B1 - Viral Replication
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What are the six steps of virus replication?
Attachment
Fusion
Uncoating
Biosynthesis
Assembly
Release
What are the steps of virus attachment?
Diffusion over to host cell (E.g. HIV)
Binding to low affinity receptor (E.g. heparan sulphate)
Binding to primary receptor (E.g. CD4 or DC-SIGN)
Binding to co-receptors (CCR5 or CXCR4)
What low affinity receptor does HIV bind to?
Heparan sulphate
What co-receptors does HIV bind to?
CCR5/CXCR4
What is fusion from without?
Enveloped virus attached to receptors on cell surface
Virus fuses with membrane and capsid is released into host cell
E.g. pseudorabies virus
What is receptor mediated endocytosis?
Enveloped virus attached to receptors on cell surface
Virus internalised and placed inside endosome (pH ~5-6)
Acidic environment causes conformational change in viral proteins
Virus fuses with vesicle and genome is released into cytosol
E.g. Influenza virus
How can non-enveloped viruses be internalised?
Virus attaches to receptors on cell surface
Virus internalised and placed inside endosome (pH ~5-6)
Acidic environment causes conformational change of viral proteins
Genome and associated proteins escape the vesicle via a pore formed by viral proteins
How many different classes of virus are there based on replication patterns? What are they?
DNA
Single stranded DNA (ssDNA)
Double stranded DNA (dsDNA)
Double stranded DNA (dsDNA) + Reverse Transcriptase
RNA
Double stranded RNA (dsRNA)
Single stranded (-) RNA (ss(-)RNA)
Single stranded (+) RNA (ss(+)RNA)
Single stranded (+) RNA (ss(+)RNA) + Reverse Transcriptase
How are DNA virus genomes usually replicated and transcribed?
Usually done using host polymerases
However some viruses can encode their own DNA/RNA polymerases
E.g. Pox virus
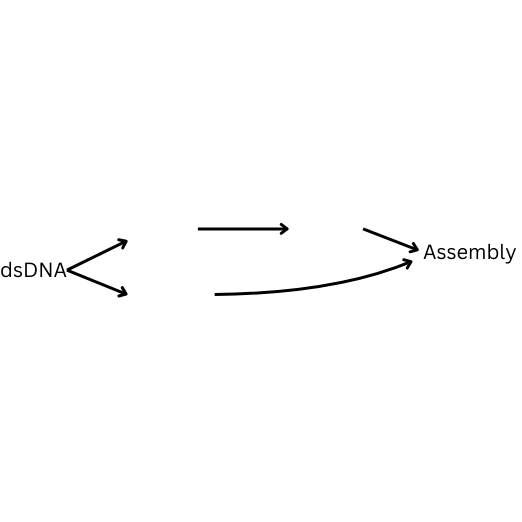
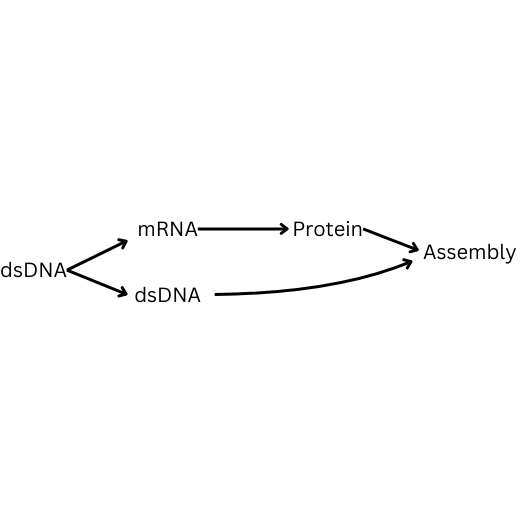
How is double stranded DNA replicated? Fill in the blanks.
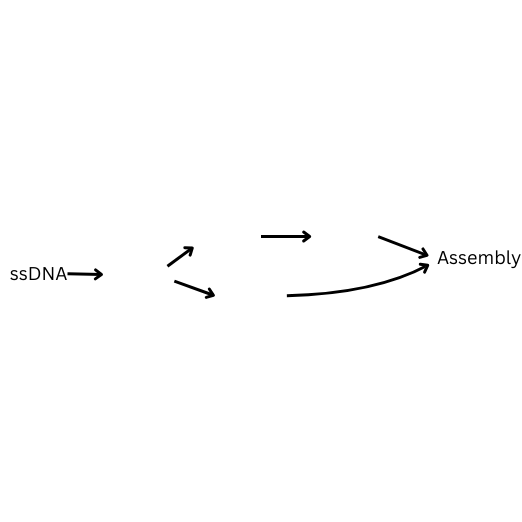
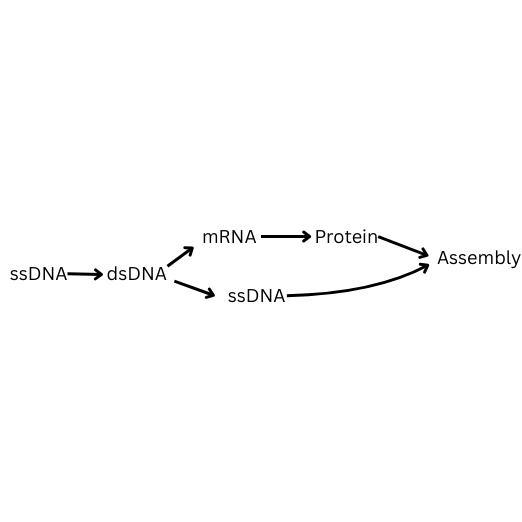
How is single stranded DNA replicated? Fill in the blanks.
No Reverse Transcriptase
How are RNA virus genomes usually replicated and transcribed?
Done by virus polymerases
Host cell DNA/RNA polymerases can only use DNA as a template so RNA viruses MUST encode their own polymerases to use RNA as a template
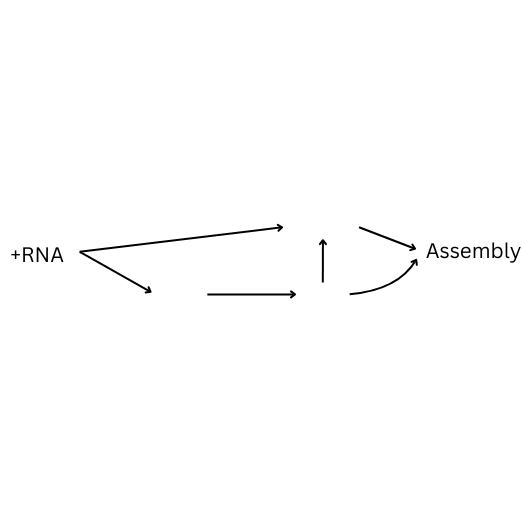
How is positive single stranded RNA replicated? Fill in the blanks
No Reverse Transcriptase
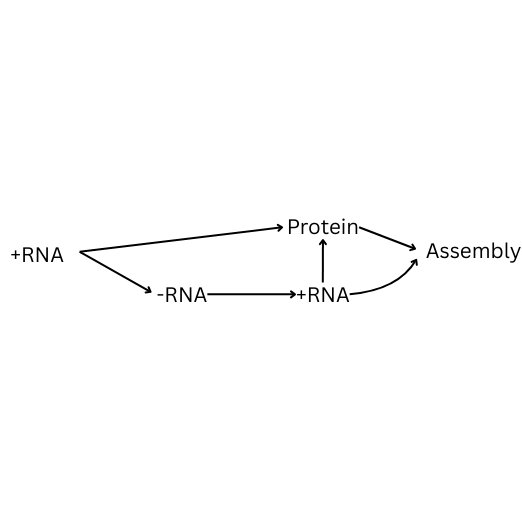
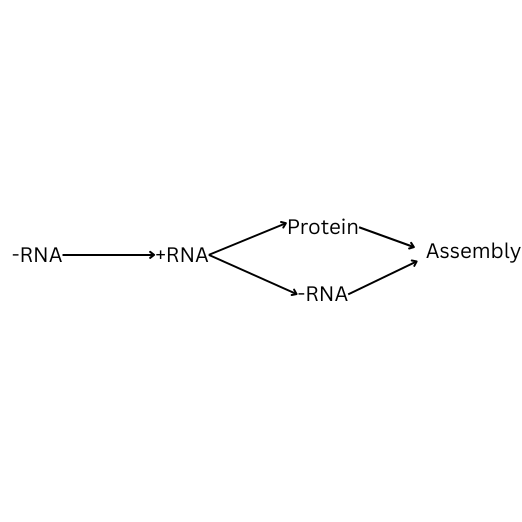
How is negative single stranded RNA replicated? Fill in the blanks.
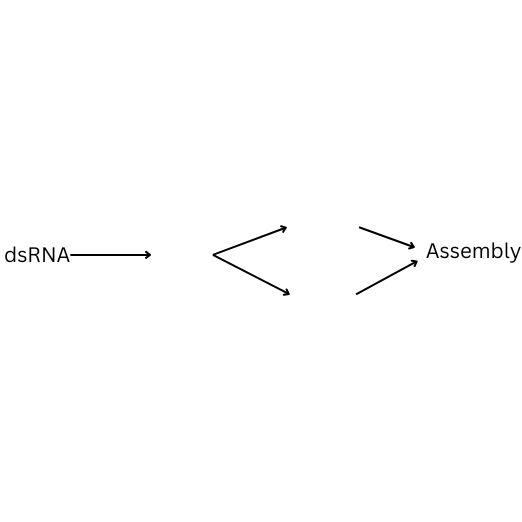
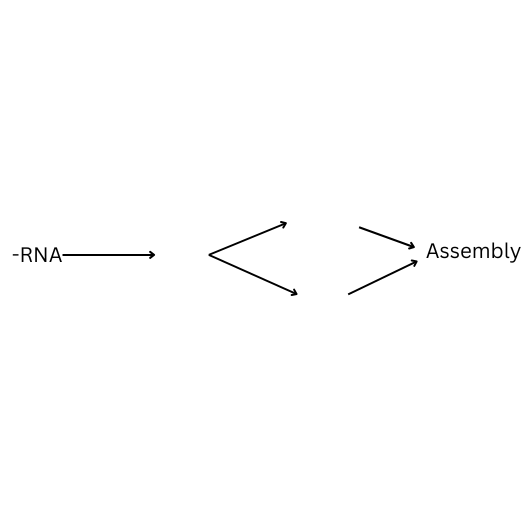
How is double stranded RNA replicated? Fill in the blanks.
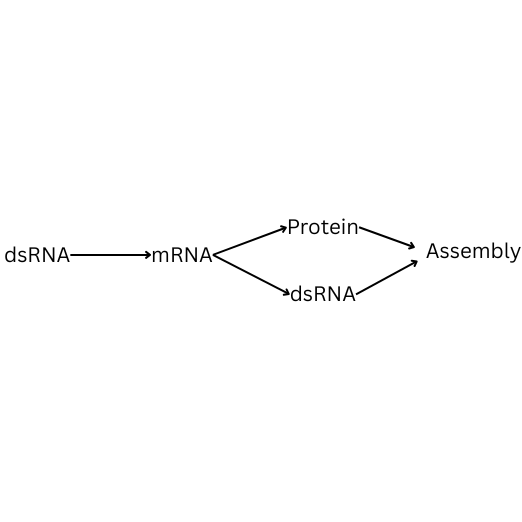
What does the enzyme Reverse Transcriptase allow viruses to do?
Synthesise DNA from an RNA template.
This can allow viruses to integrate viral genes into the host genome
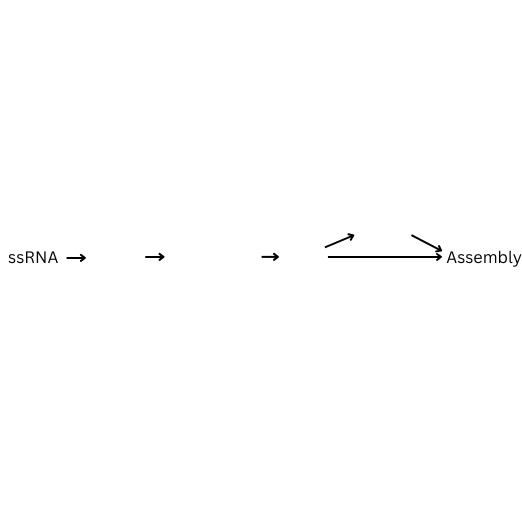
How is single stranded RNA replicated using Reverse Transcriptase? Fill in the blanks.
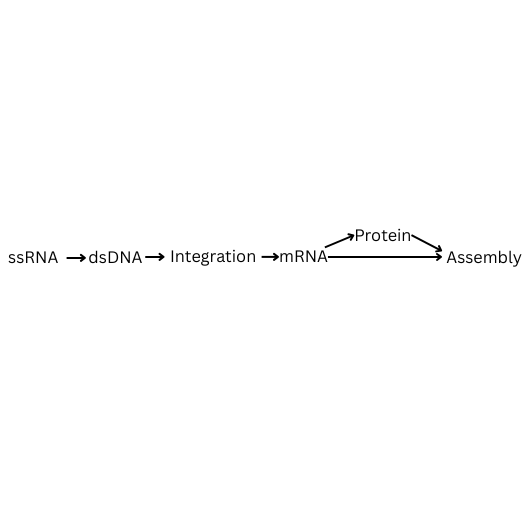
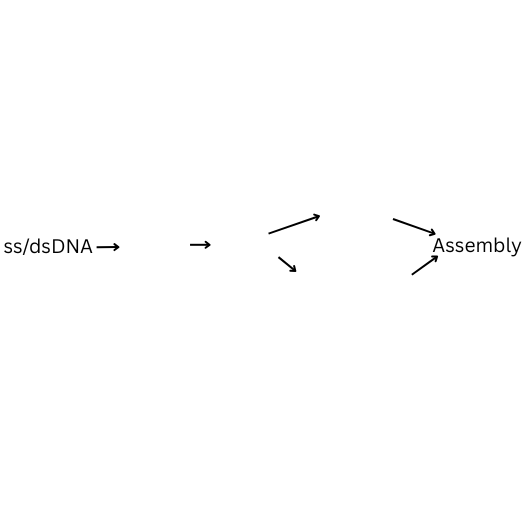
How is double stranded DNA replicated using Reverse Transcriptase? Fill in the blanks.
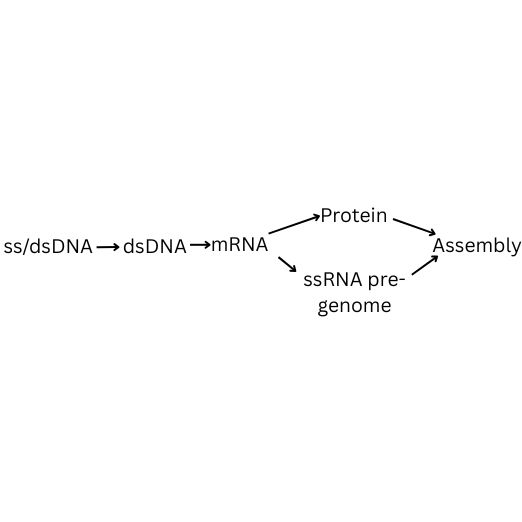
What is RdRp?
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)
What are structural viral proteins?
Proteins which form part of the virus particle
What are non-structural proteins?
Proteins which are not incorporated into the virus particle
E.g. enzymes involved in transcription
Virus particles escape post translational modifications by the host cell. True or False.
False.
Viral proteins undergo all the same range of post translational modifications as host cell proteins
Some viruses even encode a single large polyprotein which needs to be post-translationally cleaved into individual viral proteins
What are the 5 main virus structural shapes?
Naked icosahedral
Naked helical
Enveloped icosahedral
Enveloped helical
Complex
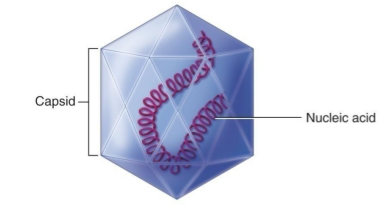
What virus shape is this?
Naked Icosahedral
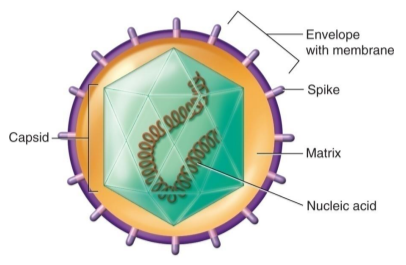
What virus shape is this?
Enveloped Icosahedral
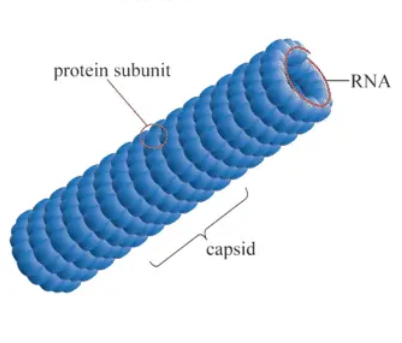
What virus shape is this?
Naked helical
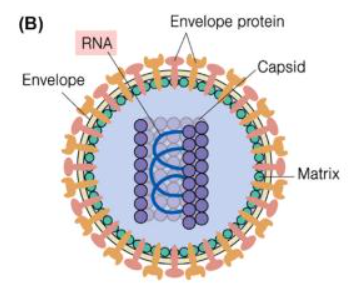
What virus shape is this?
Enveloped helical
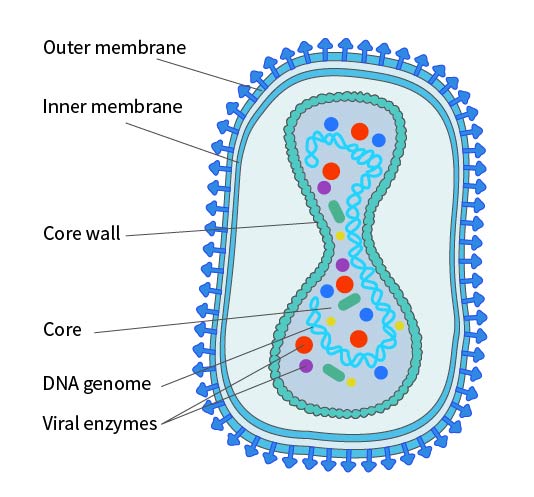
What virus shape is this?
Note: Not all complex viruses look like this. Complex just refers to the fact the virus has a complex and unique structure to it.
Bacteriophages are also usually complex viruses
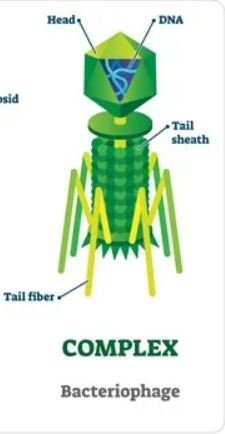
What are three ways a virus can be released from a cell?
Cell lysis
Budding
Virus spread via pores between cells
Inducing fusion between their membrane