NURS 203: Unit 5 - Neurological System: Sensory Response(Lab 5 Review)
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
2 Sensory Pathways of the Body
- Spinothalmic tract
- Posterior (dorsal) columns
Spinothalmic Tract
The sensory pathway that contains sensory fibres that transmit the sensations of pain, temperature, and crude or light touch
Posterior (Dorsal) Columns
The sensory pathway that contains the sensory fibres that conduct the sensations of position, vibration, and finely localized touch
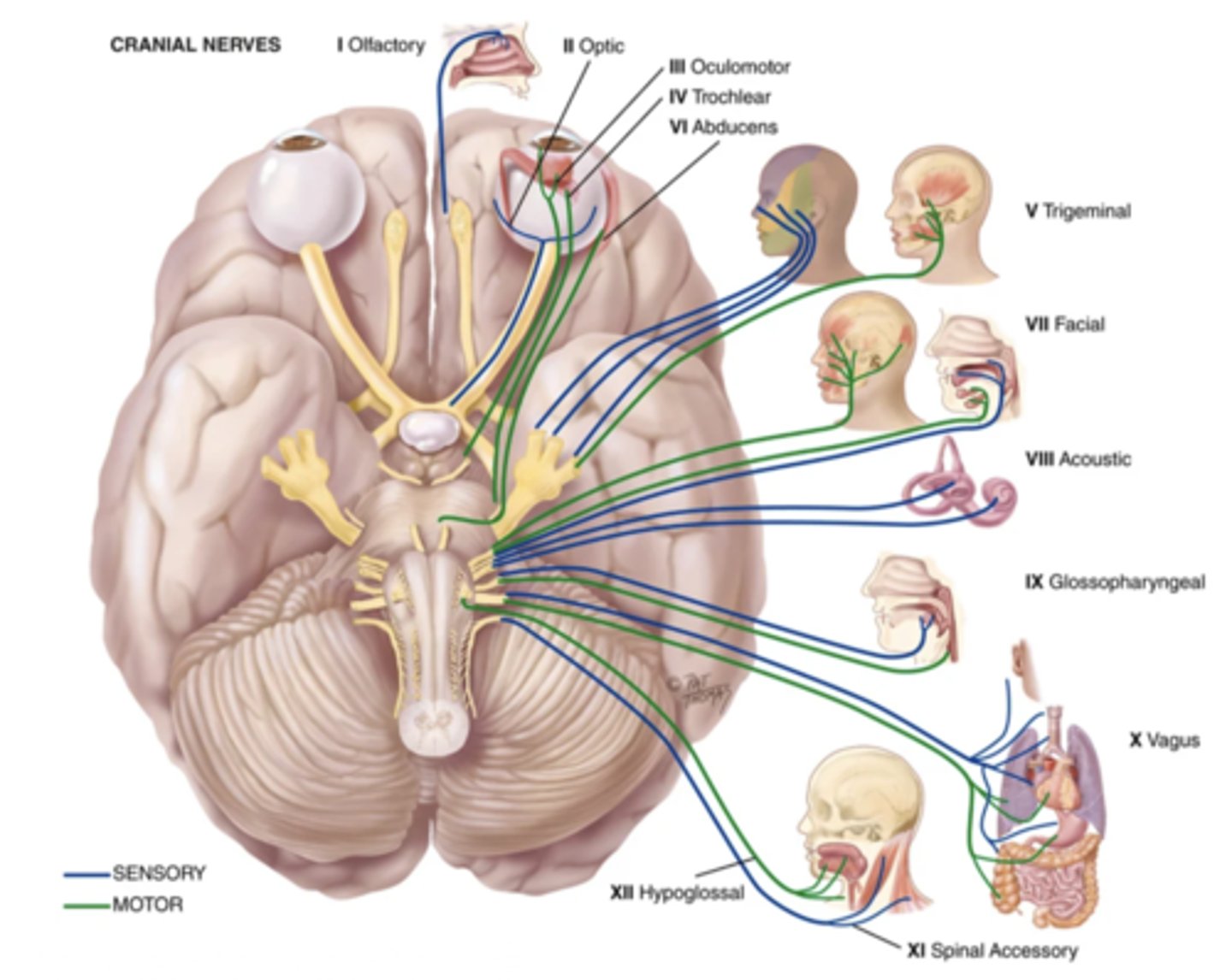
Cranial Nerves
- 12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
- Considered as lower motor neurons
12 Cranial Nerves
1.) Olfactory
2.) Optic
3.) Oculomotor
4.) Trochlear
5.) Trigeminal
6.) Abducens
7.) Facial
8.) Acoustic (Vestibulocochlear)
9.) Glossopharyngeal
10.) Vagus
11.) Spinal Accessory
12.) Hypoglossal
(Oh Only Octopuses Try Taming Adventurous Foxes Admiring Gloomy Vampires Stalking Humans)
Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter More
- Sensory (Olfactory nerve - CN I)
- Sensory (Optic nerve - CN II)
- Motor (Oculomotor nerve - CN III)
- Motor (Trochlear nerve - CN IV)
- Both (Trigeminal nerve - CN V)
- Motor (Abducens nerve - CN VI)
- Both (Facial nerve - CN VII)
- Sensory (Acoustic (vestibulocochlear) nerve - CN VIII)
- Both (Glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX)
- Both (Vagus nerve - CN X)
- Motor (Spinal accessory nerve - CN XI)
- Motor (Hypoglossal nerve - CN XII)
Function of the Olfactory Nerve (CN I)
Smell
What to Assess for the Olfactory Nerve
- Patency
- Sense of smell
Anosmia
Decrease or loss of smell
Function of the Optic Nerve (CN II)
Vision
What to Assess for the Optic Nerve
- Visual acuity
- Ocular fundus
Function of the Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)
- Controls most extraocular movement
- Opening of eyelids
- Pupil constriction
- Controls shape of lens
Function of the Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)
Downward/inward movement of the eye
Function of the Abducens Nerve (CN VI)
Lateral movement of the eye
What to Assess for the Oculomotor, Trochlear, and Abducens Nerve
- Palpebral fissures
- Pupils
- Extraoccular movements
Nystagmus
Back-and-forth oscillation of the eyes
Characteristics to Note for a Nystagmus
- Presence in one or both eyes
- Type of movement
- Amplitude
- Frequency
- Plane
Function of the Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
- Muscles of mastication
- Sensation of face and scalp, cornea, and mucous membranes of the mouth and nose
What to Assess for the Trigeminal Nerve
- Motor function
- Sensory function
- Corneal reflex
3 Areas to Assess the Sensory Function of the Trigeminal Nerve
- Forehead (ophthalmic)
- Cheek (maxillary)
- Jaw (mandibular)
Corneal Reflex
- A reflex that makes someone blink in response to corneal stimulation by a cotton wisp
- Only tested if someone has an abnormal facial sensation or movements
Function of the Facial Nerve (CN VII)
- Facial muscles
- Closing of the eyes
- Labial speech
- Closing of the mouth
- Taste (anterior 2/3rds of the tongue)
- Saliva and tear secretin
What to Assess for the Facial Nerve
- Mobility
- Facial symmetry
- Sense of taste (only if there is facial nerve injury)
Function of the Acoustic (Vestibulocochlear) Nerve (CN VIII)
Hearing and equilibrium
What to Assess for the Acoustic Nerve
- Hearing acuity
- Whispered voice test
- Weber test
- Rinne test
Function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)
- Phonation
- Swallowing
- Taste (posterior 1/3rds of the tongue)
- Gag reflex
- Parotid gland
- Carotid reflex
Function of the Vagus Nerve (CN X)
- Talking
- Swallowing
- General sensation from carotid body, carotid sinus, pharynx, and viscera
- Carotid reflex
What to Assess for the Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerve
- Tongue
- Gag reflex
Function of Accessory Nerve (CN XI)
Movement of trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles
What to Assess for the Accessory Nerve
- Muscle symmetry
- Muscle strength
Function of the Hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII)
Movement of tongue
What to Assess for the Hypoglossal Nerve
- Tongue
- "Light, light, dynamite"
Objective Data to Assess for the Sensory System
- Spinothalmic tract
- Posterior column tract
What to Assess for the Spinothalmic Tract
- Pain
- Temperature
- Light touch
What to Assess for the Posterior Column Tract
- Vibration
- Kinaesthesia
- Fine touch
What to Assess for Fine Touch
- Stereognosis
- Graphaesthesia
- Two-point discrimination
- Extinction
- Point location
Stereognosis
The ability to recognize objects by feeling their forms, sizes, and weights, with the eyes closed
Graphaesthesia
The ability to "read" a number by having it traced on the skin
Two-Point Discrimination
The ability to distinguish the separation of two simultaneous pinpoints on the skin
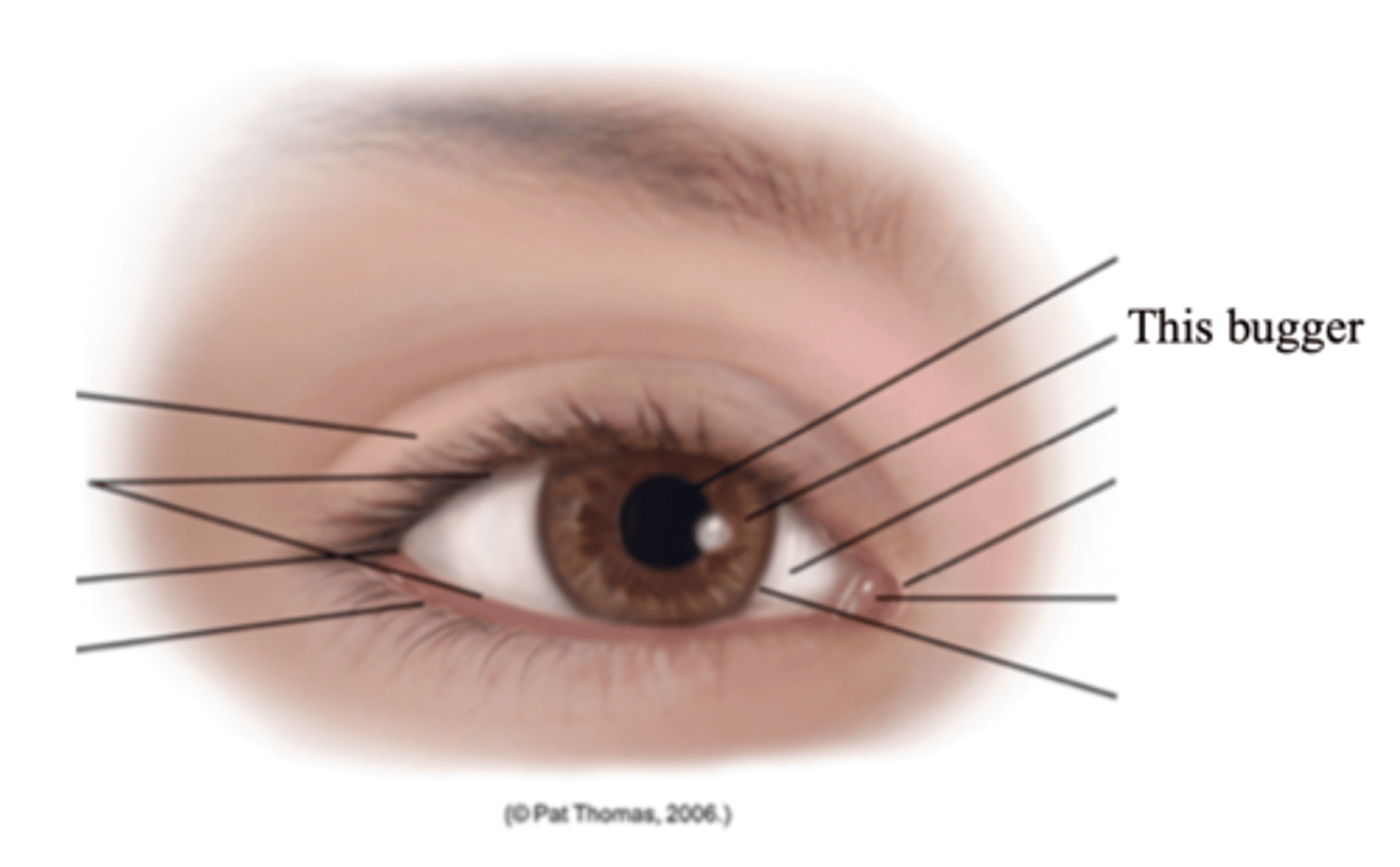
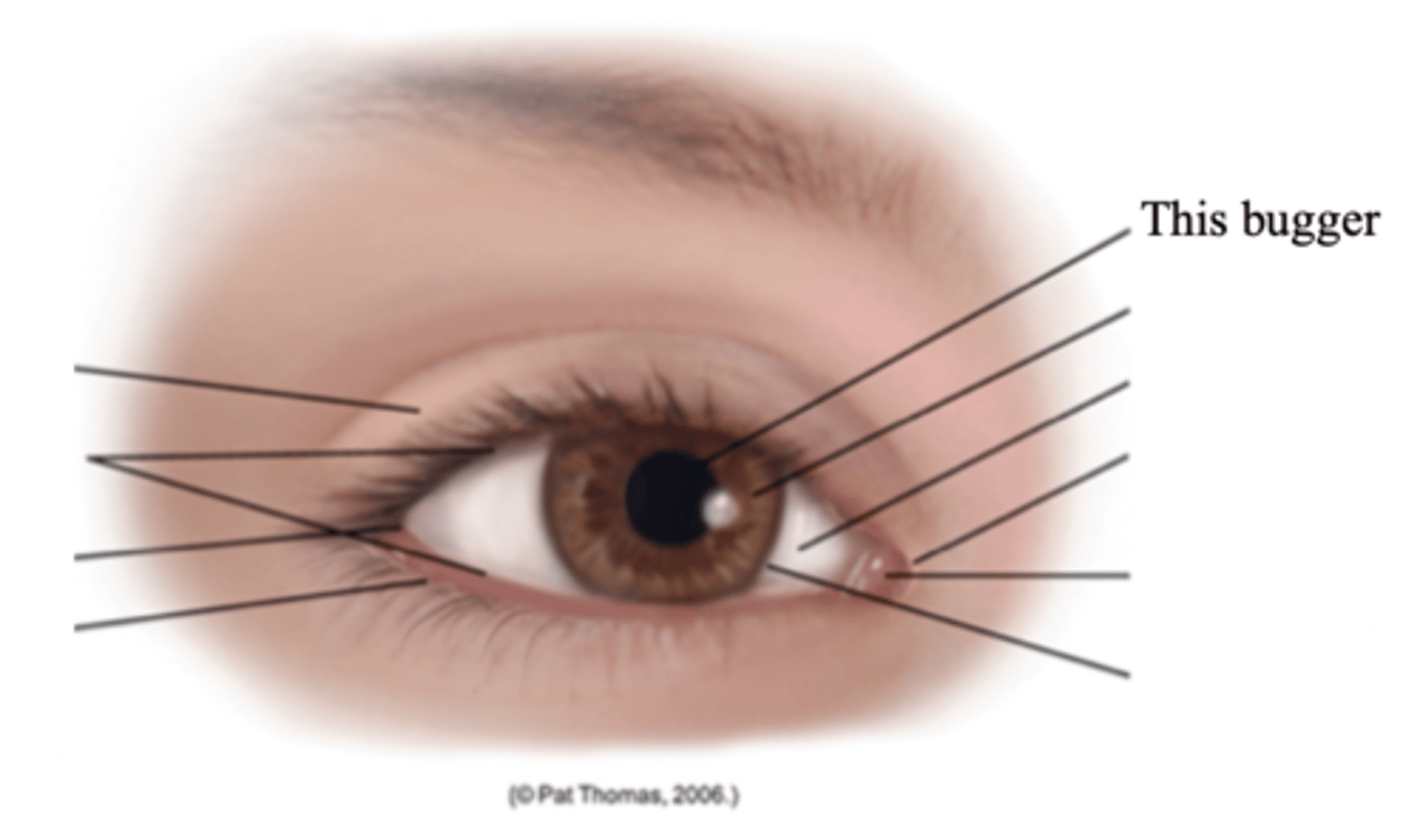
Major External Anatomy of the Eyes
- Eyelids
- Palpebral fissure
- Limbus
- Canthus
- Caruncle
- Tarsal plates
- Meibomian glands
- Conjunctiva
- Lacrimal apparatus
(Mnemonic Here)
Eyelids
Two movable flaps of skin that further protect the eye from injury, strong light, and dust
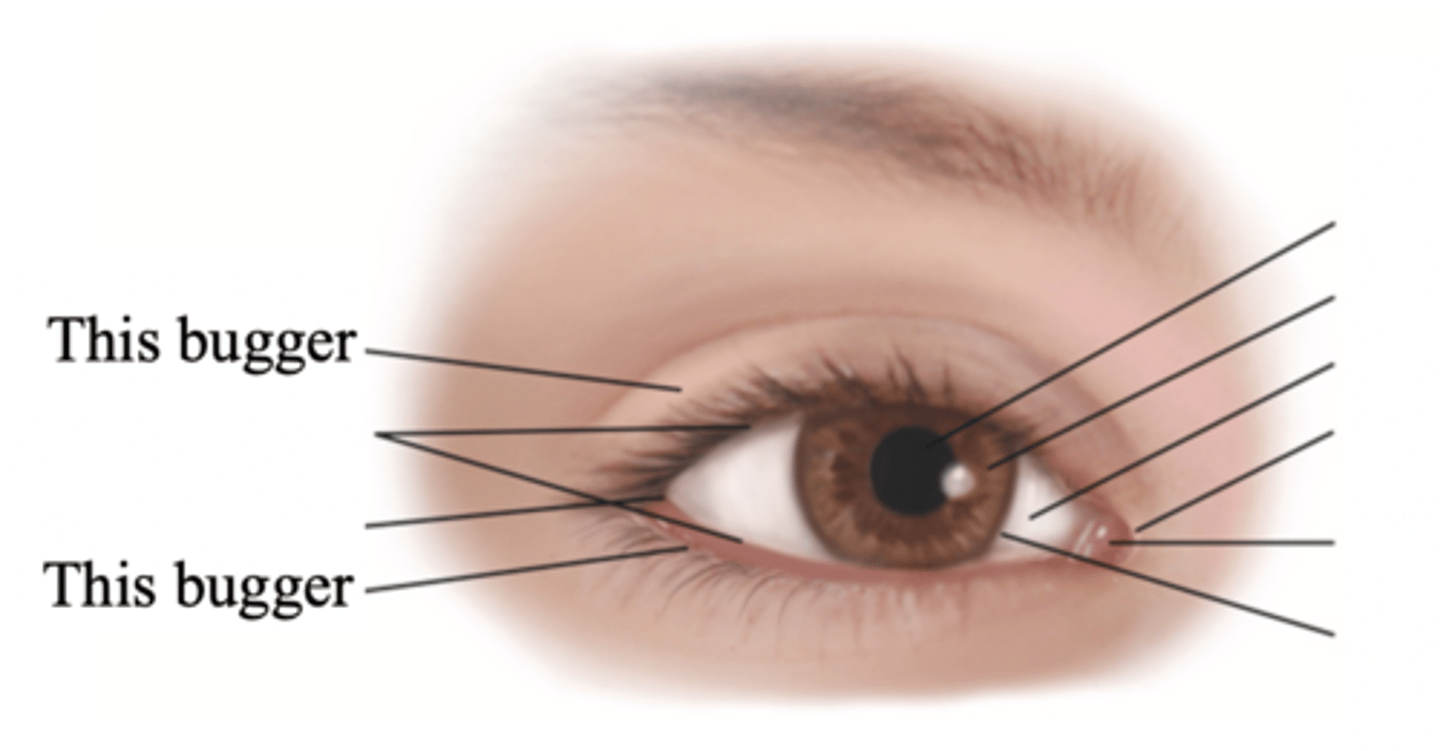
Palpebral Fissure
The elliptical open space between the eyelids
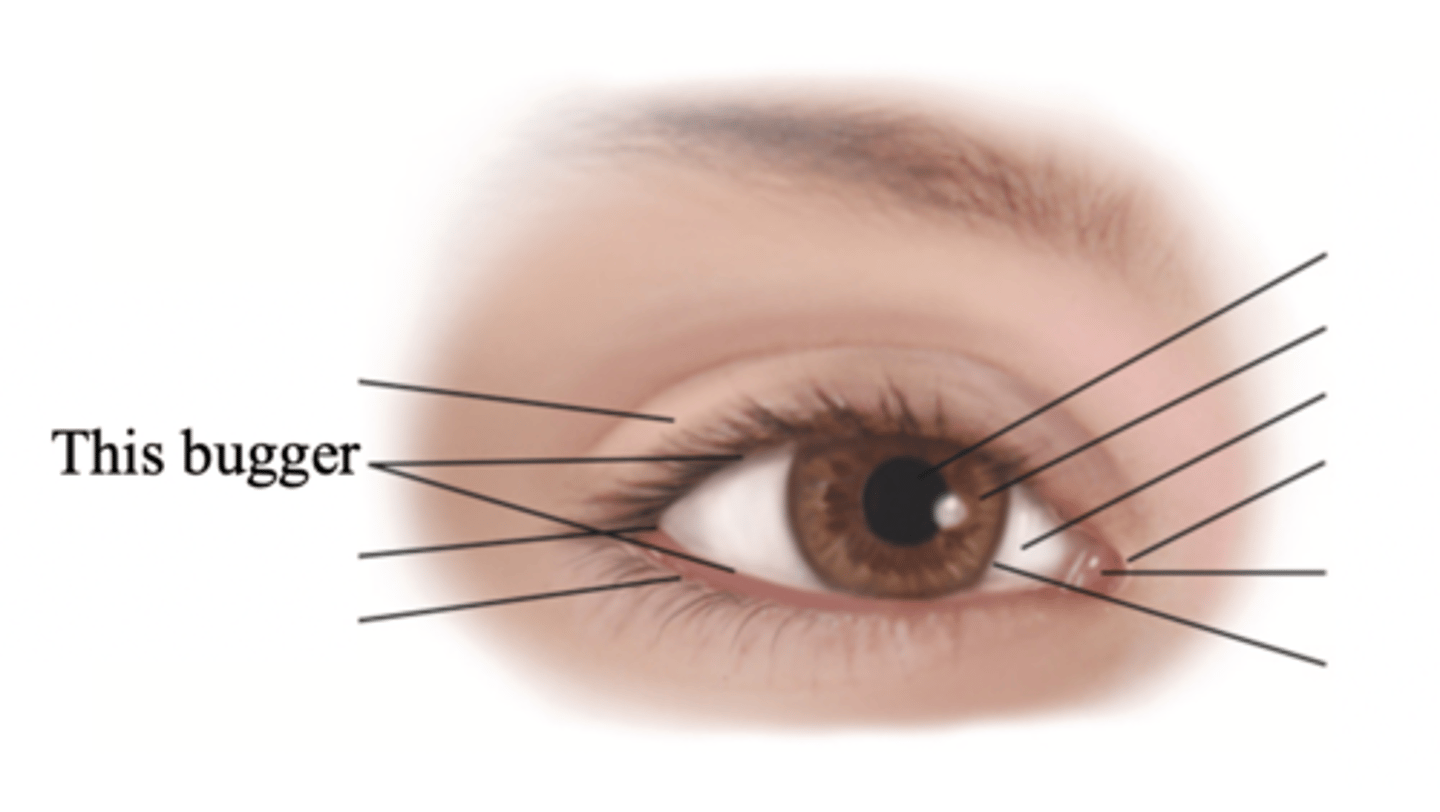
Limbus
The border between cornea and sclera
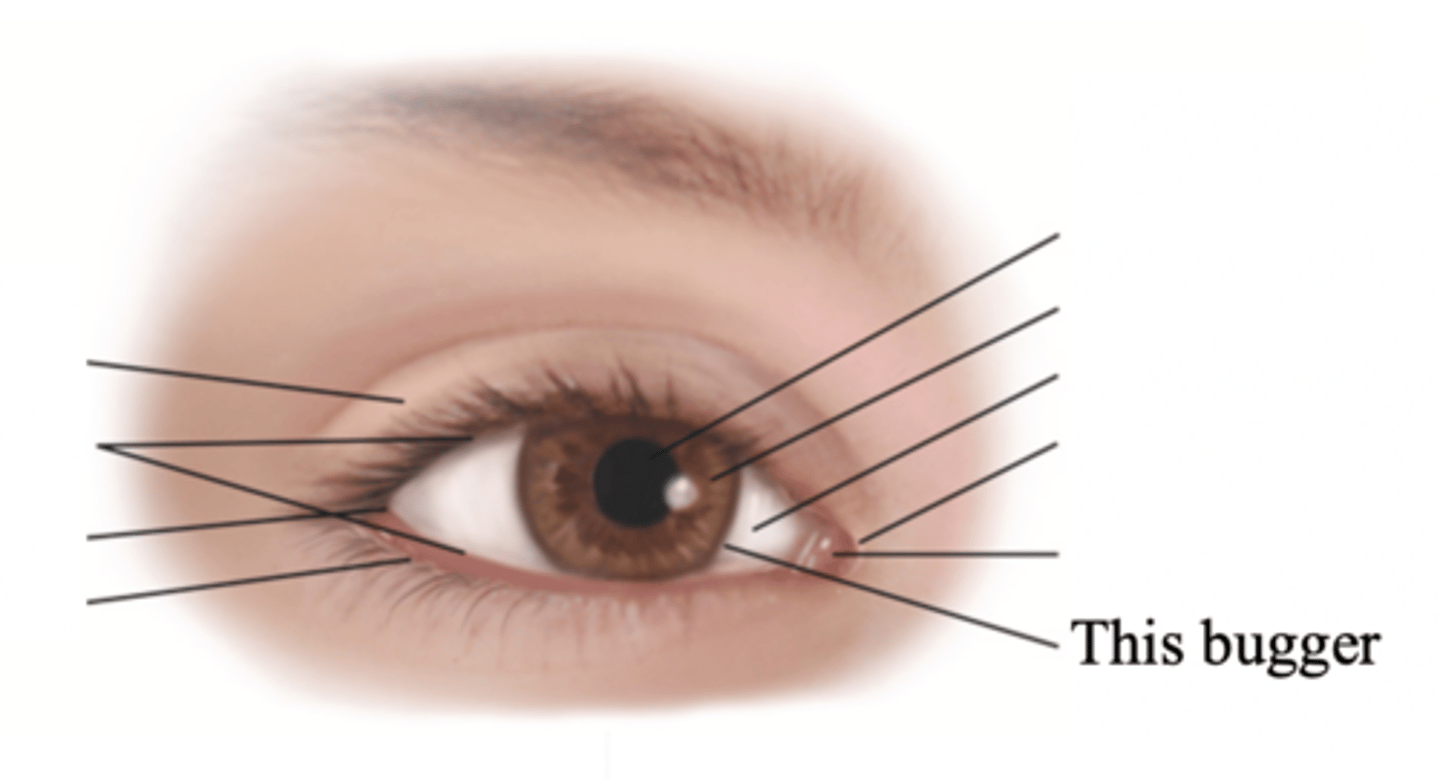
Canthus
The corner of the eye; the angle where the eyelids meet
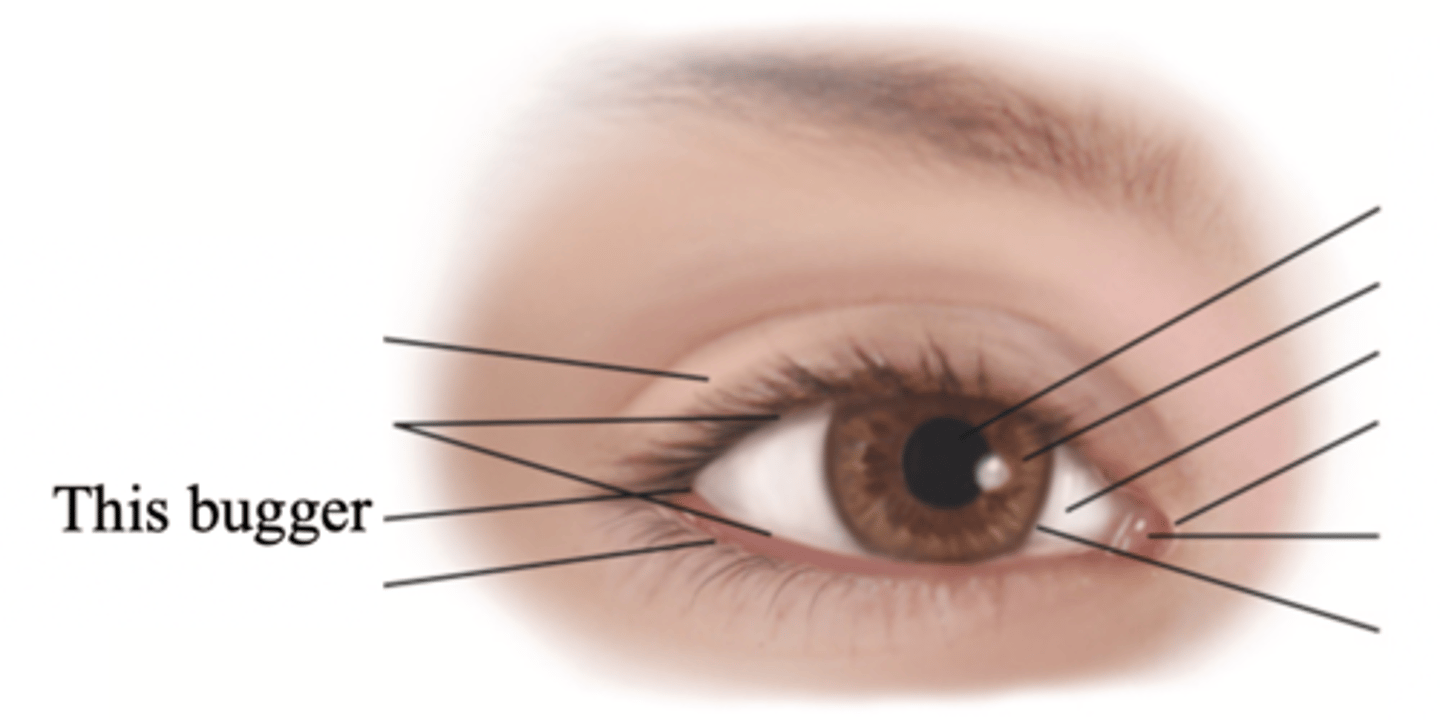
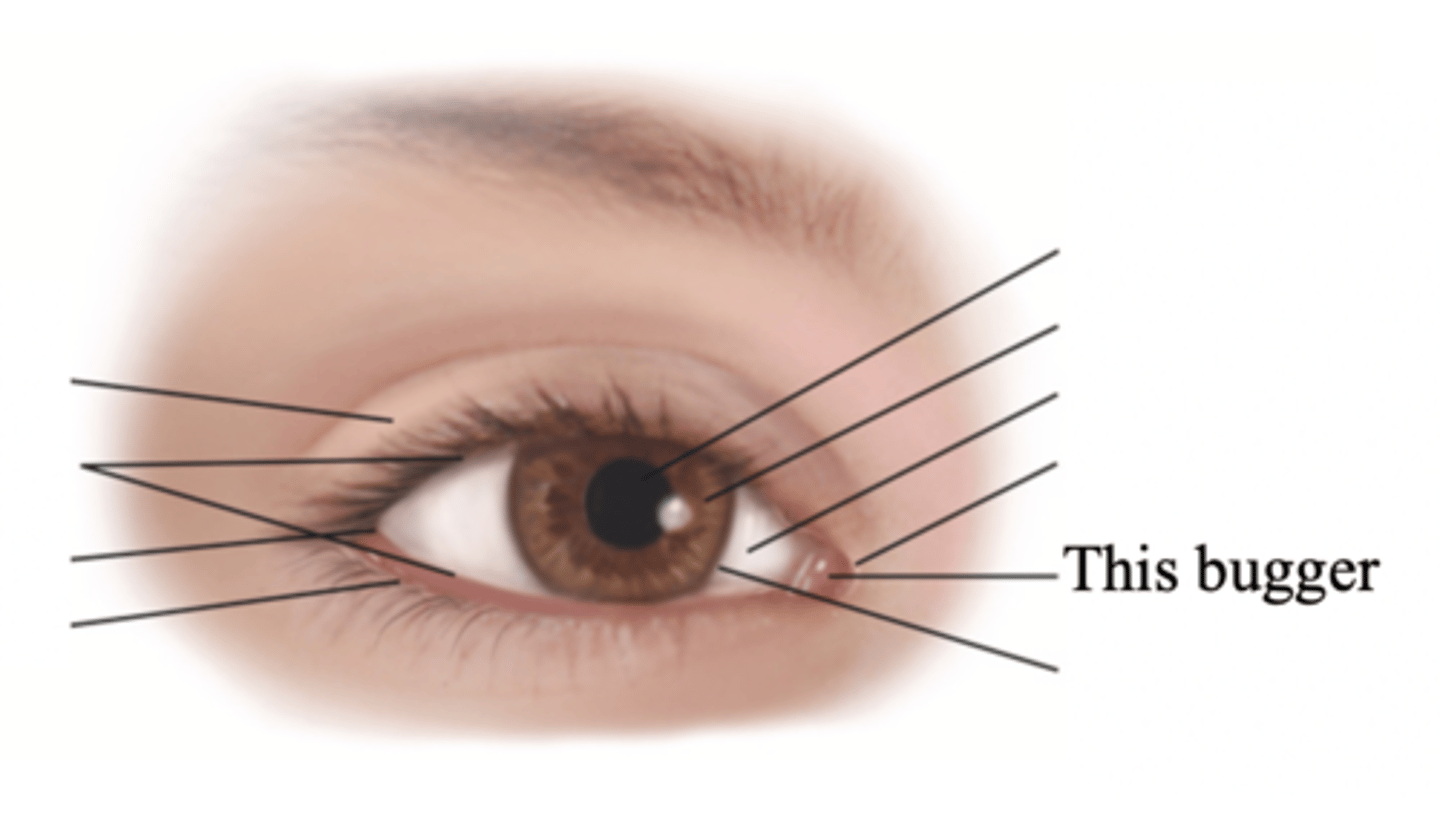
Caruncle
A small fleshy mass containing sebaceous glands
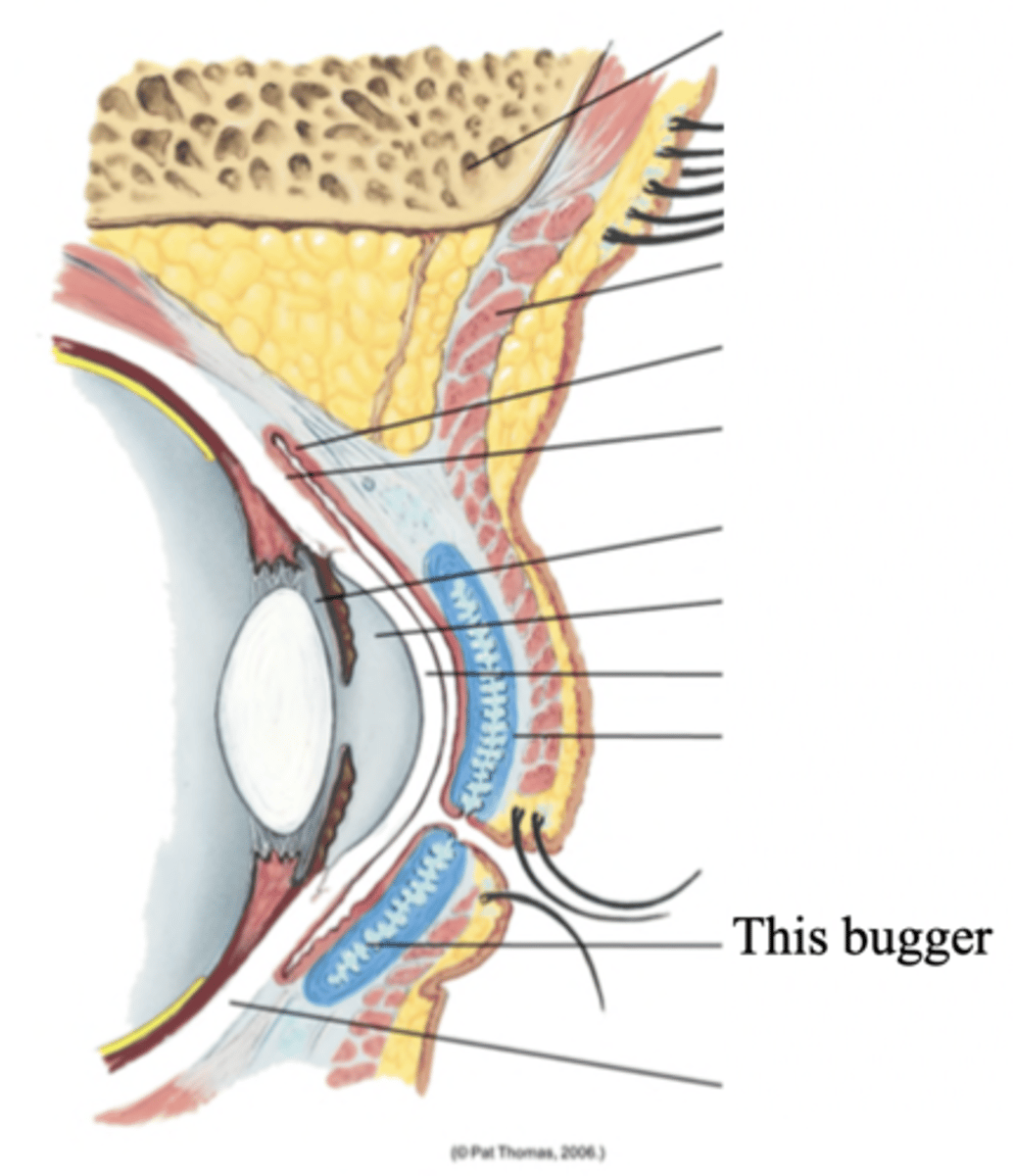
Tarsal Plates
Connective tissue within the upper eyelids that gives it shape
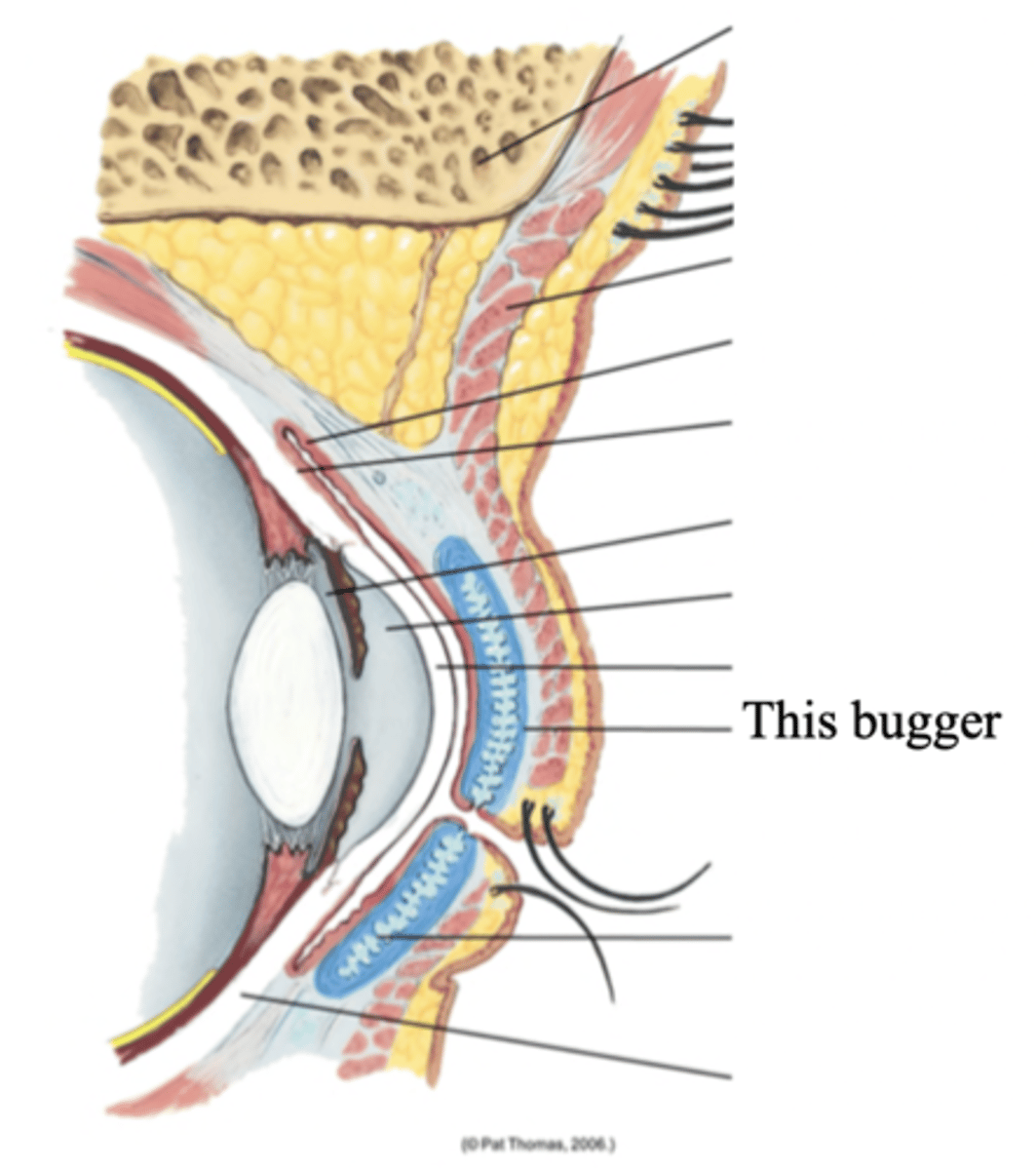
Meibomian Glands
Modified sebaceous glands in the tarsal plates that secrete an oily lubricating material onto the eyelids
Conjunctiva
A transparent protective covering of the eye
Palpebral Conjunctiva
The conjunctiva that lines the eyelids and is clear, with many small blood vessels
Bulbar Conjunctiva
The conjunctiva that overlies the opeyeball, with the white sclera showing through
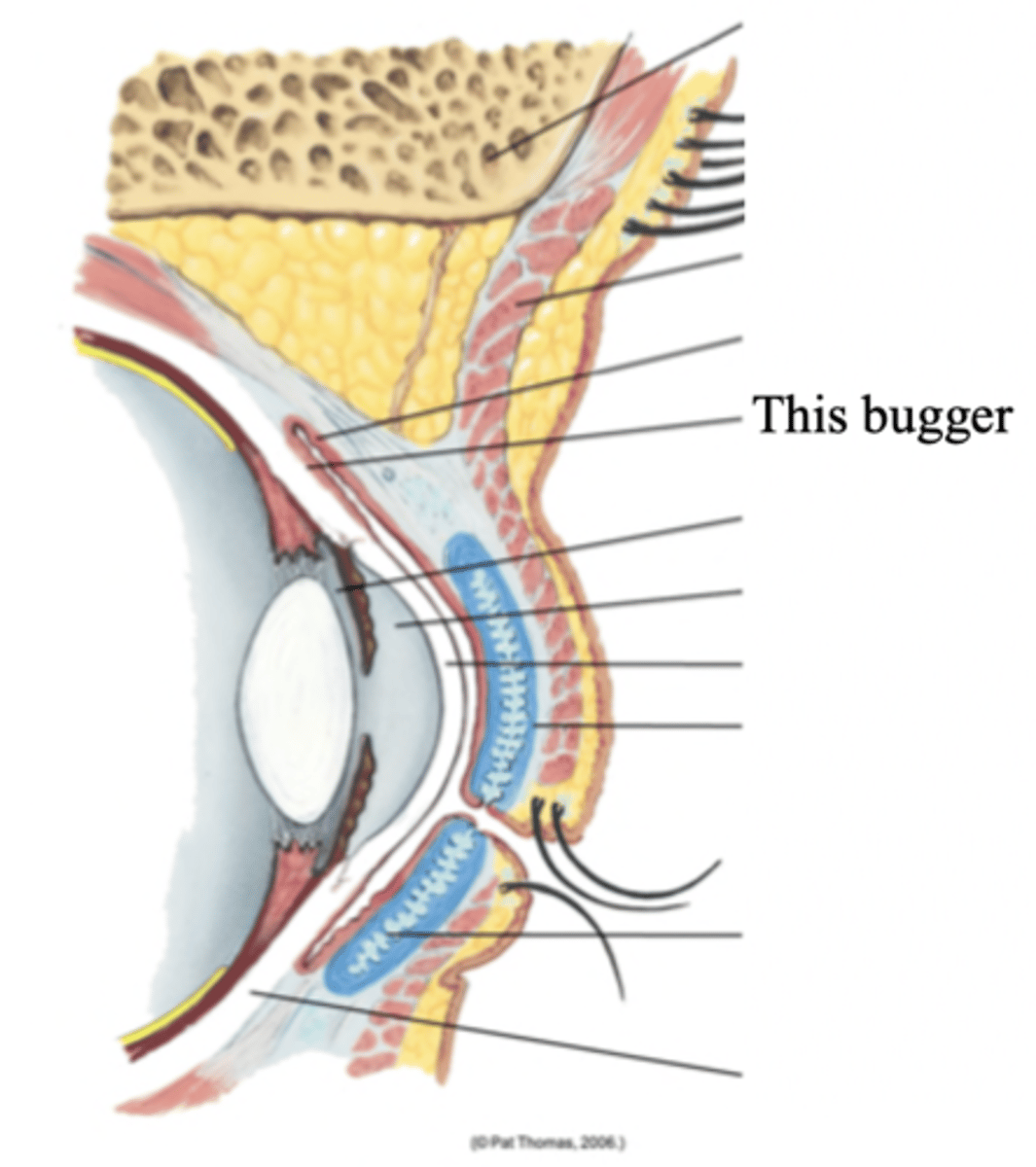
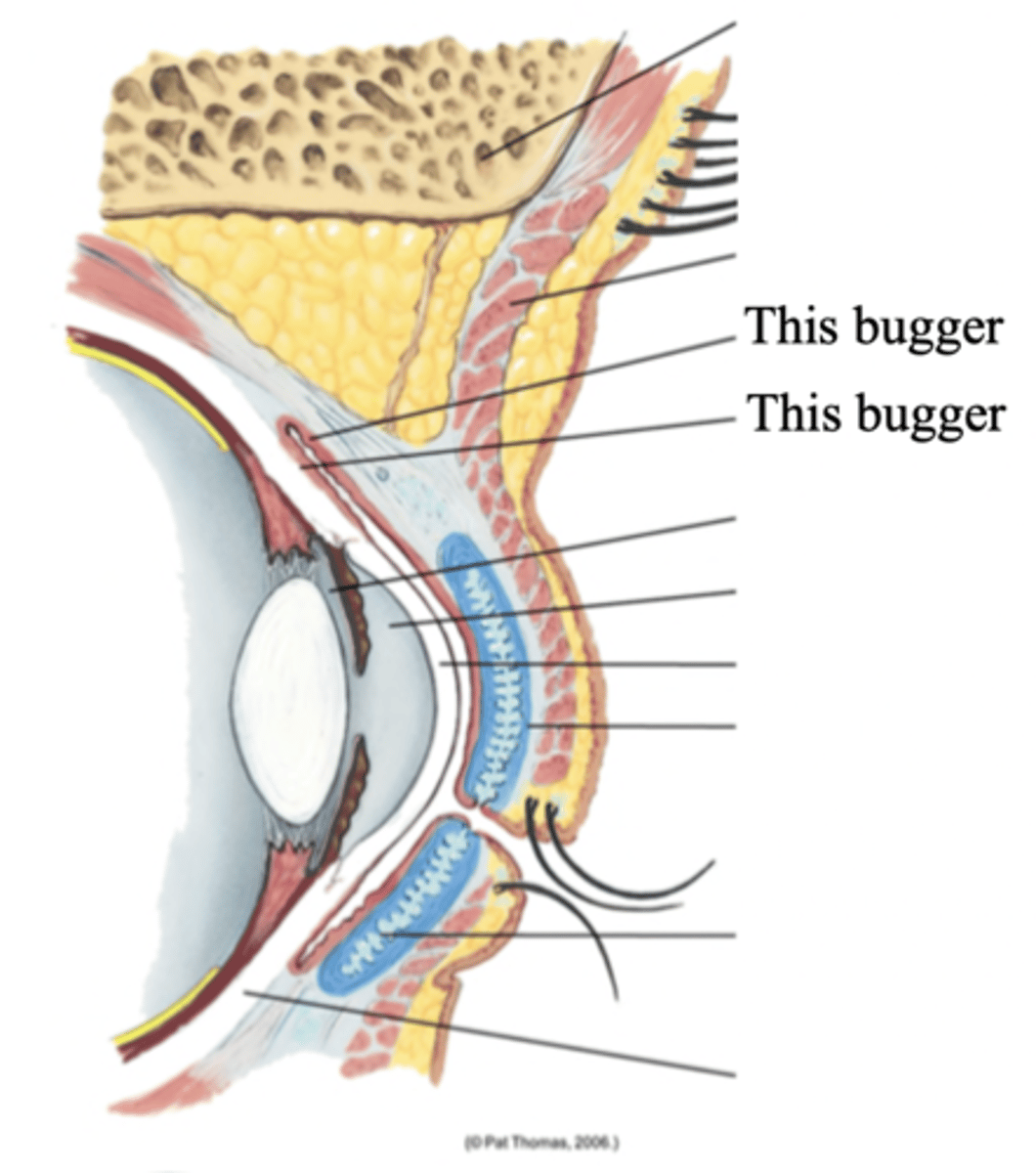
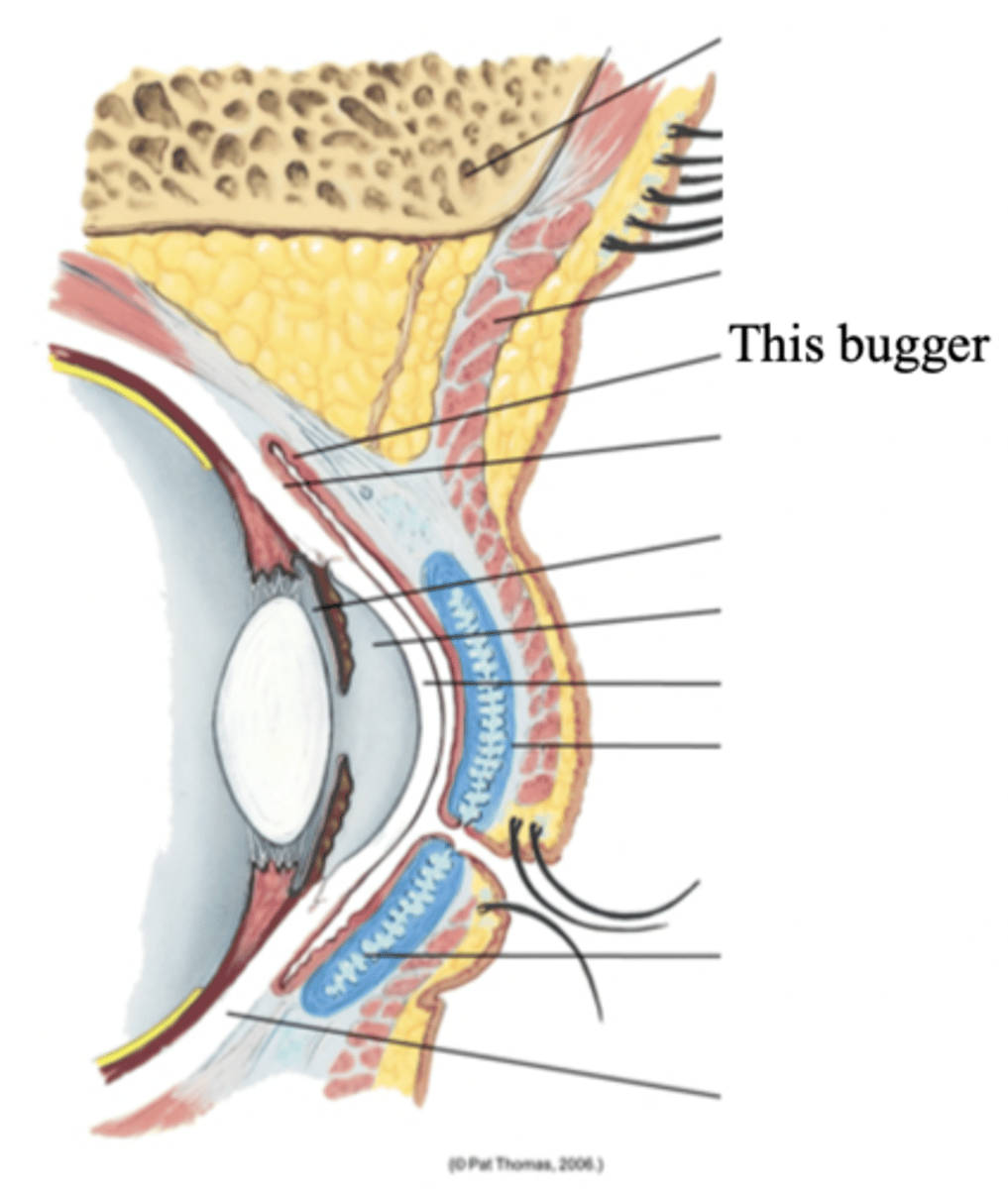
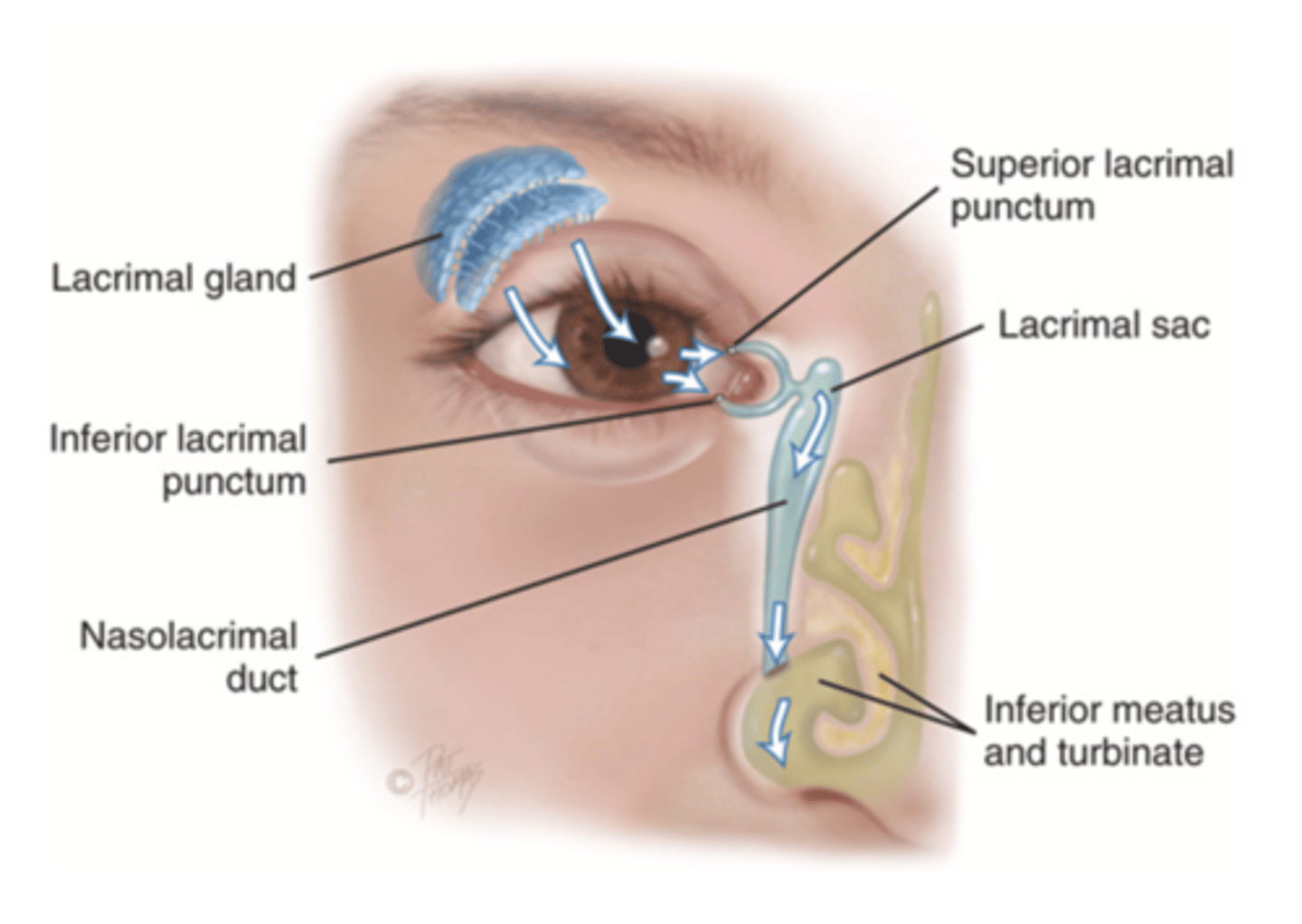
Lacrimal Apparatus
The structures in the eye that provides constant irrigation to keep the conjunctiva and cornea moist and lubricated
4 Straight Muscles of the Eye
- Superior rectus
- Inferior rectus
- Lateral rectus
- Medial rectus
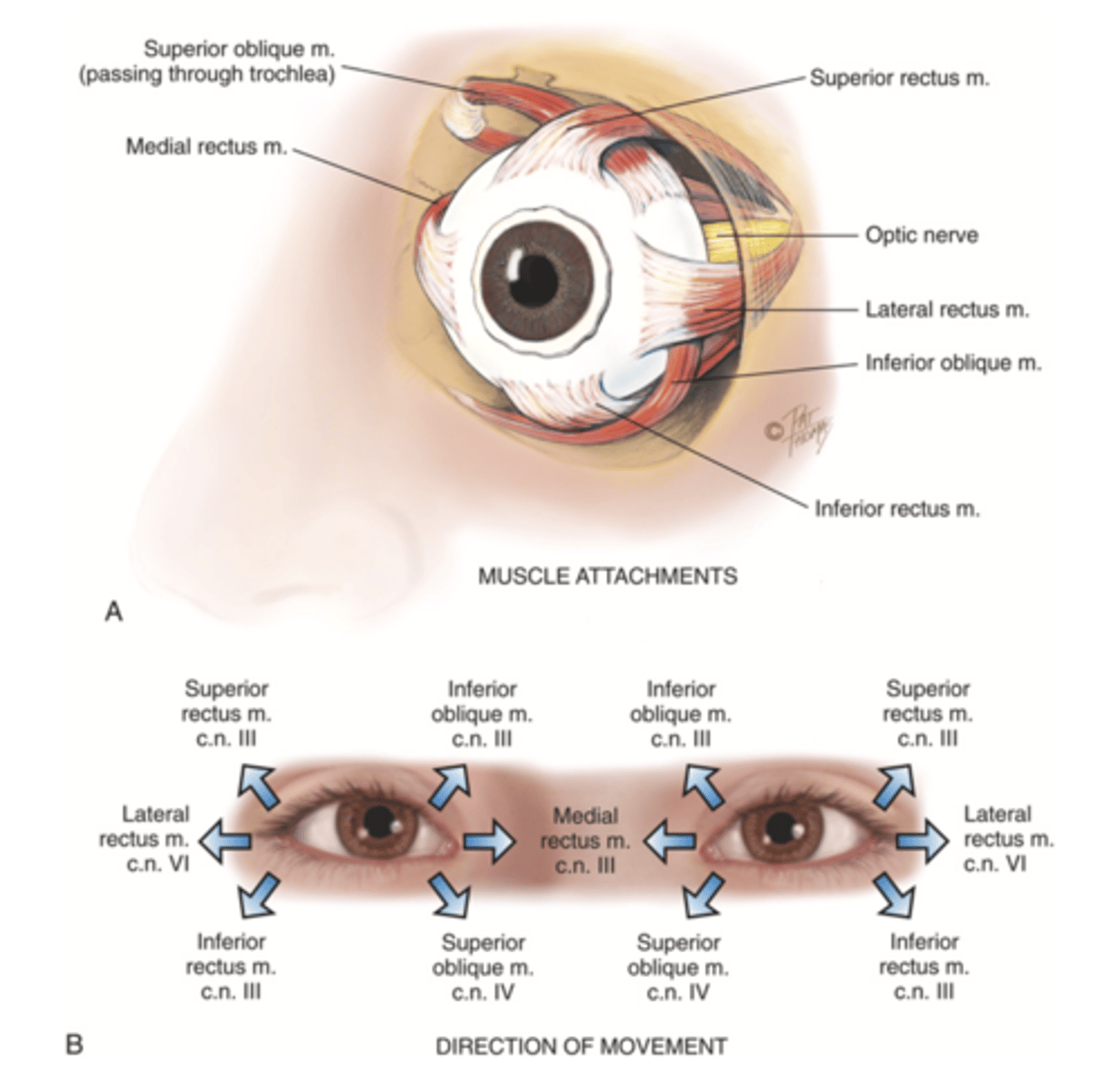
2 Oblique Muscles of the Eye
- Superior oblique
- Inferior oblique
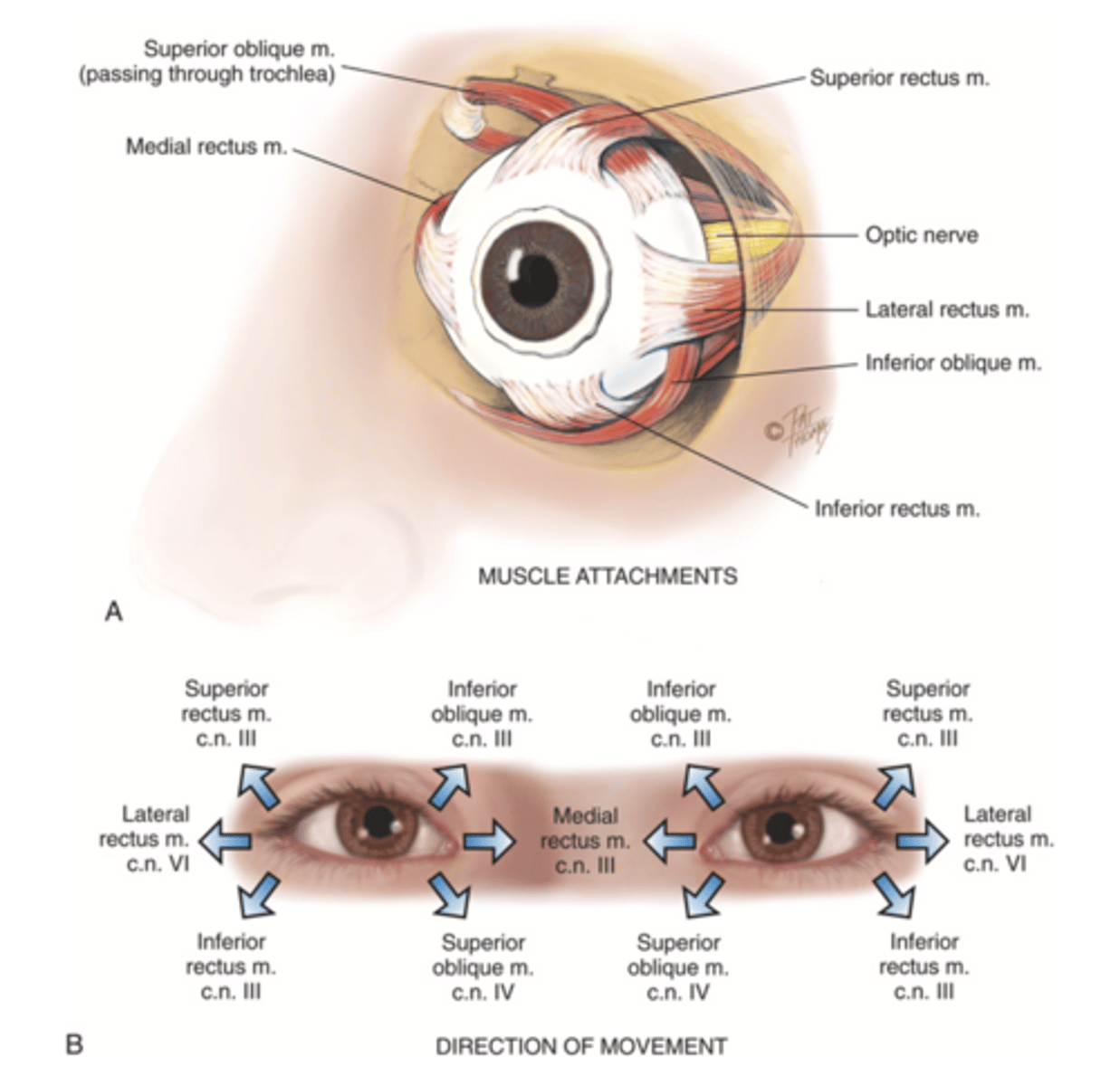
3 Cranial Nerves the Stimulates the Extraocular Muscles
- Abducens
- Trochlear
- Oculomotor
3 Layers/Coats of the Eye
- Outer fibrous sclera
- Middle vascular choroid
- Inner nervous retina
Sclera
A tough, protective, white covering of the eye that makes up its outer layer; the white part of the eye
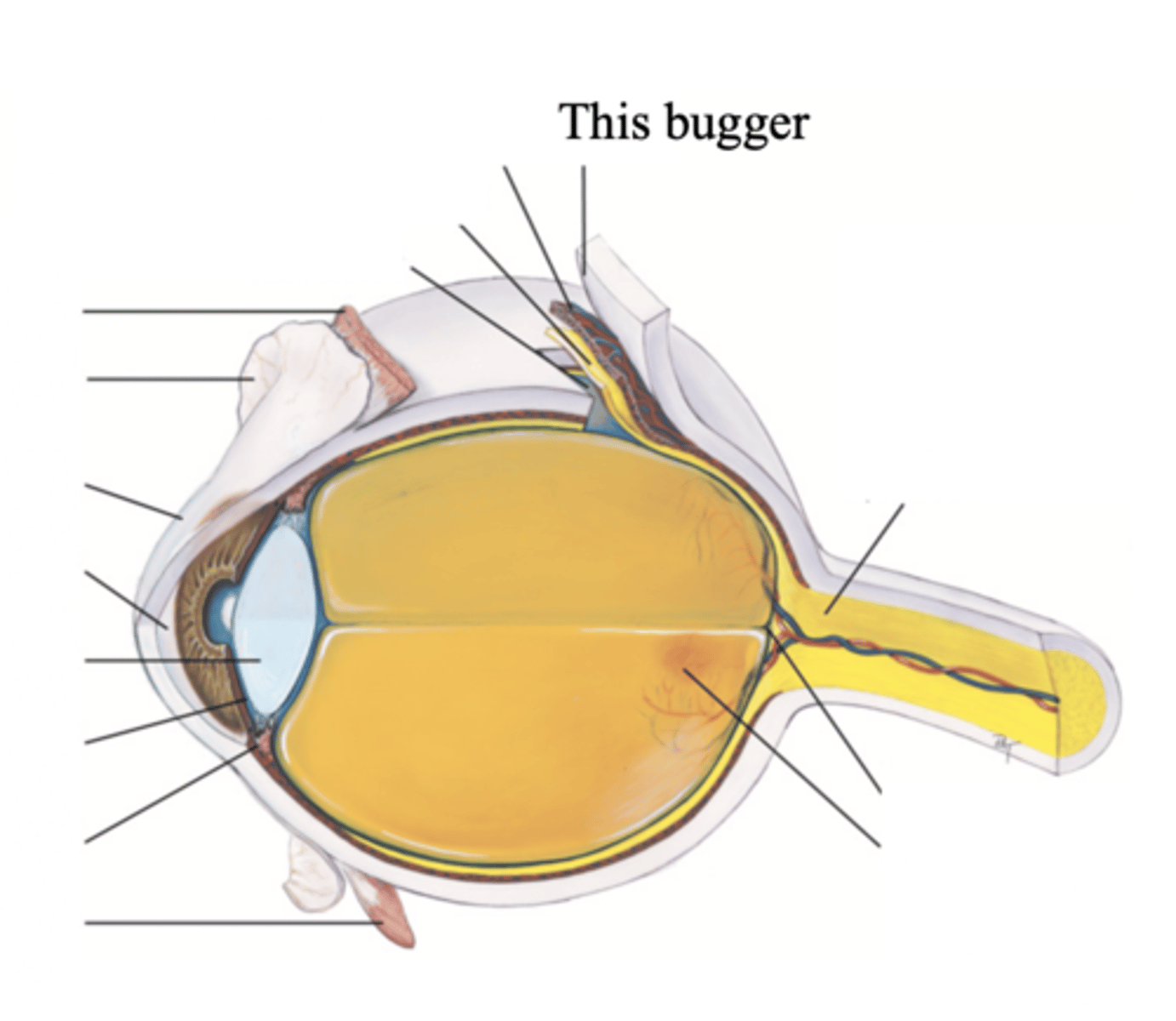
Major Structures in the Outer Fibrous Sclera
Cornea
Cornea
The clear tissue that covers the front of the eye
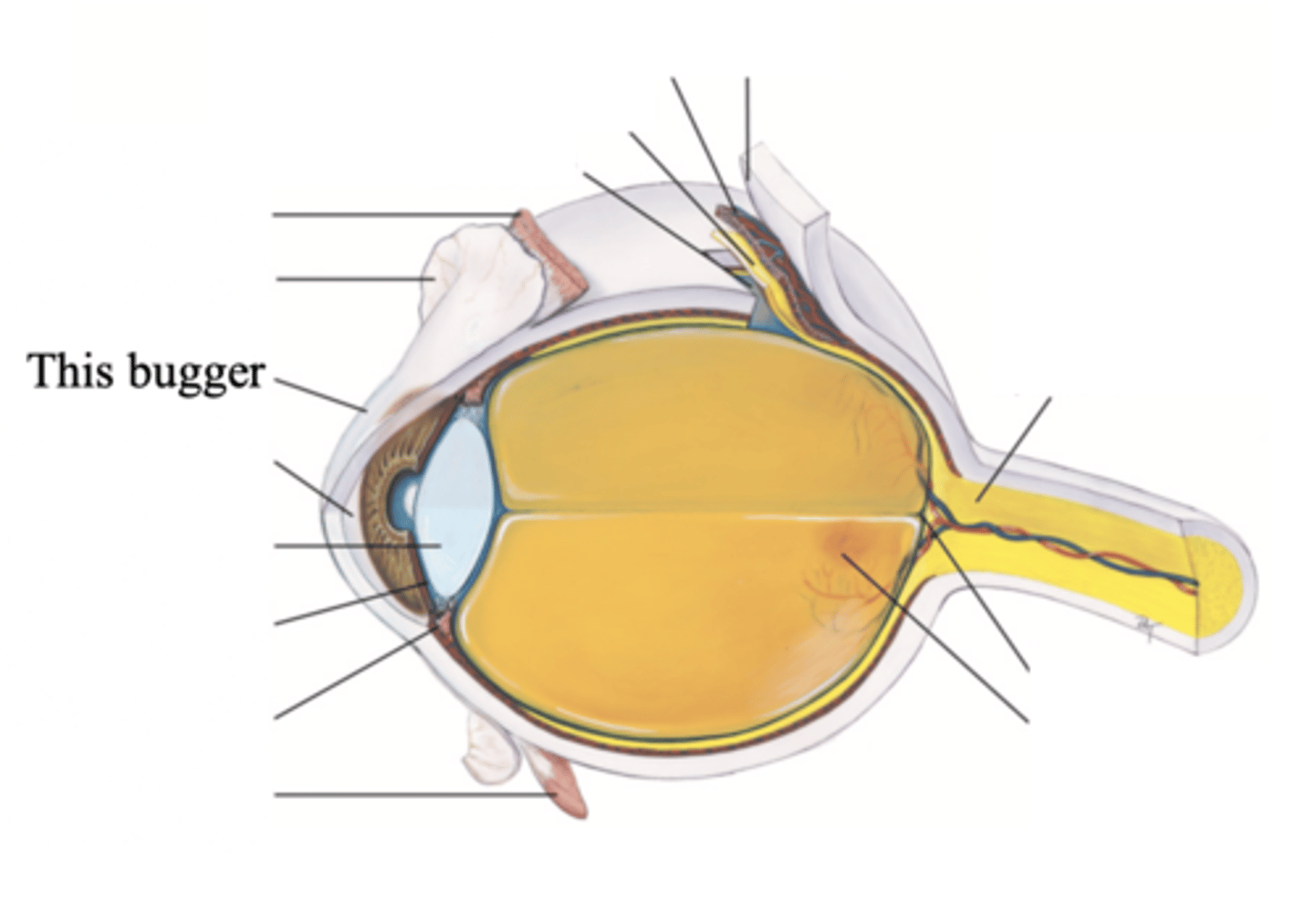
Choroid
The middle, vascular layer of the eye, between the retina and the sclera
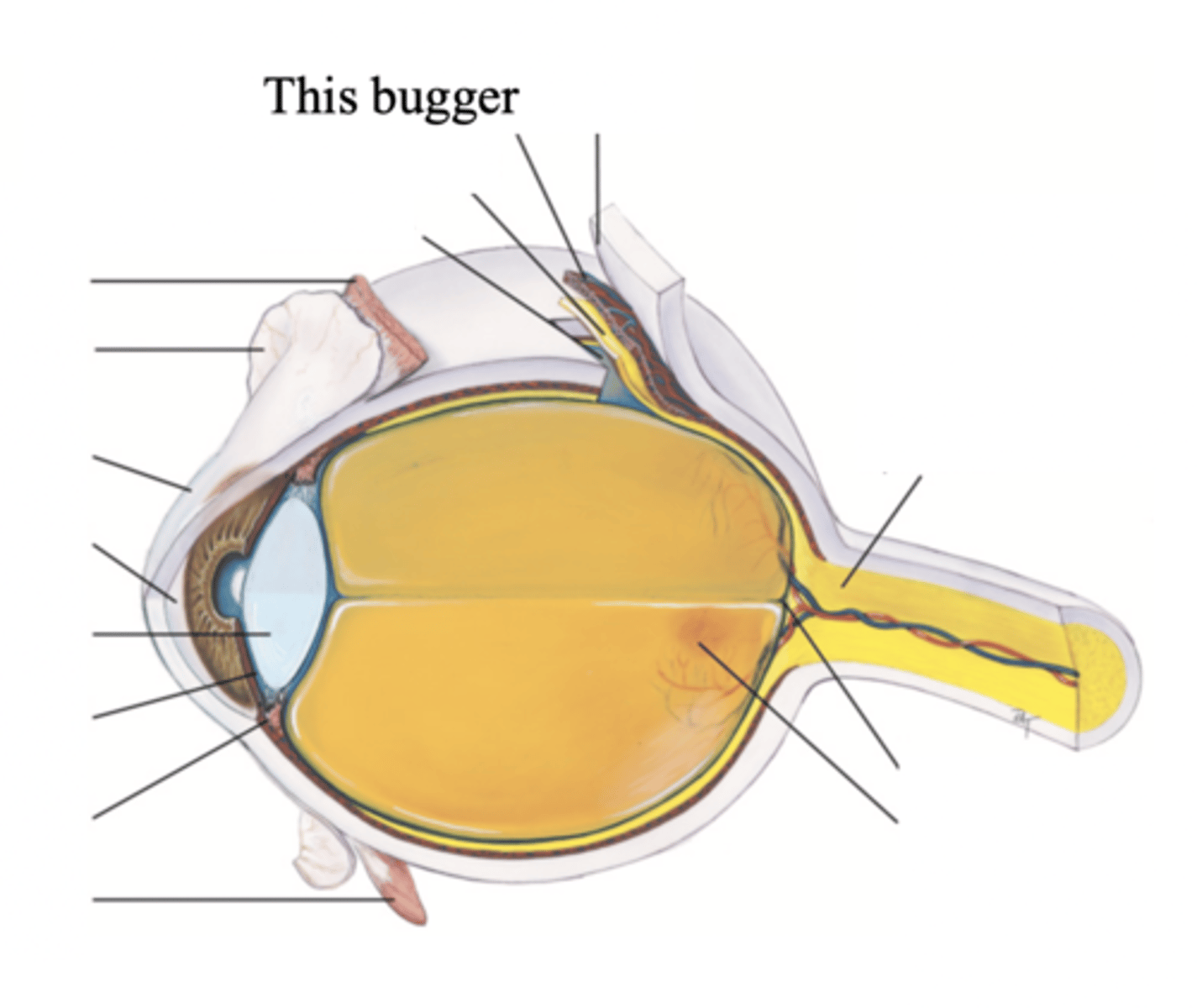
Major Structures in the Middle Vascular Choroid
- Ciliary body
- Iris
- Pupil
- Lens
- Anterior chamber
- Posterior Chamber
Ciliary Body
Structure surrounding the lens that connects the choroid and iris. It contains ciliary muscles, which control the shape of the lens, and it secretes aqueous humor.
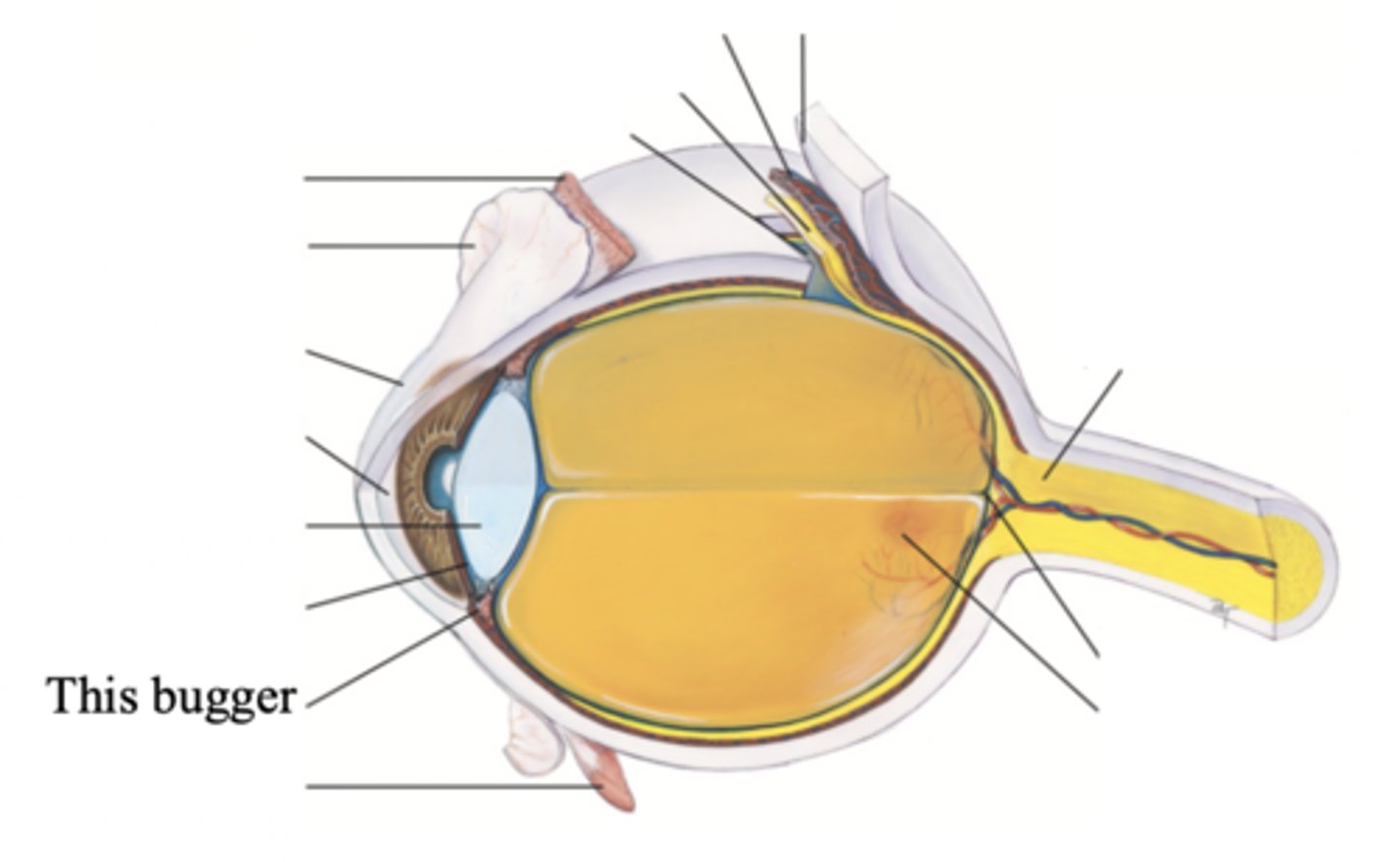
Iris
A ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening
Pupil
The opening through which light enters the eye; round and regular
Lens
A transparent biconvex disc located just behind the pupil and serves as a refracting medium that keeps viewed objects in continual focus on the retina
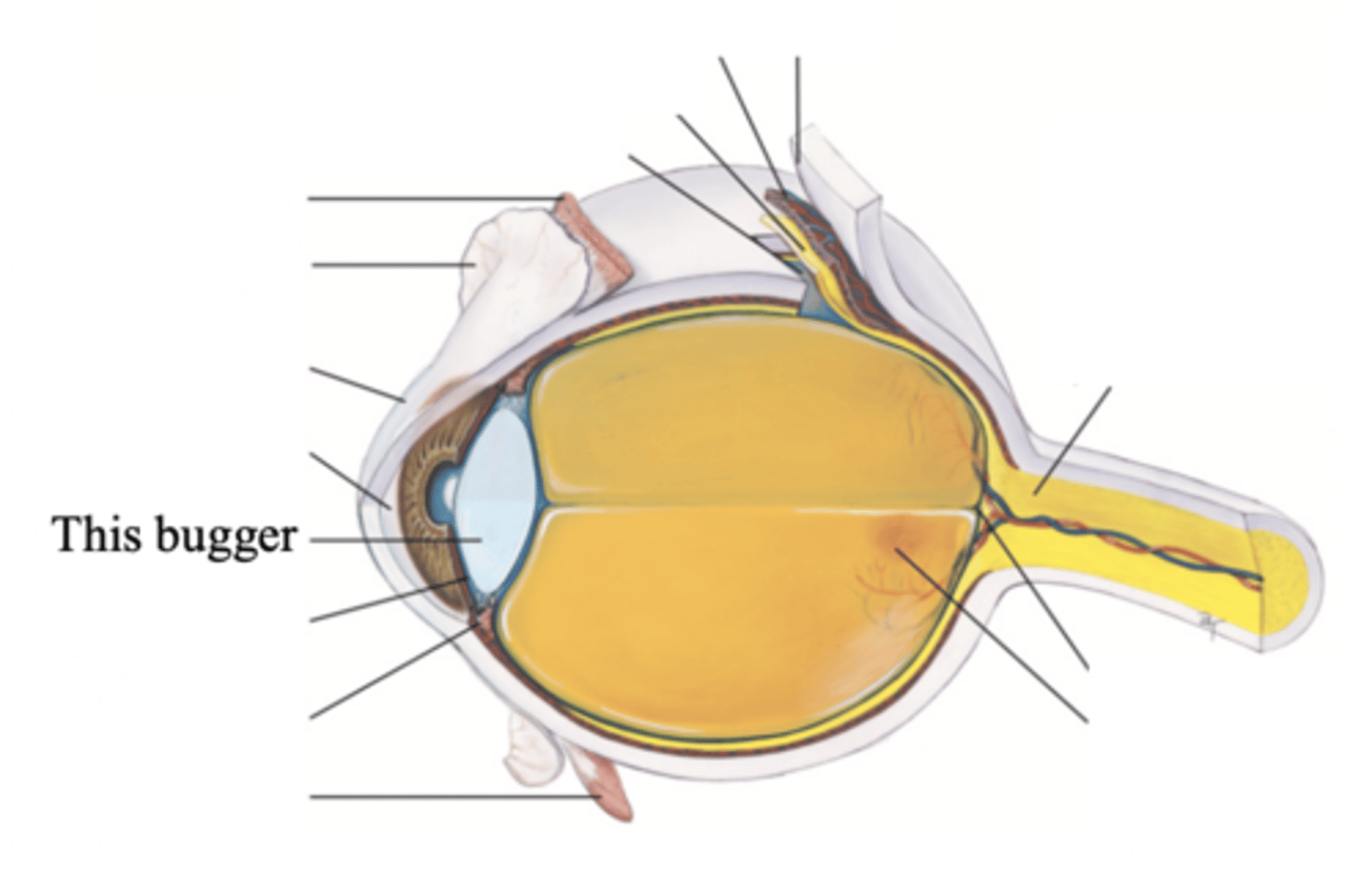
Anterior Chamber
- The chamber located posterior to the cornea and anterior to the iris and lens
- Contains clear, watery aqueous humor produced by the ciliary body which delivers nutrients to the surrounding tissues drain metabolic wastes
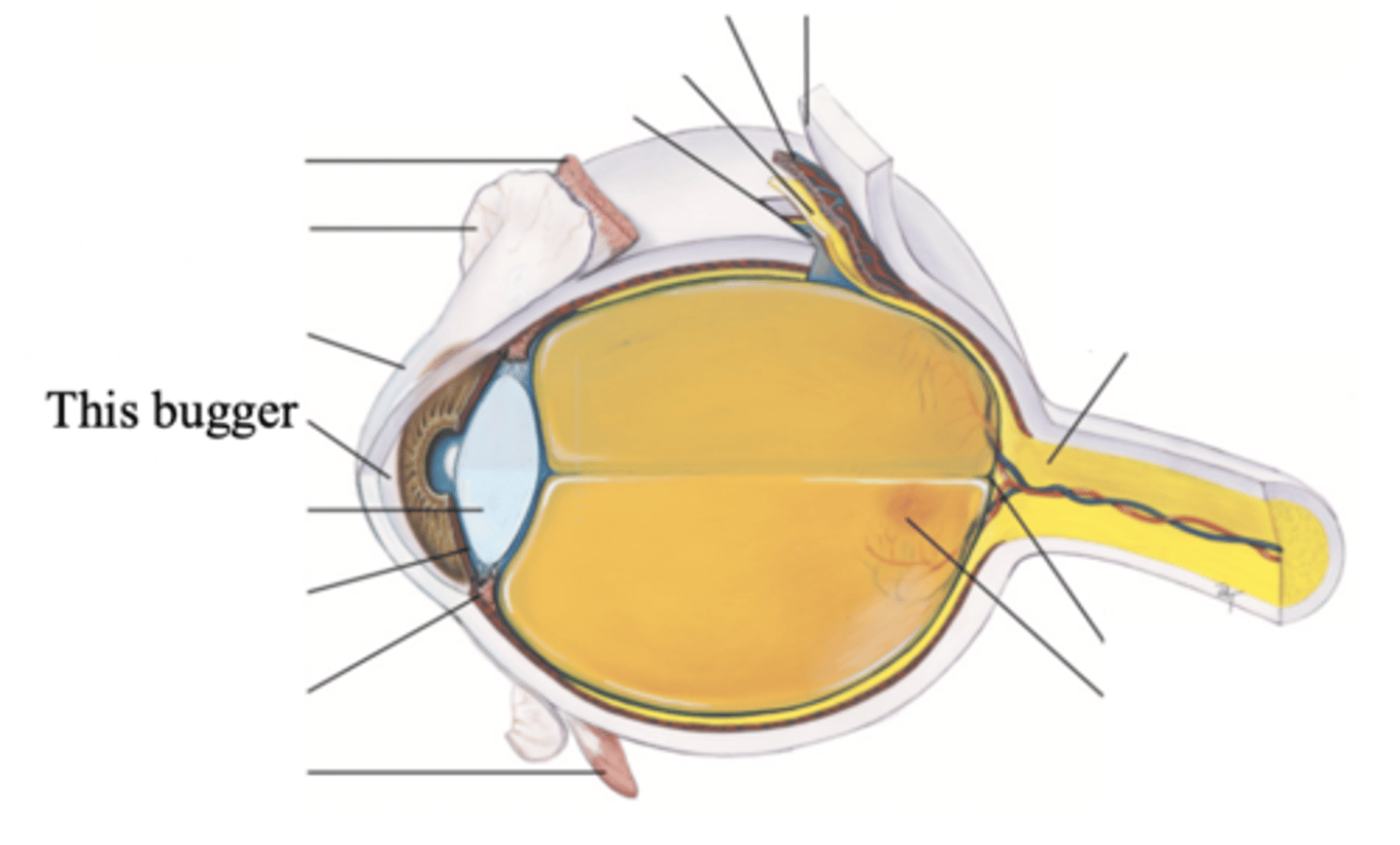
Posterior Chamber
The chamber located behind the iris to the sides of the lens
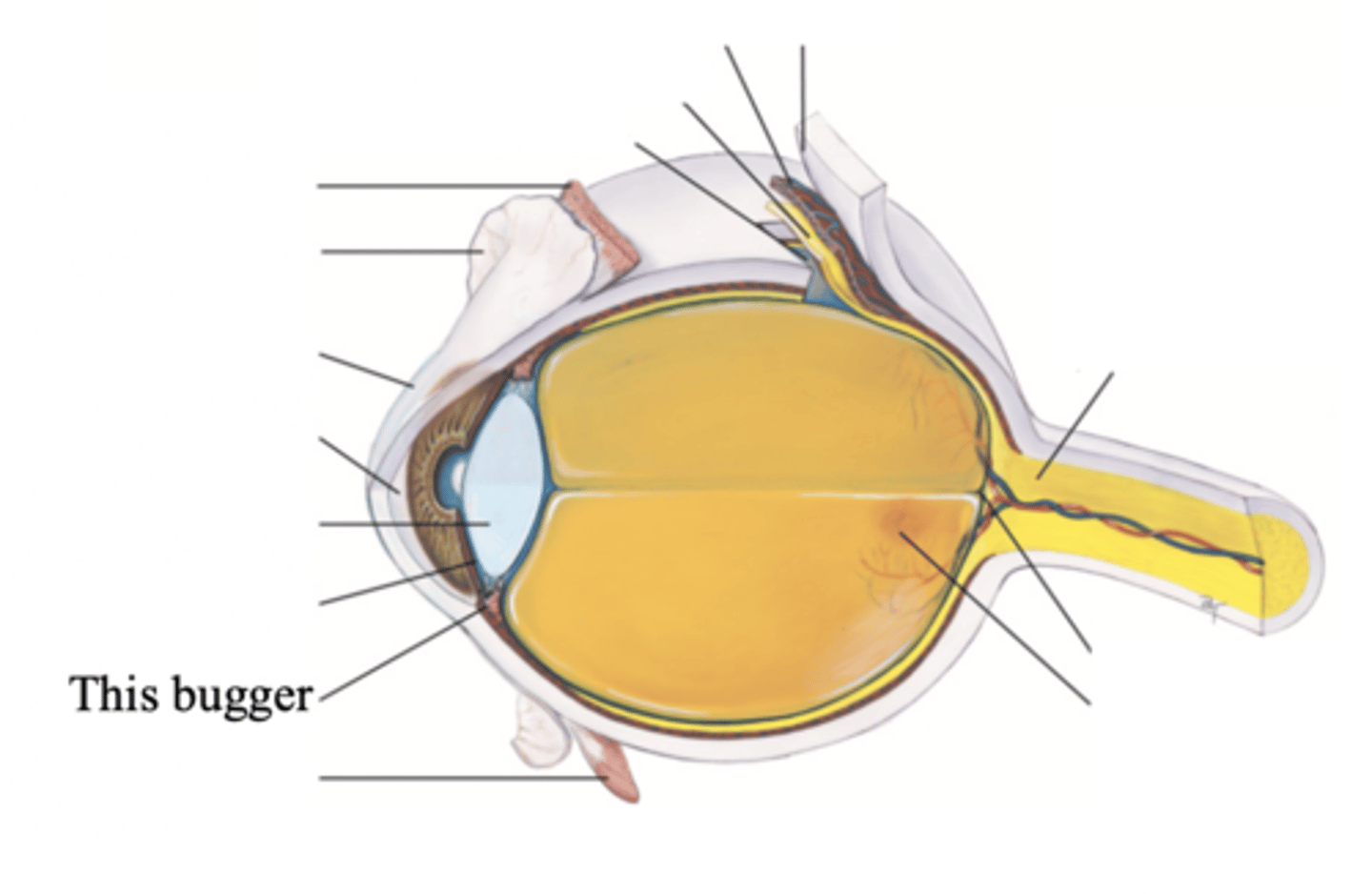
Major Structures of the Inner Nervous Retina
- Optic disc
- Retina vessels
- Macula
- Fovea centralis
Retina
The visual receptive layer of the eye in which light waves are changed into nerve impulses
Optic Disc
The area in which fibres from the retina converge to form the optic nerve
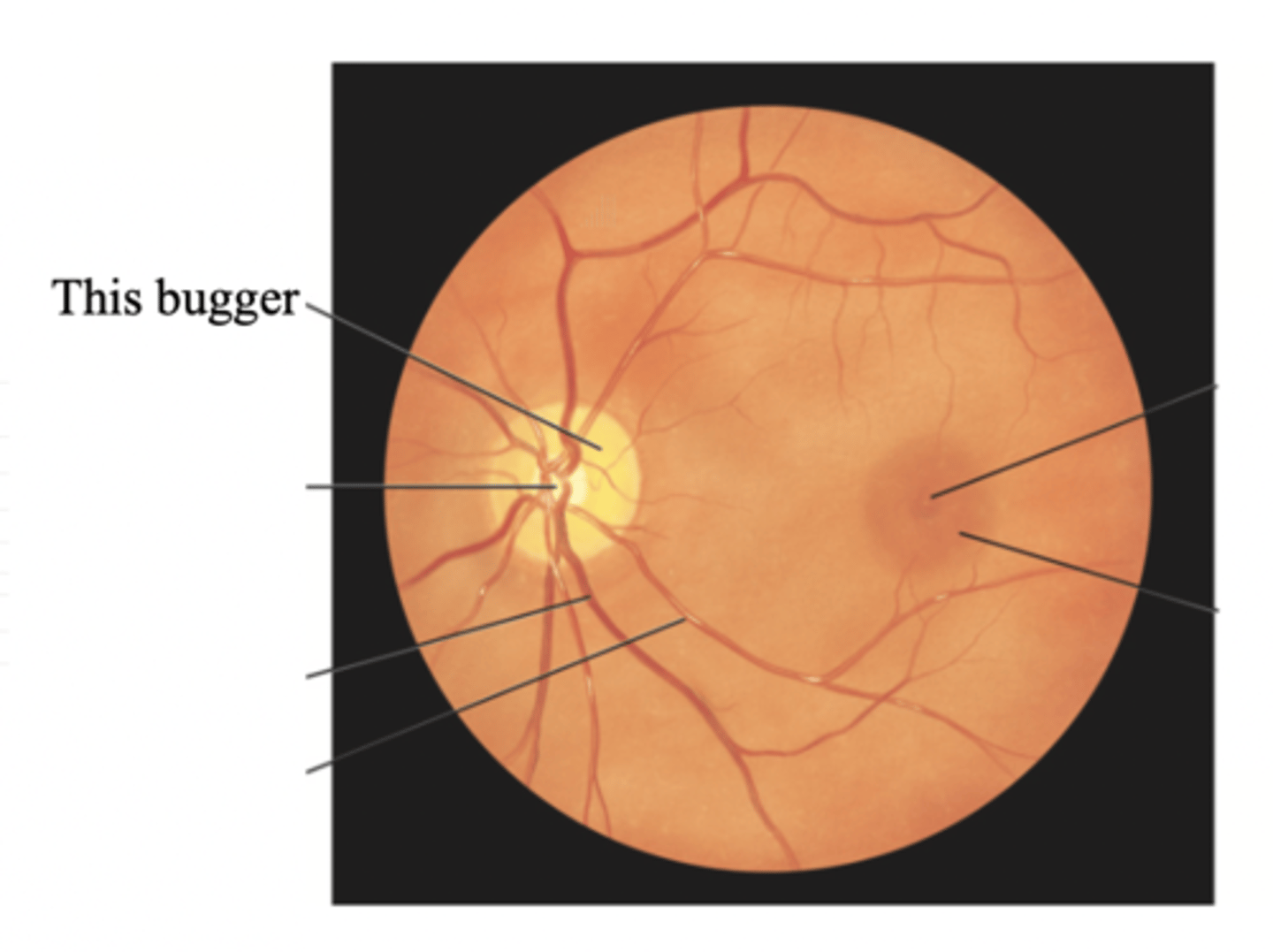
Retinal Vessels
Vessels of the retina, which normally include a paired artery and extend to each quadrant, growing progressively smaller in caliber as they reach the periphery
Macula
Round darker area of the ocular fundus that mediates vision only from the central visual field
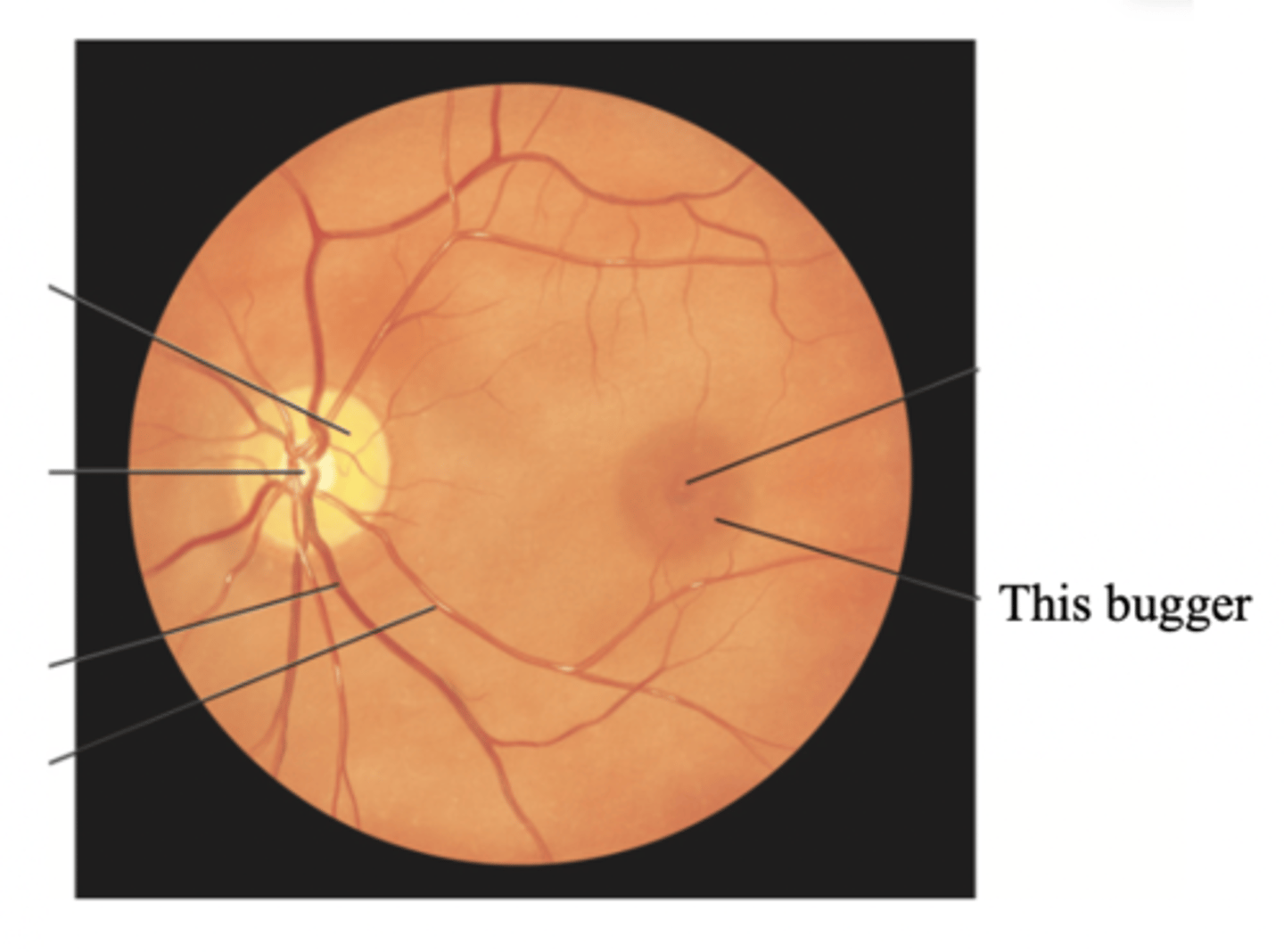
Fovea Centralis
Tiny pit or depression in the retina that is the region of clearest vision
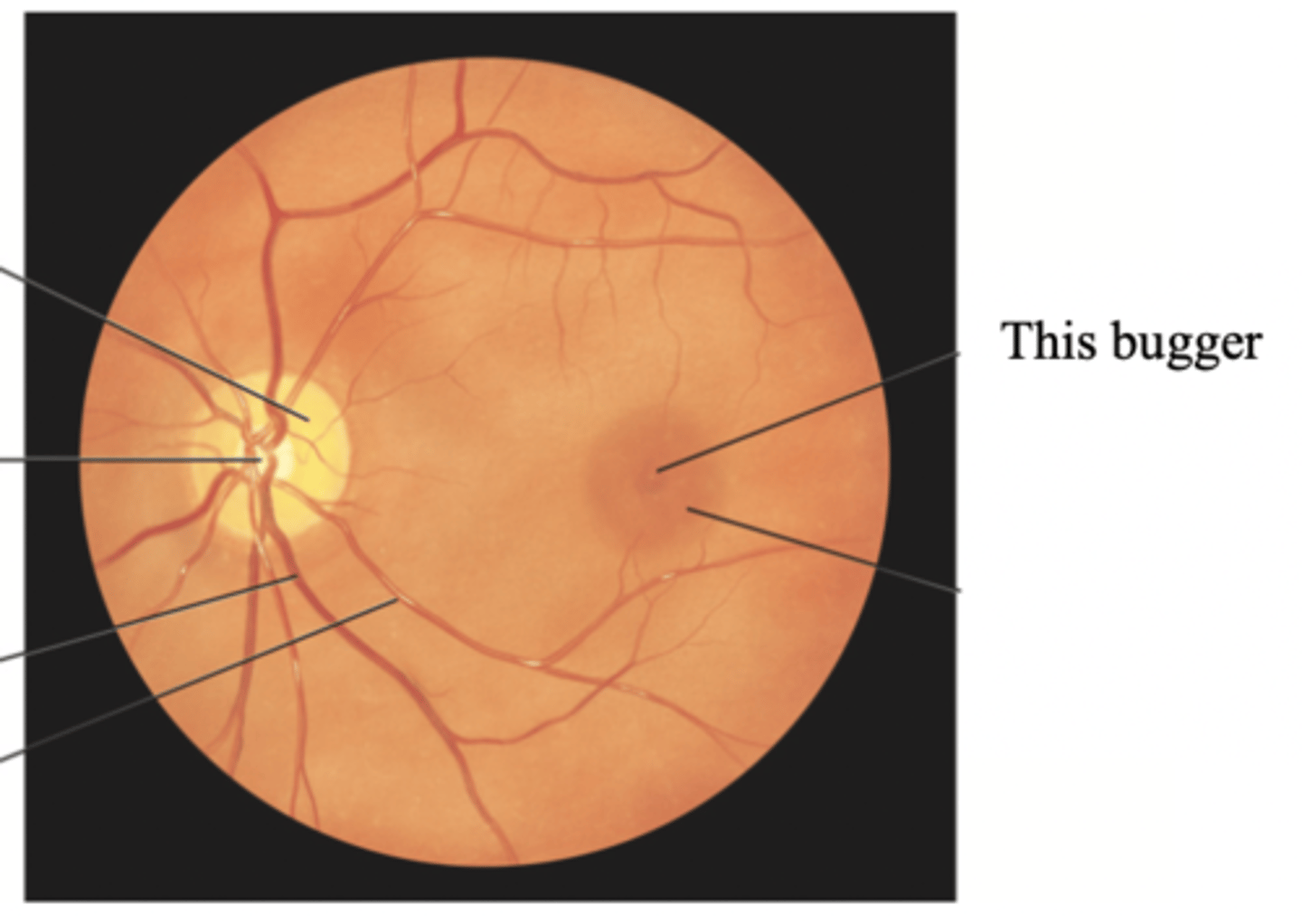
Pupillary Light Reflex
The normal constriction of the pupils when bright light shines on the retina
Fixation
A reflex direction of the eye toward an object attracting a person's attention
Accomodation
The adaptation of the eye for near vision by increasing the curvature of the lens through movement of the ciliary muscles
Developmental Considerations Related to the Eyes for Infants and Children
- Peripheral vision is intact for newborns
- Can can fixate on a single image with both eyes simultaneously (binocularity) by 3-4 months
- Macula matures at 8 months
- Decrease in farsightedness by 7-8 years
- The eyeball reaches adult size by 8 years
Developmental Considerations Related to the Eyes for Adults
- Presbyopia
- Macular degeneration
- Cataracts
- Glaucoma
- Diabetic retinopathy
Myopia
Nearsightedness
Hyperopia
Farsightedness
Presbyopia
A condition in which the lens loses elasticity, becoming hard and glasslike, which decreases the lens's ability to change shape to accommodate for near vision
Cataracts
Clouding of the lens
Glaucoma
Increased intraocular pressure
Diabetic Retinopathy
A condition in which the blood vessels in the retina becomes blocked or damaged due to a high blood sugar level, eventually leading to loss of vision
Subjective Data to Assess for the Eyes
- Visual difficulty
- Pain
- Strabismus/diplopia
- Redness/swelling
- Watering/discharge
- History of ocular problems
- Glaucoma
- Use of glasses or contact lenses
- Self-care behaviours
- Medications
- Coping with vision changes/loss
Strabismus
A deviation in the anteroposterior axis of the eye
Diplopia
The perception of two images of a single object
Additional Health History Questions Related to the Eye for Infants/Children
- Mother's vaginal infection during delivery
- Developmental milestones
- Routine vision testing
- Safety measures
Additional Health History Questions Related to the Eye for Older Adults
- Movement and visual difficulty
- Glaucoma testing
- Cataracts
- Dryness of eyes
- Decreased activities
Equipment Needed for an Objective Physical Exam of the Eye
- Snellen eye chart
- Handheld visual screener
- Opaque card or occluder
- Penlight
- Applicator stick
- Opthalmascope
Objective Assessments for an Eye Exam
- External ocular structures
- Central visual acuity
- Visual fields
- Extraocular muscle function
- Anterior ocular structures
- Ocular fundus
What to Inspect for External Ocular Structures
- Eyebrows
- Eyelids
- Eyeballs
- Conjunctiva and sclera
- Lacrimal apparatus
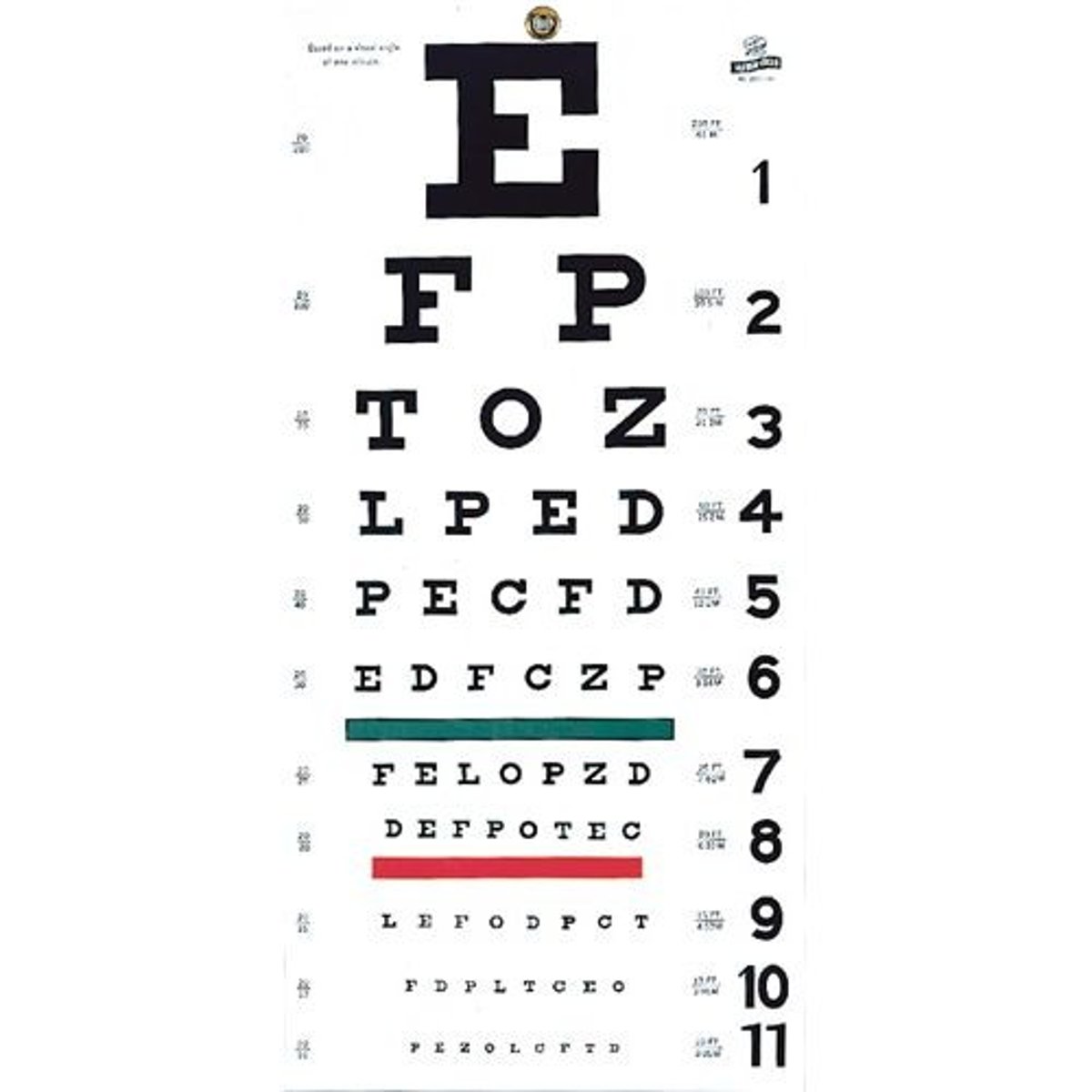
Snellen Eye Chart
Eye chart used by eye care professionals and others to measure visual acuity
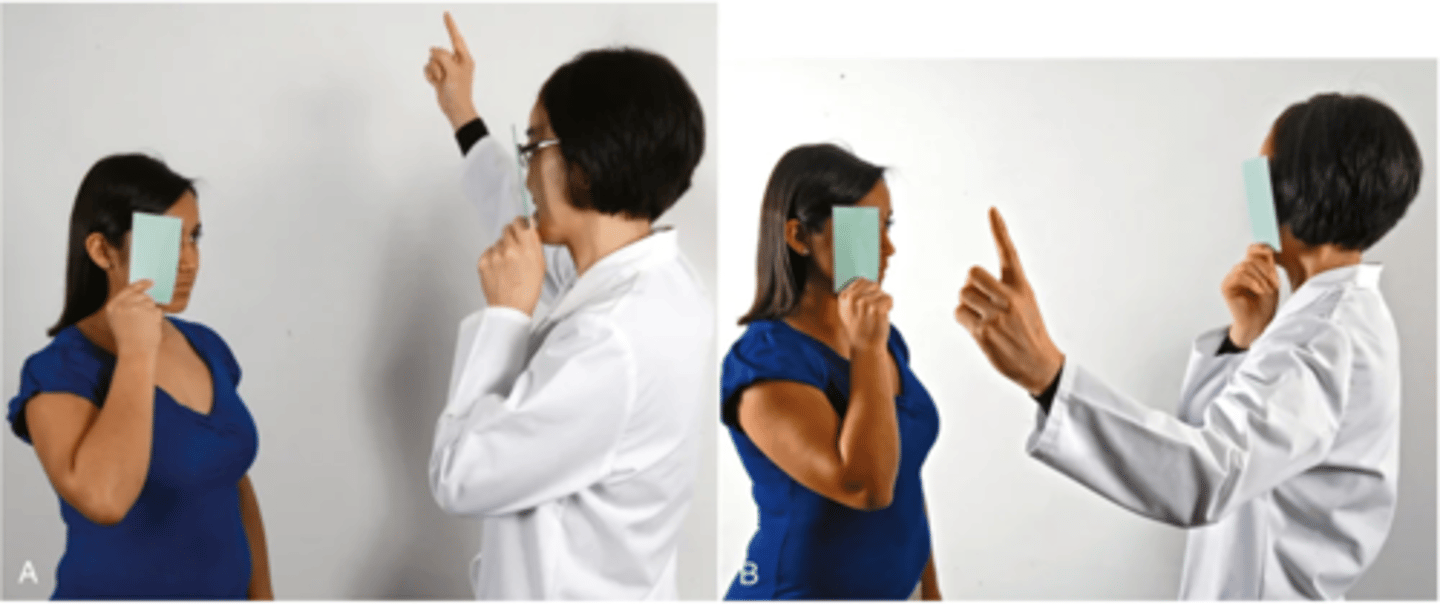
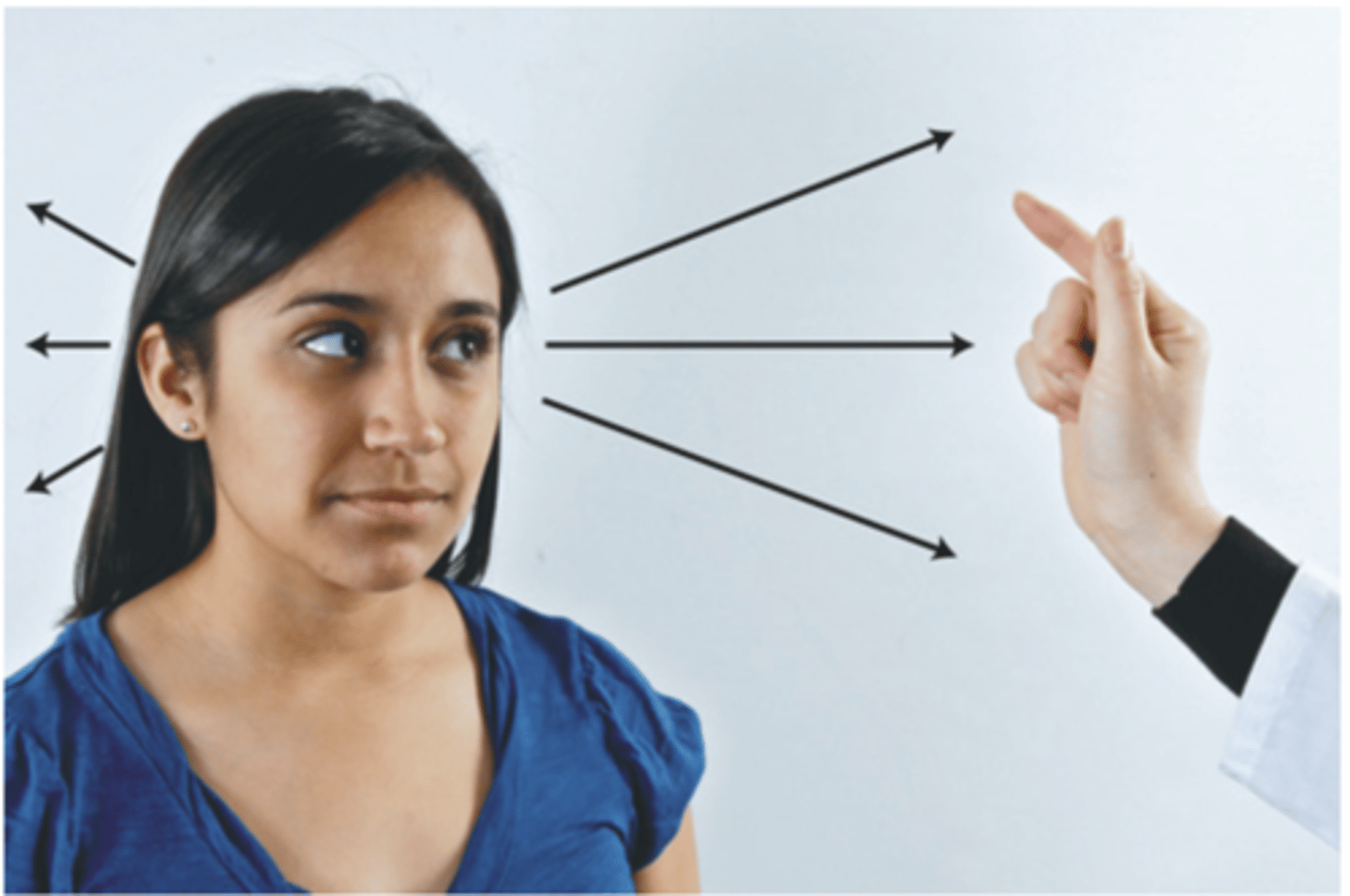
Confrontation Test
A gross measure of peripheral vision where the patient's peripheral vision is compared with your own, if yours is normal; tests visual fields

What to Inspect for Extraocular Muscle Function
- Corneal light reflex
- Cover-uncover test
- Diagnostic positions
Corneal Light Reflex (Hirschberg's Test)
A test in which you shine a light toward the patient's eyes and assess the reflection of the light on the corneas; they should be on the same spot on each eye
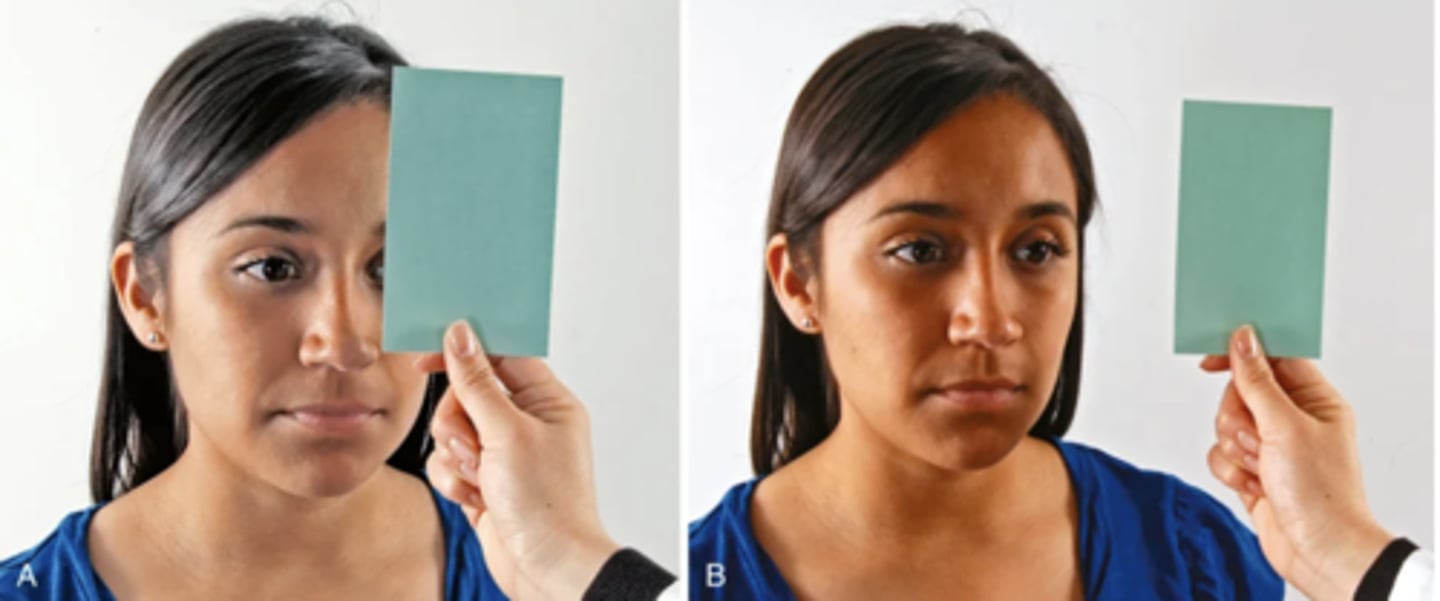
Cover-Uncover Test
- A test in which you cover one eye of the patient and ask them to stare straight ahead
- Detects small degrees of deviated alignment
- A normal response is a steady fixed gaze of the steady eye

Diagnostic Positions Test
- A test in which you move your fingers through the six cardinal positions of gaze and ask the patient to follow it
- Reveals any muscle weakness during movement
- A normal response is parallel tracking of the object with both eyes.
What to Inspect for Anterior Ocular Structures
- Cornea
- Lens
- Iris
- Pupil
PERRLA
- Pupils equal
- Round
- Reactive to light and accommodation
What to Inspect for the Occular Fundus
- Red reflex
- Optic disc
- Retinal vessels
- Fundus background
- Macula