CNA Foundations
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Integumentary System
The body system that includes the skin, hair, nails, and associated glands. It serves as a protective barrier against infection, helps regulate body temperature, prevents dehydration, and allows for the sensation of touch, heat, and pain.
Why do CNAs need to know about the integumentary system?
To prevent bed sores and pressure ulcers
Clean, dry and intact
Describes healthy skin that is free from dirt, moisture, and any open areas or wounds. The skin is hygienic, not wet or sweaty, and has no cuts, tears, or breakdowns.
Pressure Ulcer
An injury to the skin and underlying tissue caused by prolonged pressure on the skin, often over bony areas like the tailbone, hips, or heels. Also known as a bed sore or pressure sore, it can range from red, unbroken skin to deep wounds exposing muscle or bone.
Pathogen
A type of microbe that causes disease or infection in the body. All pathogens are microbes, but not all microbes are pathogens.
Microbe
A microscopic organism, such as a bacterium, virus, fungus, or protozoa. Some microbes are harmless or even helpful, like those that aid digestion.
How do you prevent pressure ulcers in bed ridden patients?
Reposition them every 2 hours
Which points on the body are most likely to develop pressure ulcers?
Heels
Ankles
Hips
Tailbone (sacrum/coccyx)
Elbows
Shoulder blades
Back of the head
Knees
Urinary System
Removes waste and extra fluids through urine. Main parts: kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Helps balance fluids and electrolytes.
Digestive System
Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and removes waste. Includes mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas.
What does the small intestine absorb?
Nutrients
What does the large intestine absorb?
Electrolytes and water
Dysuria
Painful/difficult urination
Hematuria
Blood in urine
Nocturia
Frequent urination at night
Urinary Incontinence
Involuntary loss/leakage of urine
Reflex Incontinence
Loss of urine without warning due to a spinal cord injury or nerve damage; the bladder empties automatically.
Stress Incontinence
Leaking urine during activities that put pressure on the bladder, like coughing, sneezing, or lifting.
Urge Incontinence
Sudden, strong urge to urinate followed by involuntary leakage; often linked to overactive bladder.
Urinary Urgency
A sudden, strong need to urinate immediately, often hard to control.
Catheter
A device put into the bladder to drain urine
Indwelling Catheter
A catheter that remains in the bladder
Condom Catheter
An external catheter used for males. It fits over the penis and is connected to a drainage bag to collect urine.
Constipation
Passage of stool that is dry and hard
Defecation
To pass feces through the rectum
Dehydration
A condition that occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, leading to a lack of necessary water for normal body functions.
Diarrhea
Loose feces
Enema
A procedure in which liquid is inserted into the rectum through the anus to stimulate a bowel movement or relieve constipation.
Flatulence
The accumulation of gas in the stomach or intestines, leading to the release of gas through the rectum (passing gas).
Peristalsis
Muscle contractions that move food, liquid, and waste through the digestive tract.
Stoma
An opening created surgically on the body’s surface, often for the passage of waste
Suppository
A small, solid medication designed to be inserted into the body, usually through the rectum, where it melts and is absorbed for treatment.
How often should you toilet someone?
Every 2 hours
Urine Color Chart
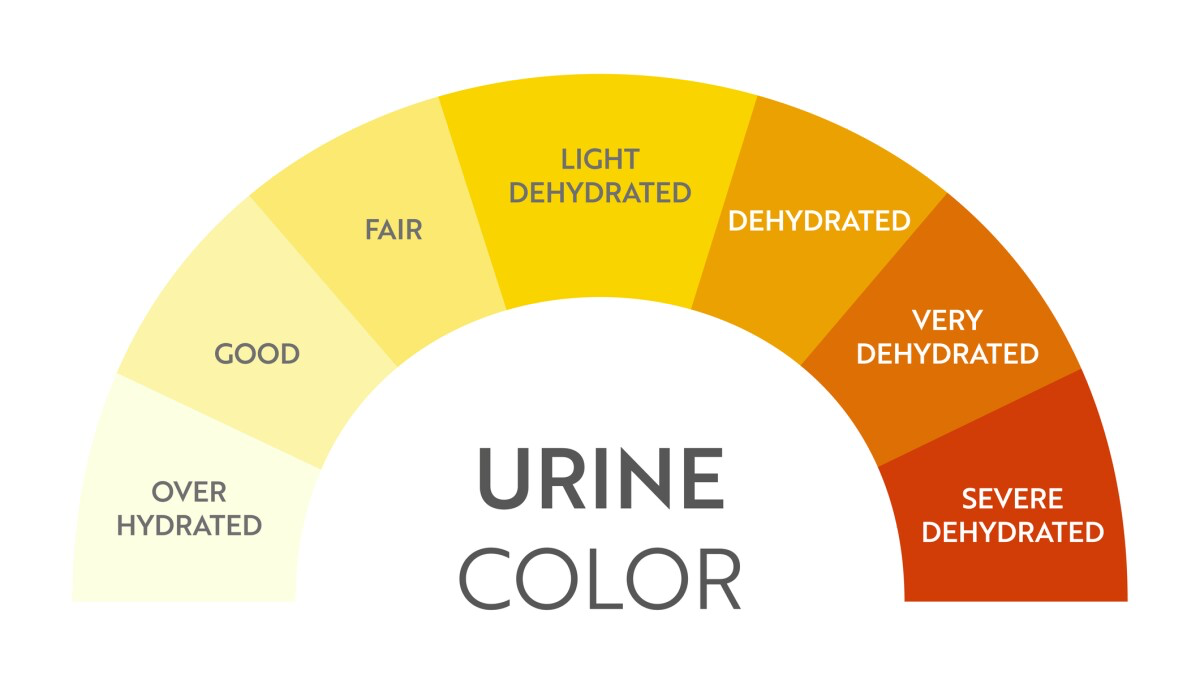
A CNA should immediately flush the urine of a patient after emptying their catheter. (True/False)
False (let nurse see it prior)
What is the number one source of HAIs (hospital acquired infections)?
Poor catheter maintenance
CNAs should measure urine in the drainage bag. (True/False)
False
In which unit is urine measured?
mL
Colostomy
A surgical procedure where a part of the colon is brought to the surface of the abdomen, creating an opening (stoma) for the elimination of waste into a bag.
Ileostomy
A surgical procedure where the ileum (last part of the small intestine) is brought to the surface of the abdomen, creating an opening (stoma) for waste elimination into a bag (looser stool than colostomy).
Cardiovascular System
The heart and blood vessels work together to circulate blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products. Includes the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Typical adult resting heart rate
60-100 bpm
Where should you typically check someone’s pulse?
The radial artery
Which vital sign do you use the brachial artery for?
Blood Pressure
Diastole
The phase of the heartbeat when the heart relaxes and fills with blood.
Systole
The phase of the heartbeat when the heart contracts and pumps blood out into the arteries.
Arrhythmia
An irregular or abnormal heartbeat, where the heart may beat too fast, too slow, or in an erratic pattern.
Hypertension
High blood pressure, a condition where the force of the blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high.
Dysrhythmia
n abnormal heart rhythm, which can include irregular, too fast, or too slow heartbeats. It’s often used interchangeably with arrhythmia.
Angina
Chest pain or discomfort caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, often triggered by physical activity or stress. It can feel like pressure, tightness, or a squeezing sensation
Carotid Artery
The main blood vessels in the neck that supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain, neck, and face.
Brachial Artery
The major artery in the upper arm that supplies blood to the arm and hand. It is commonly used to measure blood pressure.
Radial Artery
The artery located in the wrist, on the thumb side of the forearm. It is often used to check pulse rate.
Blood Pressure
The force of blood against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps it around the body
Two parts of blood pressure
systolic (pressure when the heart beats) and diastolic (pressure when the heart rests between beats).
Respiratory System
The body system responsible for breathing, bringing in oxygen, and expelling carbon dioxide. It includes the nose, throat, windpipe, lungs, and diaphragm.
Average Respiration Rate (adults)
12-20 per minute
Apnea
A temporary cessation of breathing, often occurring during sleep.
Cyanosis
A bluish or purplish tint to the skin, lips, or nails due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. It often indicates a respiratory or circulatory problem.
Dyspnea
Difficulty or labored breathing, often described as shortness of breath. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, including asthma, heart failure, or lung disease.
Hyperventilation
Rapid or shallow breathing that can lead to a decrease in carbon dioxide levels in the blood. It may occur due to anxiety, stress, or medical conditions.
Hypoventilation
Shallow or slow breathing that leads to an inadequate intake of oxygen and a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood. It can result from respiratory or neurological conditions.
Hypoxemia
Low oxygen levels in the blood, which can lead to symptoms like shortness of breath, confusion, and a bluish tint to the skin.
Hypoxia
A condition where there is a deficiency of oxygen in the tissues of the body, despite normal blood oxygen levels.
Orthopnea
Difficulty breathing while lying flat, often relieved by sitting or standing up.
Pulse Oximetry
A non-invasive method used to measure the oxygen saturation level in the blood, usually via a sensor placed on the fingertip or earlobe. It helps assess how well oxygen is being delivered to the body's extremities.
Respiratory Arrest
A condition in which breathing stops completely, requiring immediate medical intervention to restore normal breathing. It can be caused by airway obstruction, injury, or medical conditions.
Tachypnea
Abnormally rapid breathing, typically over 20 breaths per minute in adults. It can be caused by fever, anxiety, lung disease, or other conditions.
Tracheostomy
A surgical procedure in which an opening (stoma) is created in the trachea (windpipe) to allow for breathing, often through a tube. It is typically done when the upper airway is blocked or to assist with long-term ventilation.
Acceptable BOL (Blood Oxygen Level)
95-100%
Musculoskeletal System
The system of bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints that provides structure, support, movement, and protection for the body.
Atrophy
The wasting or shrinking of muscle tissue or organs due to disuse, aging, or a medical condition.
Fowler’s Position
A seated position where the head of the bed is elevated to 45 degrees. It is often used to help with breathing, improve comfort, or facilitate certain medical treatments.
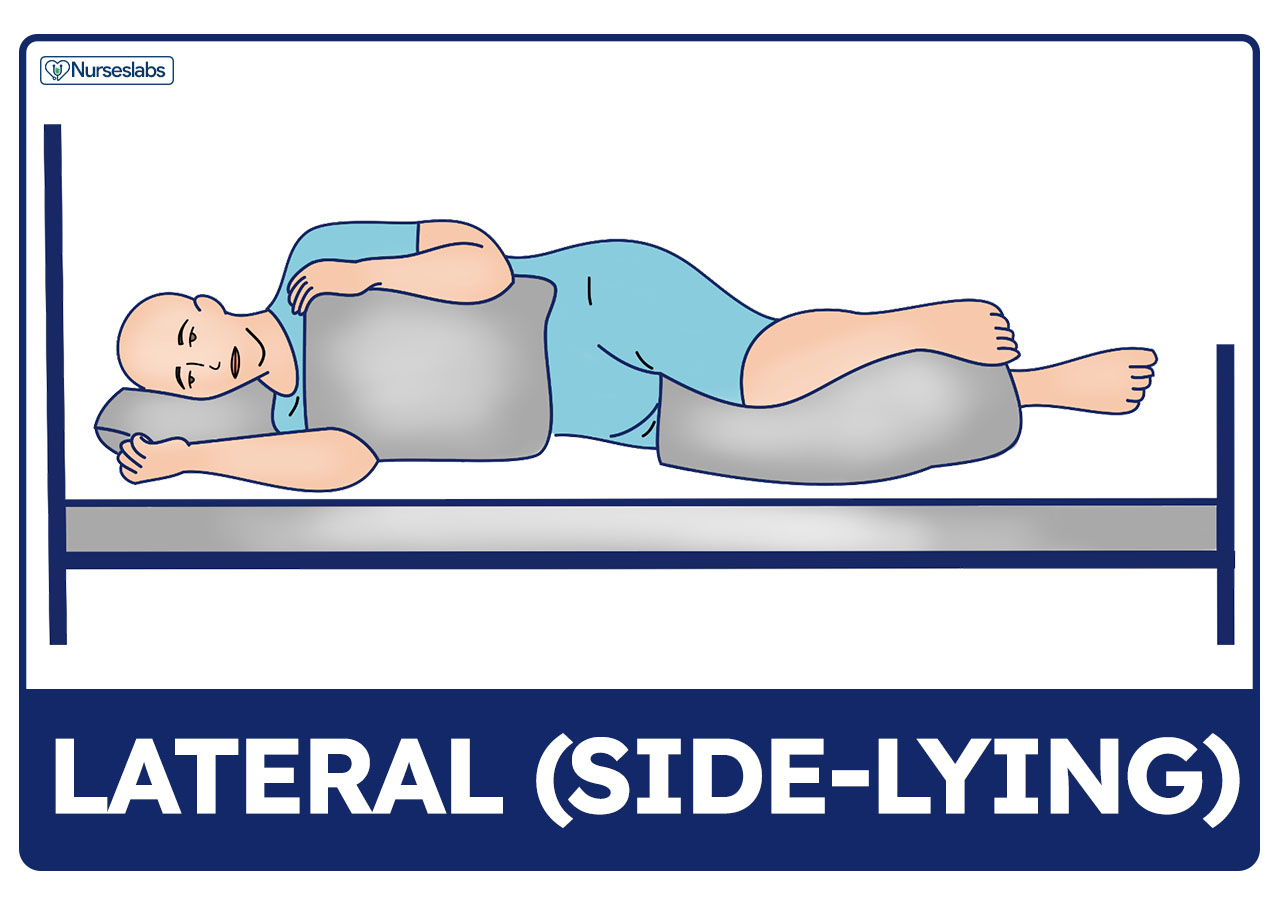
Lateral Position
A side-lying position where the patient rests on their left or right side. It is commonly used for comfort, to prevent pressure sores, or during certain medical exams and procedures.
Prone Position
A position where the patient lies flat on their stomach, face down. It is used for certain medical procedures or to help improve lung function in specific conditions.
Side-Lying Position
A position where the patient lies on their side, with the upper leg bent and supported by pillows for comfort. It is often used for sleeping or during medical procedures to reduce pressure on certain areas of the body.
Supine Position
A position where the patient lies flat on their back, facing upward. It is commonly used for examinations, surgeries, and resting.
High Fowler’s Position
A seated position where the head of the bed is elevated to 90 degrees. It is commonly used to assist with breathing, improve comfort, or during certain medical treatments like eating or speaking.
Semi-Fowlers
A seated position where the head of the bed is elevated to 30 degrees
Shoulder Flexion
Arm straight up to ear
Shoulder Extension
Arm Straight next to torso
Shoulder Abduction
Arm out and parallel to the floor raised straight up towards the ear.
Shoulder Adduction
Arm out and parallel to the floor raised straight down towards feet.
How many repetitions are typically done when performing range of motion exercises?
3
When testing the ROM of the shoulder, what is the correct hand placement?
Under the shoulder
What should the position of the bed be whenever you leave a patient’s room?
Low and locked
A CNA needs a doctor’s order to put up a 3rd and 4th side rail. (True/False)
True