03. Digital Modulation
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
digital modulation
This is the transmittal of digitally modulated analog signals between two or more points in a communication system.
digital modulation
This can be propagated through Earth’s atmosphere and used in wireless communication system.
digital radio
Example of Digital Modulation
ease of processing
ease of multiplexing
noise immunity
Advantages of Digital Modulation Over Traditional Analog System (HINT: EEN)
Low speed voice band data comm. modems
High speed data transmission systems
Digital microwave and satellite comm. systems
PCS (Personal Communication Systems) telephone
Applications of Digital Modulation (HINT: LHDP)
analog
What type of carrier does digital modulation have?
SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) Improvement
Why Digital Modulation?
more spectrum
Simple hardwares create more or less spectrum?
less spectrum
Complex hardwares create more or less spectrum?
High spectral efficiency
High power efficiency
Robust to multipath
Low cost and ease of implementation
Low carrier-to-co channel interference ratio
Low out-of-band radiation
Constant or near constant envelop
Bandwidth efficiency
Power efficiency
Important Criteria in Digital Modulation (HINT: HHR-LLL-CBP)
Bandwidth efficiency
This is the ability to accommodate data within a limited bandwidth.
data rate and pulse width
In Digital Modulation, there is a tradeoff between __ and __.
power efficiency
This is a criterion that pertains to the ability to preserve the fidelity of the digital message at low power levels.
noise immunity
In terms of power efficiency, by increasing signal power, this increases ___.
pulse modulation
Sampling analog information signal
pulse modulation
Converting samples into discrete pulses
pulse modulation
It includes many different methods of converting information into pulse form for transferring pulses from a source to a destination.
analog pulse modulation (APM)
digital pulse modulation (DPM)
2 Categories of Pulse Modulation
pulse modulation
sampling analog information signal
pulse modulation
converting samples into discrete pulses
pulse modulation
transport the pulses over physical transmission medium
pulse amplitude modulation (PAM)
pulse width modulation (PWM)
pulse position modulation (PPM)
pulse code modulation (PCM)
4 Methods of Pulse Modulation (HINT: 4Ps)
PAM
PWM
PPM
Examples of Analog Pulse Modulation
PCM (pulse code modulation)
Example of Digital Pulse Modulation
sampling
It is the process of taking periodic sample of the waveform to be transmitted.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] The more samples taken, the more final outcome looks like the original wave.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] If fewer samples are taken, then other kinds of information could be transmitted.
sampling theorem (Nyquist’s theorem)
It is used to determine the minimum sampling rate for any signal so that the signal will be correctly restored at the receiver.
Nyquist’s theorem
It states that the original information can be reconstructed at the receiver with minimal distortion if the sampling rate in the pulse modulation system is equal to or greater than twice the maximum information signal frequency.
sampling at fs > 2fm(max)
This sampling rate creates a guard band between fm(max) and the lowest frequency component (fs-fm(max)) of the sampling harmonics.
guard band
When sampling at fs > 2fm(max), it creates a ______ between fm(max) and the lowest frequency component (fs-fm(max)) of the sampling harmonics.
low pass filter (LPF)
When sampling at fs > 2fm(max), it creates a guard band between fm(max) and the lowest frequency component (fs-fm(max)) of the sampling harmonics. Therefore, a more practical ____ can be used to restore the modulating signal.
aliasing
When the sampling rate is fs < 2fm(max) or less than the minimum value, distortion will occur, which is called _____.
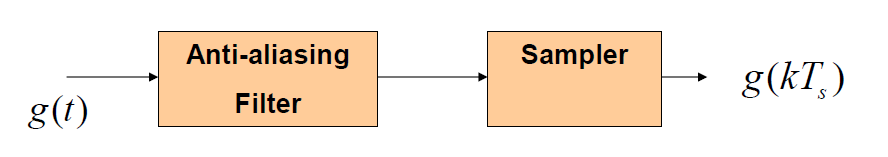
anti-aliasing filter
Aliasing effect can be eliminated by using an _____ prior to sampling and using a sampling rate slightly higher than the Nyquist rate (fs=2W).
anti-aliasing filter
analog pulse modulation (APM)
In ______, the carrier signal is in the form of pulse waveform, and the modulated signal is where one of the characteristics (either amplitude, width, position) is changed according to the modulating/audio signal.
pulse waveform
What form does the carrier signal have in APM?
PAM
PWM
PPM
3 Common Techniques of APM
pulse amplitude modulation (PAM)
The simplest form of pulse modulation
PAM (pulse amplitude modulation)
The amplitude of a constant width, constant position pulse (carrier signal) is varied according to the amplitude of the modulating signal.
digital train of pulses
In PAM, the modulating signal is sampled by the ____ and the process if based upon the sampling theorem.
sampling theorem
In PAM, the modulating signal is sampled by the digital train of pulses and the process is based upon the ____.
pulse width modulation (PWM)
It is the technique of varying the width of the constant amplitude pulse proportional to the amplitude of the modulation signal.
Pulse Duration Modulation (PDM)
pulse width modulation (PWM) is also known as _____.
modulating signal
In PWM, either the leading edge, trailing edge, or both may be varied by the _______.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] PWM gives better signal to noise performance than PAM.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] PWM has advantage, when compared with PPM, that is its pulse are of varying width and therefore of varying power content.
power content
PWM has advantage, when compared with PPM, that is its pulse are of varying width and therefore of varying _______.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] PWM still works if synchronization between transmitter and receiver fails, whereas PPM does not.
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM)
This is when the position of a constant-width and constant-amplitude pulse within prescribed time slot is varied according to the amplitude of the modulating signal.
constant transmitter power output
PPM has the advantage of requiring _________.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] A disadvantage of PPM is it is dependent on transmitter-receiver synchronization.
amplitude changes
PPM has less noise due to ______.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] PPM has less noise due to amplitude changes, bacause the received pulses may be clipped at the receiver, thus removing amplitude changes caused by the noise.
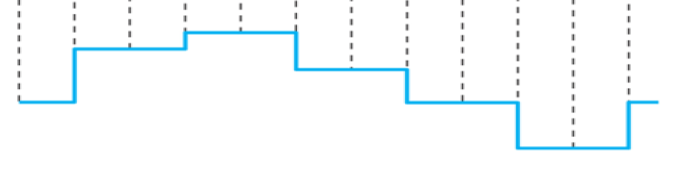
PAM
pulse amplitude modulation (PAM)
Modulation in which the amplitude of pulses is varied in accordance with the modulating signal.
PWM
pulse width modulation (PWM)
Modulation in which the duration of pulses is varied in accordance with the modulating signal.
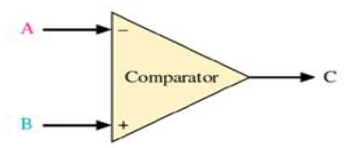
comparator and integrator
PWM makes use of ____ and _____.
high
If A < B, then C is?
low
If A > B, then C is?
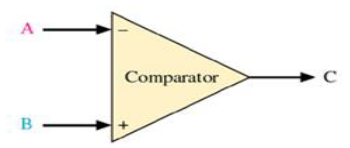
integrator
It can be used to recover a signal in PWM.
PPM
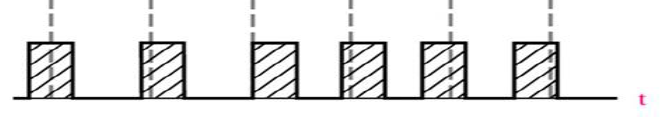
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM)
Modulation in which the temporal positions of the pulses are varied in accordance with some characteristic of the modulating signal.
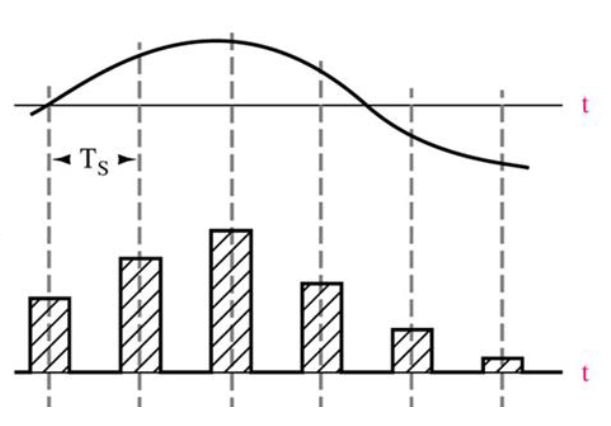
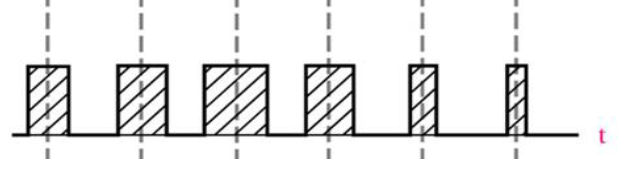
natural sampling and flat-top sampling
How to encode analog waveforms? (from analog sources into baseband digital signals?
natural sampling output waveform
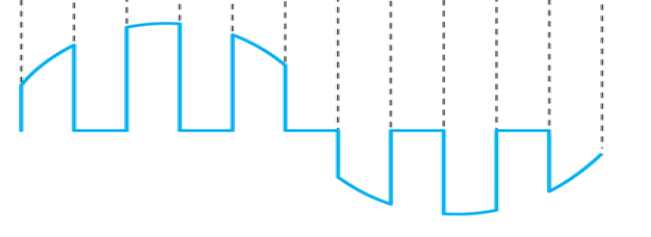
flat-top sampling output waveform