General Human Anatomy: Biology 201 - Study Guide Questions
1/101
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Define anatomy:
The study of structures (The study of the composition and organization of living things)
Define physiology:
The study of function
What are the subdivisions of microscopic anatomy?
Histology (study of tissues) and cytology (study of cells)
What are the categories of macroscopic anatomy? Define each category:
Surface anatomy (on top), regional (specific areas of the body), and systemic (various organ systems)
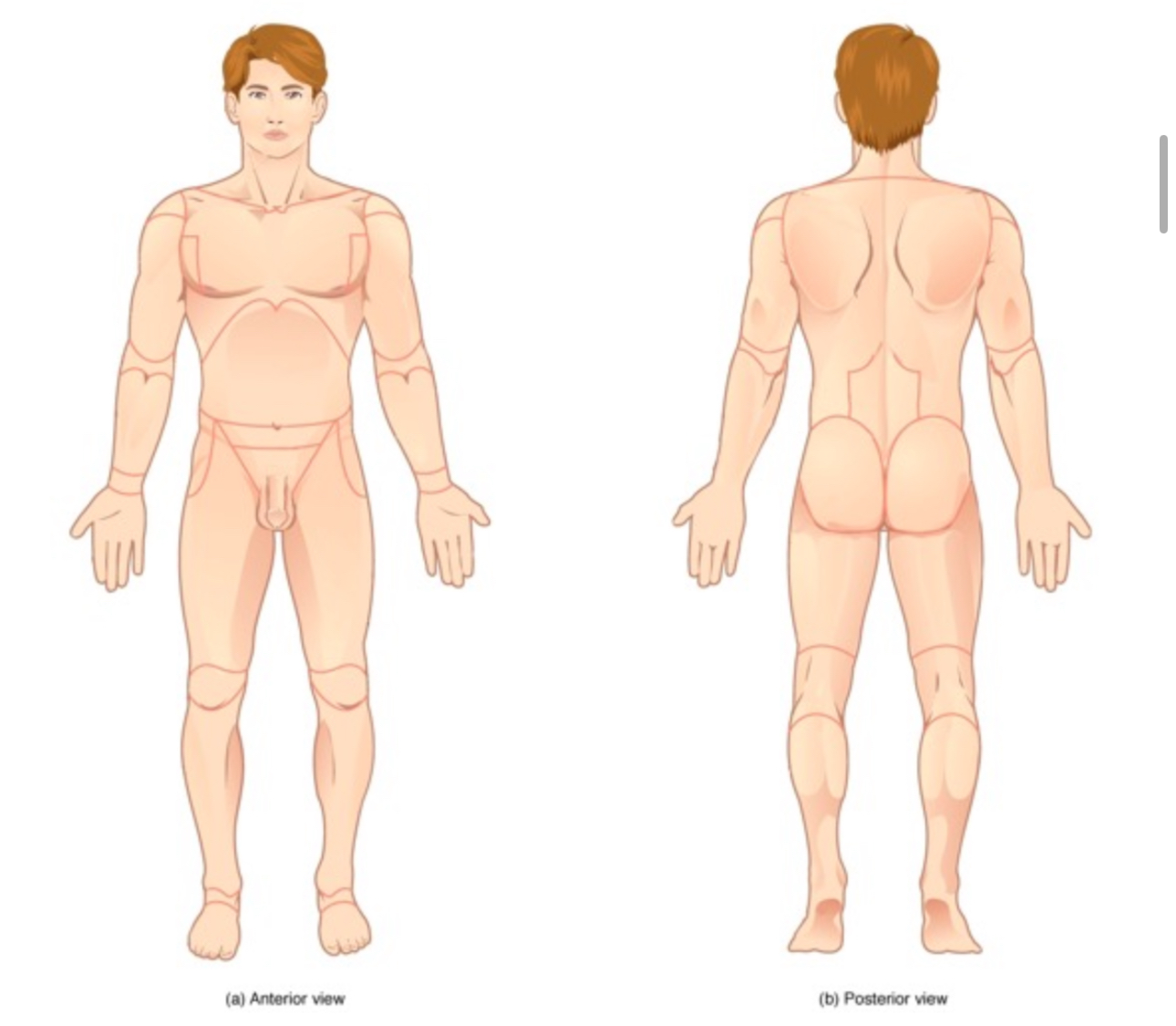
Define standard anatomical position (SAP). Be able to recognize SAP on a diagram:
The body is standing upright, feet are parallel and shoulder width apart, head is level and facing forward, arms are at the sides of the body, and palms are facing forward
Define supine:
Lying down freely up
Define prone:
Lying down freely down
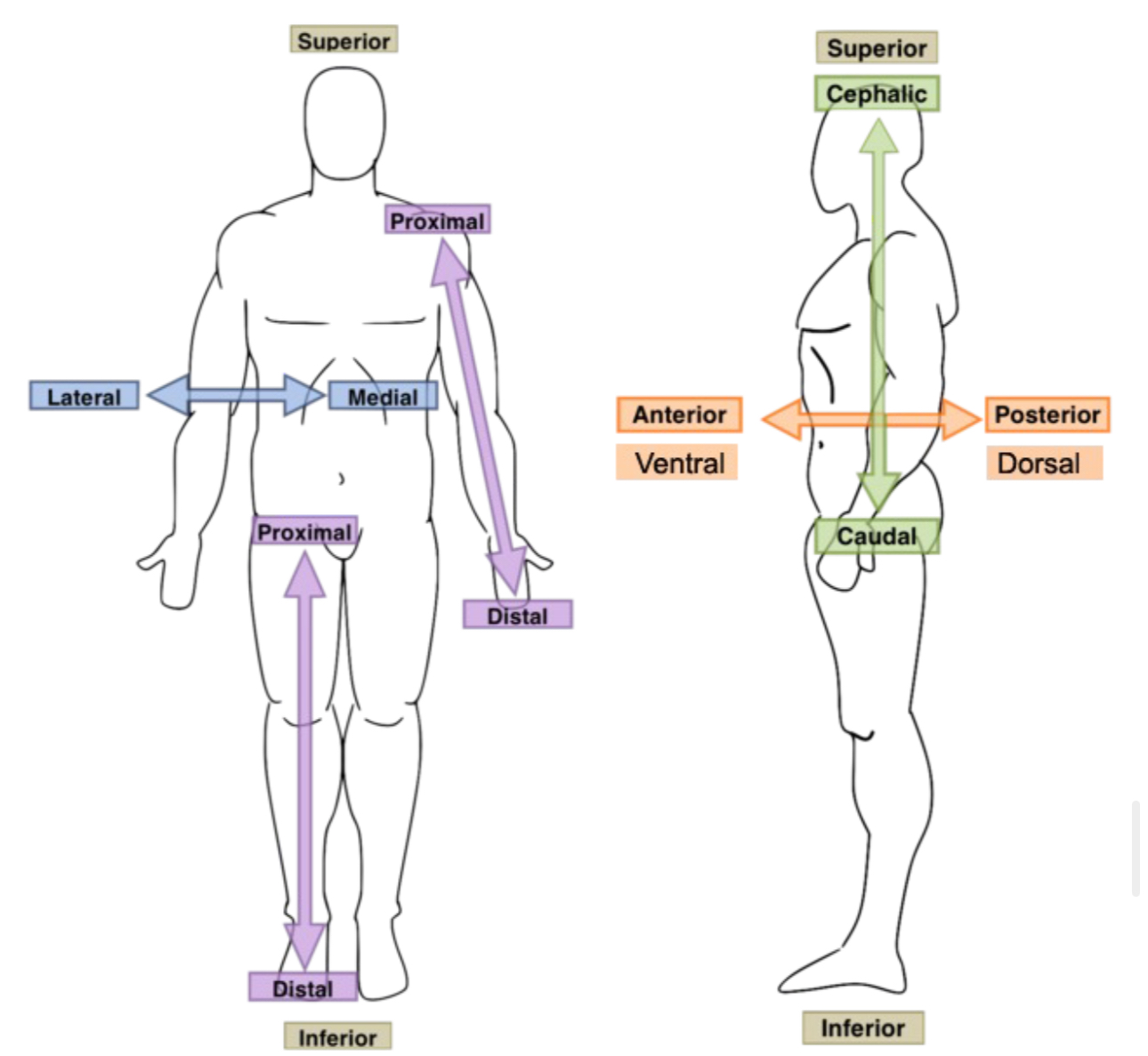
What are the types of planes that divide the human body?
Frontal, transverse, and sagittal
Define frontal plane. Recognize a frontal cut in an image:
Divides the body into anterior and posterior sections
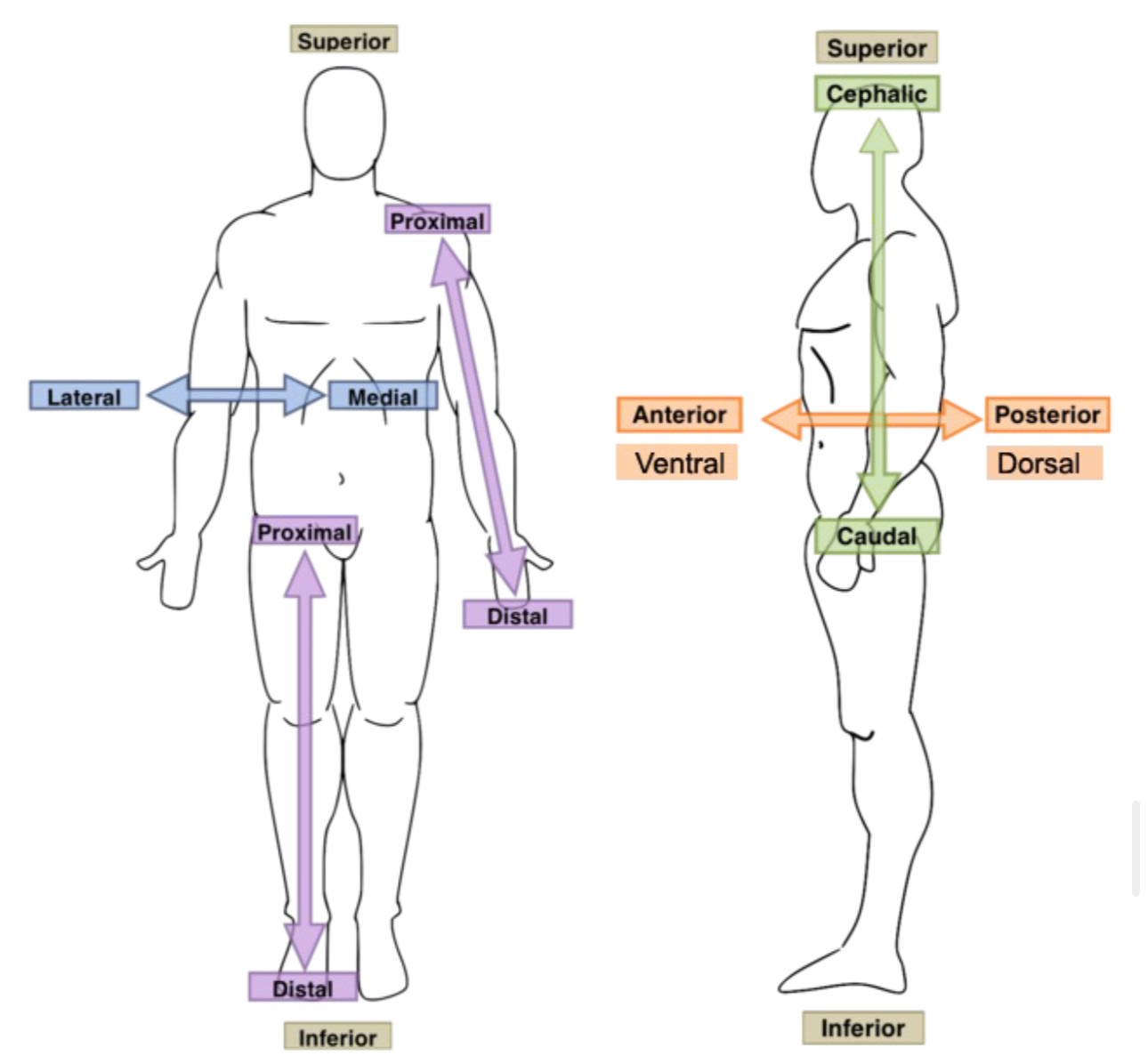
Define transverse plane. Recognize a transverse plane in an image:
Divides the body structure into superior and inferior sections
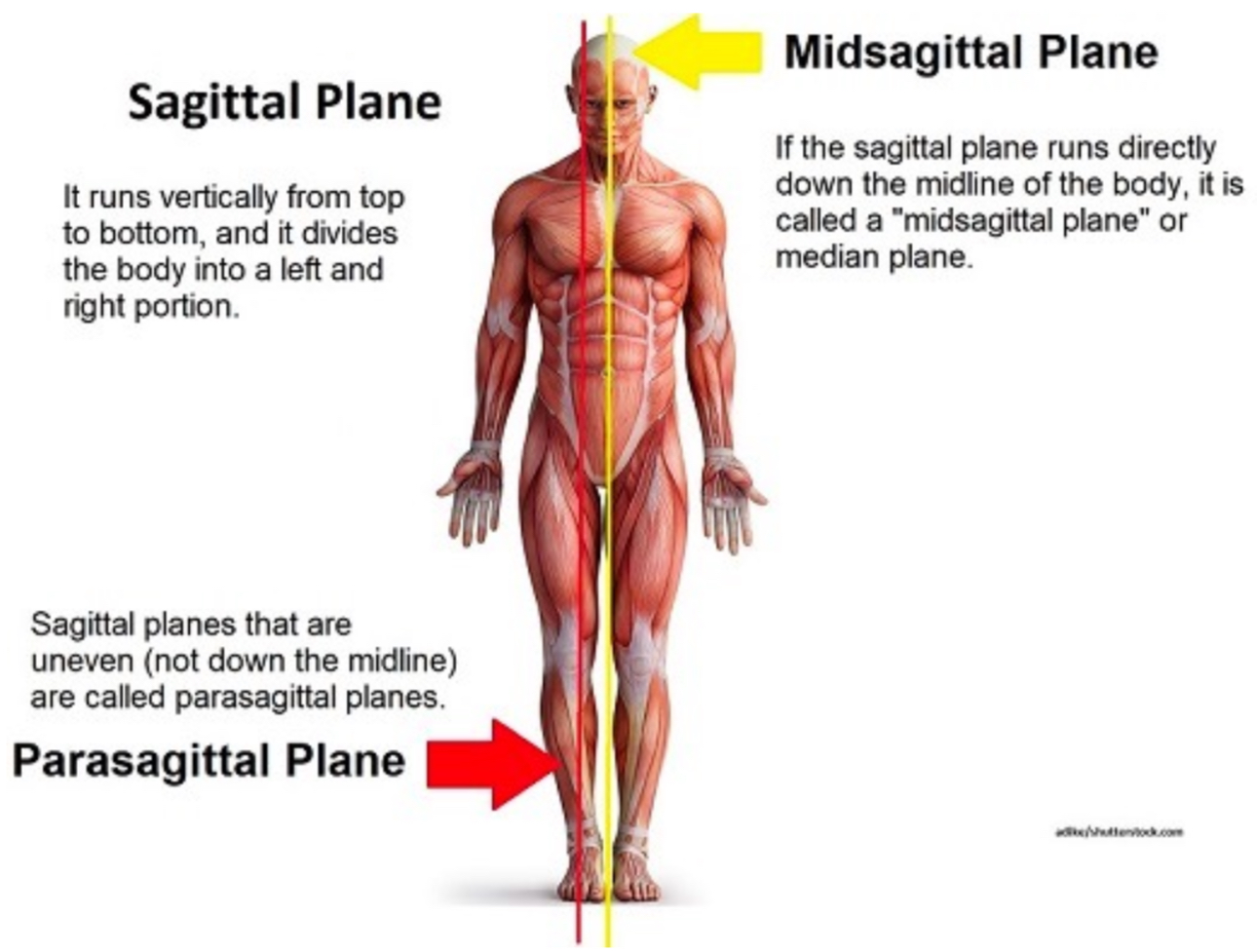
Define sagittal and parasagittal planes. Recognize sagittal cuts in an image:
Divides the body into left/right halves
Define the following anatomical terms:
Anterior (touches the front (ventral), posterior (towards the back (dorsal), superior (towards the head or above), inferior (touches the feet or below), medial (towards the midline (center), lateral (away from the midline (to the side), bilateral (on bothsides), deep (on the inside, underneath anterior structure), superficial (on the outside, near surface or outup of another structure), proximal (closest to the part of attachment on the trunk), and distal (furthest from the point of attachment on the trunk).
What are the regions of the human body? What parts of the body make up each region?
Axial (head, neck, and trunk) and appendicular (limbs and appendages)
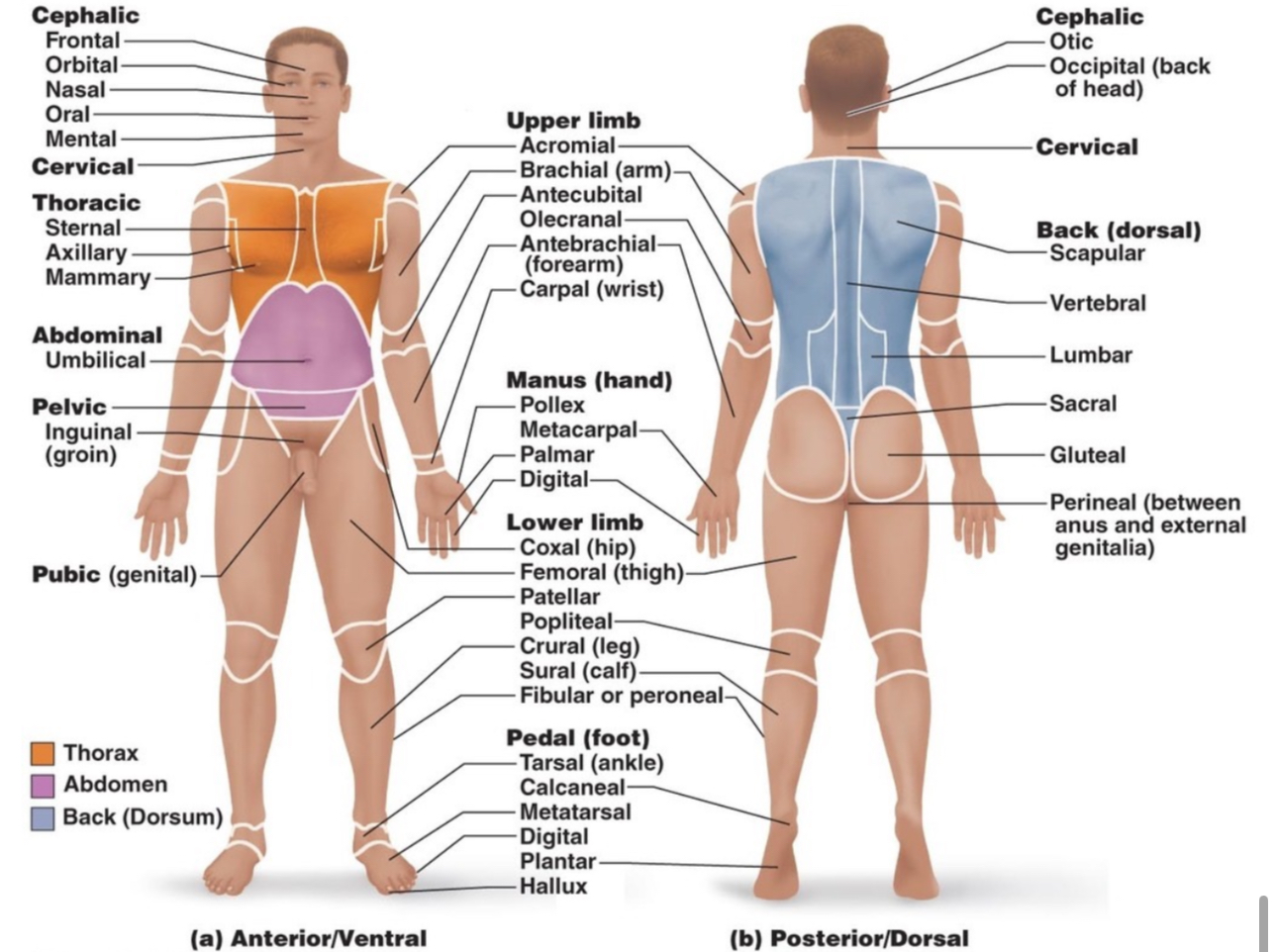
Anatomical Regions
What are the internal body cavities? Know what major organs are in each cavity:
Cranial cavity (brain), spinal cavity (spinal cord), thoracic cavity (lungs and heart), and abdominopelvic cavity (digestive organs, bladder, and reproductive organs)
What is the pleural sac? Pericardial sac?
Pleural sac (houses the lumgs) 2 sacs, 1 for each lung and pericardial sac (houses the heart)
What is the function of serous membranes? Where do you find them in the human body?
Produces serous fluid that helps reduce friction; located in thoracic cavity (lungs, heart, and closed cavities)
What are the types of serous membranes?
Parietal layer and visceral layer
Where is the parietal layer located? Visceral layer?
Parietal layer (lines in the cavity (surrounds) and visceral layer (lines the organs (surrounds)
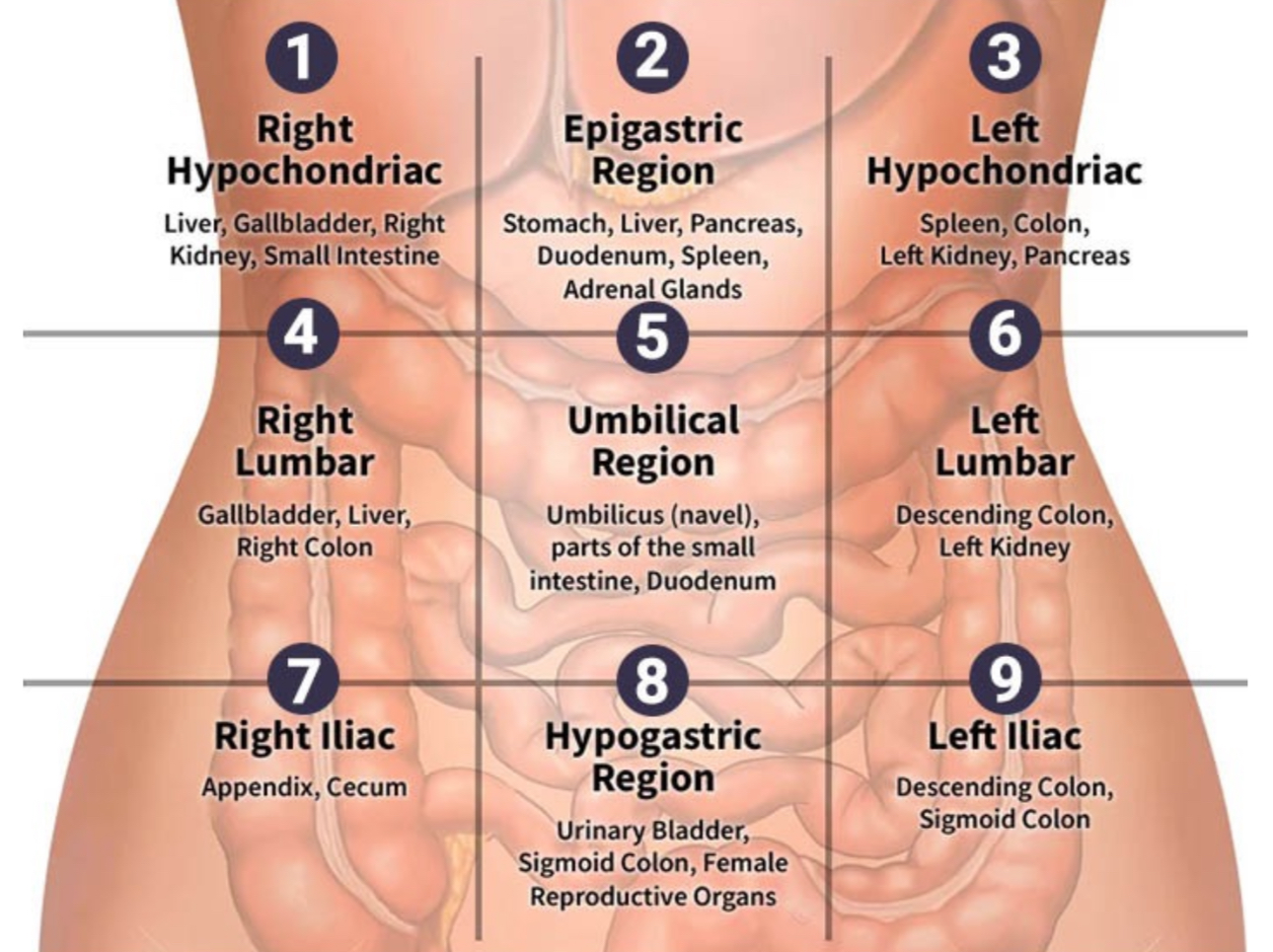
What are the abdominopelvic regions of the human body? Be able to identify them in an image:
Right hypochondria, epigastric region, left hypochondria, right lumbar, umbilical region, left lumbar, right iliac, hypogastric region, and left iliac
Define cytology:
The study of cells
What determines the function of the cells?
Determined by shape and other characteristics
Define eukaryote:
The cell that processes a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
What are the components of the plasma membrane? What is the function of each component?
Phospholipids (control permeability of the cells), cholesterol (affects membrane fluidity), cell surface protein (makers to identify cell type, and bind hormones and proteins), and transmembrane protein (are passageways for Ions and polar molecules to pass through the non-polar interior)
What are microvilli? What is their function?
Are protrusions of the cellular membrane and increases the surface area of the cell (involved in absorption/secretion and numerous in the small intestine)
Define histology:
Study of the tissues and their functions
Define tissues:
Groups of similar cells and extracellular products that carry out a common function
What are the types of tissues?
Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue
What are the characteristics of epithelial tissues?
Cells are closely joined together (allows for the formation of surface and linings), little to no matrix, can be innervated (contains nerves), avascular (lacks blood supply/no blood), anchored to a basement membrane, and easily regenerated
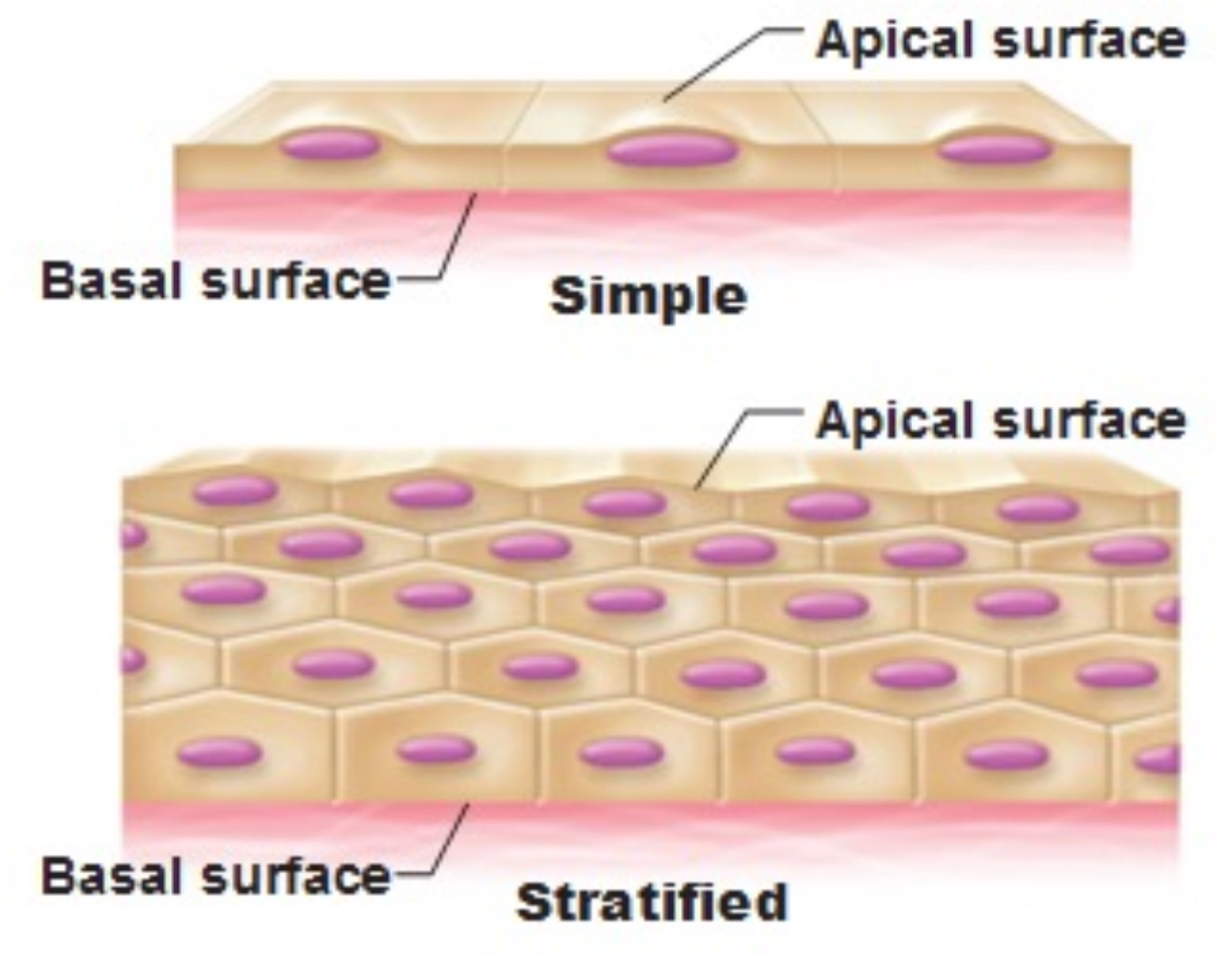
What are the different surfaces of the epithelial tissue? Define each layer. Recognize each layer on an image:
Apical surfaces (exposed surface (top), basal surface (attached layer (middle/center), and basal lamina adhesive sheet (bottom)
Where are epithelial tissues located on the human body?
Internal and exterior lining of organs (body surfaces and cavities)
What are the functions of epithelial tissues?
Provide physical protection (protects against friction and dehydration, prevents chemicals or other infectious agents from entering the body), movement of materials (allows for diffusion of materials, diffusion/filtration), produced secretion, provides sensory information to the nervous system, and absorption (uptake of material)
How are epithelial tissues classified?
Numbers of layers and cell shape
What are the layers of epithelial tissue? Define each layer term:
Simple layer (single layer) and stratified (multiple layer)
Where are simple epithelia found in the body? What is its function?
Found in areas within the body that are protected and have little to no friction; involved in secretion, absorption, or friction
Where are stratified epithelia found in the body? What is its function?
Found in areas that experience stress/friction, indicated in skin and within large intestines
What are the shapes of epithelial cells? Define each shape:
Squamous is thin, flat cells, cuboidal is cube shaped cells or square, columnar is height is significantly large than (rectangular), and transitional changes shapes but consist of all 3
What are the types of glands in the human body?
Endocrine glands and exocrine glands
Where do endocrine glands release products? Give an example of a product released by endocrine glands:
Products are secreted directly into the intercellular fluids (matrix) and/or blood stream, hormone secretion, lacks ducts
Where do exocrine glands release products? Give an example of a product released by exocrine glands:
Products are secreted via ducts onto the surface of the skin or internal passageway; sweating, secretion of saliva within the mouth, secretion of digestive system
What are the functions of connective tissues?
Structural support, cushioning, protection, energy storage, transport of nutrients, connection/binding of structures, and red and white blood cell production
What are the components of connective tissue?
Cells, protein fibers, and ground substance (matrix)
What are the types of protein fibers found in connective tissue? What is the function of each?
Collagen fibers (strength), elastin fibers (stretch and flexibility), and reticular fibers (provides structural support)
What is ground substance? What does it consist of?
Non-living, fluid-like material produced by cells and consists of proteins, carbohydrates, and water
What is matrix? What does it consist of?
Fluid part of tissues and non-living extracellular material and consists of ground substances and protein fibers
What cell types make up areolar connective tissue? What is the function of each?
Fibroblasts (produces matrix), macrophages (engulf cellular debris), and mast cells (produce and release histamines).
What forms the extracellular matrix of areolar connective tissue?
Collagen, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers
What is the function of areolar connective tissue?
Attaches skin to underlying muscles, fills spaces between organs, and surrounds/supports blood vessels
Where in the body is areolar connective tissue located?
Below the skin, around the organs, and attaching blood vessels to organs
What cell makes up adipose connective tissue?
Adipocytes (lipid filled fibroblasts)
What forms the extracelluar matrix of adipose connective tissue?
Semi liquid ground substance
What is the function of adipose connective tissue?
Long time energy storage
Where in the body is adipose connective tissue located?
Subcutaneous (under skin), surrounding organs
What forms the extracellular matrix of reticular connective tissue?
Mesh like network of reticular fibers
What is the function of reticular connective tissue?
Support and provides framework for lymphoid fibers
What forms the extracellular matrix of dense regular connective tissue?
Dense, parallel collagen bundles
What is the function of dense regular connective tissue?
Compromises tendons and ligaments and synovial sacs