Econ1000 Midterm
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapter 1-5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
What is Economics about?
How individuals, businesses and governments make the best choices to get what they want and how their choices interact in markets.
Why can’t you get everything you want in life? Economic answer
You are limited by time, money and energy
What is Opportunity Cost?
The cost of your choice, what you are giving up vs what you get.
How does scarcity affect opportunity cost?
It means every choice has a trade off. What you get must be greater than what you give up.
What are incentives in econ?
rewards and punishment for choices
What are PPFs?
Production Possibility Frontier and it shows the max combination for products an services with existing information.
The ability to produce a product or service at a lower cost than another individual.
Absolute Advantage
Lowest opportunity cost
Comparative Advantage
Opportunity Cost formula
Give up/Get
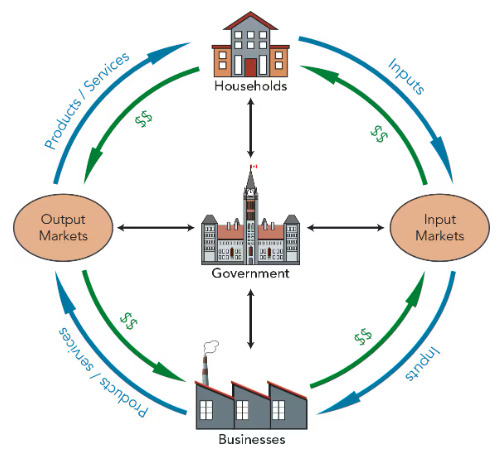
Circular flow of economy
What are “Inputs” in economy
individual households own all inputs, the productive resources used to produce products and services
What are the 4 types of inputs?
Labour (workers), natural resources, capital equipment, entrepreneurial ability
What are input markets
Where businesses buy the inputs they need to produce products and services
Term for where businesses sell their products and services
Output market
What does the Goverment do in the economic flow model
set the rules of the market
What are positive statements?
Things that can be checked, always true or false through fact checking.
What are normative statements?
value judgments or options about things that cannot be checked
What is microeconomics?
Analyzes the choices made by individuals in households, individual businesses, and governments and how those choices interact in the markets
Key 1 to Smart Choices
Choose only when additional benefits are greater than additional OPPORUNITY COSTS
Key 2 to Smart Choices
Count only ADDITIONAL benefits and ADDITIONAL opportunity costs
Key 3 to Smart Choices
be sure to count ALL benefits and costs including IMPLICIT costs and externalities
Positive Externalities
benefits that affect others who are external to a choice or trade
Negative Externalities
Costs that affect others who are external to a choice or trade
Economists use the term demand for what?
To summarize all the influences on consumers choices
How to determine your ability and willingness to pay for something?
How badly do you want it? What are your wants and preferences? What will you give up? What are the substitutes available? How much can you afford?
Whats another way to say marginal benefit?
Additional benefit or additional value
How does quantity affect marginal benefits?
Marginal benefits decrease with quantity
What is the water/diamond paradox
The marginal benefit is low for water even though the total benefit of all water consumed is high. But, the marginal benefit of diamonds is high because diamonds are scarce which makes its total benefits low.
Define quantity demanded
The amount you are able and willing to pay at a given price
What is the relationship between price and quantity demanded?
When prices rise, quantity demanded decreases because when something becomes more expensive, people economize its use
Market demand
sum of all the demands all individuals that are able and willing to pay for a product or service
Law of Demand
If the price of a product or service rises the quantity demanded of the product or service decreases and if the price falls the quantity demanded increases
What is a demand curve?
A graph of quantity and price (x and y), and shows their relationship when all other influences on demand beside price do not change
How to read a demand curve as a demand curve?
From any price go over and down the demand curve to quantity
How to read a demand curve as a marginal benefit curve
From any quantity or any x -axis go up and over the curve to price
What can affect demand? (brief)
If the prices of a product or service changes, it affects quantity demanded and if anything else changes, it affects demand
5 ways to change market demand
Preferences, prices of related products, income, expected future prices, number of consumers
How does prerferences affect market demand
Ads try to increase your preference for their product or service so may be more willing to pay for a higher price and prefer it
Does an increase in consumers’ willingness and ability to pay lead to?
Increase In demand
How does prices of related products affect market demand
Substitutes can be used in place of other products and compliments are used together to satisfy the same want
How does Income affect market demand
With more money your willingness and ability to pay goes up and lowers your real opportunity cos of spending. More get less give up.
How does expected future prices affect market demand
Your decisions can be based on future prices and if they’re expected to rise or fall
Normal good vs inferior good
A normal good is what you buy more of when your income goes up and inferior goods are what you buy less of when your income goes up
How does number of consumers affect market demand
Change in demand changes according to how many are willing and able to pay
What is an example of real life opportunity cost?
Giving up time to watch TV or play a video game to work extra hours and get more pay. What you give up is your time on the TV and what you get is more income.
Additional opportunity cost of increasing the quantity of whatever is being supplied. Decisions for supply only.
What is MARGINAL COST
marginal benefit for demander
decreases as you buy more supply
marginal benefit for supplier
increases the more you supply
What are sunk costs?
Past paid expenses that cannot be recovered like rent or insurance or tuition
What is the economic term for supply?
Overall willingness to sell a product or service
What is quantity supplied?
The quantity you actually plan to supply at a given price, taking in account everything that affects your willingness to supply
Marginal Opportunity Cost Formula for comparing 2 outcomes
y1-y2/x1-x2
What is marginal Opportunity Cost?
Any cost relevant to a smart decision
What causes and happens when marginal opportunity costs change
differences in alternative uses of your time or differences in efficiency and equipment in producing multiple services/products
Market Supply
the sum of all the supplies of all businesses willing to produce a product or service
Law of Supply
If the price of a product or service increases so does quantity supplied because more money covers opportunity costs of production
What does a supply curve do?
Show the relationship between price and quantity supplied only when price change
How does technology change supply and supply curve?
increase productivity with new and better technology reduces costs and increases supply or willingness to supply. that is a rightward shift of the supply curve
How does prices of related products or services change supply and supply curve?
Supply curve shifts right if demand for related product goes down
How does price of inputs change supply and supply curve?
Lower input prices increase market supply and shift the supply curve rightward. Lower inputs meaning businesses can get more supplies.
How does expected future prices change supply and supply curve?
When future prices are expected to rise, supply decreases in the present which causes the supply curve to shift leftward
How does number of businesses change supply and supply curve?
Increases market supply so supply curve shifts rightward, especially if more business enter the market
How does environment change supply and supply curve?
Pandemics, natural disasters, global warming, wars political instability can reduce supply shifting the supply curve leftward
What is the economic term for a market?
Interaction where there are competing bids from buyers and demanders and offers from sellers and negations on both sides that result in an exchange.
What is a smart choice in the market?
When the marginal benefit of the product is at least as great as its price or marginal opportunity cost and for the seller the price set is as great as their estimate of marginal opportunity cost/ next best offer
What is voluntary exchange
cooperative exchange where both sides win. buyer gets a good deal and seller gets money and returning customer
What are property rights
Rules that ensure that when you own something no one can take it away from you by force
Examples of property rights
Physical property like land and cars, financial property like stocks and bonds and intellectual property like music and patents
Where do prices come from?
They are the result of a market of competing bids and offers and consumers comparing prices and businesses comparing supply costs
What determines price
all law of supply and demand and the push and pull of negations costs and smart choices
What happens when price rises
Quantity demanded decreases, buyers become more smart with their money and look for substitutes but the higher prices increases a businesses willingness to supply
Shortage
Where quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied and consumers experience long lineups and out of stock items
How to correct a shortage
Increase the price/supply so less people are frustrated by excesses demand and consumers rethink their choices
What is a frustrated seller
Surplus, when there's excess supply and unsold products . Businesses desperate for sales will cut their prices or throw in extra of what there is excess of.
Market clearing price
Price that equalizes quantity demanded and quantity supplied (preventing surplus and shortages)
Equilibrium Price
Exactly balances forces of competition and cooperation to coordinate the smart choice of consumers and businesses and at equilibrium there is no tendency for change
How does increase in demand, change demand.
If a product were to be trendy, the demand curve shifts rightward. A decrease in demand shifts demand curve leftward
Changes in supply
Increase in supply and increase in improvement causes cheaper production and shifts supply curve rightward
What decreases supply
Less workers, expensive inputs, rising prices and less consumers shifts the supply curve leftward
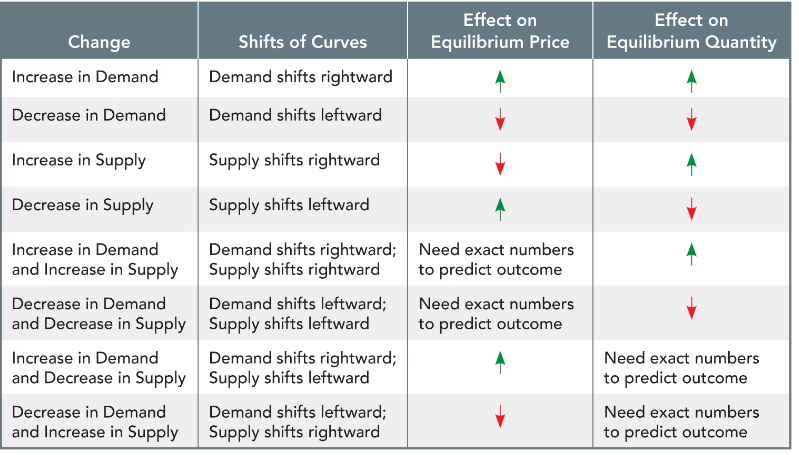
How to change equilibrium
Increase in demand raises equilibrium [rice and quantity and an increase in supply lowers equlibrium price but increases quantity Increase
Where is consumer surplus
Under the marginal benefit curve but above the equilibrium price
What is the market demand curve
It combines the willingness and ability to pay all consumers.
What is consumer surplus
The difference between the amount a consumer is willing and able to pay and the price ACTUALLY paid. Usually the extra money consumers are saving on.
Where is the producer surplus
Below the equilibrium price but above the marginal cost or supply curve
What is the market SUPPLY curve
It combines the supply decisions of all businesses in a market and the minimum price they are willing to accept to cover the cost of the production
Producer surplus
Extra revenue, difference between the amount a seller is willing to accept and price actually accepted
What is deadweight loss
When you either produce too little and lose money from sales or produce too much and not make enough from production
Why may businesses have sales?
Because they will make it up in volume
Price of Elasticity
Measures consumers responsiveness and price making decisions
Elasticity
measures how much quantity demanded responds to a change in price
Inelastic demand
When a product or service has a small response in quantity demanded when its price rises. Consumers have a low willingness to shop elsewhere
Elastic demand
When a small rise in price decreases the quantity demanded by a lot. Consumers have a high willingness to shop elsewhere
How to calculate elasticity
Price of elastcity of demand = % change in quantity demanded/% change in price
elasticity and their values
0<= inelastic <1, 1=unit elastic, elastic >1
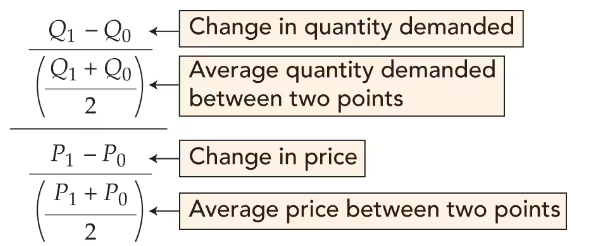
What is the mid point formula
What 3 factors affect elasticity
If there’s available substitutes, time to adjust to change in price, how much of ones income is spent on that item