Quiz 7: Pharmacotherapy (Tschumperlin)
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
Why is the prevalence of HF increasing over time?
aging population + patient indentify earlier
( better HTN, CAD tx +improved MI survival) → more people live long enough to develop HF,
What is the 5-year mortality after HF diagnosis?
approximately 50%
Why does HF have mortality similar to many cancers?
persistent neurohormonal activation leads to progressive structural remodeling, not just symptoms
Why are hospitalizations a critical target in HF management?
hospitalization signals clinical decompensation, predicts mortality, and worsens outcomes
What does Stage C heart failure represent?
structural heart disease WITH symptoms of HF
AHA/ACC: Stage A
at risk for structural heart disease
AHA/ACC: Stage B
asymptomatic
AHA/ACC: Stage D
end stage heart failure
Why is once-diagnosed HF never reversible to earlier stages (A → B → C → D)?
structural myocardial changes are progressive even if symptoms improve

Which NYHA class corresponds to symptoms with less-than-ordinary exertion?
Class III
NYHA Class I
no symptoms with ordinary activity
NYHA Class II
SOB and fatigue with ordinary activity
NYHA Class IV
SOB and fatigue at rest
How does NYHA class differ from ACC/AHA stage?
NYHA fluctuates with symptoms; ACC/AHA is permanent once criteria met

Define HFrEF
LVEF ≤40% (reduced EF / systolic dysfunction)
Why do HFrEF patients respond better to neurohormonal therapies than HFpEF patients?
HFrEF is primarily neurohormonal-driven remodeling, which is drug-modifiable
What EF defines HFpEF?
≥50% with elevated filling pressures
Why is HFpEF harder to treat?
the issue is diastolic compliance, not contractility, and there is no single targeted mechanism
Why does HFpEF maintain normal EF despite symptoms?
the ventricle is stiff, causing ↓ filling, preserving EF but lowering cardiac output
Which systems are activated in HF compensation?
RAAS, SNS, ADH
Why does chronic RAAS/SNS activation worsen HF long-term?
it causes cardiac remodeling, fibrosis, vasoconstriction, and volume overload
What are the four foundational drug classes in HFrEF?
1. ARNI/ACEI/ARB
2. Evidence-based β-blocker
3. SGLT2 inhibitor MRA(spironolactone/eplerenone)
Why must all four pillars be started as early as possible?
each acts on different disease pathways, and delaying therapy predictably increases mortality
AHA/ACC HF Guidelines
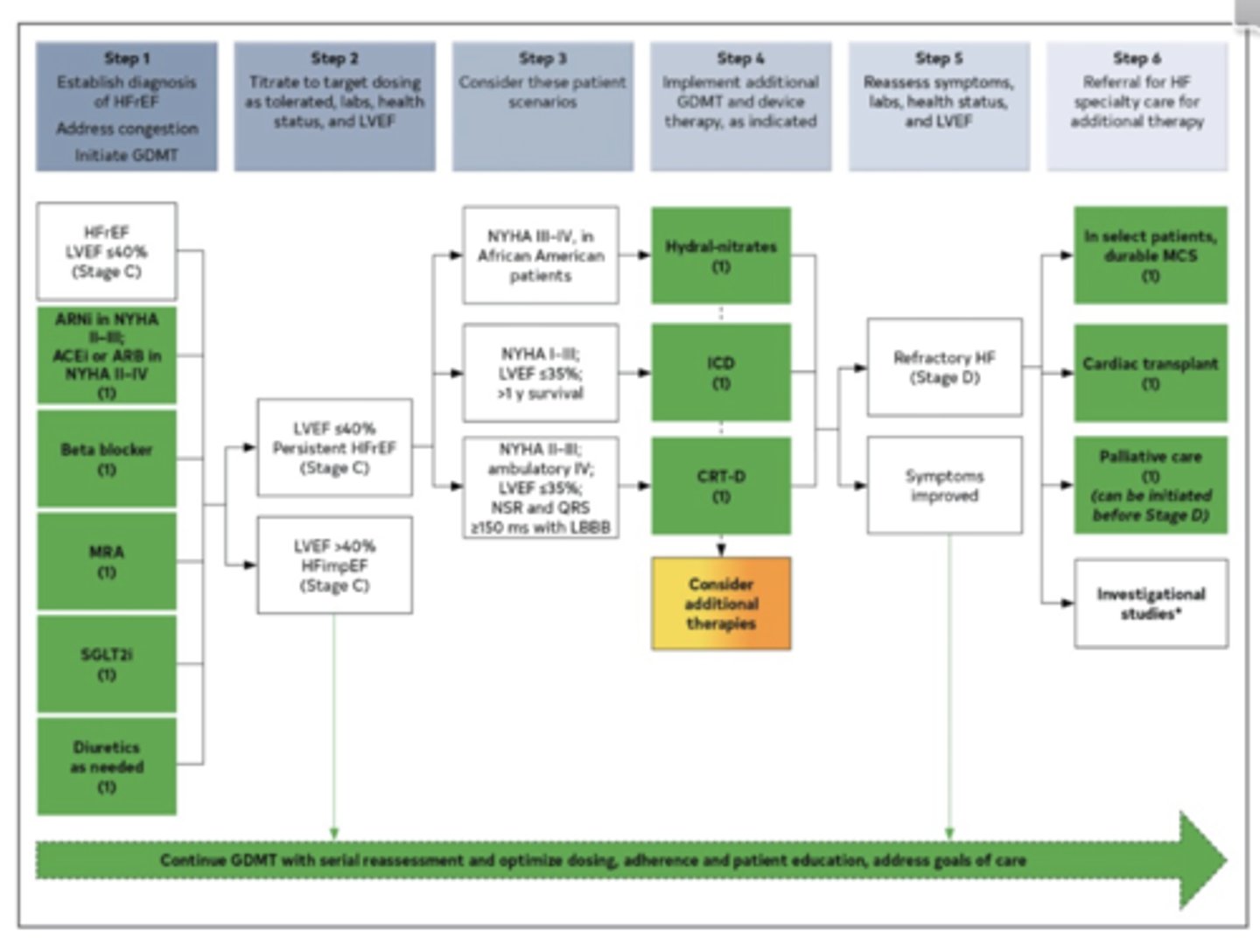
What is the target dose of sacubitril/valsartan?
97/103 mg BID
Sacubitril/valsartan: Starting dose and titration?
Start 24/26 mg BID (or 49/51 mg BID if stable)
- double every ~2 weeks to target
What adverse effect of sacubitril/valsartan may limit titration?
hypotension (due to vasodilation)
Why must ACE inhibitors be stopped 36 hours before starting sacubitril/valsartan?
to prevent life-threatening angioedema from dual neprilysin + ACE inhibition
Why is ARNI preferred over ACEI in HFrEF?
ARNI reduces CV death + hospitalization more (PARADIGM-HF trial)

What is the target dose of lisinopril for HFrEF?
20-40 mg daily
Starting Dose for HF: Lisinopril
2.5-5 mg once daily
What is the target dose of enalapril for HFrEF?
10-20 mg daily
Starting Dose for HF: Enalapril
2.5 mg BID
What is the target dose of ramipril for HFrEF?
10 mg once daily
Starting Dose for HF: Ramipril
1.25-2.5 mg once daily
What are the key adverse effects of ACE inhibitors?
dry cough, hyperkalemia, renal dysfunction, angioedema
What is the main safety concern when combining ARNI with ACE inhibitors?
Angioedema → requires 36 hr washout when switching from ACEI to ARNI
When to use ACEI instead of ARNI?
If ARNI cost, hypotension, or 36-hour washout needed post-ACEI prevents transition

What is the primary role of ARBs in HFrEF?
reduce mortality in HFrEF and are used when ACEi or ARNI aren't feasible (ACEi intolerance) or as a bridge to ARNI to avoid the ACEi washout

What is the general titration strategy for ARBs in HFrEF on the slides?
start low and uptitrate every 1-4 weeks as tolerated
When switching from an ARB to ARNI, do you need a washout?
No washout is needed (only ACEI requires washout)
What is the HF starting dose for losartan and its target dose?
Start 25-50 mg once daily
- target 150 mg once daily (HF targets)
What is the HF starting dose for valsartan and its target dose?
Start 40 mg twice daily
- target 160 mg twice daily (HF targets)
What are the key adverse effects of ARBs?
hyperkalemia and renal dysfunction, but no cough
What monitoring is required for ARNI, ACEI, and ARBs?
BP, K⁺, and renal function (SCr)
What are the approved β-blockers for HFrEF?
carvedilol, metoprolol succinate, and bisoprolol
β-blocker Target Dose for HF: Carvedilol
25 mg BID (<85 kg) or 50 mg BID (≥85 kg)
β-blocker Target Dose for HF: Metoprolol
200 mg daily
β-blocker Target Dose for HF: Bisoprolol
10 mg daily
Why must β-blockers be started low and titrated slowly?
acute negative inotropy can worsen HF if overloaded → ensure euvolemia first
Why should beta blockers be started only when the patient is euvolemic?
initiating during congestion can worsen heart failure symptoms due to initial decrease in contractility
During BB titration, what is the main marker of intolerance, and what do you adjust?
fatigue / dizziness / low heart rate → reduce dose, do NOT discontinue unless severe
What side effects are common when first starting or increasing beta blockers?
fatigue, dizziness, worsening HF symptoms if volume overloaded
What must be ensured before increasing BB dose?
patient must be euvolemic (not fluid overloaded)
HR returns 1 month later. HR now 55-62 on max tolerated beta blocker. Weight stable. What is the best action?
continue current dose
3 multiple choice options
Which two SGLT2 inhibitors are guideline-directed for HFrEF?
dapagliflozin 10 mg daily & empagliflozin 10 mg daily
When is SGLT2 inhibitor use contraindicated in HFrEF?
patient is on ESRD or dialysis
Why do SGLT2 inhibitors work even without diabetes?
benefit is hemodynamic & cellular, not glucose-dependent
Why do SGLT2 inhibitors improve heart failure outcomes?
reduce preload and afterload via osmotic diuresis + improve cardiac metabolism
What is the main adverse effect of SGLT2 inhibitors?
genital yeast infections due to glucosuria
When should SGLT2 inhibitors be held temporarily?
during acute illness or dehydration
When is MRA indicated in HFrEF?
if EF ≤35% and K+ <5.0 and eGFR >30
Which MRA is more likely to cause gynecomastia?
spironolactone
What should be checked 3-7 days after starting or increasing MRA dose?
potassium and serum creatinine
Why monitor potassium closely?
hyperkalemia risk, especially with ACEI/ARB/ARNI
What is the purpose of diuretics in HF?
symptom relief, not mortality benefit
Why should diuretics not be used alone without GDMT?
they do not halt disease progression
What is the preferred initiation sequence in stable HFrEF?
start ARNI + β-blocker + SGLT2i + MRA as soon as tolerated
Why don't we wait to titrate one drug fully before adding another?
delaying therapy increases mortality because each class has additive benefit
NS has EF 35%, mild symptoms, BP 135/78, HR 68. Which is the most appropriate initial GDMT sequence?
start ACEI/ARB/ARNI + beta blocker + MRA + SGLT2 inhibitor
3 multiple choice options
A patient with symptomatic heart failure and an ejection fraction of 39% would ?belong to which category?
HFrEF
3 multiple choice options
Which of these agents is NOT a pillar of HFrEF therapy?
Furosemide
3 multiple choice options
For a HFrEF patient, metoprolol succinate is titrated to which of following targets?
Dose
3 multiple choice options
What is dyspnea on exertion and what does severity correlate with?
shortness of breath during activity; less activity needed = more severe HF
Why do HF patients experience a non-productive cough?
pulmonary congestion from fluid accumulation
What is pulmonary edema and its key sign?
fluid in lungs; may cause pink, frothy sputum
What is orthopnea?
dyspnea when lying flat, relieved by sitting up
What is Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND)?
sudden nighttime shortness of breath due to increased venous return when lying down
What causes peripheral edema in HF?
fluid retention → swelling in legs/ankles (sock line often noted)
Why do HF patients experience GI fullness and nausea?
liver congestion → early satiety, bloating
Why is fatigue common in HF?
reduced cardiac output → hypoperfusion of tissues
What physical sign suggests peripheral hypoperfusion?
cool extremities
What HF symptom results from decreased cerebral perfusion?
confusion, lethargy, impaired cognition
What lab trends may indicate renal hypoperfusion?
rising SCr or worsening kidney function over time
Why do HF patients experience polyuria early on?
increased natriuretic peptide release due to fluid overload
Why does nocturia occur?
increased nighttime renal perfusion when sympathetic tone drops in sleep
What is jugular venous distention (JVD) a sign of?
volume overload / congestion
What is the normal JVP measurement?
about 3 cm
What heart sound is associated with increased preload?
S3 gallop ("ventricular gallop")
hat heart sound is associated with stiff, non-compliant ventricle?
S4 gallop
What are pulmonary rales/crackles caused by?
fluid in alveolar spaces
What causes hepatomegaly in HF?
hepatic venous congestion
What test measures ejection fraction in HF?
echocardiogram
When is cardiac catheterization used in HF?
to evaluate ischemic vs non-ischemic etiology
What does a BNP >100 pg/mL suggest?
Heart failure (rule-in)
Why may BNP be lower in some HF patients?
obesity reduces BNP levels
Why may BNP be higher even without worsening HF?
renal dysfunction or older age increases BNP
How often should HF patients weigh themselves?
daily, ideally in the morning before eating
How much weight gain should trigger patient self-intervention/call?
>3 lbs/day or >5 lbs in a week
Why is daily weight monitoring critical in HF?
weight changes reflect fluid shifts, not dietary calories