higher chemistry unit 1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
monotomic gases
stable
low mp/bp
He, Ne
weak intermolecular forces (LDFs)
single atom only
metallic lattice
formed by metal atoms packed closely together
held by delocalized electrons
allows metals to conduct electricity and heat
high mp/bp
covalent molecular
solids -P4, S8, C(fullerene)(60)
gases - H2, O2, N2, Cl2
Low mp/bp
covalent network
B, C, Si
C- Diamond
- graphite →conducts electricity
very high mp/bp
strong covalent bonds are broken
electronegativity
the measure of attraction an atom in the bond has for the electrons in the bond
Across a period, electronegativity…
increases as there are more protons so theres an increased nuclear charge.
Down a group, electronegativity…
decreases as there are no other electron shells so theres an increased shielding effect.
Across a period, atomic size…
decreases as there are more protons so theres an increased nuclear charge
Down a group, atomic size…
increase as there are more electron shells so theres an increased nuclear charge.
first ionization energy
energy needed to remove one mole of electrons
second ionization energy
energy needed to remove more electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms
Across a period, ionization energy…
increases as there are more protons so theres an increased nuclear charge
Down a group, ionization energy…
decreases as there are more electron shells so theres an increased shielding effect
Equations for sodium
1st IE= Na→ Na++e-
2nd IE= Na+→ Na2++e-
3rd IE= Na2+→ Na3++e-
4th IE= Na3+→ Na4++e-
ionic bonding
metal and non metal
structure- ionic lattice
high mp/bp
conducts in solution
not sold form
polar covalent
uneven share of electrons in the bond
different EN values
resulting in positive and negative charges.
non polar covalent
equal share of electrons in the bond
same EN values
resulting in no charges.
LDFs
weakest intermolecular force
experienced with all atoms and molecules
uneven distribution of electrons
force of attraction between a temporarily dipole and an induced dipole
PD-PDi’s
intermolecular forces that occur between polar molecules.
force of attraction between oppositely charged of neighboring polar molecules
hydrogen bonding
arises when theres a high electronegativity difference, H bonded to N,O,F.
strongest intermolecular forces
mp
solid → liquid
bp
liquid→gases
solubility
how easy a substance dissolves in a solvent
viscosity
how thick a substance is
intermolecular force that is the less viscous
LDFs
intermolecular force that is the most viscous
hydrogen bonds
more viscous as…
there is a greater degree of hydrogen bonding so theres more hydroxyl groups
stronger hydrogen bonds
splitting up redox
hints
pick out species which are similar
ignore balancing if it cancels out or simplifies
copy exactly from data booklet
splitting up redox example
K+Pb2+→K++Pb
K→K++e- oxidation
Pb2++2e- →Pb reduction
splitting up a redox with spectator ions
recognize the charge on the ions
cancel out spectator ions
ignore balancing if it cancels out
splitting up a redox with spectator ions example

oxidising agent
substance that accepts electrons
reducing agent
substance that donates electrons
oxidising and reducing agents example
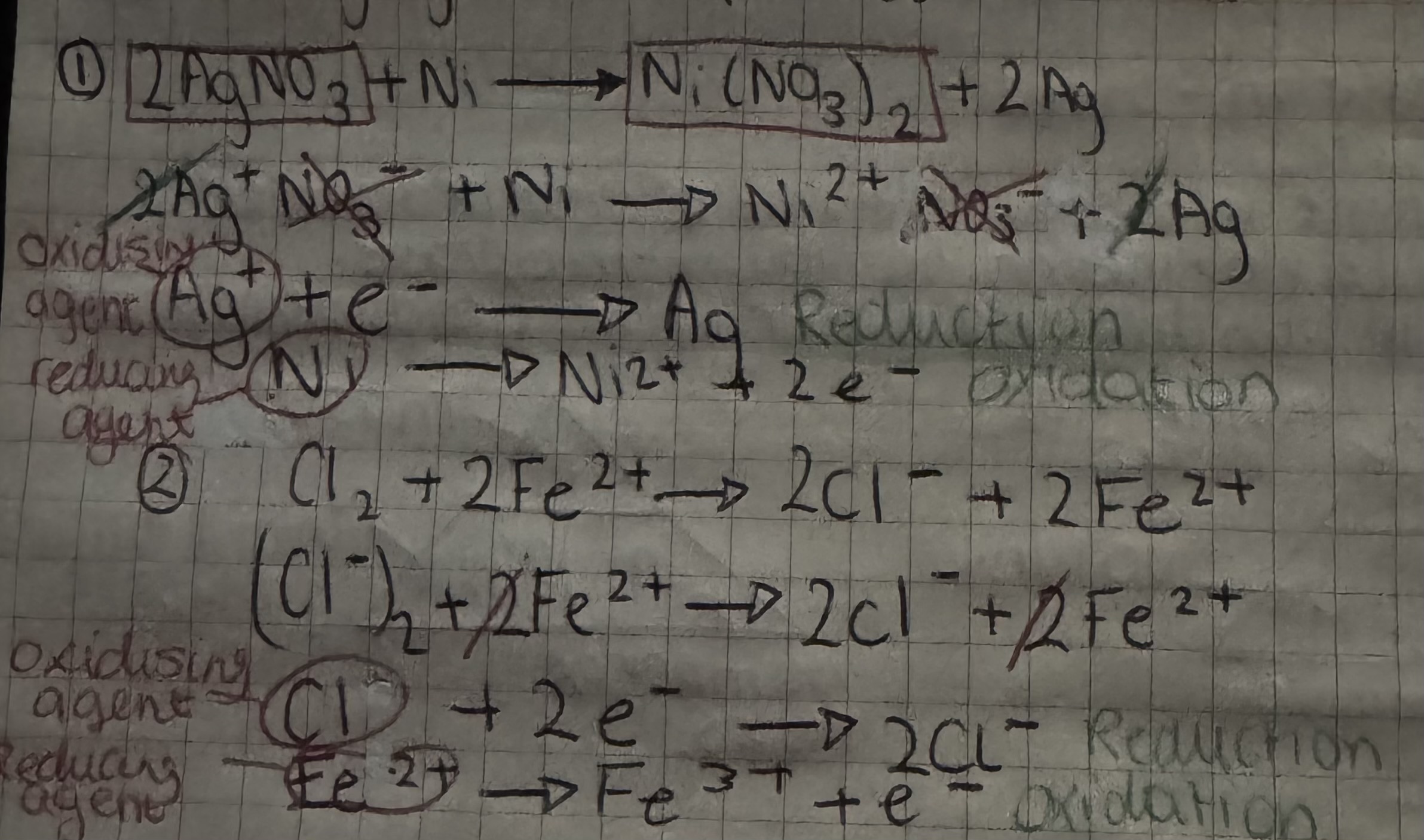
writing more complex redox: identifying oxi/red agents
write all reactant species
remove spectator
write oxi & red equations
identify oxi & red agents
writing more complex redox: identifying oxi/red agents- example

writing complex ion-electron equations
balance the central atom (non oxygen) by adding a number in front of this atom
balance oxygen molecules by adding water molecules
balance hydrogen by adding hydrogen ions
balance the charge by adding electrons
writing complex ion-electron equations- example
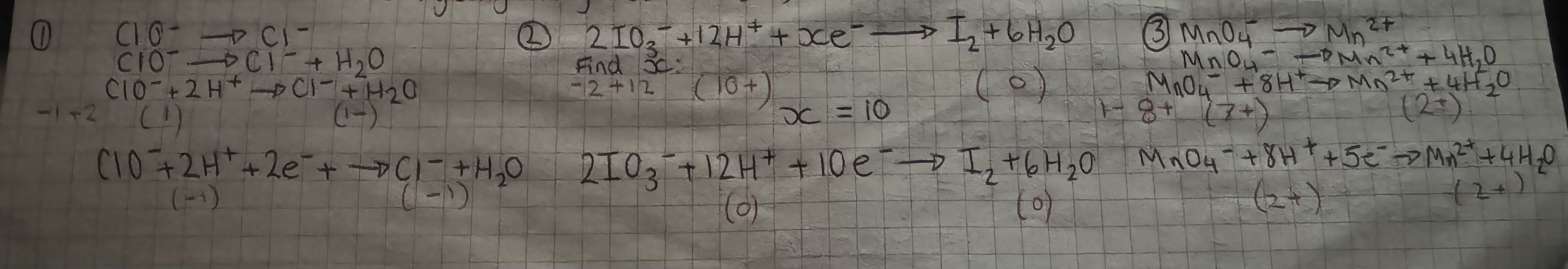
standard solution
a solution of accurately known concentrations
preparing standard solution
dissolve sample in a small volume of distilled water
transfer multiple rinsing into a volumetric flask
fill flaskwith distilled water to the graduation mark.
titration calculation example
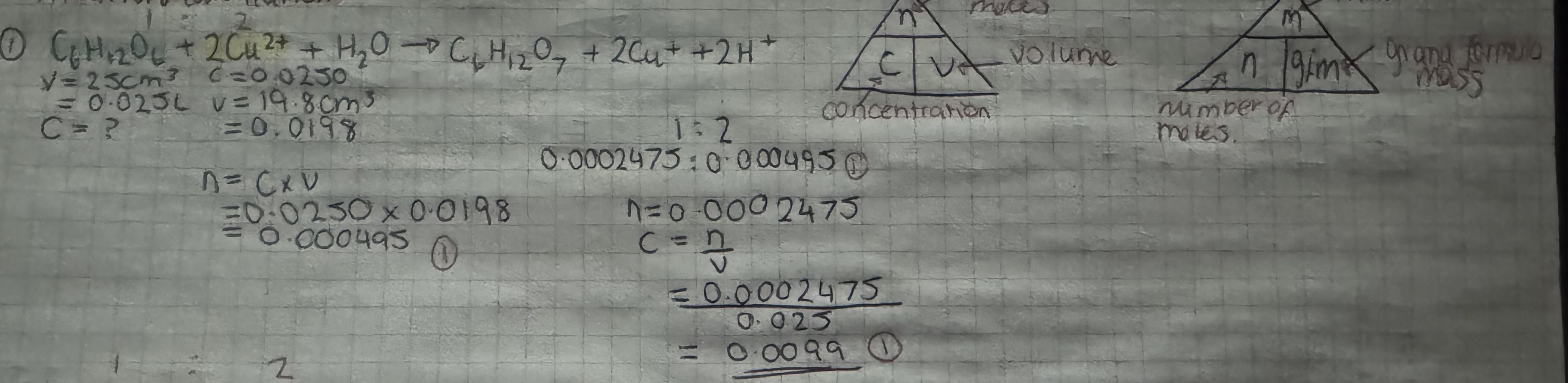
standard solution diagram
