CSCC BIO 2301 PRST Review
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Reasoning outcomes: Diffusion and Osmosis
Given a description of a change in the distribution of solutes within the body, the student will correctly predict the concenquent change in the flow of solutes in water
Reasoning outcomes: Synaptic Comminication
The student will recognize the interactions between natural neurotransmitter agonist, antagonist, reuptake inhibitors, synaptic enzyme inhibitors on the postsynaptic cell membrane
Reasoning outcomes: Data Interpretation
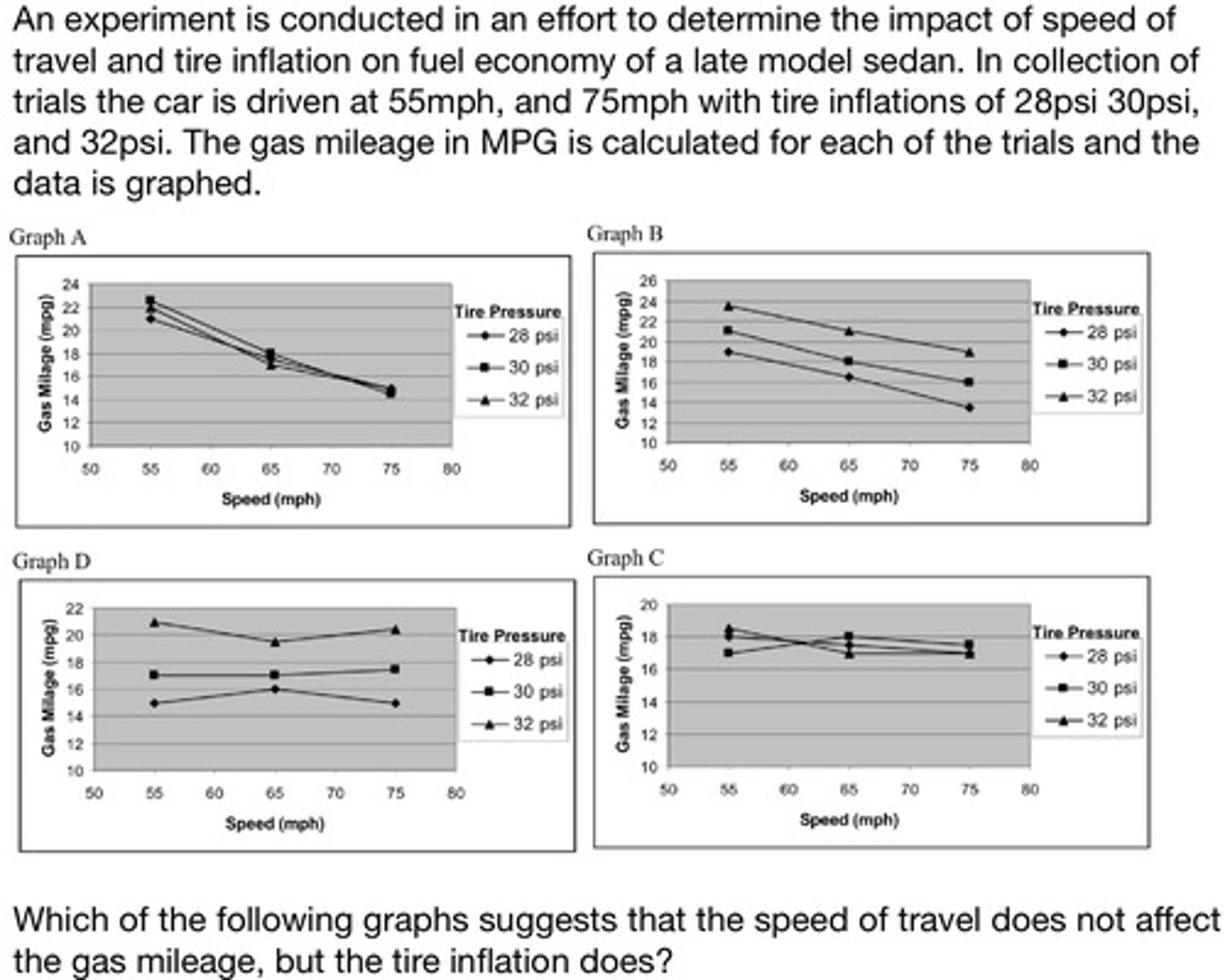
Examining data presented in graph form, the student will recognize the presence or absence of correlation between a parameter graphed along the X axis and a parameter graphed along the Y axis, as well as a parameter that changes between lines defined in a legend box and a parameter graphed along the Y axis
Reasoning outcomes: Consensual Reflexes
Given a description of the affarent and efferent components of a consensual reflex, and the results of a clinical examination of the reflex, the student will interpret the signs and draw reasonable conclusions regarding the status of the components of the reflex mechanism
Reasoning outcomes: Motor Function
Based upon signs surrounding clinical evaluation of a patients ability to maintain balance including a Rhomberg test and associated analysis, the student will draw a conclusion regarding the state of the patients cerebellar, vestibular, and proprioceptive function
Reasoning outcomes: Endocrine Feedback and Homeostasis
Given a description of the relationships between hormones within an endocrine system and the influence of this system on physiologic parameters, the student will use this information and an understanding of the principles of homeostasis to predict how a disturbance in the endocrine system will affect the secretion of associated hormones and physiologic parameters.
Reasoning outcomes: Blood Pressure Homeostasis
Given a description of the relationship between cardiovascular variables and blood pressure, the student will use this information and knowledge of the principles of homeostasis to predict how a disturbance in the blood pressure or one of these variables will affect the other elements of the system
Reasoning outcomes: Blood Gas and pH Homeostasis
Given a description of the relationships between ventilation, blood gas levels, and blood pH, the student will use this information and knowledge of the principles of homeostasis to predict how a disturbance in one of these variables will affect the others in the system
Reasoning outcomes: Fluid and Electrolyte Homeostasis
Given a description of the factors that influence the secretion of the major fluid and electrolyte associated hormones, and the effects of those hormones, the student will use this information and an understanding of the principles of homeostasis to predict how the secretion of these hormones will change, and how fluid and electrolyte levels will change after a specific disturbance in fluid and electrolyte balance
Diffusion
Movement of solutes, penetrating solutes only or movement without membrane
Osmosis
Movement of water since solutes are nonpenitrating, membrane involves
Osmolarity
Defined as total solute concentration of solution
Tonicity
Refers to the concentration of non penetrating solutes within a solution and the affect that has on the cell membrane
Consensual reflexes
In consensual reflexes, a unilateral stimulus produces a bilateral response
Agonists
Drugs that mimic actual neurotransmitters. They bind to the receptor for that neurotransmitter and activate the receptor just like the neurotransmitter would have
Antagonist
Drugs that bind to the neurotransmitter receptor but they do not activate the receptor, but in fact block it preventing the real neurotransmitter from acting on that receptor
Reuptake inhibitors
Drugs that may block the reuptake of neurotransmitter back into the axon terminal leading to a buildup of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft. This leads to an increase in the number of action potentials being generated by the postsynaptic neuron
Synaptic enzyme inhibitors
Drugs that block the enzymes that are supposed to destroy excess neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft. This leads to excess neurotransmitter in the cleft and too many action potentials will be generated
Rhomberg test
Remember the cerebellum keeps the body balanced and motor activities on course by monitoring sensory feedback. Cerebellum can maintain balance with 2 out of 3 senses, but not with just one and this is the basis for the Rhomberg test.
If swaying with eyes open, it's probably a cerebellum problem
Positive Rhomberg sign suggests a problem with either vestibular or proprioceptive
Respiratory acidosis
Result of abnormal CO2 retention from hypoventilation.
In respiratory acidosis there is an elevation in arterial PCO2, H+, and HCO3- levels
Respiratory Alkalosis
Excessive loss of CO2 from the body as a result of hyperventilation.
In respiratory alkalosis there is a decrease in PCO2 levels, H+ levels, and HCO3- levels
Know ROME

Metabolic Alkalosis
Increased pH
RR will decrease
CO2 will increase
Metabolic Acidosis
Decreased pH
RR will increase
CO2 will decrease
To lower plasma osmolarity:
Increase ADH
Decrease Renin and Aldosterone
To increase plasma osmolarity:
Increase Renin and Aldosterone
Decrease ADH
To increase fluid volume/blood pressure:
Increase ADH, Renin, Aldosterone
To decrease fluid volume/blood pressure:
Decrease ADH, Renin, Aldosterone
What is suggested by the following pattern of pupillary light response? Light shined in the left eye causes only the left pupil to constrict. Light shined in the right eye causes only the left pupil to constrict.
Damage to cranial nerve III on the right side
Which of the following would be useful if an individual was unable to produce a particular neurotransmitter?
A muscarinic agonist
Which of the following would decrease the stimulation of the postsynaptic cell by neurotransmitter?
A nicotinic antagonist
A hypothetical drug is administered which constructs blood vessels in the periphery (increasing resistance) without directly affecting other tissues. Which of the following will occur as a concequence of administering this drug?
An increase in blood pressure and a decrease in cardiac output
Which of the following would occur after an injection of TSH?
Increased Thyroid Hormone secretion and decreases TRH secretion
Dehydration will result in which of the following?
Increased ADH and decreased ANF secretion
Increased blood osmolarity will result in which of the following?
Increased ADH and decreased Aldosterone secretion
An individual displays a resting tremor. Which of the following motor deficits consistent with this sign?
Basal ganglion lesion
An individual with a positive Rhomberg sign can detect the position of his limbs in space. Which of the following motor deficits is consistent with these signs?
Vestibular deficit
The ascending loop of Henle traverses the renal medulla in close proximity to one another. Water is reabsorbed from the descending limb. Sodium is reabsorbed by active transport from the ascending limb.
How would a decrease in the reabsorbtion of sodium along the ascending limb affect the reabsorbtion of water along the descending limb?
The decreased osmotic gradient would cause a decrease in water absorption
Which of the following categories of drugs would be useful if an individual was suffering from an inadequate secretion of a particular neurotransmitter? Agonist, Antagonist, Synaptic enzyme inhibitor, Reuptake inhibitor
Agonist, Synaptic enzyme inhibitor, reuptake inhibitor
Which of the following would be useful if an individual was completely incapable of producing a particular neurotransmitter?
Agonist
Understand the pupillary light reflex
The pupillary reflex is a consensual reflex in which light entering either eye will cause both pupils to constrict. The sensory information travels to the brain via CN II while the motor signals which constrict the pupil travel along CN III
Consider the following relationships in electrolyte homeostasis: 1) increased osmolarity stimulates ADH secretion and inhibits aldosterone secretion. 2) ADH causes water retention (which leads to decreased osmolarity). 3) aldosterone causes sodium retention, potassium excretion, and leads to increased osmolarity. 4) low blood pressure causes both ADH and aldosterone secretion.
How will ADH secretion, aldosterone secretion, urine sodium levels and blood potassium levels change if one consumes a meal with excess sodium?
Increased ADH secretion, decreased aldosterone secretion, increased urine sodium, increased blood potassium (with the body excreting the extra sodium, it would retain more potassium)
Consider the following relationships in electrolyte homeostasis: 1) increased osmolarity stimulates ADH secretion and inhibits aldosterone secretion. 2) ADH causes water retention (which leads to decreased osmolarity). 3) aldosterone causes sodium retention, potassium excretion, and leads to increased osmolarity. 4) low blood pressure causes both ADH and aldosterone secretion.
How will ADH secretion, blood sodium levels and blood potassium levels change if one develops an adrenal tumor that secretes an excess of aldosterone?
Increased ADH secretion, increased blood sodium, decreased blood potassium
Consider the following endocrine relationships:
TRH stimulates TSH secretion
TSH stimulates thyroid hormone secretion
Thyroid hormone secretion inhibits TRH and TSH secretion
Thyroid hormones increase metabolic rate which produces heat
TRH also stimulayes PRL secretion
Sweating helps the body reduce temperature
How would the secretion of TRH, TSH, and prolactin change after an injection of thyroid hormones. Would this injection be likely to increase or decrease sweating?
Decreased TRH, TSH, and PRL due to negative feedback; increased sweating to compensate for the excessive heat production due to increased metabolic rate
Consider the following endocrine relationships:
TRH stimulates TSH secretion
TSH stimulates thyroid hormone secretion
Thyroid hormone secretion inhibits TRH and TSH secretion
Thyroid hormones increase metabolic rate which produces heat
TRH also stimulayes PRL secretion
Sweating helps the body reduce temperature
If the pituitary could not make TSH, how would this change TRH, Thyroid hormone, and PRL secretion? Would this be likely to increase or decrease sweating?
Decreased thyroid hormone secretion, increased TRH secretion, increased PRL secretion; decreased sweating due to diminished heat production due to low metabolic rate
Blood pressure is proportionate to cardiac output and resistance. Consider the homeostatic responses to the following challenges.
How will blood pressure and resistance change after the administration of a drug that specifically reduces cardiac output?
Decreased blood pressure, increased resistance
Blood pressure is proportionate to cardiac output and resistance. Consider the homeostatic responses to the following challenges.
How will cardiac output and resistance change if an individual lies down causing an increase in blood pressure at the carotid and aoritic baroreceptors?
Decreased cardiac output, decreased resistance
Low blood pH, high carbon dioxide, and low oxygen will all increase ventilation. Increasing blood carbon dioxide will decrease pH. All of these relationships are reversible.
How will ventilation, carbon dioxide, and oxygen change if an excessive vomiting of stomach acid leads to an increase in blood pH?
Decreased ventilation, incrwsed blood carbon dioxide, decreased oxygen
Low blood pH, high carbon dioxide, and low oxygen will all increase ventilation. Increasing blood carbon dioxide will decrease pH. All of these relationships are reversible.
Barbiturates suppress ventilation, how will carbon dioxide, oxygen and pH levels change?
Increased carbon dioxide, decreased oxygen, decreased pH
Graph C
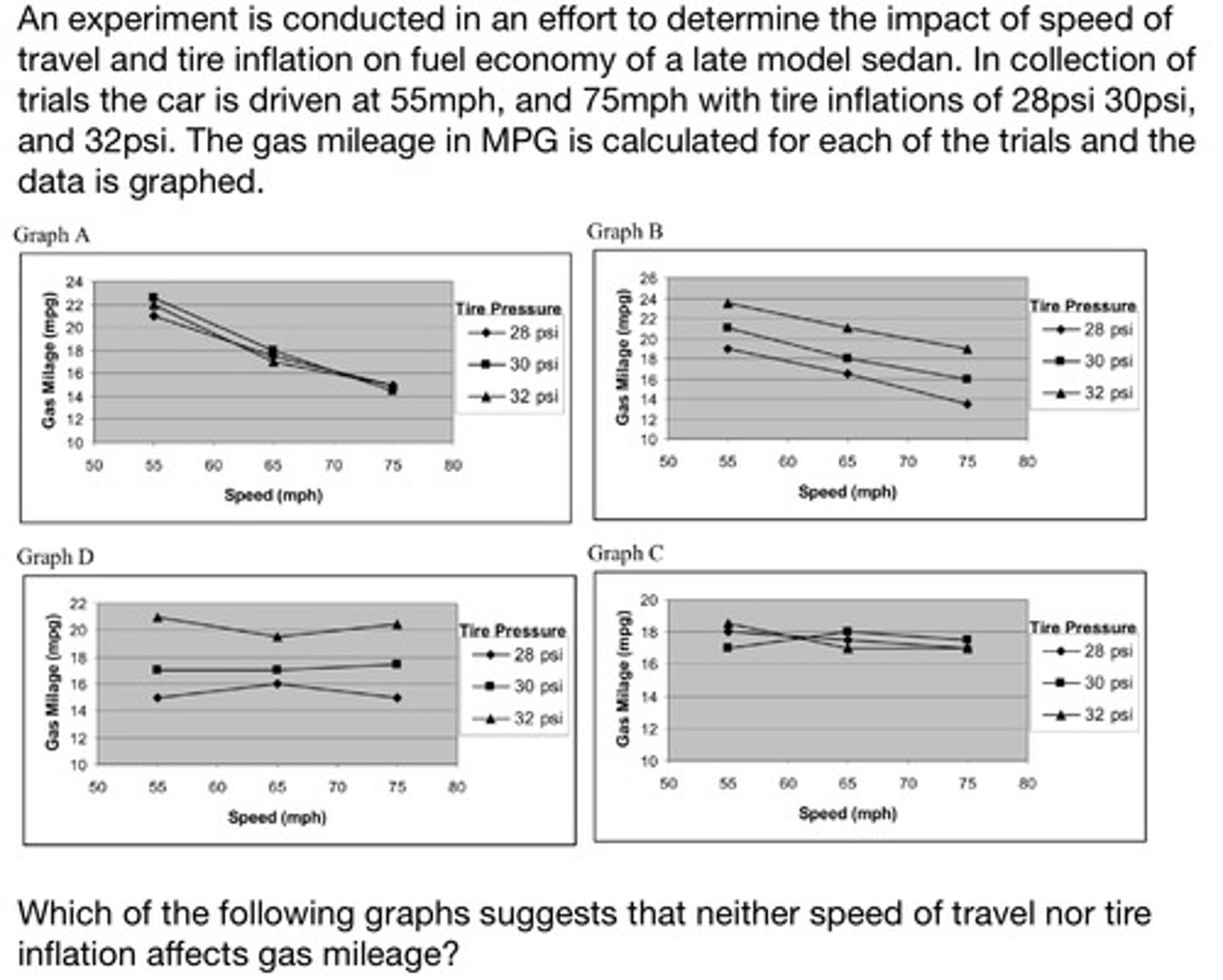
Graph B
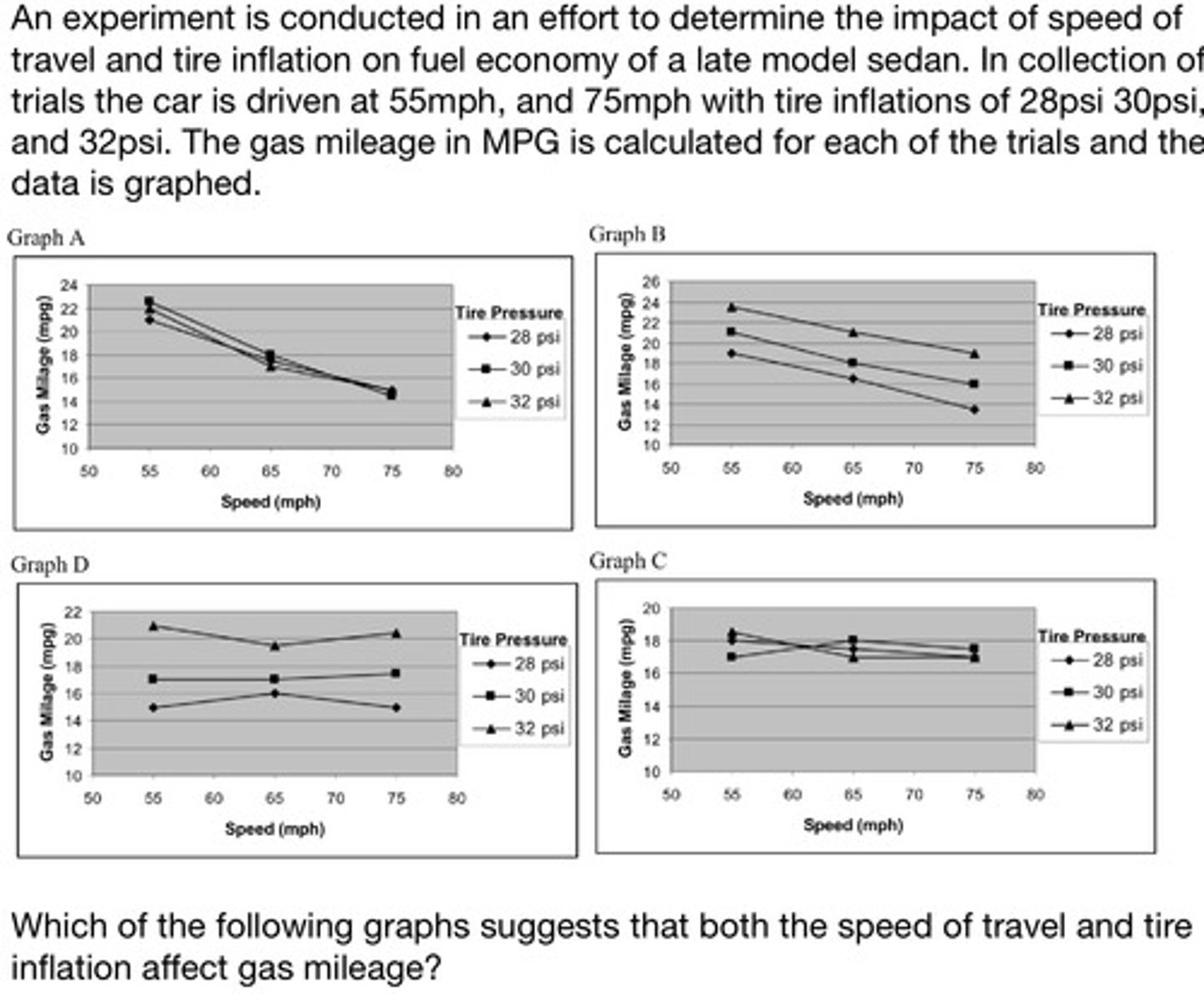
Graph A
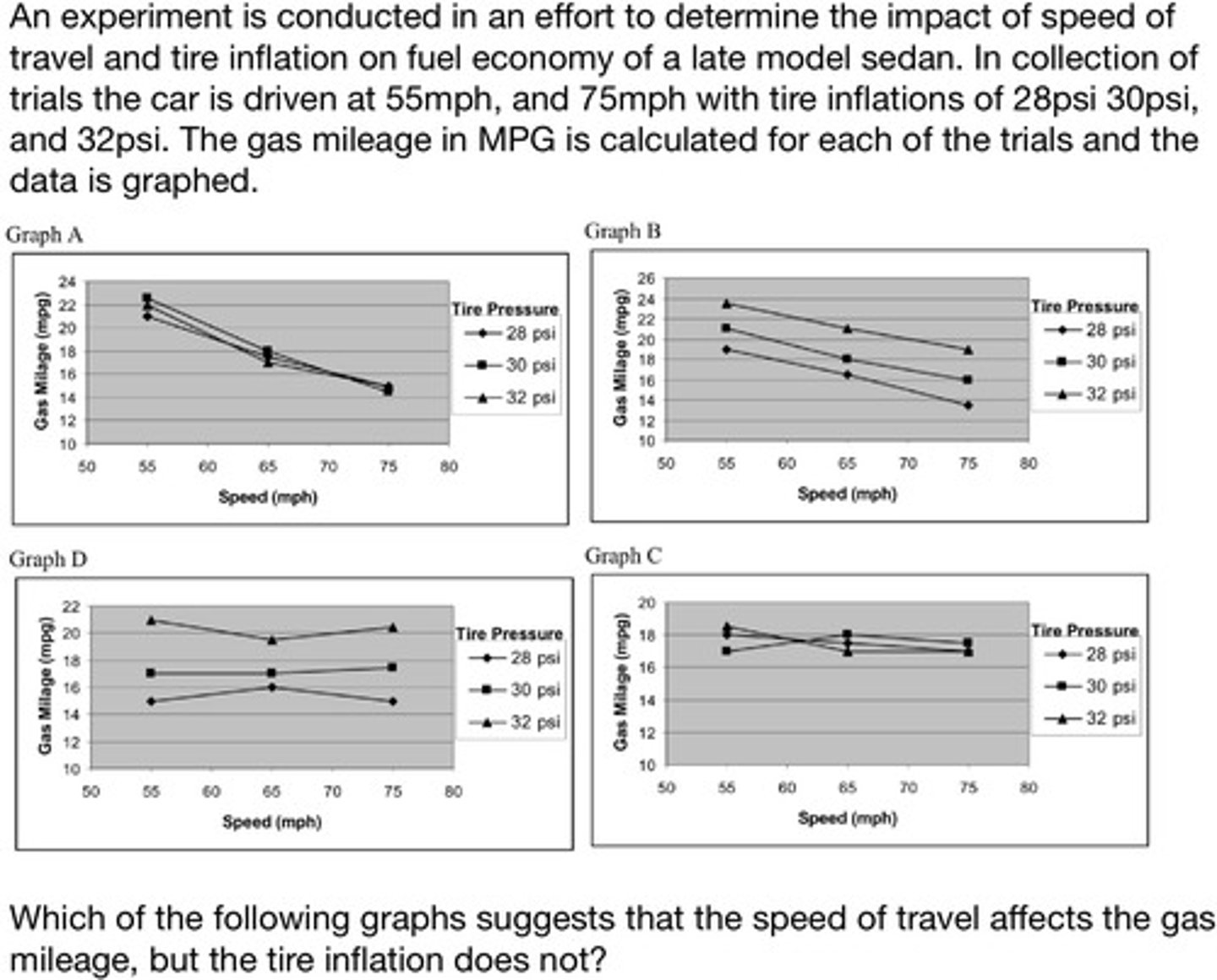
Graph D