Chapter 8 Control Gene expression
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Does every cell have the same genome
yes
Why does a cell change it’s gene expression
in response external signals
What is the main way to regulate the central dogma
Transcription control, in other words making RNA in the first place
Whats a cool fun fact about portein
most proteins need post-translational modifications to be fully active
If the 3’ end carries an OH group what does the 5’ end carry
a Phosphate group
How does is there regulation from RNA to mRNA
Splicing
How is exporting of mRNA regulated
where it’s moved from different cell via the 3’ UTR and weather it’s degraded or not
What is the formation of most regulator proteins
alpha heliceis
Why are most regulator proteins alpha helicies
Because it allows the protein to fit into major grooves of DNA and form tight associations with it’s base pairs
Where do regulator proteins/homeodomains interact
major grooves but can be minor grooves to
How do regulator proteins detect the specific sequence of DNA it wants to target
it uses it’s amino acid’s hydrogen bond (ionic bond and hydrophobic interactions) to ‘feel’ the dna sequence it wants to target
When homeodomains and regulators hydrogen bond with the DNA does it disrupt the base pair hydrogen bond interaction
No
What is a homeodomain
When a regulator protein interacts with DNA
What is translational control on mRNA
we can control when mRNA is translated
(it can exist outside of the nucleus but untranslated just sitting there waiting for it to be translated)
What is example of protein activity control
phosphorylation of protein to turn it on or off
How many different types of controls of protein activity/making is there
roughly 7
In Logo Diagrams what does each letter represent
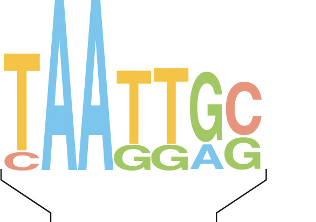
The nucleotide frequency that a protein regonizes in a specific sequence of ONE STRAND
Where does transcription regulator bind too
regulatory sequences
What does transcription regulators dimer do
it increases strength of protein DNA interaction
What must happen for transcription regulators to be dimer
the sequence that the monomer binded to must be repreated
How is DNA regulated
either it can be tightly coiled by nucleosomes/histomes or very loose and accessible
What is chromsome
DNA in it’s most packed state nothing can bind to DNA
What two proteins recognize a transcription regulator and binds to it to unwinding chromatin fibers
histone acetyltransferases and ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complex
How does ATP-Dependent chromatin remolding complex work
Binds to transcription regulator that sits on top of chromatin fiber and starts to unwind the chromatin fiber near by
How does histone acetyltransferase work
adds acetyl groups to histone so proteins can bind to it and start transcription
Is there long distance interaction with enhancers and transcription factor
Yes
What does an Enhancers do
They increase probability of transcription working and rate, but they can be found thousands of base pairs away
How do enhancers reach promoter region
2 ways either a clamping technique or just attracting the general transcription factors
What binds to enhancer region
an activator protein
What does an activator protein do
stabilize overall sequence that promotes transcription by binding to a mediator complex
What does a mediator complex do
acts as a mediator between activator protein and transcription factors to stabilize and start RNA polymerase
How is the clamp between enhancer and promoter region created
by chromosome loop-forming clamp proteins (2 is needed)
What is the more formal name for the loop the chromosome loop forming clamp proteins create
topological associated domains
What is the difference between transcription regulator and transcription factor
Transcription regulators are not found at promotor regions while transcription factors are found there
True or False: A single transcription regulator can help express many different genes
True
How do some cells turn on transcription due to external stimuli
They have an activator protein that binds to a transcriptional regulator to turn on transcription
What 3 regulation factor make a cell act like a stem cell
Klf4, Sox2, Oct4
How does a cell get locked into their fate
Some times a gene makes a protein, that protein circles back increase transcription of that gene this allows cells to keep their identity even after dividing as the same process will occur
Is there memory from cell dividing
yes, because once you make a protein it can feedback and increase transcription (have to be an activator)
Why can’t you have a memory as a repressor
because it turns the “gene” off
Can transcription regulators activate/repress different genes
yes because they will bind different transcription factors
What does miRNA do
they fold on themselves and a portion of it is broken down on each other than the RISC protein comes and unwinds it to make it single stranded
What does the miRNA and RISC complex do
if it all the bases pairs on miRNA and mRNA match then RISC + miRNA complex degrades the mRNA via nuclease found in RISC
if some of the base pairs from mRNA and miRNA align then mRNA gets either degraded or stuck so it can’t go through translation where nuclases can destroy it
What is RNA interference
a defense mechanism with double stranded RNA is cleavage by dicer protein, and the small pieces pair with RISC to target viral RNA that initially hit
What is LncRNA
long non coding RNA it’s used to bind to protein to the bind to DNA