ED 25. Light
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Photoreceptors
Photoreceptors are the ‘Detectors’:
PSII
Cryptochrome
Phototropin
Zeaxanthin
Phytochrome
Arabidopsis thaliana
model organism - ‘botanists fruit fly’
analysis of mutants lacking some responses to light
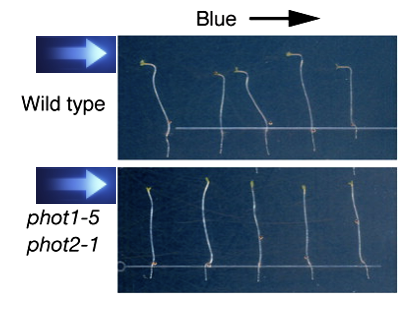
- nph1 (non-phototropic hypocotyl) - phototropin 1 gene
- phototropins are blue light sensing chromo-proteins
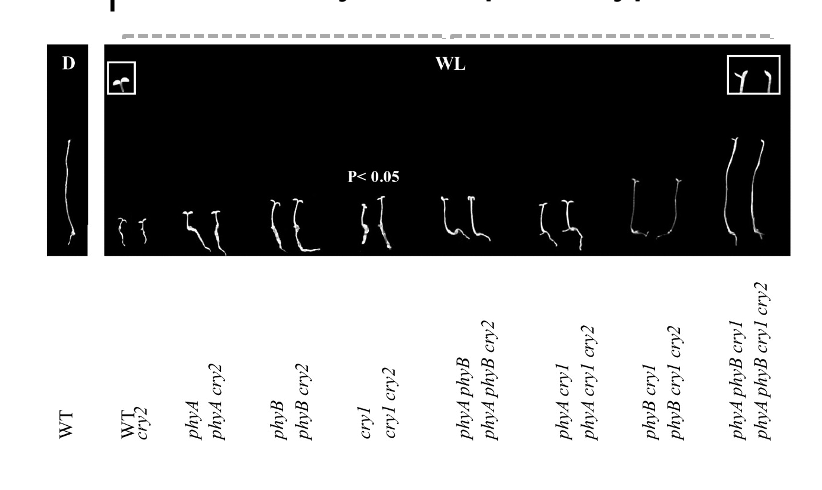
Loss of photoreceptor function dramatically alters phenotype
Colour pic Figure 3. De-etiolation in Arabidopsis seedlings. Genotypes shown are: wild type (A), and mutants in phyA (B), phyB (C), phyBDE (D), phyABE (E) and phyABDE (F).
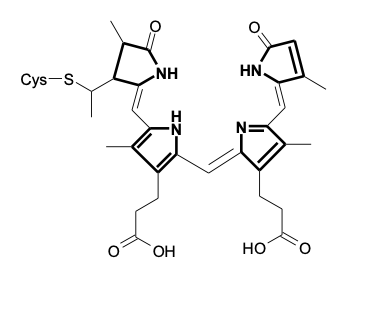
Phytochromes are red-light photoreceptors
phytochromes are light absorbing molecules found in all green plants
they respond mainly to red and far-red light
dimetric proteins
tetrapyrrole chromophore - phytochromobilin
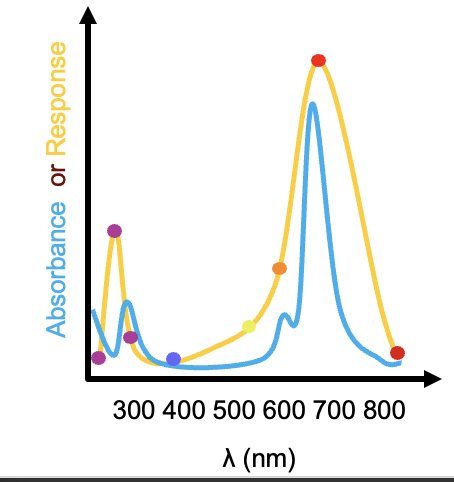
Action spectra help identify chromophores
measure germination of seedlings exposed to different coloured lights
compare this to phytochrome absorbance spectrum
Photomorphogenesis
photomorphogenesis - this is the control of growth and morphology by light
De-(etiolation
Circadian rhythms
Flowering
High irradiance response
measures quantity of light
irradiance is quantum flux - units micromol photons per m2 per second
tells the plants to start chlorophyll synthesis and stop etiolation response
Phytocrhome-A and cryptochrome
Low fluence response
measures quality of light (ratio of red to far-red), mainly Phytochrome-B
Fluence - > micromol photons per m2 (time not so important)
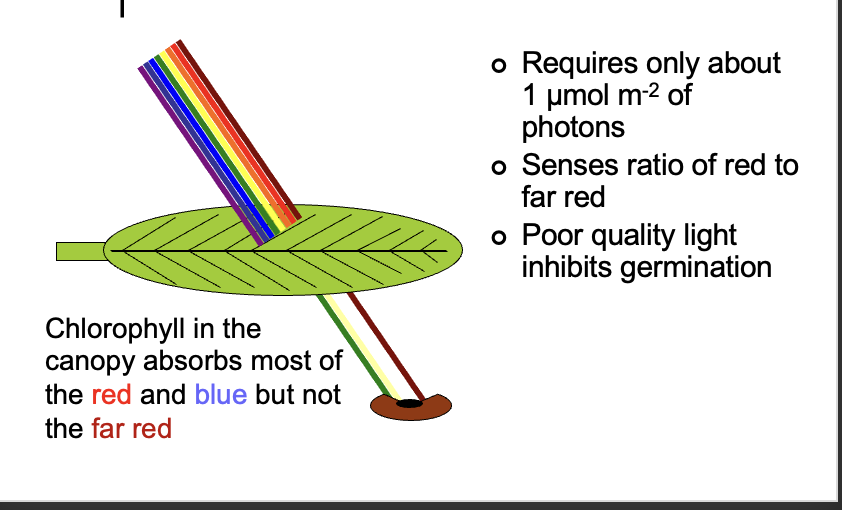
lettuce seeds need light to germinate
red light stimulated germination but far red reversed the effect

Red to far-red ratio
Mechanism of LFR
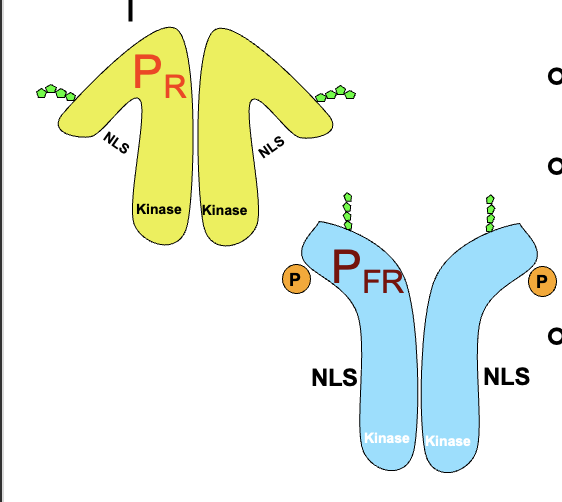
phytochromes exist in two forms that are interconverted by red and far-red light
phytochromes are synthesised as inactive PR which absorbed red light
PFR is the active form, and absorbs far-red
High [PFR] → lack of shading → stimulates germination → adaptive
PFR slowly reverts to inactive PR form
Photoreversible process
![<ul><li><p>phytochromes exist in two forms that are interconverted by red and far-red light </p></li><li><p>phytochromes are synthesised as inactive P<sub>R</sub> which absorbed red light </p></li><li><p>P<sub>FR</sub> is the active form, and absorbs far-red </p></li><li><p>High [P<sub>FR</sub>] → lack of shading → stimulates germination → adaptive </p></li><li><p>P<sub>FR</sub> slowly reverts to inactive P<sub>R</sub> form</p></li><li><p>Photoreversible process </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3aecbd4e-ce71-44d3-bc4a-36f2e9260dbd.png)
Phytochrome signalling
PFR has exposed NLS
PFR kinase activity starts a signalling cascade
PFR acts on transcription factors
Biological clock
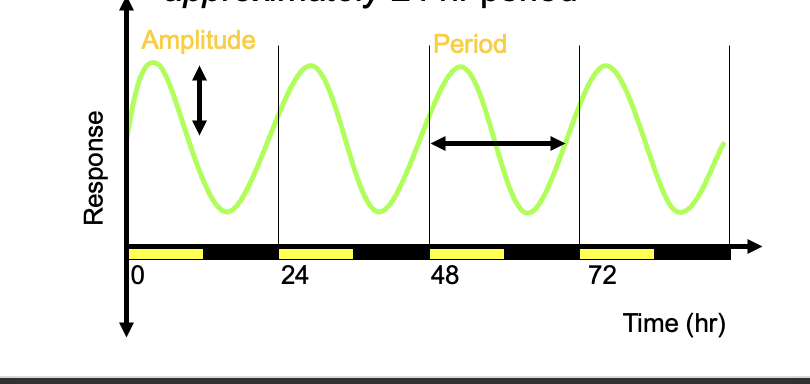
circadian rhythms are controlled buy a biological clock
can anticipate the needs of the day → stomata open before dawn, flower opening (photonasty) to match pollinator activity
Period
the oscillator usually runs with an approximately 24hr period
Free-running
if plants are grown under constant conditions, they will free run
many plants show free running period faster or slower than 24hr

Attentuation
if the plants are kept in a constant environment for a long time, circadian rhythms fade away
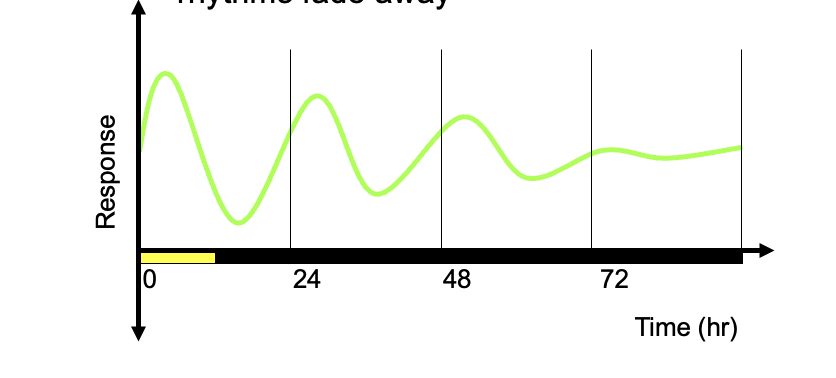
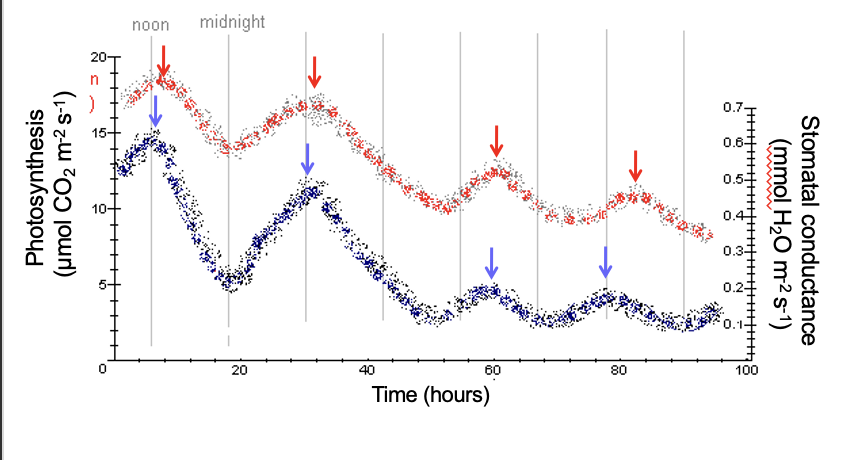
Real data: stomatal rhythm under constant light
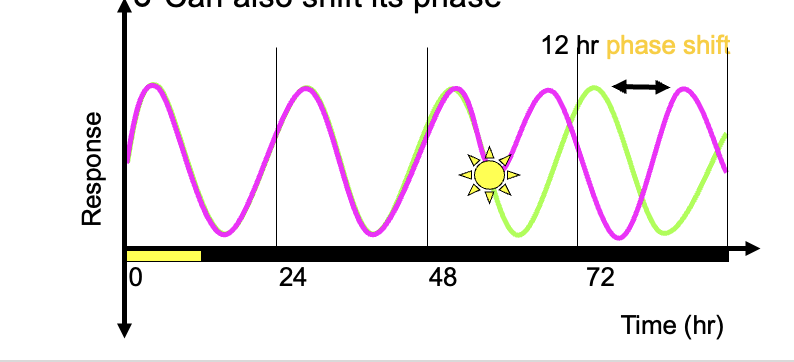
The clock is entrained by Zeitgebers
normal zeitgeberis daybreak which resets the clock daily
can also shift its phase
Genetic observations
We cannot ‘see’ the biological clock directly
look at functions it controls
free-running period is genetically controlled

Clock genes and mutants suggest a mechanism - three genes at once
Many genes show rhythmic transcription

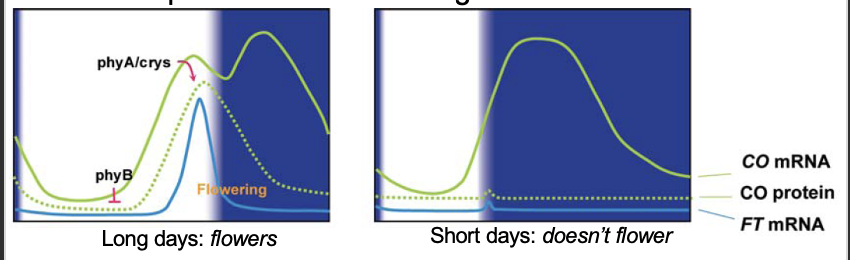
Connecting photoreceptors and the clock
circadian transcription of flowering gene CO
PHYB causes CO protein degradation
PHYA and CRY stabilise CO protein in long days
CO protein induces FT expression
FT protein is the flowering hormone