Lecture 4: Pathogenesis & Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Pathogen
A microbe that causes disease

Pathogenicity
The ability of a microorganism to cause disease
Pathogenesis
The development of a disease
Colonization
The microbe's initial invasion into the host
Infection
Multiplication of a pathogen --> leads to disease
Infectious diseases
Diseases that are caused by the pathogen directly invading the body's tissues
Microbial intoxication
A disease that results from the ingestion of a toxin that was produced by a pathogen

How does location of pathogens prevent infection?
Microbes may land in a place they cannot enter the body (such as intact skin)
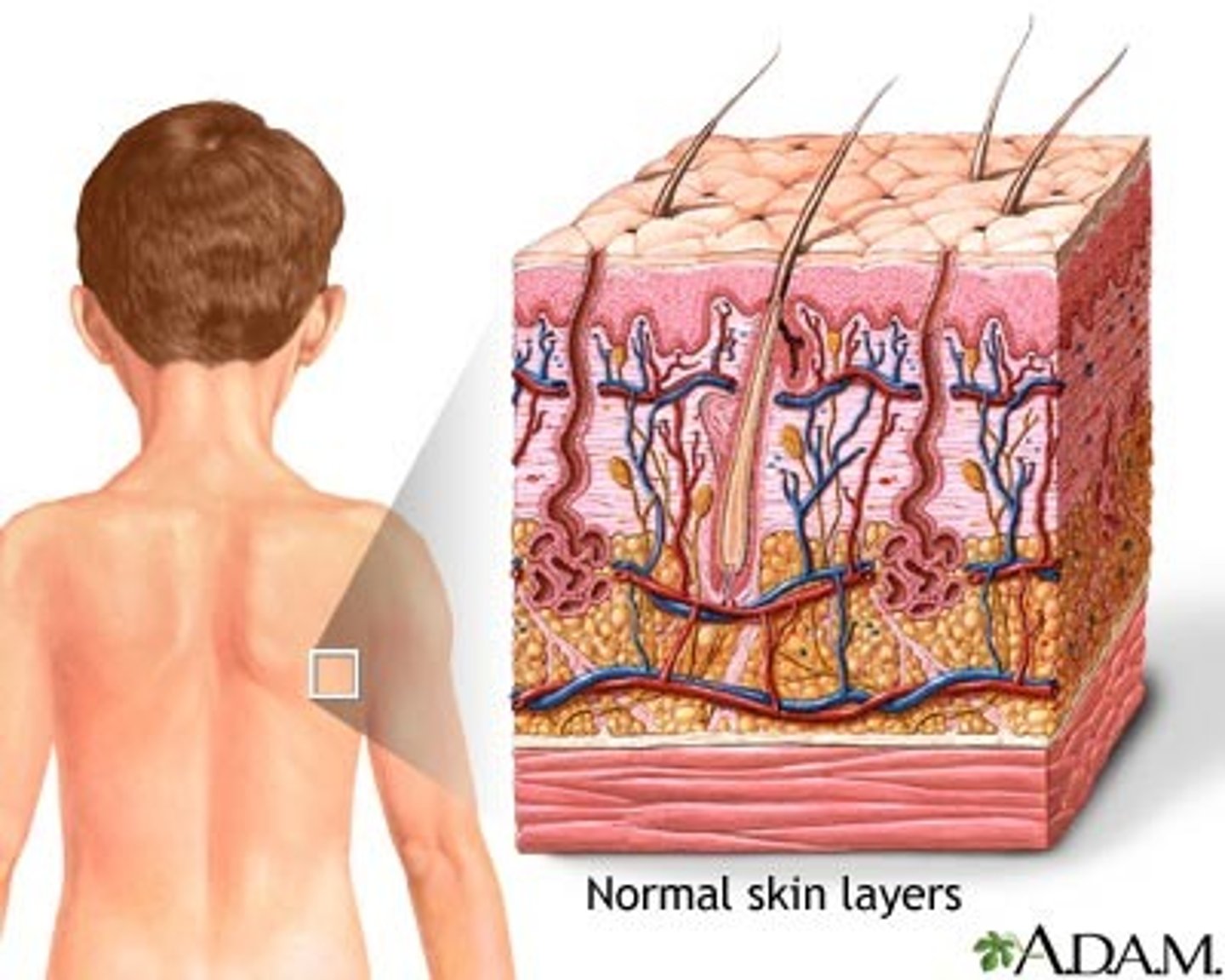
How do natural antimicrobial factors prevent infection?
Enzymes in tears and saliva can destroy bacterial cell walls
Microbial antagonism
Bacteria in the human microbiome bacteria can inhibit the growth of pathogens
How do phagocytic cells prevent infection?
Phagocytic cells eat pathogens before they can invade tissues
How does overall health prevent infection?
Immunocompromised persons are more susceptible to infections
How can people acquire immunity to pathogens?
Through previous exposure and vaccines
Incubation period
The period between initial infection and the appearance of signs and symptoms

Prodromal period
The period in which vague signs and symptoms appear

Period of illness
The period in which the disease is the most severe (characterized by inflammation and tissue damage)

Convalescent period
Recovery from infection

Signs
Objective changes a clinician can observe and measure
Symptoms
Subjective characteristics of disease felt only by the patient
Localized infection
An infection that occurs in a specific location in the body and has local symptoms
Systemic infection
An infection that spreads throughout the whole body
Primary infection
Initial infection
Secondary infection
An opportunistic infection after a primary infection
Steps of pathogenesis
1. Entry
2. Attachment to tissue
3. Multiplication
4. Invasion/spread of pathogen
5. Evasion of immune system
6. Damage to host tissues
Virulence
The ability of a microbe to produce disease
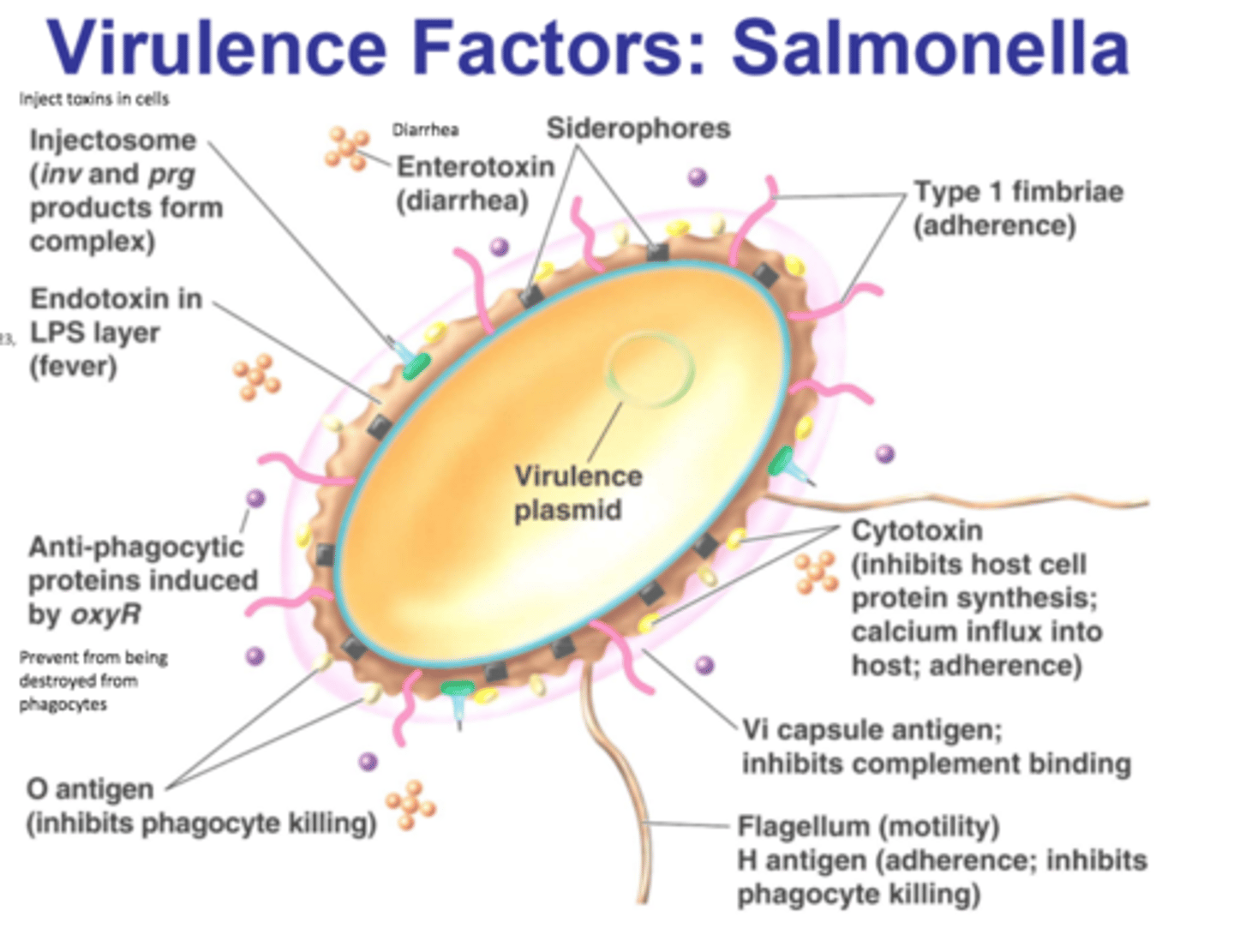
Virulence factors
Traits of a microbe that allow it to complete pathogenesis
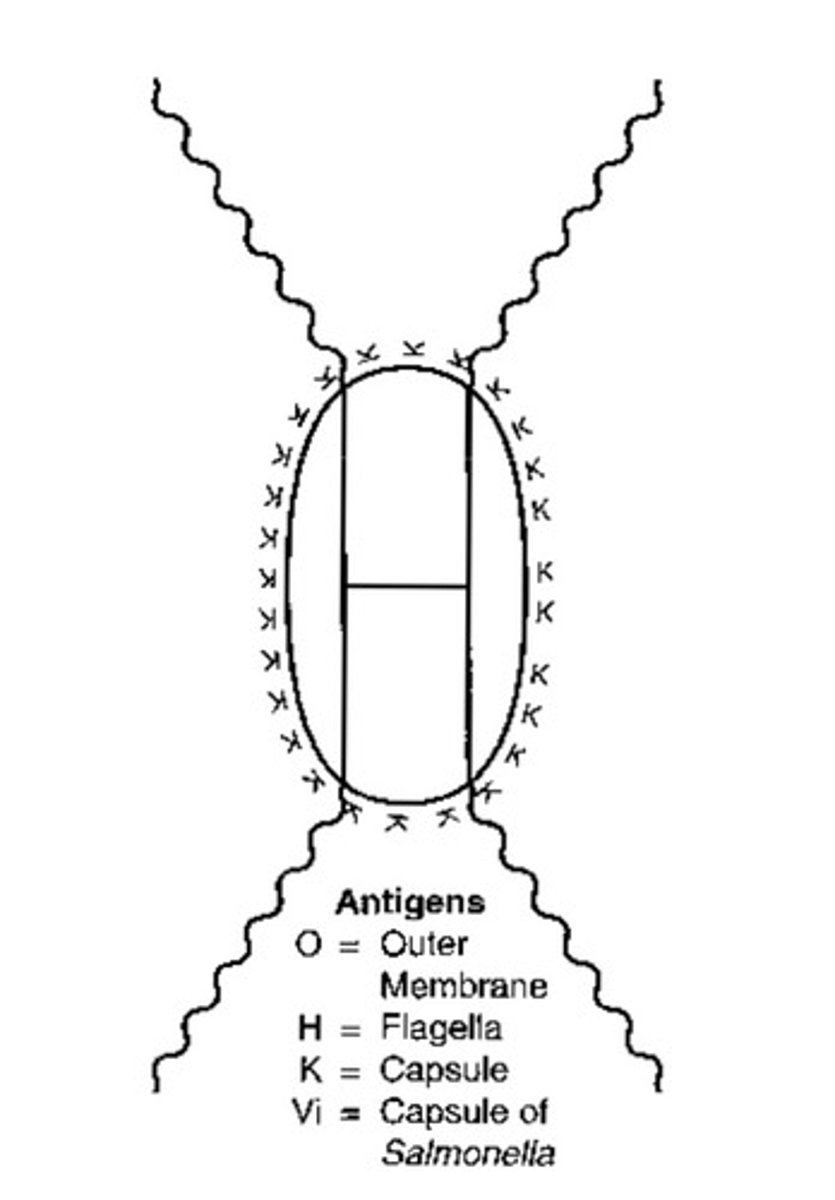
Adhesion factors
Structures that allow the pathogen to attach to the host cell
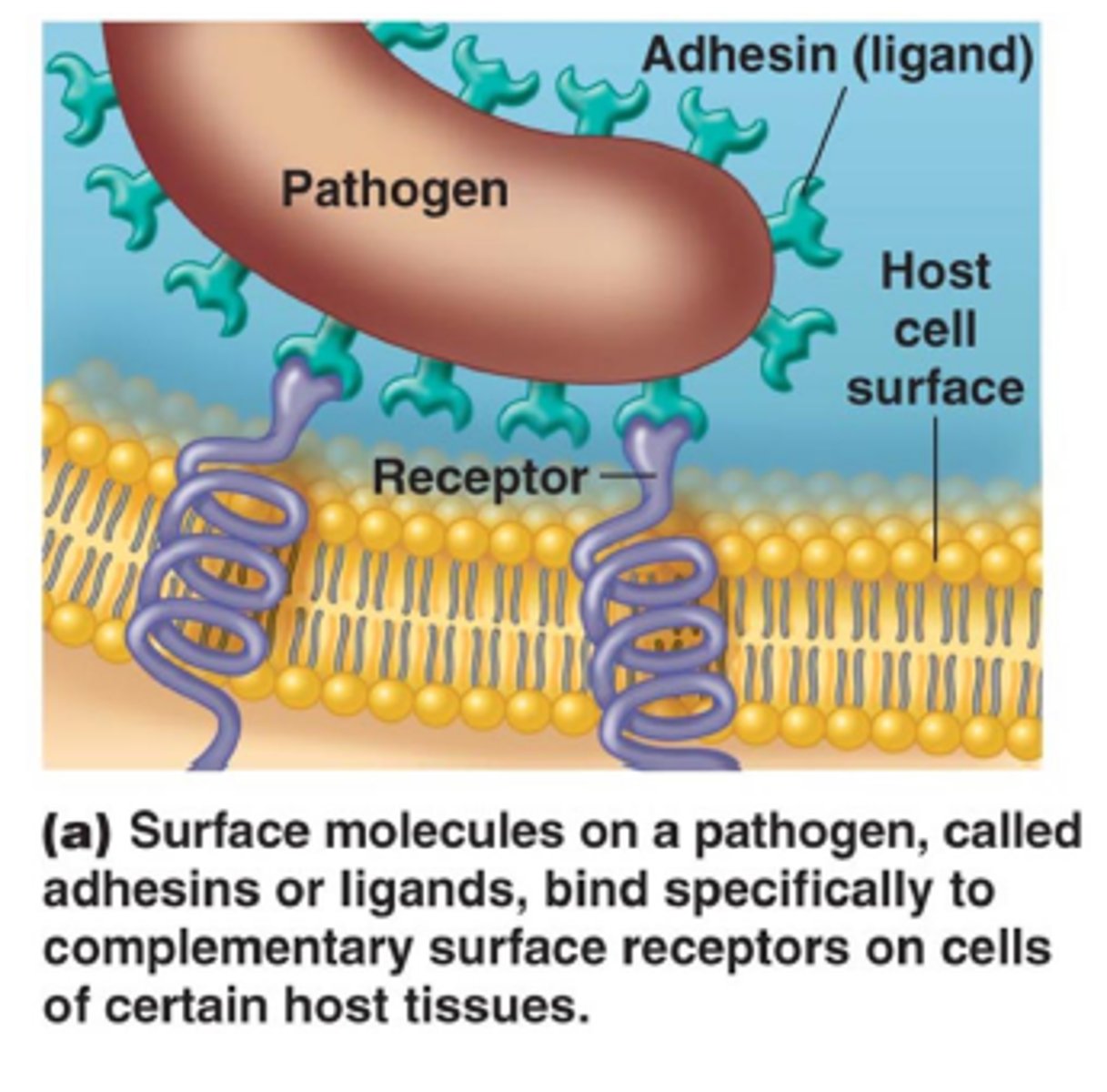
Adhesins (ligand)
Molecules found on the pathogen's surface that enable it to recognize and bind to host cells
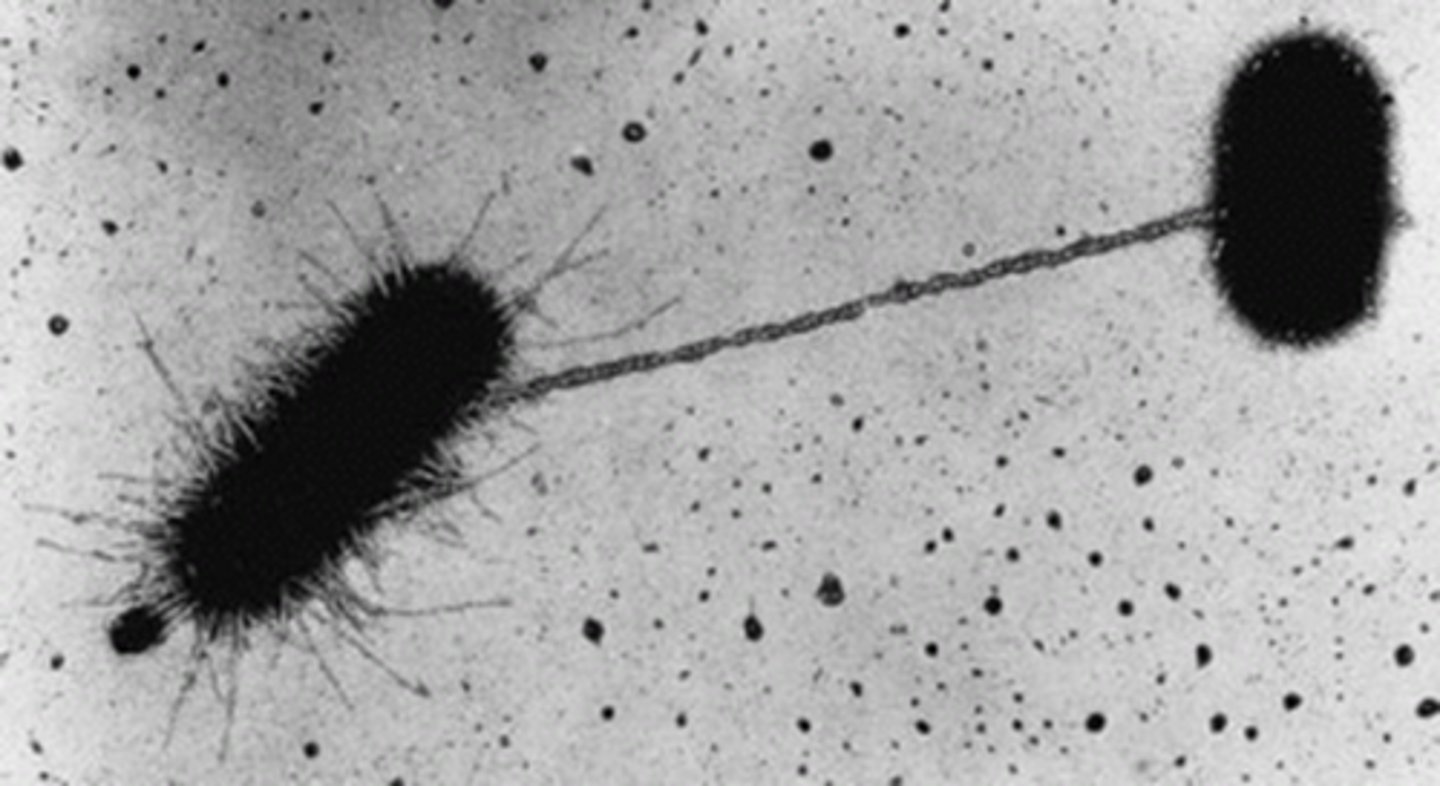
How are pili used to promote infection?
Pili allow bacteria to anchor themselves to body tissues
Invasion factors
Allow pathogens to break into host cells and evade barriers
Exoenzymes
Enzymes secreted by pathogens that break down and inflict damage on tissues
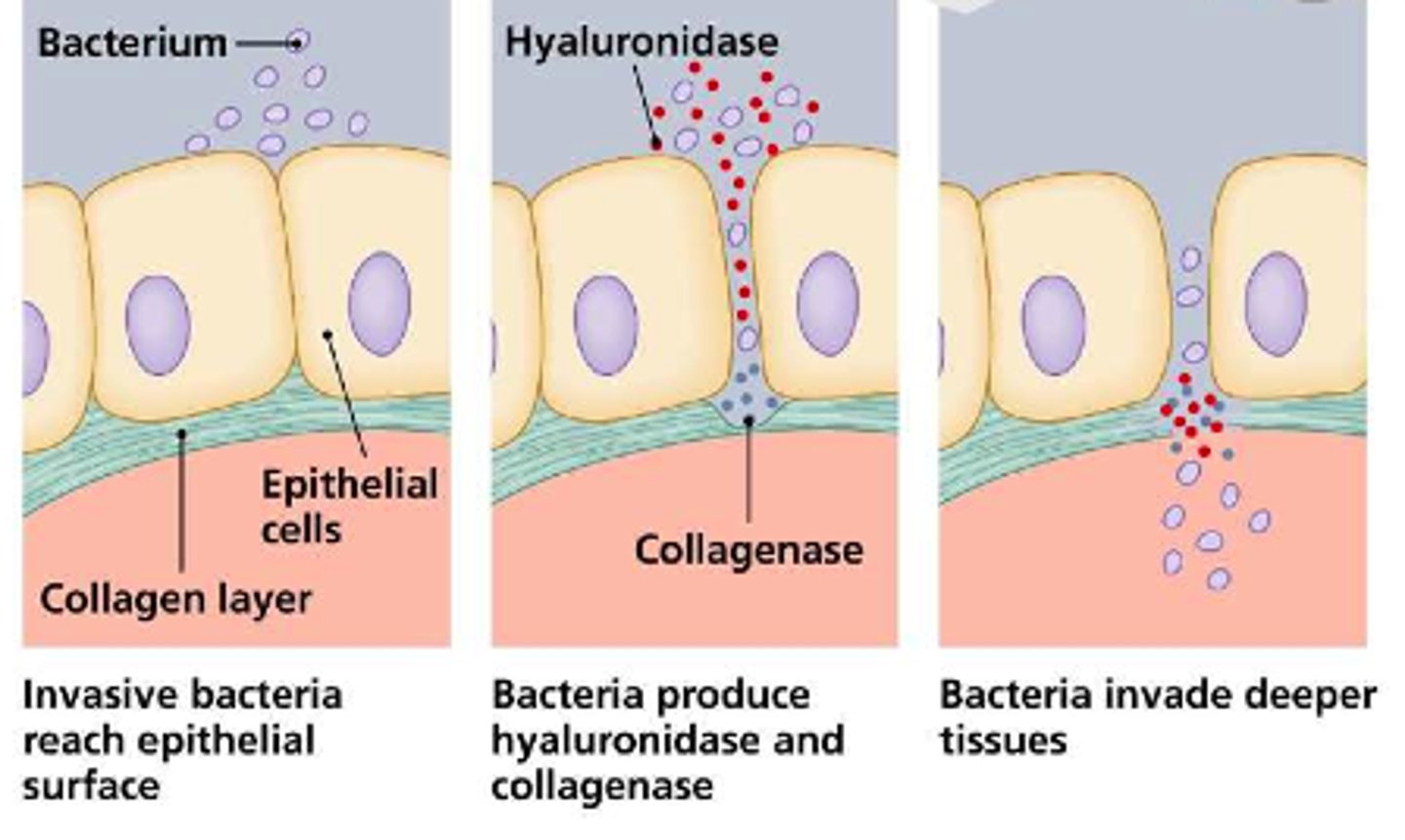
Evasion factors
Allow pathogens to evade the host's immune system
Capsules
A membrane around bacterium that prevent them from being eaten by phagocytosis
Antigenic variation
Bacterium can alter their surface proteins in order to hide from the immune system
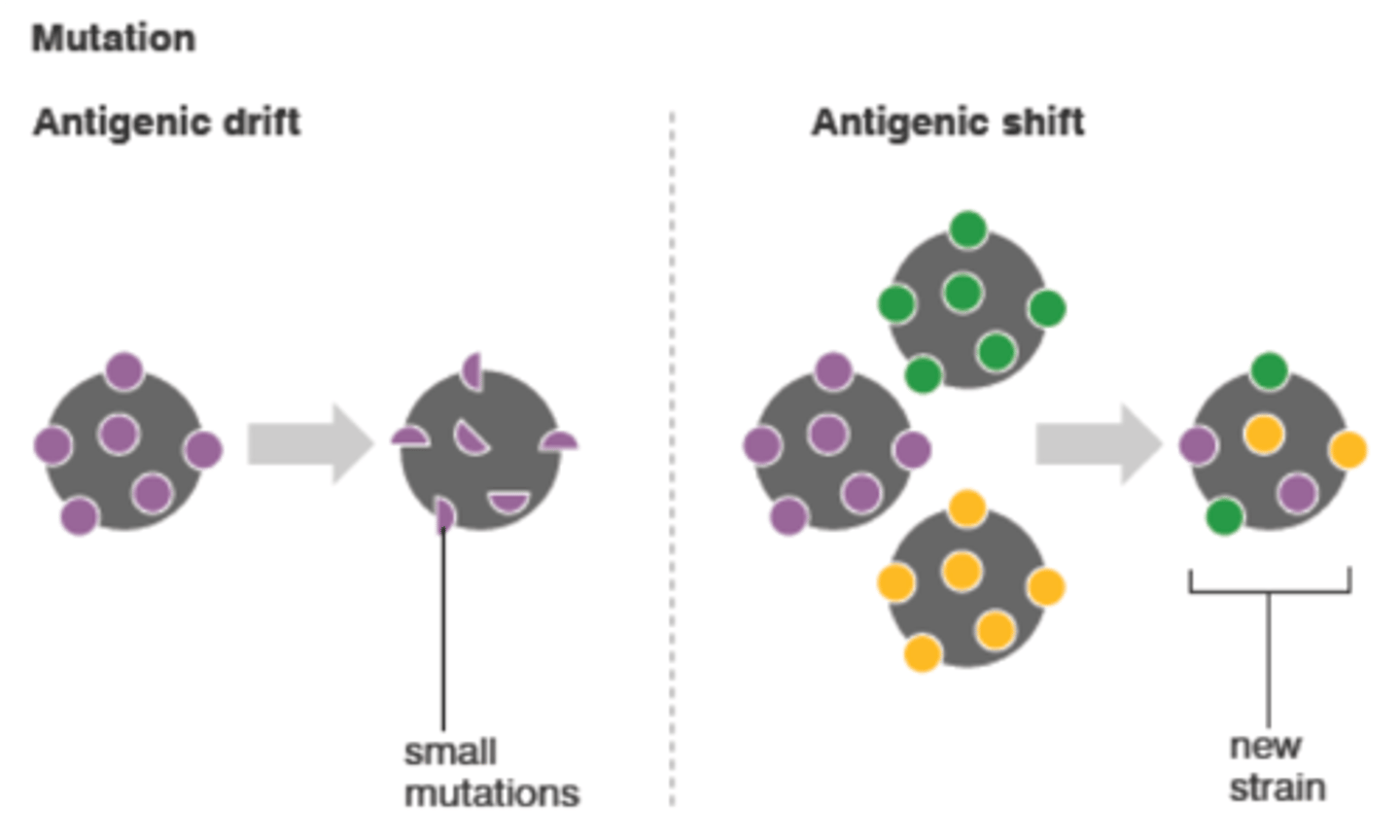
Drifts
Minor antigenic variations
Shifts
Major antigenic variations
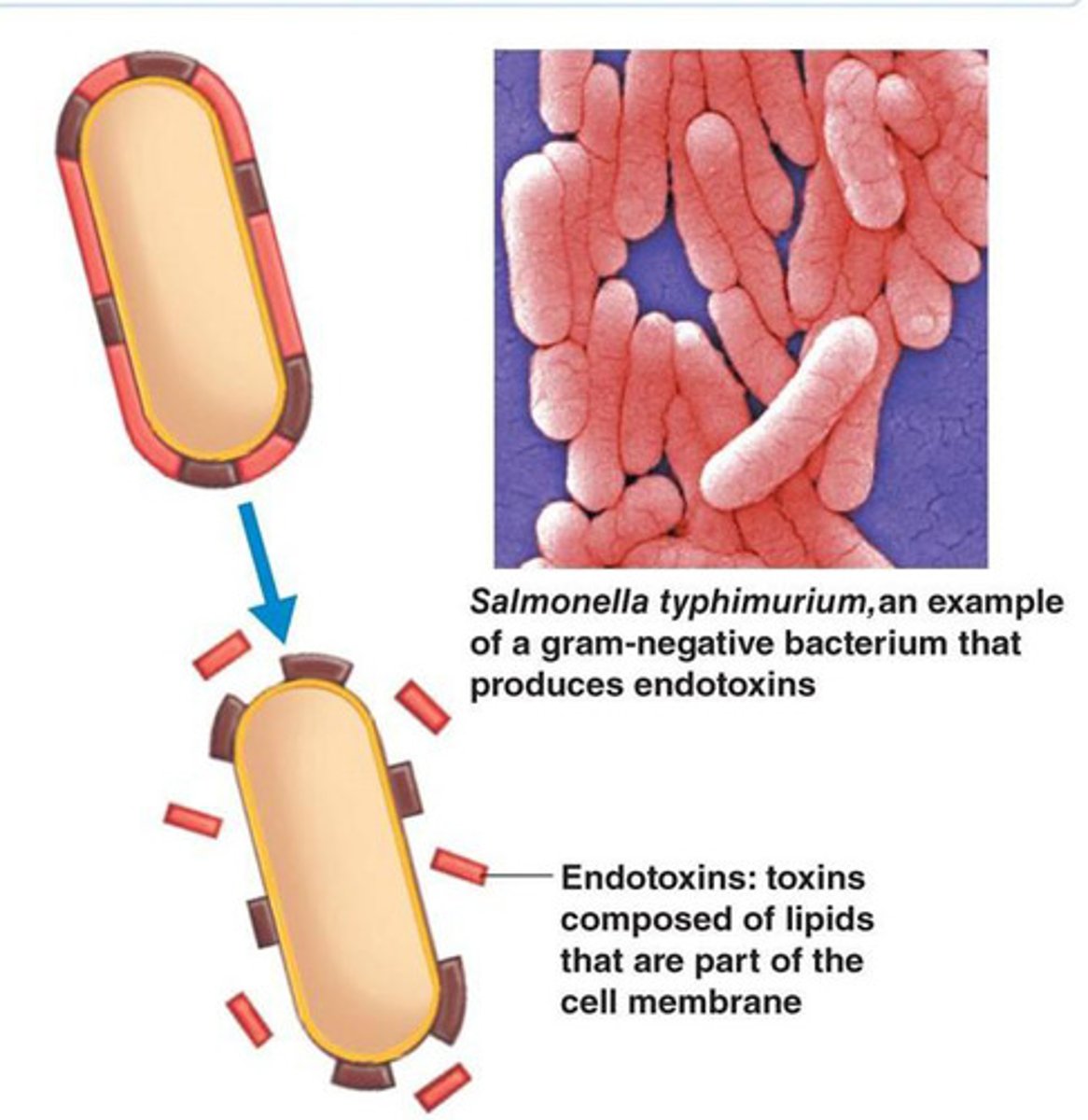
Endotoxins
A toxin that is part of the cell walls of gram-negative bacteria wall --> released only when bacteria die and their cell walls break down
Septicemia
Infection in the bloodstream
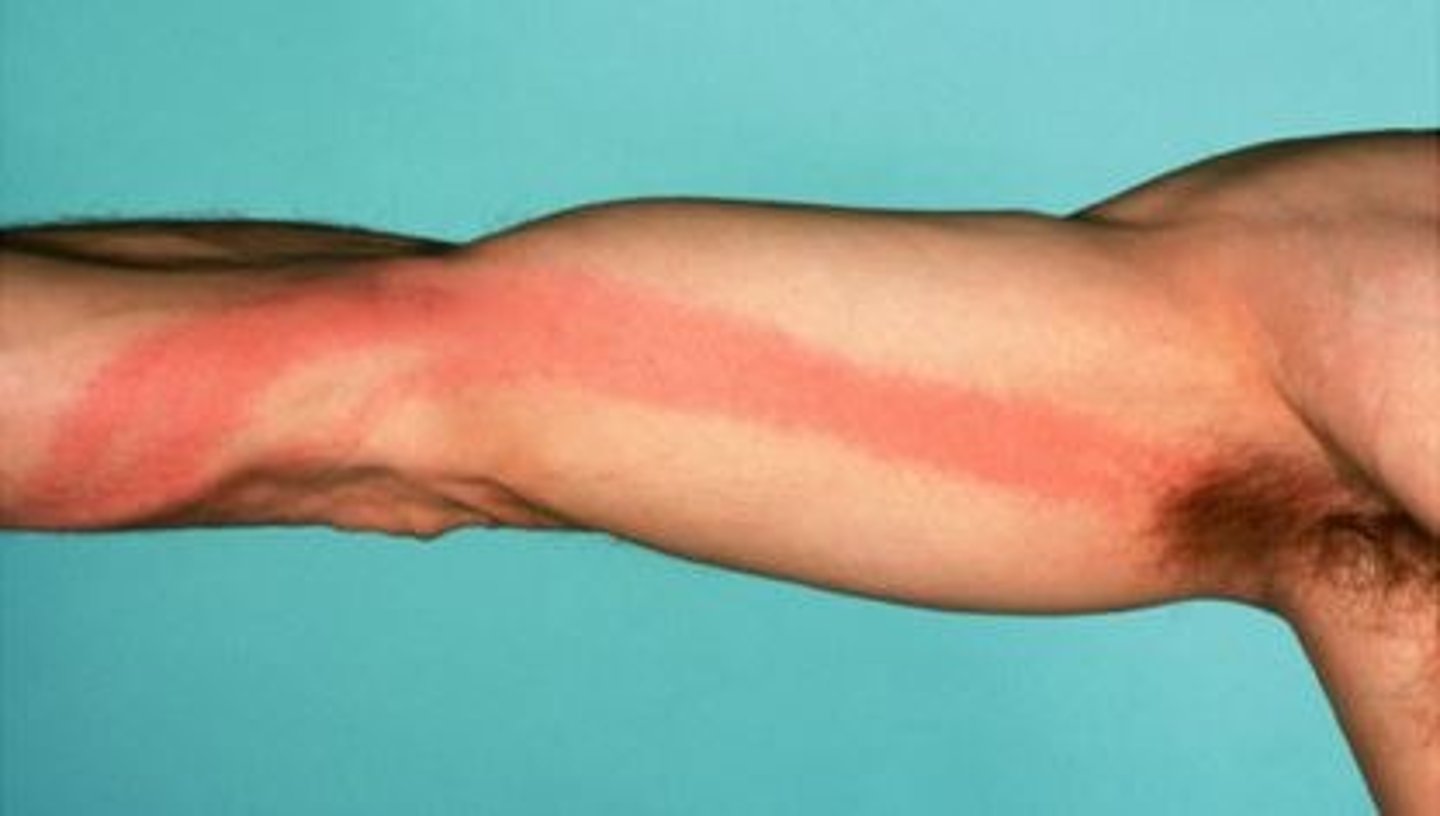
Exotoxins
Toxic substances that pathogens secrete into their environment
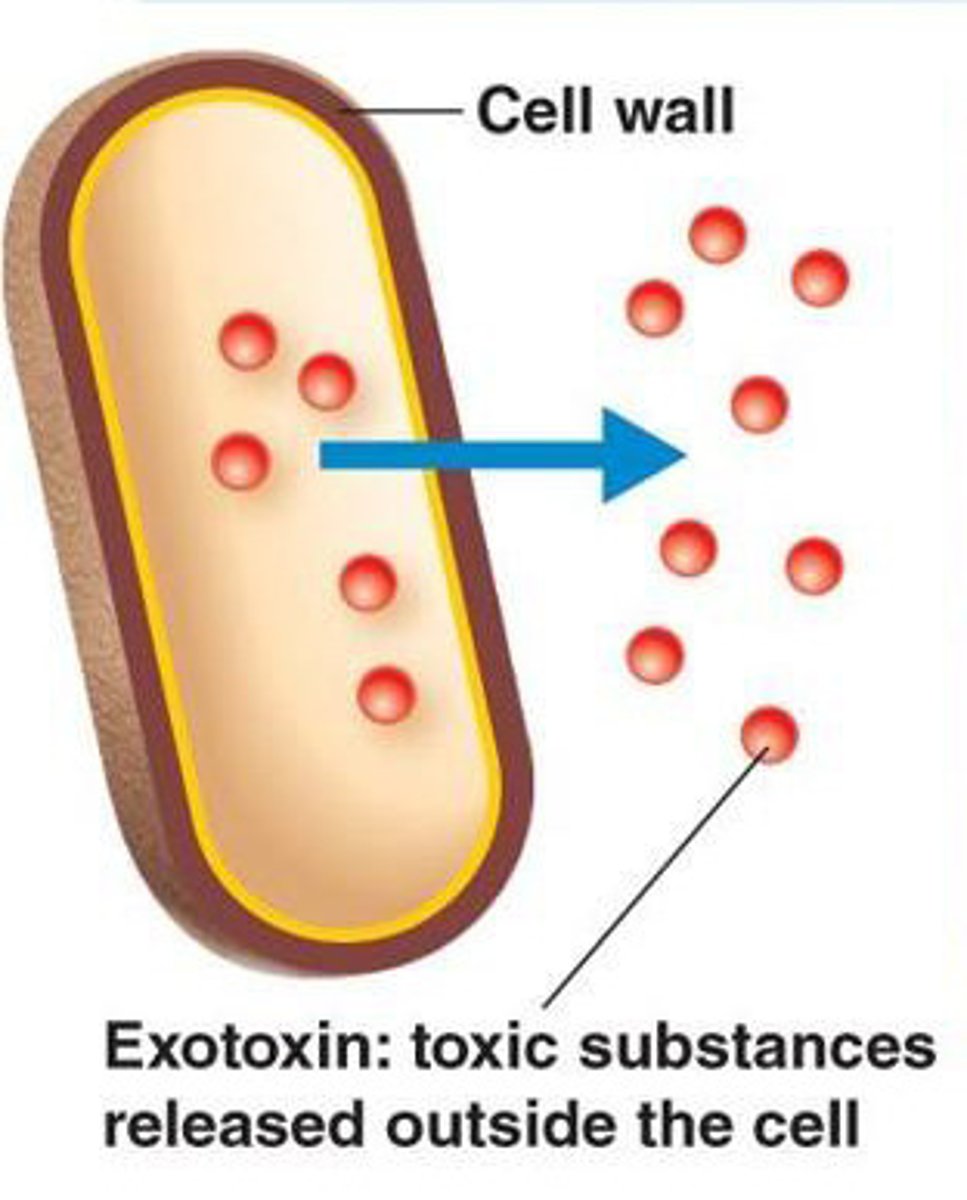
Enterotoxins
Exotoxins that affect cells lining the gastrointestinal tract
Neurotoxins
Exotoxins that affect the nervous system
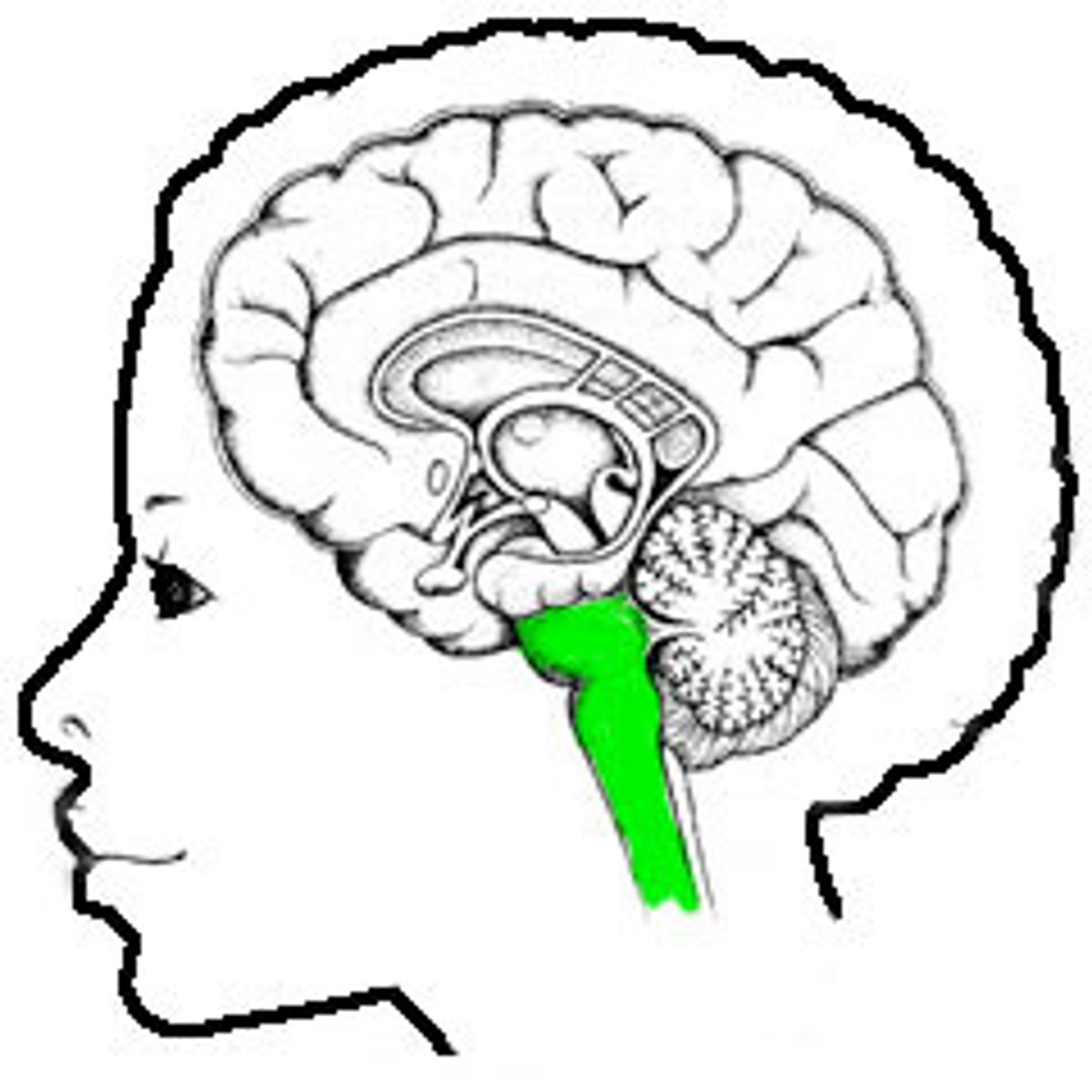
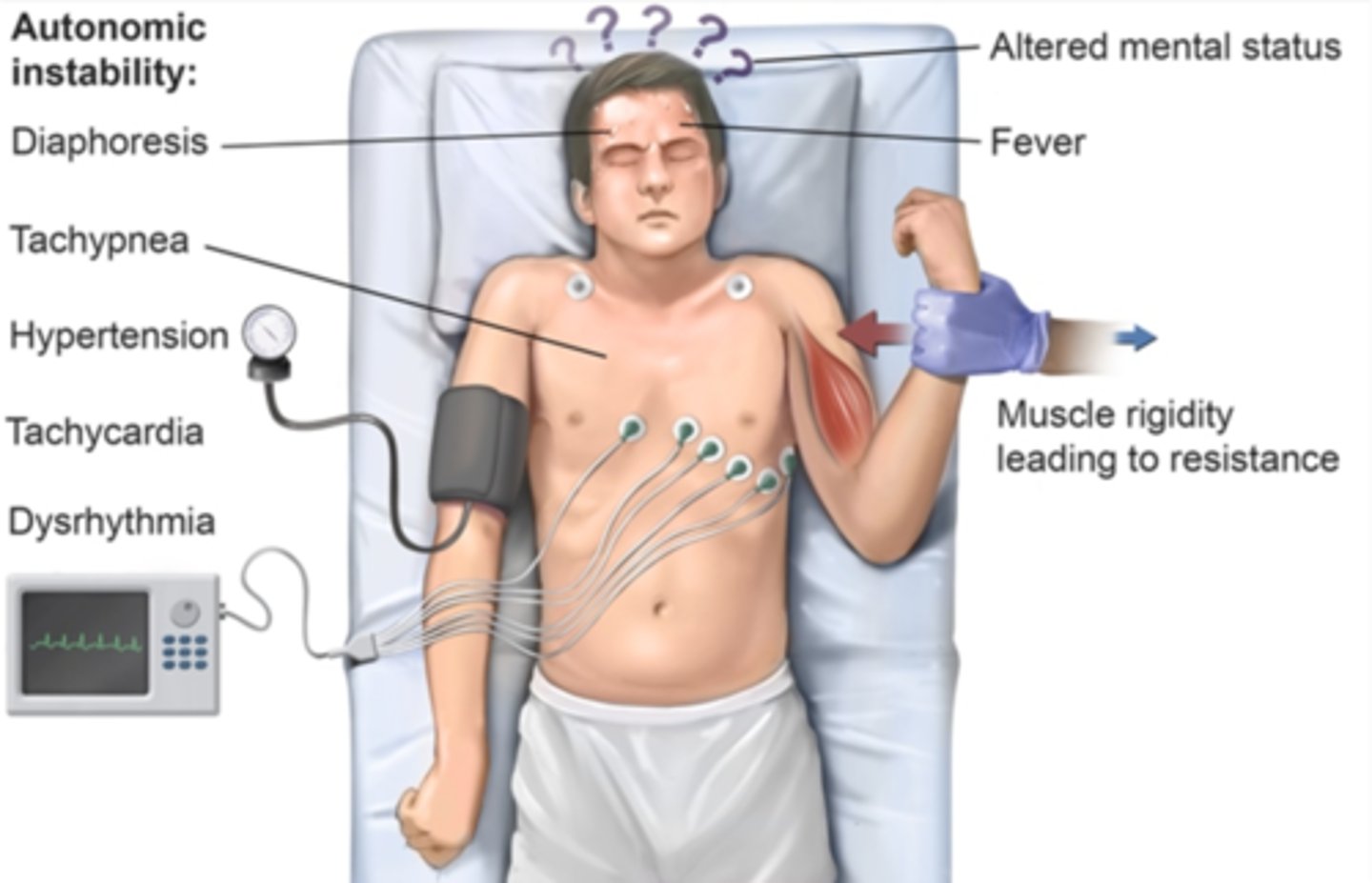
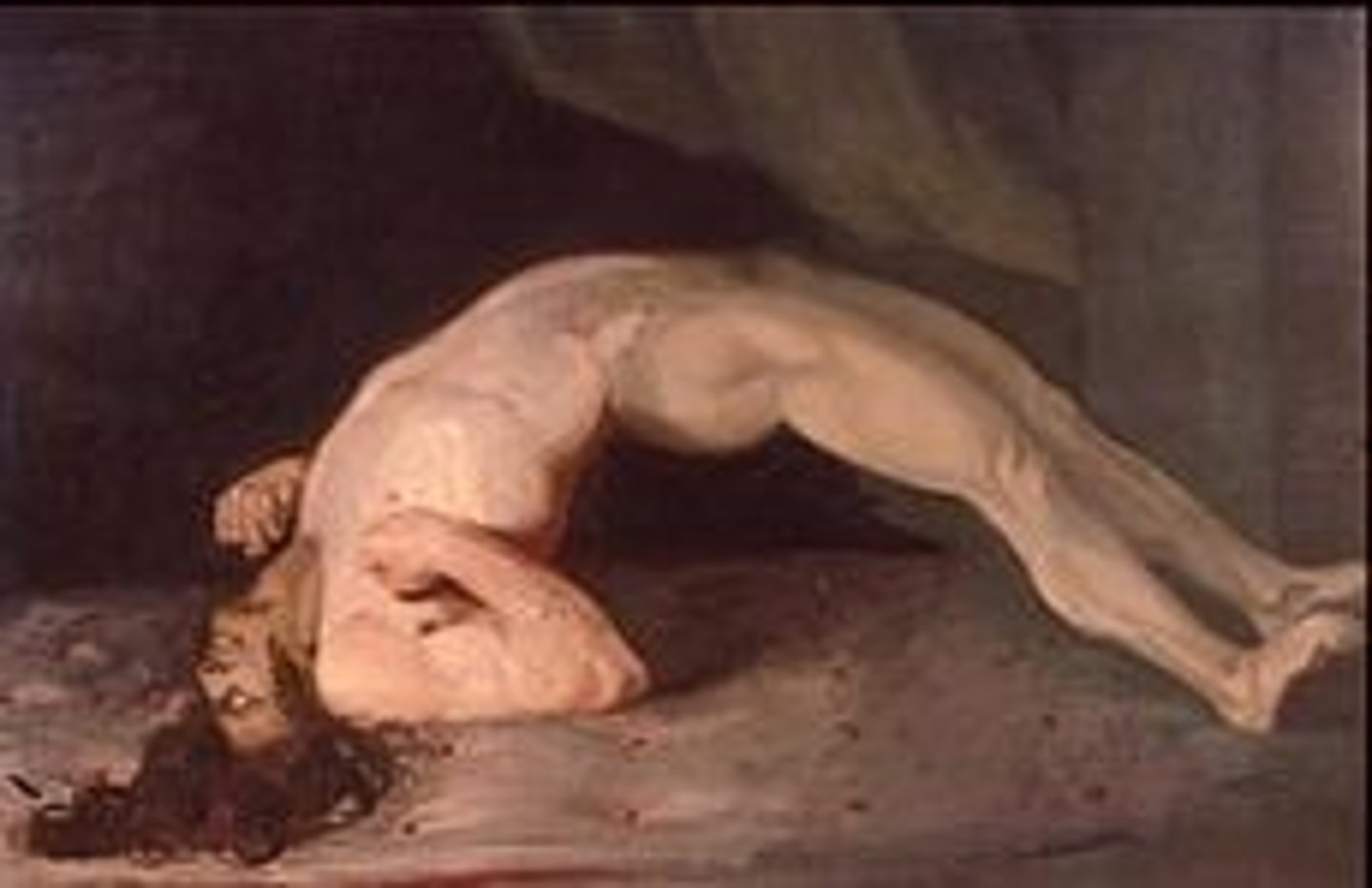
Opisthotonus
Abnormal posture seen in severe tetanus --> the back becomes extremely arched due to muscle spasms

Clinical specimens
Collected from patients and used to diagnose/follow the progression of infectious diseases
What happens when specimens are improperly selected, collected, or transported?
The disease may not be correctly identified
Appropriate specimen
Healthcare providers must ensure that they take a specimen from the appropriate place
When should the specimen be collected?
Before antimicrobial therapy
Where should the specimen be collected?
In a sterile, disposable container
How can the specimen be protected?
Labeling a specimen and placing it in the correct temperature can prevent it from being damaged/contaminated
Bacteremia
The presence of bacteria in the blood
Septicemia vs bacteremia
Bacteremia is the presence of bacteria in the blood, septicemia is the presence and multiplication of bacteria in the blood
Phlebotomy
Incision into a vein (the technical term for drawing blood)
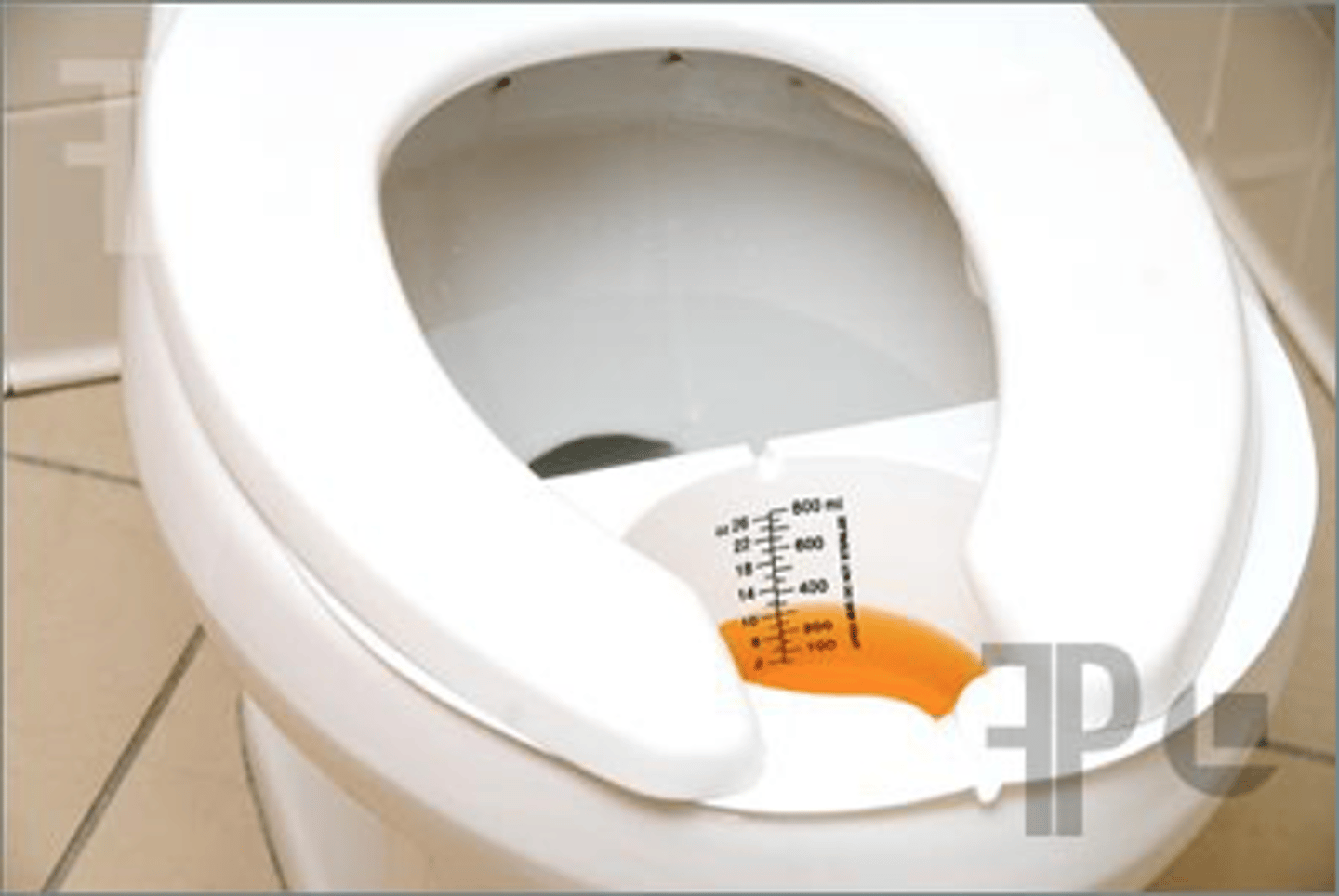
Why is urine a good specimen?
Urine is almost always sterile!
Clean-catch collection
The external urethra is cleaned with an antiseptic wipe --> removing the resident microbiota

Midstream collection
Urine sample collected in the middle of a flow of urine

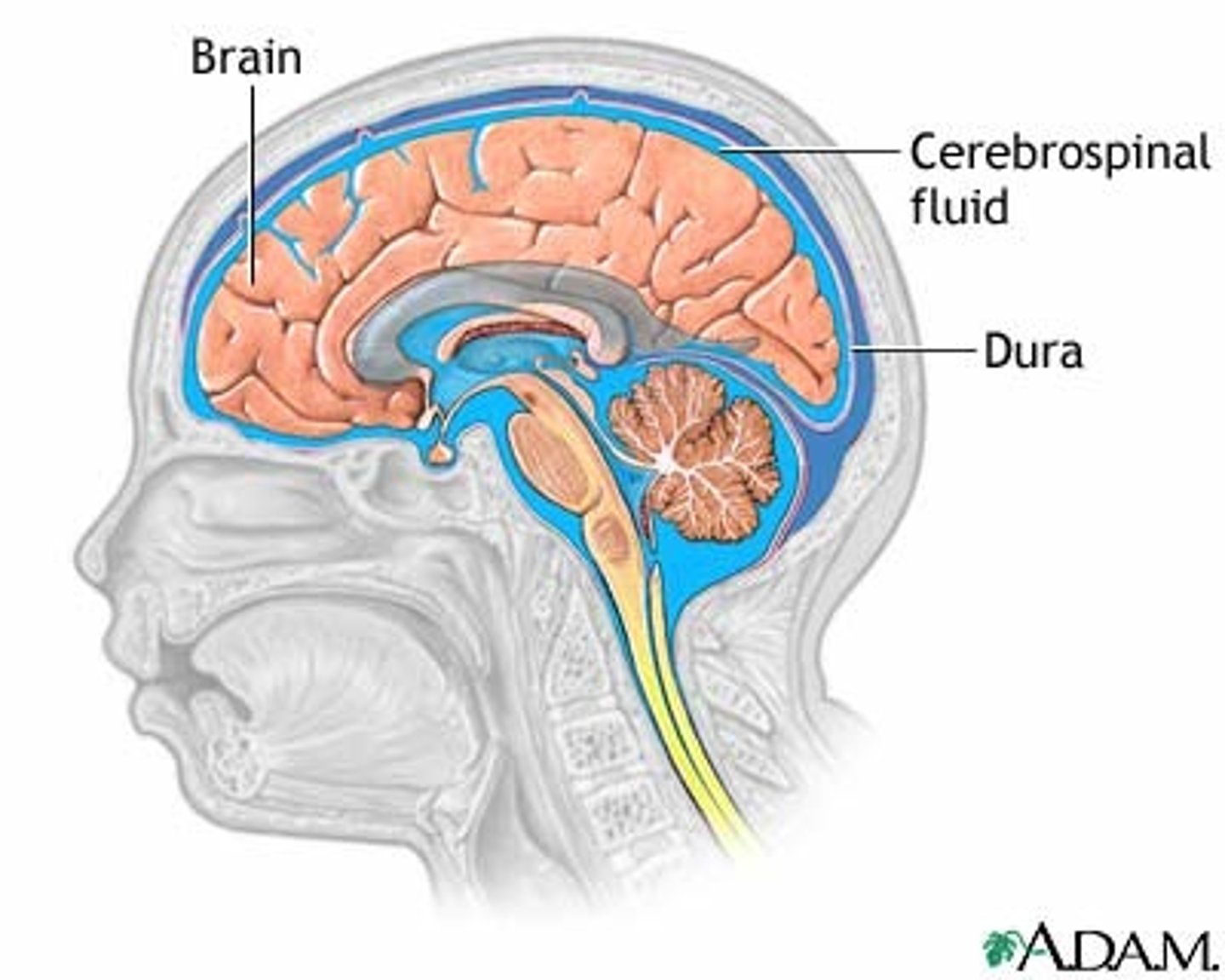
Cerebrospinal fluid
The fluid in and around the brain and spinal cord
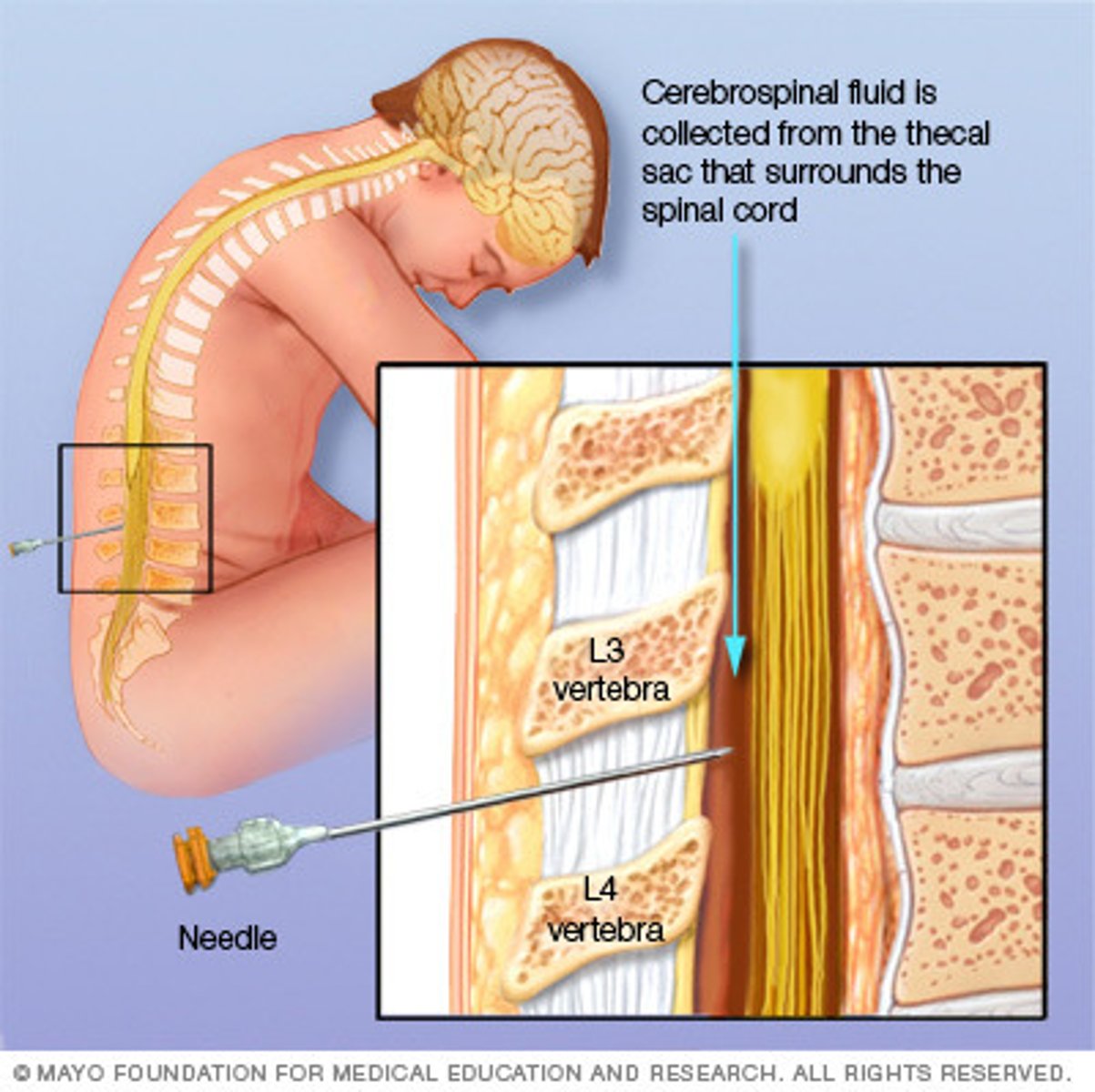
Spinal tap
A procedure in which a needle is inserted between L3 and L4 in order to withdraw CSF
STAT
Immediately

Sputum
Mucous expelled from the lungs by coughing
When should a sputum specimen be collected?
First thing in the morning, as mucous builds up over night
What are throat swabs collected for?
They are used to test for acute pharyngitis
Pharyngitis
Inflammation of the pharynx (sore throat)
How are specimens collected from shallow wounds?
Using swabs

How are specimens collected from deep wounds?
Using needles

Why is it important to process fecal specimens quickly?
A decrease in temperature could kill some pathogens
Clinical health
Deals with personal healthcare issues and treatment (at the individual level)

Public health
Deals with healthcare issues and treatment on a community/societal level

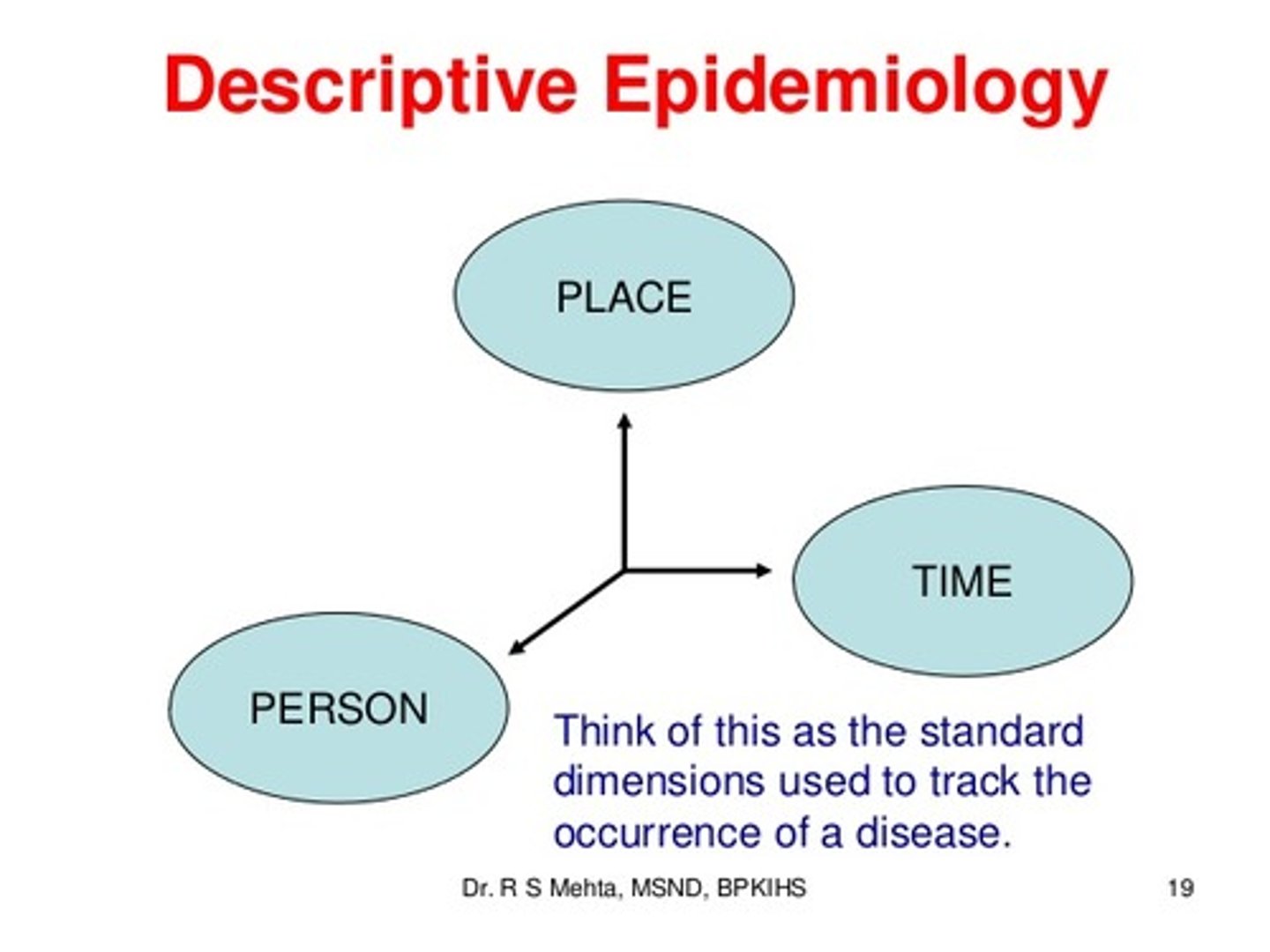
Epidemiology
The study of the incidence, spread, and control of diseases that affect large numbers of people
Distribution of disease
HOW a disease spreads in a population (who, when, where)
Determinants of disease
Factors that influence the likelihood of disease
Descriptive epidemiology
Epidemiology concerned with the investigation of the distribution of disease
Analytic epidemiology
Epidemiology concerned with the investigation of the determinants of disease
Sir Austin Bradford Hill
British epidemiologist who came up with a set of criteria to determine whether exposure causes a specific disease
Strength of association
How strong is the relationship? strong? moderate? weak?
Consistency
Have other studies consistently found a similar association?
Specificity
Does one exposure lead to one disease?
Temporality
Does the exposure come before the disease?
Biological gradient
Does the disease severity increase with increasing levels of exposure?
Plausibility
Does the association make sense in the light of current biological knowledge?
Coherence
Do new findings align with known facts about the disease?
Experimentation
When someone is no longer exposed, does the disease resolve?
Analogy
Has a similar relationship been observed between similar exposures and similar diseases?
Risk ratio
Incidence
The number of new cases of a disease
Prevalence
The percentage of people within a population who have a specific disease
Mortality
Death rate
Endemic
A disease that has a steady incidence rate in a population over time
Epidemic
A regional outbreak of a disease
Pandemic
An epidemic that is geographically widespread
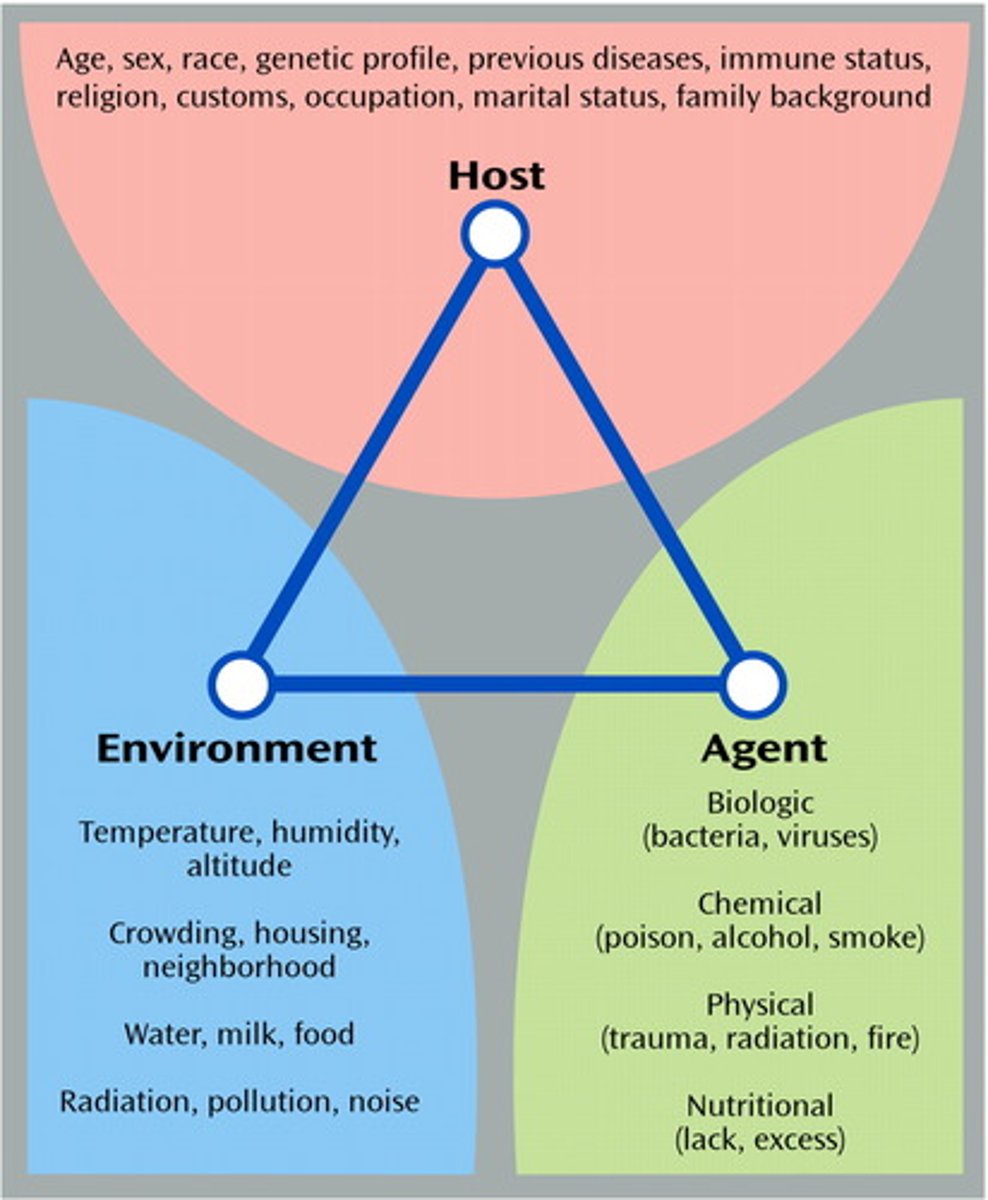
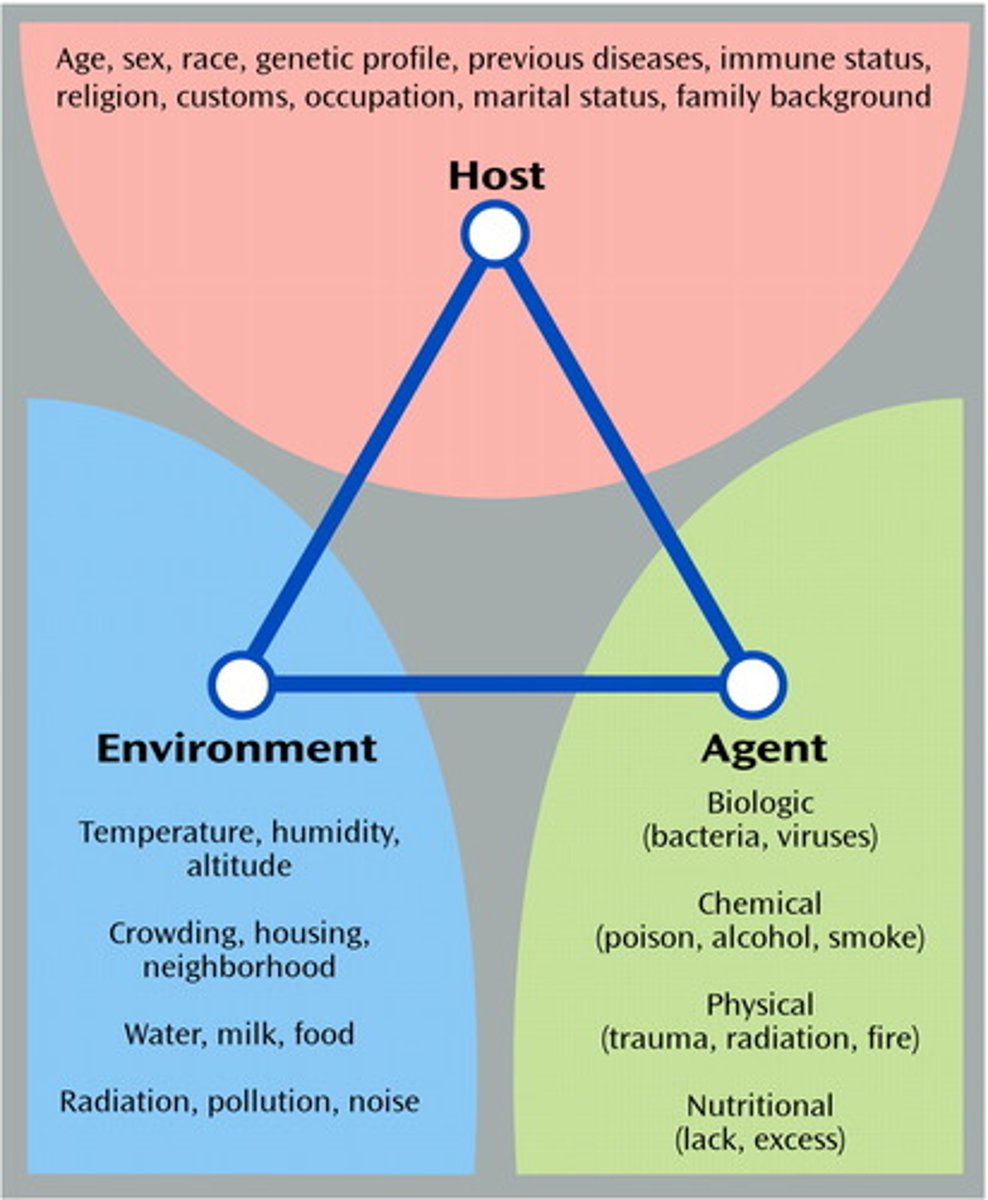
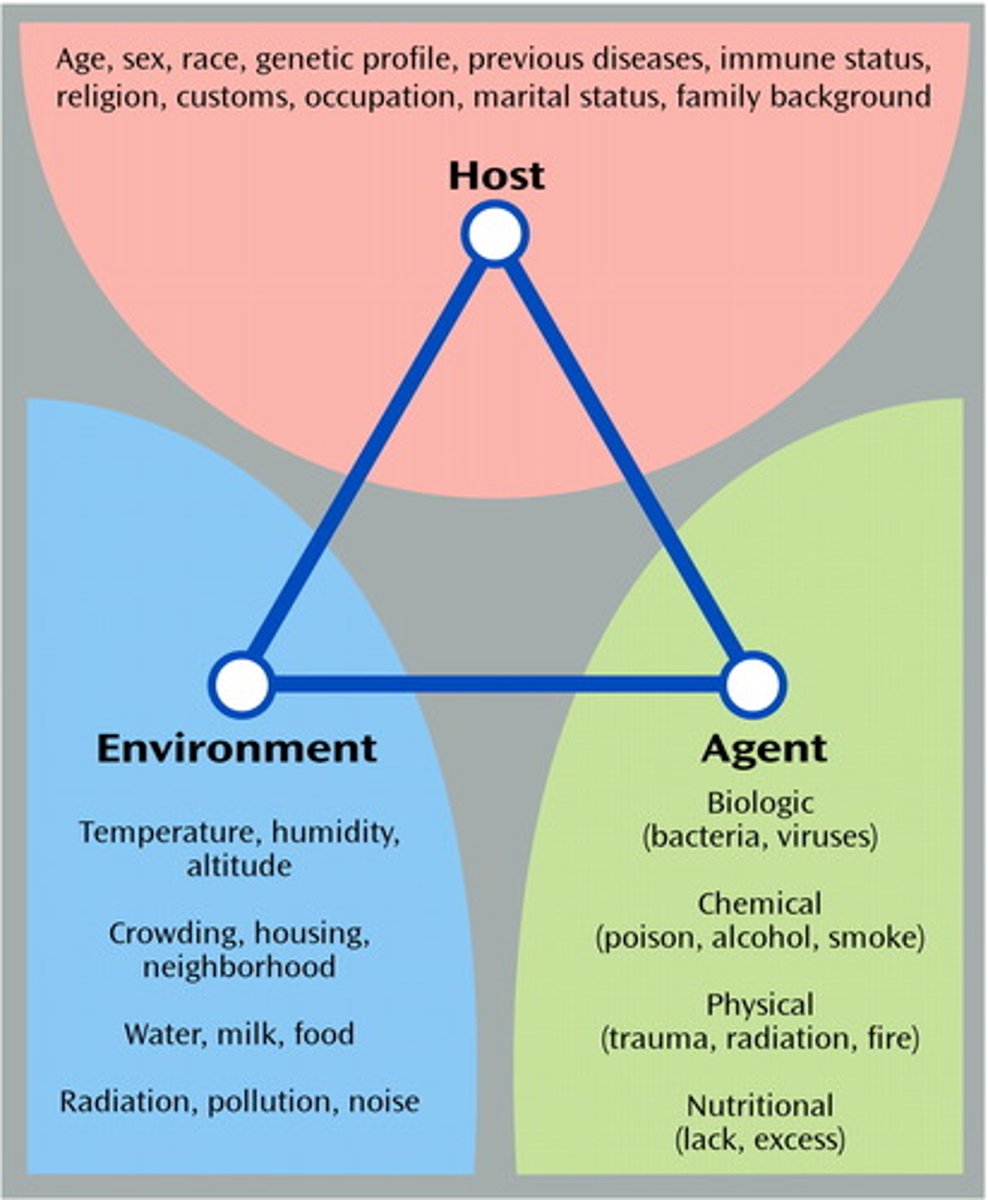
Epidemiologic triad
Host, agent, environment
Chain of infection
1. Infectious agent
2. Reservoir
3. Portal of exit
4. Mode of transmission
5. Portal of entry
6. Susceptible host
Reservoir
The habitat in which the agent lives, grows, and multiplies
Living reservoirs
Humans, animals, insects

Non-living reservoirs
Soil, water, food

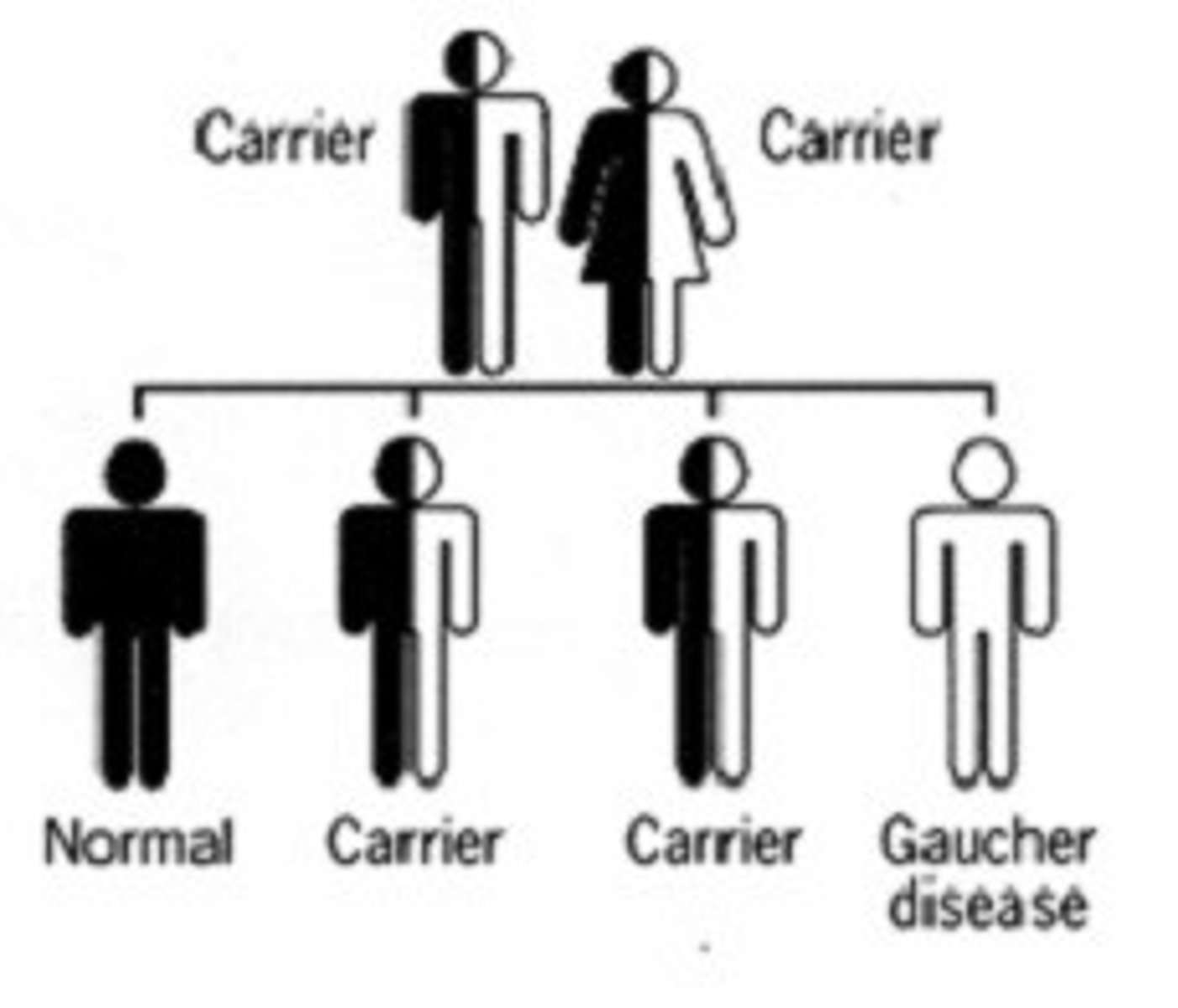
Carriers
People who are colonized with a particular pathogen (which is not currently causing an infection) but who transmit it to others
Zoonotic disease
A disease that can be passed between animals and humans

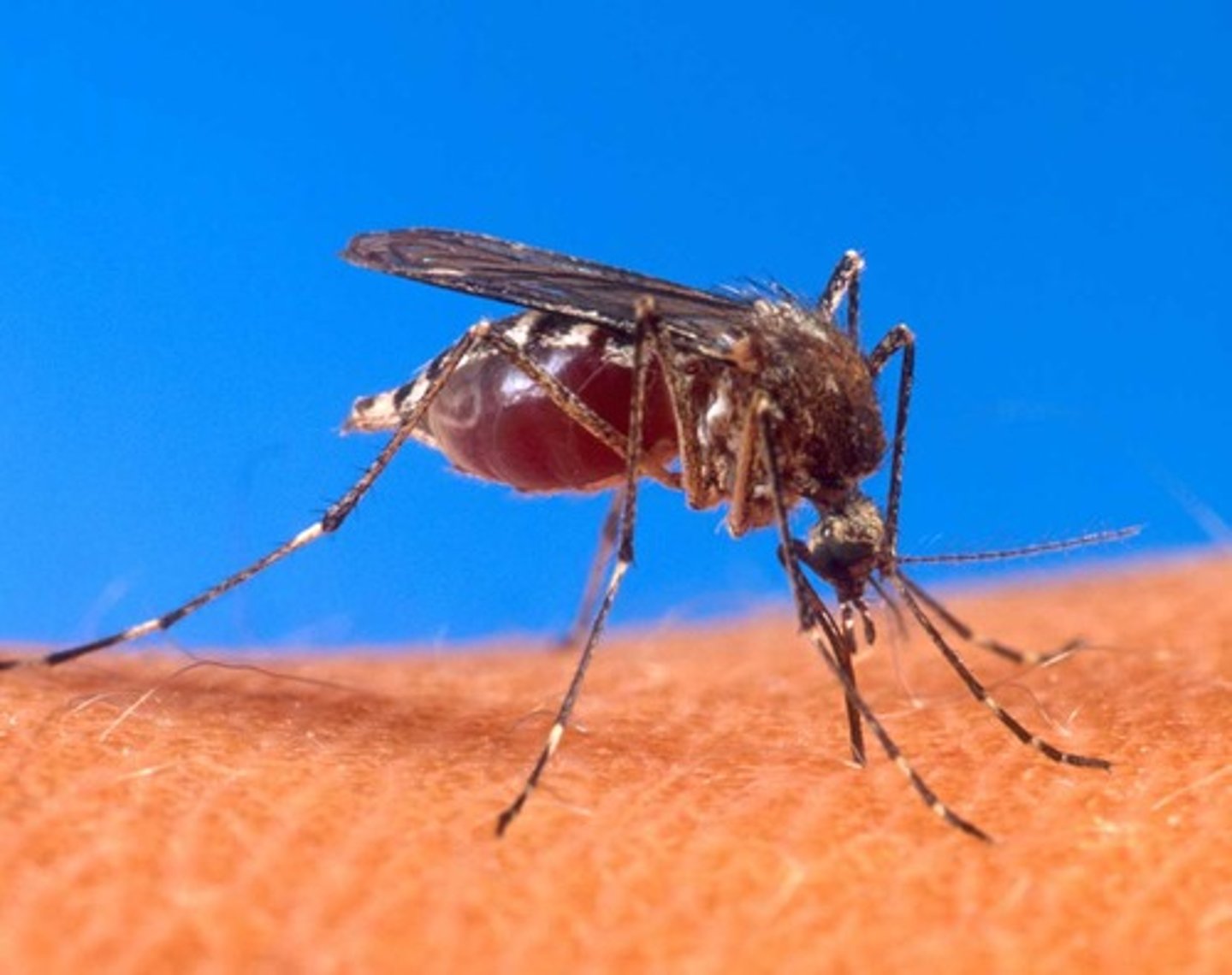
Vectors
Organisms that carry pathogens from person to person
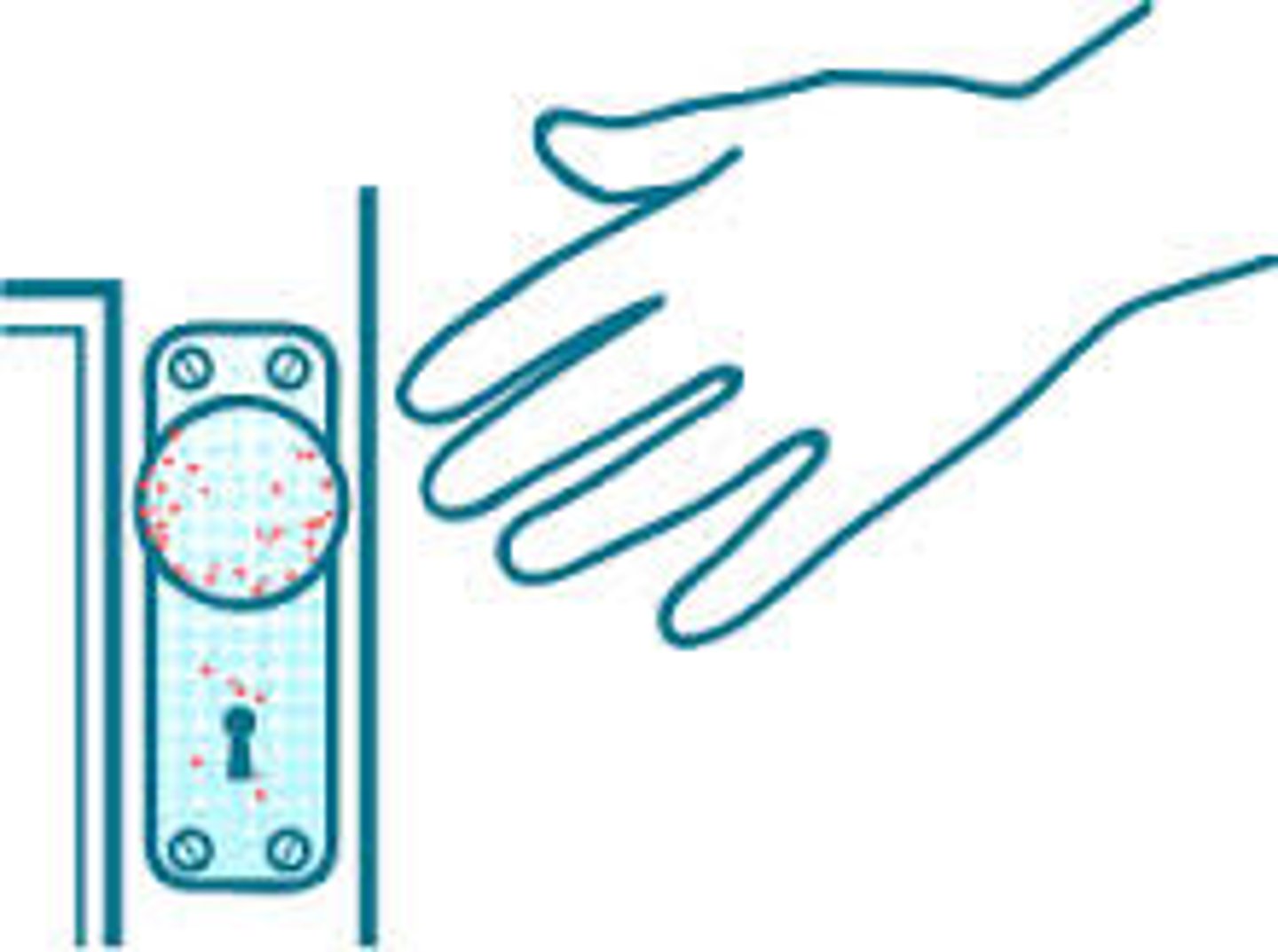
Fomites
Inanimate objects that transfer pathogens from person to person

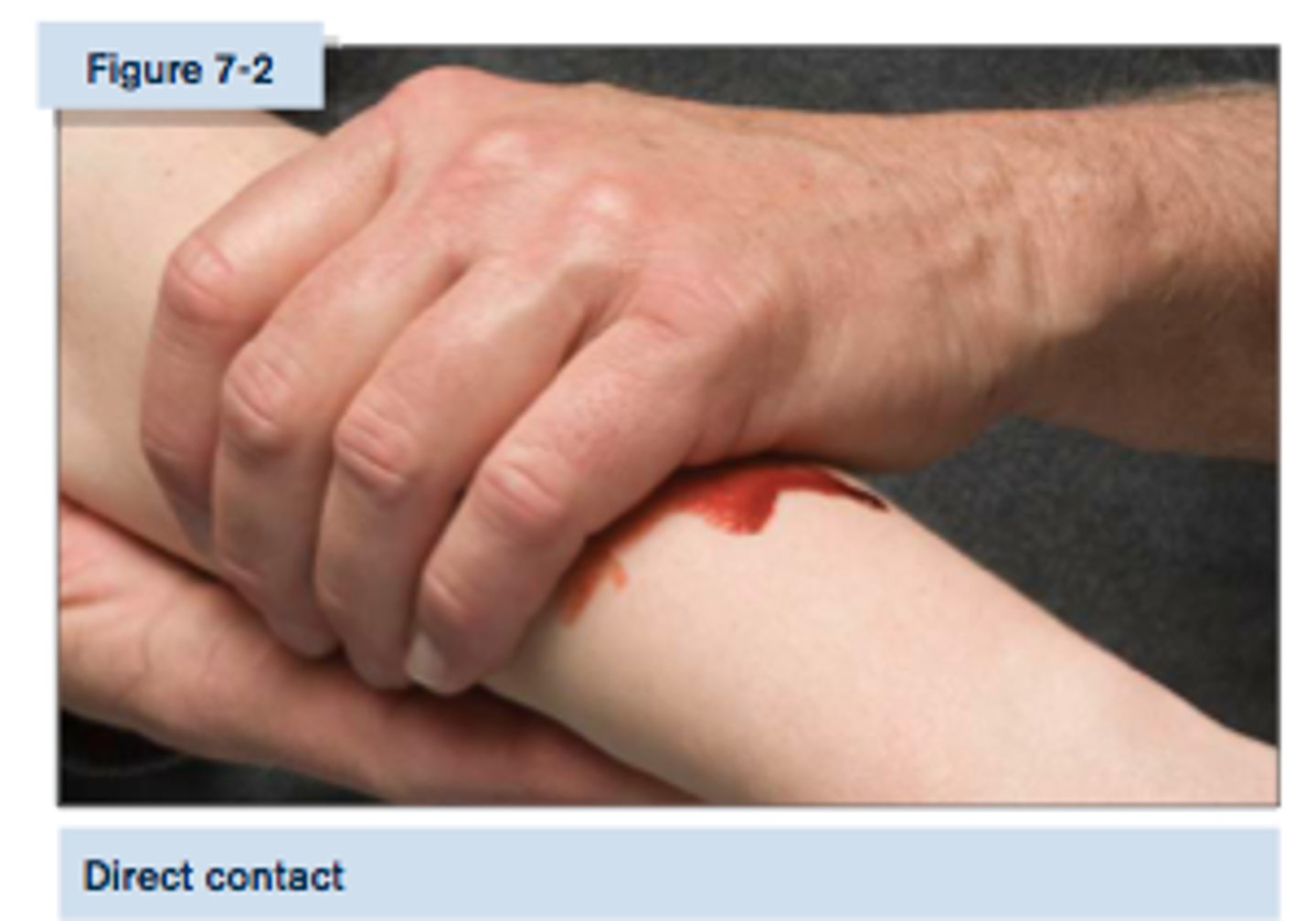
Direct contact
Touching or coming in contact with a infected person's blood or saliva
Indirect contact
Exposure/transmission of a disease through droplets, vectors, food/water, or fomites