Module 7.1 (VTE)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- acute inflammation
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
A. hypercoagulable state
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- cancer
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
A. hypercoagulable state
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- estrogen therapy
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
A. hypercoagulable state
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- pregnancy
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
A. hypercoagulable state
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- thrombophilia
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
A. hypercoagulable state
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- atherosclerosis
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
B. endothelial injury
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- central venous catheter
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
B. endothelial injury
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- trauma/surgery
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
B. endothelial injury
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- venous valve disease
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
B. endothelial injury
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- immobility
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
C. circulatory stasis
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- left ventricular dysfunction
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
C. circulatory stasis
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- previous VTE
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
C. circulatory stasis
What part of Virchow's Triad does this fall under:
- venous insufficiency
A. hypercoagulable state
B. endothelial injury
C. circulatory stasis
D. all of the above
C. circulatory stasis
If patients are symptomatic, these symptoms are indicative of:
- swelling
- pain
- warmth
A. DVT
B. CAD
C. PE
D. none of the above
A. DVT
If patients are symptomatic, these symptoms are indicative of:
- cough
- chest pain
- shortness of breath
- palpitation
A. DVT
B. CAD
C. PE
D. none of the above
C. PE
Which of the following lab tests can be considered when evaluating a patient for a VTE? (select all)
A. D-dimer
B. CBC
C. CMP
D. INR
A. D-dimer
B. CBC
C. CMP
D. INR
What lab test in the diagnosis of VTE rules out but does not rule in?
A. D-dimer
B. CBC
C. CMP
D. INR
A. D-dimer
NP came into the hospital, and a D-dimer was ordered. The D-dimer test was positive, does she have a VTE?
maybe, we do not know for sure other things can contribute to a positive D-dimer (pregnancy)
note: does not RULE IN
NP came into the hospital, and a D-dimer was ordered. The D-dimer test was negative, does she have a VTE?
no
What should be used to make a proper diagnosis of DVT? (gold standard)
A. D-dimer
B. doppler ultrasound
C. CT scan
D. PET scan
B. doppler ultrasound
What should be used to make a proper diagnosis of PE?
A. D-dimer
B. doppler ultrasound
C. CT scan
D. PET scan
C. CT scan
What pharmacologic options do we have for VTE prophylaxis?
- low molecular weight heparin
- fondaparinux
- warfarin
- unfractionated heparin
- apixaban
- dabigatran
- edoxaban
- rivaroxaban
What are non-pharm options for VTE prophylaxis? (Select all)
A. resumption of ambulation ASAP
B. graduated compression stockings
C. intermittent pneumatic compression device
D. inferior vena cava filter
A. resumption of ambulation ASAP
B. graduated compression stockings
C. intermittent pneumatic compression device
D. inferior vena cava filter
What is the level of risk for developing DVT without thromboprophylaxis in this patient?
- patients undergoing minor surgery and fully ambulatory
- patients who are medically ill and fully ambulatory
A. low (<10%)
B. moderate (10-40%)
C. high (40-80%)
D. insanely high (81%+)
A. low (<10%)
What is the level of risk for developing DVT without thromboprophylaxis in this patient?
- most patients undergoing general, gynecological, or urological surgeries
A. low (<10%)
B. moderate (10-40%)
C. high (40-80%)
D. insanely high (81%+)
B. moderate (10-40%)
What is the level of risk for developing DVT without thromboprophylaxis in this patient?
- most patients who are hospitalized for an acute medical illness (Ex. MI, ischemic stroke, CHF)
A. low (<10%)
B. moderate (10-40%)
C. high (40-80%)
D. insanely high (81%+)
B. moderate (10-40%)
What is the level of risk for developing DVT without thromboprophylaxis in this patient?
- patients who are at moderate DVT risk and high risk for bleeding
A. low (<10%)
B. moderate (10-40%)
C. high (40-80%)
D. insanely high (81%+)
B. moderate (10-40%)
What is the level of risk for developing DVT without thromboprophylaxis in this patient?
- patients undergoing major lower extremity orthopedic surgery (ex. hip or knee arthroplasty, hip fracture repair)
A. low (<10%)
B. moderate (10-40%)
C. high (40-80%)
D. insanely high (81%+)
C. high (40-80%)
What is the level of risk for developing DVT without thromboprophylaxis in this patient?
- spinal cord injury
A. low (<10%)
B. moderate (10-40%)
C. high (40-80%)
D. insanely high (81%+)
C. high (40-80%)
What is the level of risk for developing DVT without thromboprophylaxis in this patient?
- major trauma
A. low (<10%)
B. moderate (10-40%)
C. high (40-80%)
D. insanely high (81%+)
C. high (40-80%)
What is the level of risk for developing DVT without thromboprophylaxis in this patient?
- patients who are at high DVT risk and high risk for bleeding
A. low (<10%)
B. moderate (10-40%)
C. high (40-80%)
D. insanely high (81%+)
C. high (40-80%)
What is the suggested prevention strategy in this patient population for DVT prophylaxis?
- patients undergoing minor surgery and fully ambulatory
- patients who are medically ill and full ambulatory
A. early and aggressive ambulation
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
D. no prophylaxis
A. early and aggressive ambulation
What is the suggested prevention strategy in this patient population for DVT prophylaxis?
- most patients undergoing general, gynecological, or urological surgeries
A. early and aggressive ambulation
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
D. no prophylaxis
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
What is the suggested prevention strategy in this patient population for DVT prophylaxis?
- most patients who are hospitalized for an acute medical illness (ex. MI, ischemic stroke)
A. early and aggressive ambulation
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
D. no prophylaxis
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
What is the suggested prevention strategy in this patient population for DVT prophylaxis?
- patients who are at moderate DVT risk and high risk for bleeding
A. early and aggressive ambulation
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
D. no prophylaxis
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
What is the suggested prevention strategy in this patient population for DVT prophylaxis?
- patients undergoing major lower extremity orthopedic surgery
A. early and aggressive ambulation
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
D. no prophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
What is the suggested prevention strategy in this patient population for DVT prophylaxis?
- spinal cord injury
A. early and aggressive ambulation
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
D. no prophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
What is the suggested prevention strategy in this patient population for DVT prophylaxis?
- major trauma
A. early and aggressive ambulation
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
D. no prophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
What is the suggested prevention strategy in this patient population for DVT prophylaxis?
- patients who are at high DVT risk and high risk for bleeding
A. early and aggressive ambulation
B. UFH 5000 units SQ q8h or q12h, LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), mechanical thromboprophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
D. no prophylaxis
C. LMWH fondaparinux (at recommended doses), Warfarin (INR goal: 2-3), oral factor Xa inhibitor, oral direct thrombin inhibitor, mechanical thromboprophylaxis
This is the MOA of what drug class?
- activity against factor Xa and thrombin
A. fondaparinux
B. heparin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
D. warfarin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
These are the advantages for what drug class
- predictable response
- improved bioavailability
- longer half life
- no need for monitoring for most patients
A. aspirin
B. heparin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
D. warfarin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
What is the enoxaparin dose for a hip fracture repair? (Select all)
A. 30 mg once daily
B. 30 mg q12h
C. 40 mg once daily
D. 40 mg q12h
B. 30 mg q12h
C. 40 mg once daily
What is the enoxaparin dose for a knee surgery?
A. 30 mg once daily
B. 30 mg q12h
C. 40 mg once daily
D. 40 mg q12h
B. 30 mg q12h
What is the enoxaparin dose for an acutely ill patient in hospital?
A. 30 mg once daily
B. 30 mg q12h
C. 40 mg once daily
D. 40 mg q12h
C. 40 mg once daily
For VTE prophylaxis, if CrCl <30ml/min, use 30 mg SC once daily are the directions for what drug?
A. fondaparinux
B. dalteparin
C. enoxaparin
D. heparin
C. enoxaparin
This is the MOA of what drug class?
- selectively inhibits factor Xa
A. fondaparinux
B. heparin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
D. warfarin
A. fondaparinux
These are the potential indications for what drug?
- hip replacement surgery
- knee replacement surgery
- hip fracture surgery
- general surgery
- medical illness
A. fondaparinux
B. heparin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
D. warfarin
A. fondaparinux
This is the dose for what drug?
- 2.5 mg once daily, starting 6-8 hours after surgery
A. fondaparinux
B. heparin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
D. warfarin
A. fondaparinux
These are the clinical pearls for what drug?
- if CrCl <50 ml/min --> ??? dose
- do NOT use if CrCl <30 ml/min
- patients who weigh less than 50kg should not use this drug for VTE prophylaxis
A. fondaparinux
B. heparin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
D. warfarin
A. fondaparinux
This is the dose for what drug?
- 5000 units SC q8h or 5000 units SC q12h
A. fondaparinux
B. heparin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
D. warfarin
B. heparin
What factors does warfarin inhibit?
II, VII, IX, X
Warfarin is dosed to achieve an INR between?
2-3
These are the clinical pearls to consider for what drug?
- patient, patient, patient, and patience
- food
- alcohol
- tobacco
- exercise
- drug interactions --> antibiotics
- monitoring --> every 12 weeks?
A. fondaparinux
B. heparin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
D. warfarin
D. warfarin
These are the cautions for what drug?
- hypersensitivity to ____________
- pregnancy
- history of _______ induced skin necrosis
- inability to obtain regular PT/INR measurements
- inappropriate medication use or lifestyle behaviors
A. fondaparinux
B. heparin
C. LMWH (enoxaparin/dalteparin)
D. warfarin
D. warfarin
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-after knee surgery: 10mg once daily x 12 days
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
A. rivaroxaban
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-after hip surgery: 10mg once daily x 35 days
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
A. rivaroxaban
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-after hospitalization: 10mg once daily x 31-39 days
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
A. rivaroxaban
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-prolonged ppx: 10 mg once daily
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
A. rivaroxaban
For treatment of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
- 15 mg twice daily with food x 21 days; then 20 mg once daily with food
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
A. rivaroxaban
For what drug do you not need to take with food for the 10 mg dose, but should be taken with food for doses 15mg+
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
A. rivaroxaban
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-prolonged ppx: 2.5 mg twice daily
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
B. apixaban
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-after knee surgery: 2.5 mg twice daily x 12 days
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
B. apixaban
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-after hip surgery: 2.5 mg twice daily x 35 days
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
B. apixaban
For treatment of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-10 mg BID x 7 days then 5 mg twice daily
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
B. apixaban
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-after knee surgery: not FDA approved
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
C. dabigatran
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-after hip surgery: 110 mg on day of hip replacement surgery, then 220 mg once daily for 28-35 days
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
C. dabigatran
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-prolonged ppx: 150 mg twice daily
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
C. dabigatran
For treatment of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
-150 mg twice daily
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
C. dabigatran
For prevention of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
- after knee surgery: n/a
- after hip surgery: n/a
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
D edoxaban
For treatment of VTE, this is the dose for what drug?
- 60 mg once daily (>60kg)
- 30 mg once daily (<60kg)
A. rivaroxaban
B. apixaban
C. dabigatran
D edoxaban
D edoxaban
What are the general principles for treatment of VTE?
- must confirm diagnosis
- DVT and PE are treated similarly
- treatment doses differ from prophylaxis doses
- start with parenteral anticoagulant, transition to oral therapy
- proper treatment reduces long term complications
- pay attention to duration of therapy
Which of the following are exclusion criteria to outpatient treatment? (select all)
A. patients on dialysis
B. actively bleeding
C. major surgery or trauma within the prior 2 weeks
D. decompensation
A. patients on dialysis
B. actively bleeding
C. major surgery or trauma within the prior 2 weeks
D. decompensation
know
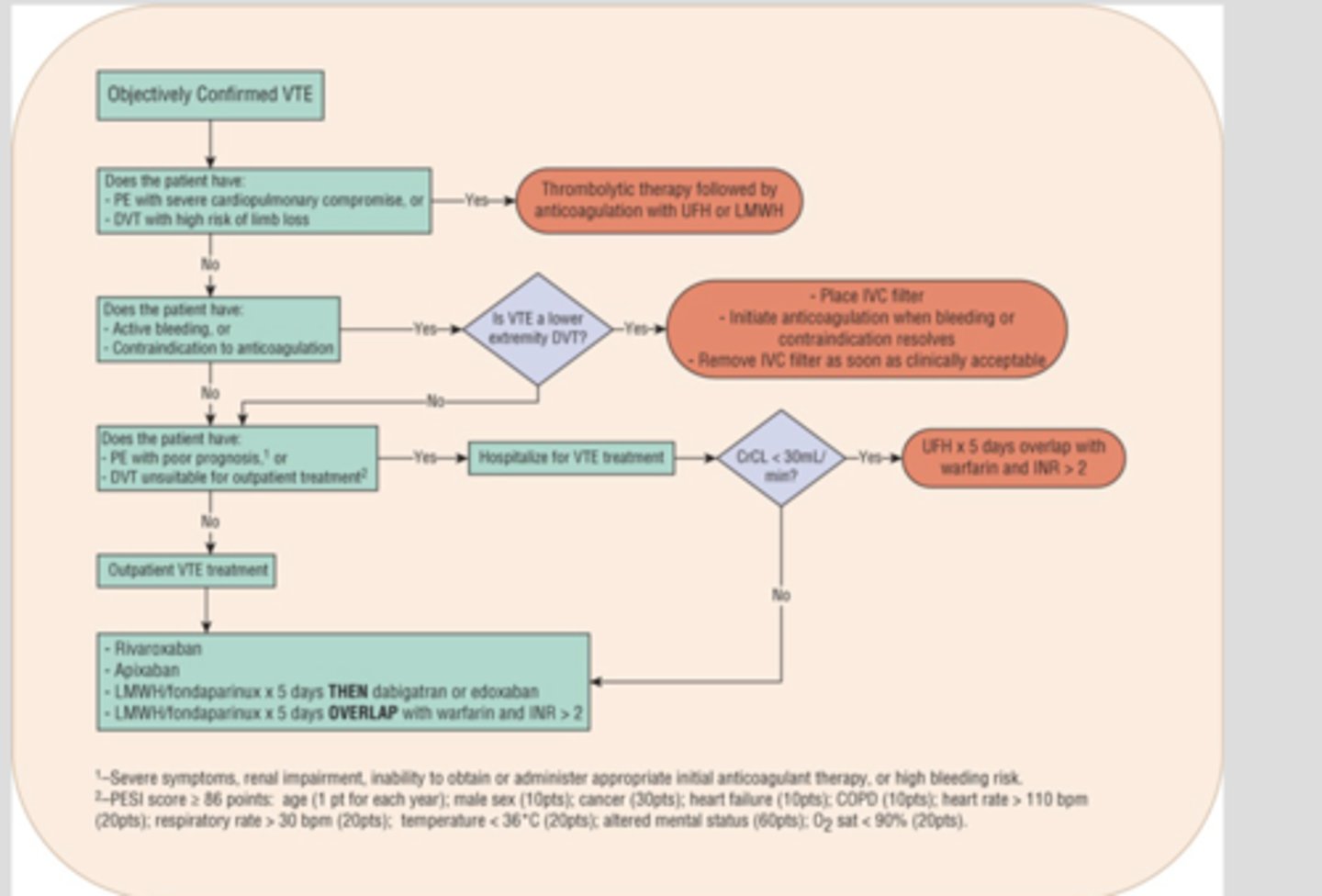
review
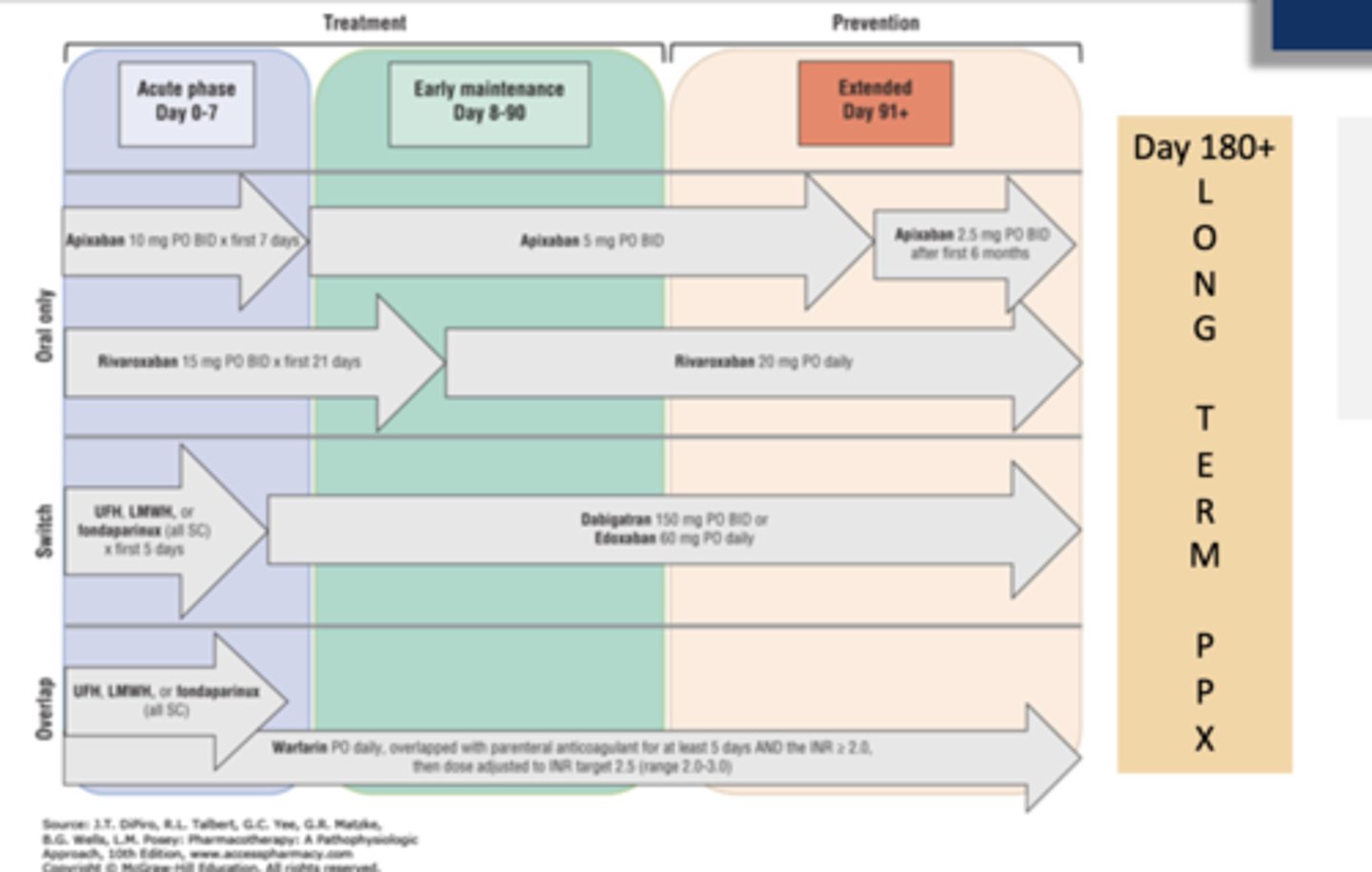
What is the treatment dose of enoxaparin for DVT?
1 mg/kg SC q12h
What is the treatment dose of dalteparin for DVT?
200 IU/kg once daily
For treatment with a LMWH, what labs should be measured at baseline? (select all)
A. SCr
B. CBC
C. platelets
D. INR
A. SCr
B. CBC
C. platelets
If CrCl is <30 ml/min, what is the enoxaparin dose for VTE treatment?
1 mg/kg once daily
For treatment with fondaparinux, what is the dose for this patient?
- weight <50kg
A. 5 mg SC once daily
B. 7.5 mg SC once daily
C. 10 mg SC once daily
D. 12.5 mg SC once daily
A. 5 mg SC once daily
For treatment with fondaparinux, what is the dose for this patient?
- weight 50-100kg
A. 5 mg SC once daily
B. 7.5 mg SC once daily
C. 10 mg SC once daily
D. 12.5 mg SC once daily
B. 7.5 mg SC once daily
For treatment with fondaparinux, what is the dose for this patient?
- weight >100kg
A. 5 mg SC once daily
B. 7.5 mg SC once daily
C. 10 mg SC once daily
D. 12.5 mg SC once daily
C. 10 mg SC once daily
Warfarin should be initiated in combination with ________ or ___________. Continue the combination for at least 5 days and until INR is therapeutic
A. apixaban
B. rivaroxaban
C. LMWH
D. fondaparinux
C. LMWH
D. fondaparinux
This drug is good for patients with renal insufficiency
A. apixaban
B. enoxaparin
C. UFH
D. dalteparin
C. UFH
If VTE was from a reversible cause, what is the duration of therapy?
A. 3 months of anticoag
B. at least 3 (to 6 to 12) months of anticoag --> then reevaluate --> long term ppx
C. long term/lifetime anticoag therapy
A. 3 months of anticoag
If VTE was from an unprovoked cause, what is the duration of therapy?
A. 3 months of anticoag
B. at least 3 (to 6 to 12) months of anticoag --> then reevaluate --> long term ppx
C. long term/lifetime anticoag therapy
B. at least 3 (to 6 to 12) months of anticoag --> then reevaluate --> long term ppx
if this is your second VTE episode, what is the duration of therapy?
A. 3 months of anticoag
B. at least 3 (to 6 to 12) months of anticoag --> then reevaluate --> long term ppx
C. long term/lifetime anticoag therapy
C. long term/lifetime anticoag therapy
This drug is not the best option for acute treatment of VTE. It can be an option for long term VTE treatment but only for patients who have taken anticoagulation therapy for at least 6 months
aspirin
When transitioning from warfarin to a DOAC, if the INR is less than 2 when can you start the DOAC?
ASAP
When transitioning from warfarin to a DOAC, if the INR is between 2-2.5 when can you start the DOAC?
next day
When transitioning from warfarin to rivaroxaban, when can you start the rivaroxaban?
A. when INR less than 3.5
B. when INR less than 3
C. when INR less than 2.5
B. when INR less than 3
When transitioning from warfarin to edoxaban, when can you start the edoxaban?
A. when INR less than 3.5
B. when INR less than 3
C. when INR less than 2.5
C. when INR less than 2.5