Cellular injury (Ren)
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Slide 1-56
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
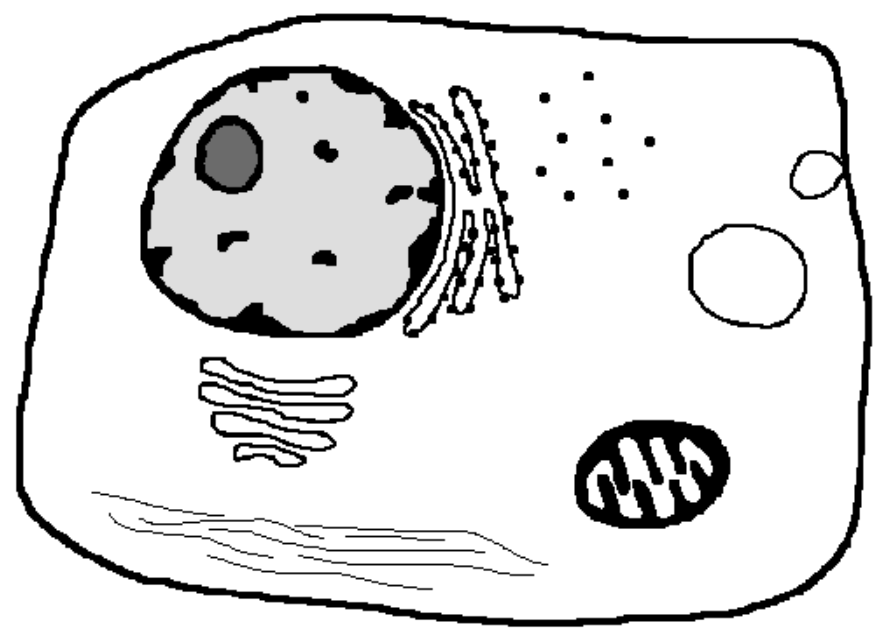
What is the structure at the bottom?
What is the large circular structure at the right?
What process is occurring at the right-most area?
Intermediate filaments
Lysosome
Pinocytosis
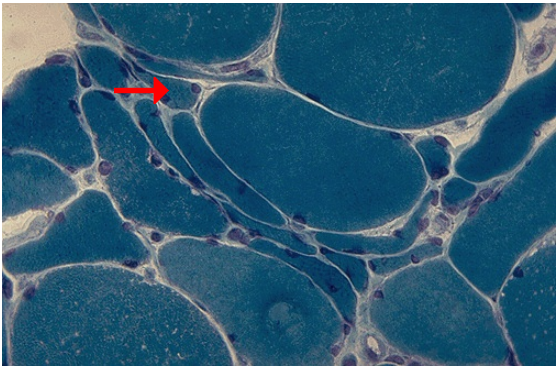
Identify the cellular adaptation
What stain is used in this slide?
What is the most common cause of this adaptation?
Atrophy of muscle fibers
Trichrome stain
Disuse atrophy
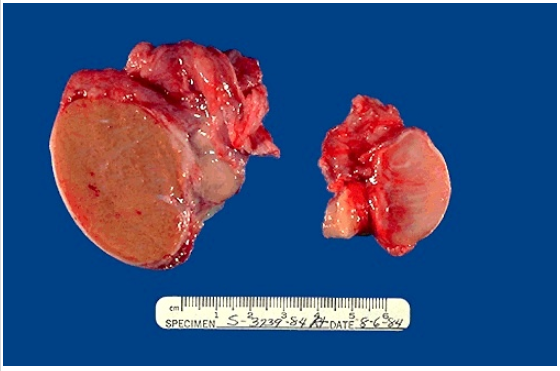
Identify the cellular adaptation
What causes this particular adaptation?
Atrophy of testis
Unilateral testicular atrophy is most likely caused by cryptorchidism
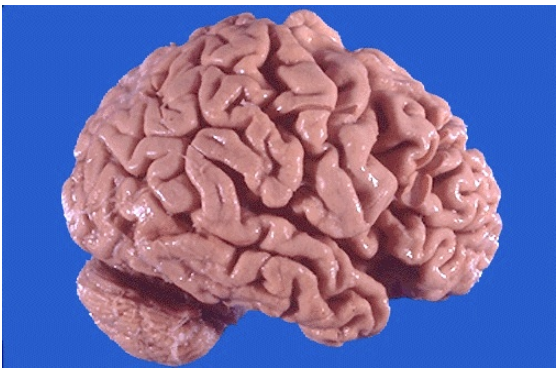
Identify the cellular adaptation
What is the clinical diagnosis?
Atrophy of cerebrum
Alzheimer disease
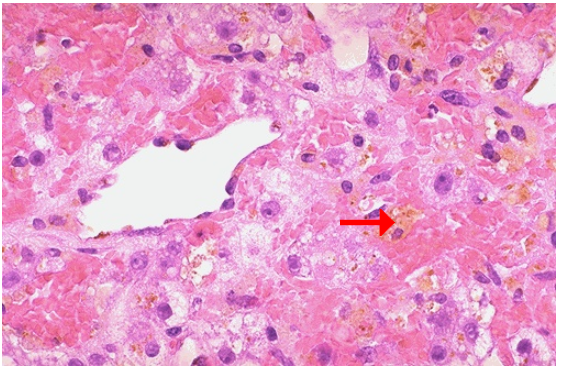
Identify
What causes this cellular adaptation to occur?
Identify the pointed structure
What cellular process is occurring?
Atrophy of centrilobular region of liver
Hypoxia
Lipochrome
Autophagocytosis
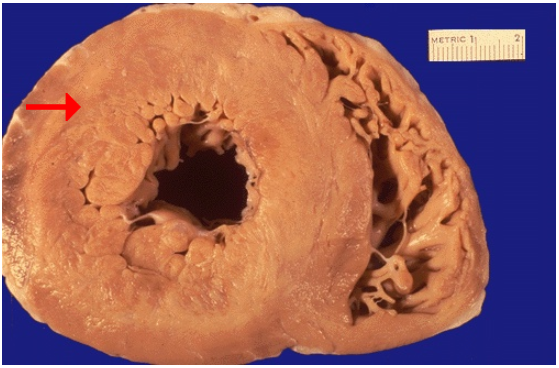
Identify
Hypertrophy of heart
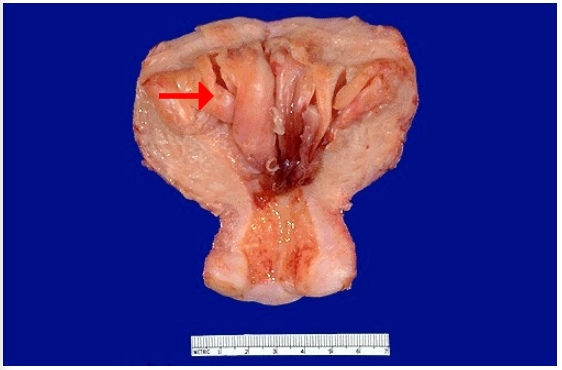
Identify
What caused this cellular adaptation?
What may the patient experience?
Hyperplasia of endometrium
Continued hormonal stimulation
Vaginal bleeding
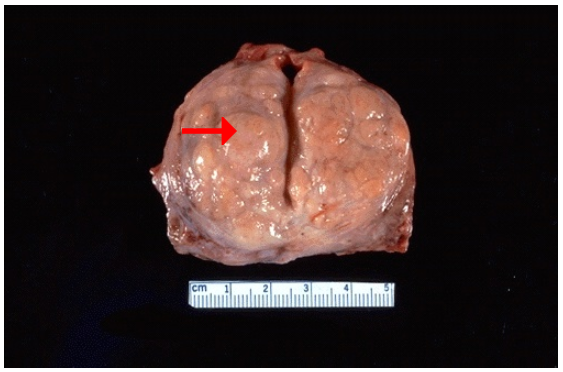
Identify
What is the estimated weight of this specimen?
What is the pattern of increase?
Is this physiologic or pathologic?
Hyperplasia of prostate
70 gm
Nodular
Pathologic
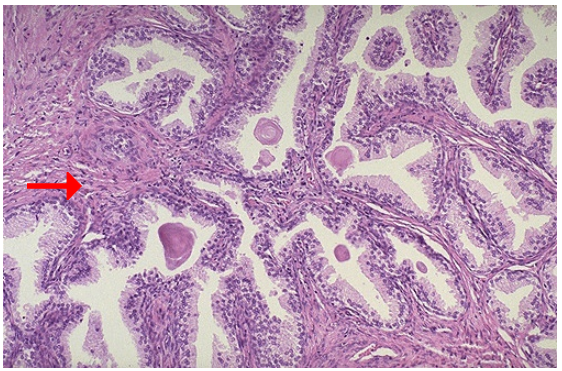
Identify
Hyperplasia, prostate
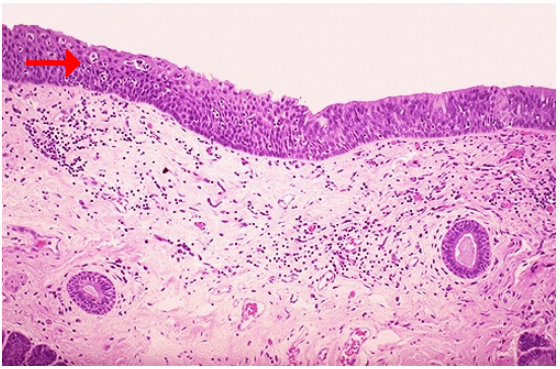
Identify
Identify the pointed structure
Squamous metaplasia of larynx
Squamous epithelium
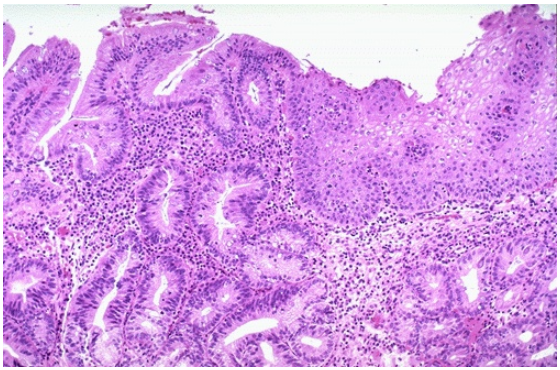
Identify
CD?
Metaplasia, gastric columnar mucosa in esophagus
GERD
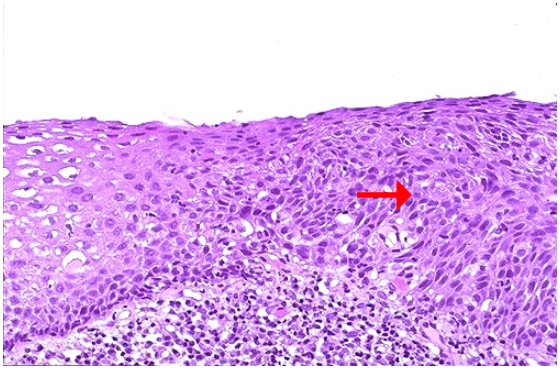
Identify
What is the pointed structure?
Dysplasia, cervix
Dysplastic epithelium
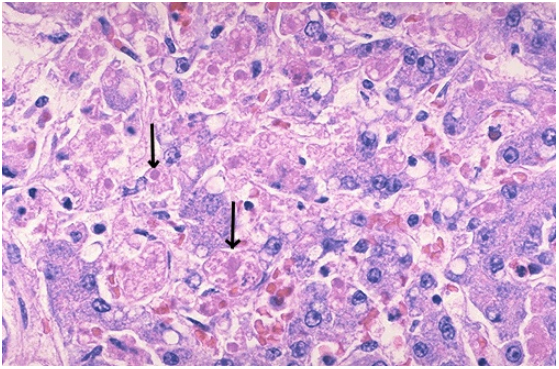
Identify the type of cell death
What cellular process is occurring?
What enzymes are involved?
Apoptosis, viral hepatitis
Apoptosis
Caspases
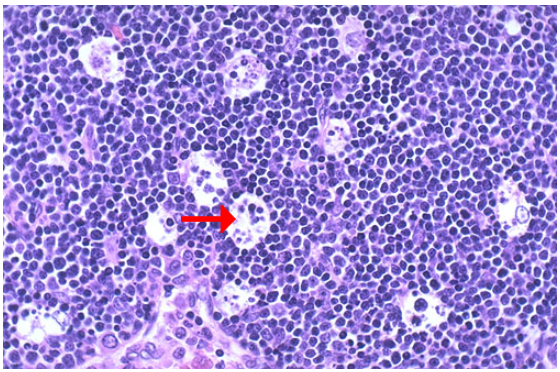
Identify the type of cell death
Apoptosis, fetal thymus
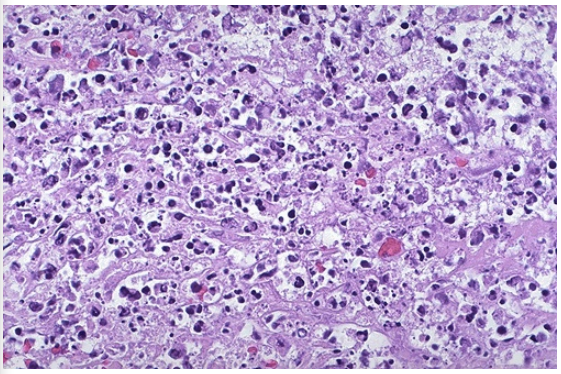
Identify the type of cell death and CD
Coagulative necrosis, myocardial infarction
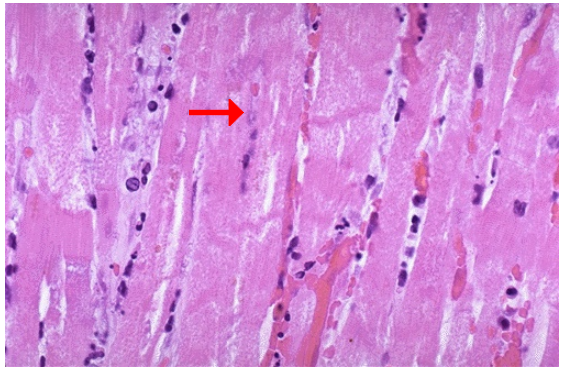
Identify the type of cell death and CD
What symptom may accompany this pathology?
Coagulative necrosis, myocardial infarction
Visceral pain
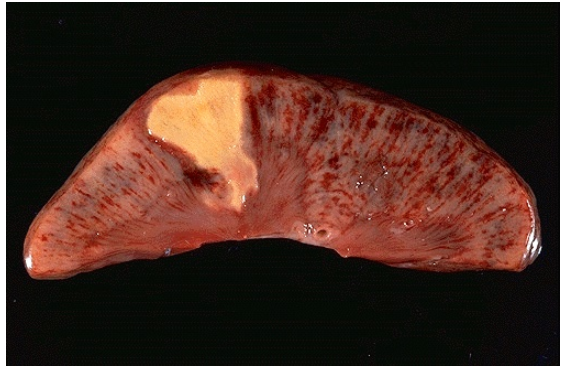
Identify the type of cell death and CD
Coagulative necrosis, renal infarction
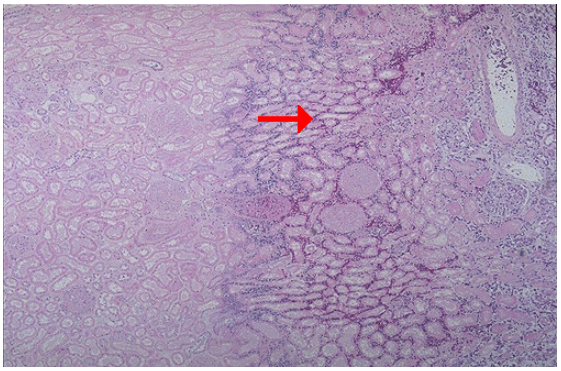
Identify the type of cell death and CD
What zone is the arrow pointing at?
Coagulative necrosis, renal infarction
Hemorrhagic zone
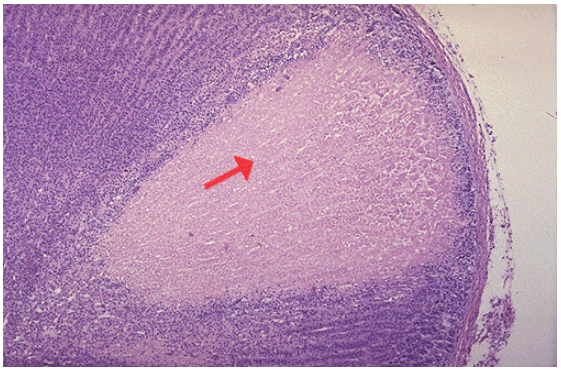
Identify the type of cell death and CD
Why is the area just under the capsule is spared?
Coagulative necrosis, adrenal infarction
Blood supply from capsular arterial branches
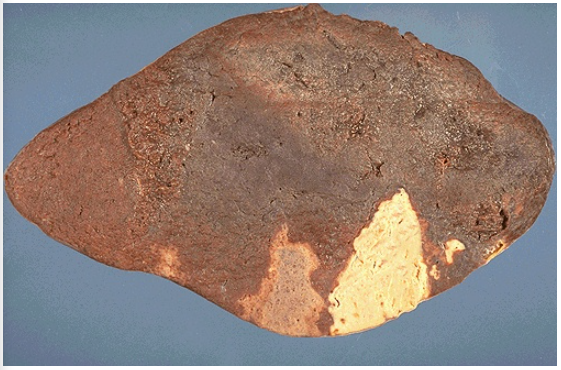
Identify the type of cell death and CD
Coagulative necrosis, splenic infarctions
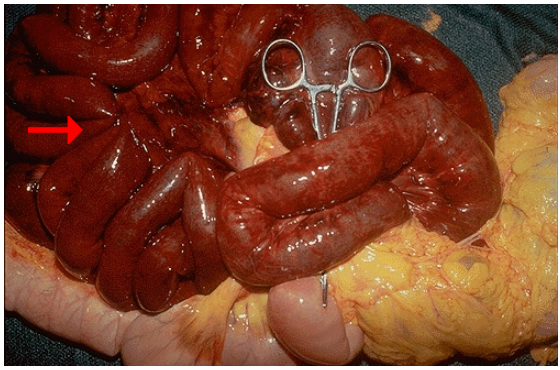
CD
Small intestinal infarction
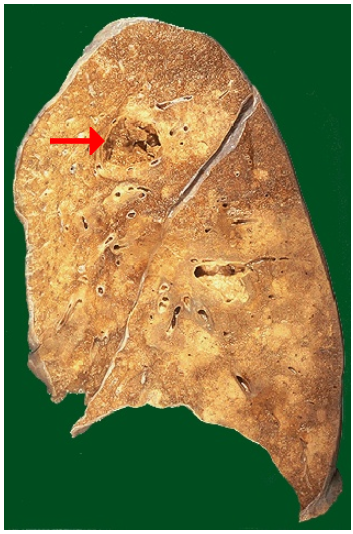
Identify the type of cell death and CD
Liquefactive necrosis, lung abscesses
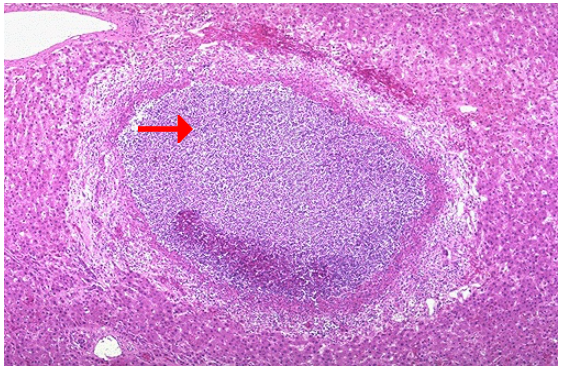
Identify the type of cell death and CD
What type of exudate is seen grossly?
Liquefactive necrosis, liver abscess
Purulent exudate
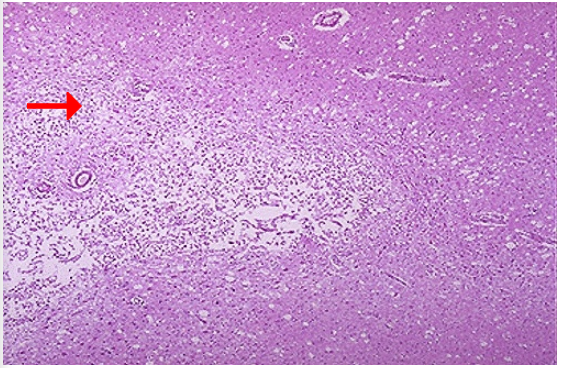
Identify what type of cell death and CD
What happens to the liquefied area when it resolves?
Liquefactive necrosis, cerebral infarction
2. Cystic space
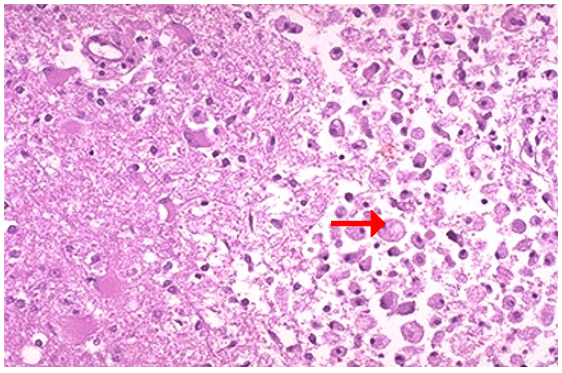
What type of cell death and CD
What are the cells on the right that cleans up necrotic cellular debris?
1.Liquefactive necrosis, cerebral infarction
2.Macrophage
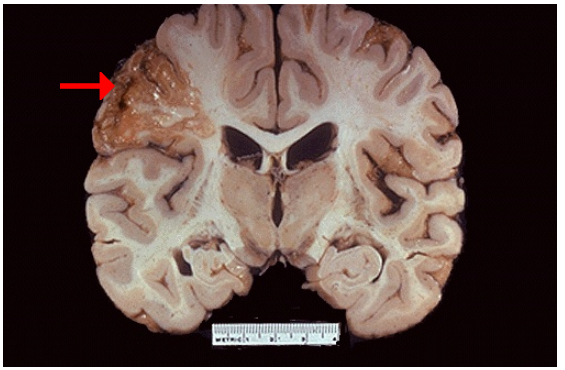
1.Identify type if cell death and CD
2.What do you call the creamy yellow material commonly seen in this type of necrosis?
3.What is left behind after removal of the dead tissue?
1.Liquefactive necrosis, cerebral infarction
2.Pus
3.Cavity
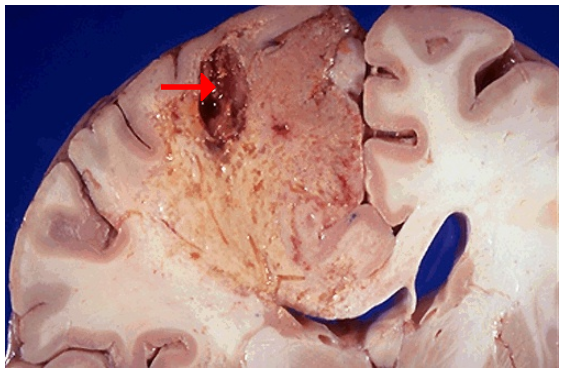
1.Resolution of a liquefactive necrosis in the brain leads to the development of?
1.Cystic space

1.Identify type of cell death
2.What do you call the grossly visible chalky-white areas seen on the cut surface?
3.Seen in what type of medical emergency?
1.Fat necrosis, pancreas
2.Fat saponification
3.Acute pancreatitis
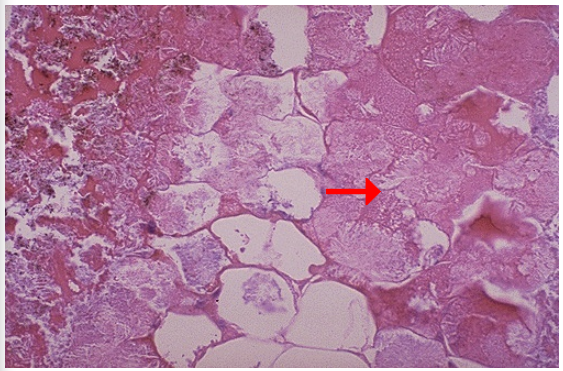
1.Type of cell death
2.Necrotic fat cells are seen on which side?
3.describe its appearance
1.Fat necrosis, pancreas
2.Right
3.vague cellular outline, lost their peripheral nuclei, cytoplasm is pink amorphous mass of necrotic material
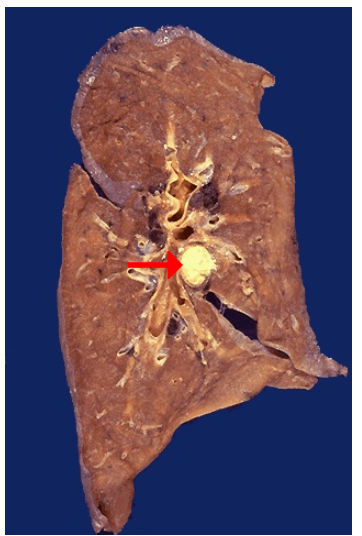
1.type of cell death
2.This type of necrosis is encountered most often in what condition?
1.Caseous necrosis, hilar lymph node
2.Tuberculosis and fungal infection
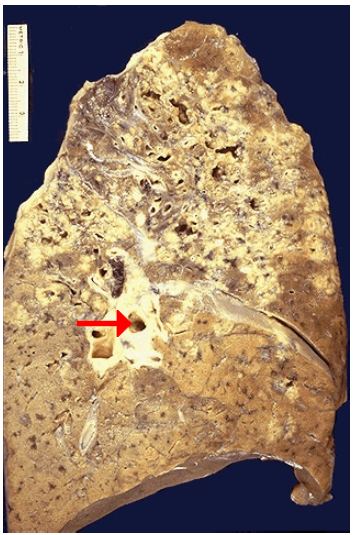
Caseous necrosis, extensive in lung
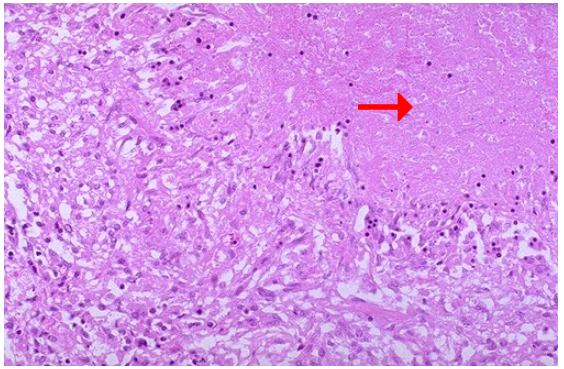
Caseous necrosis, lung
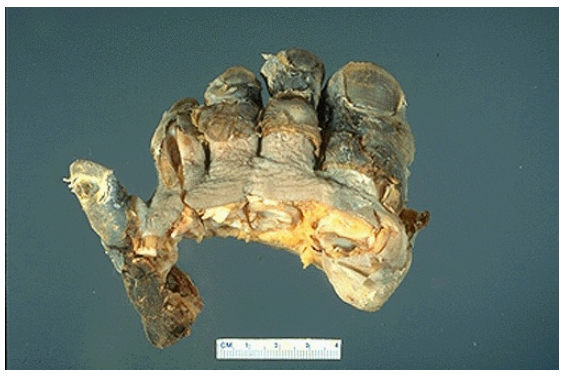
Gangrenous necrosis, foot
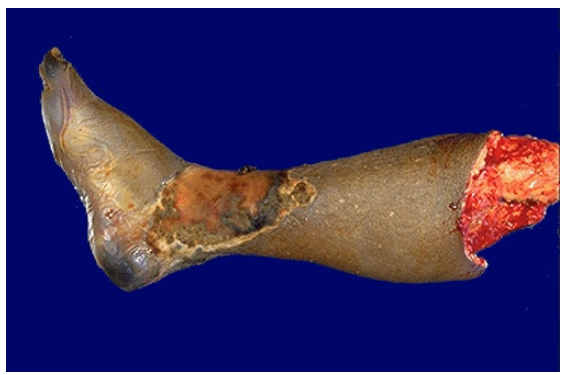
Gangrenous necrosis, lower extremity
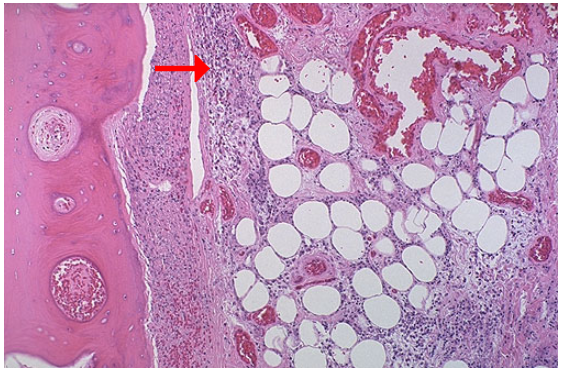
Gangrenous necrosis
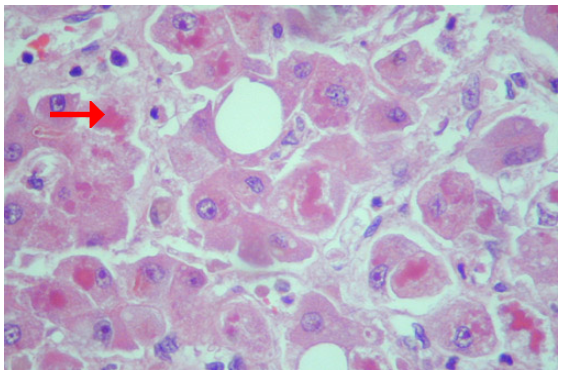
Mallory's hyaline, liver
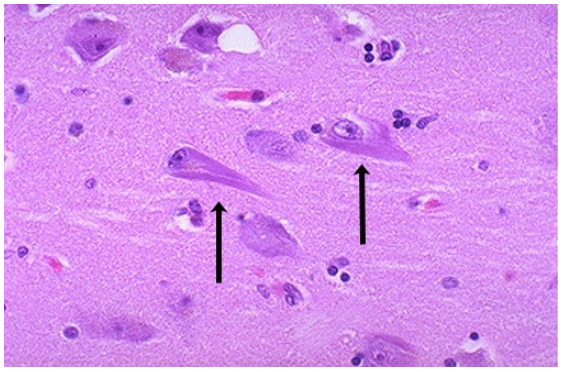
Neurofibrillary tangles, Alzheimer disease
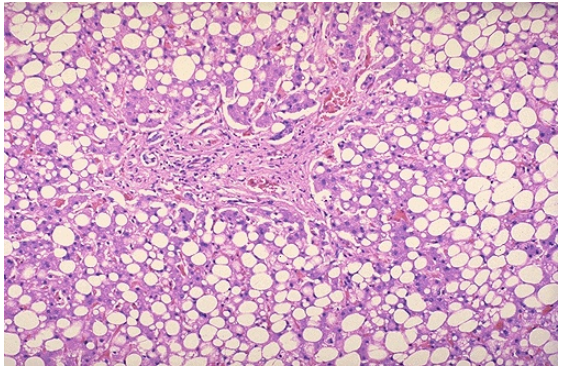
Steatosis, liver
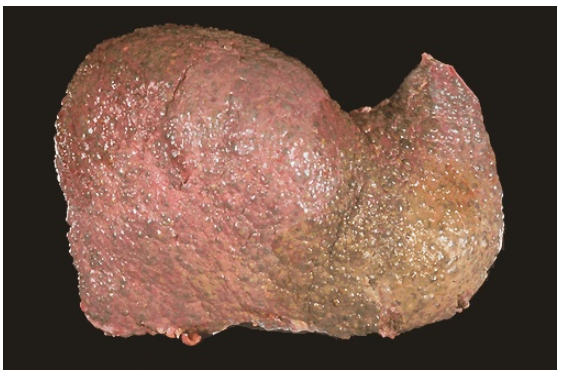
Cirrhosis, liver
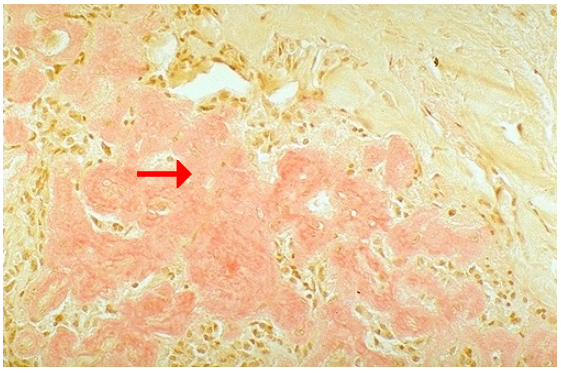
Amyloid deposition, Congo red stain
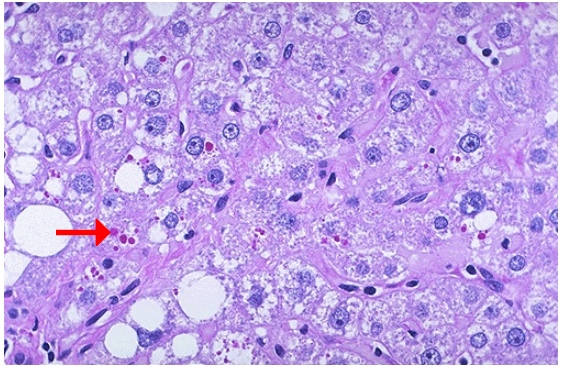
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency with globules in liver, PAS stain
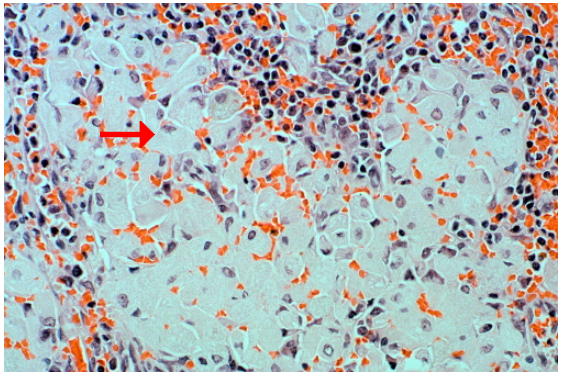
Gaucher disease, spleen
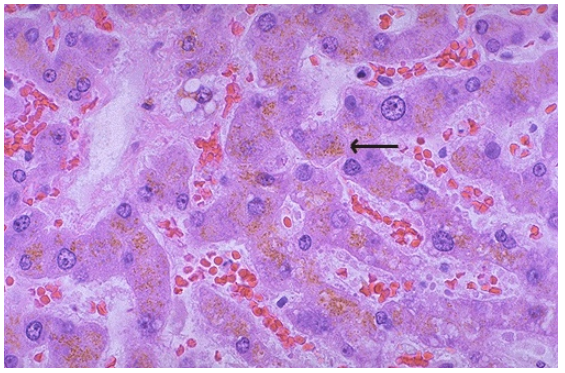
Lipochrome in hepatocytes
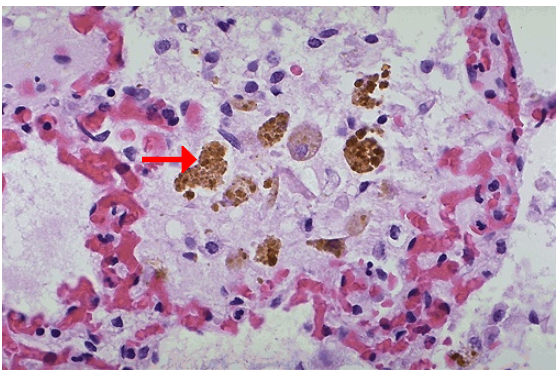
Hemosiderin in pulmonary macrophages
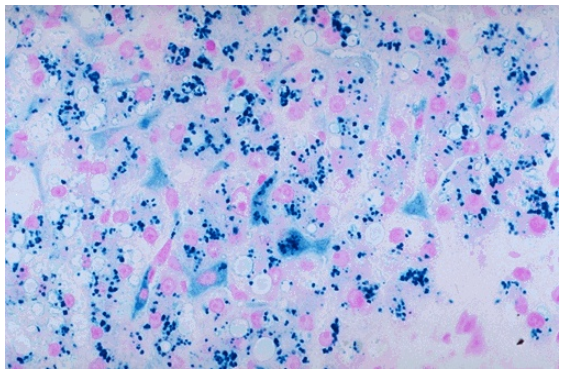
Hemosiderosis of liver, iron stain
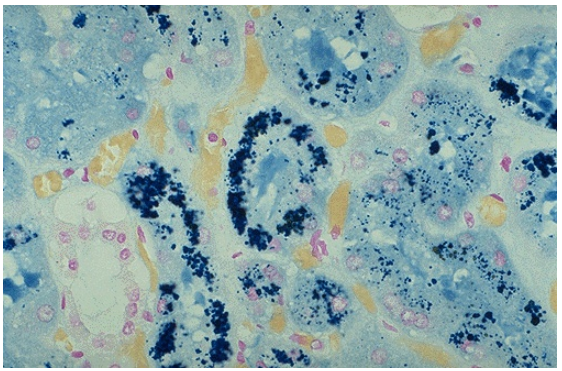
Hemosiderin deposition in renal tubules, iron stain
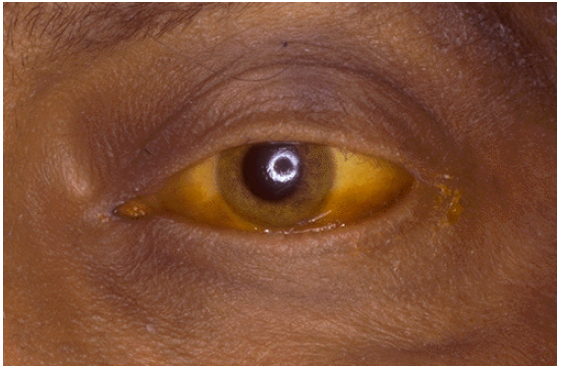
Scleral icterus (jaundice) seen in eye
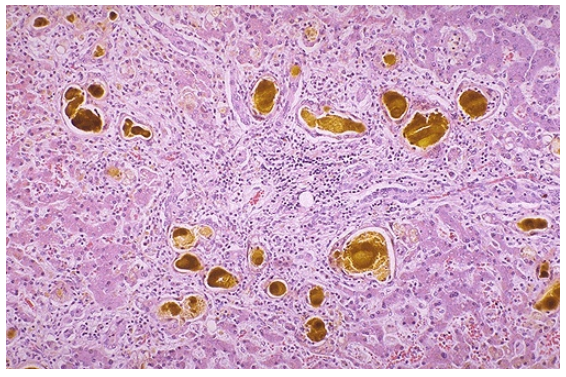
Bilirubin in liver (cholestasis)
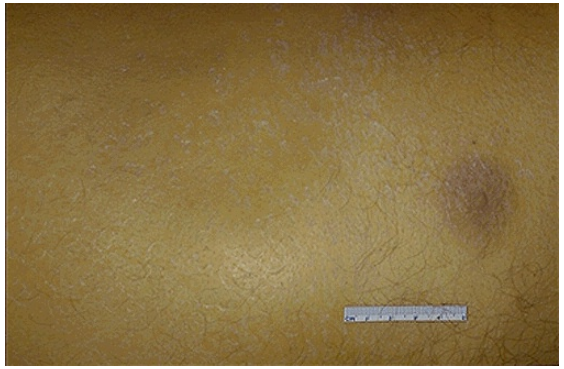
Jaundice (icterus) of skin
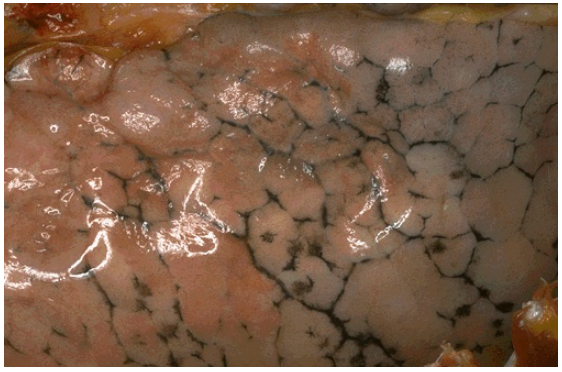
Anthracotic pigmentation seen on surface of lung
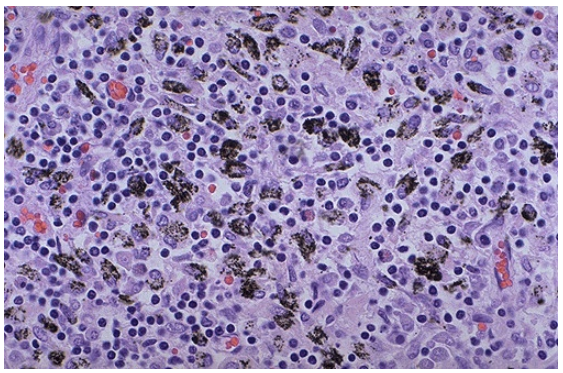
Anthracotic pigment in macrophages of hilar lymph node
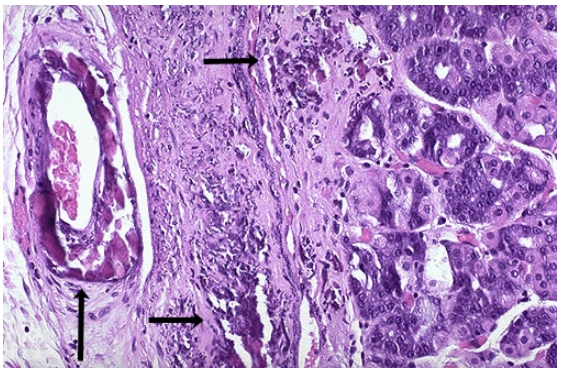
Dystrophic calcification, stomach
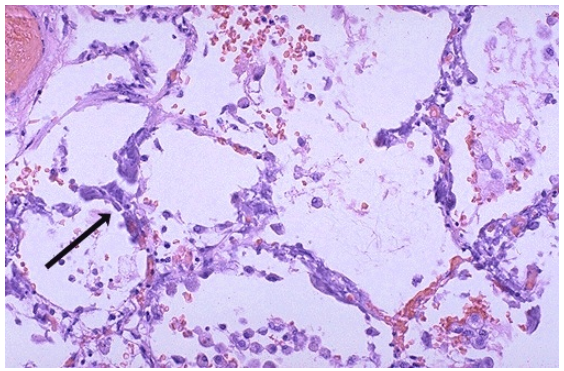
Metastatic calcification of lung with hypercalcemia