Oscillations (vibrations) waves physics
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Waves and their types.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Oscillation defintion
Vibration of particles around a mean position
Amplitude (A) defintion
An oscillating object’s maximum displacement
Period (T) definition
The time taken to complete one oscillation
Waves definition
A disturbance that transfers energy through a medium or space by having matter vibrate and move energy along each other when they make contact
What is a pulse wave
When a single wavelength is produced
Classification of waves
Mechanical or elctromagnetic
Mechanical wave
waves that require a medium to transmit energy
e.g. Water waves, sound waves and waves in strings and springs are all mechanical waves.
Electromagnetic waves
waves that do not require a medium to transmit energy
e.g. Visible light, gamma rays and radio waves are all electromagnetic waves
Transverse waves
Waves where the particles in the medium (or the fields in an electromagnetic wave) oscillate at right angles to the direction of wave travel. Can be electromagnetic or mechanical.
Crest defintion
an area of maximum positive displacement (x = +A) in a transverse wave.
Trough definition
an area of maximum negative displacement (x = -A) in a transverse wave
How do particles oscillate for transverse waves
Individual particles oscillate at right angles to the direction of wave travel
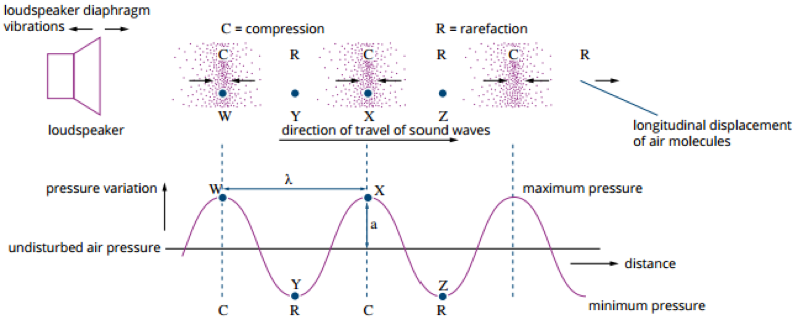
Longitudinal waves
waves where the particles in the medium oscillate back and forward in the same plane as the wave travels. e.g. Sound waves and compression waves in springs are examples of longitudinal waves. Don’t have crest and troughts
How do particles osciallte in longitudinal waves
As the backwards and forwards oscillations propagate through the medium, particles bunch together in some regions and spread apart in others.
Compression
An area where particles of the medium are bunched together in a longitudinal wave
Rarefactors
An area where particles in the medium are spread apart in a longitudinal wave.
What wave is sound waves
Sound waves are a type of longitudinal wave
How are sound waves produced
when a vibrating object causes air molecules to oscillate
Another name for sound waves
Sound waves are also called pressure waves as the compressions are areas of high pressure and the rarefactions are areas of low pressure.
What happens to sound waves when they are plotted on a graph
Become transverse, compression become crests and rarefactions become troughs