Human Anatomy and Physiology - The Skeletal System
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
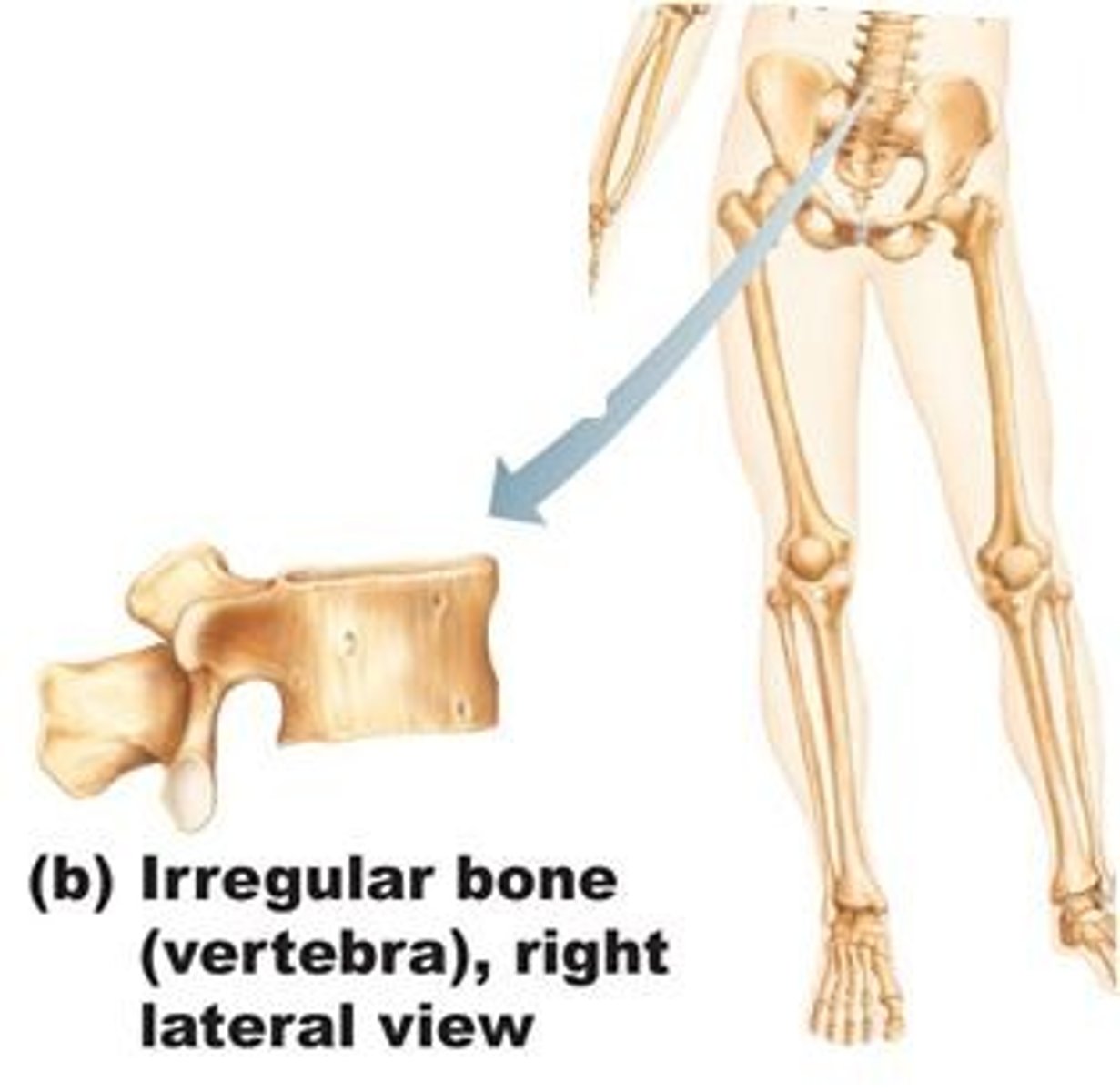
Irregular Bone
Bones that are unique to their purpose - they possess a shape which cannot be easily classified. Examples: Vertebrae of the spinal cord, many facial bones like the ones which hold or enclose the sinuses
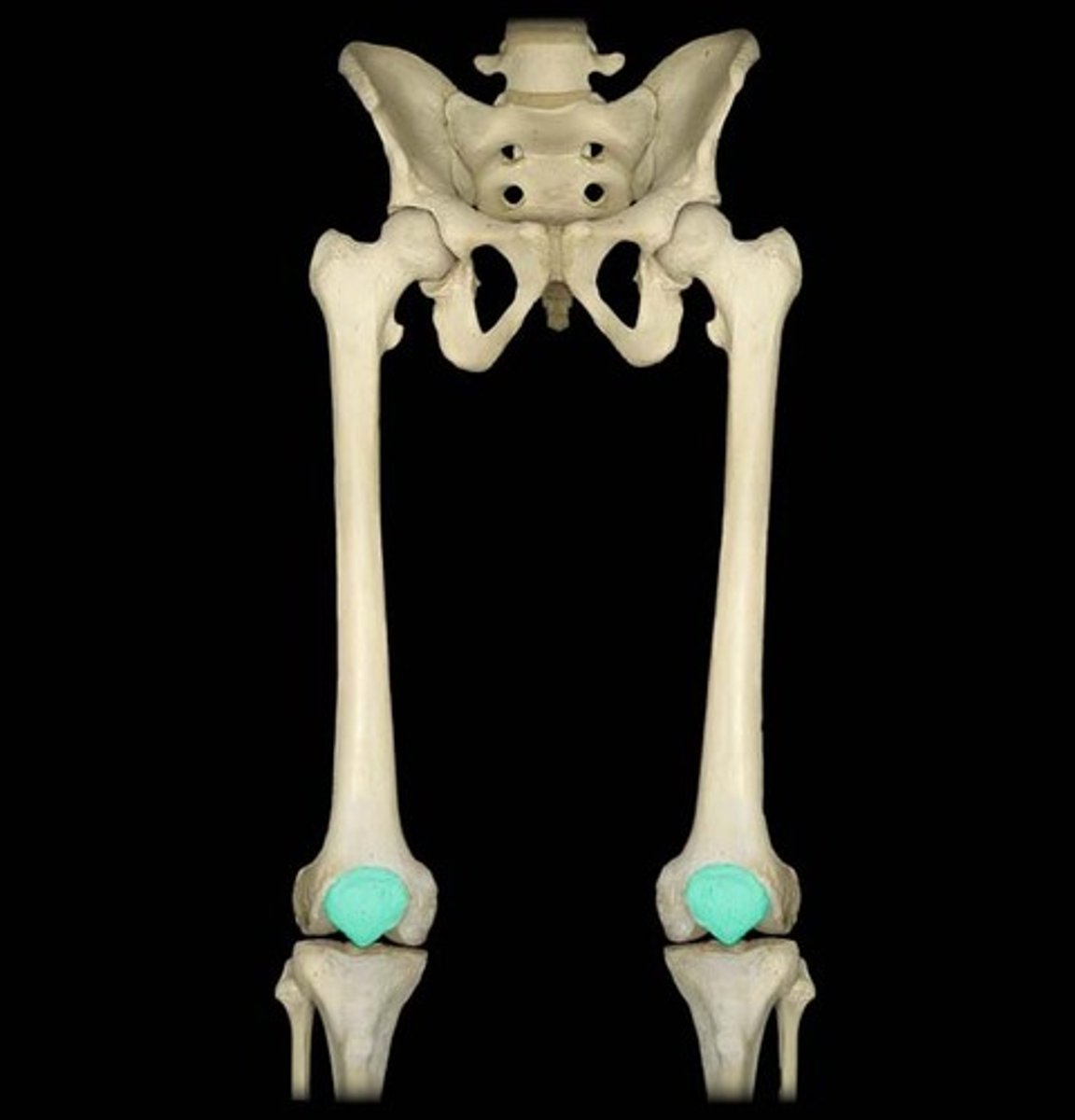
Sesamoid Bone
Small, round bones with a sesame seed-like shape. They form in the tendons of the feet, hands, and knees where a lot of pressure builds up in a joint. The patellae, of the knees, are the only common bone of this type found in common between people.
Articulation
When two bone surfaces make contact to produce a joint/connection for a specific movement or alternate function.
Projections
Indentations on a bone which indicate the attachment points of ligaments or ligaments. The size and shape indicate the force exerted or required by the tendon/ligament.
Holes
A large opening or groove in a bone which allows for nerves or blood cells to enter. The size indicates the quantity of nerves or blood vessels required.
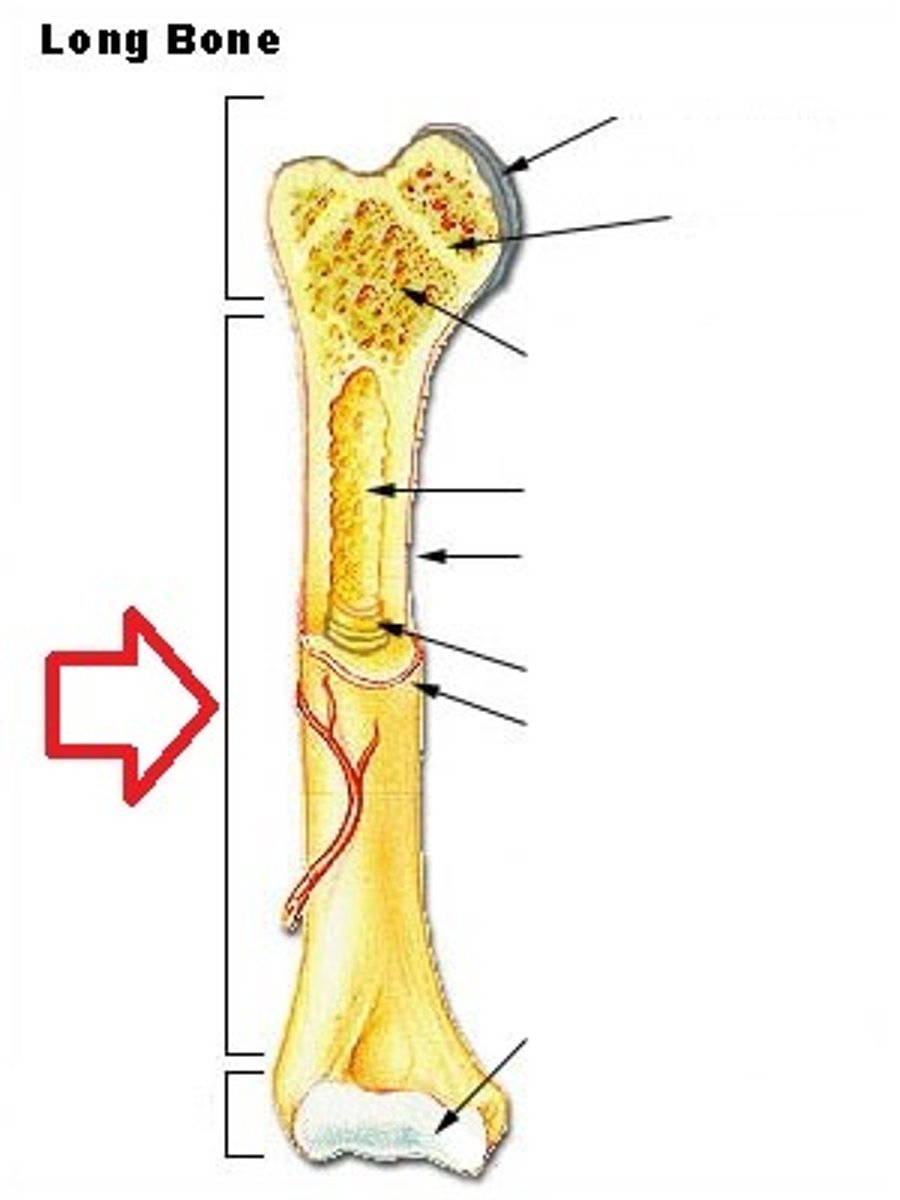
Epiphysis
The wider section at the end of a long bone filled with spongy bone and red blood cell marrow.
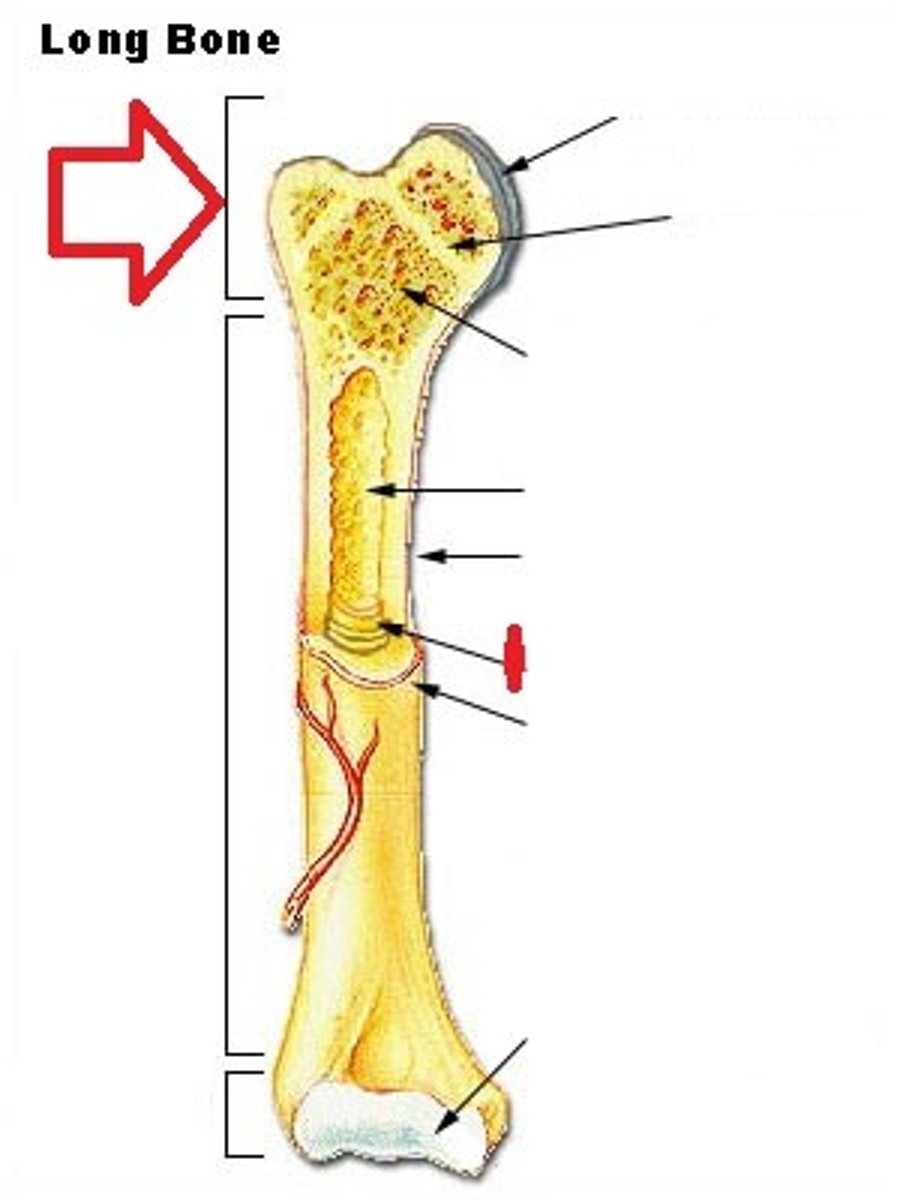
Metaphysis
The narrow area of a long bone where the epiphysis and diaphysis meet. Contains the epiphyseal plate (growth plate), a layer of cartilage in a growing bone.

Diaphysis
Tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of a long bone. This shaft is made of compact bone and is filled with yellow marrow. Also contains the medullary cavity.
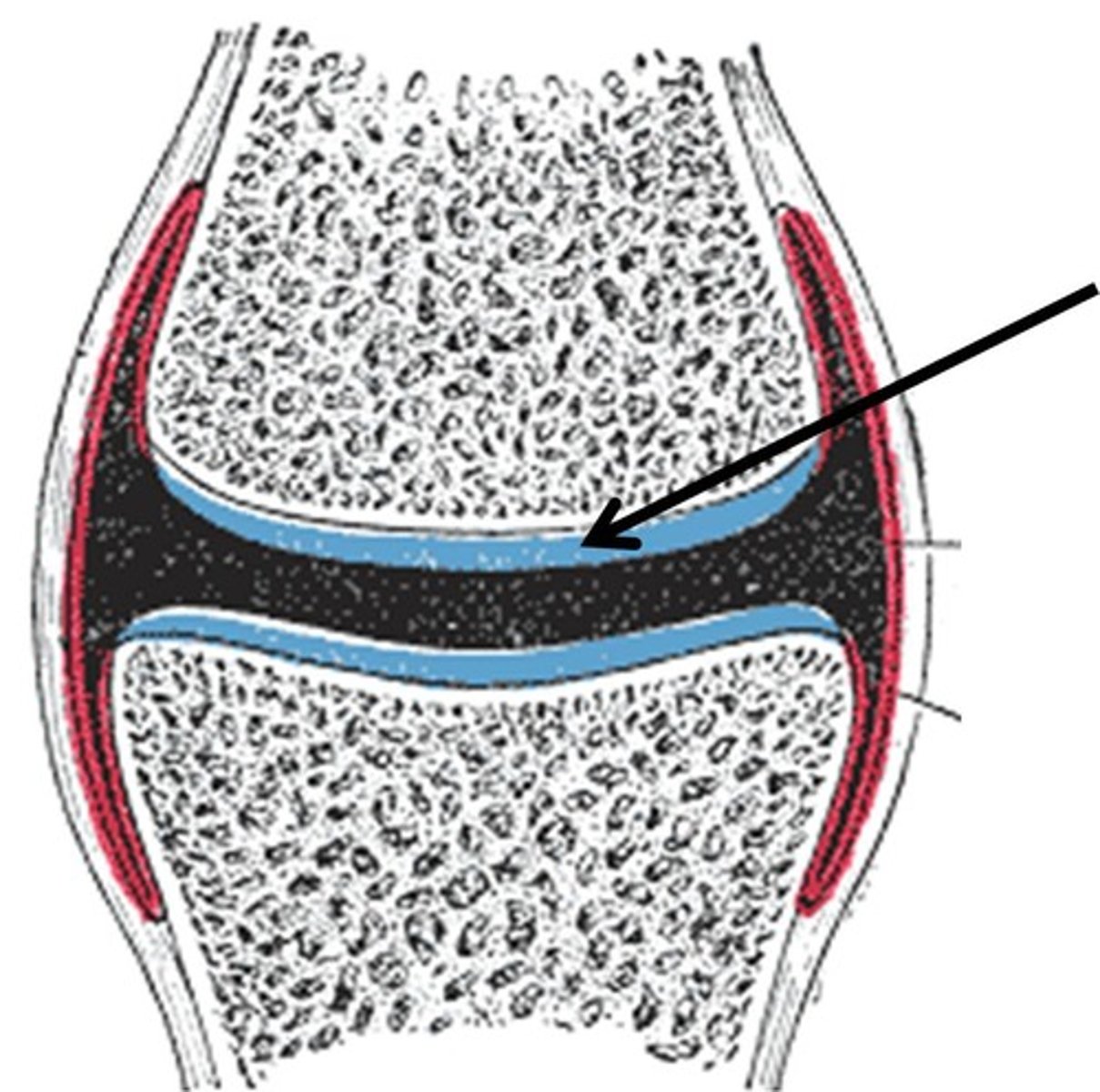
Articular Cartilage
A thin layer of cartilage between a joint/connection of two bones which acts as a shock absorber and provides protection from friction.
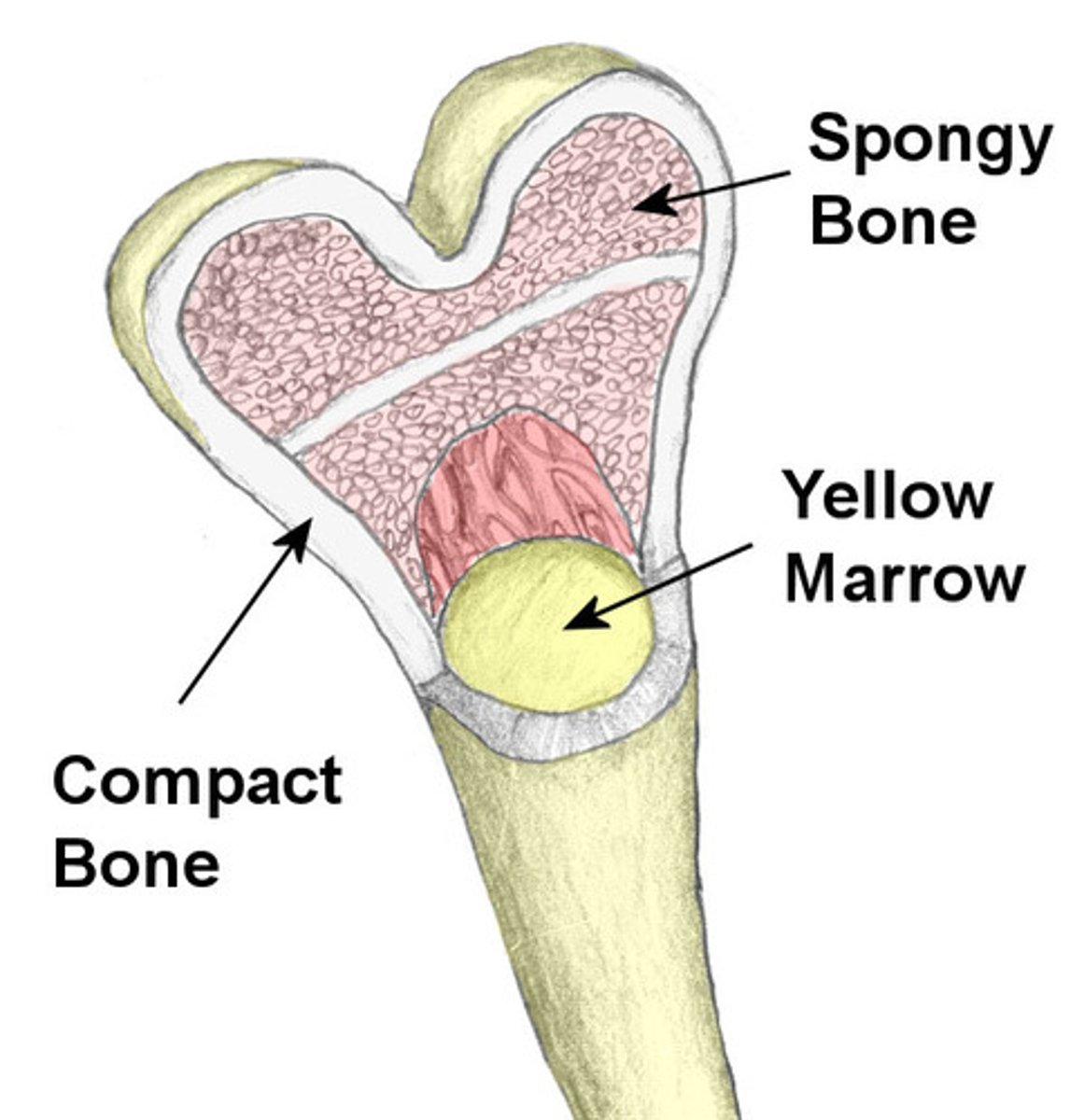
Yellow Bone Marrow
In the medullary cavity within the diaphysis and produces fat, cartilage, and bone. Yellow color comes from carotenoids in the fat droplets of fat cells.
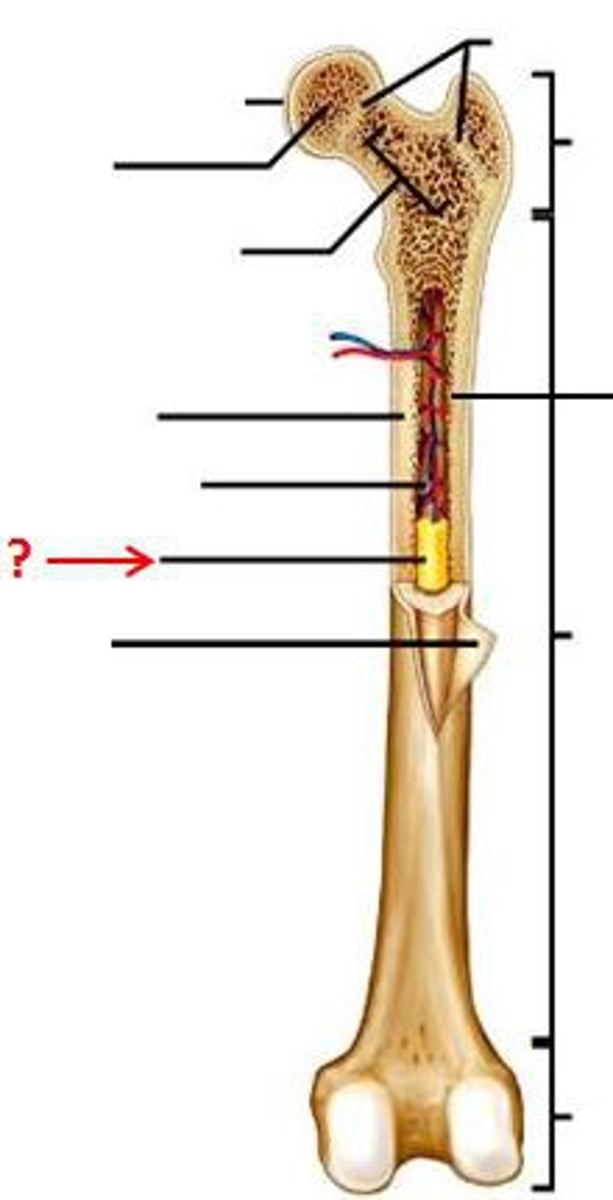
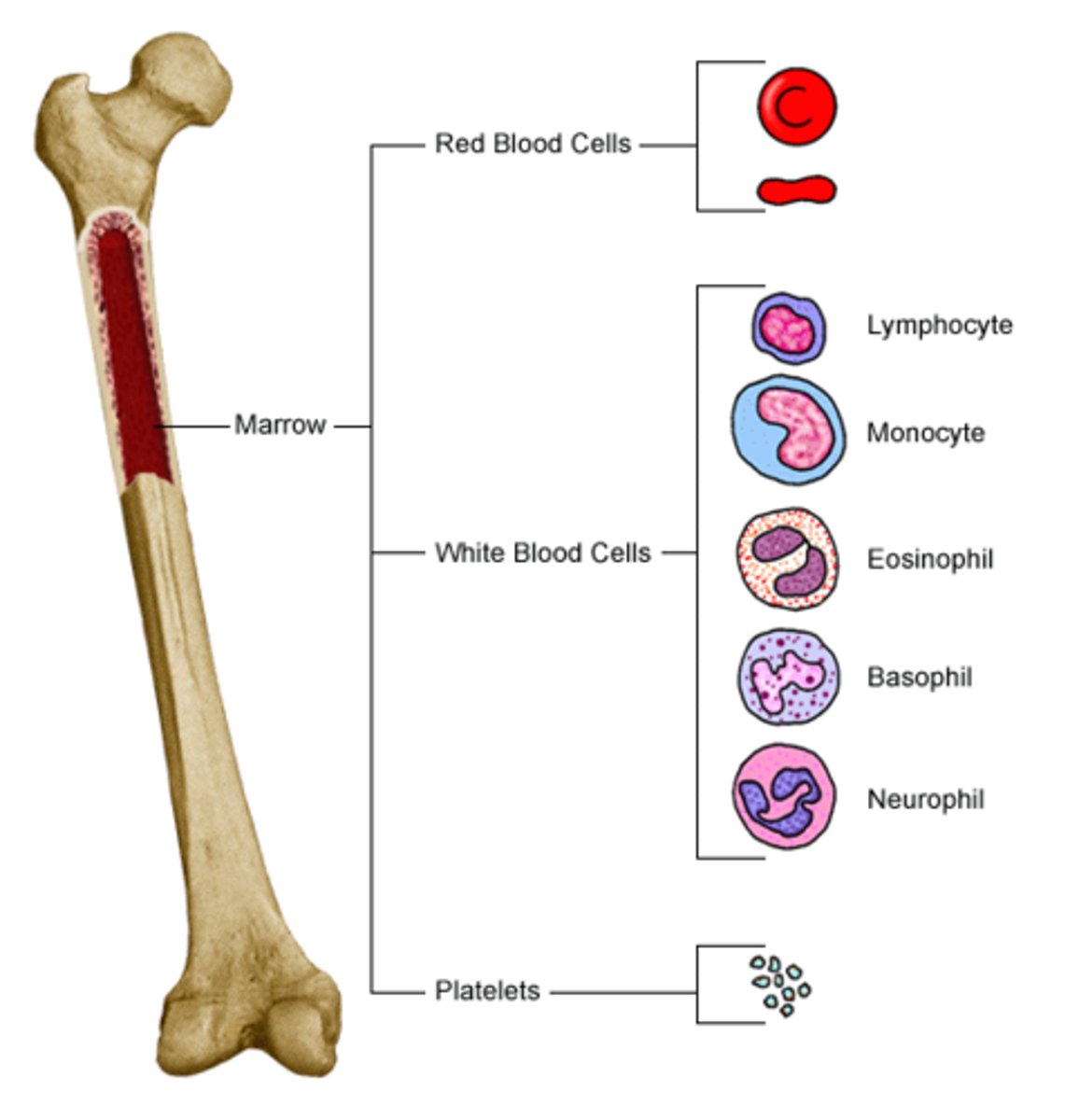
Red Bone Marrow
In the spongy bone of the epiphysis and metaphysis and produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red color comes from hemoglobin (iron rich substance) in the erythroid cells.
Periosteum
Fibrous membrane which covers the external layer of a bone, except where the epiphysis forms new joints with other bones. Contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. Ligaments and tendons attach to bones here.
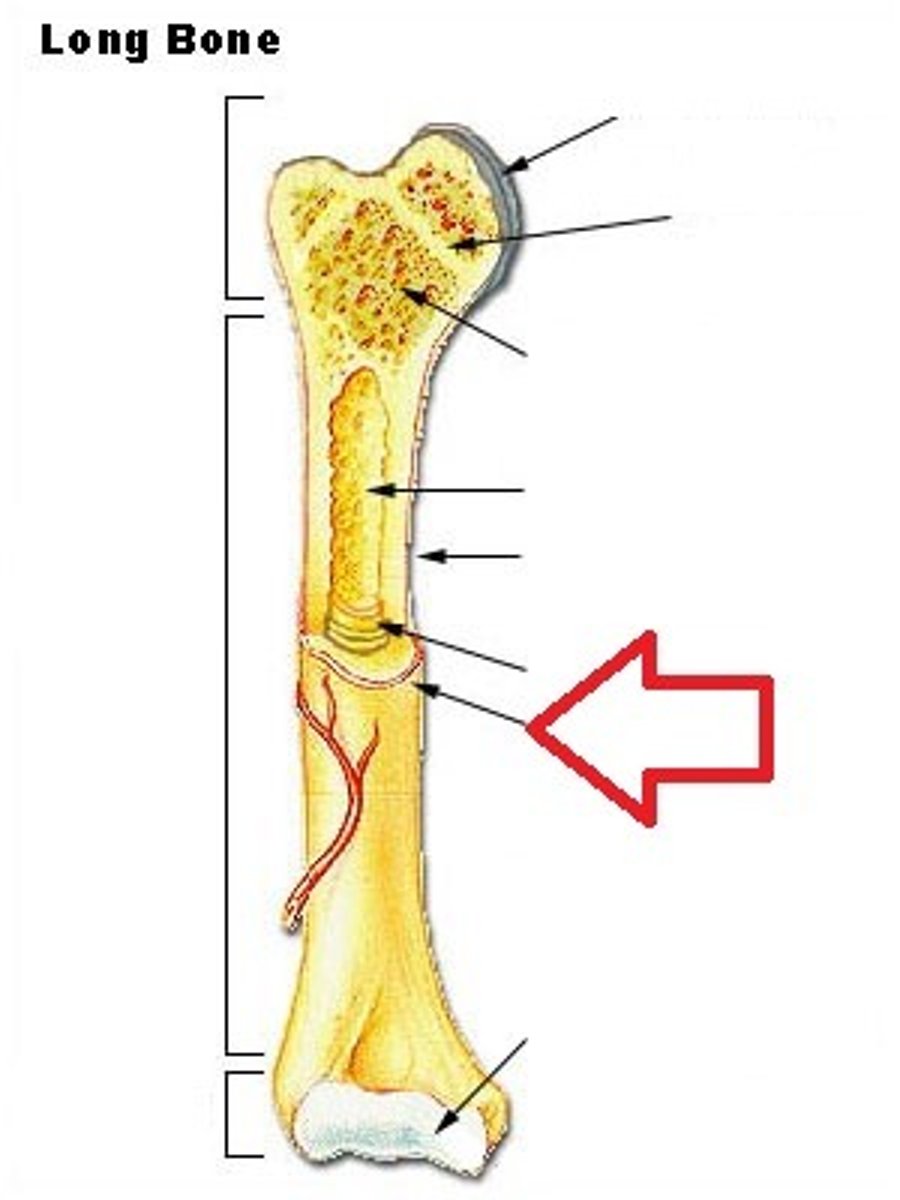
Endosteum
Delicate membranous lining of the medullary cavity. Bone growth, repair and remodeling occur here. On the interior, not exterior.
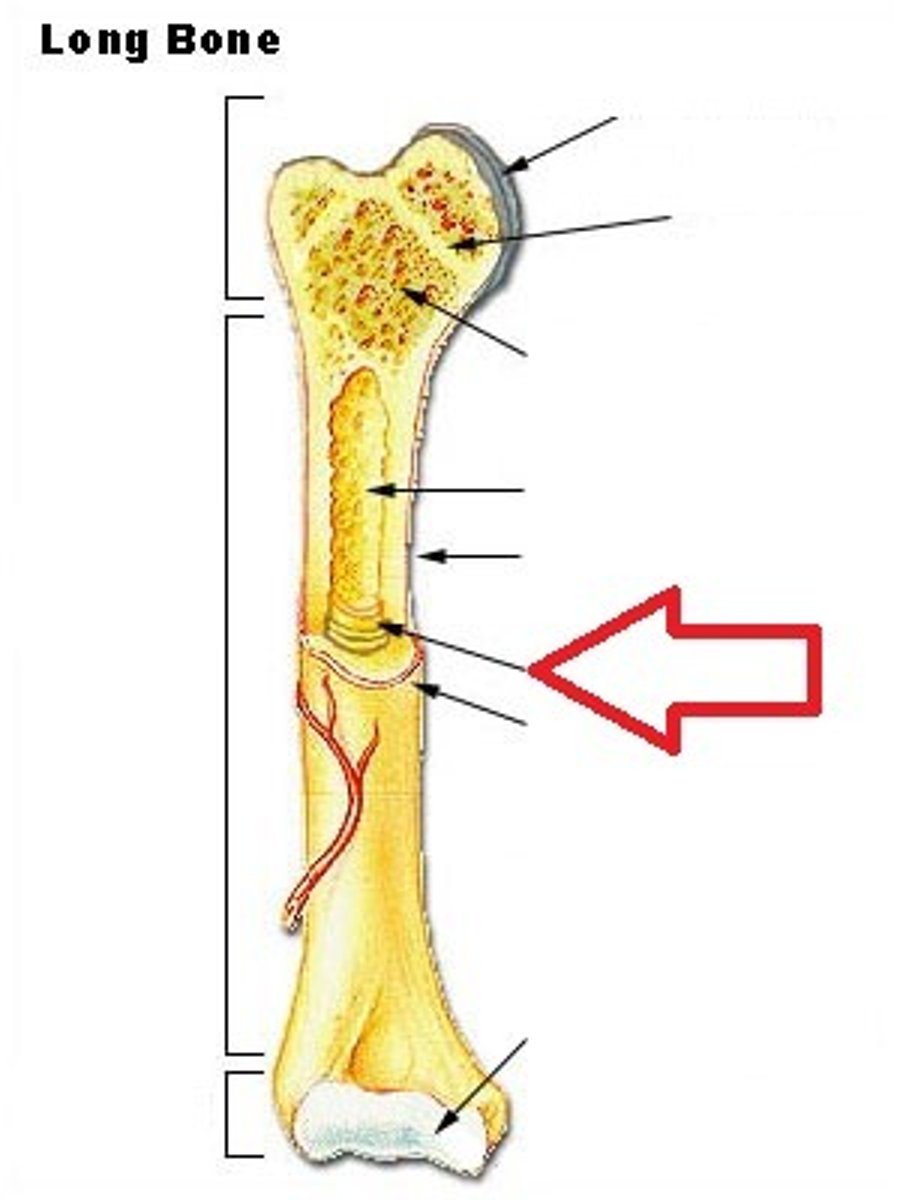
Medullary Cavity
Hollow region in the diaphysis containing yellow marrow. Lined by membranous lining known as the endosteum.
Osteocyte
Primary cell of mature bone and the most common bone cell. Located in a lacuna and is surrounded by bone tissue. Maintains the mineral concentration of the matrix through the secretion of enzymes. Does not perform mitosis.
Osteoblast
Responsible for forming new bone by synthesizing and secreting collagen matrix and calcium salts, not through mitosis. Once the secreted matrix around this cell solidifies, it becomes trapped and becomes an osteocyte.
Osteogenic/ Osteoprogenitor
The ONLY bone cells which perform mitosis. Immature cells are found in deep layers of the periosteum and marrow. They eventually develop into osteoblasts.
Osteoclast
Responsible for bone absorbation/breakdown for repair work or unnecessary bone. Originate from monocytes and macrophages, white blood cells.
Collagen
A structural protein in the extracurricular space of connective tissues which provides a soft framework while adding strength and flexibility.
Hydroxylapatite
Main phosphate mineral that makes up teeth and bone. Made up of calcium, phosphate, and one molecule of hydroxide: Ca5(PO4)3(OH)
Cartilage
Smooth elastic tissue; rubber-like padding that covers and protects the end of the epiphysis of long bones.
Compact Bone
The denser bone out of the two types of bone tissues. In long bones, this type of bone makes up the diaphysis
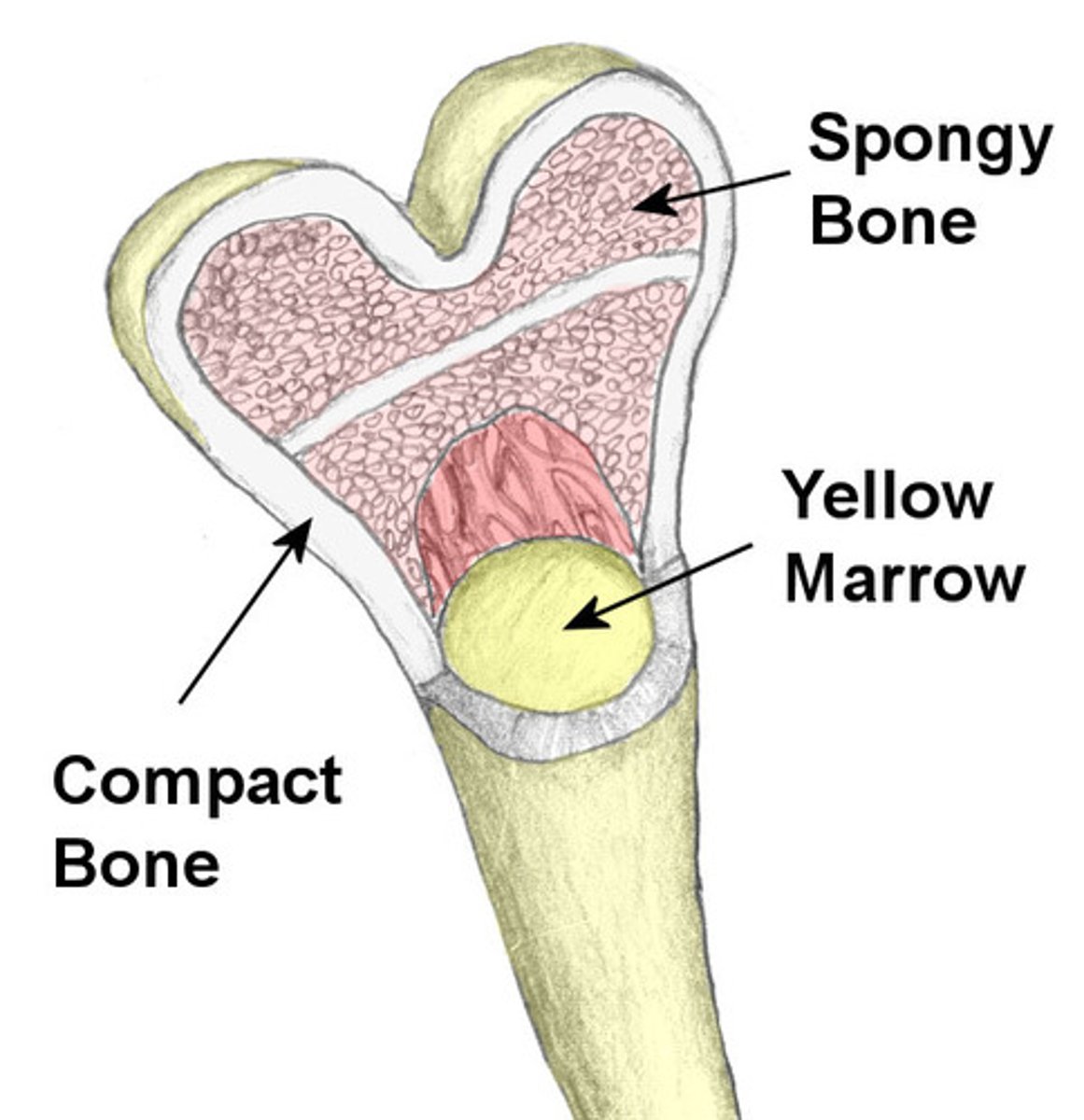
Spongy Bone
Also known as Cancellous bone, this bone is less dense and is located inside the epiphysis of long bones. Made up of a lattice-like network of matrix spikes called trabeculae.
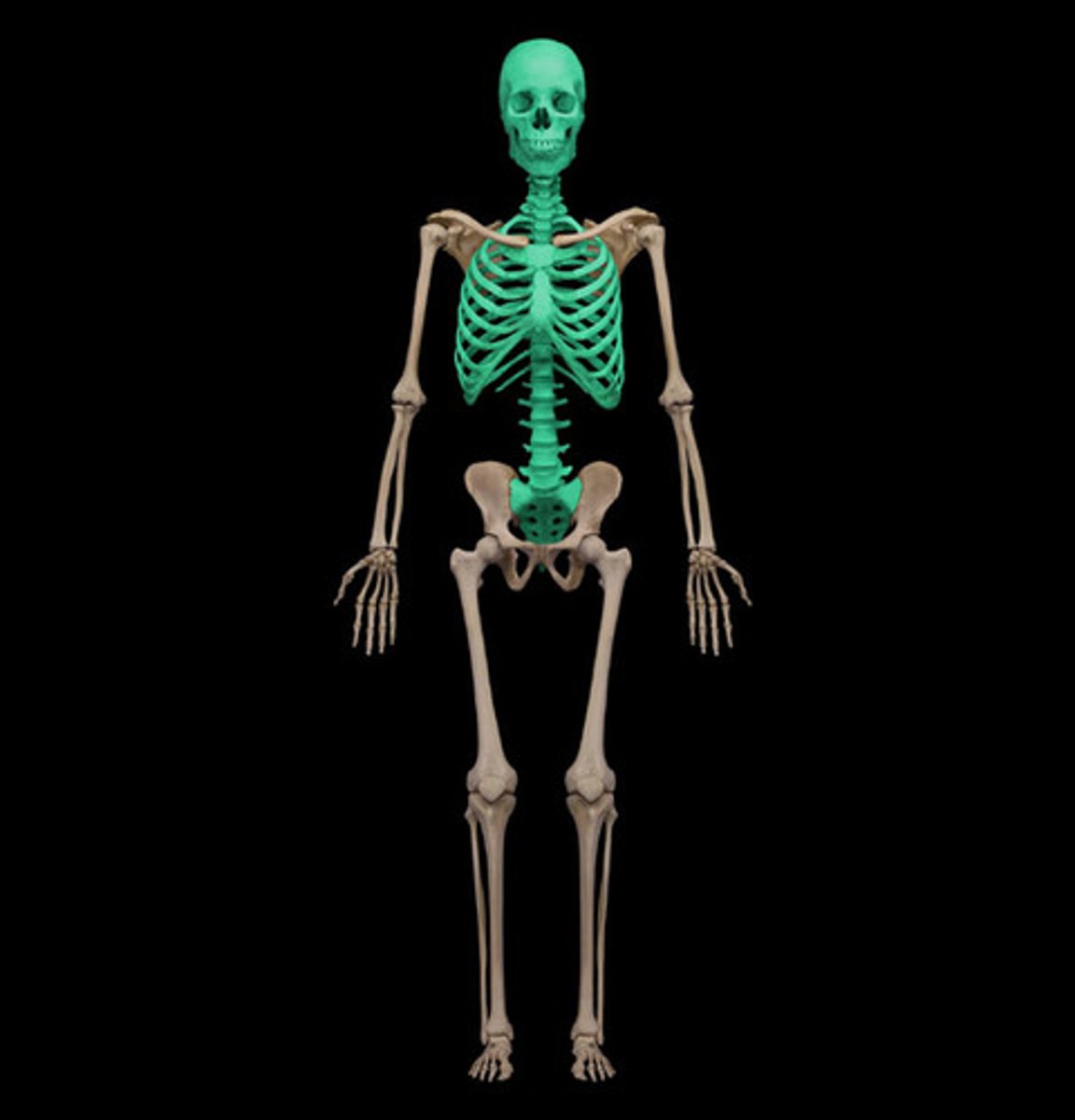
Axial Skeleton
The section of the skeleton, made up of 80 bones, which includes the cranium, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles, vertebral column, sternum bone, and ribs.
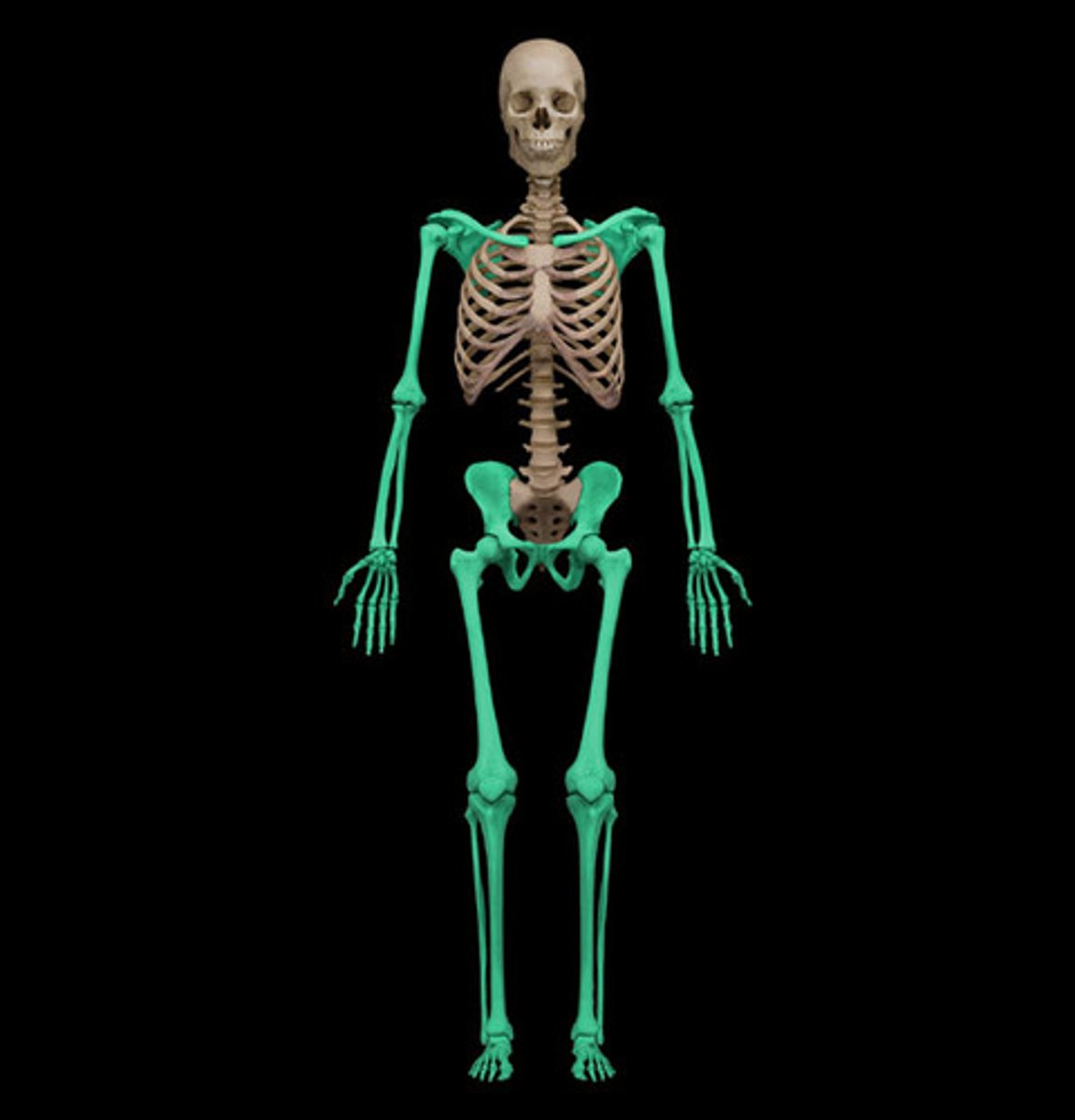
Appendicular Skeleton
The section of the skeleton, made up of 126 bones, which includes the pectoral girdle, left and right clavicle and scapula, arms and forearms, and the left and right humeras, ulna, and radius.
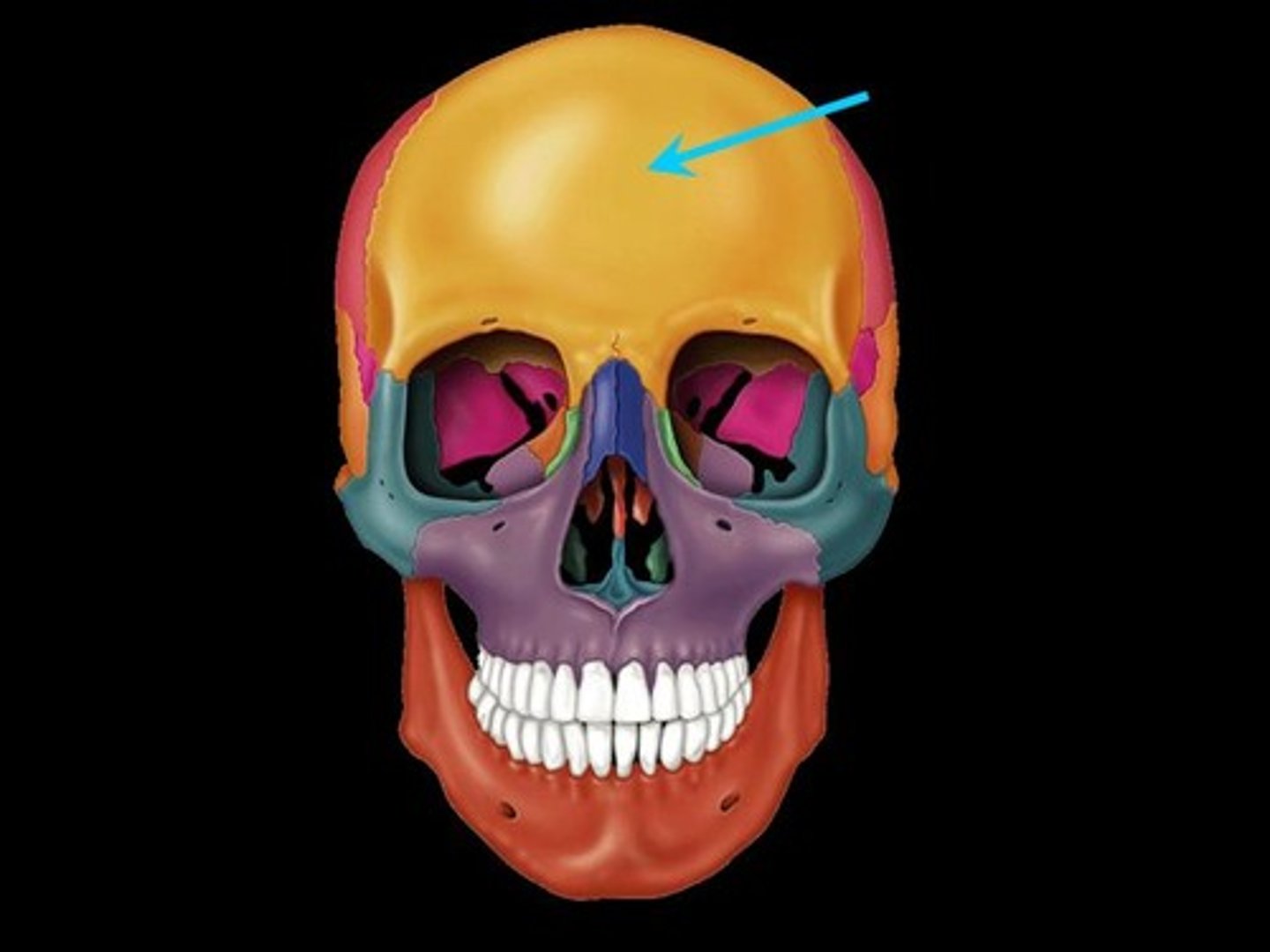
Frontal Bone
The bone of the cranium which forms the front or forehead of the skull and the upper parts of the eye sockets.
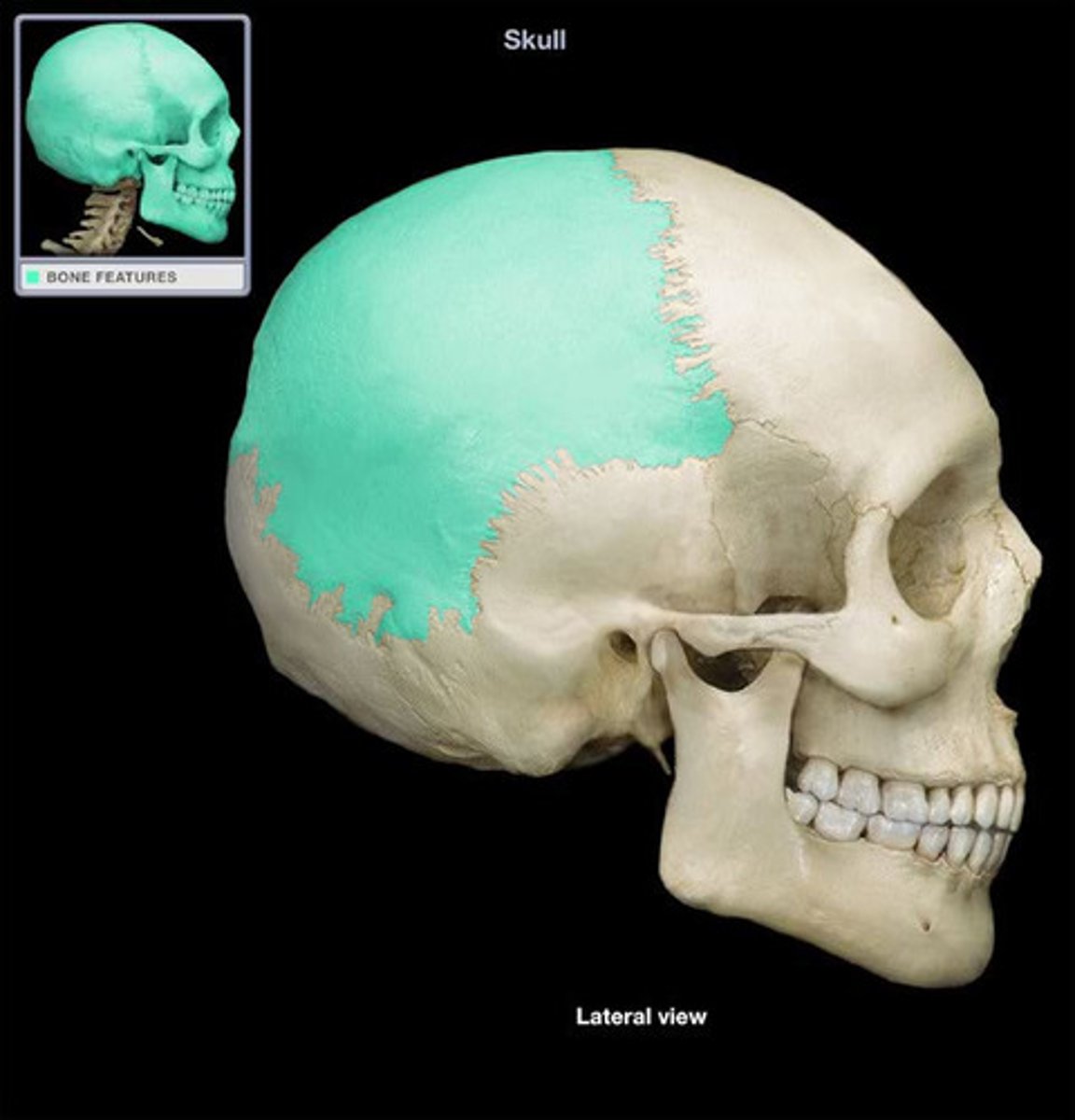
Parietal Bone
The bone which creates the central side and upper back of the cranium.
Temporal Bone
A pair of bones which form the lower part of the side of the cranium and enclose the middle and inner ear.
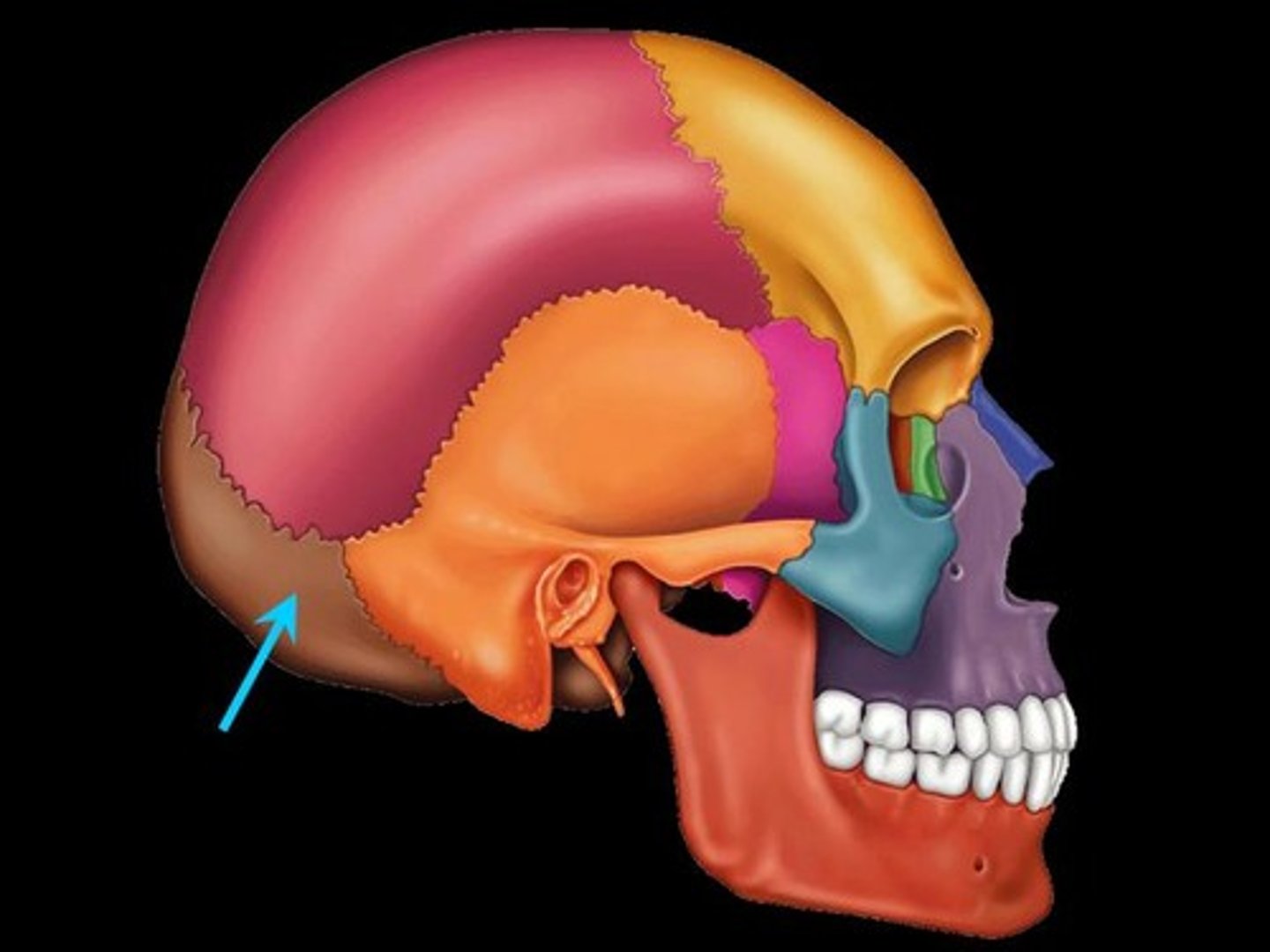
Occipital Bone
The bone of the cranium which forms the bottom, posterior side of the skull in which the vertebra of the vertebrae passes through.
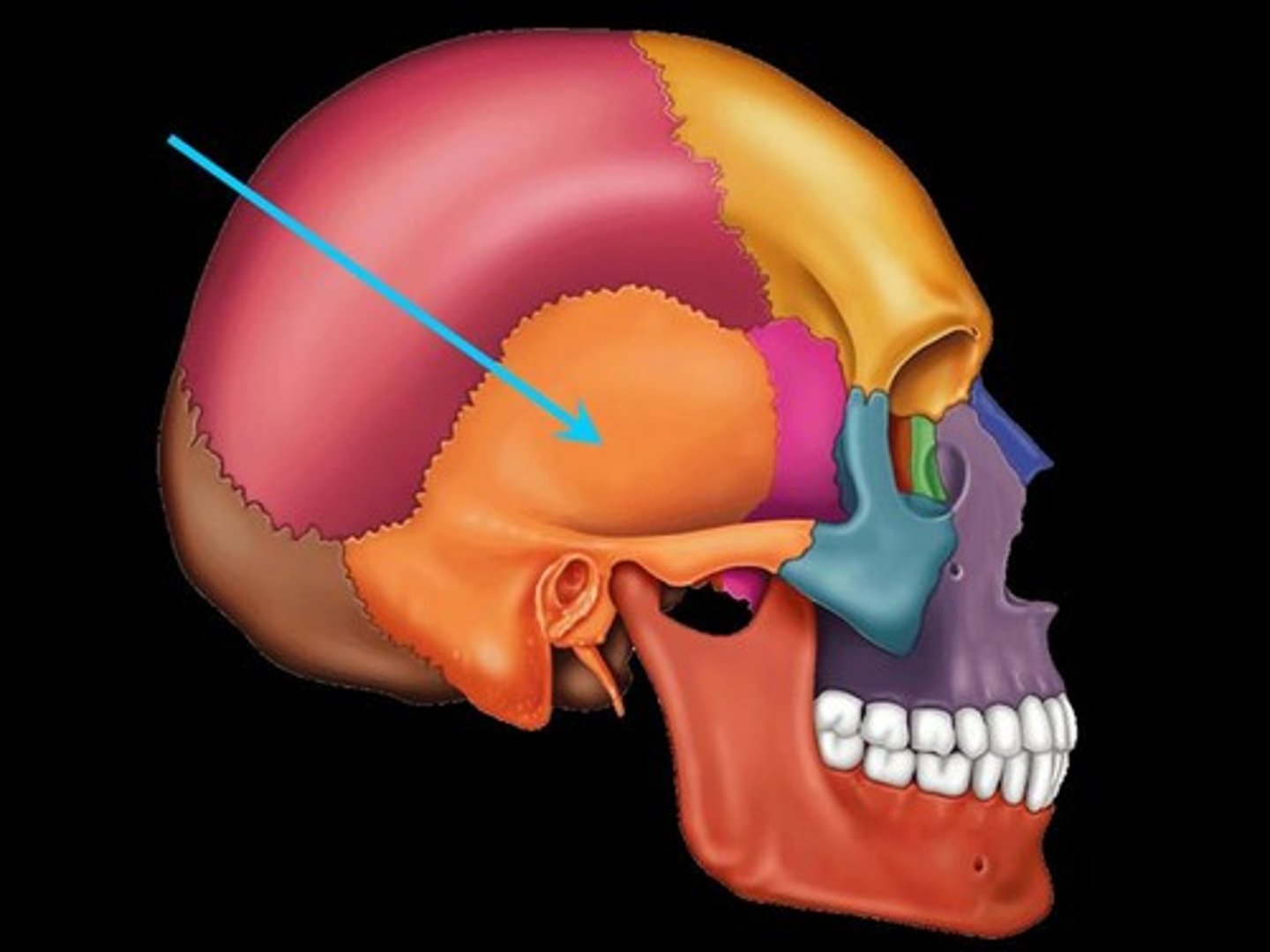
Sphenoid Bone
A compound bone located in the middle of the skull. While it is visible on the lateral side, it extends inside of the skull behind the eyes and below the front of the brain. It has two broad sides, which look like wings and contains air-filled sinuses.
Ethmoid Bone
A square bone at the root of the nose, to the left and right of the nasal bone, forming part of the cranium, and having many perforations through which the olfactory nerves pass to the nose.
Maxilla
the upper jaw bone of the cranium of human beings and most vertebrates. It also forms parts of the nose and eye socket of humans.
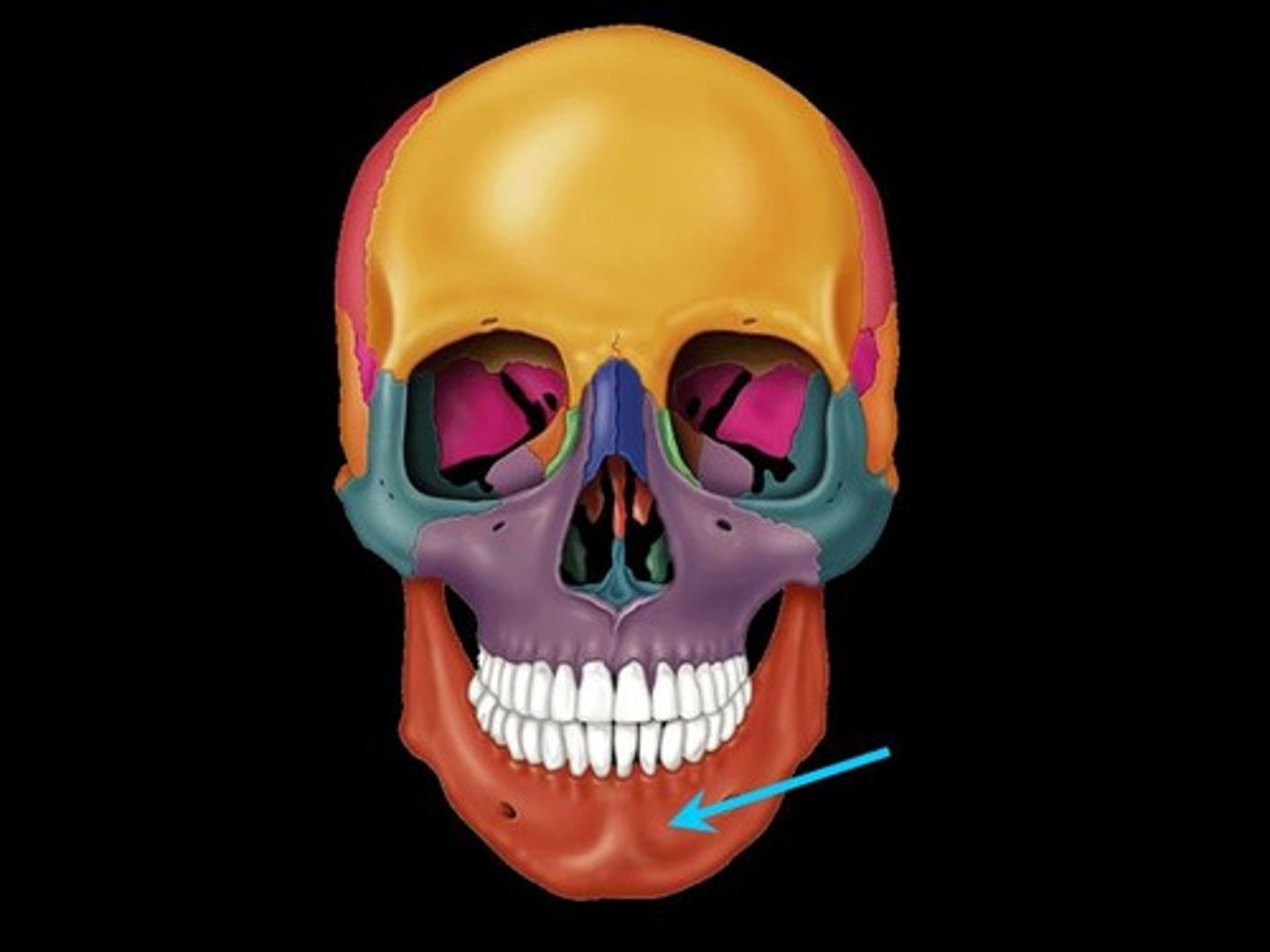
Mandible
the lower jaw bone for mammals and fish
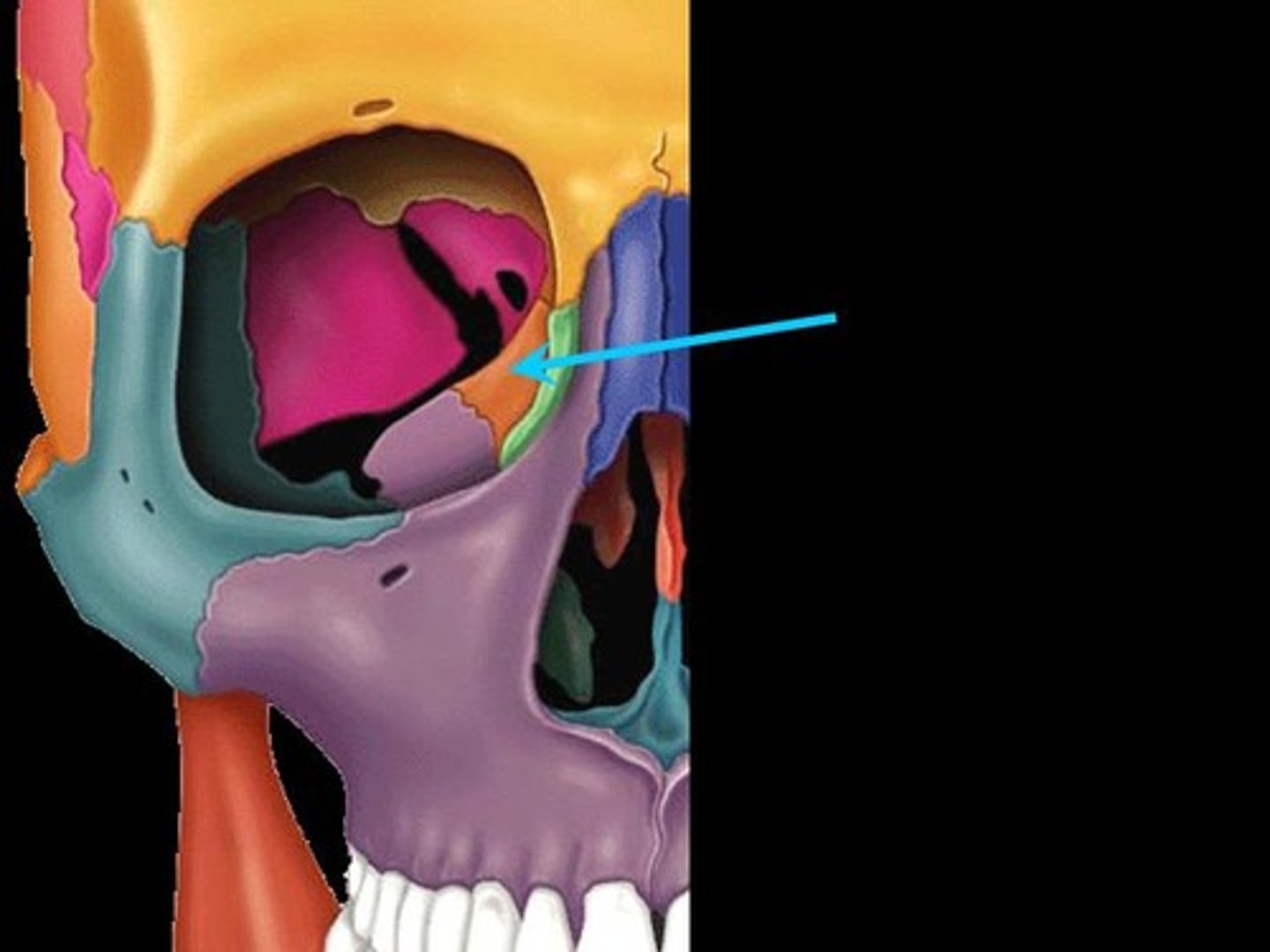
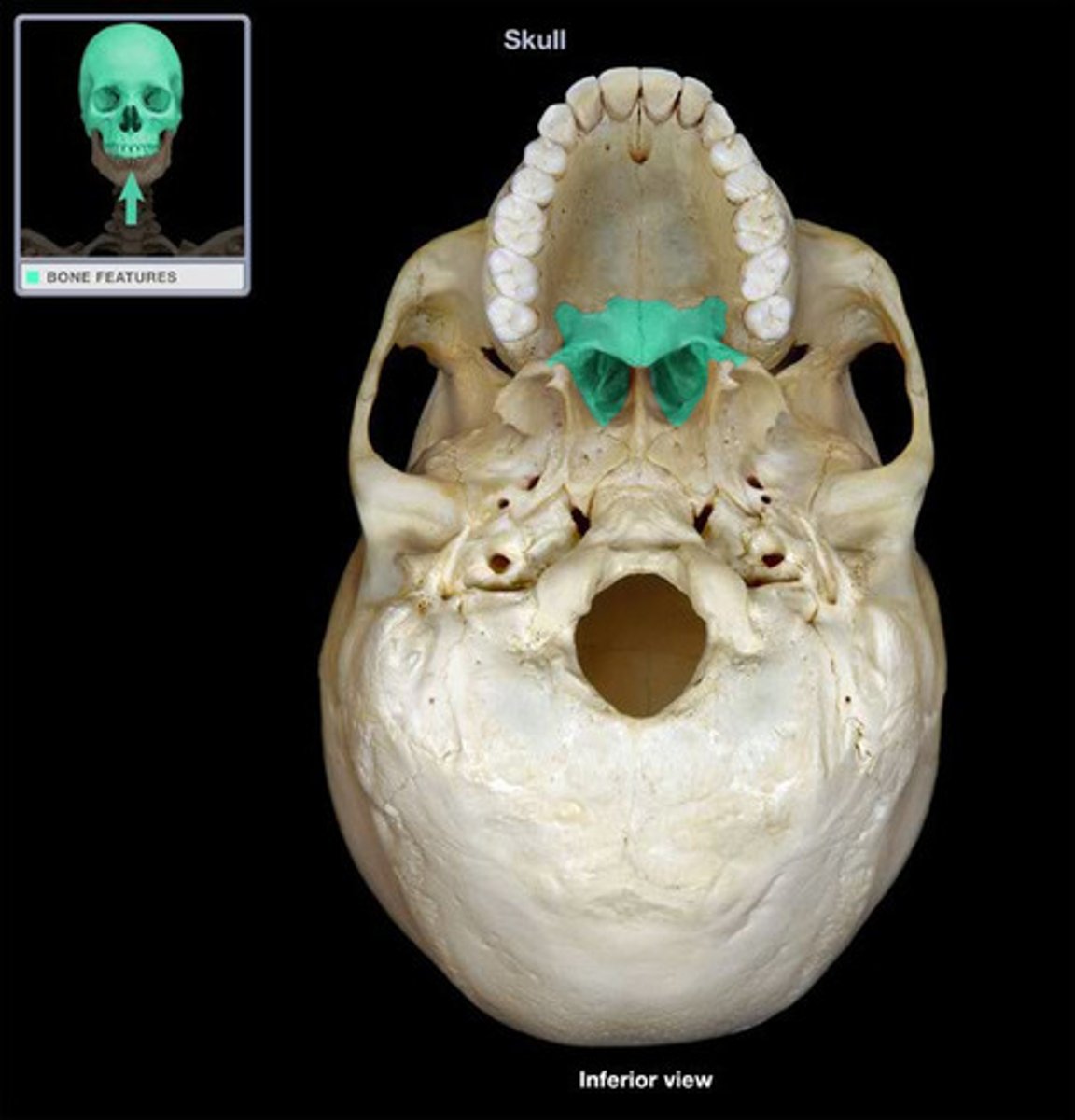
Palatine Bone
two bones within the skull forming parts of the eye socket, nasal cavity, and the hard palate.
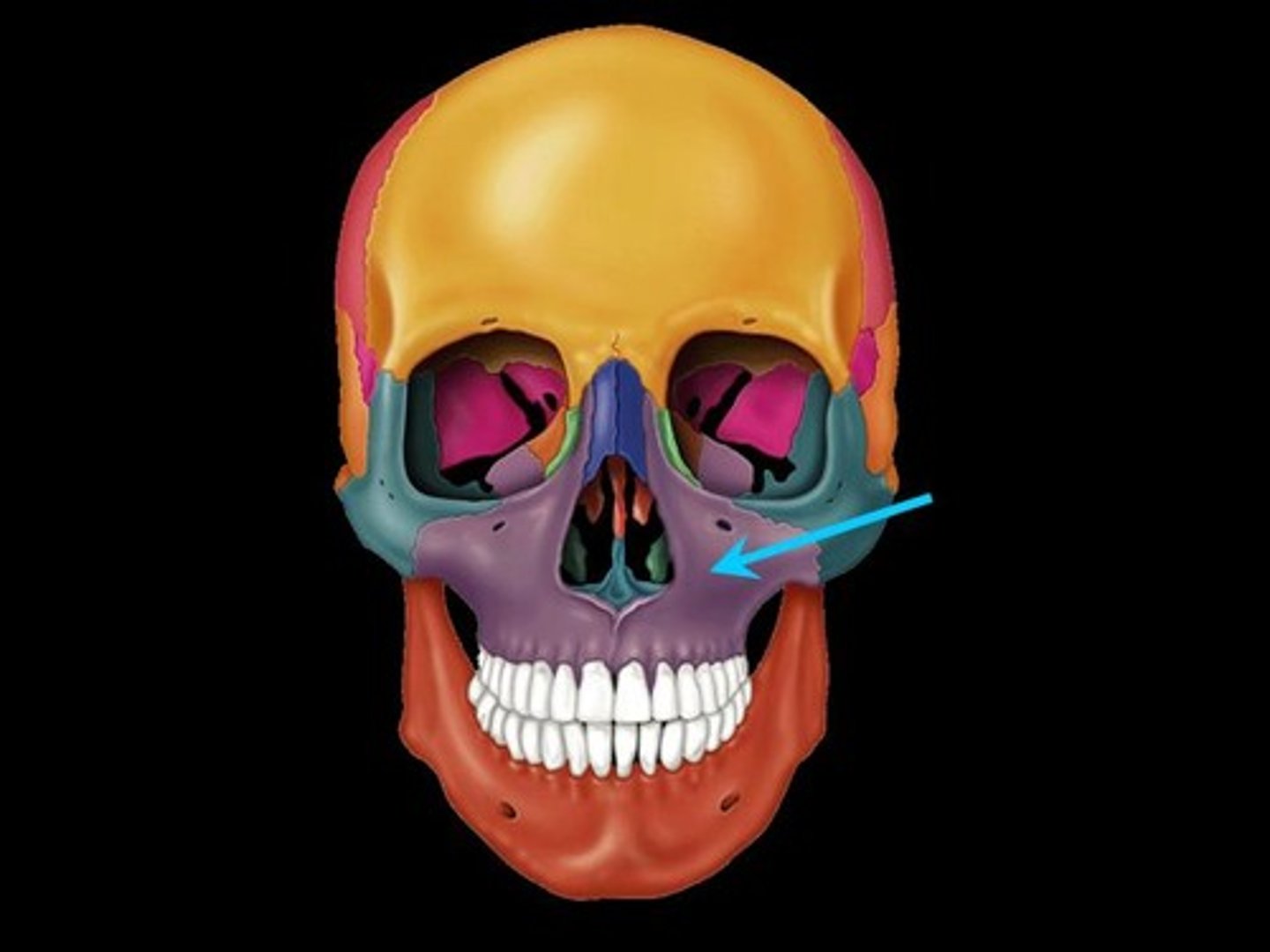
Zygomatic
The bone that forms the outer part of the cheek and the outer side of the eye socket.
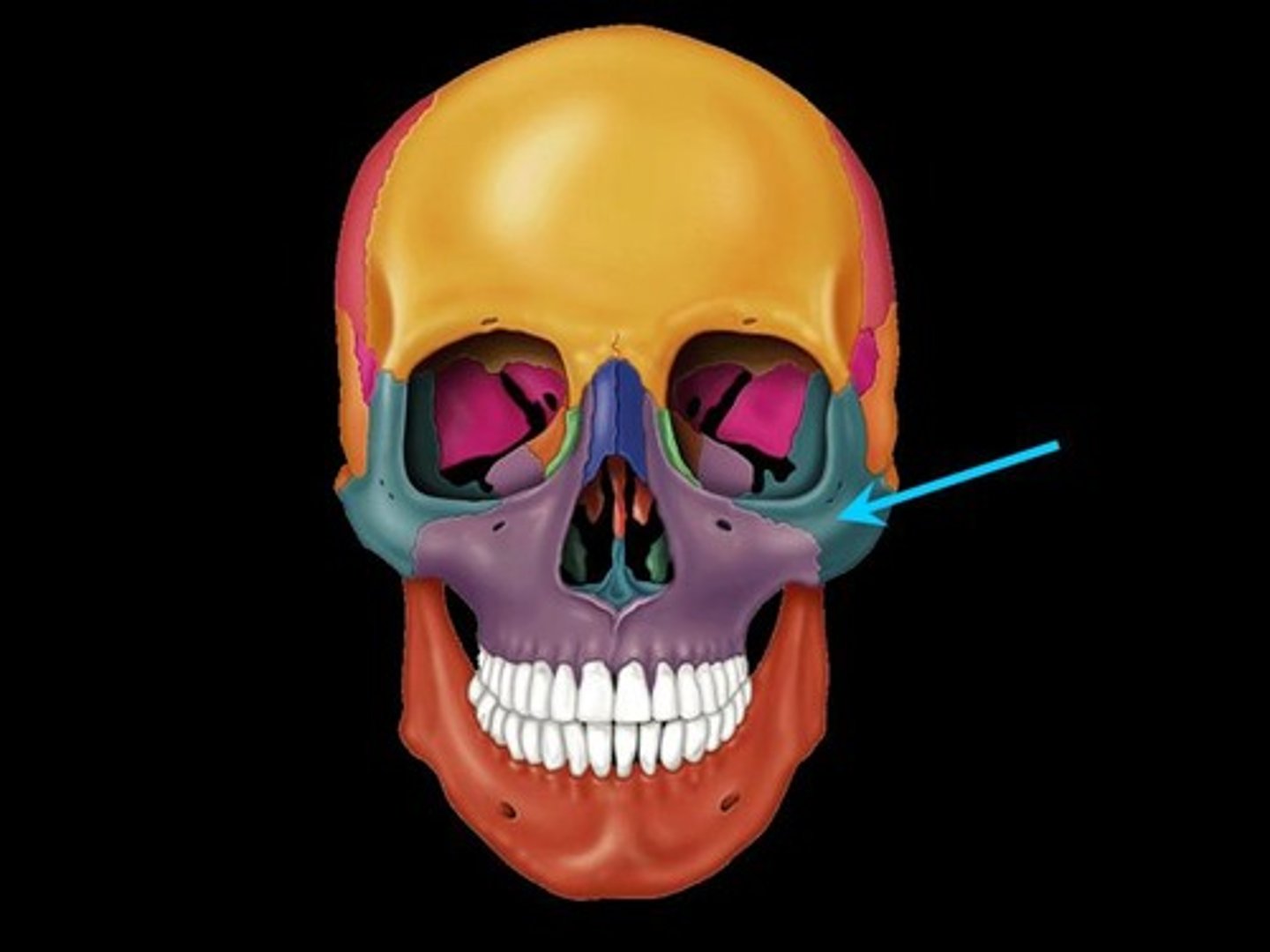
Nasal bone
two small, oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals. They are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face, and form "the bridge" of the nose.
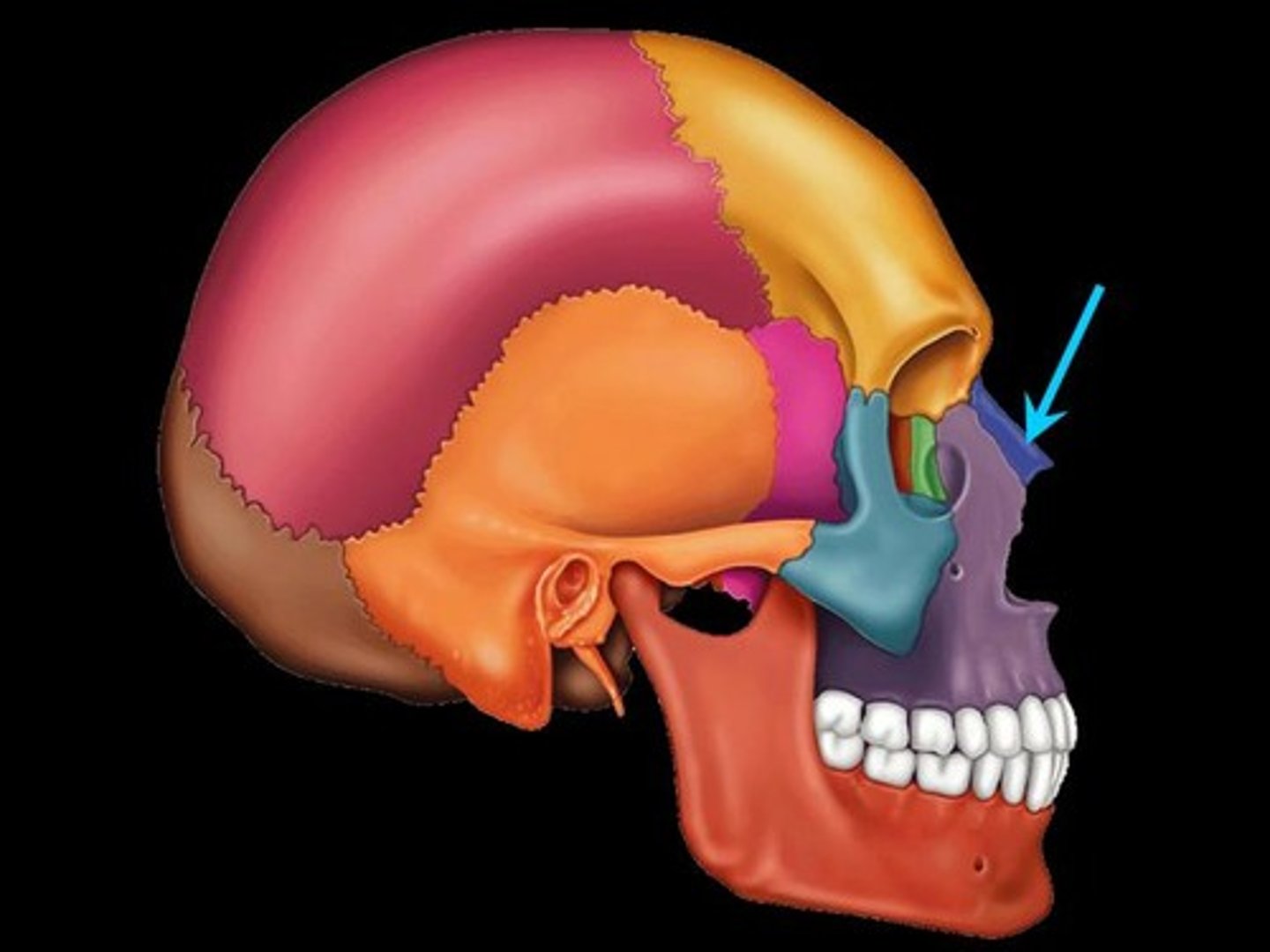
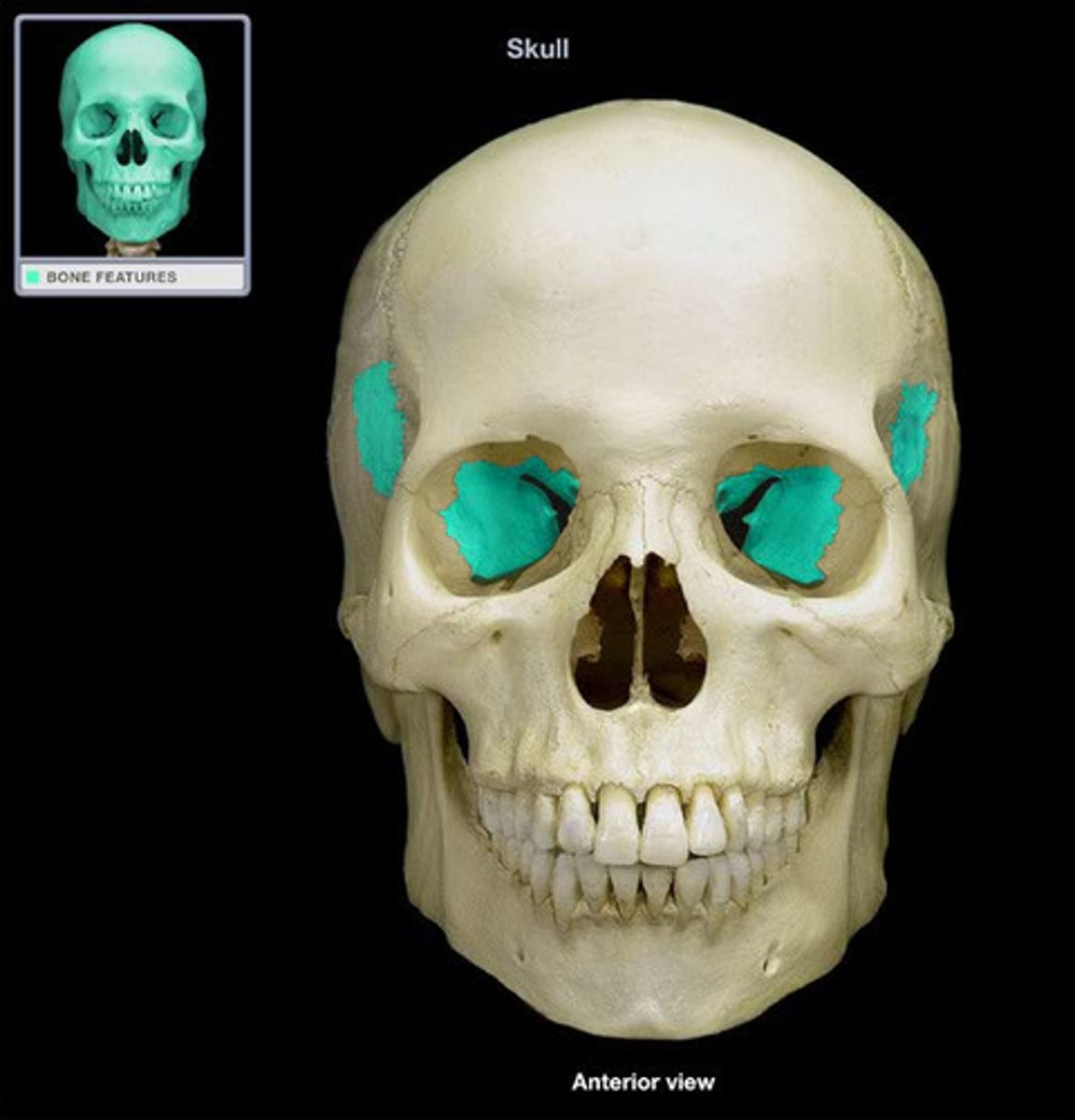
Lacrimal Bone
A small bone forming part of the eye socket proximal to the external nose.
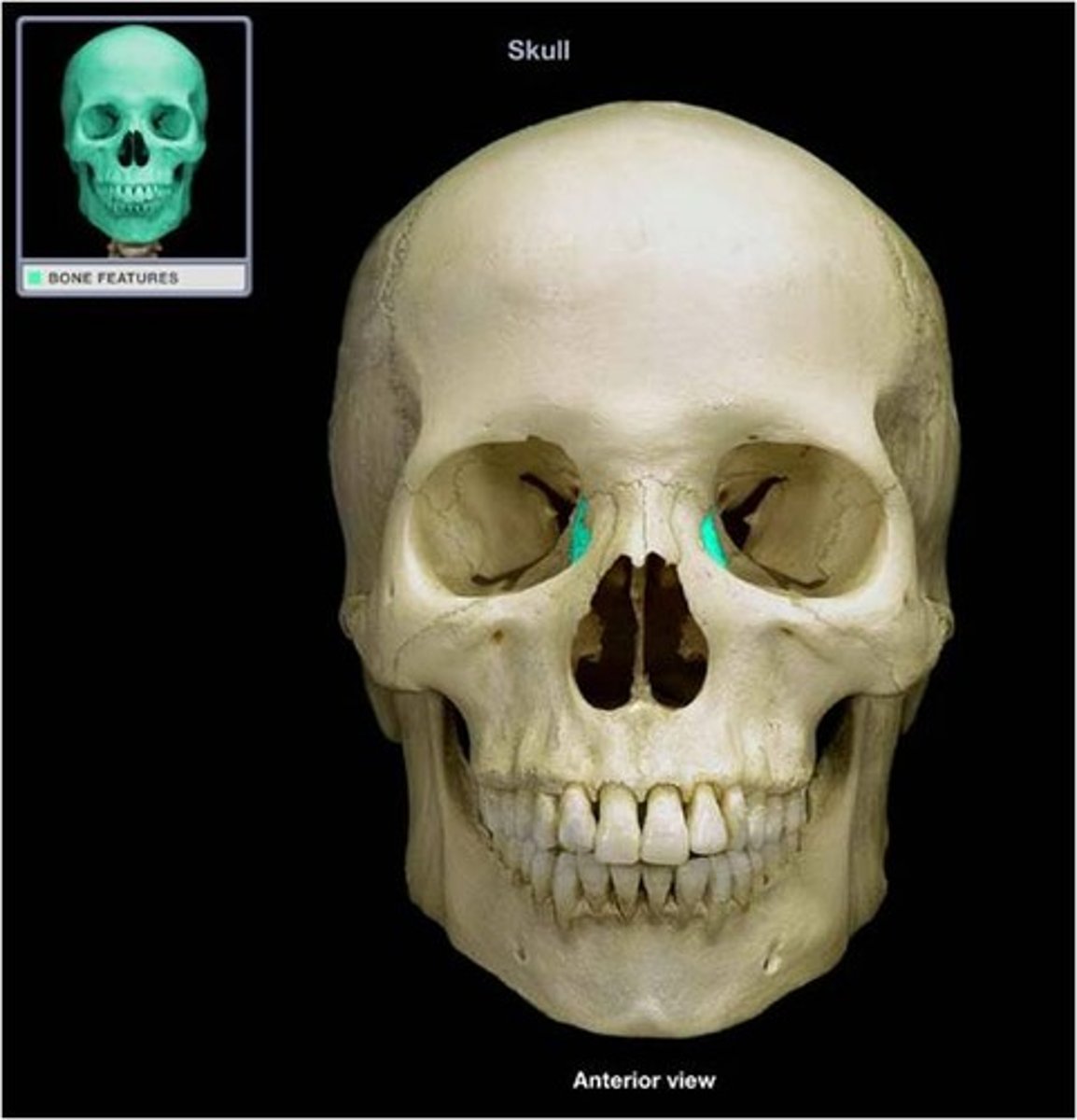
Vomer Bone
One of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with (comes in contact with) the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones.
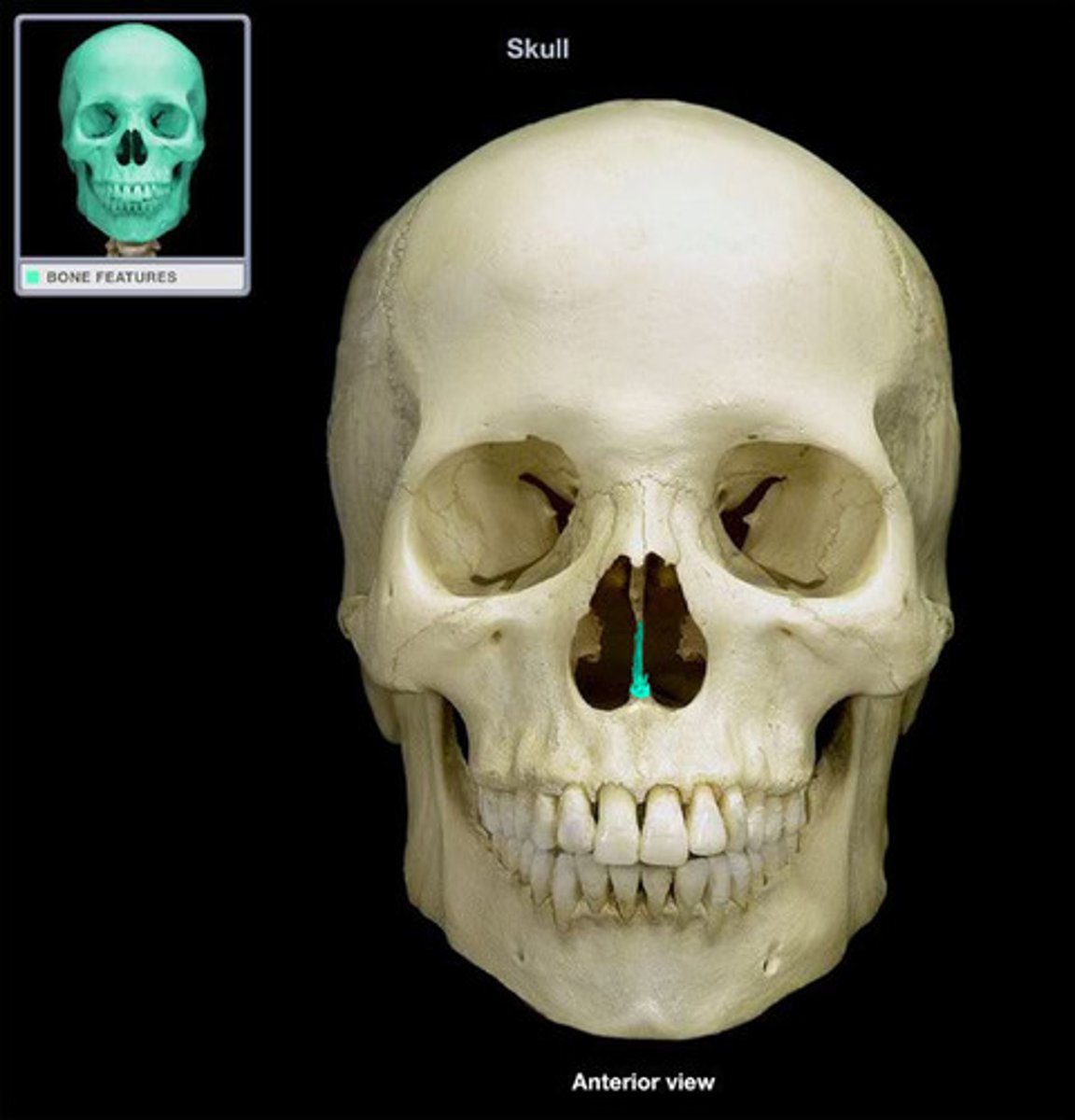
Interior Nasal Conchae
One of the turbinates in the nose. It extends horizontally along the lateral wall of the nasal cavity and consists of a lamina of spongy bone, curled upon itself like a scroll.
Malleus
A small bone in the middle ear that transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus.
Incus
A small anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations between the malleus and stapes.
Stapes
a small stirrup-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations from the incus to the inner ear.
Hyoid
A U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue.
Cervical Vertebrae
Seven irregular bones or vertebral bodies (C1-C7) that provide support and structure for the cervical spine which connects to the head.
Axis
the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine. It produces a pivot joint by which the atlas, which carries the head, rotates.
Atlas
the first cervical vertebra (C1) of the spine which carries the head and permits it to rotate and pivot. It is named after the god in Greek mythology that carries the world on his shoulders.
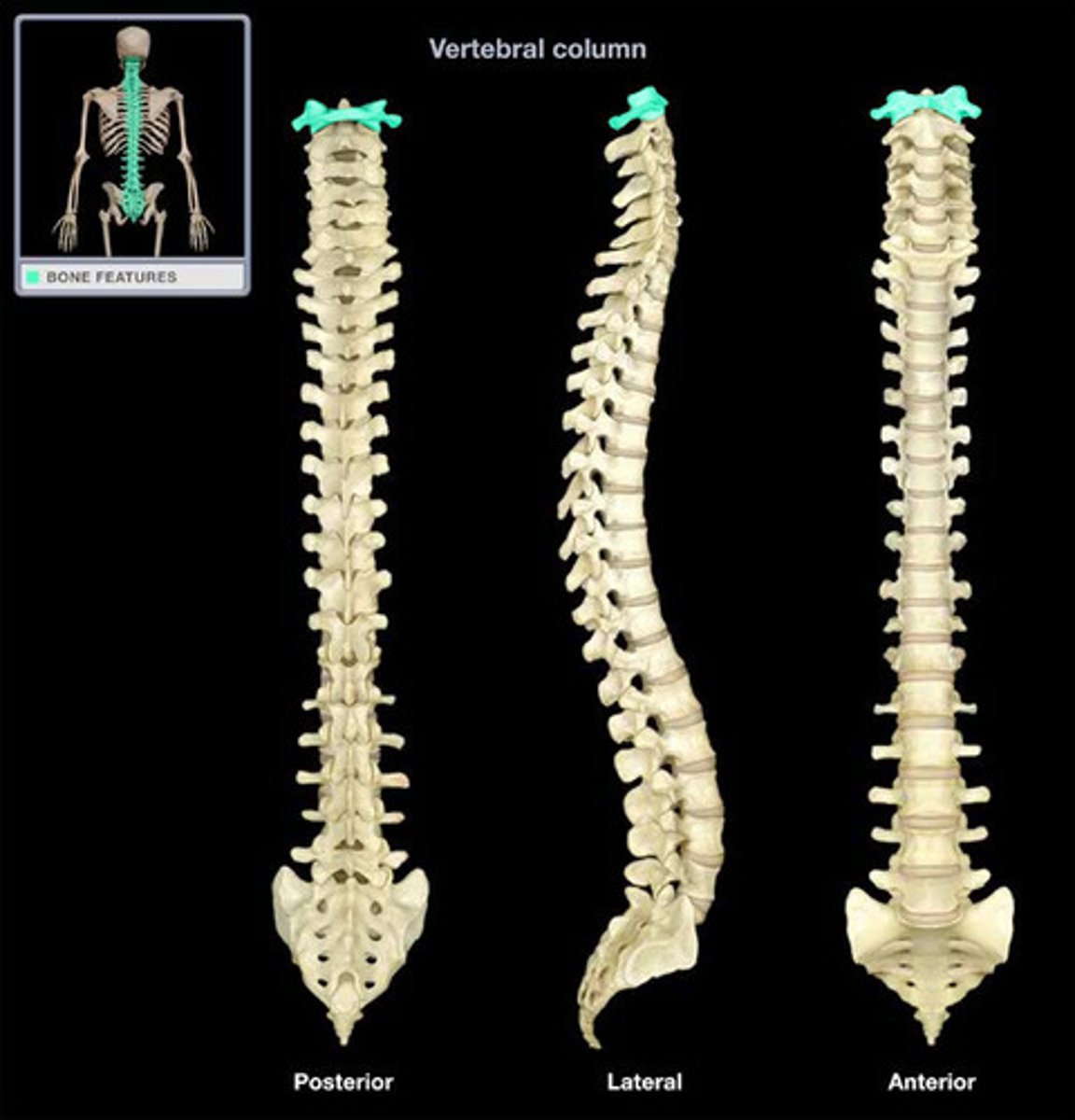
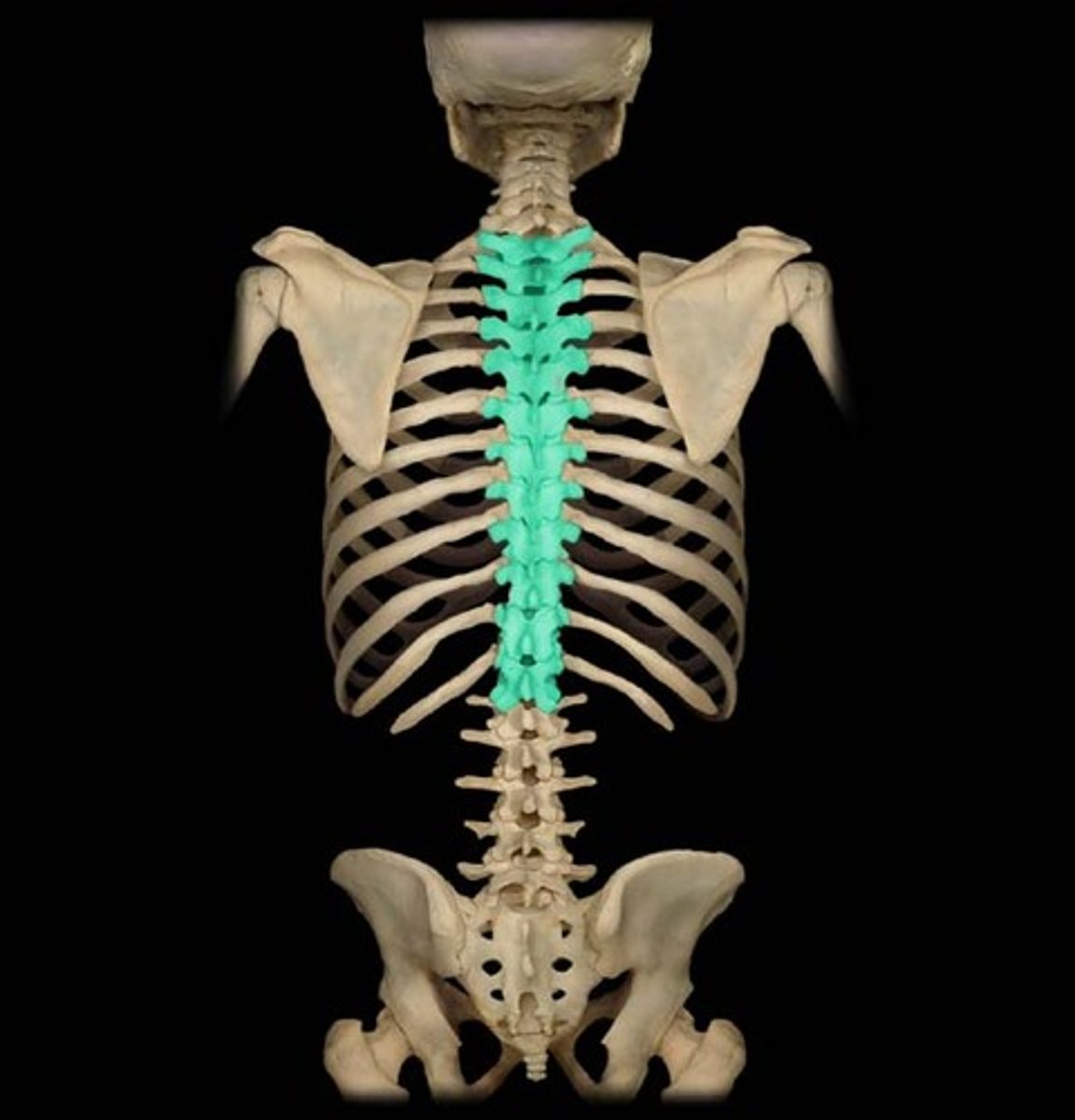
Thoracic Vertebrae
The twelve irregular bones or vertebral bodies (T1-T12) by which the ribs attach through articular cartilage or facets.
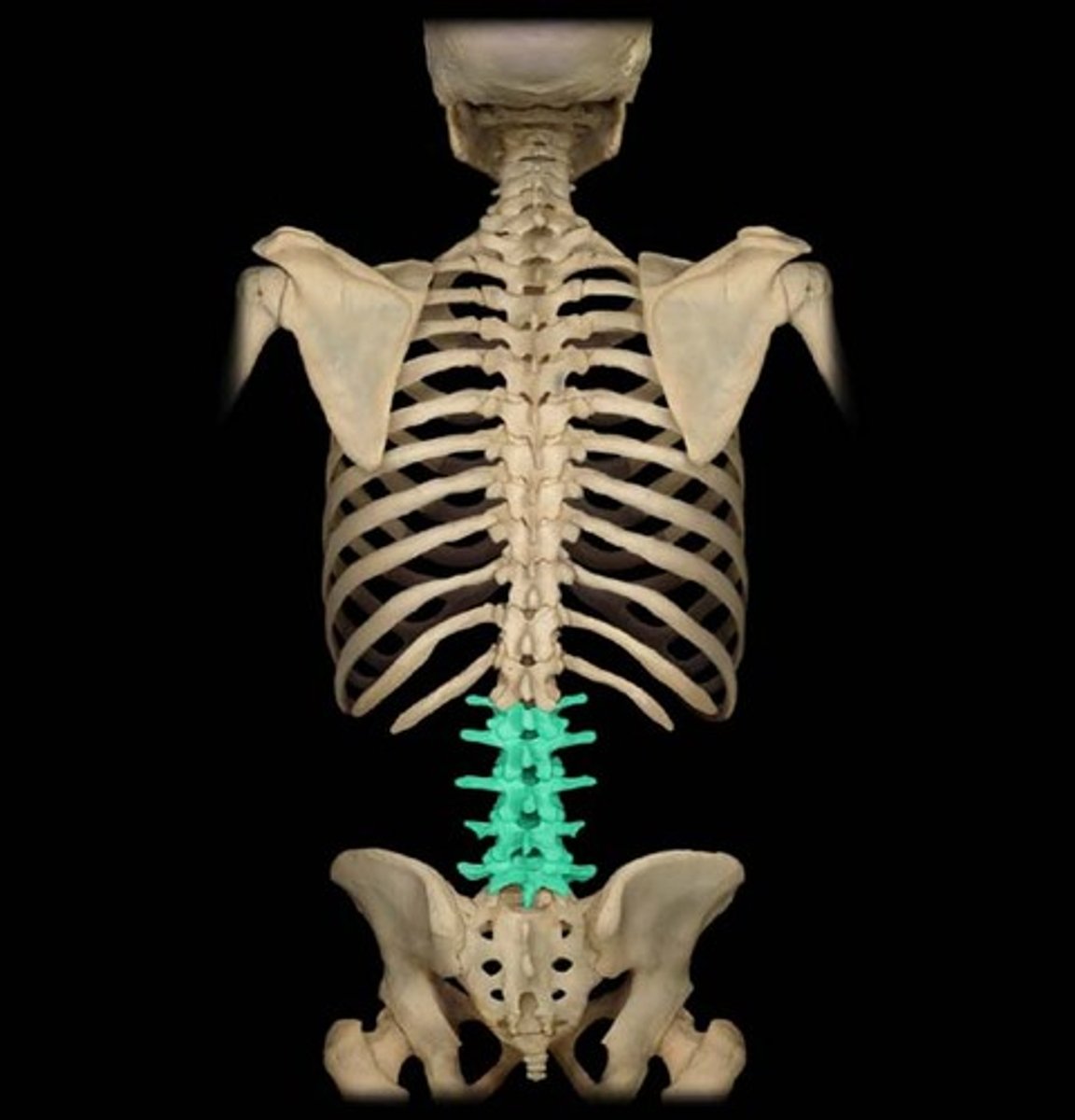
Lumbar Vertebrae
The five irregular bones or vertebral bodies (L1-L5) which are situated between the thoracic vertebrae and the 5 fused sacral vertebrae.
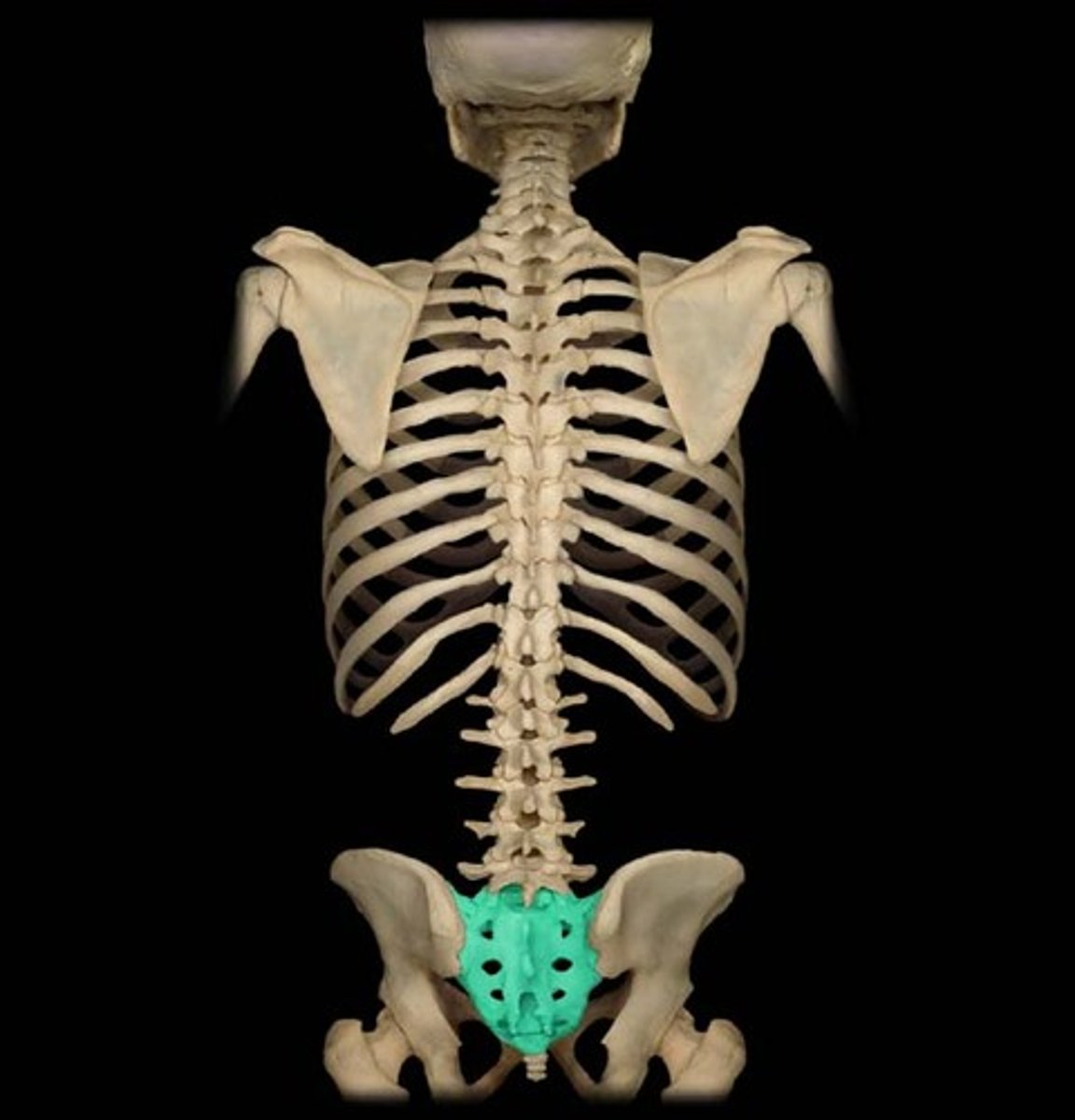
Sacrum
A triangular bone in the lower back formed from fused sacral and coccygeal vertebrae. It is situated between the two hipbones of the pelvis.
Coccyx
a small, triangular bone at the base of the spinal column. Formed by 3-5 coccygeal vertebrae.
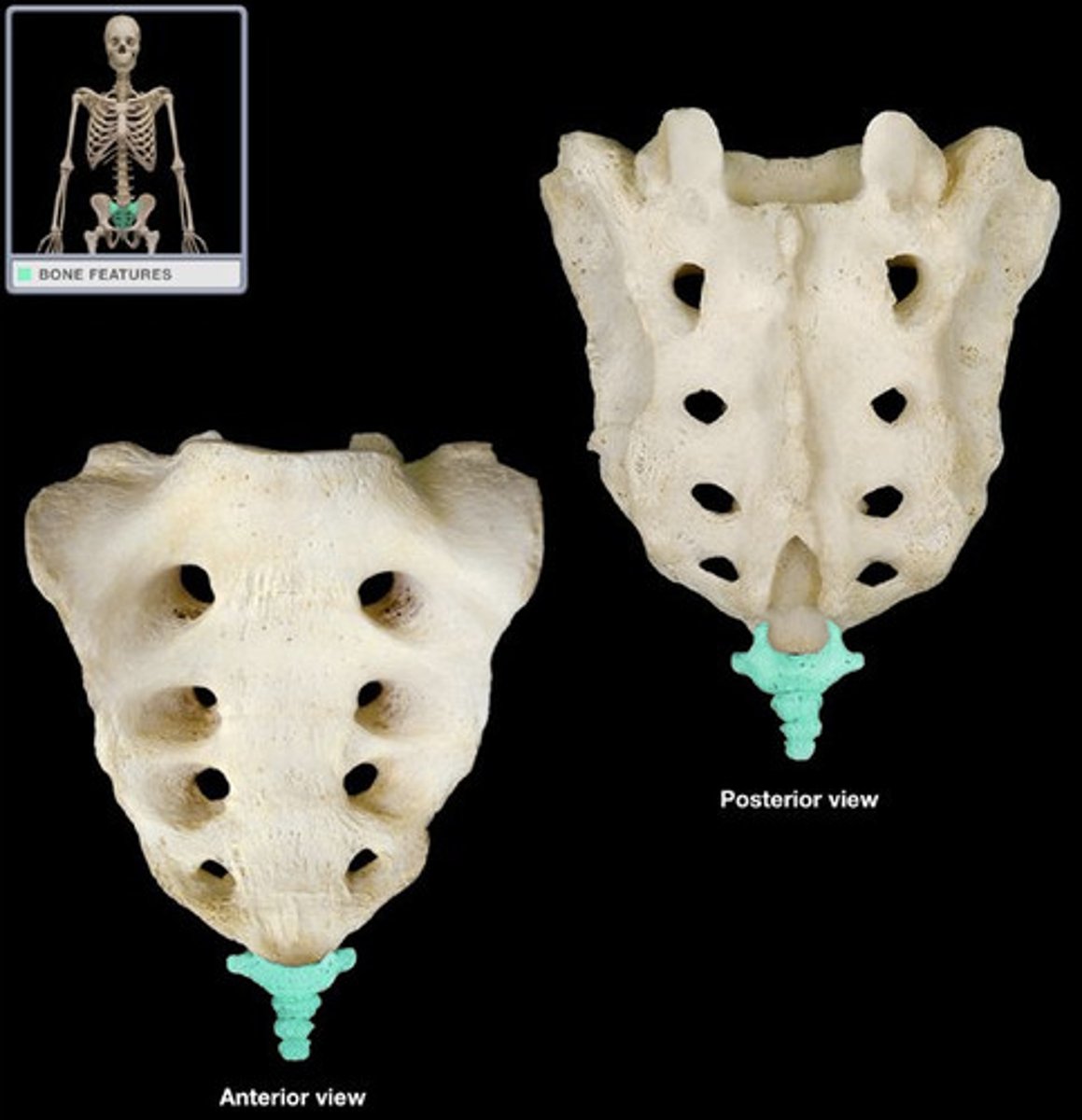
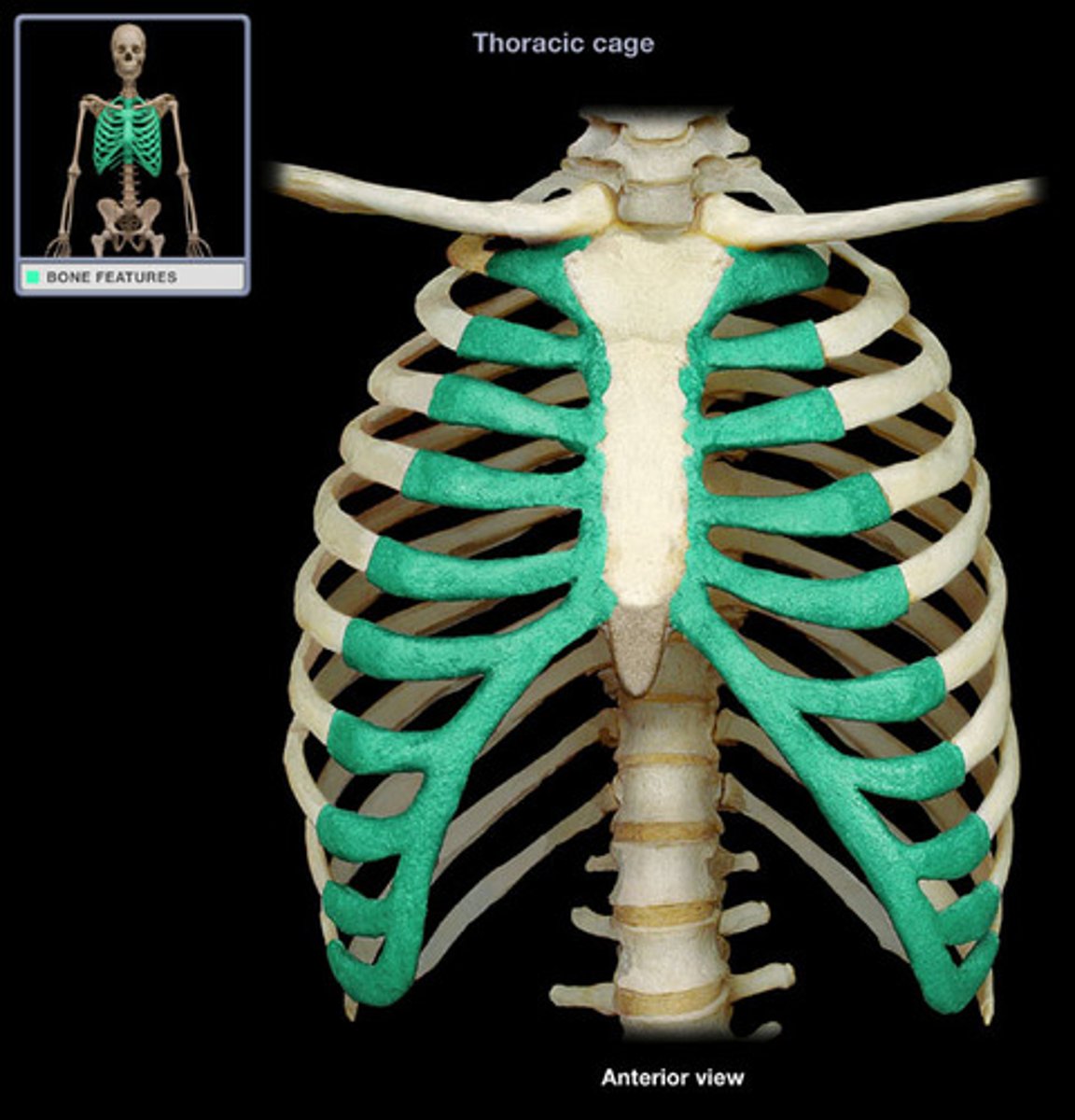
Ribs
Classified as flat bones, as they are flat and curved, these bones form a "cage" which surrounds and protects the heart, lungs, and other internal organs.
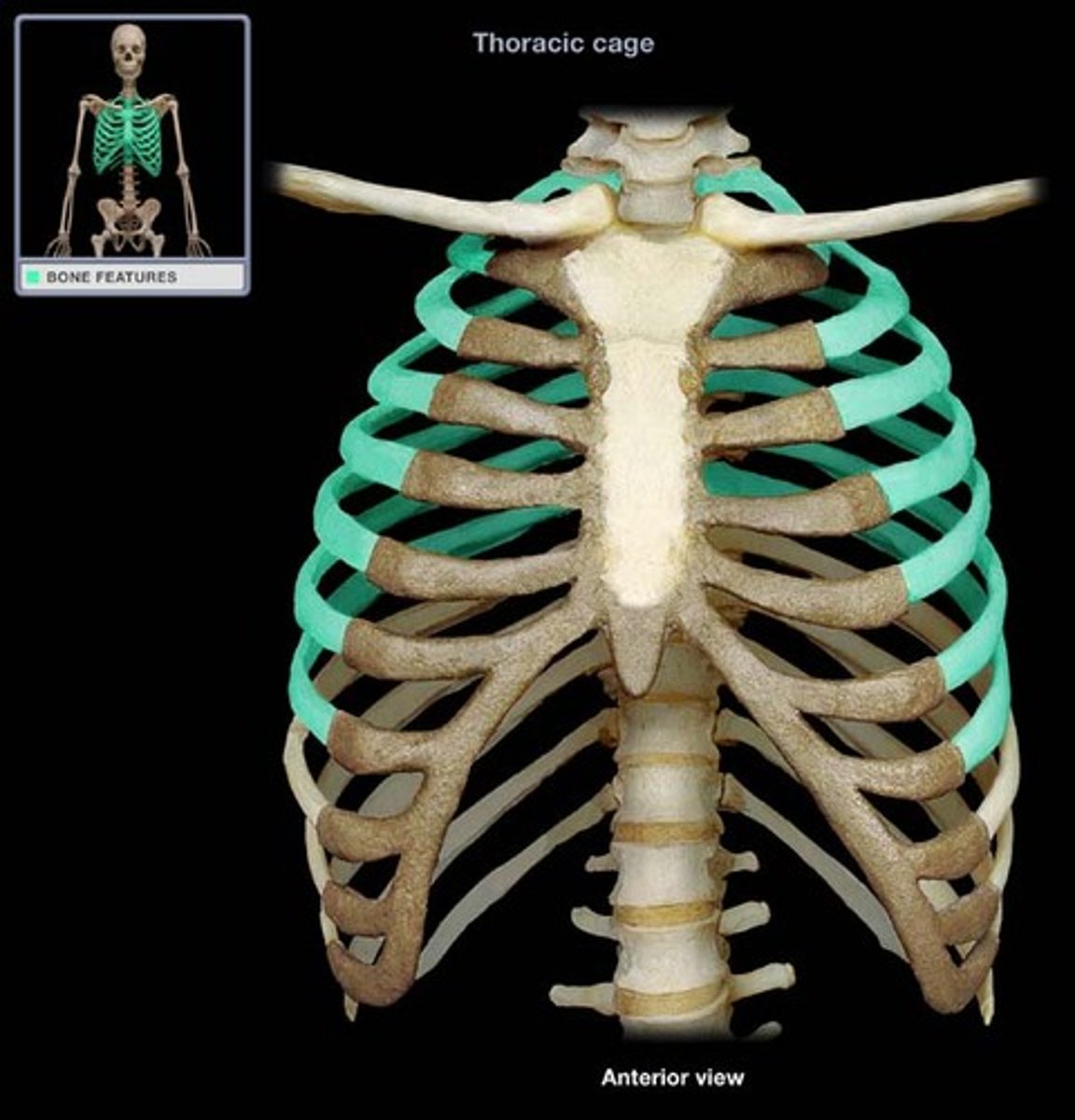
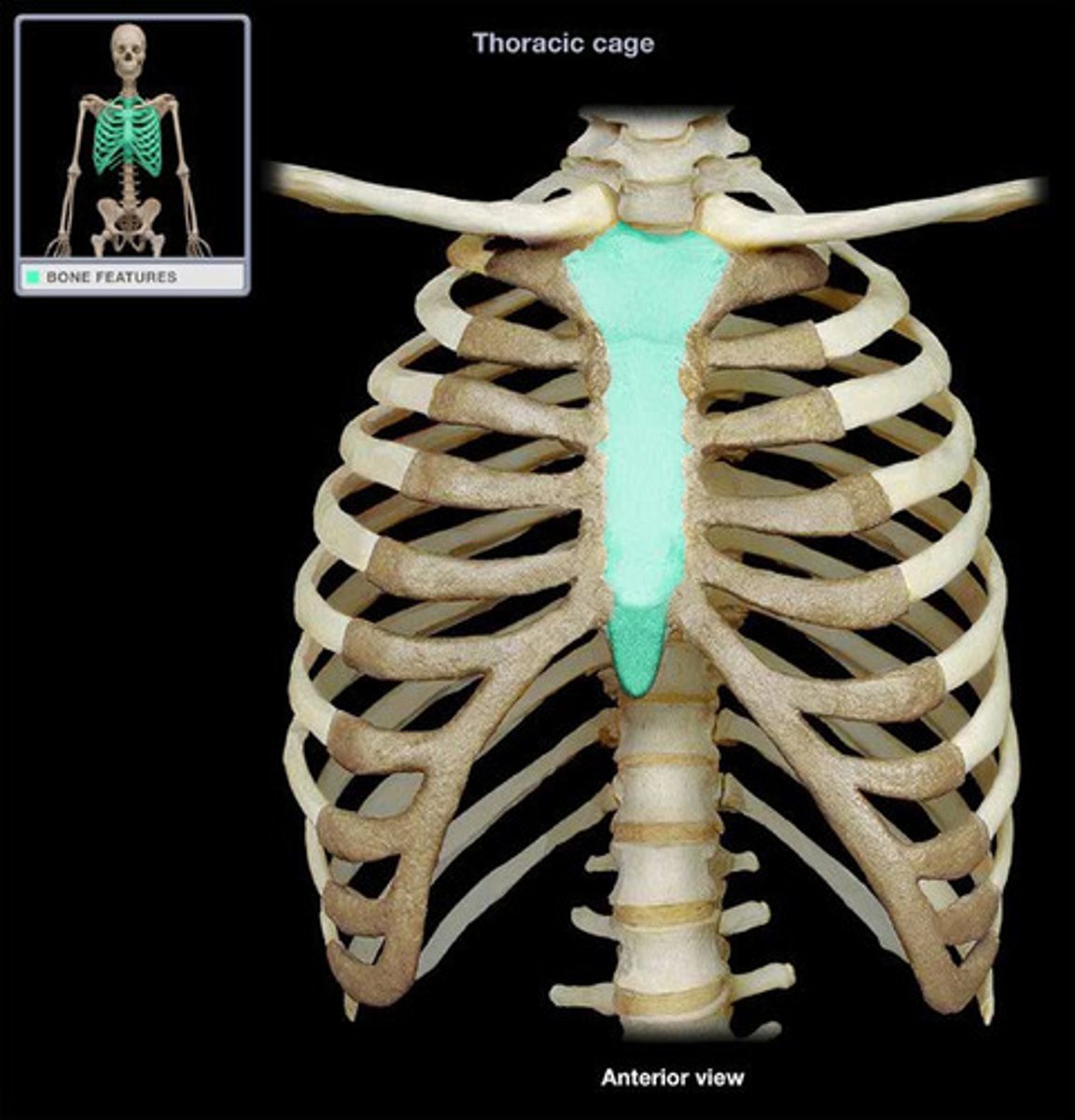
Sternum
A flat bone, or series of bones, which extends along the median line of the ventral portion of the body. It connects to the clavicles and true ribs.
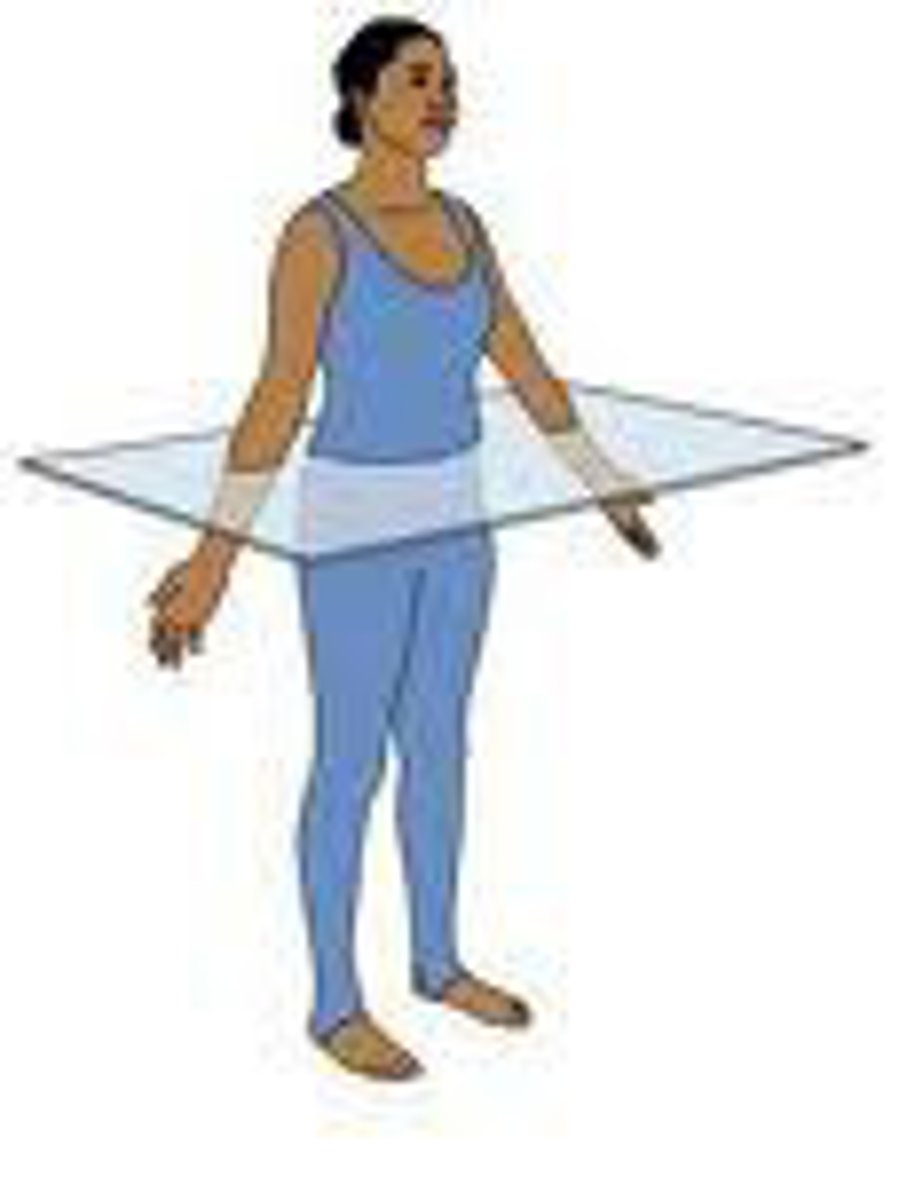
Transverse plane
A plane which divides the body into superior and inferior or proximal and distal parts.
Sagittal/Median plane
A plane which divides the body into left and right (lateral) sections.
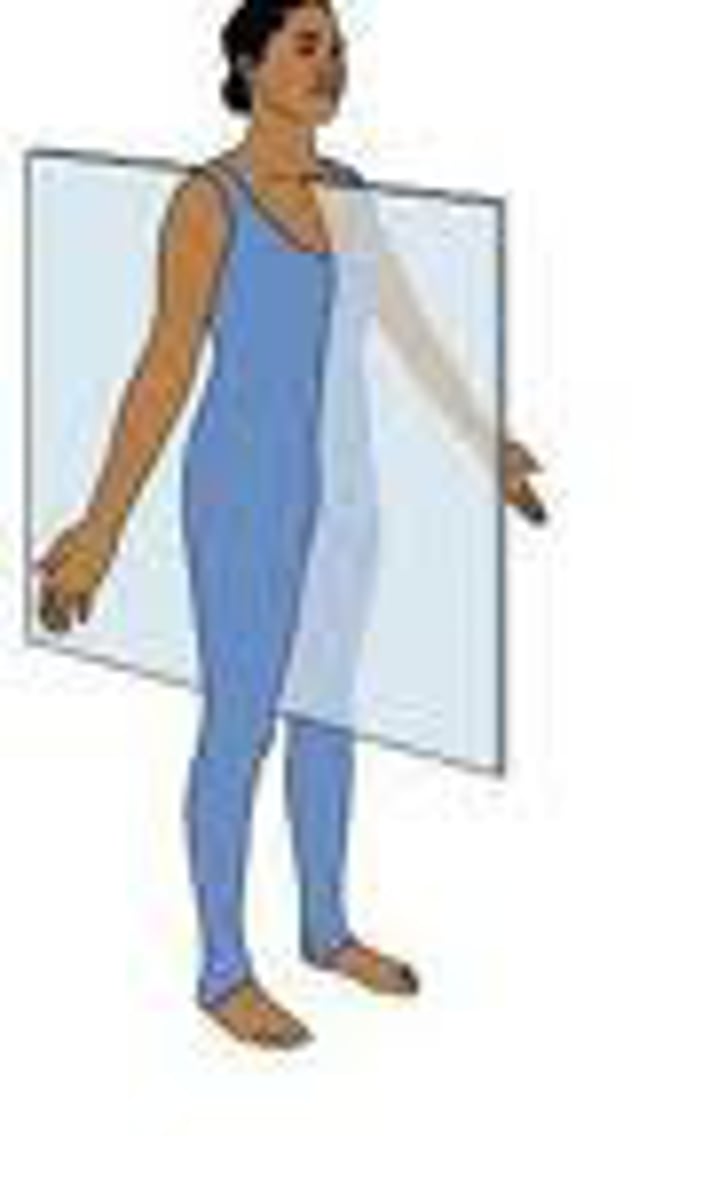
Coronal/frontal plane
A plane which divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections.

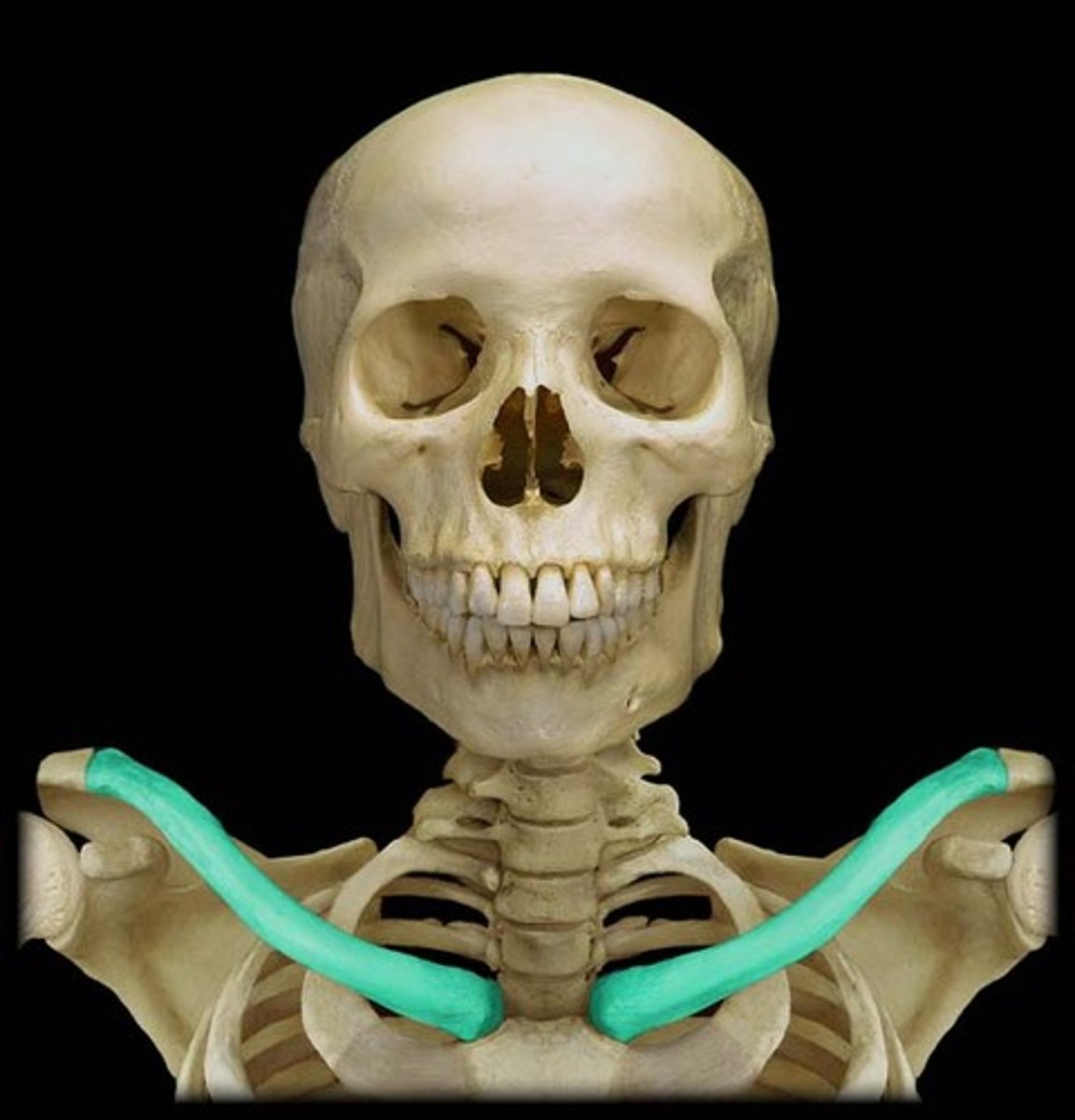
Clavicle
Two slender irregular/modified long bones which articulate with the sternum and form a part of the anterior shoulder.
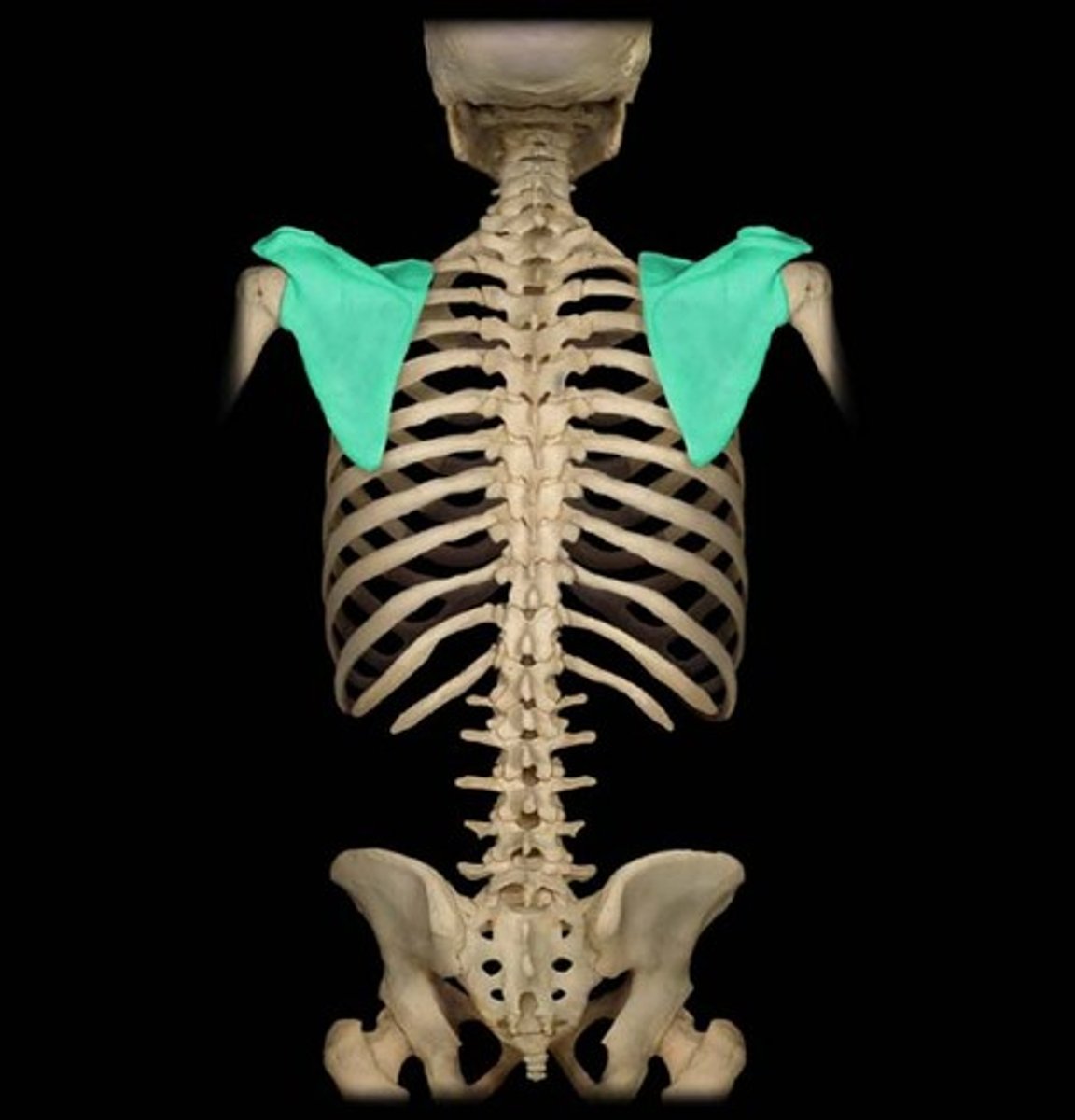
Scapula
Two flat, triangular bones, each forming the posterior shoulder in humans known as the shoulder blade.
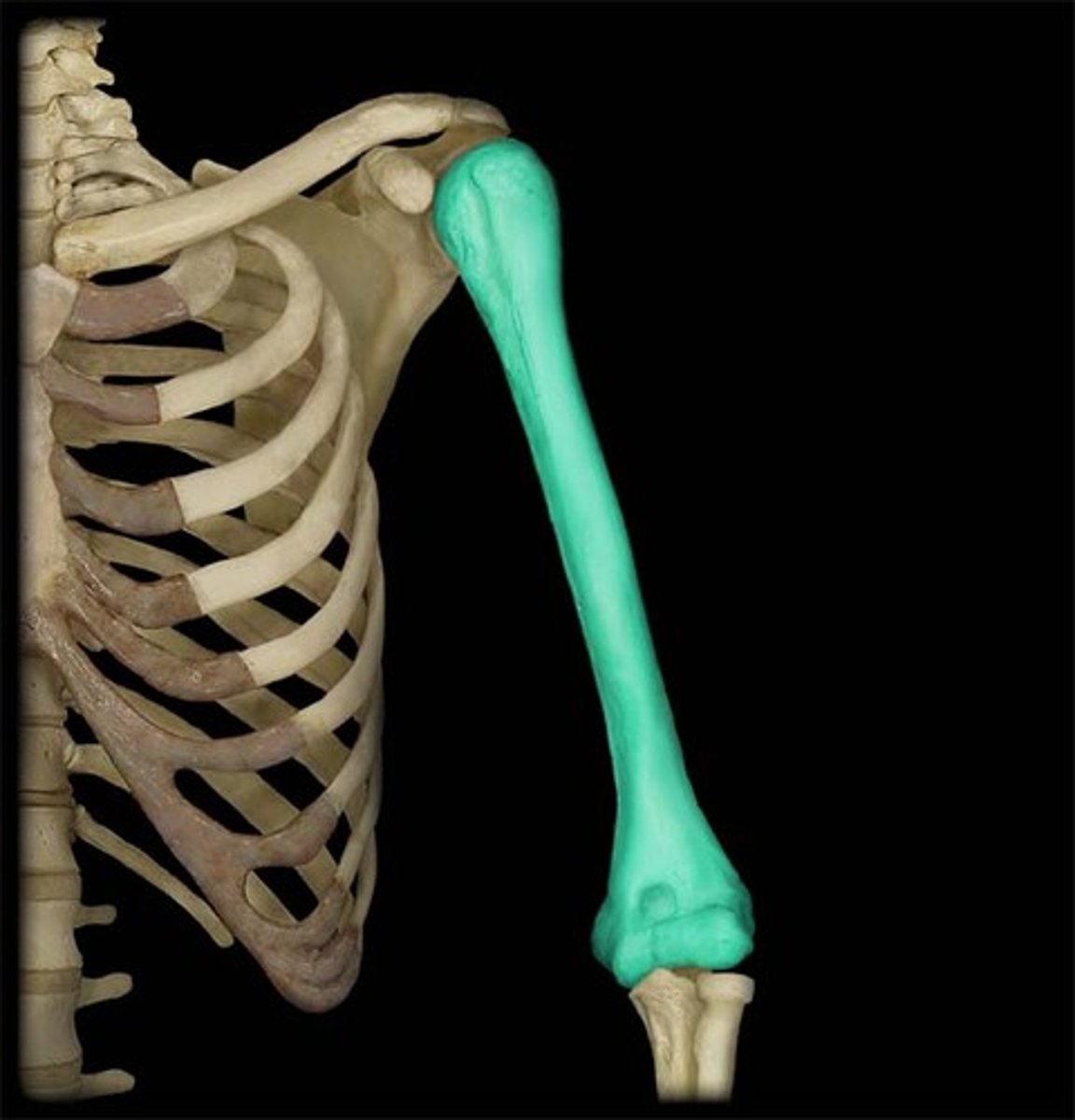
Humerus
The long bone of the upper arm or forelimb, forming joints at the shoulder and elbow. Articulates with the pectoral girdle (clavicles and scapula) at the shoulder and with the radius and ulna at the elbow.
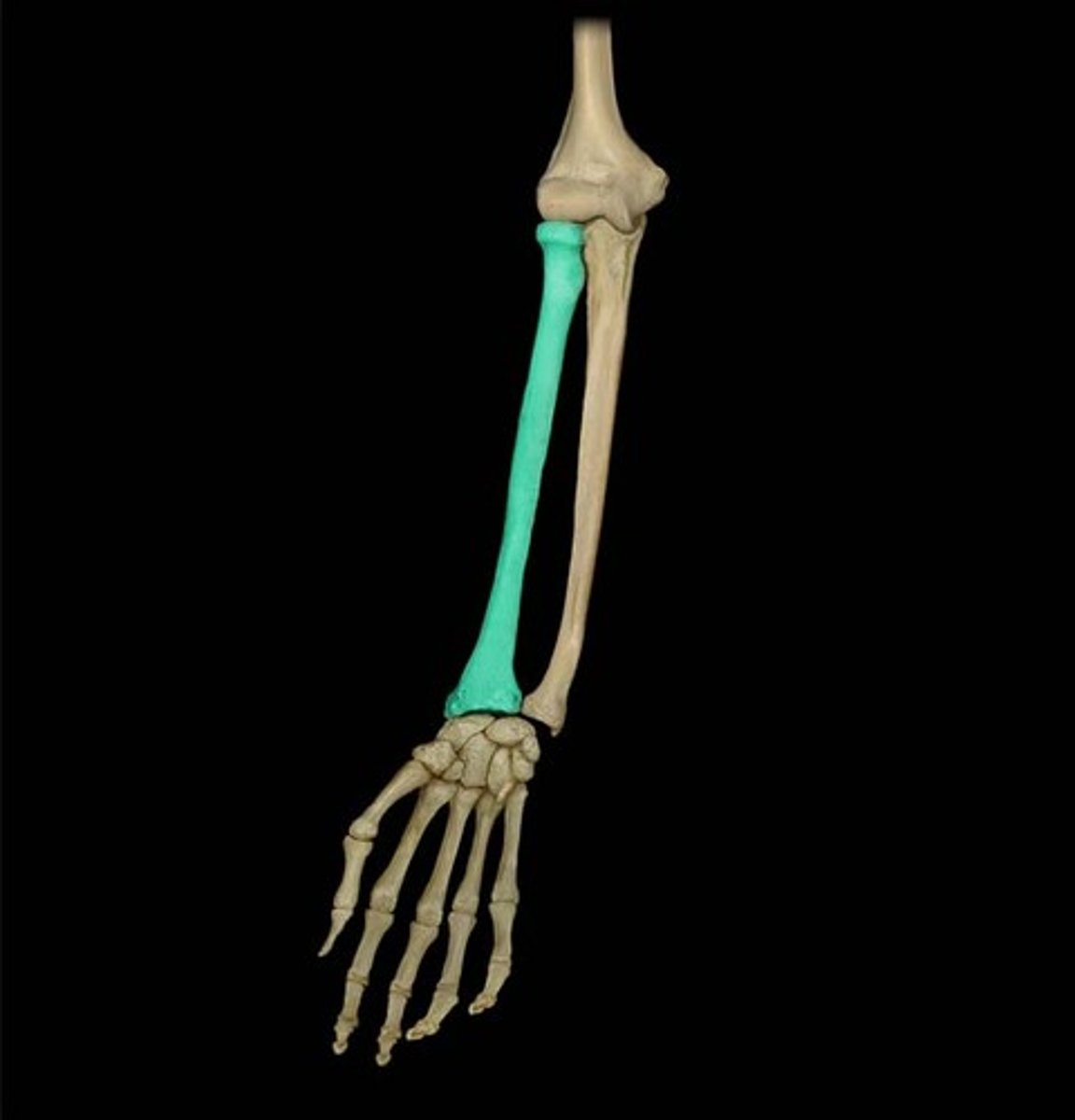
Ulna
the thinner and longer of the two bones of the human forearm, on the side OPPOSITE to the thumb.
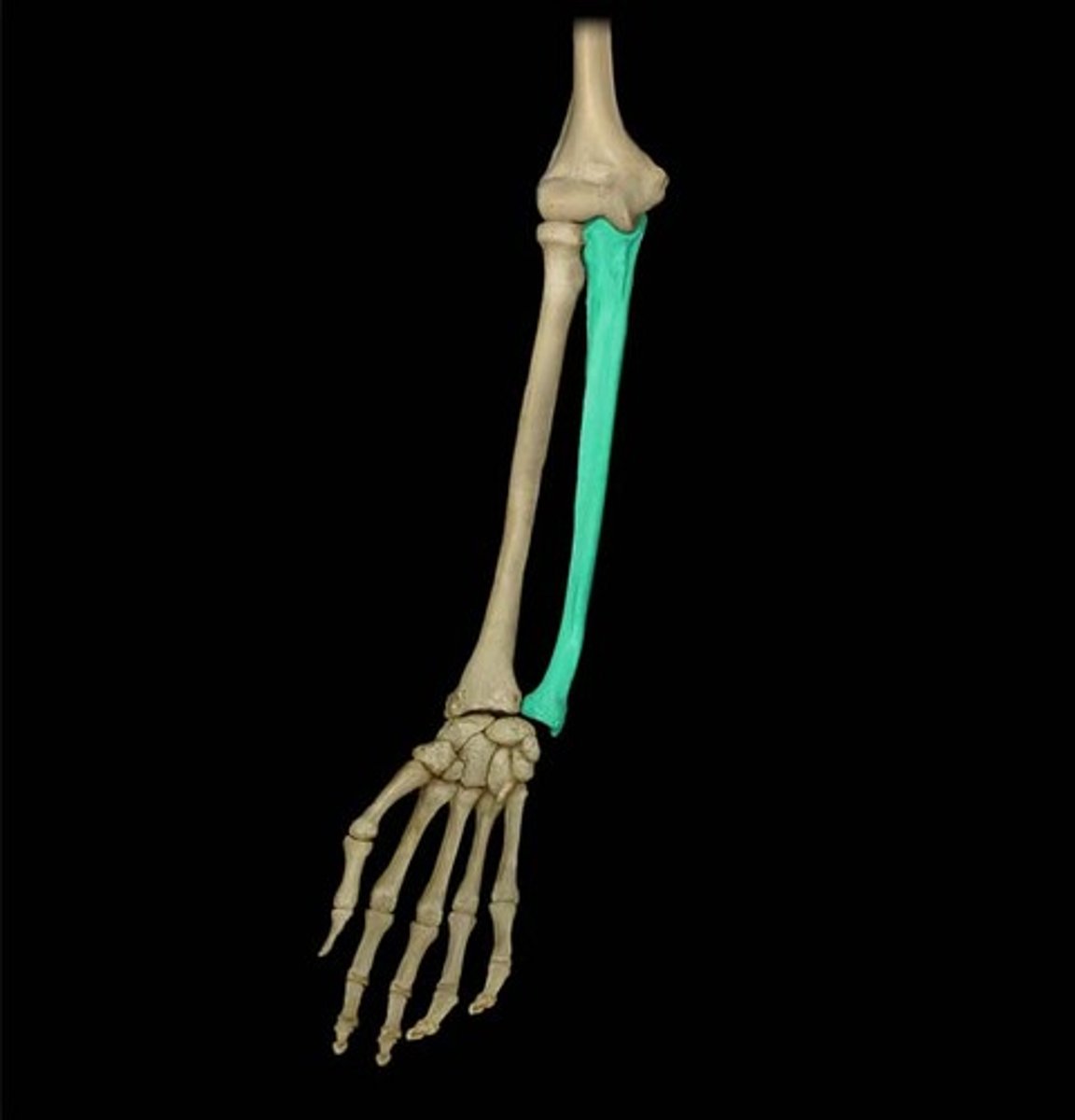
Radius
one of the two long bones of the forearm. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist while running parallel to the ulna.
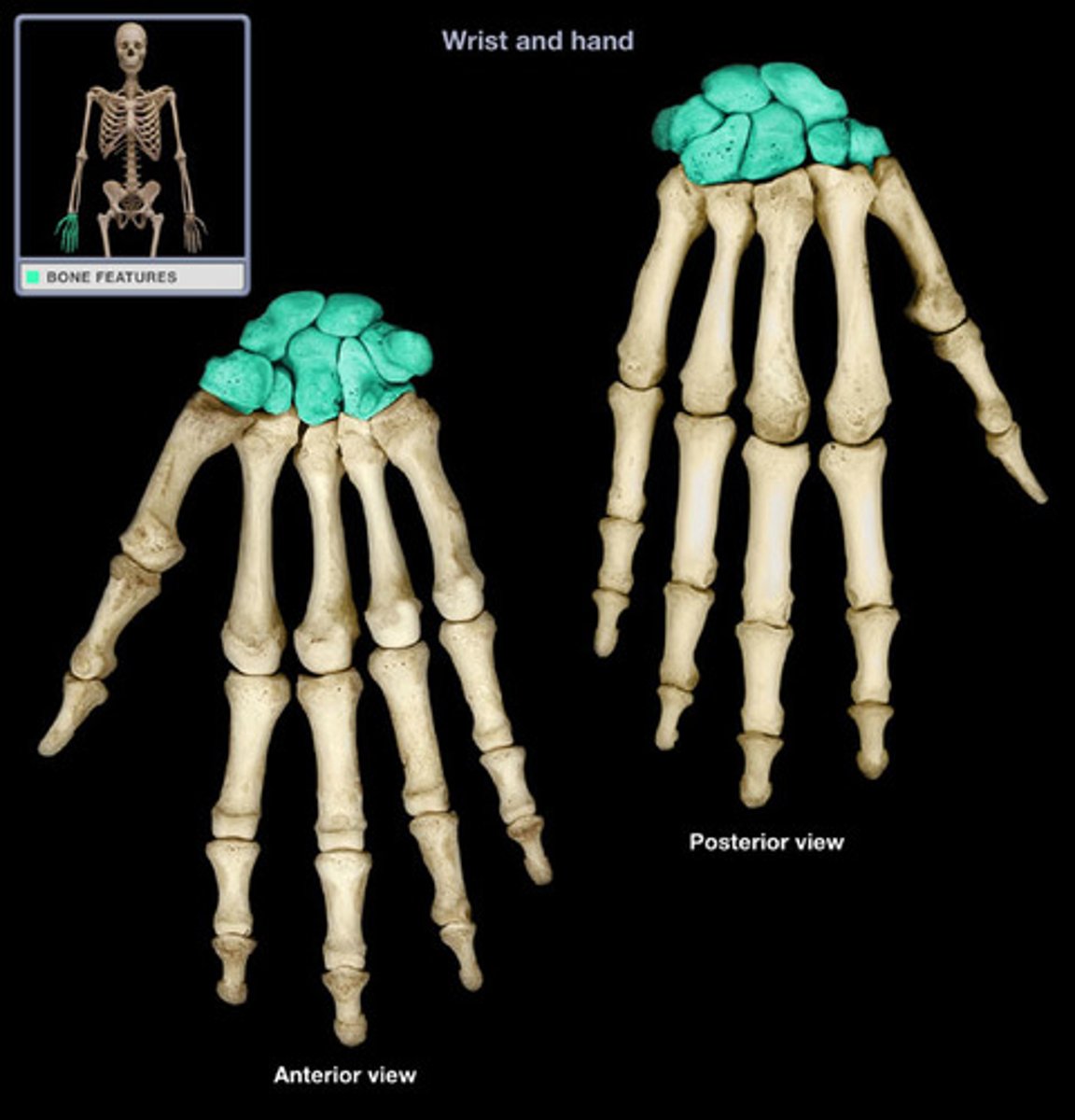
Carpal bones
the eight, short bones which makes up the human wrist and allow the hand to pivot at the forearm.
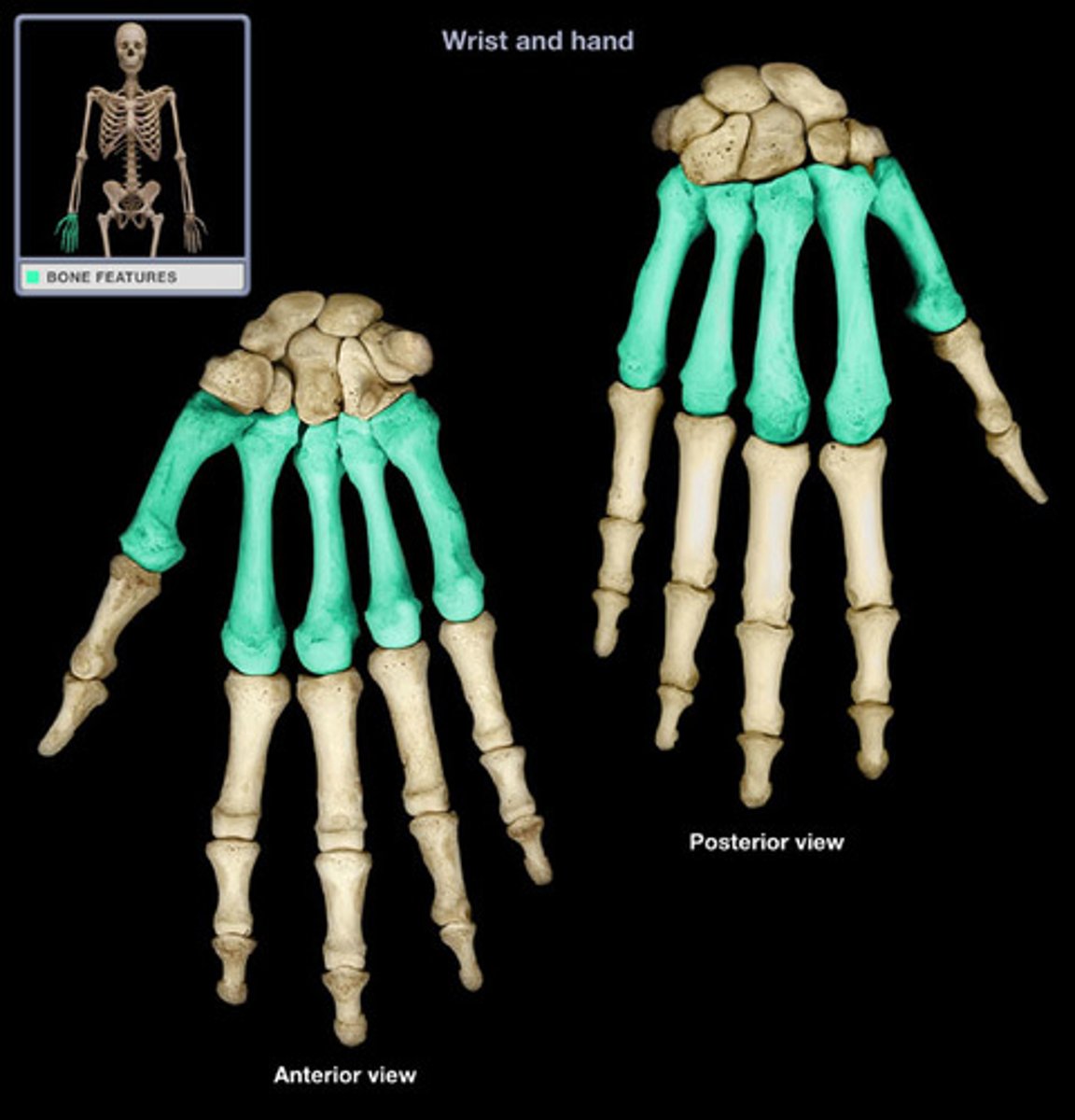
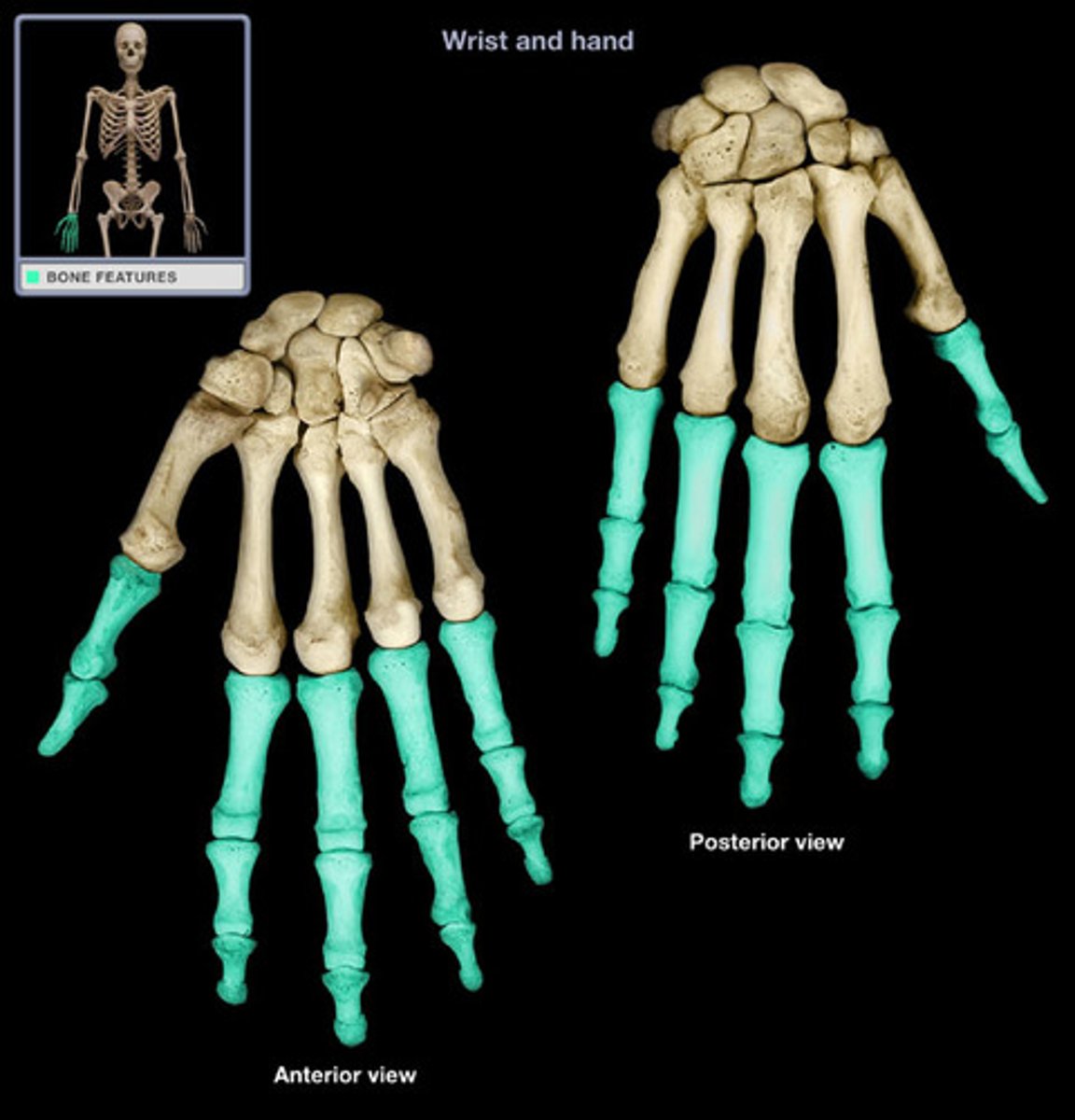
Metacarpal bones
the five, long bones which make up the palm of the human hand and are situated, and articulate, in-between the carpals and phalanges.
Phalanges
the fourteen, long bones which make up the fingers of the human hand and toes of the human foot. The thumb is made up of two phalanges while the rest of the digits are made up of three. They articulate with the metacarpals.
Pelvis
the large, funnel-shaped structure at the lower end of trunk of humans and other vertebrates by which the legs are attached.
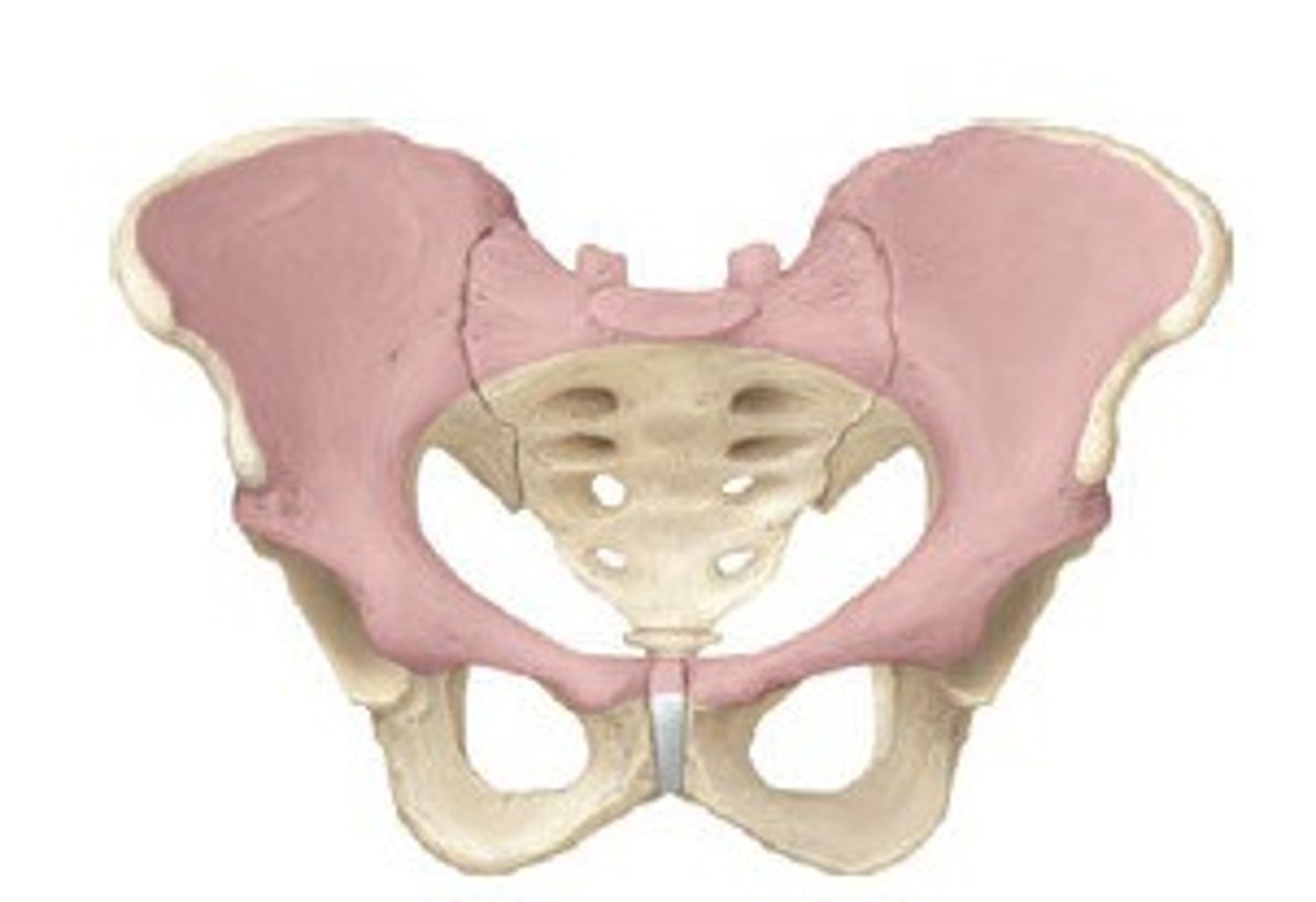
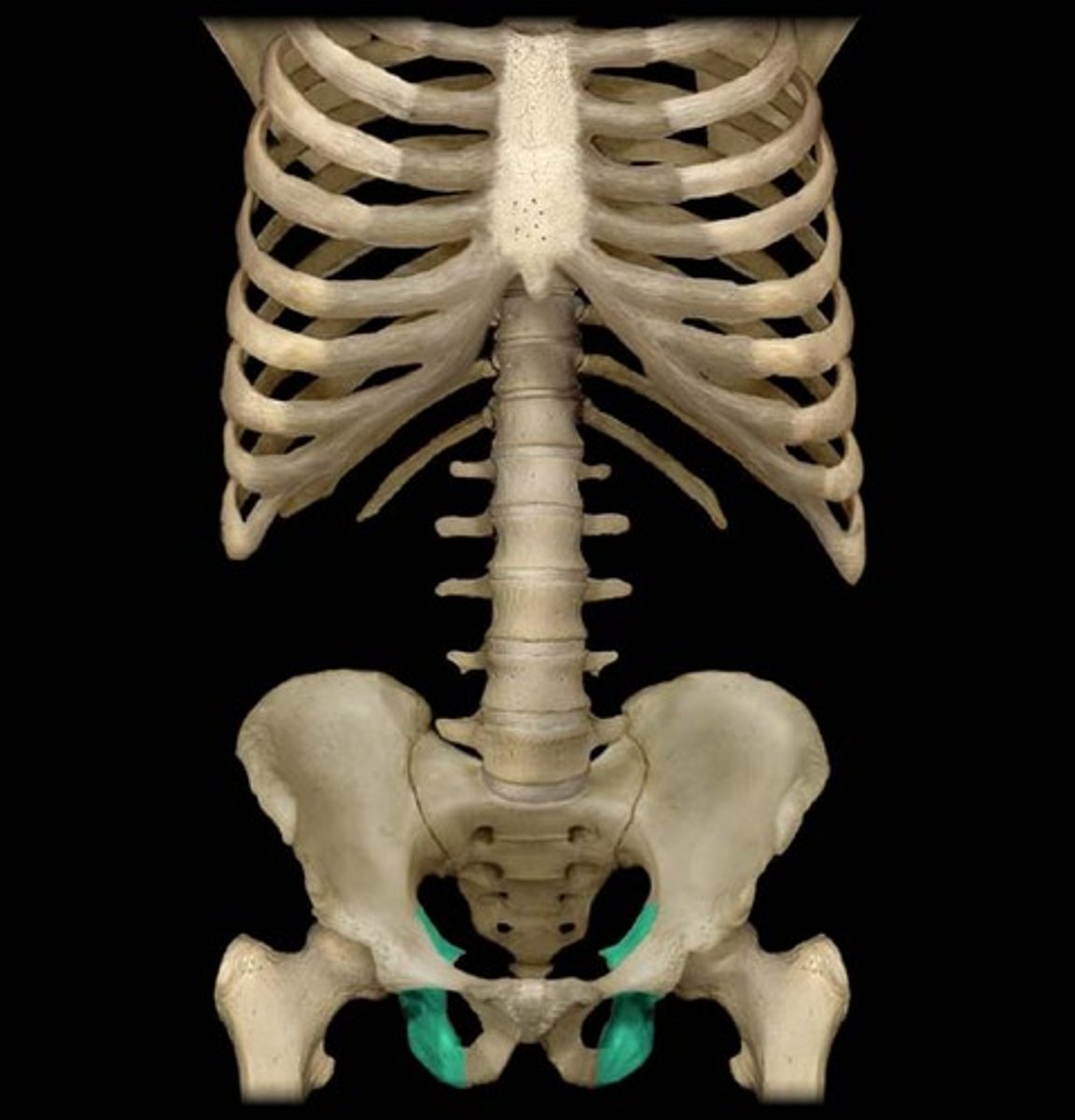
Ischium
The curved, irregular bone at the base of each half of the pelvis. Articulates with the pubic arch and produces a hole on each side of the pelvis.
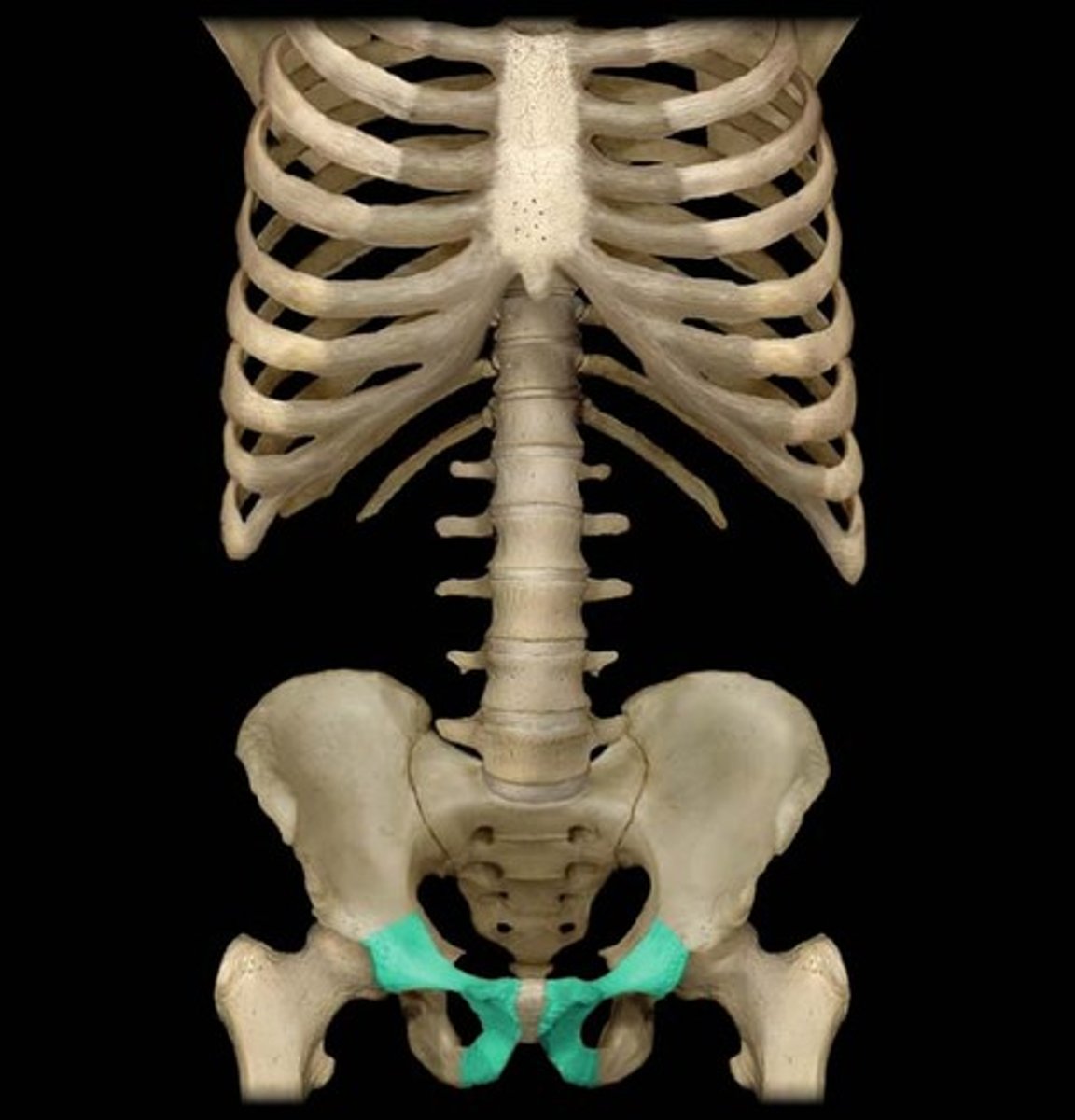
Pubis
two irregular bones, which articulate with the pubic arch, and define the two sides of the pelvis. Just above the ischium on both sides.
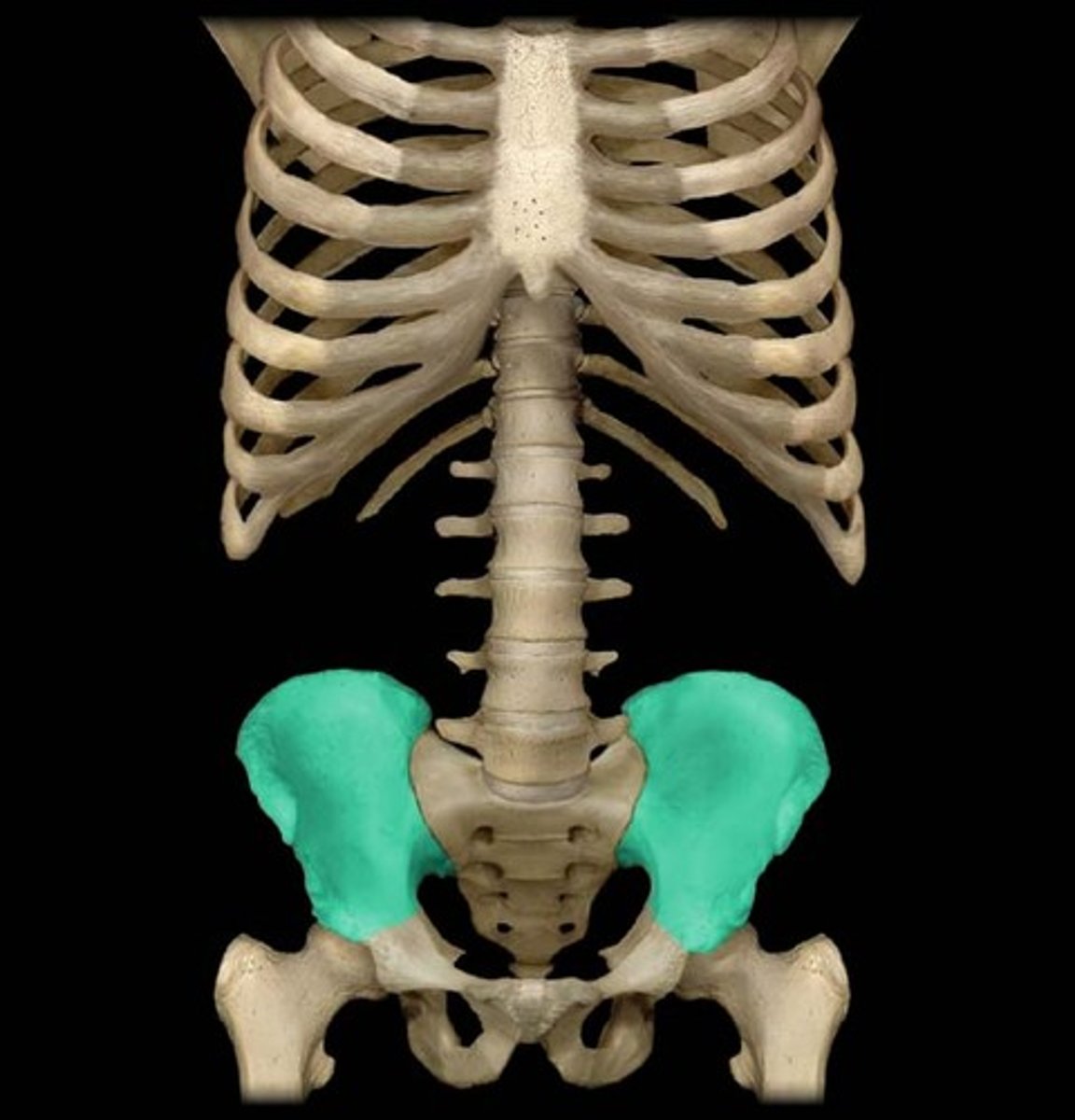
Ilium
the large, irregular bone which forms the upper section of each half of the pelvis.
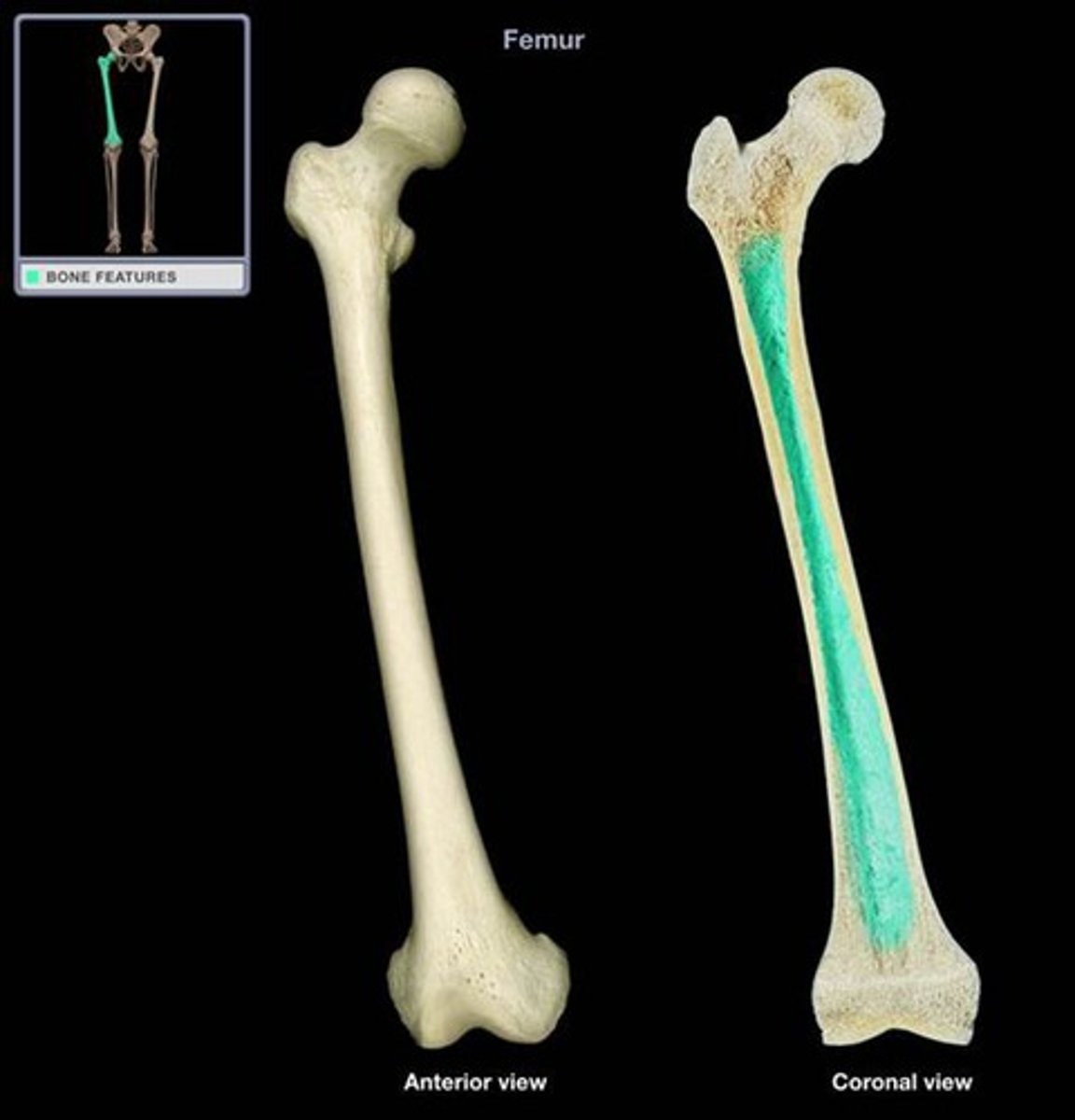
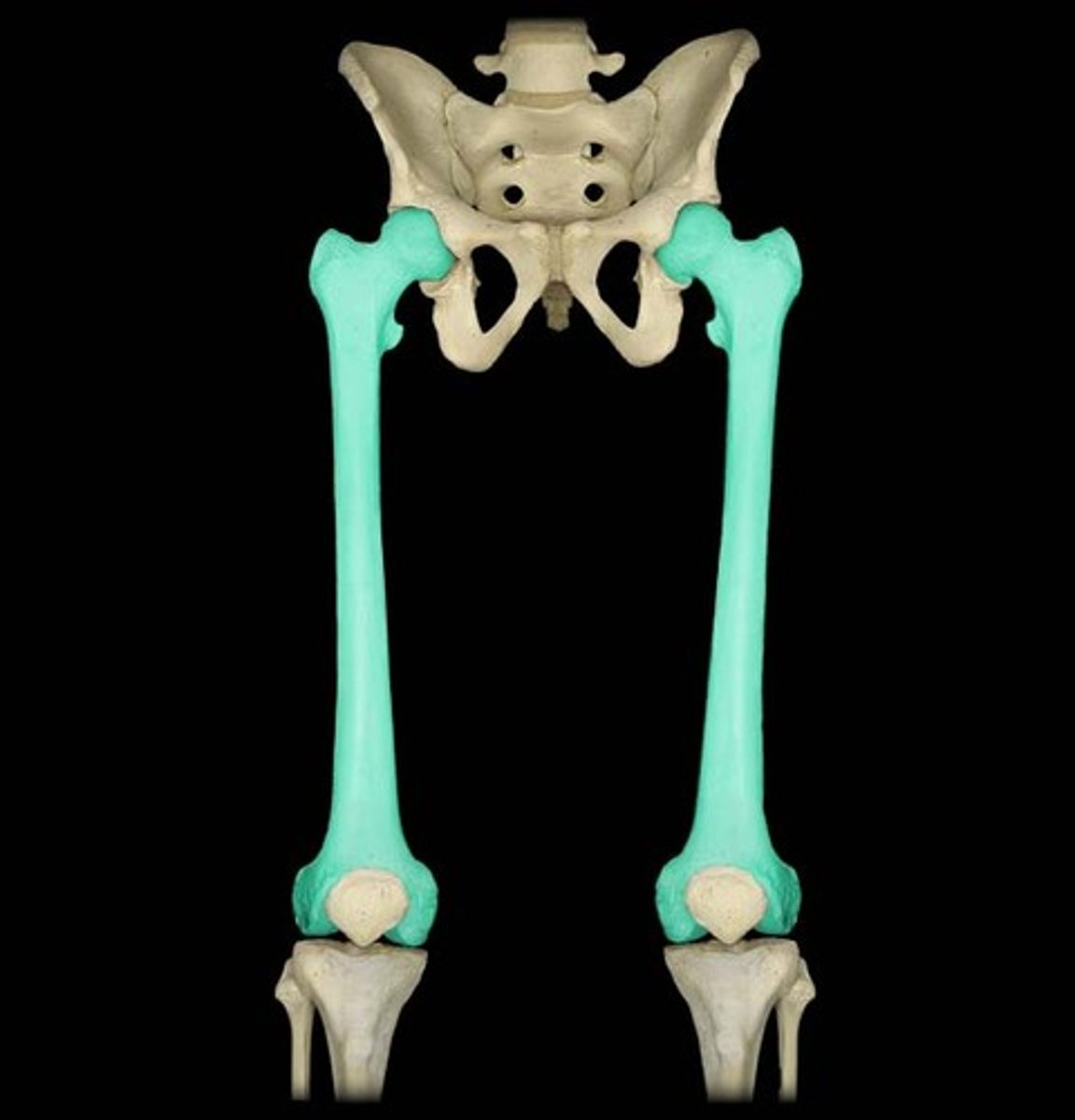
Femur
the long bone of the upper hind limb which articulates with the tibia at the knee joint and the pubis at the pelvis.
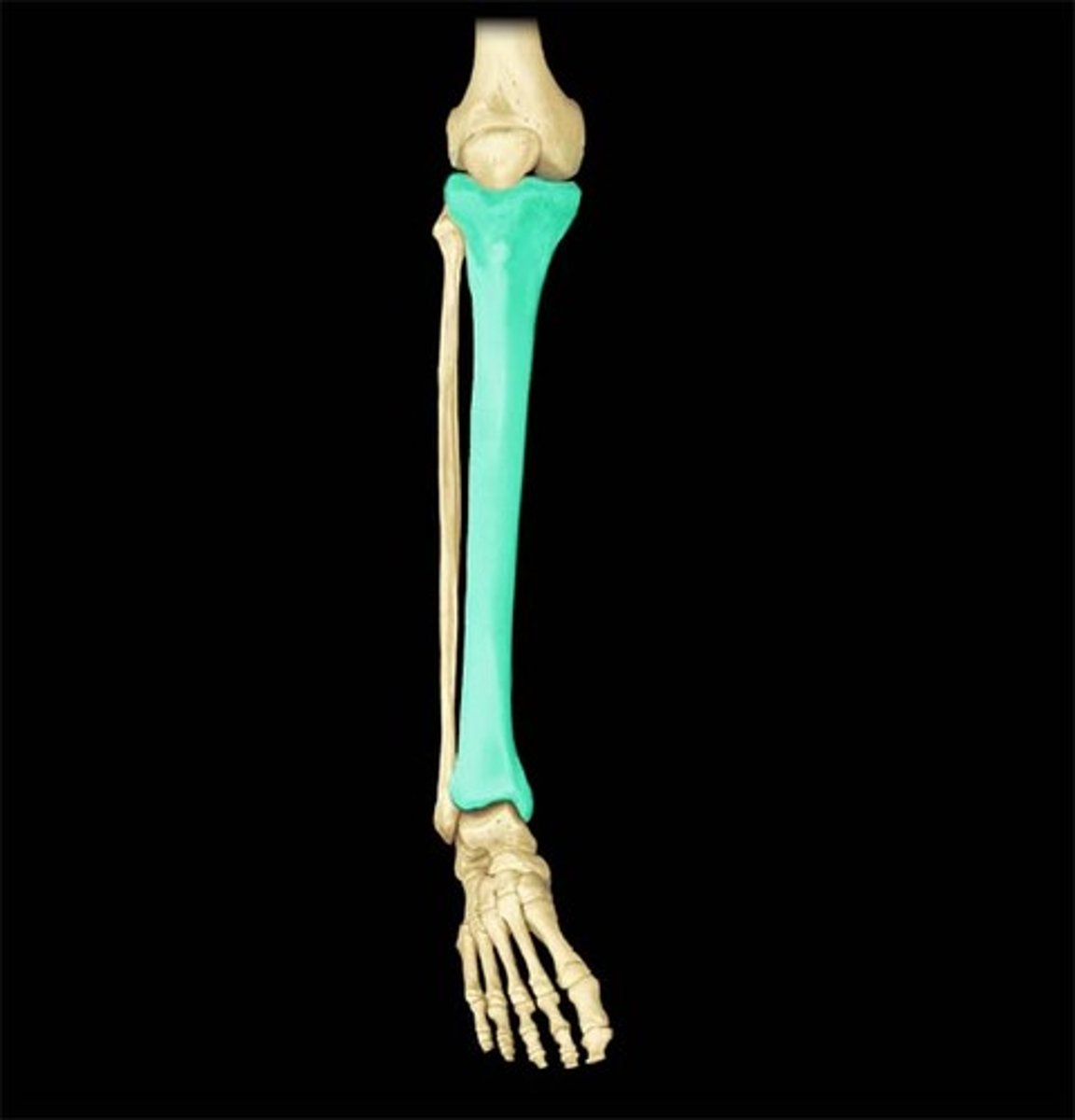
Tibia
the larger one of the two long bones which articulates between the knee and the ankle and parallel with the fibula.
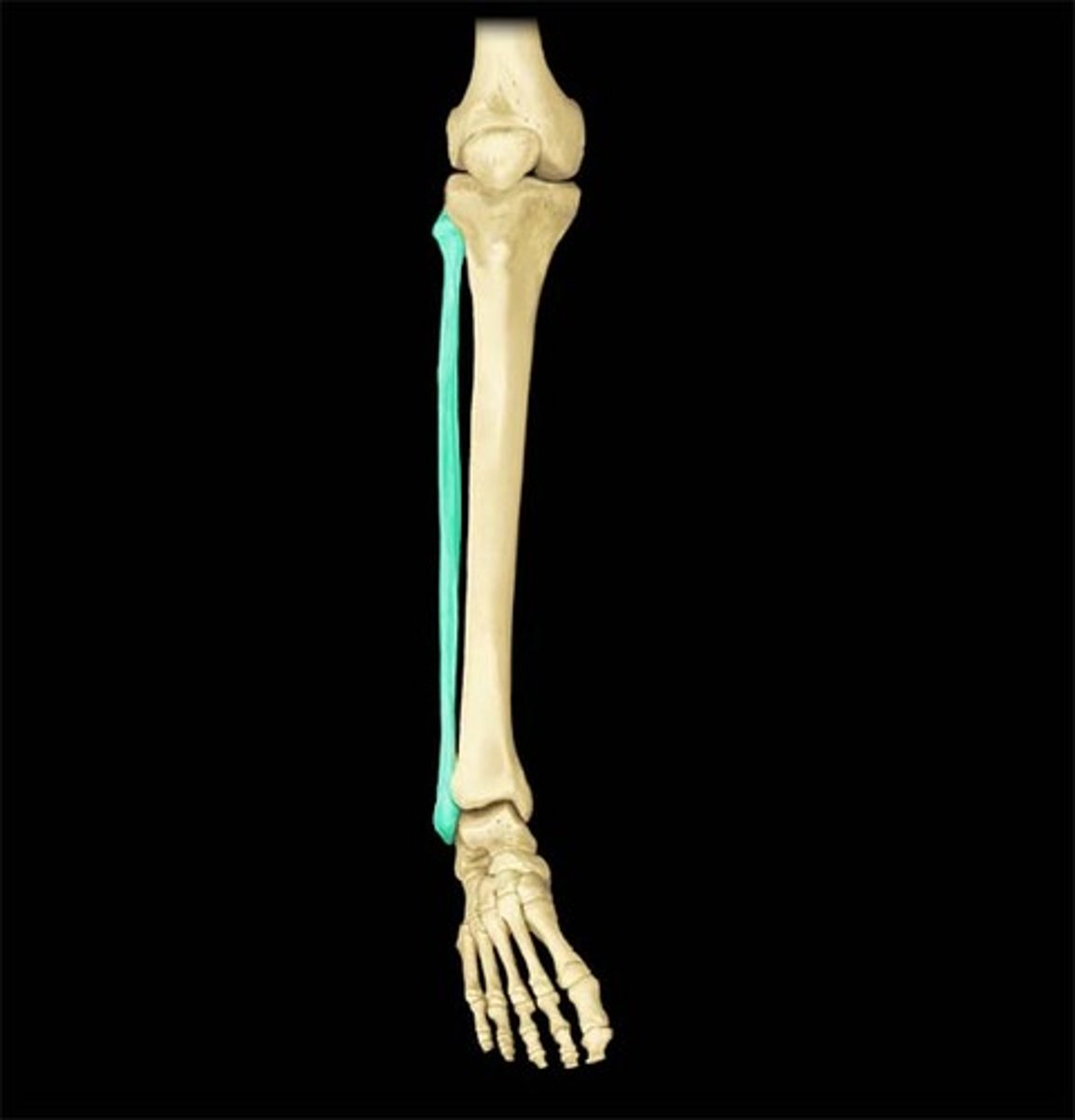
Fibula
the shorter one of the two long bones which articulates between the knee and the ankle, parallel with the tibia.
Patella
the sesamoid bone which resides underneath the patellar ligament which protects the knee joint between the fibula, tibia, and femur.
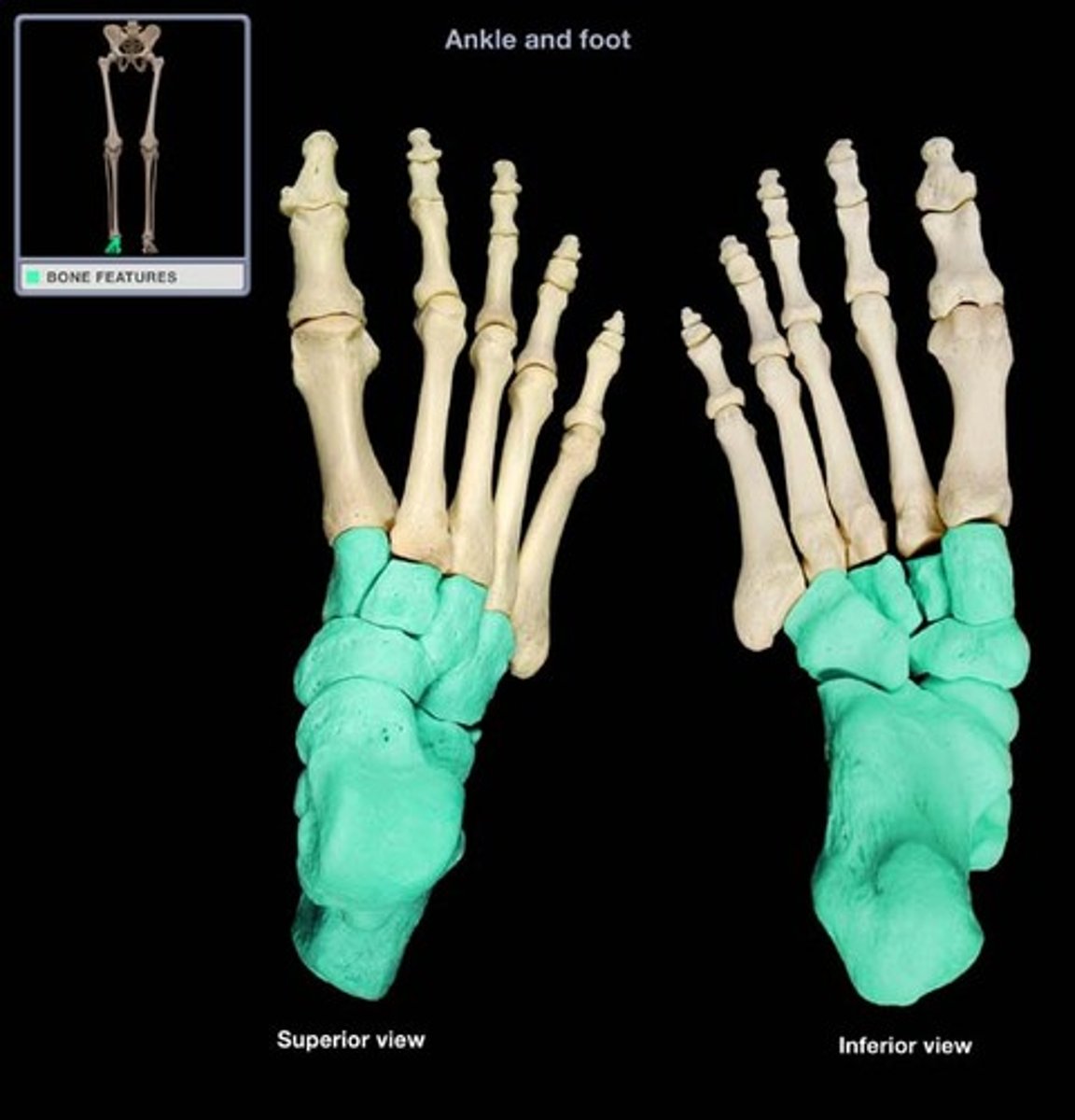
Tarsals
the short bones of the foot which make up the heel and articulate with the metatarsals, fibula, and tibia.
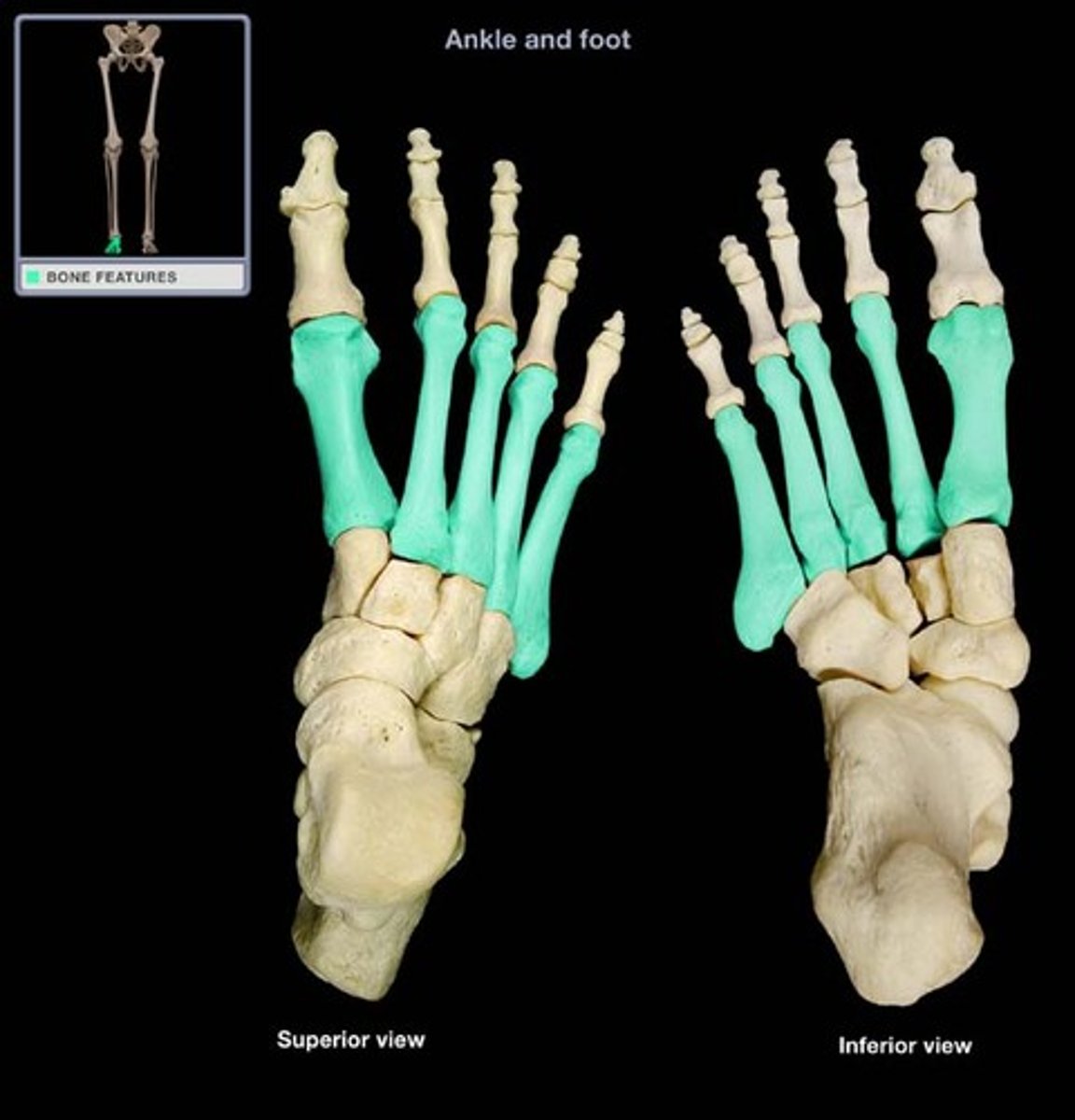
Metatarsal
the five, long bones which make up the middle of the foot and articulate with the tarsals and phalanges.
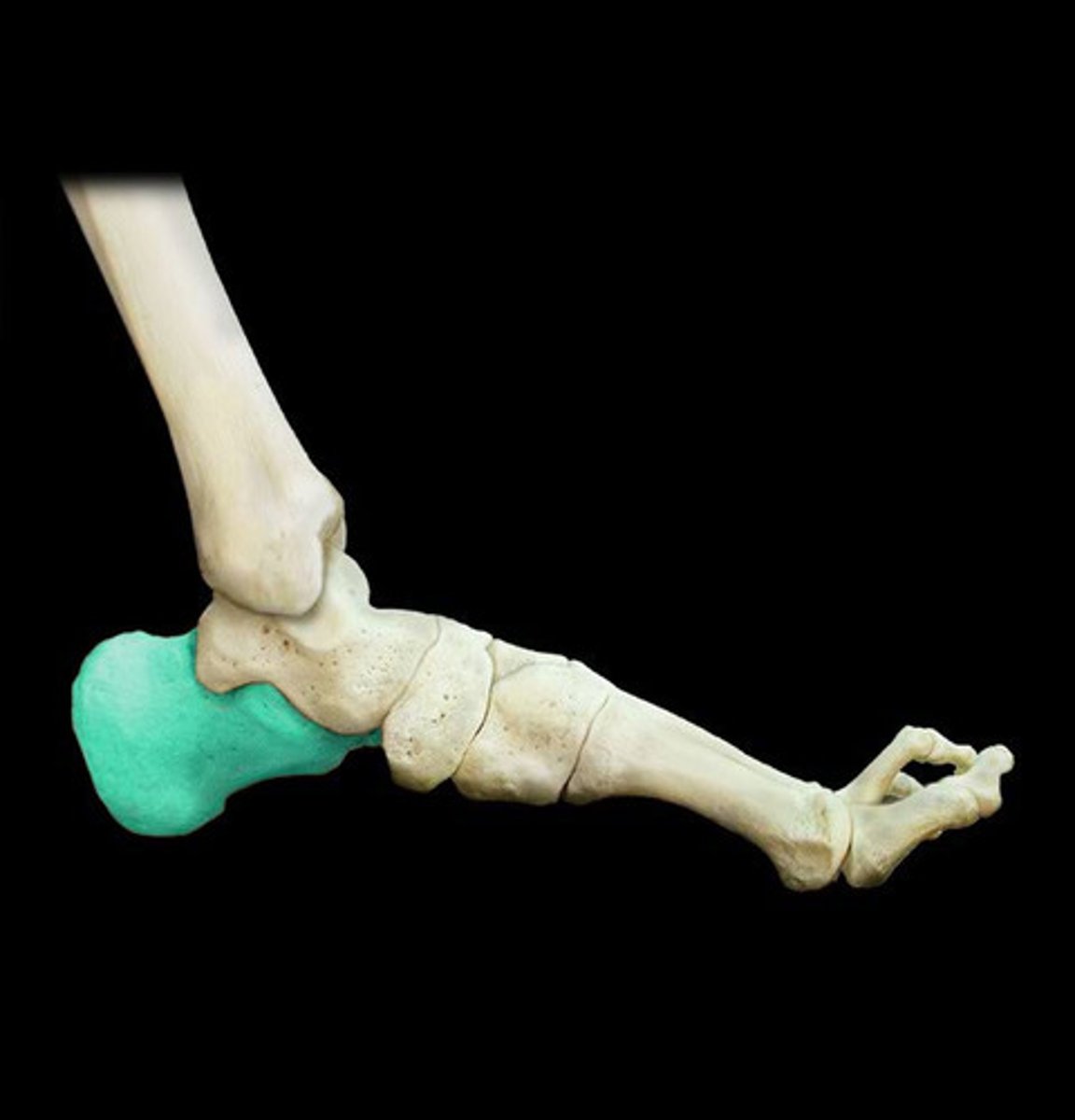
Calcaneus
the short bone that forms the foundation of the rear part of the foot and articulates with the talus and cuboid.
Talus
the short bone of the ankle that articulates with the tibia, calcaneum, and navicular.
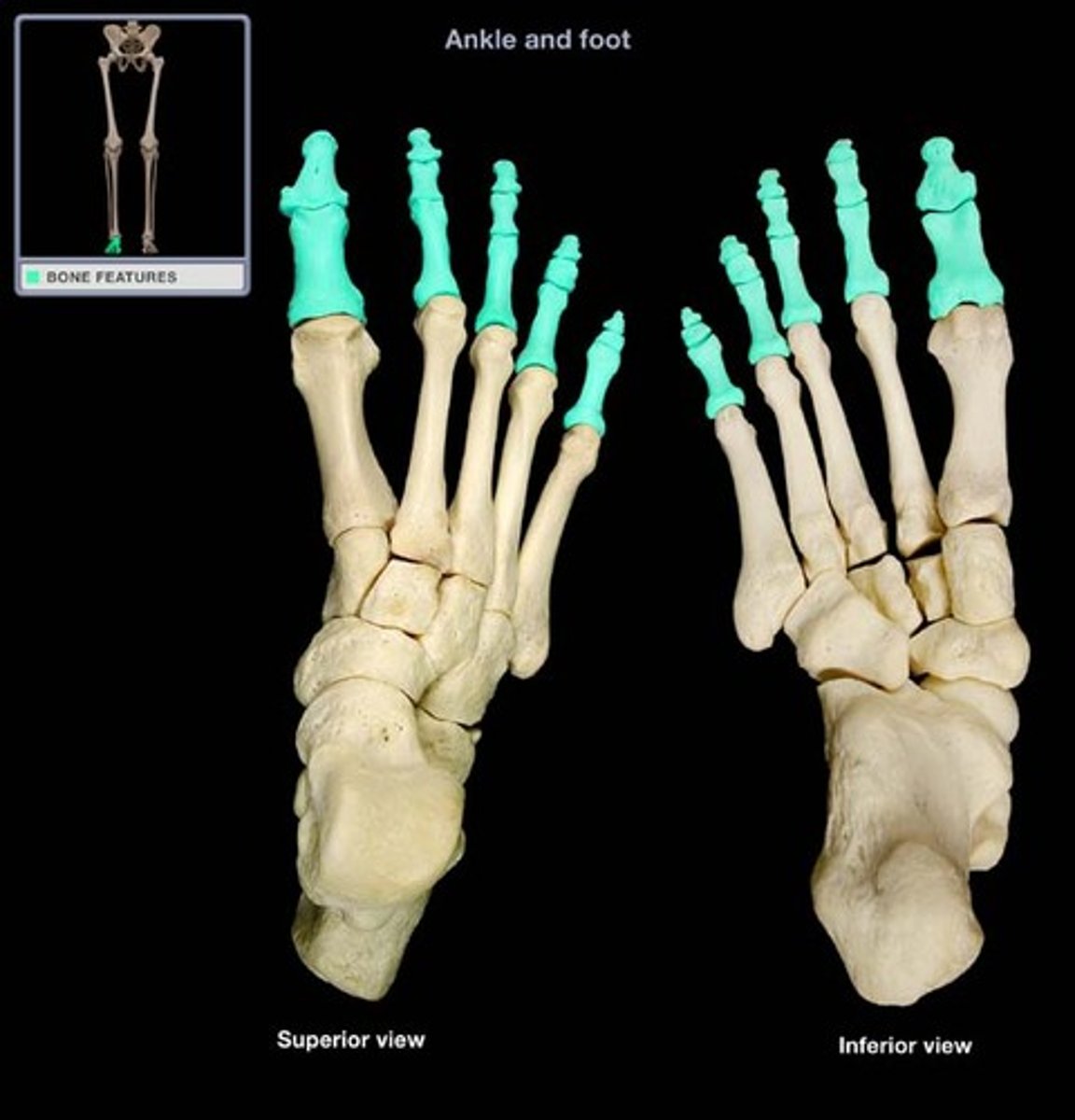
Phalanges
the long bones of the foot, three for each toe except for the hallux (great toe), which articulate with the metatarsals and are distal to the body overall.
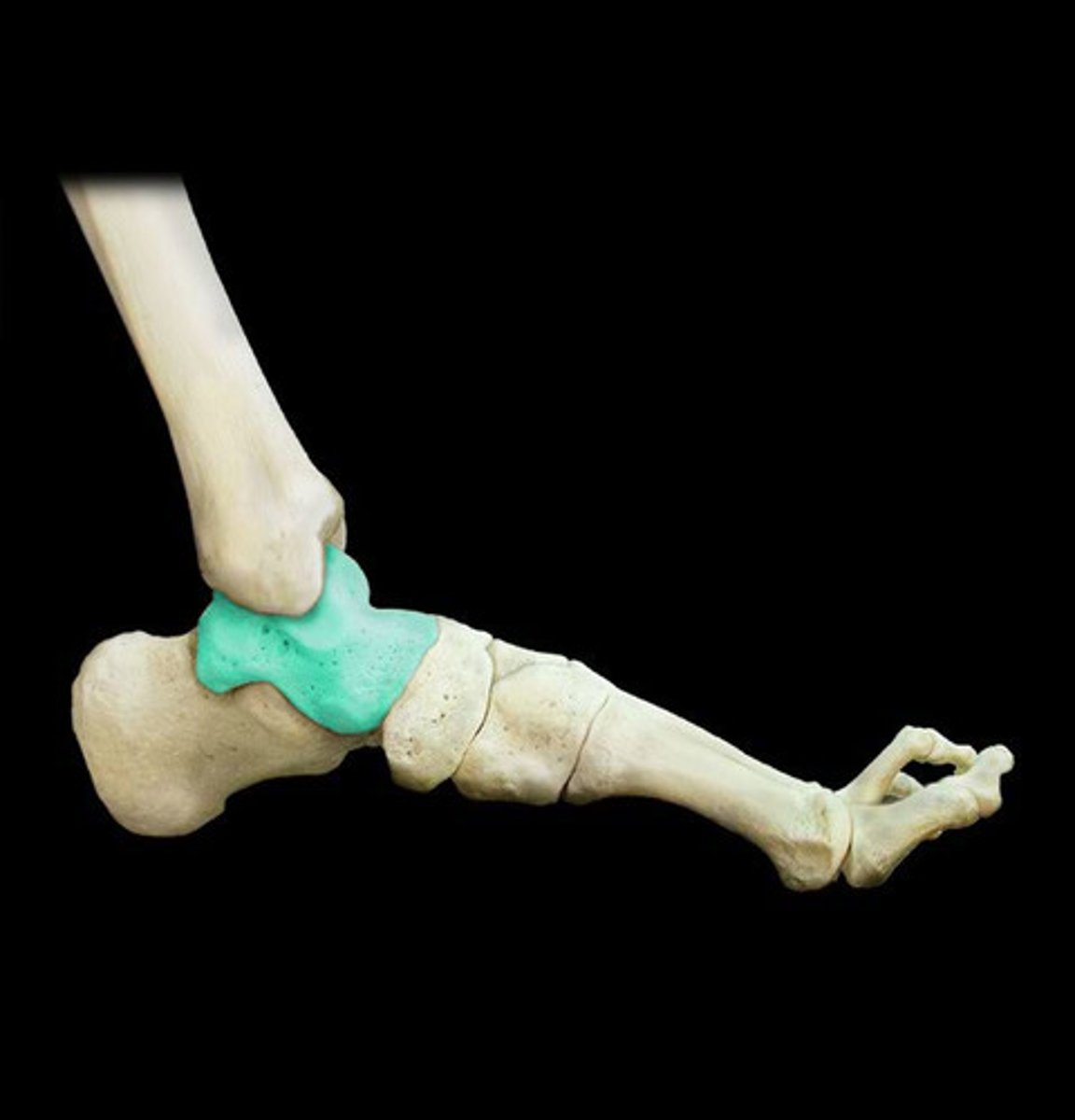
Cartilaginous/Amphiarthrosis Joints
joints that are connected entirely by cartilage which provide a descent range of motion; more than fibrous joints but less than synovial joints.
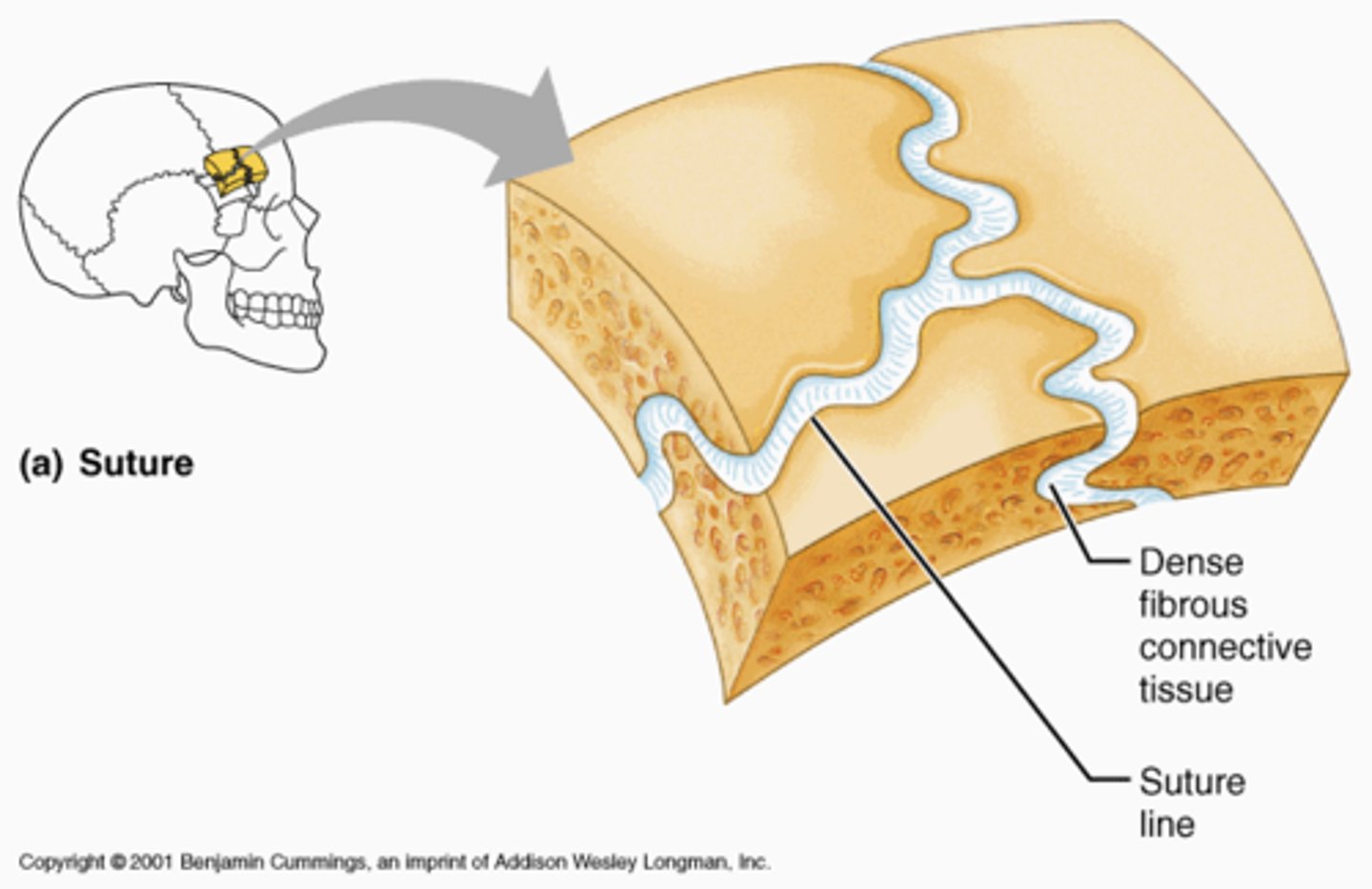
Fibrous/synarthrosis joint
joints which have no joint cavity (projections), but rather connect bones through connective tissue (cartilage). Often develop over time from childhood to adult.
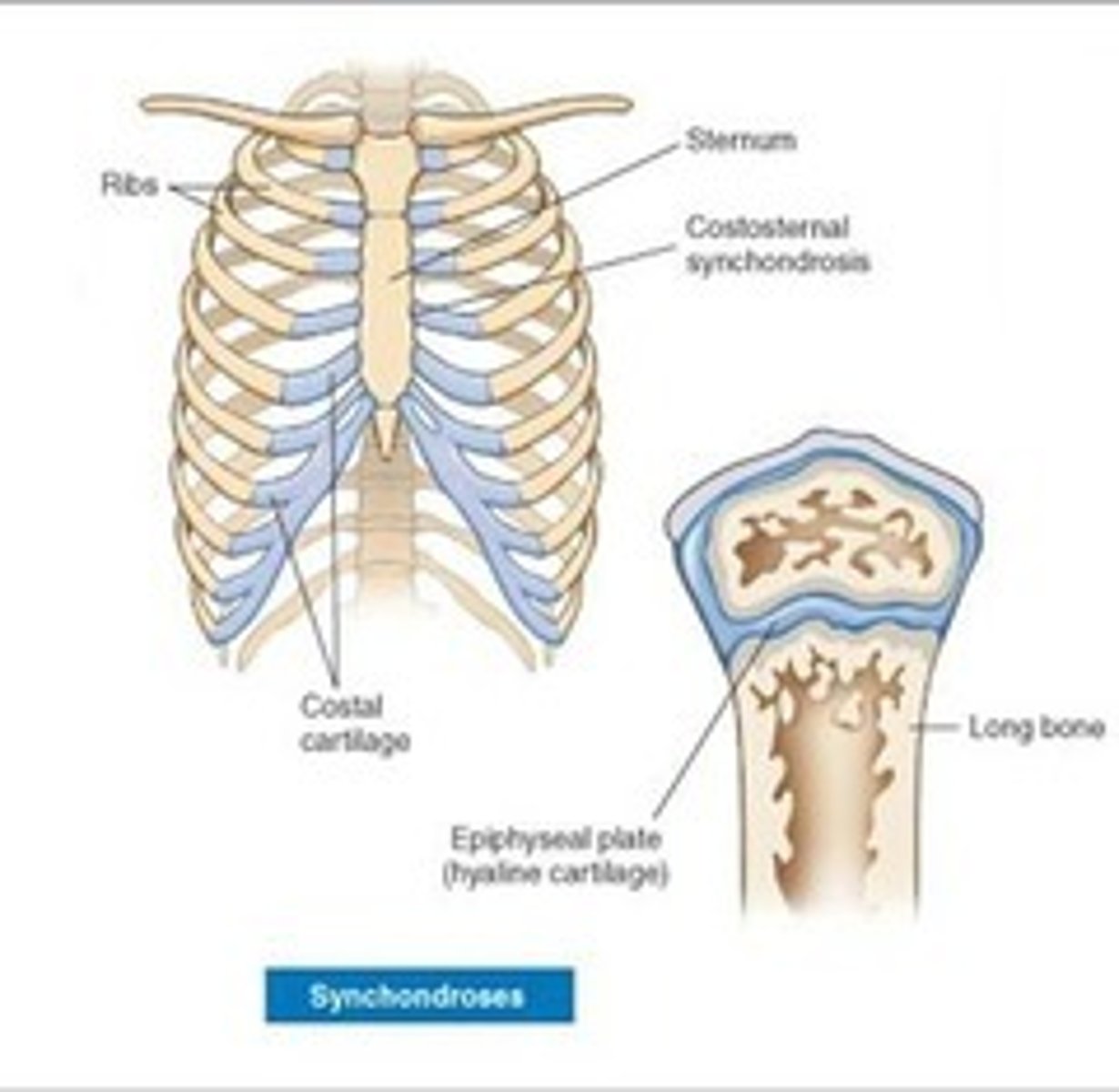
Synchondrosis
an almost immovable joint between bones bound by a layer of cartilage - like the cartilage which connects the true ribs to the sternum.
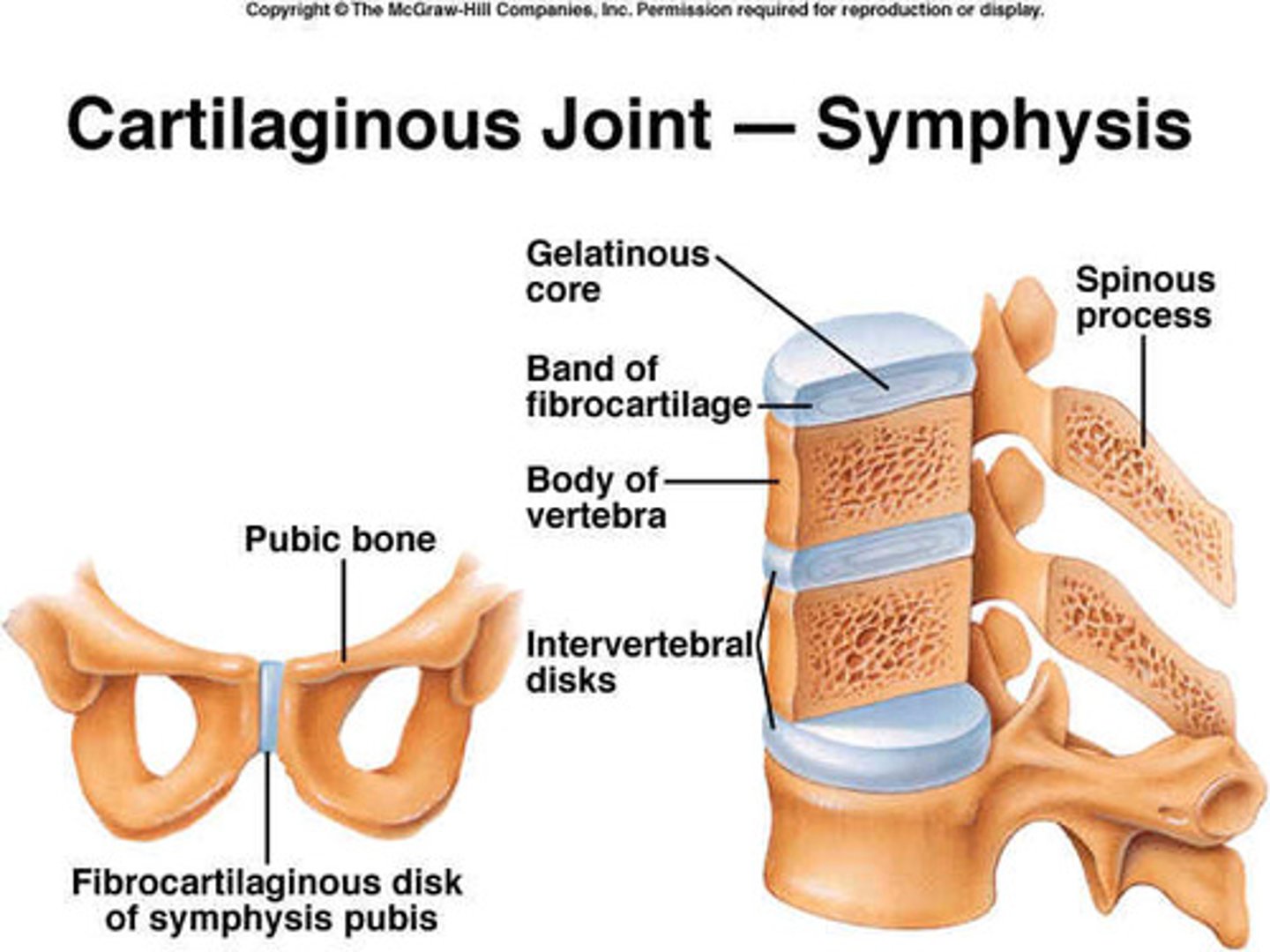
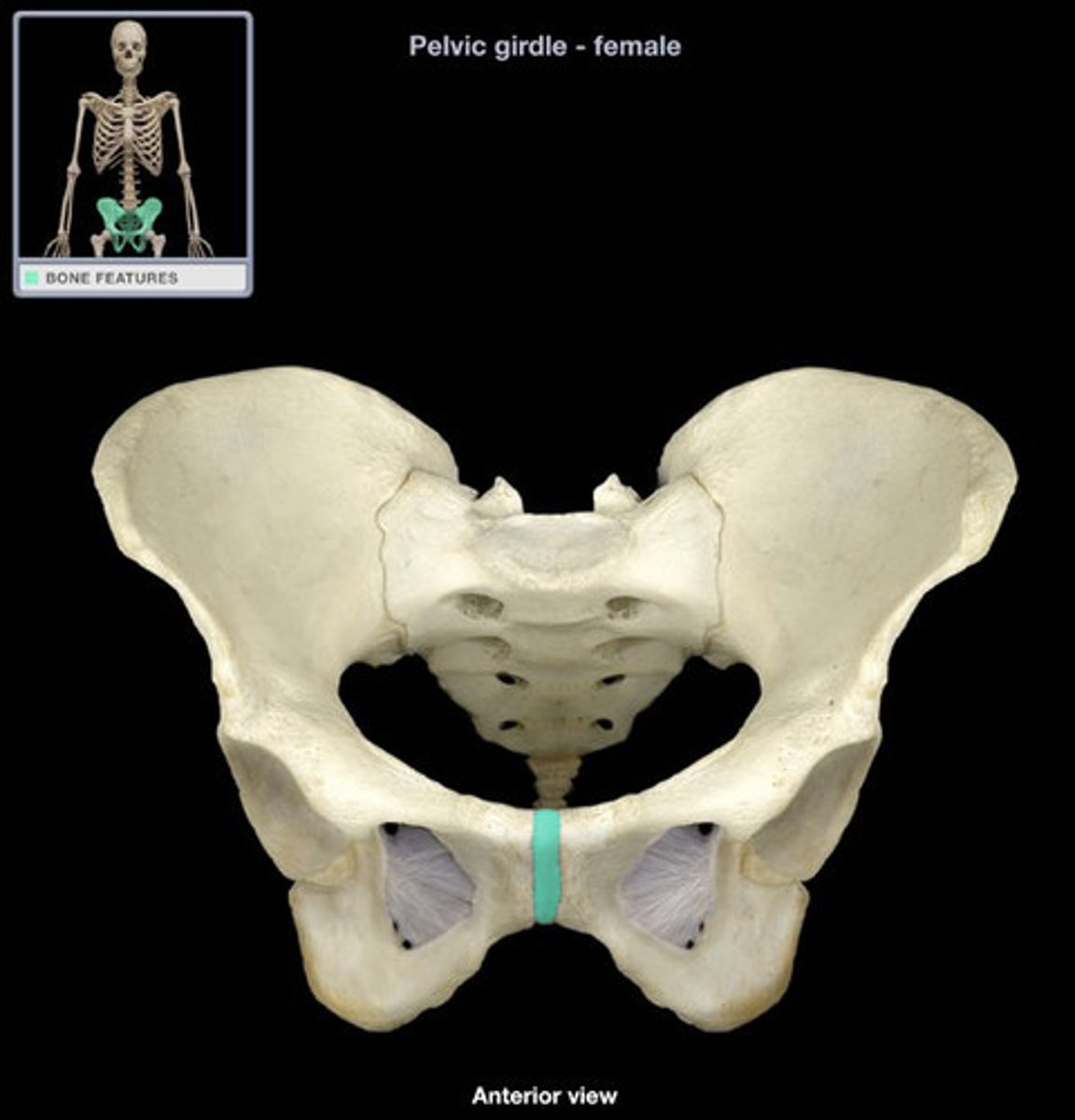
Symphysis
a location where two bones are closely joined by fibrocartilage (collagen fibers), but where limited movement can still occur.
Suture
strongly united, immovable joints between adjacent cranial bones which protect the brain.
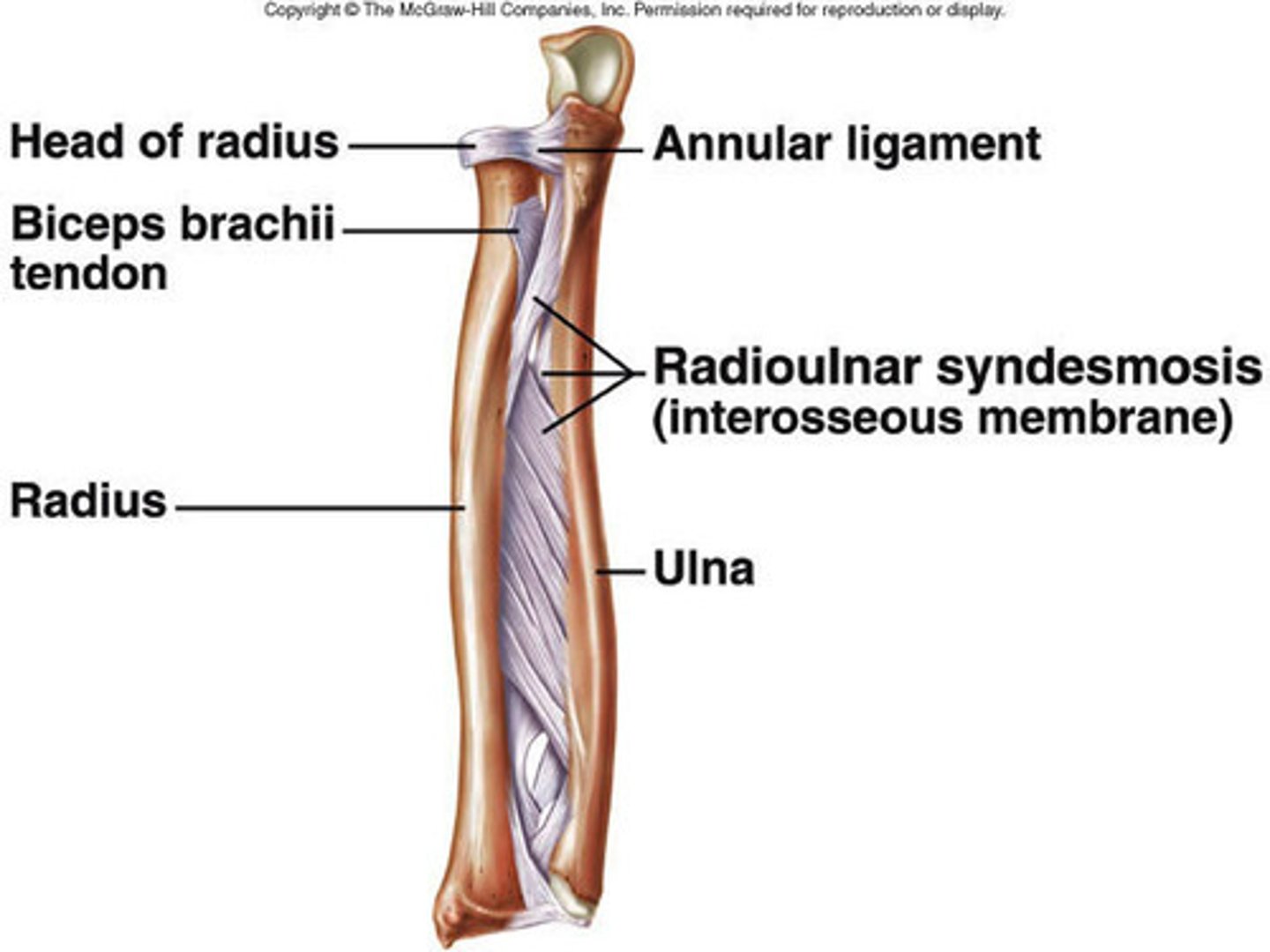
Syndesmosis
when two parallel bones are united by fibrous connective tissue.
Synovial/Diarthrosis joint
joint which provides the most range of motion. joins bones with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. Filled with synovial fluid.
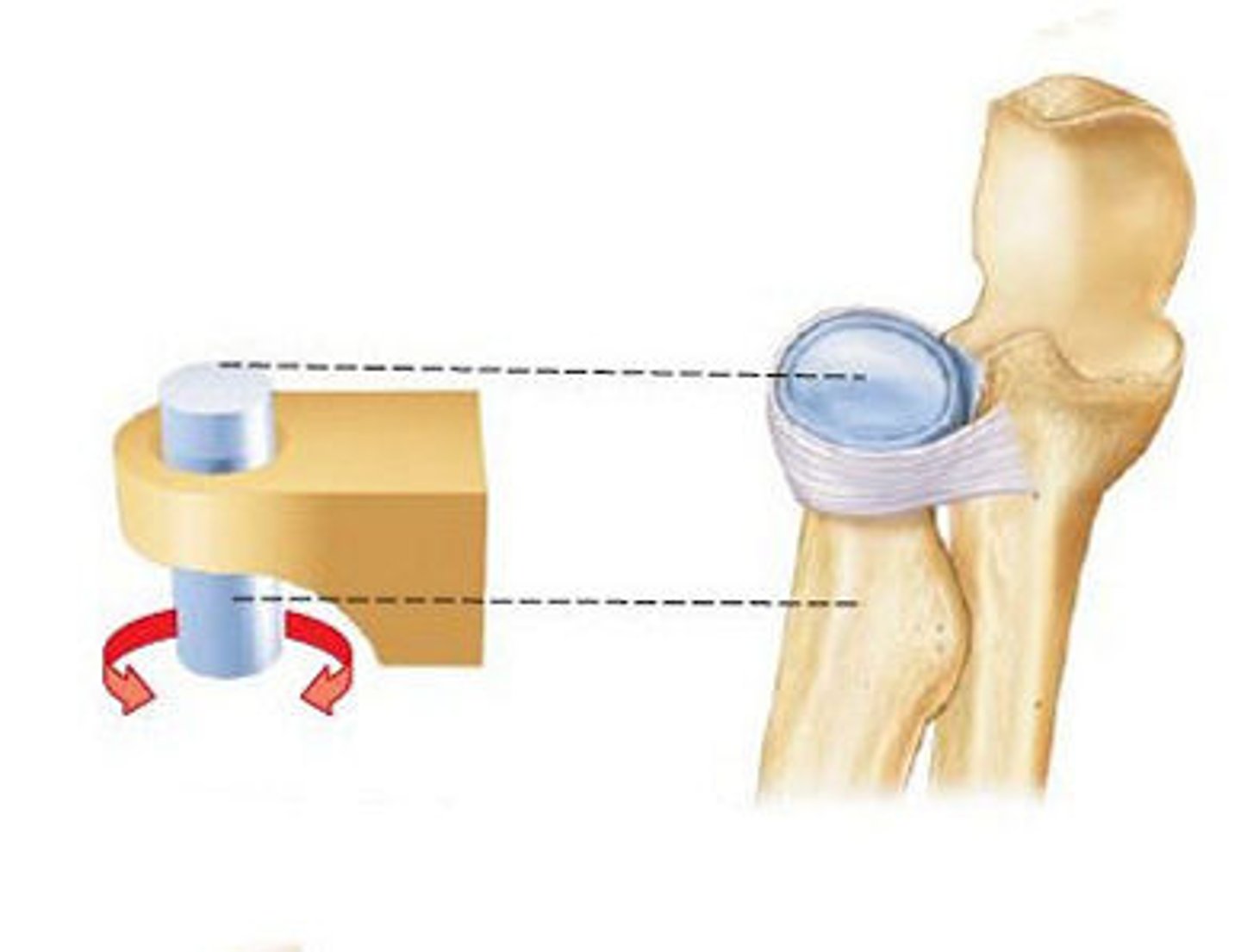
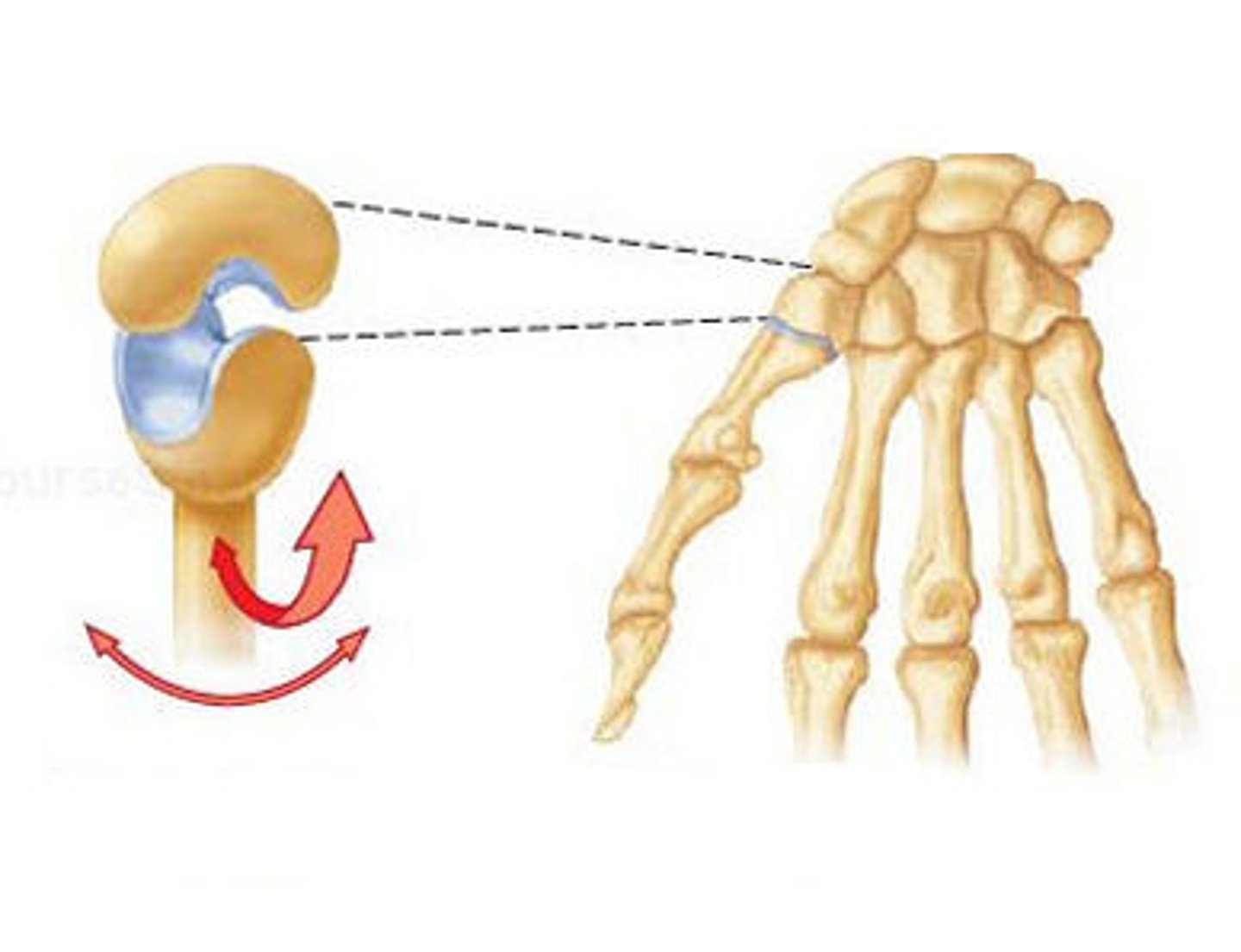
Pivot joint
Rounded portion of a bone is enclosed within a ring formed partially by the articulation with another bone partially by a ligament. The bone rotates around this ring.
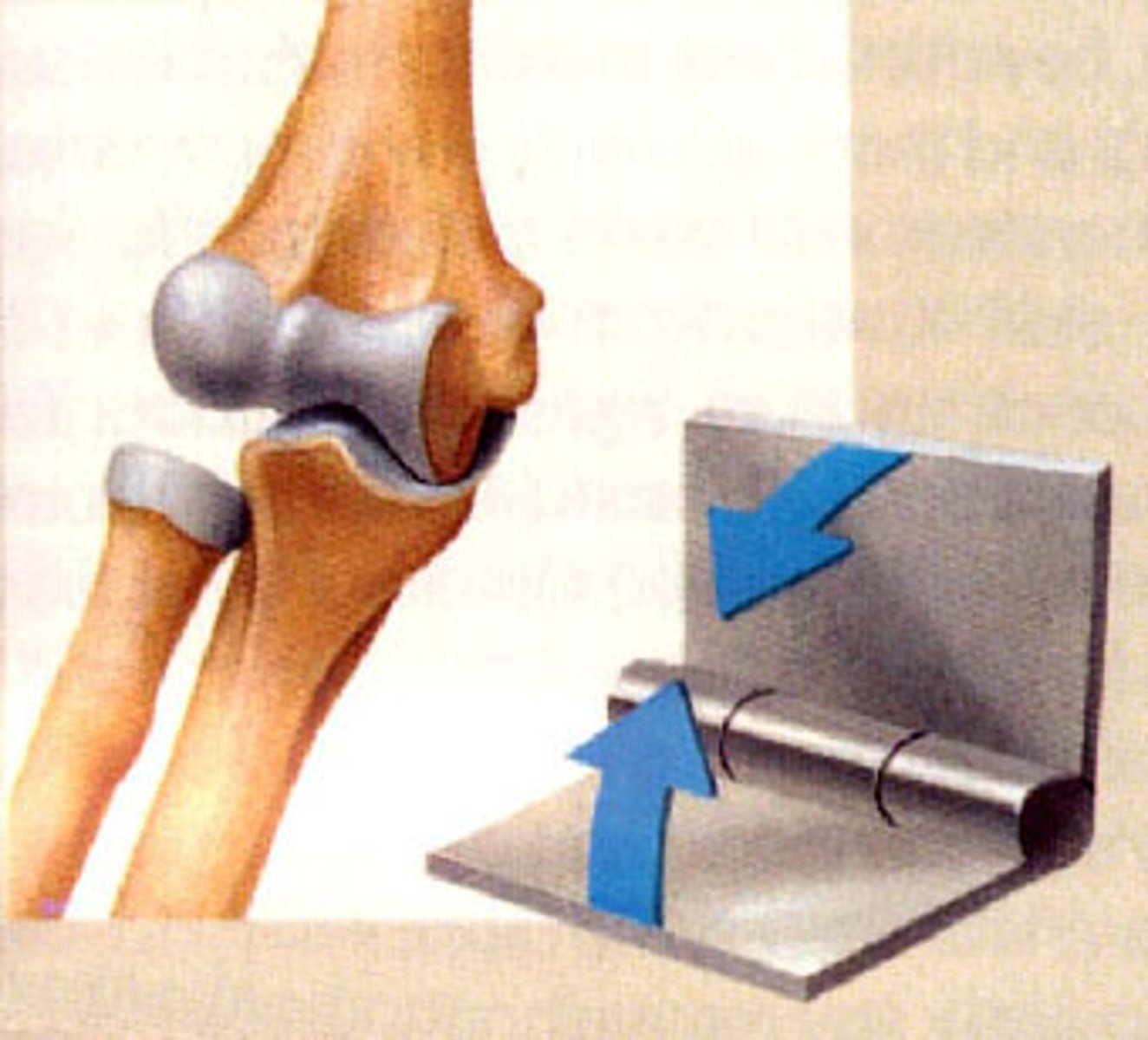
Hinge
type of joint which allows only for bending and straightening motions along a single axis. Convex end of one bone articulates with the concave end of another. Other known as a uniaxial joint.
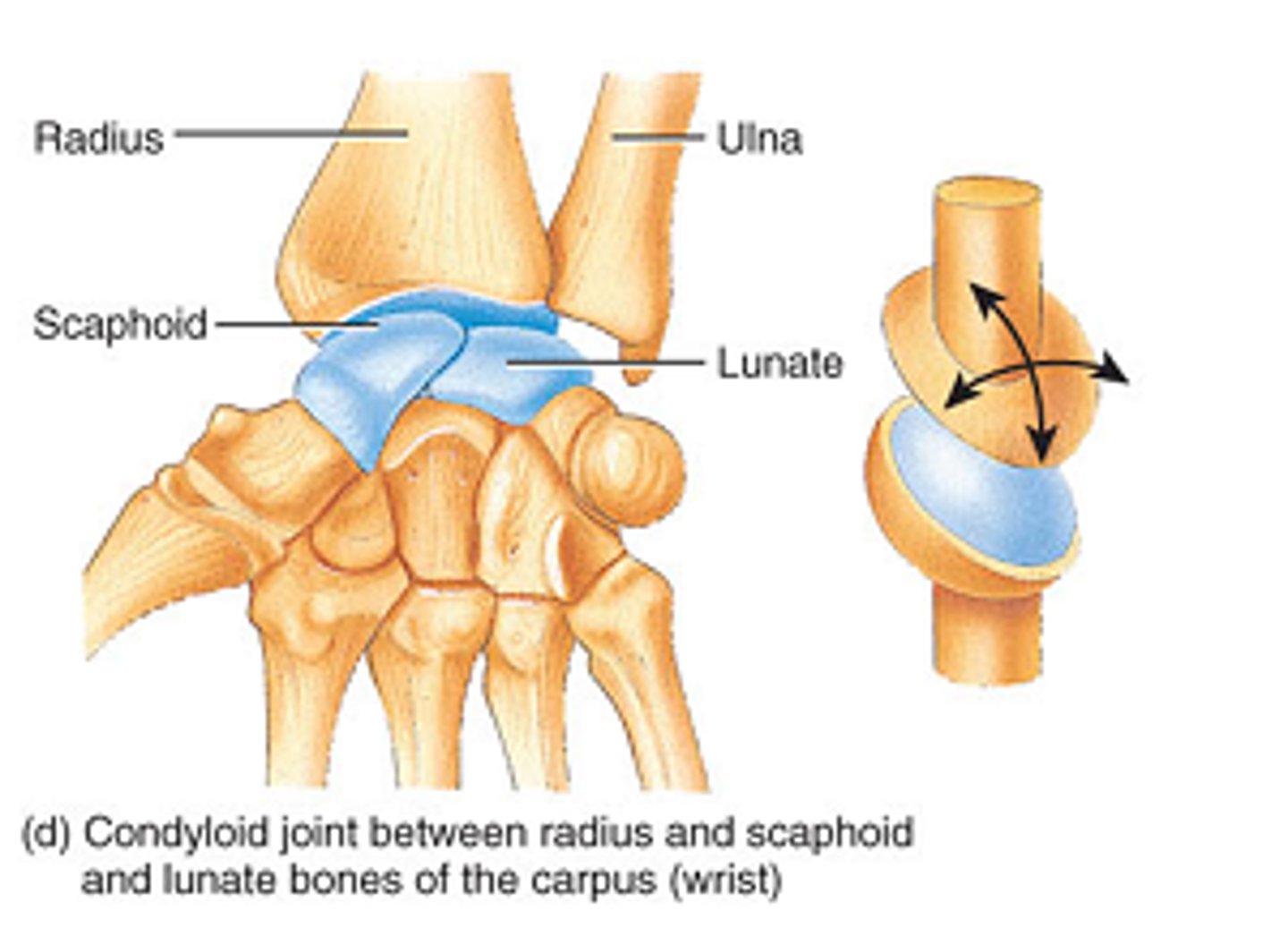
Condyloid/Ellipsoidal Joint
an oval articular surface that is received into an elliptical cavity. This permits movement in two planes, allowing flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction.
Saddle Joint
Both of the articulating surfaces for the bones have a saddle shape, which is concave in one direction and convex in the other.
Plane Joint
Articulating surfaces of the bones are flat or slightly curved and of approximately the same size, which allows the bones to slide against each other.
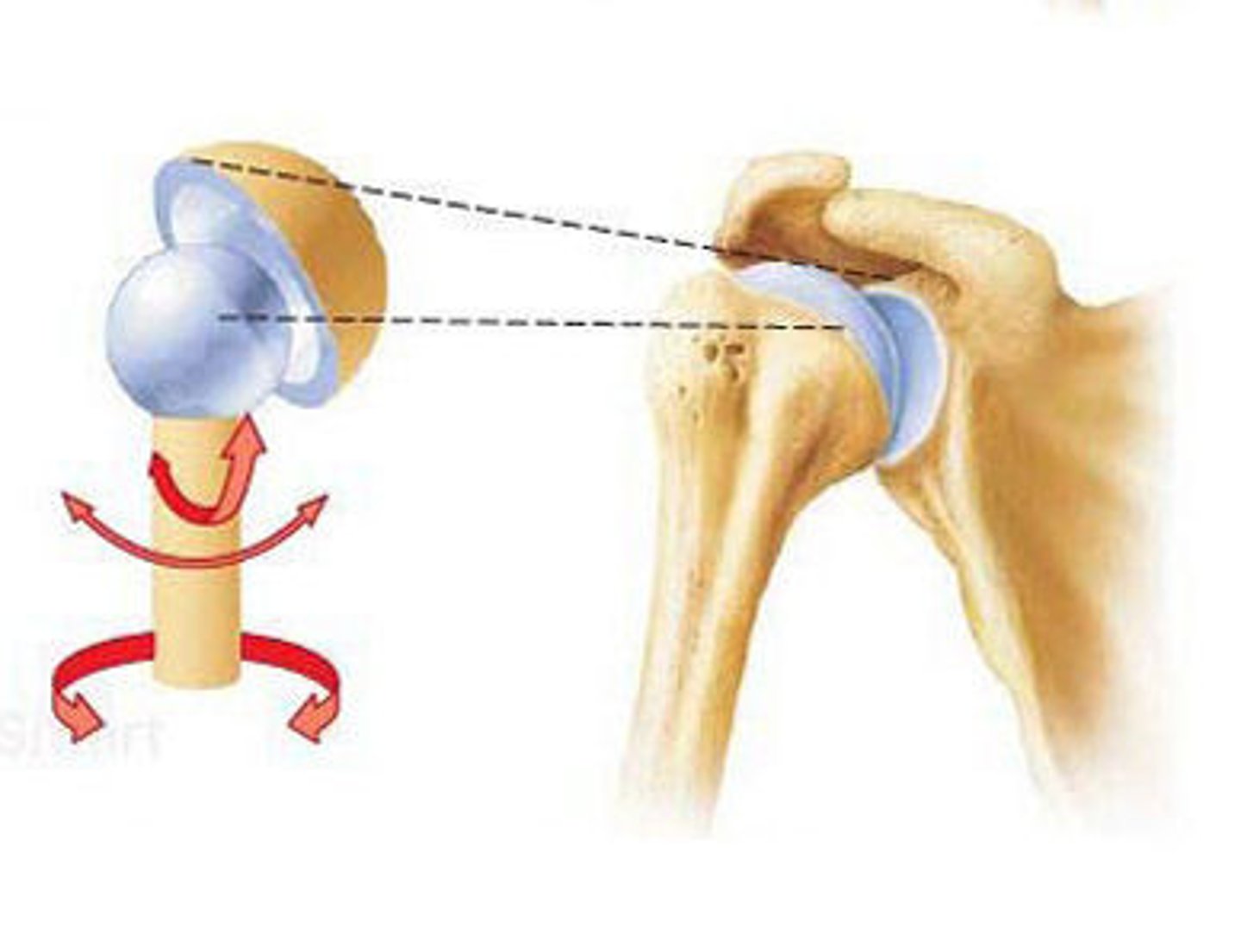
Ball and Socket
Joint with the greatest range of motion.
Rounded head of bone which fits into the concave articulation (socket) of the adjacent bone. Classified as multiaxial joints.
Flexion
Movements which occur in the sagittal (anterior and posterior) plane. Moving the head, or vertebral column, towards your anterior side.
Extension
Movements which occur in the sagittal (anterior and posterior) plane. Moving the head, or vertebral column, towards your posterior side.
Abduction
Involves the movement of limbs, hands, fingers, or toes in the coronal plane (medial-lateral).
Moving a limb, or hand, away from the lateral sides of the body.
Adduction
Involves the movement of limbs, hands, fingers, or toes in the coronal plane (medial-lateral). Moving a limb, or hand, towards the lateral sides of the body.
Circumduction
involves moving joints in a circular pattern via a combination of flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and additional movements.
Lateral rotation
involves rotating the shoulder or hip to the lateral side.
Medial rotation
involves rotating the anterior side of the shoulder or hip towards the midline of the body.
Supination
Rotating the forearm so that the palm faces up.
Pronation
Rotating the forearm so that the palm faces down.
Dorsiflexion
when you lift the front of your foot.
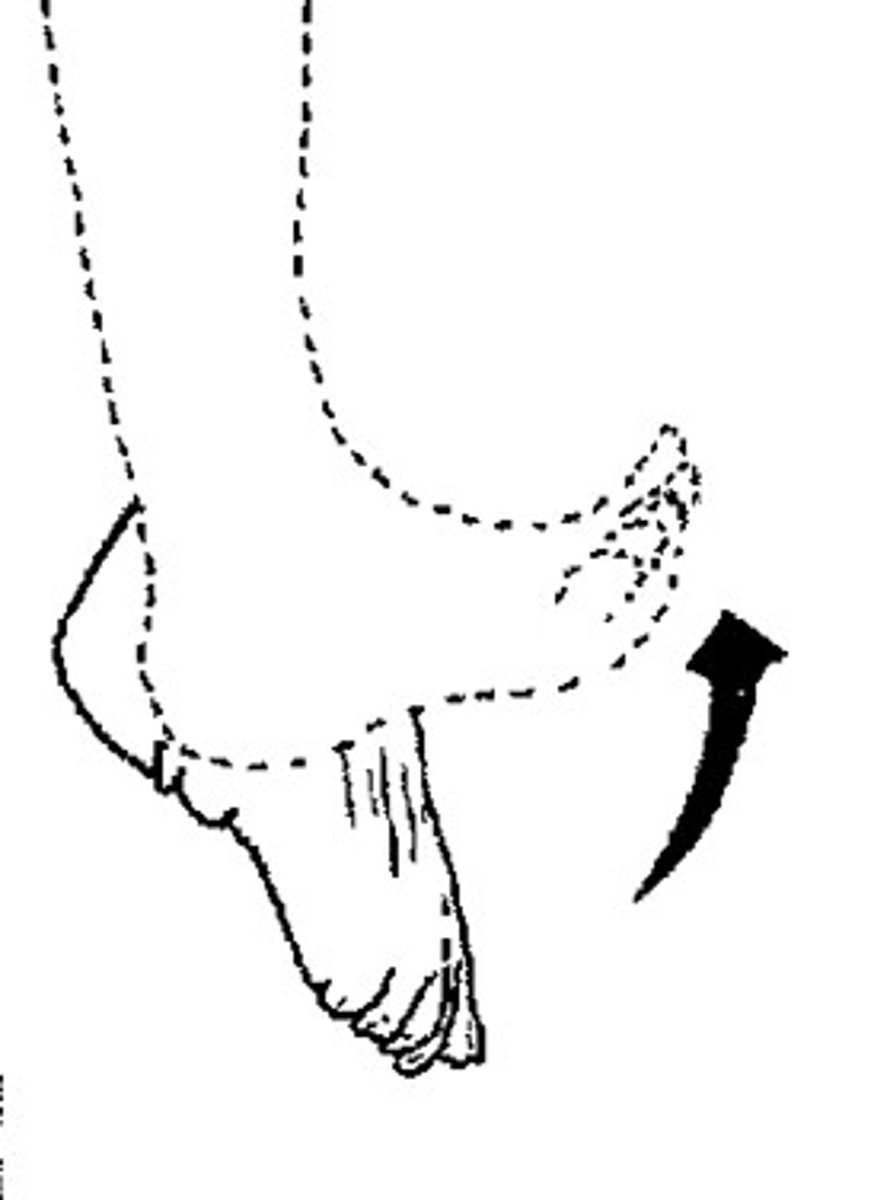
Plantar Flexion
lifting the heel of the foot.