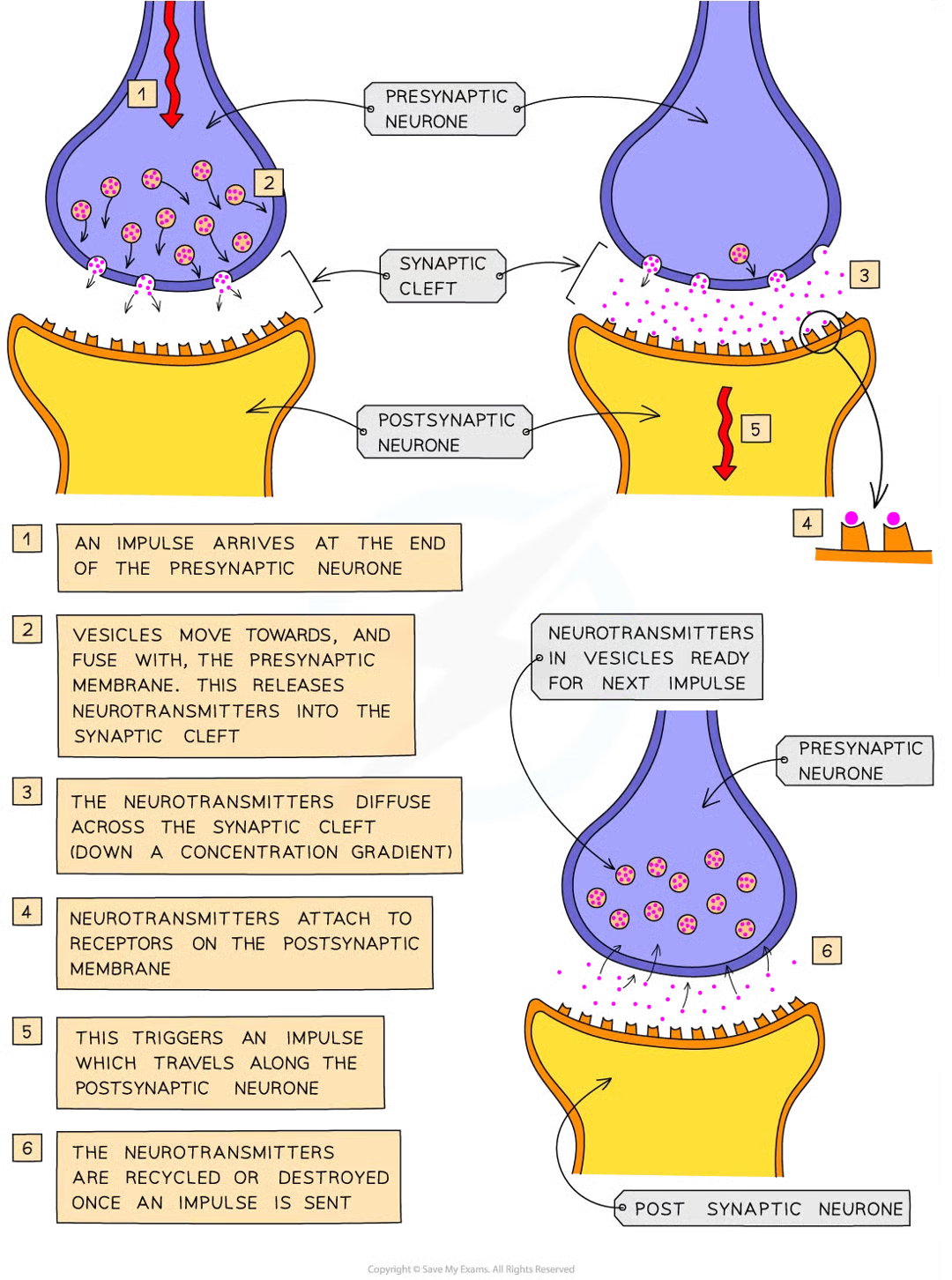
synaptic transmission - basic mechanism
electrical impulses cant jump across synapses
when elcetrical impulse arrives at end of axon on presynaptic neurone, chem messengers called neurotransmitters released from vesicles at presynaptic memb
nts diffuse across synpatic cleft and bind temporarily w receptor mols on postsynaptic membrane
stimulates postsynaptic neurone to generate elec impulse that then travels down axon to postsynaptic neurone
nts destroyed/recycled to prevent continued stimulation of 2nd neurone which cld cause repeated impulses to be sent
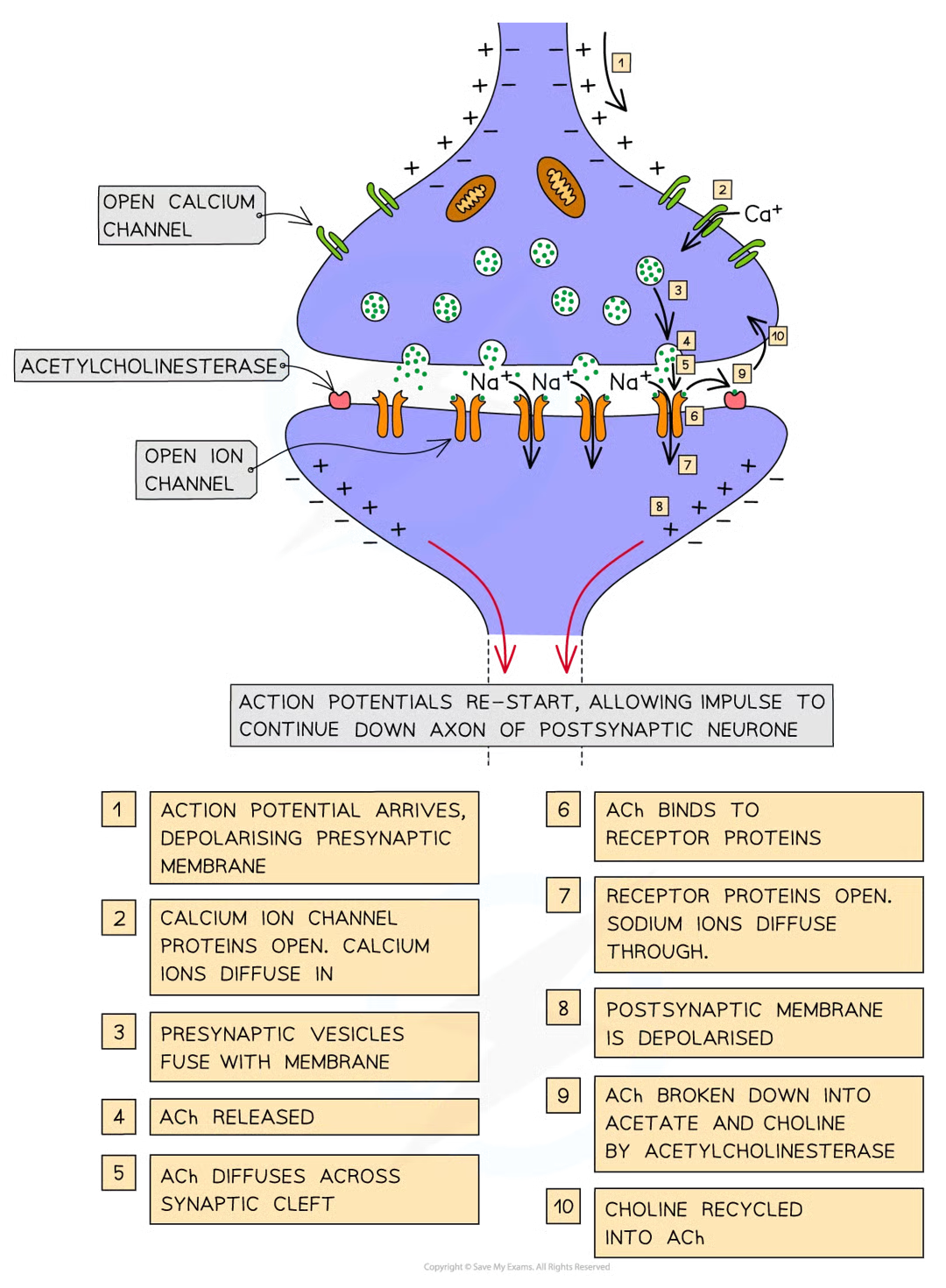
process of synaptic transmission w ACh - detailed mch
arrival of action potential at presynaptic memb causes depolarisation of memb
stimulates voltage-gated ca2+ channel proteins to open
ca2+ diffuse down elcetrochemical gradient from tissue fluid surrounding synapse (high conc of ca2+) into cytoplasm of presynaptic neurone (low conc of ca2+)
stimulates ACh containing vesicles to fuse w presynaptic memb releasing ACh mols into synaptic cleft
ACh mols diffuse across synaptic cleft and temp bind to receptor proteins in postsynaptic memb
causes conformational change in receptor proteins which open, allowing na+ to diffuse down electrochemical gradient into cyto of postsynaptic neurone
na+ cause depolarisation of postsynaptic memb, re-starting electrical impulse that can now continue down axon of postsynaptic neurone
orevent na+ channels from staying permanently open and to stop permanent depolarisation of postsynaptic memb, ACh mols broken down and recycled
enzyme acetylcholinesterase catalyses hydrolysis of ACh mols into acetate and choline
choline absorbed back into presynaptic memb and reacts w acetyl coA to form ACh and packaged into presynaptic vesicles ready to be used when another action potential arrives
how many diff nts
40+
acetylcholine
ACh, key nt used thru nervous system
cholinergic synapses
synapses that use nt ACh
when does striated muscle contract
when it receives an impulse from a motor neurone via the neuromuscular junction
why do calcium ions diffuse into the neurone
when impulse travelling along axon of motor neurone arrives at presynaptic membrqane, action potential causes this
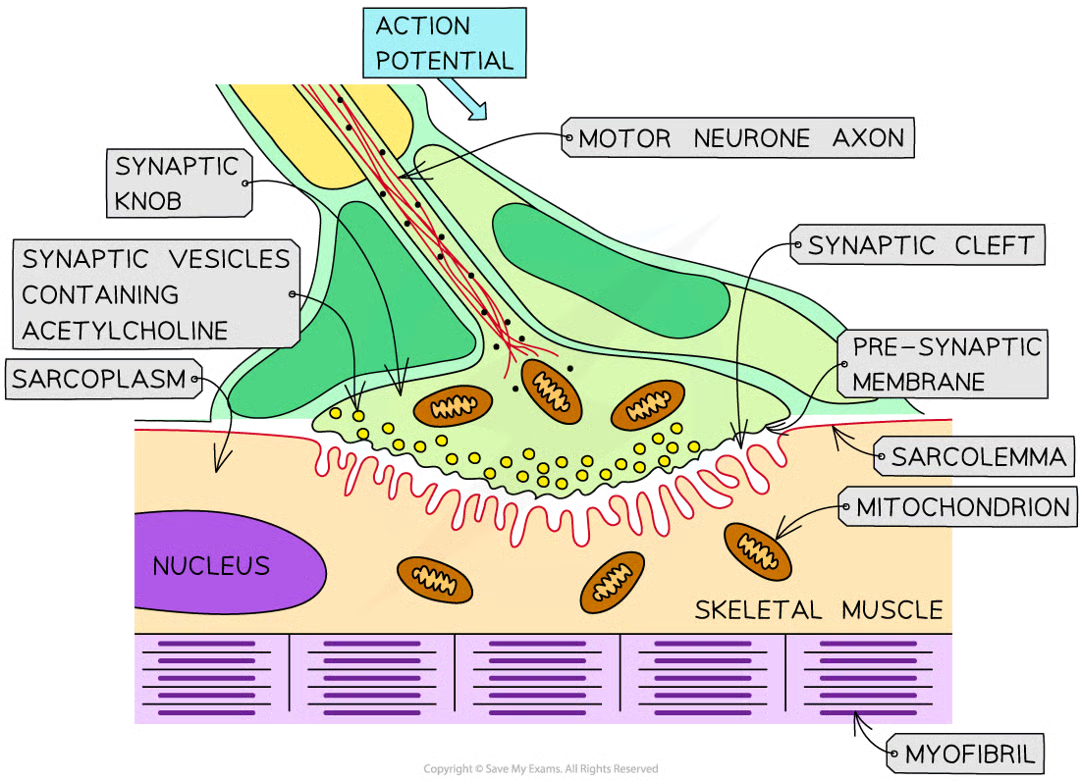
steps before muscle contraction/sliding filament model can begin
inward diffusion of ca2+ ions stimulates vesicles containing nt acetylcholine to fuse w presynaptic memb
ACh released diffuses across neuromuscular junction and binds to receptor proteins on sarcolemma (surface memb of muscle fibre cell)
stimulates ion channels in sarcolemma to open, allowing na+ to diffuse in
depolarises sarcolemma generating action potential that passes down t-tubules towards centre of muscle fibre
action potentials cause voltaged-gated ca2+ ion channel proteins in membs of sarcoplasmic reticulum (whcih lie v close to t tubules) to open
ca2+ ions diffuse out of sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) and into sarcoplasm surrounding myofibrils
ca2+ ions bind to troponin mols stimulating them to change shape
causes troponin and tropomyosin proteins to change position on thin (actin) filaments
myosin binding sites exposed to actin mols
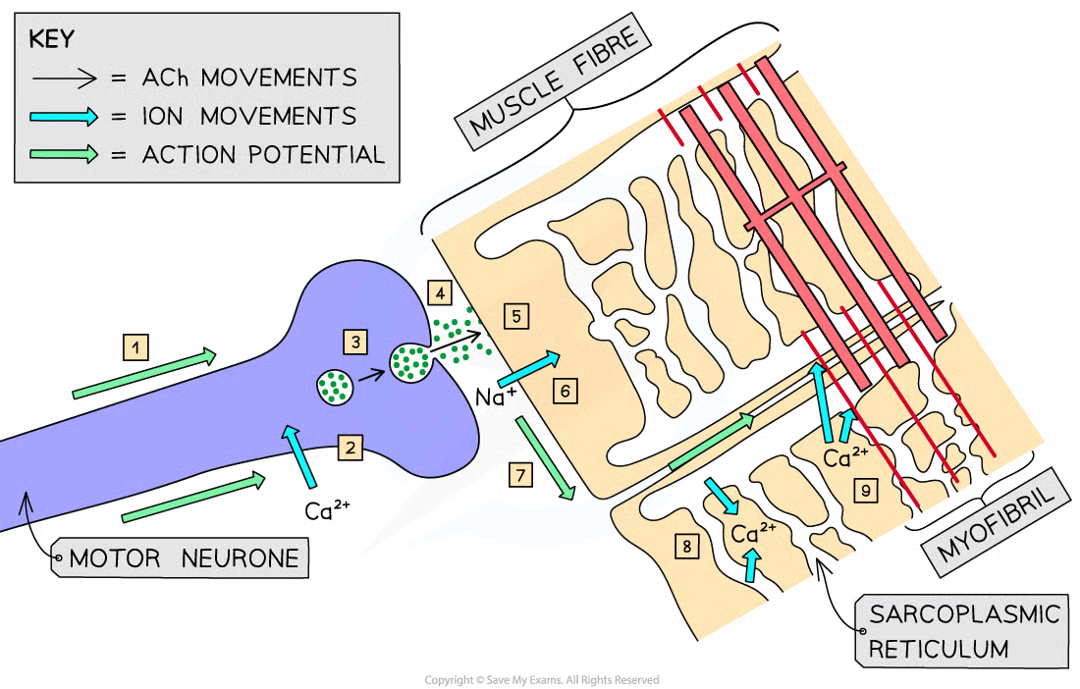
how myofibrrils within muscle fibres stimulated to contract
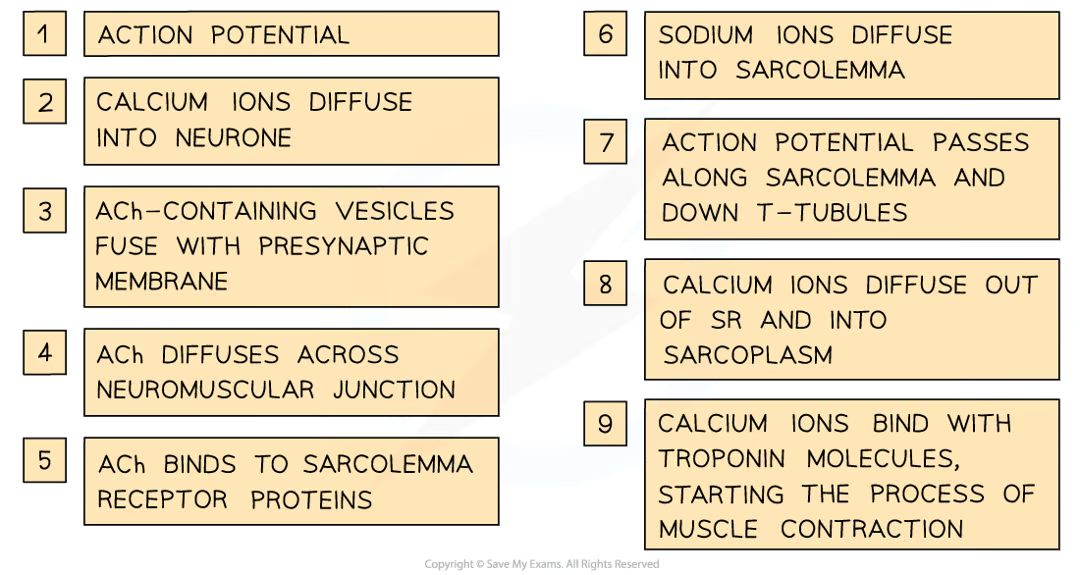
striated muscle
makes up muscles in body attached to skeleton (striated=striped/streaky) made of muscle fibres
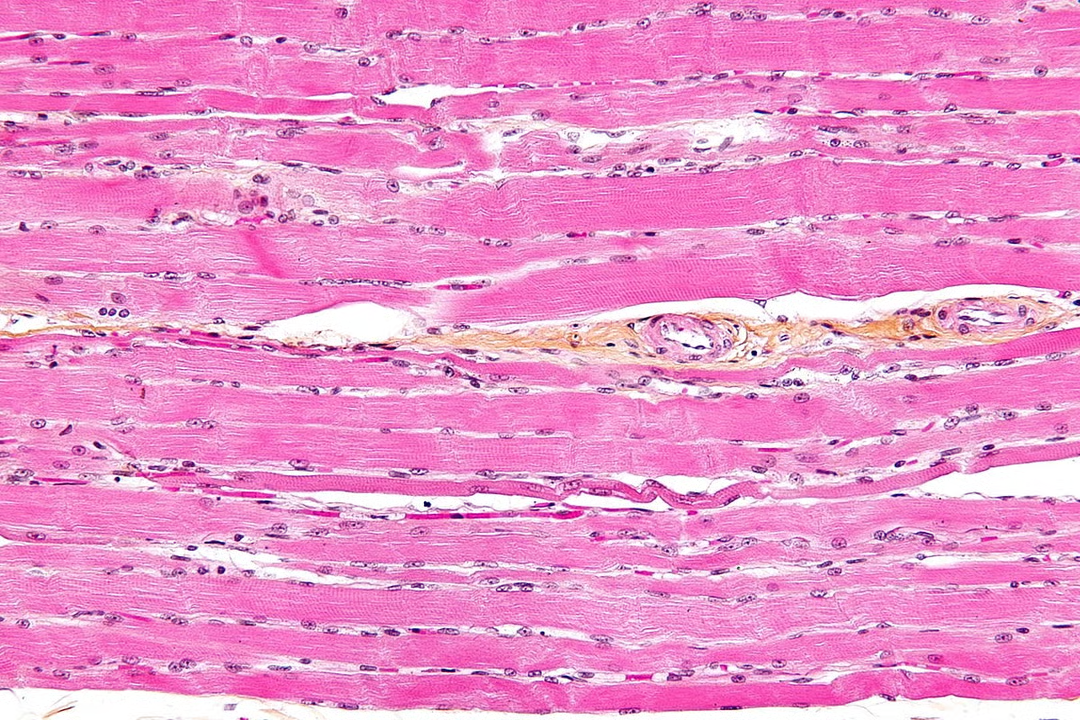
3 muscle fibre features that make it a highly specialised cell like unit
each contains an organised arragnement of contractile proteins in cytoplasm
each surrounded by csm
each contains many nuclei which is why nto usually referred to as cedlls
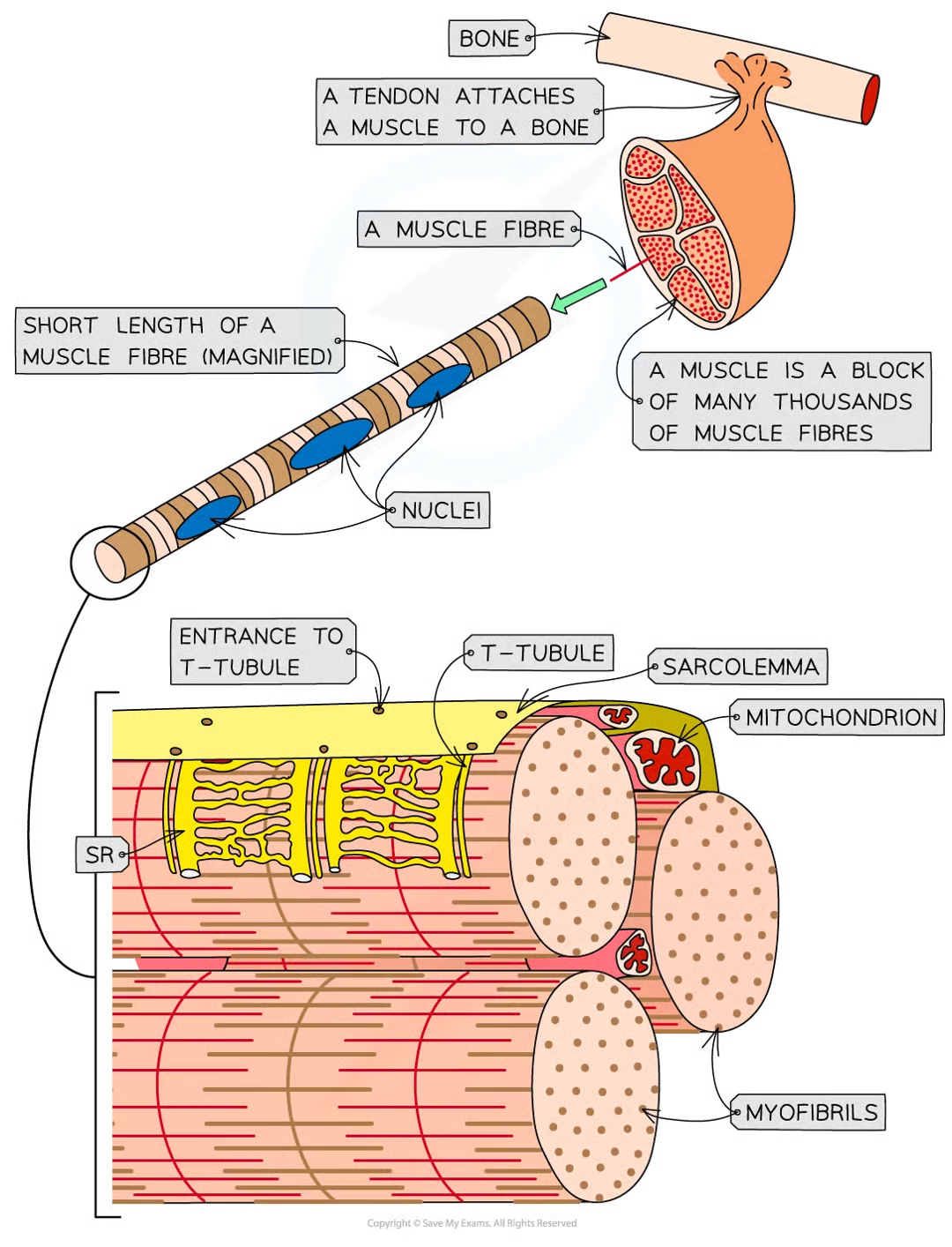
diff parts of muscle fibres w diff names to equivalent parts
csm = sarcolemma
cyto = sarcoplasm
what does sarcoplasm contain and why
mitoch for carrying out aerobic resp to generate atp required for muscle contraction
myofibrils (bundles of actin and myosin filaments) which slide past each other during muscle contraction
myofibrils: qhere, what, how
located in sarcoplasm
made up of 2 types of protein filament:
thick made of myosin
thin made of actin
arranged in particular order creating diff types of band and line
6 parts of myofibril + description
h band - only thick myosin fils present
i band - only thin actin fils present
a band - contain areas where only myosin fils are present and areas where myosin and actin fils overlap
m line - attachment for myosin fils
z line - attachment for actin fils
sarcomere - section of myofibril between 2 z lines
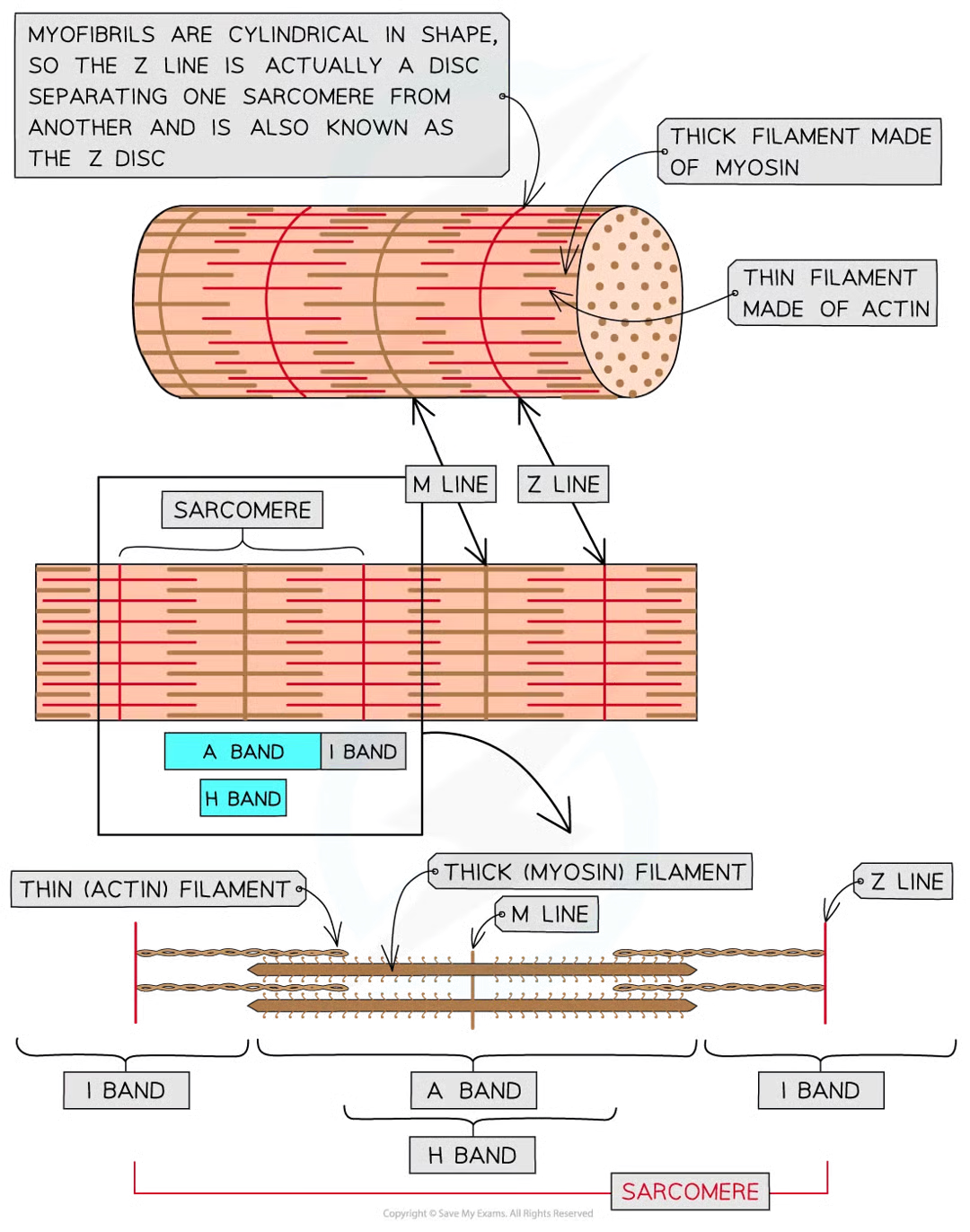
3 features of thick filaments (made of myosin mols)
fibrous protein mols w globular head
fibrous part of mysoin mols anchors mol into thick filament
in thick filament many myosin mols like next to each other with their globular heads all pointing away from the M line
5 features of thin filaments (made of actin mols)
globular protein mols
many actin mols link tg to form chain
2 actin chains twist tg to form 1 thin filament
fibrous protein (tropomyosin) twisted around 2w actin chains
another protein known as troponin is attached to actin chains at regular intervals
how does sliding filament model of muscle coontraction occur -detailed:
action potential arrives at neuromuscular junction
ca2+ released from sarcoplasmic rfeticulum
ca2+ bind to troponin mols stimulating shape change
troponin and tropomyosin proteins change position on actin (thin) filaments
myosin binding sites exposed on actin mols
glob heads of myosin mols bind with these sites, forming cross-bridges between 2 types of filament
myosin heads move and pull the actin filaments towards the centre of the sarcomere causing the muscle to contract a very small distance
atp hydrolysis occurs at myosin heads, providing energyt required for myosin heads to release actin filaments
myosin heads move back to og positions and bind tfo new binding sites on actin fils closer to z disc
myosin heads move again pulling actin fils even closer to centre of sarcomere causing it to shorten once more and pulling z discs closer together
myosin heads hydrolyse atp once more to detach again
as long as troponin and tropomysoin not blocking myosin-binding sites and muscle has a supply of atp process repeats until muscle fully contracted
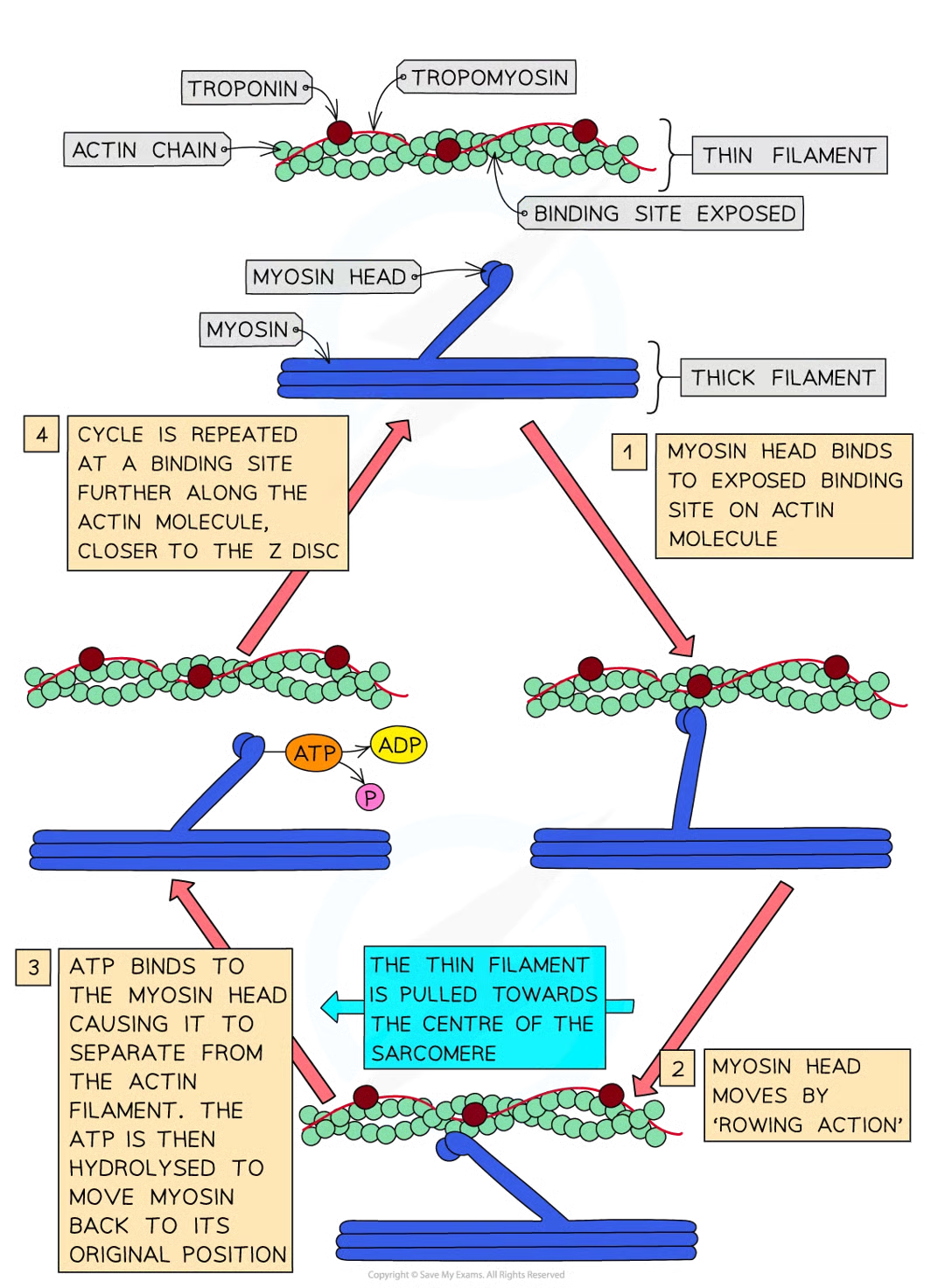
what happens during muscle contraction
sarcomeres within myofibrils shnorten as the z discs are pulled closer together
venus flytrap
carnivorous plant that can gain nitrogen compounds by trappind and digesting small animals, mainly insects.
structure of venus flytrap
the specialised leaf divided into two lobes on either side of midrib
inside of lobes is red and has nectar secreting glands on edges to attract insects
each llobe has 3 stiff sensory hairs that detech gtouch
if insect touchnes one hair action potential generated which causes 2 lobes to fold along midrib capturing insect
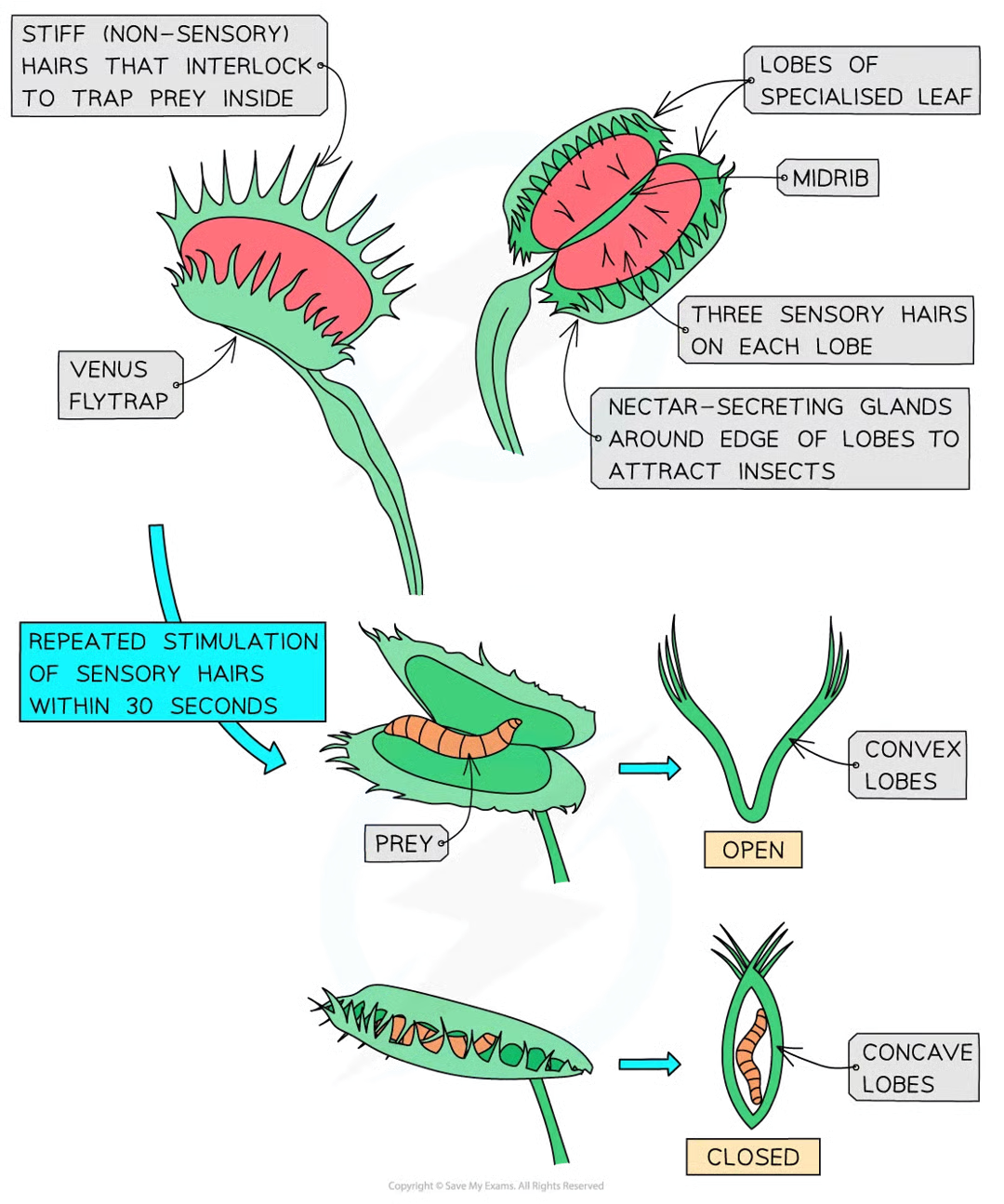
how is the closure of the trap achieved
when sensory hairs are touched repeatedly, generating an action potential as follows:
insect lands on leaf and touches sensory hairs
ca2+ ion channels in cells at base of hair open
ca2+ flows in and generates receptor potential
if 2 of the sensory hairs are stimulated at the same time or one hair twice within 30s an action potential occurs and is propagated across cells of trap (if no repeat stim then trap resets to beginning so plant doesnt waste energy if insect not present)
cells at base of trap change shape and trap closes (sealing requires ongoing activation of sensory hairs which happen when prey continue to move inside closed trap)
further stim causes ca2+ to enter gland cells where they stimulate exocytosis of vesicles containing digestive enzymes
trap stays closed for up to week so prey is digested and nutrients absorbed
receptor potential
change in membrane potential that occurs in a receptor cell due to an initial stimulation; if this reaches a threshold then it can result in an action potential
plant hormones/plant growth regulators
responsible for most communication within plangts
auxin
type of plant growth regulator that influences many aspects of growth including elongation growth which determines the overall length of roots and shoots
principle chemical in group of auxins made by plants
IAA (indole 3-acetic acid) → auxin
when is IAA synthesized
growing tips of roots and shoots (i.e. in meristems where cells divide)
3 stages where growth in meristems occur:
cell divisions by mitosis
cell elongation by absorption of water
cell differentiation
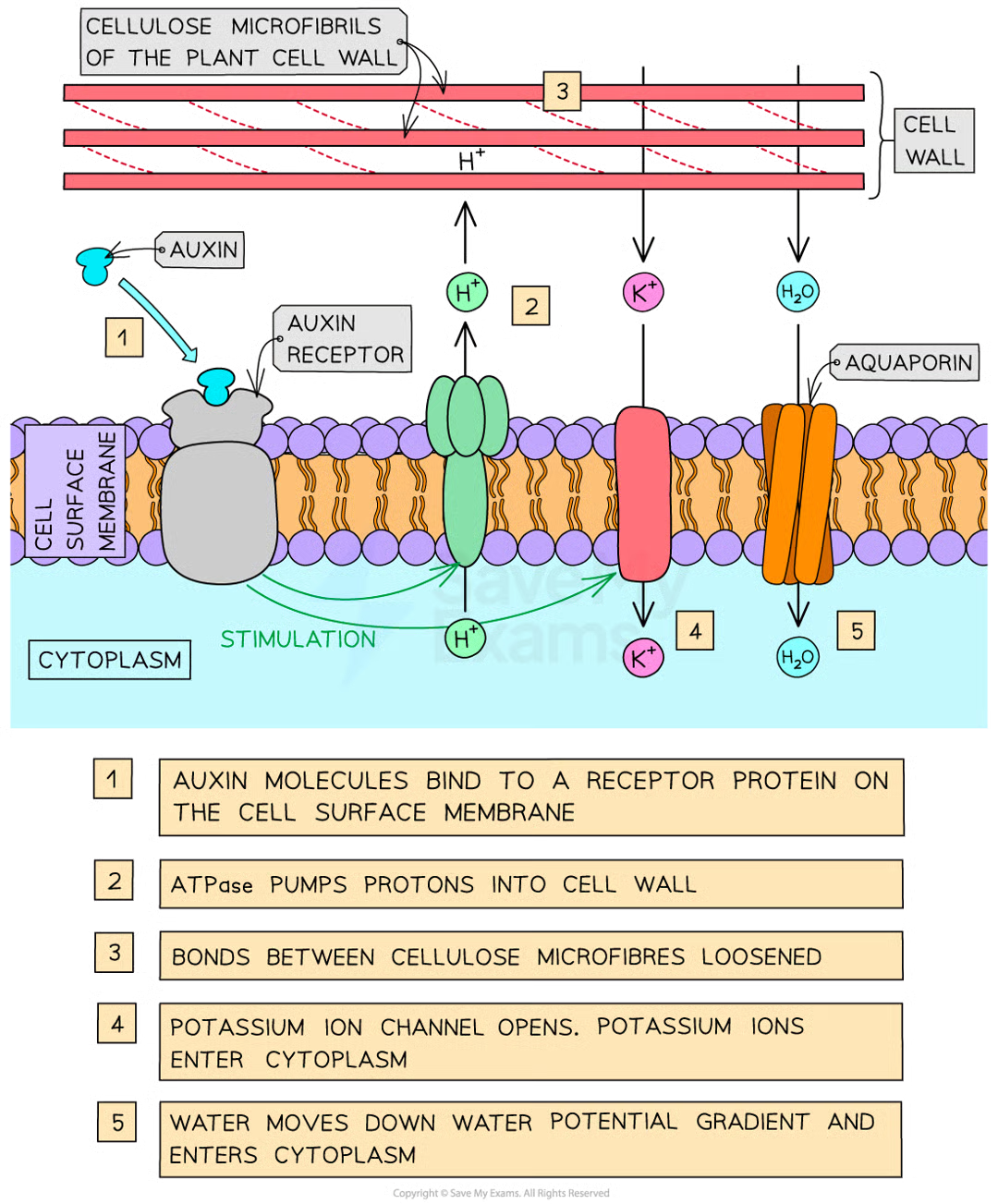
iaa controls growth by elongation
how is growth controlled by elongation
auxin molecule bind to receptor protein on csm
auxin stimulates atpase proton pumps to pump h+ from cyto to cell wall across csm
acidifies cell wall (lowers pH)
activates proteins (expansins) which loosen bonds between cellulose microfibs
at same time k+ channels stims to open
this leads to increase in k+ conc in cyto which decreases wp of cyto
cell absorbs water by osmosis (water enters thru aquaporins)
increased internal pressure of cell, causing cell wall to stretch (possible bc expansin)
cell elongates
gibberellins
type of plant growth regulator involved in controlling seed germination and stem elongation.
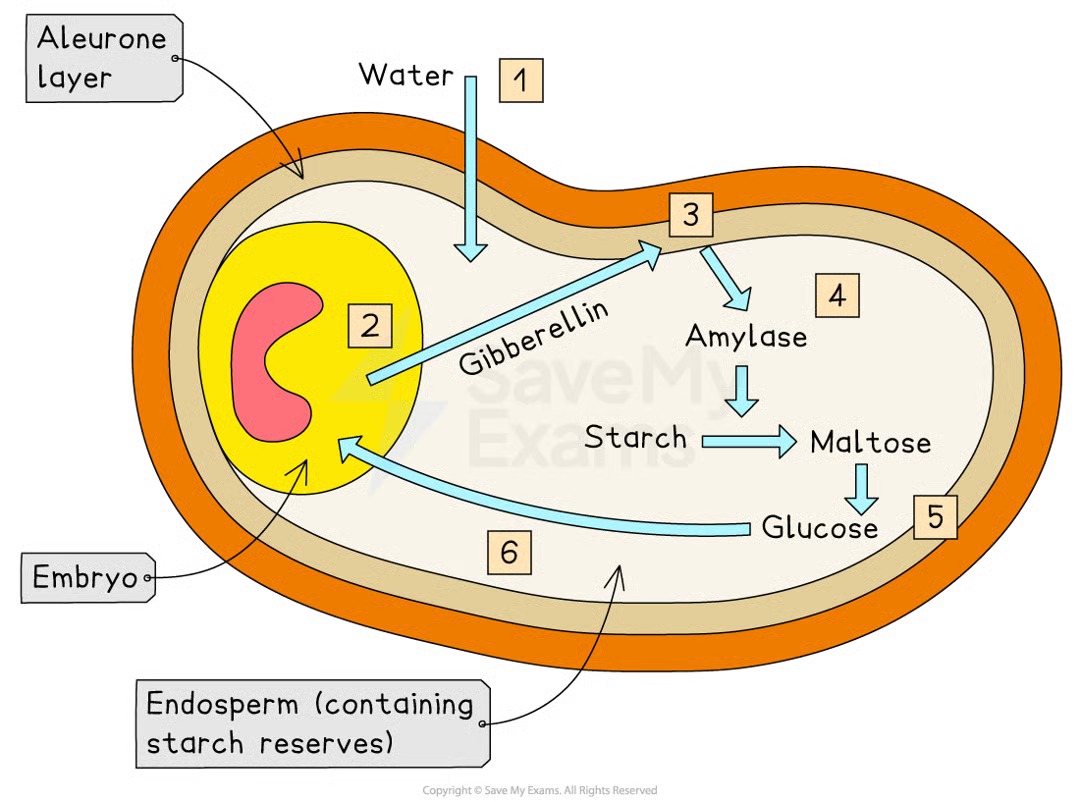
what state is barley seed in when shed fcrom parent plant
dormancy (contains very little water and is metabolically inactive) so can survive harsh conditions until theyre right for successful germination (e.g. cold winter→ spring)
what 3 things do barley seed contains:
embryo - grow into new plant when seed germinates
endosperm - starch-containing energy store surrounding embryo
aleurone layer - protein-rich layer on the outer edge of endosperm
what happens to barley seeds when conditions are right
barley seed starts to absorb water to begin germination
this stims embryo to produce gibberellins
gibberellin mols diffuse into aleurone layer and stim cells there to synth enzyme amylase
in barley seeds, it has been shown that gibberellin does this by regulating genes involved in synthesis of amylase causing increase in transcription of mRNA coding for amylase
amylase hydrolyses starch mols in endosperm, producing soluble maltose mols
maltose converted to glucose and transported to embryo
glucose can be respired by embryo, providing embryo w energy needed for it to grow
gibberellin stimulation
