4.2 Energy Flow
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Give me some background info on the sun as an energy source
All living things require a source of energy in order to survive.
Radiant energy from the sun sustains life on Earth.
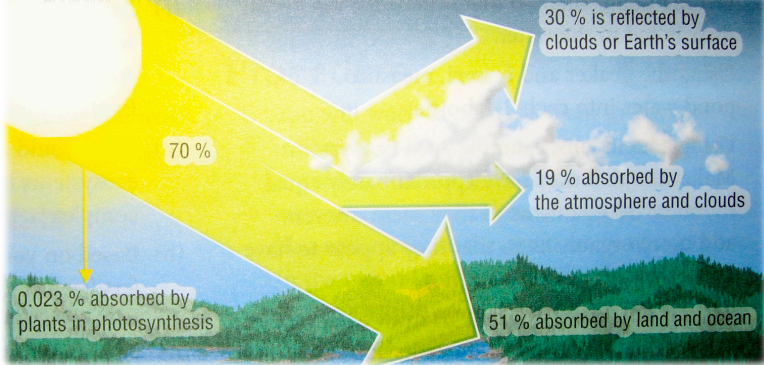
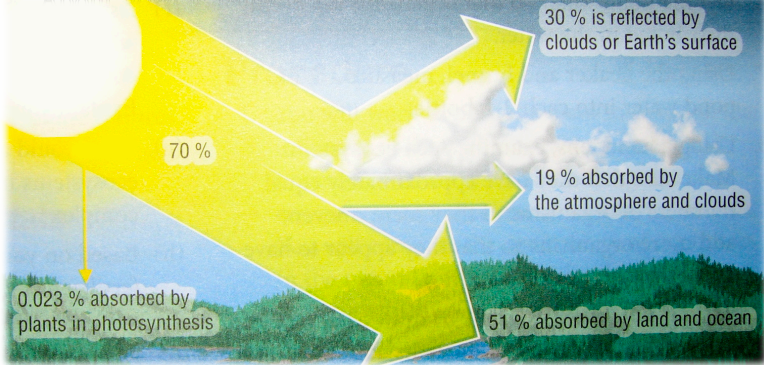
not all of the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth.
What are the specifics of rays and how they reach Earth?
30% reflected back into space
70% converted into thermal energy and absorbed by the air, sea and land
19% absorbed by atmosphere
51% absorbed by land
small percentage (0.023%) of radiant energy is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis.
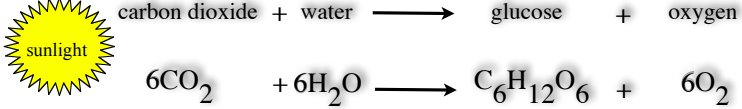
Tell me about Photosynthesis
Organisms that can photosynthesize do so by using light energy to produce chemical energy in the form of food (sugars)
Some sugars produced are stored by the plant for later use (starch), while others are used to build tissue (cellulose).
Some sugars are combined with other elements to make proteins and fats.
What does the plant do when there is no light? Tell me about it.
A plant can use the energy that was stored in food (sugars) through a process called cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration
does not require sunlight, but requires oxygen.
occurs continuously
If it were to stop, the plant would quickly die.
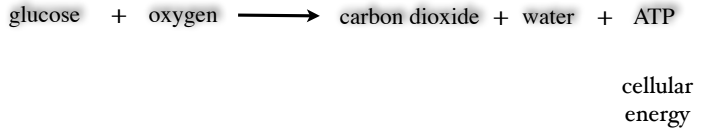
What are Autotrophs? What is the other name for them? Tell me more plz and merci beaucoup.
organism that make their own food
producers
plants produce in presence of sunlight (photosynthesis)
Plants can also use this food to release energy for survival through cellular respiration (in the light or dark).
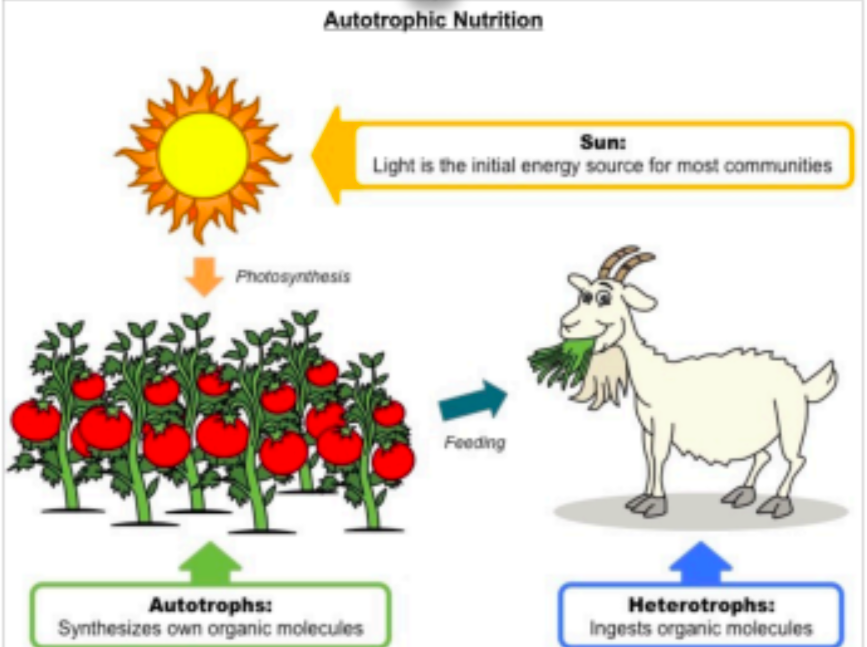
What are Heterotrophs? What is the other name for them? Tell me more plz and merci beaucoup.
Organisms that must eat other organisms to get their food
Consumers
use respiration to release the food energy to the cell
include:
Herbivore
Carnivore
Omnivore
Scavenger
Detritivores
Saprotrophs

What are Herbivores?
organisms that eat plants or other producers

What are Carnivores?
organisms that eat other animals

What are Omnivores?
organisms that eat plants and animals

What are Scavengers?
organisms that eat the remains of other animals

What are Detritivores?
heterotrophs that obtain organic nutrients from detritus by internal digestion
Detritus includes: dead leaves, feathers, hair, dead organisms and feces
Ex: earthworms, crustaceans, snails, insects

What are Saprotrophs?
heterotrophs that obtain organic nutrients from detritus by external digestion
Secrete digestive enzymes into dead organic matter, digest externally, and then absorb products
Also known as decomposers
Ex: fungi, mushrooms, bacteria

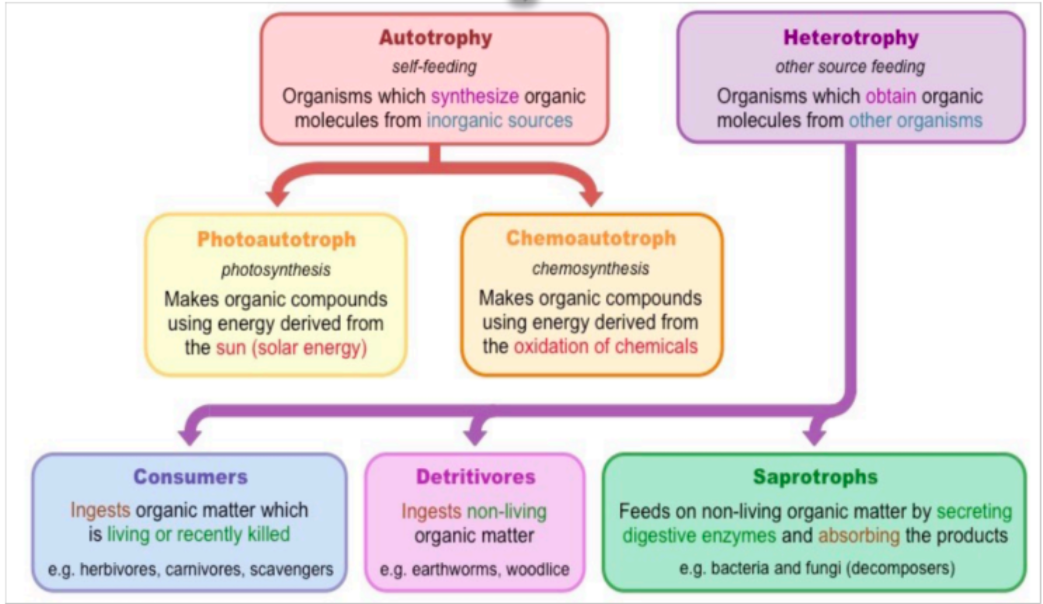
What do the Modes of Nutrition look like?
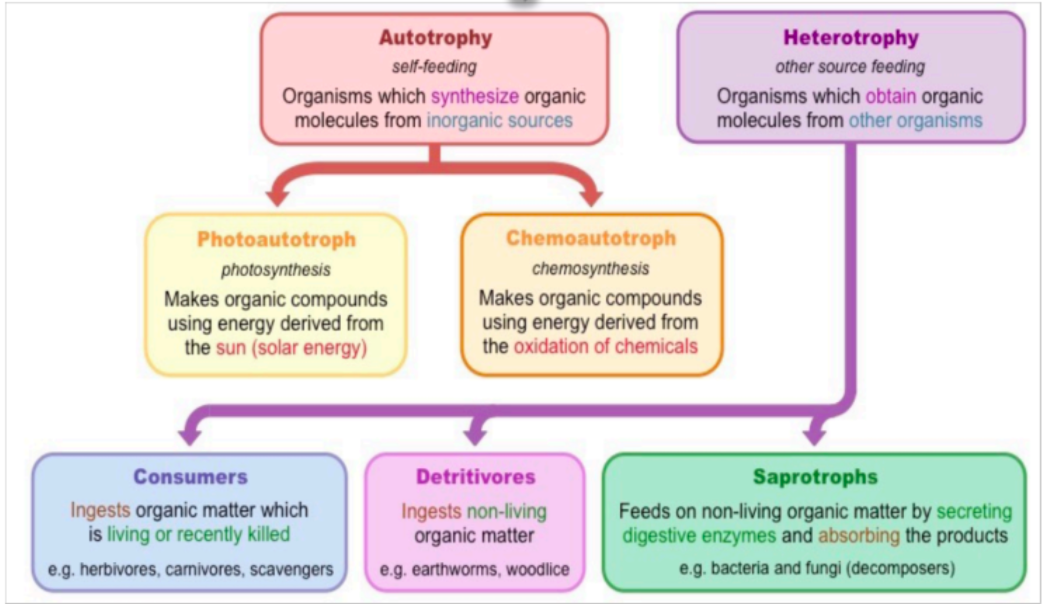
What are the types of Autotrophs (MoN)?
Photoautotroph
Chemoautotroph
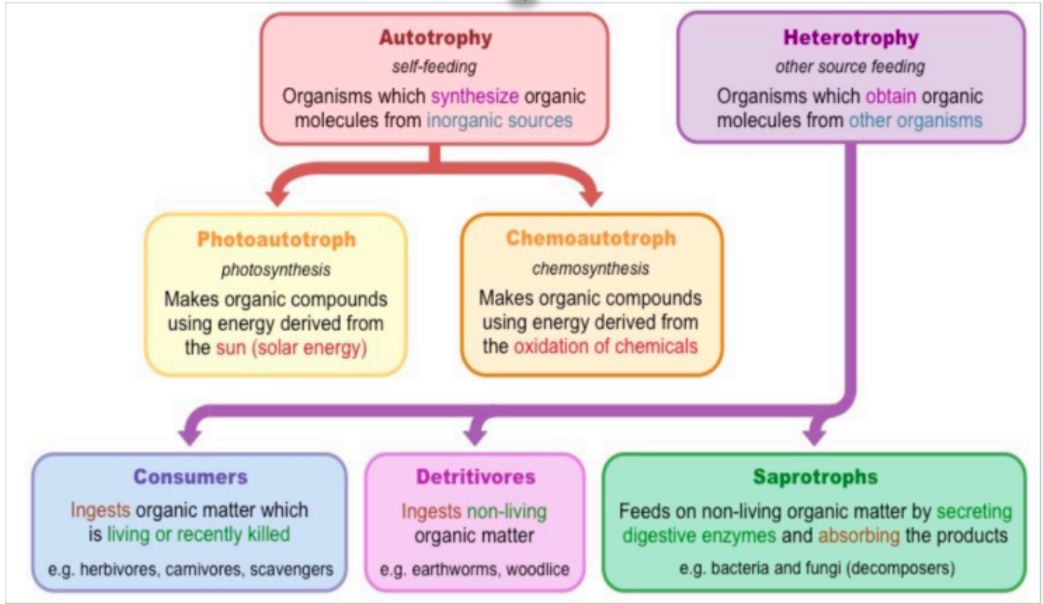
What are the types of Heterotrophs (MoN)?
Consumers
Detritivores
Saprotrophs
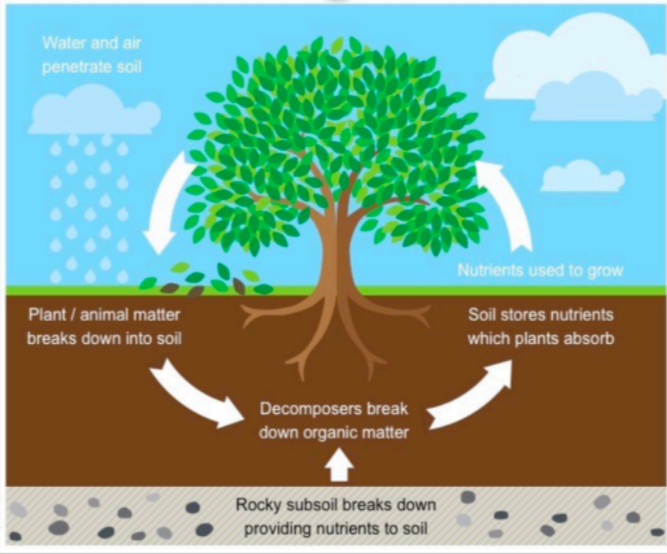
What does the Nutrient Cycle look like (in the case of trees)?
Tell me about Food Chains
simplest way to show the feeding relationships in an ecosystem
arrows point in the direction that nutrients flow
The level at which an organism feeds is known as its trophic level.

Tell me about Food Webs
food chains are part of a much more complex interaction among species.
A food web illustrates this series of interconnected food chains.
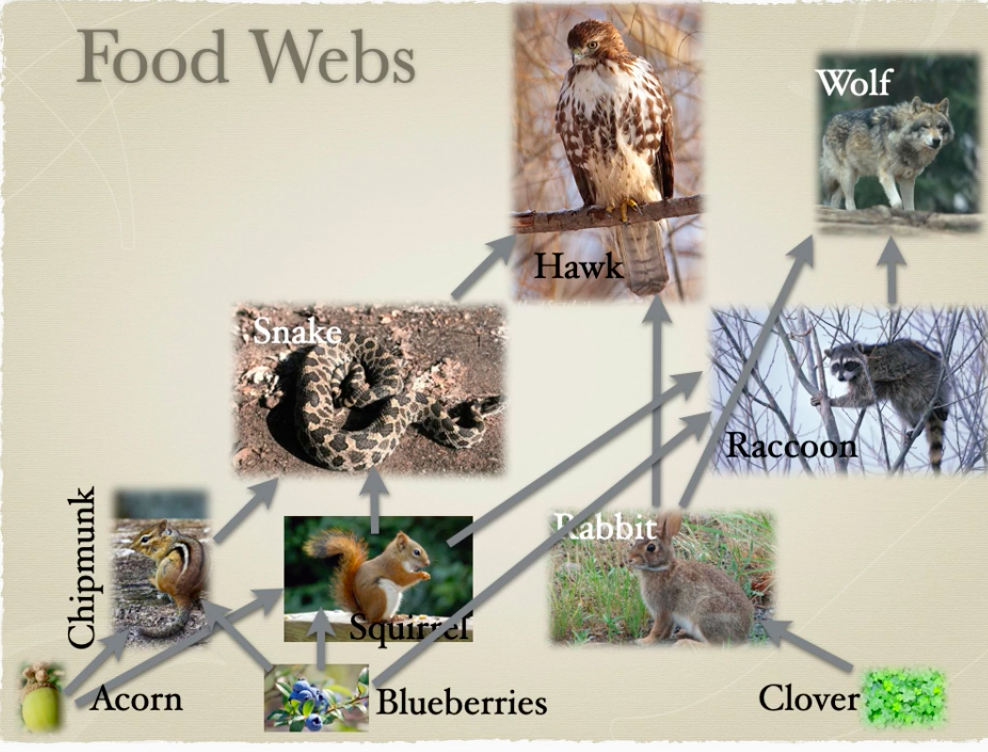
Why are Complex webs are more stable than Simple ones?
because the web may be able to tolerate the loss of one species, but not many
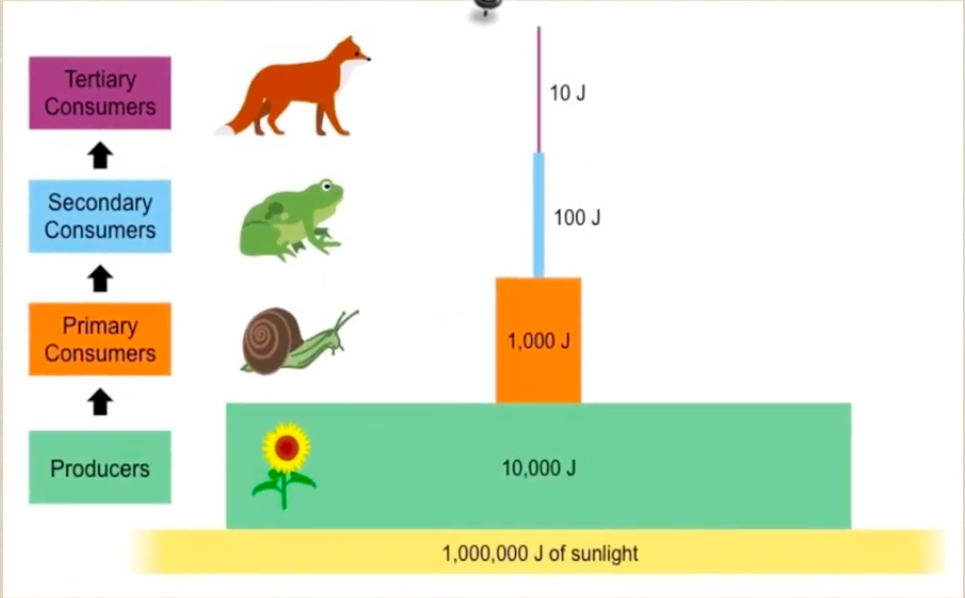
Give me some background info on Ecological Pyramids. What are the types of pyramids?
One way to visualize relationships that exist between trophic levels is with ecological pyramids. There are three types:
Energy
Numbers
Biomass
Give me some background info on Energy (J or kJ).
only 10% is transferred to the next trophic level
90% is lost to biological processes and as heat.
Energy pyramids always have a wide base. This is not always true of the other pyramids.
Give me some background info on Numbers.
usually more individuals at lower tropic levels, but not always
On a single tree there can be thousands of sap sucking insects (smaller base).
There are more grasshoppers in a prairie ecosystem than there are animals that eat them (bigger base).
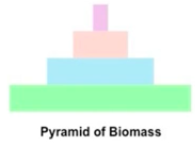
Give me some background info on Biomass.
usually more biomass at lower tropic levels, but not always
At any point in time, the biomass of algae in a pond is less than the biomass of all the creatures that feed on algae (smaller base).
The mass of all of the grain in a field is greater than the mass of the rodents and birds that feed on the grain (bigger base).