lecture 23, the peripheral nervous system
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
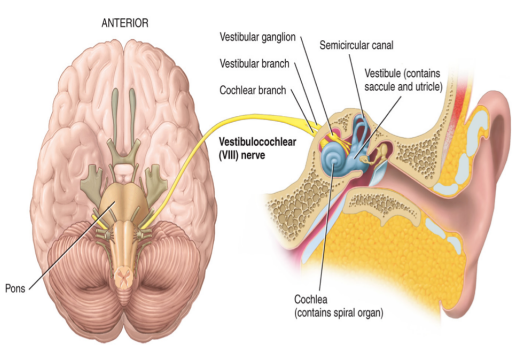
cranial nerves
located in the peripheral nervous system
there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves
10/12 are associated with the brain stem: III-XII
3/12 carry only sensory impulses
I: olfaction (smell)
II: optic (vision)
VIII: vestibulocochlear
9/12 are mixed nerves → carry both sensory and motor information
the cell bodies of the motor neurons in mixed nerves are located in nuclei of the brain stem
the cell bodies of the sensory neurons in mixed nerves are located in ganglia outside of the central nervous system
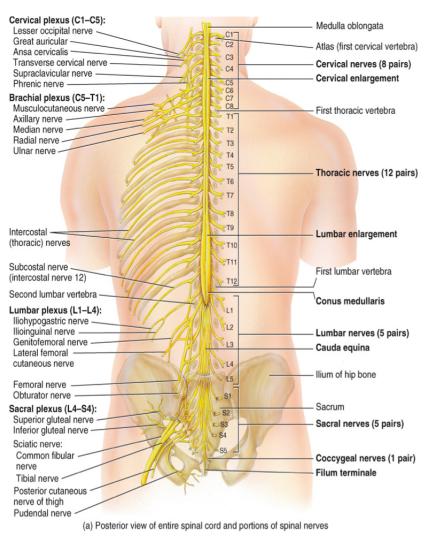
spinal nerves
there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves
all are mixed nerves containing both a sensory neuron and a motor neuron
there are
8 cervical (C1-C8)
12 thoracic (T1-T12)
5 lumbar (L1-L5)
5 sacral (S1-S5)
1 coccygeal (C0)
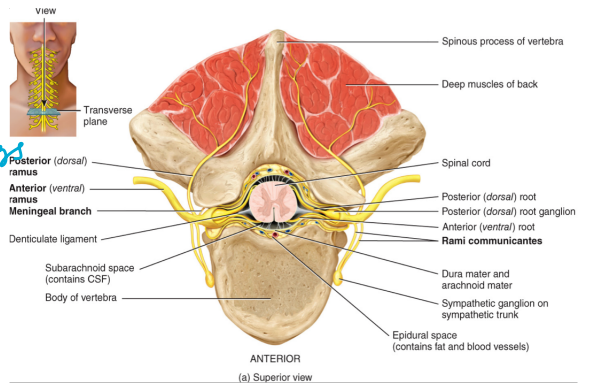
all spinal nerves have two points of attachment
the dorsal root
receives sensory information (carries in from the back)
the cell bodies are located in the dorsal root ganglion (has to go up → synapse)
the ventral route
carries motor output
the cell bodies are located in the ventral or the lateral horn
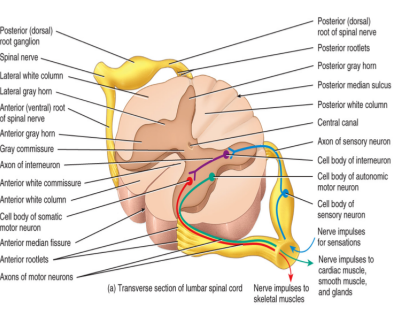
spinal nerves are located at the joint of the dorsal and the ventral root
the spinal nerves immediately branch into
the dorsal ramus → innervates the skin and the muscles of the back
the ventral ramus → innervates the thoracic nerves T1-T12 and the plexuses
the rami communicants: forms a component of the autonomic nervous system
all but the first spinal nerve leave through the intervertebral foramina of the vertebrae
branching very useful to have one wire do many things
the spinal plexuses
are formed from the ventral rami of the spinal nerves (except T2-T12)
a plexus is a nerve network
there are four plexuses
the cervical plexus: C1-C4 → the phrenic nerve → the diaphragm (if damage can’t breath on your own)
the branchial plexus: C5-T1 → the axillary, the radius, the ulna, and the median nerves
the lumbar plexus: L1-L5 → the femoral nerve
the sacral plexus: L4-S4 _. the sciatic nerve → a combination of the tibial and the fibular nerves
terminal
sciatic nerve → pinched nerve
(high to low of how bad it would be to damage)
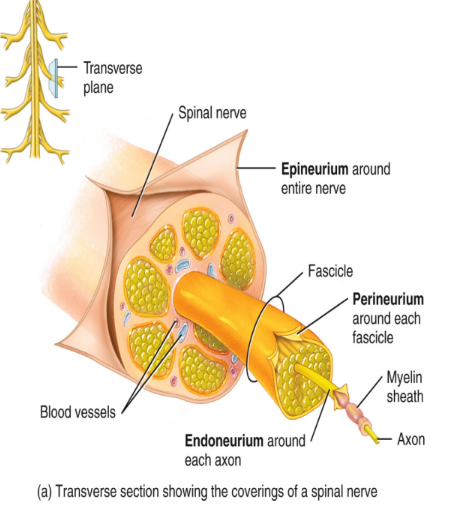
wrappings of nervous tissue
The entire nerve is wrapped in epineurium connective tissue
Each nerve fascicle is wrapped in perineurium
Each axon and corresponding myelin is wrapped in endoneurium
receptors
Afferent pathways move sensory information to the CNS
Receptors will detect a change in the environment
Stimulus → receptor → CNS
Receptors can be classified according to:
Location
Type of stimulus
Structure
receptor: location
a. Exteroceptors: detect stimuli in the external environment or very close to the body’s surface
Located in the skin (in dermis)
Example: pain, touch, etc.
b. Interoceptors: detect stimuli in the internal environment
Proprioceptors located in the joints and the muscles
Example: blood pressure
receptor: type of stimulus
Mechanoreceptors: detect pressure, touch
Thermoreceptors: detect heat and cold
Chemoreceptors: detect chemicals (have in olfactory mucosa)
Photoreceptors: detect light
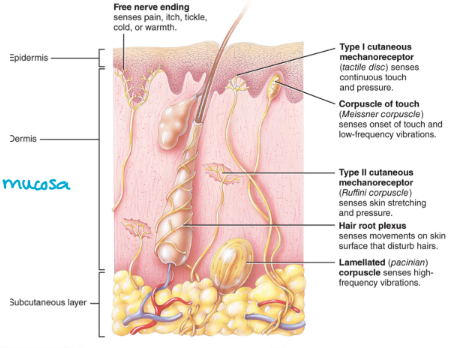
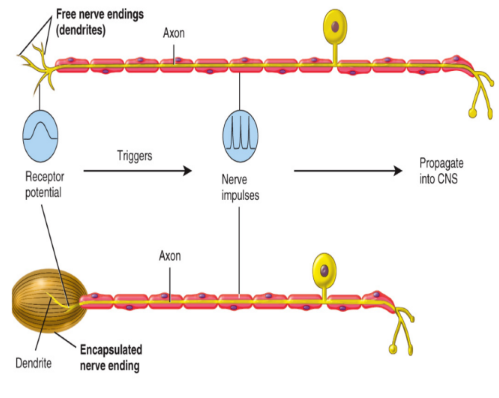
receptors: structure
a. Free nerve endings
Dendrites of sensory neurons
Example: pain, itchiness
blunted and structured
b. Encapsulated nerve endings:
The terminal dendrites of these nerves are enclosed in connective tissue
Example: Meissner’s corpuscle for touch
sensory pathways
ascending or sensory pathways
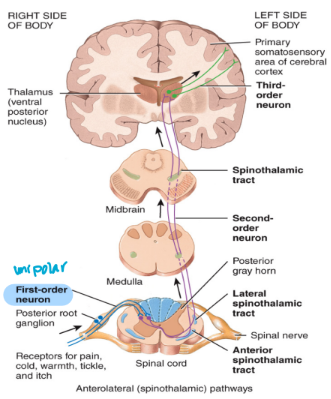
general senses contain 3 different neurons from the receptor to the cortex of the brain
1st order neuron
2nd order neuron
3rd order neuron
sensory neuron: 1st order neuron
Located in a spinal nerve
Part of the peripheral nervous system
Unipolar neurons containing receptors (sensory)
Cell body is located in ganglia outside of the central nervous system (outside)
Synapse onto 2nd order neurons in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord or the brain stem
neuronal synapse
turning the signal to an electrical signal
sensory neuron: 2nd order neuron
Cell body is located in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord or the medulla
Multipolar interneurons that carry impulses to the thalamus
Located in tracts
Decussates in the spinal cord or the medulla
post-office
motor pathway are always multipolar
in come in via brain
sensory neuron: 3rd order neuron
Cell body is located in the thalamus
Multipolar interneurons that carry impulses to the sensory cortex of the CNS
Located in tracts → because in CNS
interpret specifically
ascending tracts located in spinal cord
non-specific ascending pathway
when you are aware of a sensation but are unable to detect its origin
ex. pain
ex. spinothalamic tracts of the spinothalamic pathway
decussates in the spinal cord (crosses over)
picks up pain, temperature and sends the information to the thalamus
specific ascending pathways
sensations that you are accurately able to detect the origin of
ex. touch
ex. dorsal columns in the dorsal column pathway
decussates in the medulla
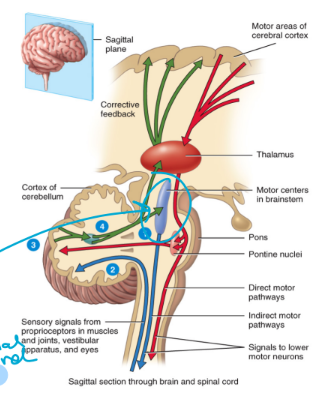
the spinocerebellar pathways
Consists of ascending tracts from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (compare plan to what is happening)
The receptor is located on the 1st order neuron
Proprioceptors that detect changes in balance and body position (present in joints)
The second order neuron goes to the cerebellum (normally goes in thalamus)
This pathway does not have a 3rd order neuron
You do not have any conscious perception of the activities in this pathway
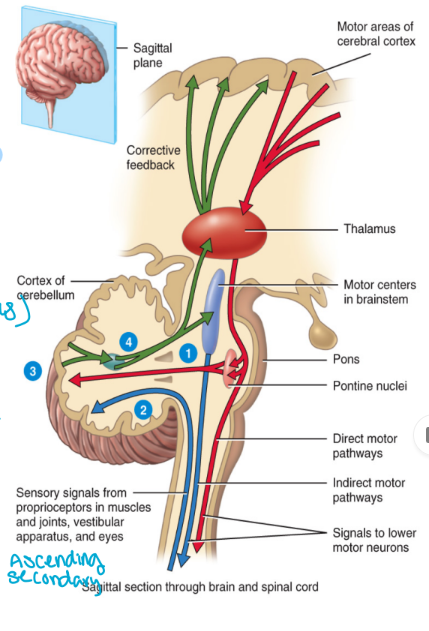
motor pathways
send output away from the CNS
Efferent pathways (exiting)
CNS → effector cells, muscles, etc.
All efferent neurons are multipolar
Consists of the:
Somatic nervous system (within your control)
Autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
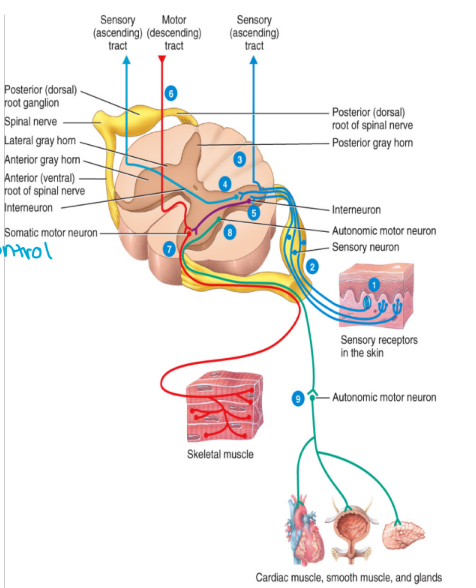
the somatic nervous system
Effector cells are all skeletal muscles
The somatic motor pathways consist of two neurons
i. Upper motor neurons
ii. Lower motor neurons
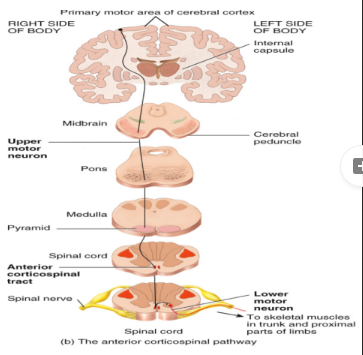
upper motor neurons
Cell bodies of these neurons are located in the cerebral cortex and the basal nuclei
Multi-polar interneurons
The descending tract of the pathway
a. Corticospinal (pyramidal tracts) tracts:
Cell bodies are located in the cortex
85% of these tracts decussate in the medulla (because they start high)
b. Indirect tracts:
Cell bodies are located in the brainstem
Upper motor neurons synapse onto lower motor neurons
decussate in spinal cord
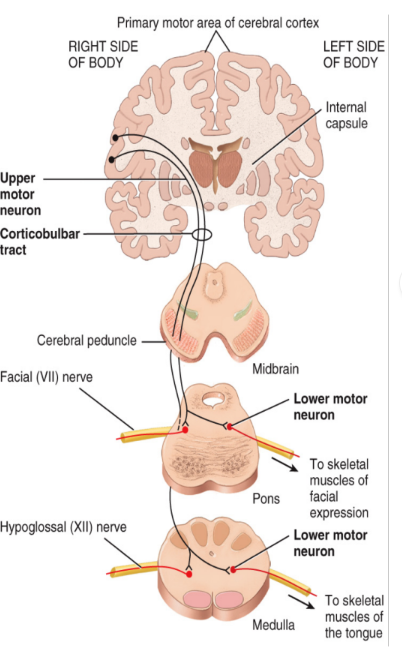
lower motor neurons
Located in the peripheral nervous system
The cell bodies of these neurons are located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
These neurons transmit information from the spinal nerves to the effectors (skeletal muscles)
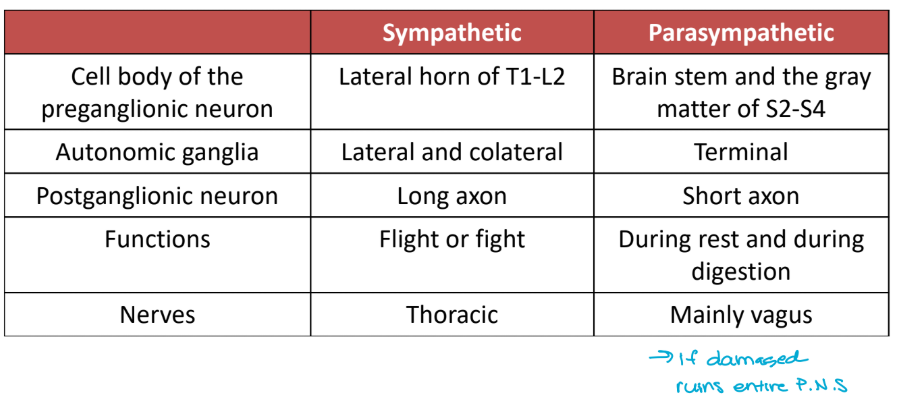
the autonomic nervous system
consists of two divisions:
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) (fight or flight)
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) (rest and digest)
the effector cells are cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
can’t control
“send message to bottle and squeeze”
consists of
a. preganglionic neurons
myelinated (insulated)
cell body is located in the brain stem or the spinal cord
also pre-synaptic
b. postganglionic neurons
unmyelinated
cell body is located in the ganglia
also post-synaptic
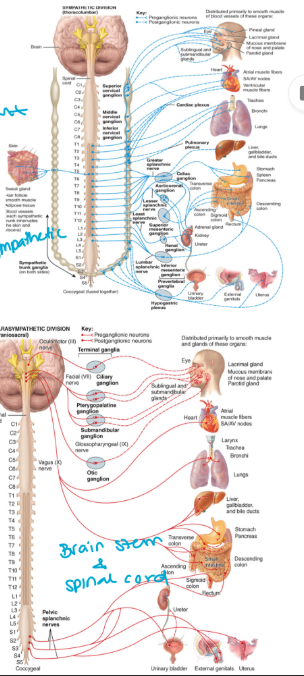
the autonomic nervous system chart