Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
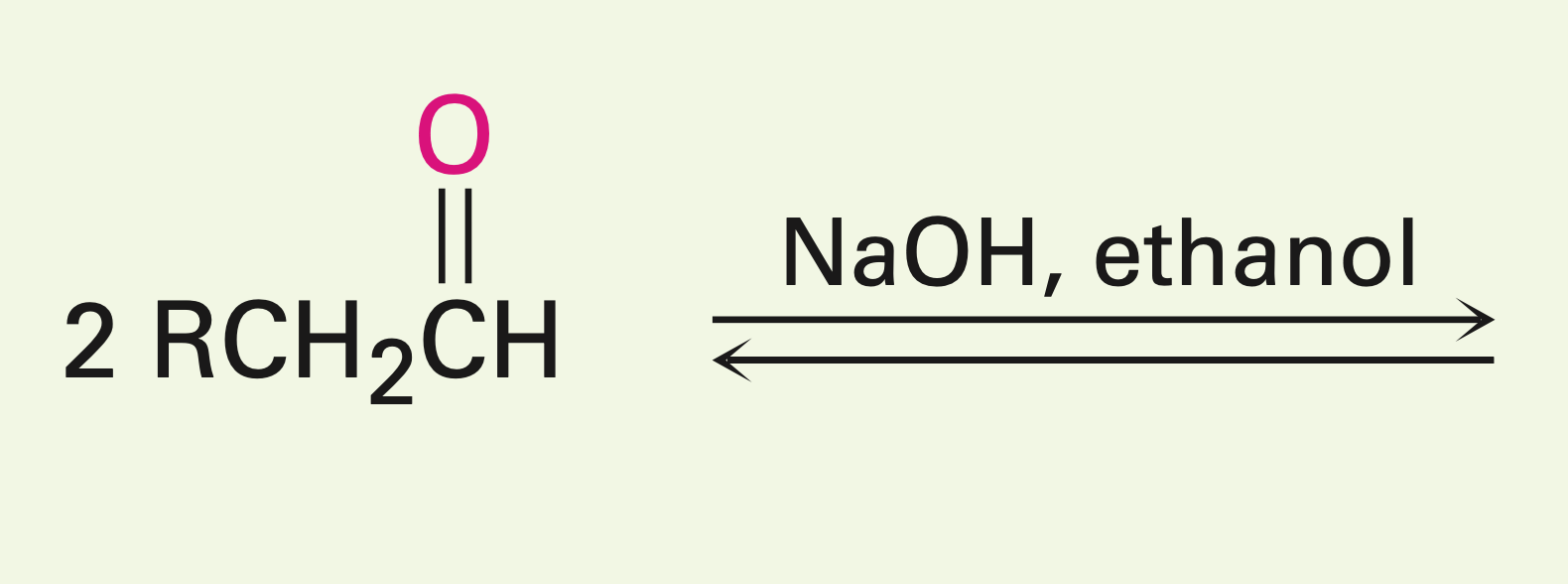
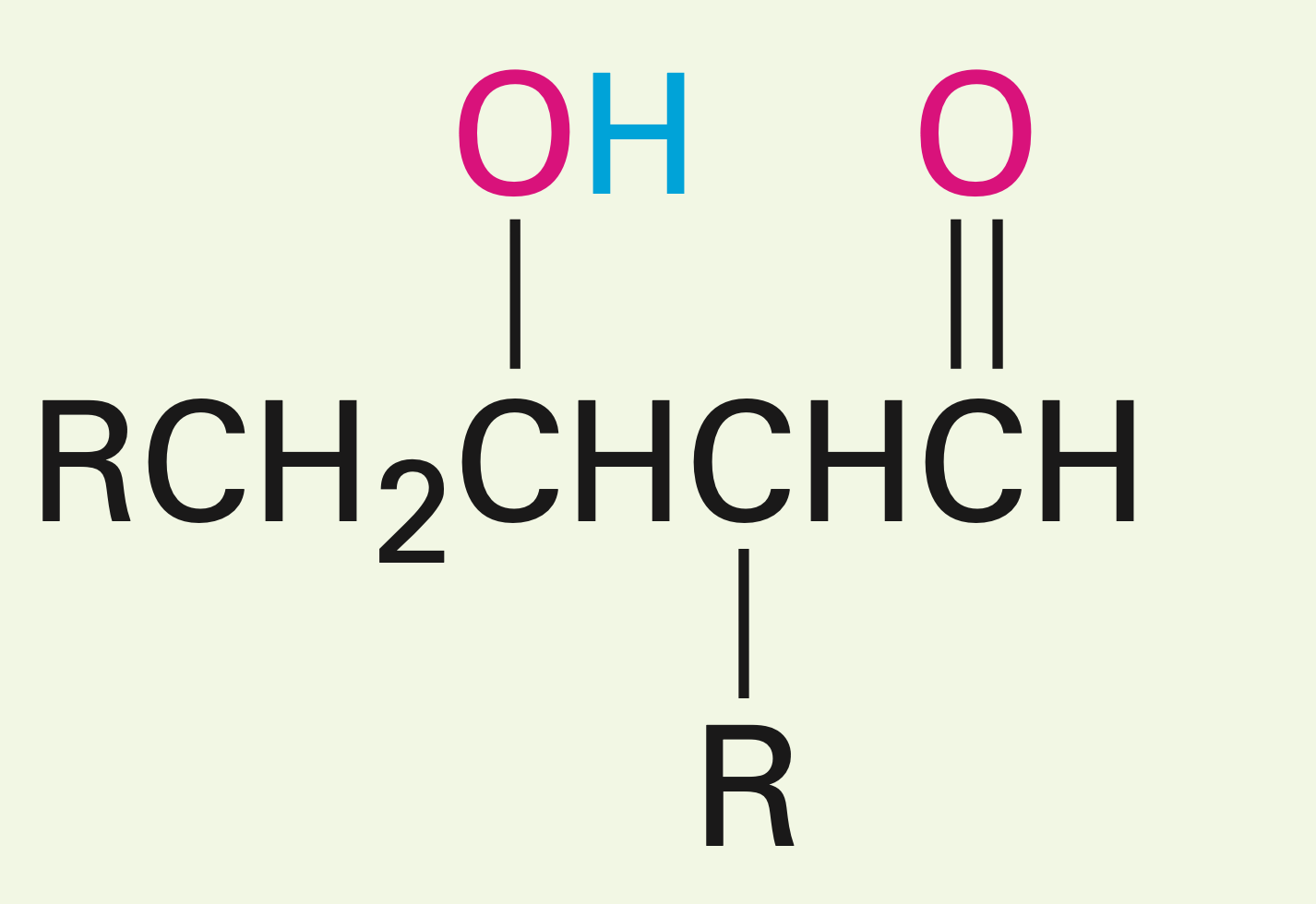
Two carbonyls in the presence of a fairly weak base.
Aldol reaction: Creates a beta hydroxy carbonyl
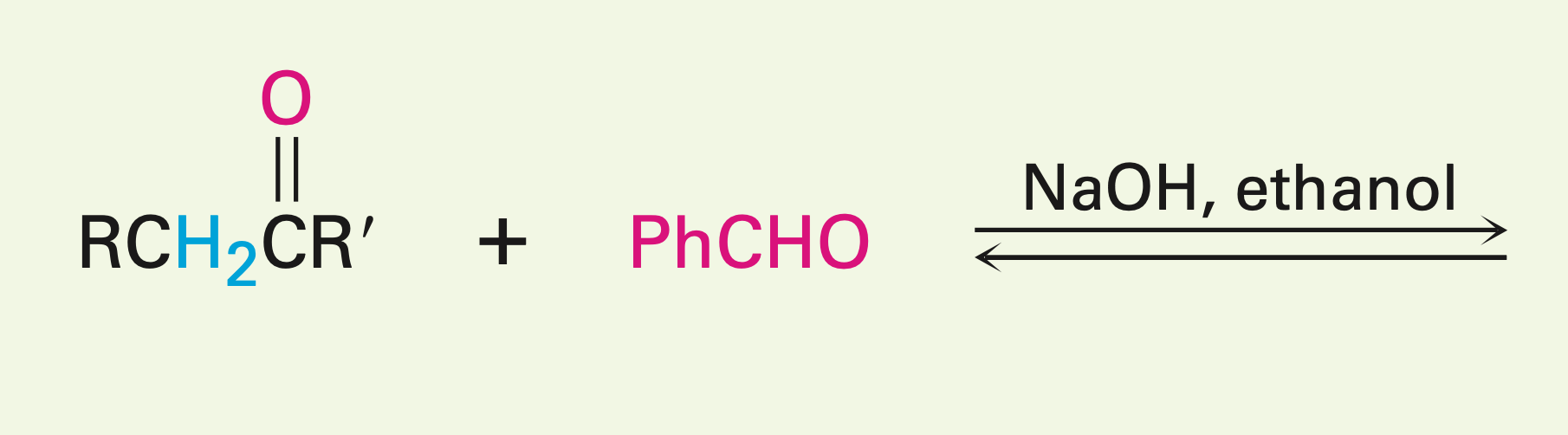
Two unsymmetrical carbonyls in the presence of a fairly weak base
Mixed aldol reactions: A definite product is certain when one of the species is unable to enolize, but it contains an unhindered carbonyl group. If one carbonyl is more acidic than the other, then it is more likely to enolize and the reaction is more successful.
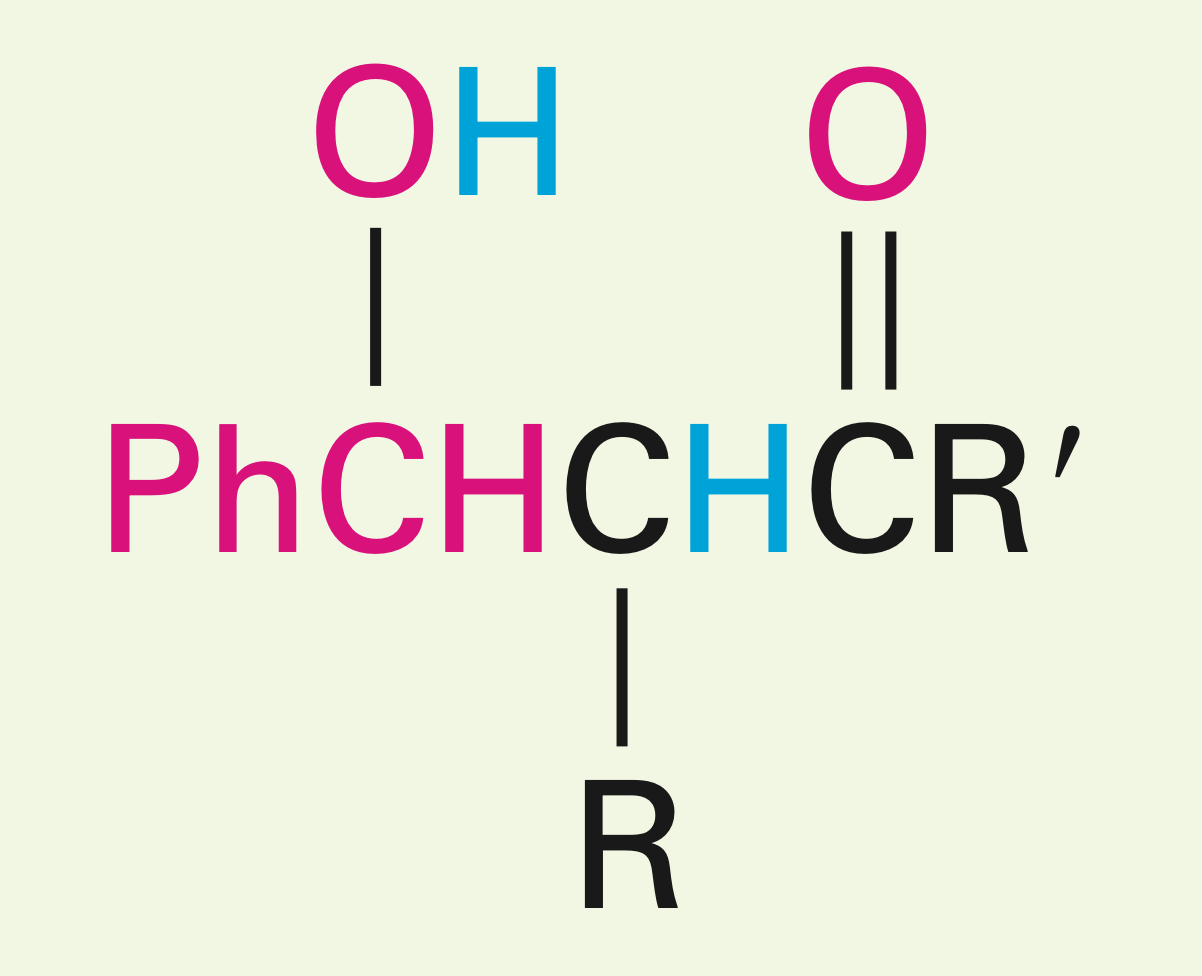
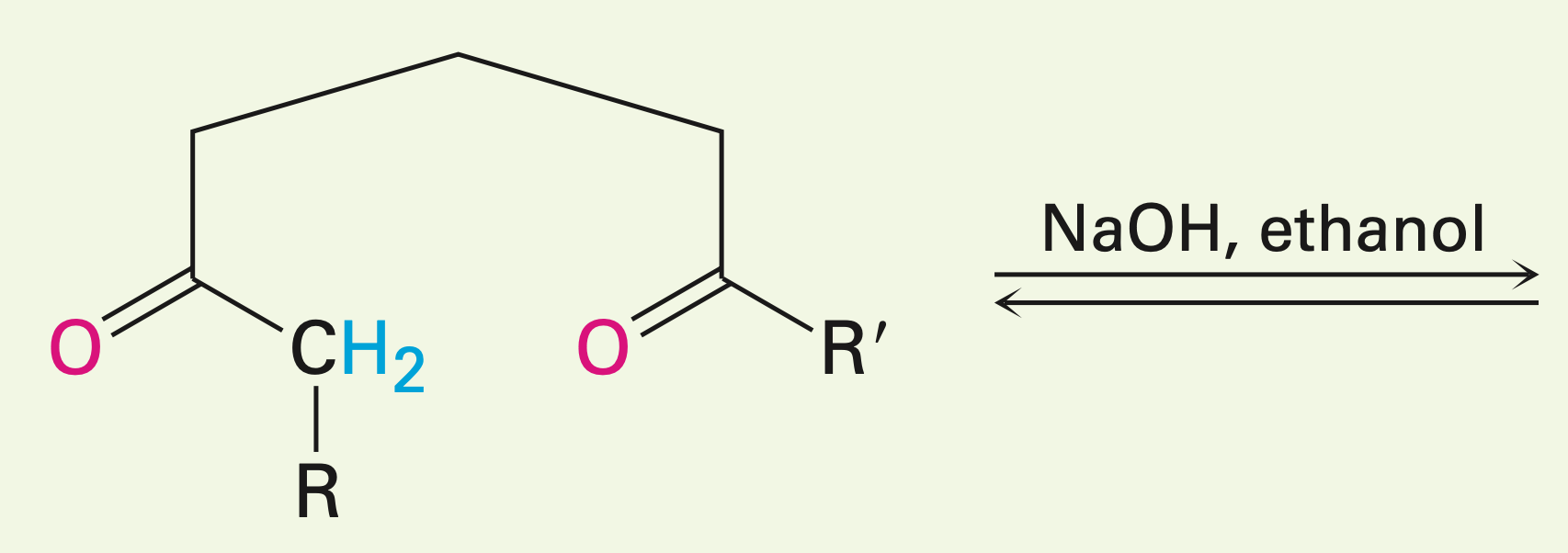
Two carbonyls within one long chain in the presence of a base
Intramolecular aldol reaction: the two carbonyls react with each other.
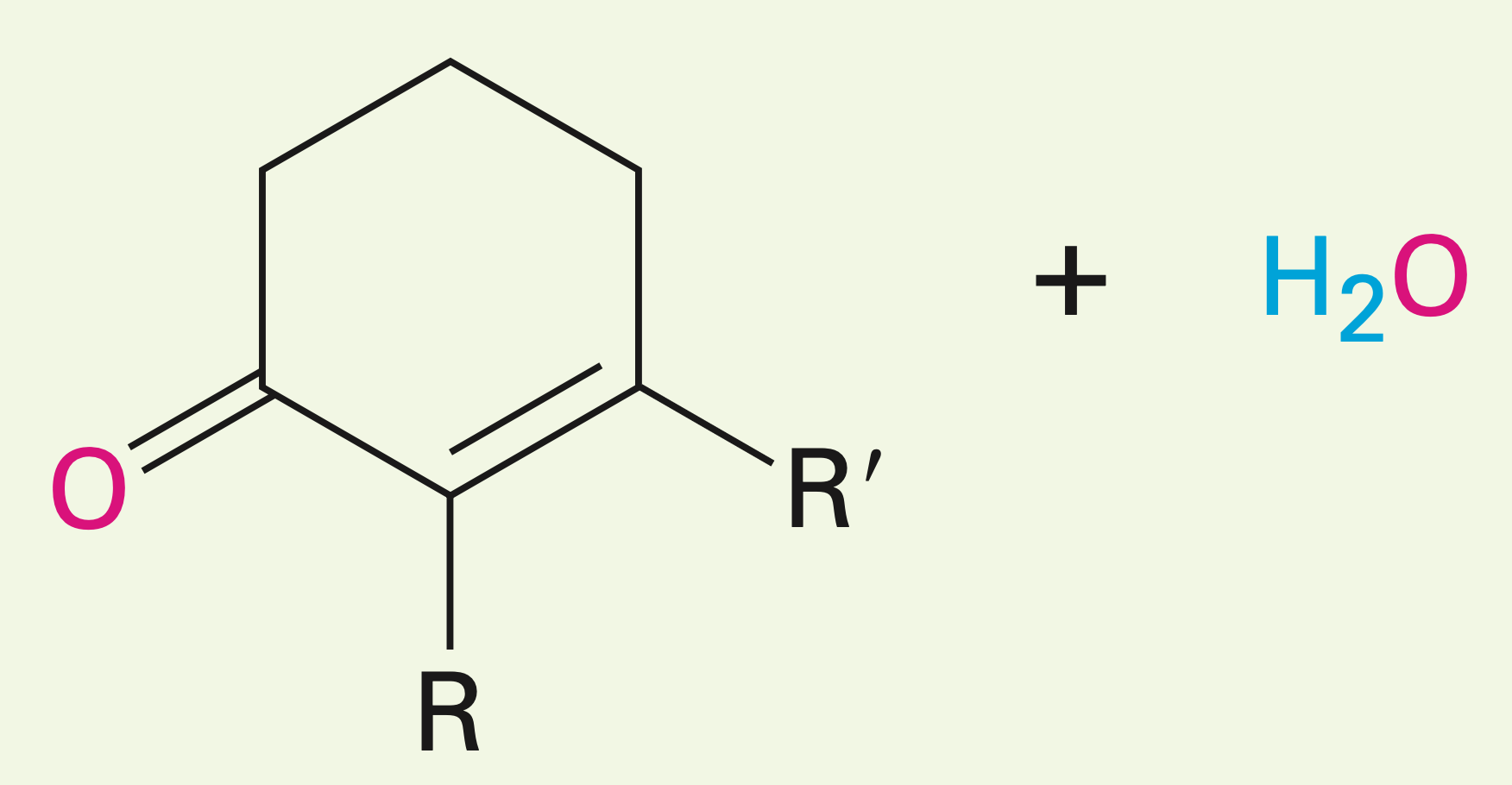
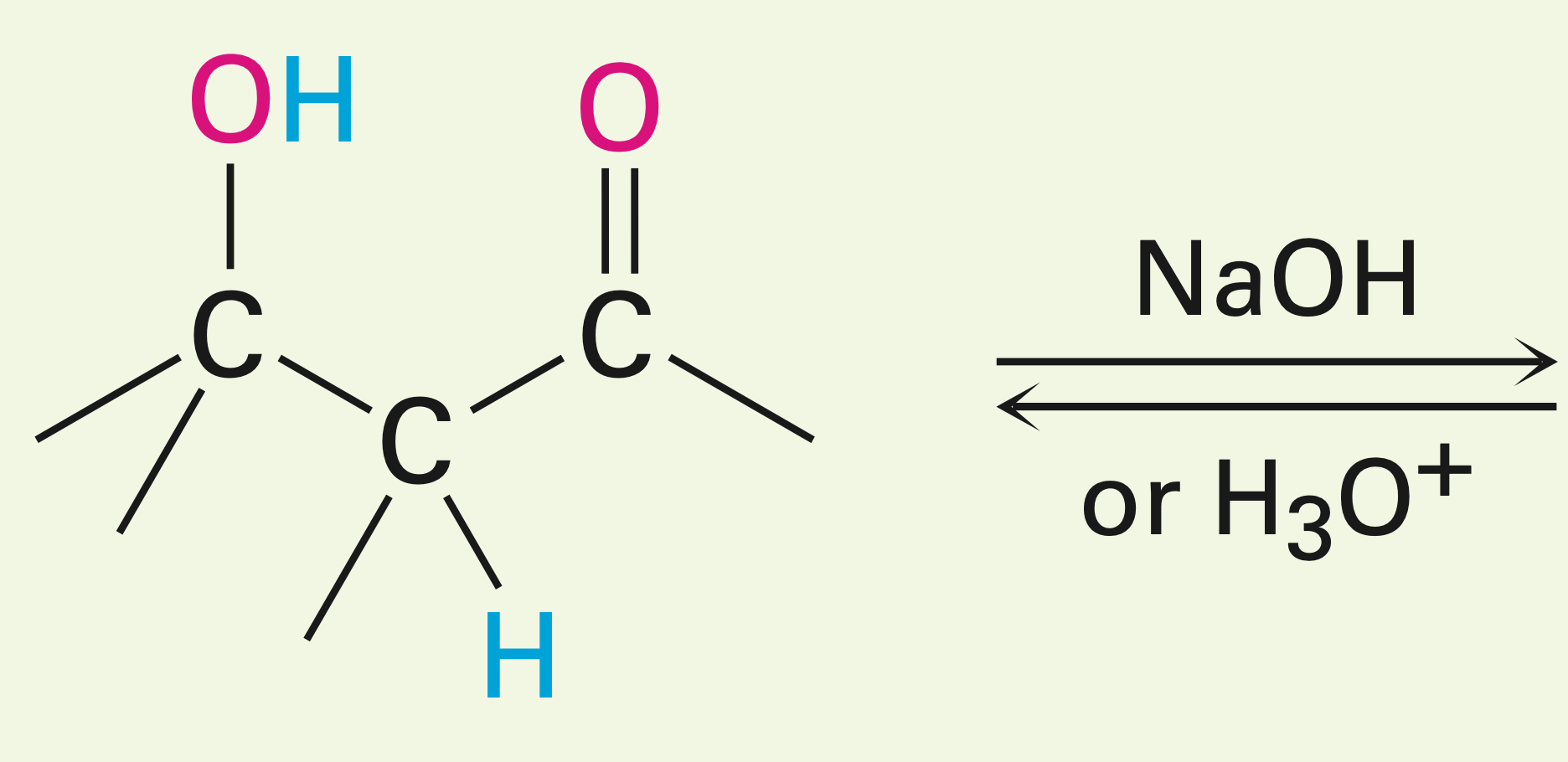
A newly made beta hydroxy carbonyl in the presence of an acid/base and heat.
Dehydration of aldol products: Turning a beta hydroxy carbonyl into an alpha-beta unsaturated carbonyl.
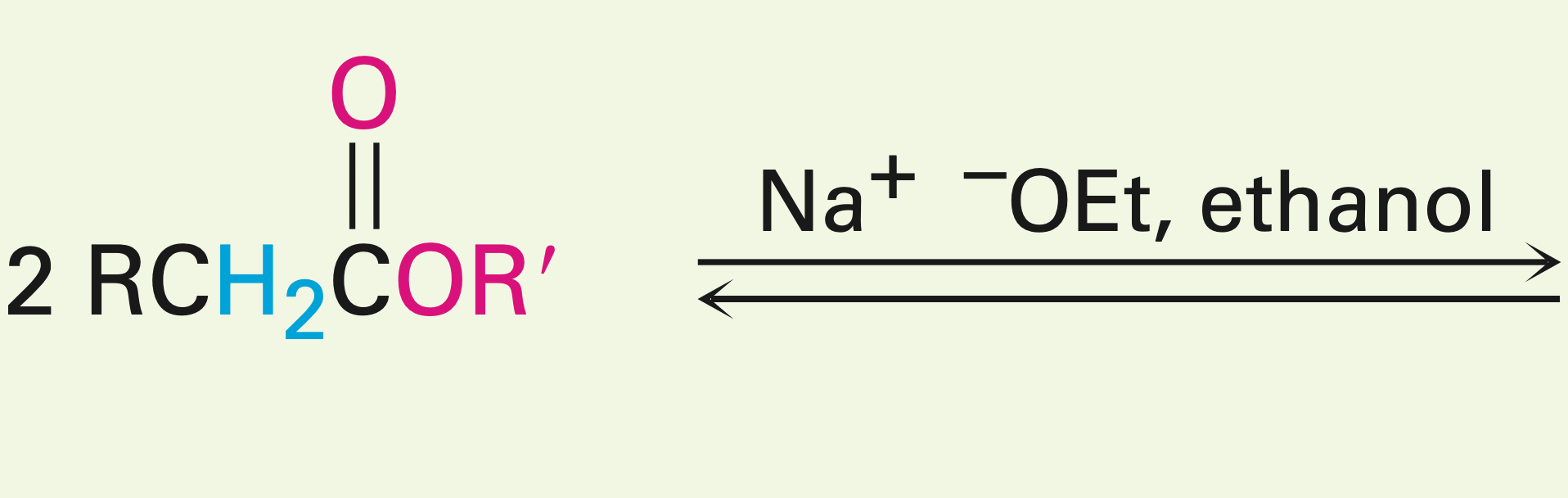
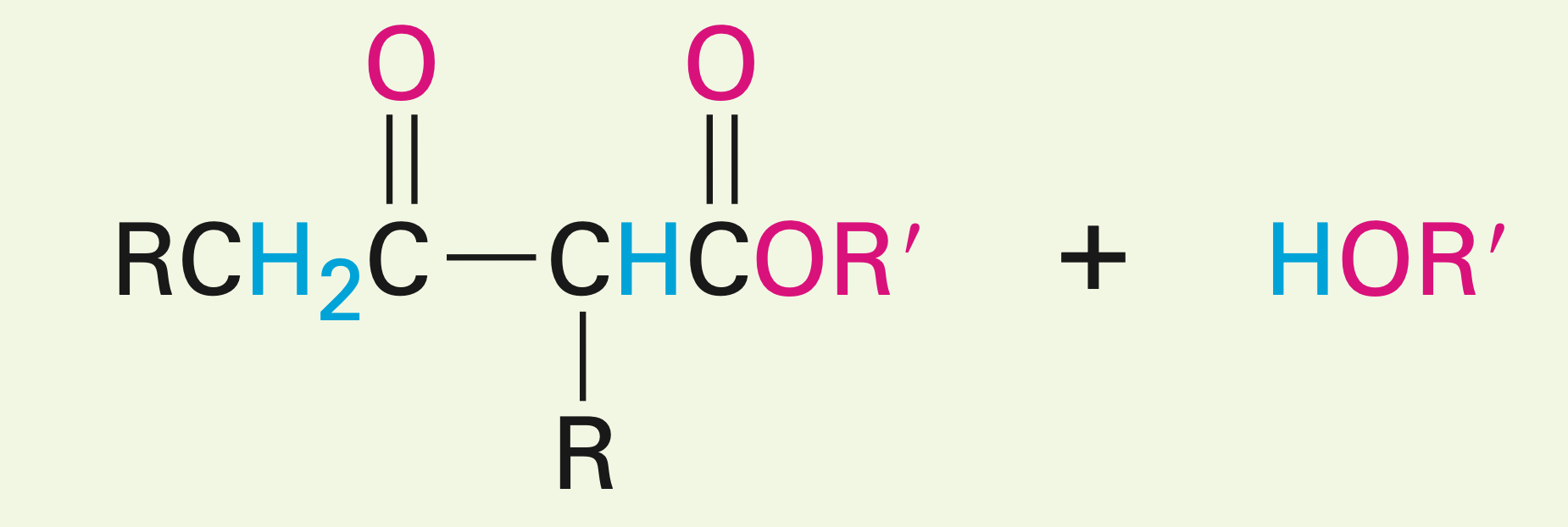
Two esters with a hydroxy oxygen in the presence of a base
Claisen condensation reaction: they yield a beta-keto ester (two carbonyls and an ester)
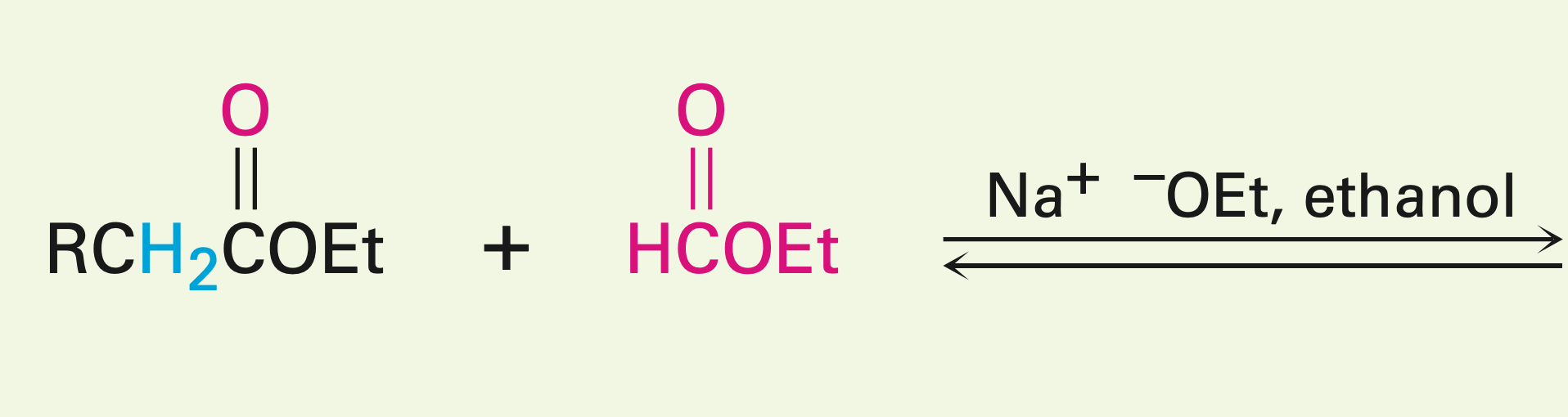
Presence of 2 unsymmetrical esters
Mixed Claisen condensation reaction: Can be carried out if one of the esters has no alpha hydrogens. It can also be carried out with a ketone, but the ester can’t have any alpha hydrogens (creates a B-diketone). NO OH is made, and one of the esters is the leaving group.
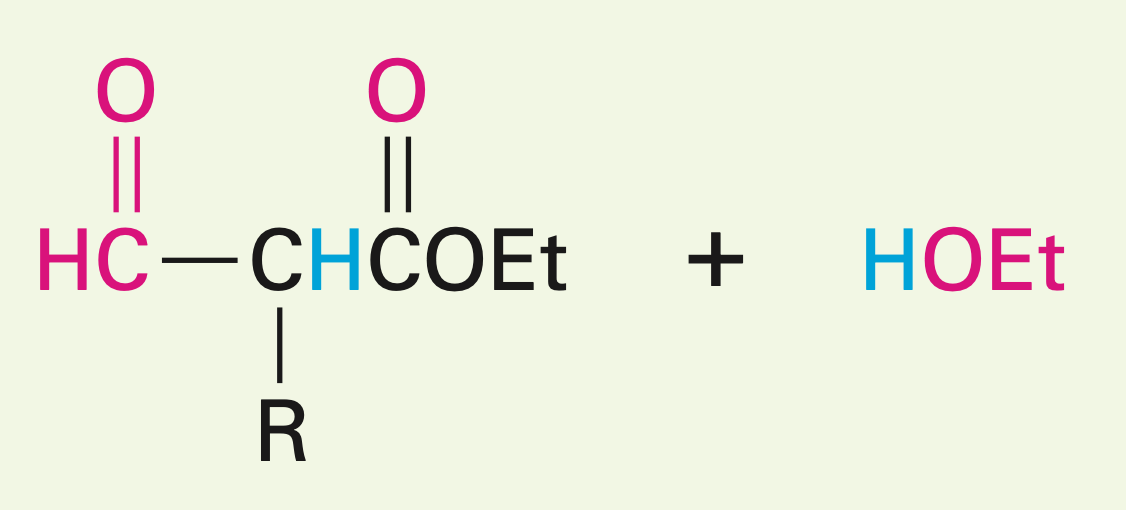
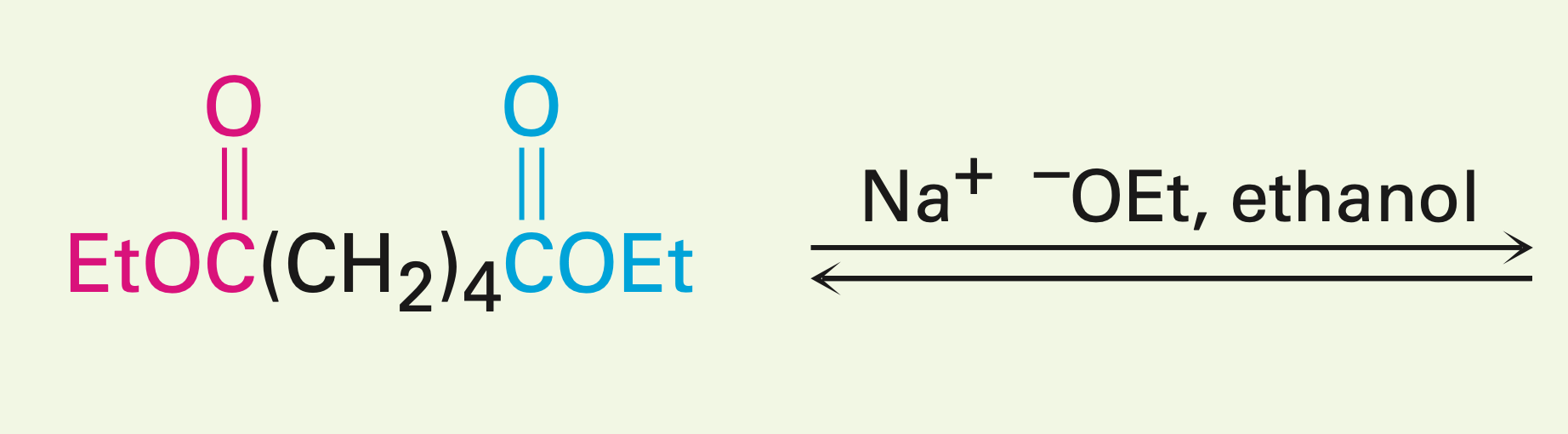
1,6 or 1,7 diester in the presence of a base
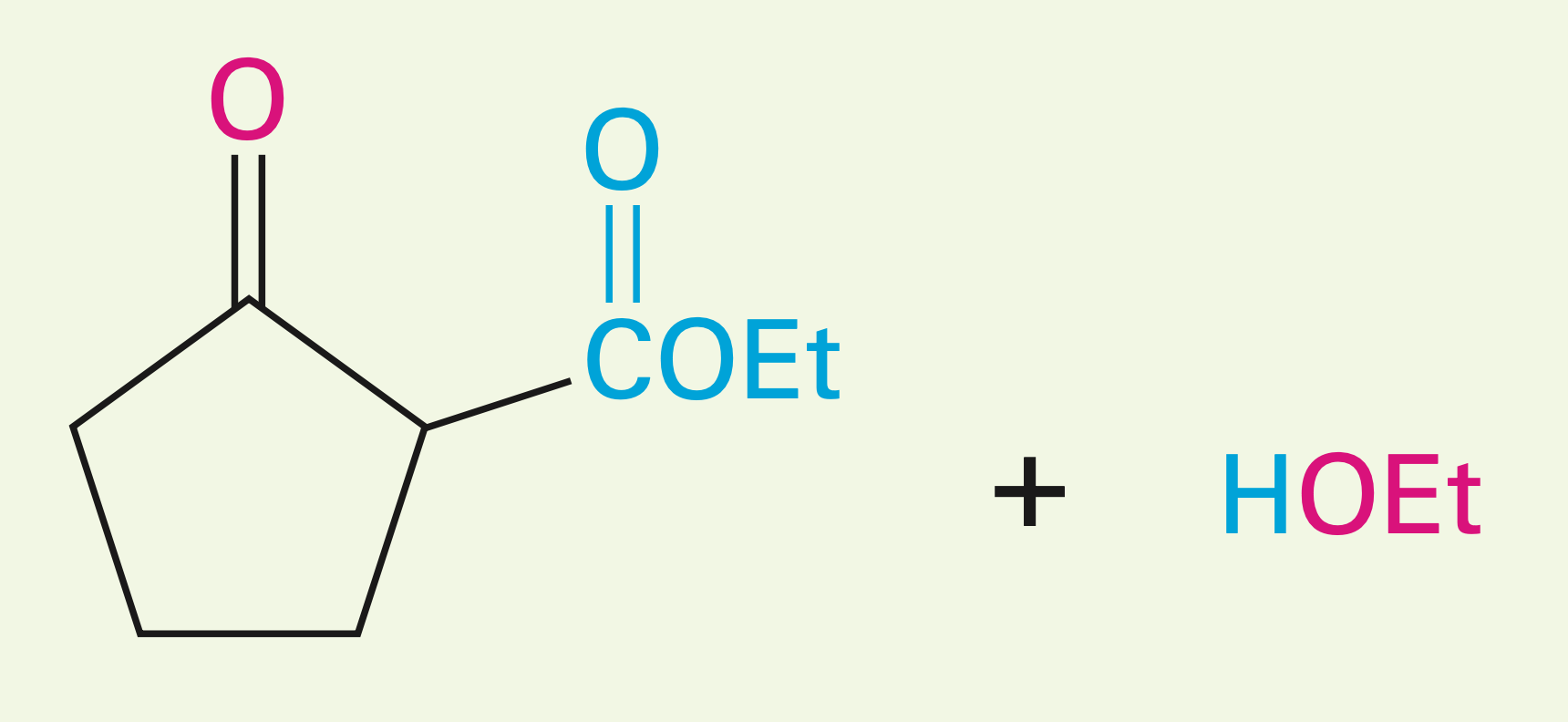
Intramolecular Claisen condensation (Dieckmann cyclization): 1-6 diesters give a five-membered cyclic B-keto ester, and 1,7-diesters give a six-membered cyclic B-keto ester
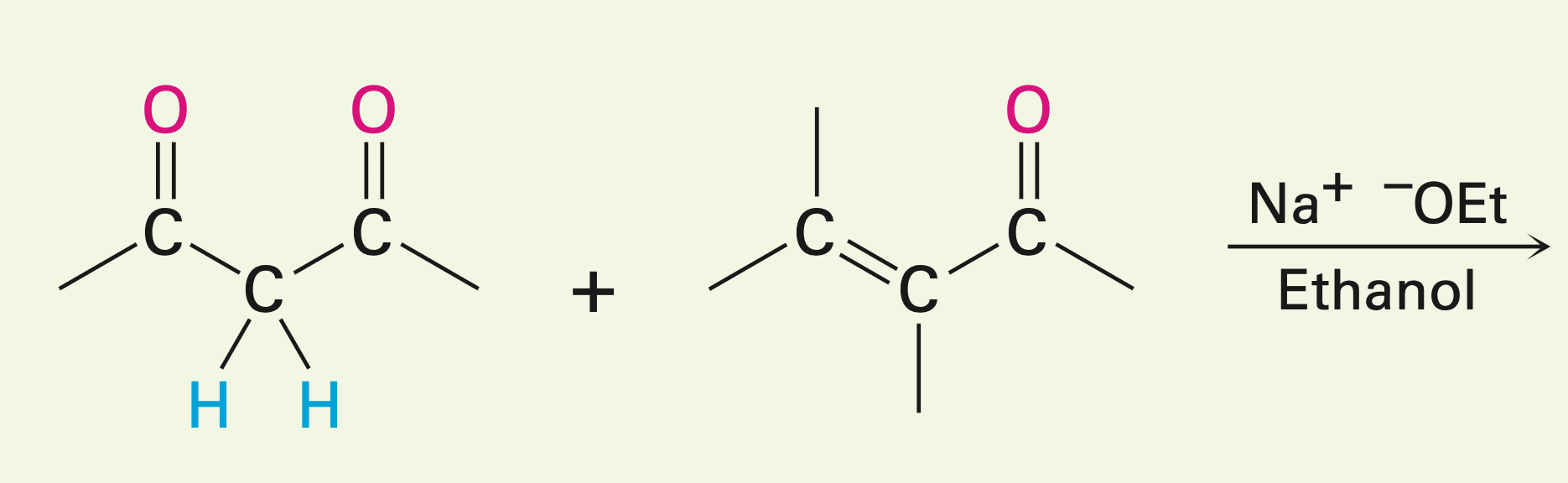
A stable enolate ion and an unhindered a,b-unstaturated ketone in the presence of a base
The Michael reaction: Adding an enolate ion to an a,b-unsaturated carbonyl compound. The enolizable compound is the donor, and the conjugated carbonyl is the acceptor. Creates a new C-C bond.
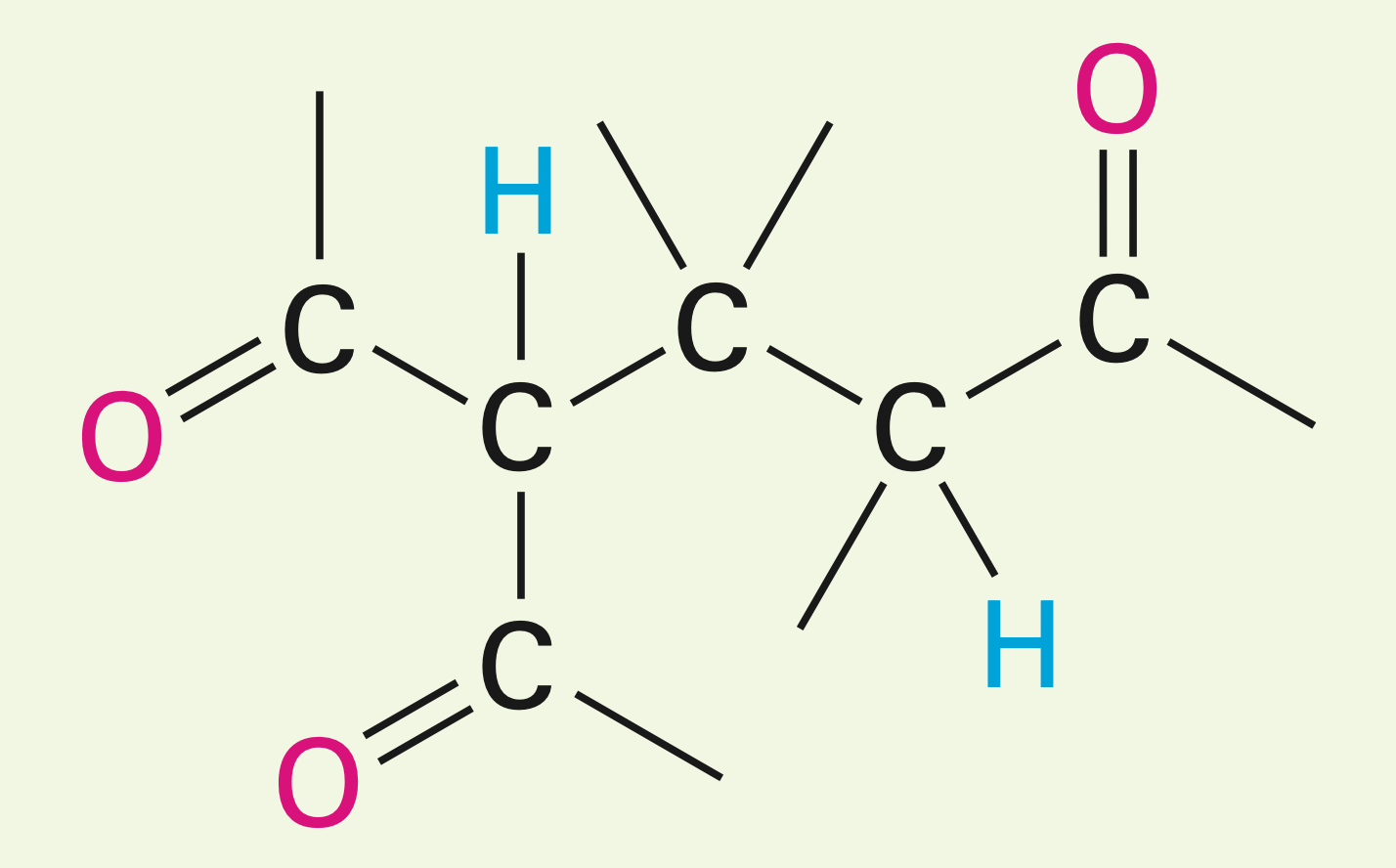
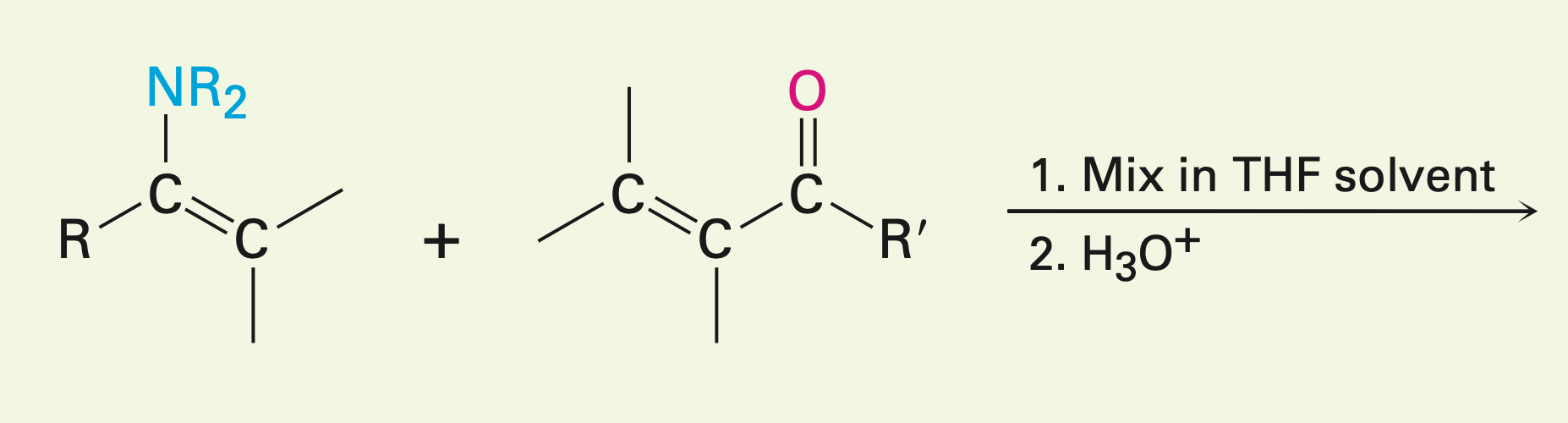
Carbonyl condensations with enamines (Stork reaction): a three step process, enamine formation, then the michael addition to an a,B-unsat. carbonyl compound, and lastly enamine hydrolysis back to a ketone.