Unit 15.2 - Emotion II: Fear and Aggression
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the differences between anger and aggression? (2 per one)
Anger
Emotion
Can be caused by a multitude of situations: hurt feelings, stress, frustration, etc.
Agression
Not an emotion
Behavioral result of anger

What is the type of aggression shown in the two images?
Predatory Agression
What is the main difference between predatory and affective aggression?
Affective is only for show, but predatory causes an animal to actually attack
Predatory aggression has ____ vocalizations while affective aggression has ____ vocalizations (less or many)
Less, many
Which form of aggression (predatory or affective) shows high sympathetic activity? Which one shows no sympathetic activity?
Predatory = no activity
Affective = high activity
What is the pathway for predatory aggression?
Cortex → Amygdala → lateral hypothalamus → medial forebrain bundle → VTA → predatory aggression
(Quiet, goal-directed attack)
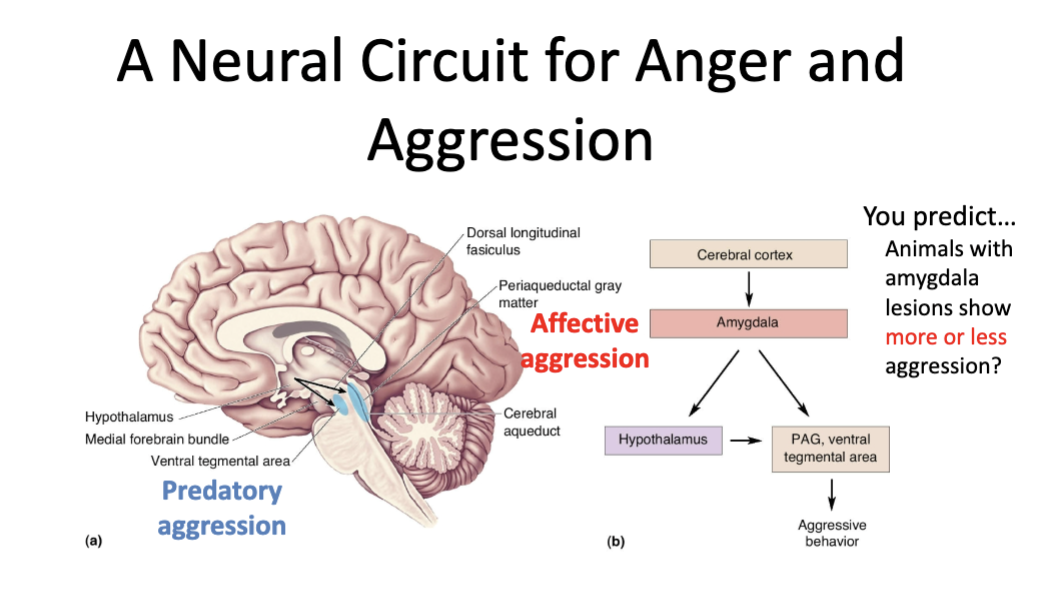
What is the pathway for affective aggression?
Cortex → Amygdala → medial hypothalamus → dorsal longitudinal fasciculus → PAG → affective aggression
(Defensive, threatening, high-autonomic arousal)
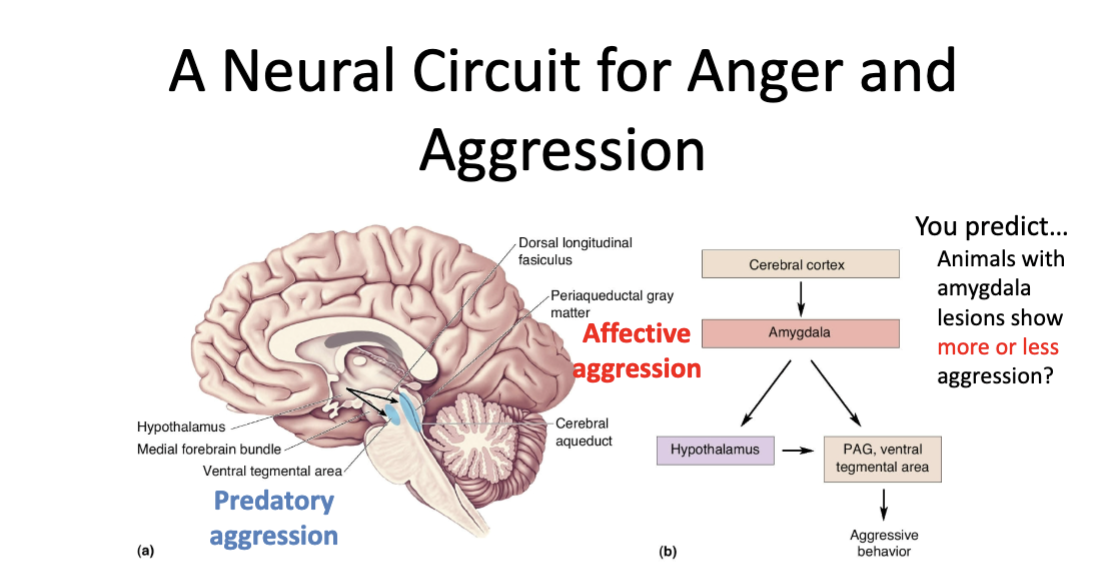
Do monkeys with amygdala lesions show more or less aggression? What happened to their “status” in the hierarchy?
They displayed less aggression, causing whoever was at the top to fall to the bottom of the hierarchy
What two surgeries were done to reduce human aggression?
Amygdalectomy
Psychosurgery
What is “roid rage”?
Uncontrolled outbursts of anger and aggression in athletes taking steroids which have a similar effect as testosterone
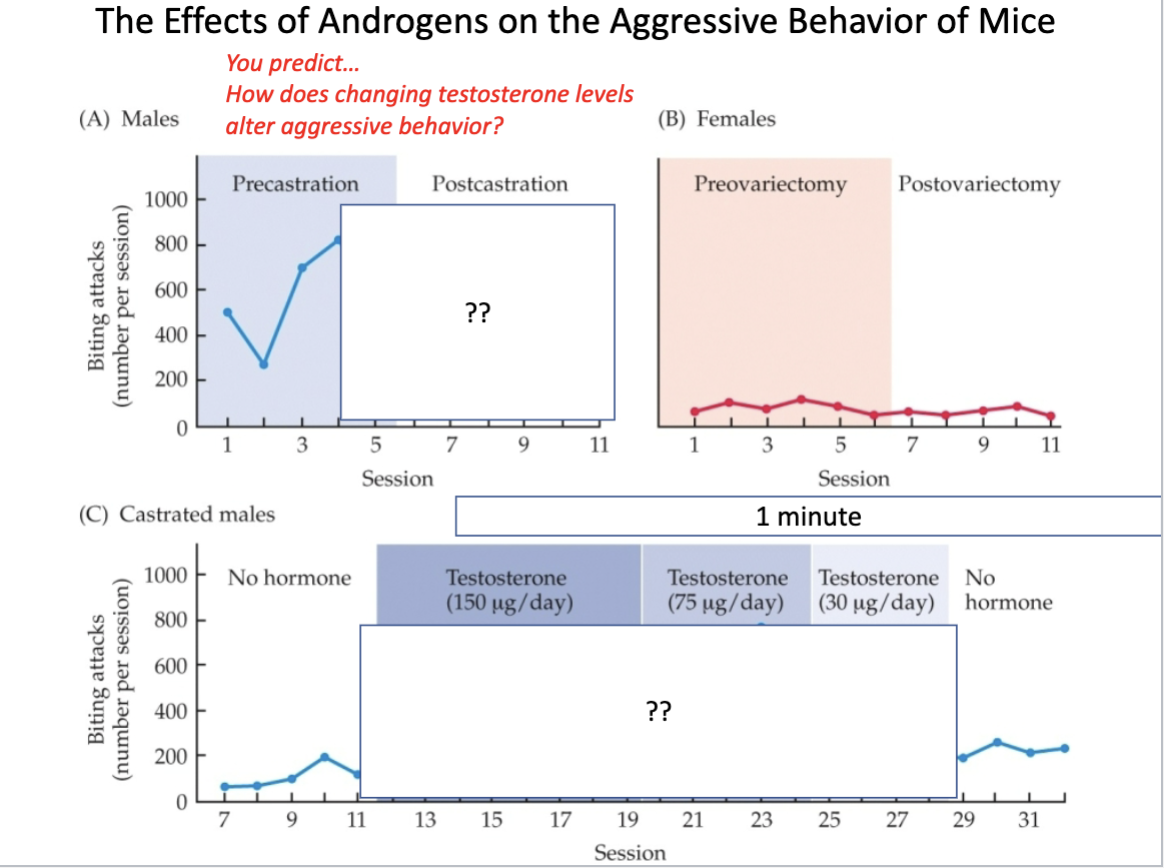
How would aggression change based on testosterone levels?
Aggression decreases with testosterone

T or F We have a very clear understanding of the relationship between testosterone and aggression in humans.
False, it is not as clear as within animals
In a study where women were given testosterone and a placebo, who bargained more fairly? What does this say about testosterone?
The women with testosterone bargained more fairly, meaning that testosterone does not always have a direct impact on anger (in women at least)
Removal of which of the following options elicits sham rage?
Removal of the cerebral hemispheres but not the hypothalamus
Removal of the hypothalamus but not the cerebral hemispheres
Removal of both
Removal of the cerebral hemispheres but not the hypothalamus
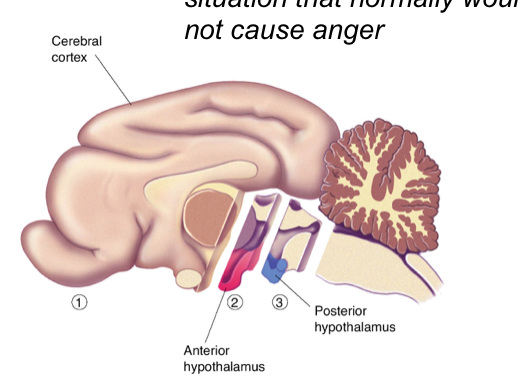
Sham rage can be revered with additional lesions in what part of the brain?
The posterior half of the hypothalamus
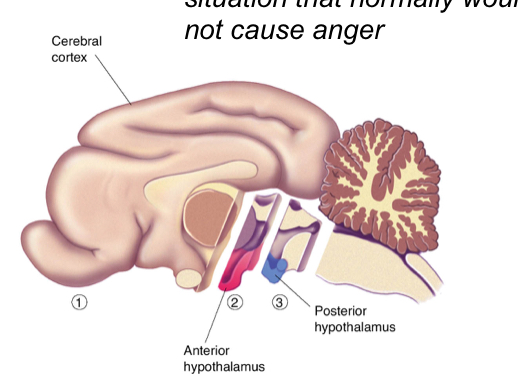
What is sham rage?
Rage in a situation that normally would not cause anger
What happens if we electrically stimulate the medial hypothalamus in cats?
The cats display affective aggression with high levels of ANS sympathetic activity
What happens if we electrically stimulate the lateral hypothalamus in cats?
The cats display predatory aggression without ANS sympathetic activity
How do we stimulate specific subpopulations of neurons in small region?
Optogenetics
What happened when scientists stimulated the hypothalamus in mice brains vs. cat brains?
Cats showed aggression mice did not
What did scientists do to test if the hypothalamus could also cause aggression in mice even though they did not from electrical stimulation? Did it work?
They used optogentics to target small set of neurons in hypothalamus. Yes, it did work, the mice showed aggression.
What symptoms do animals display (other than aggression) when stimulating the hypothalamus? (4)
Sniffing, panting, eat, or express fear
Aggression is ____ related to 5HT (serotonin) levels (inversely or directly?)
Inversely
When you block serotonin in animals, what is the result on their aggression?
They become more aggressive
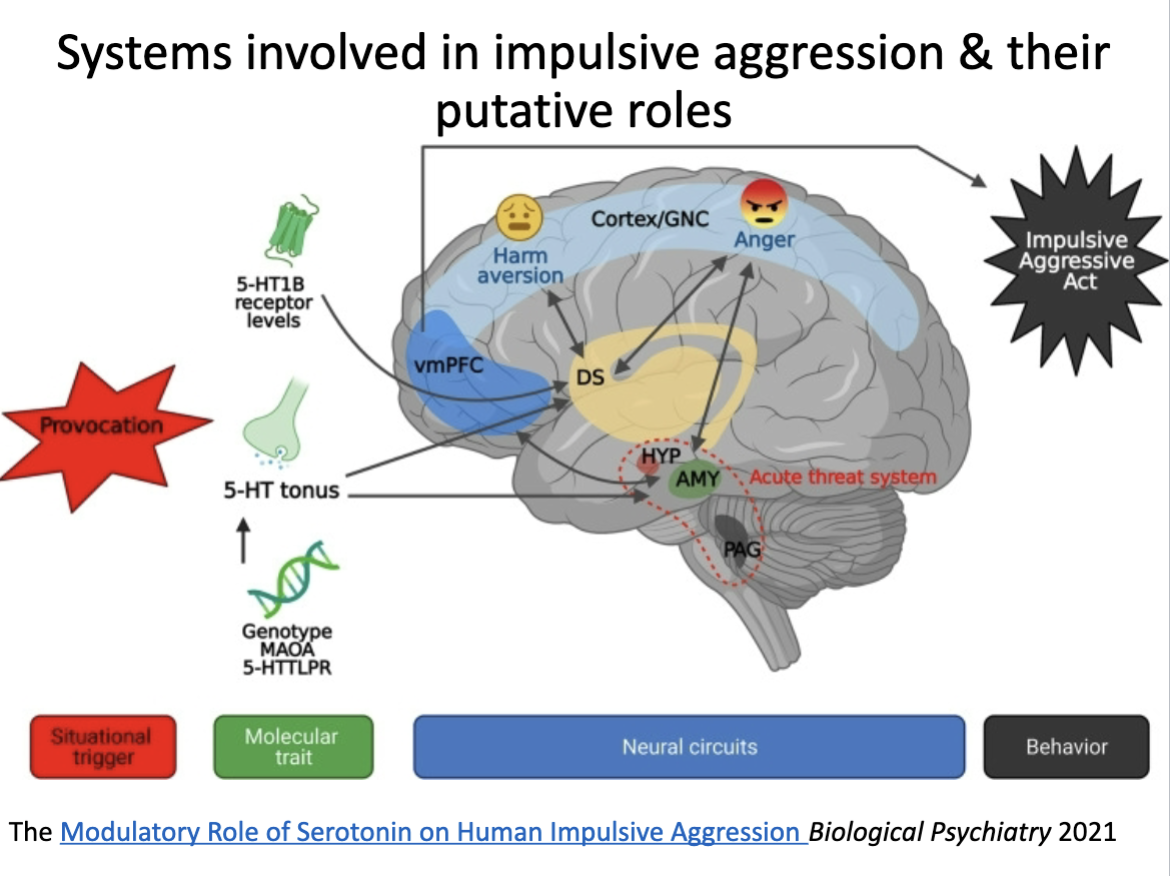
Maybe memorize?
Okie broskie
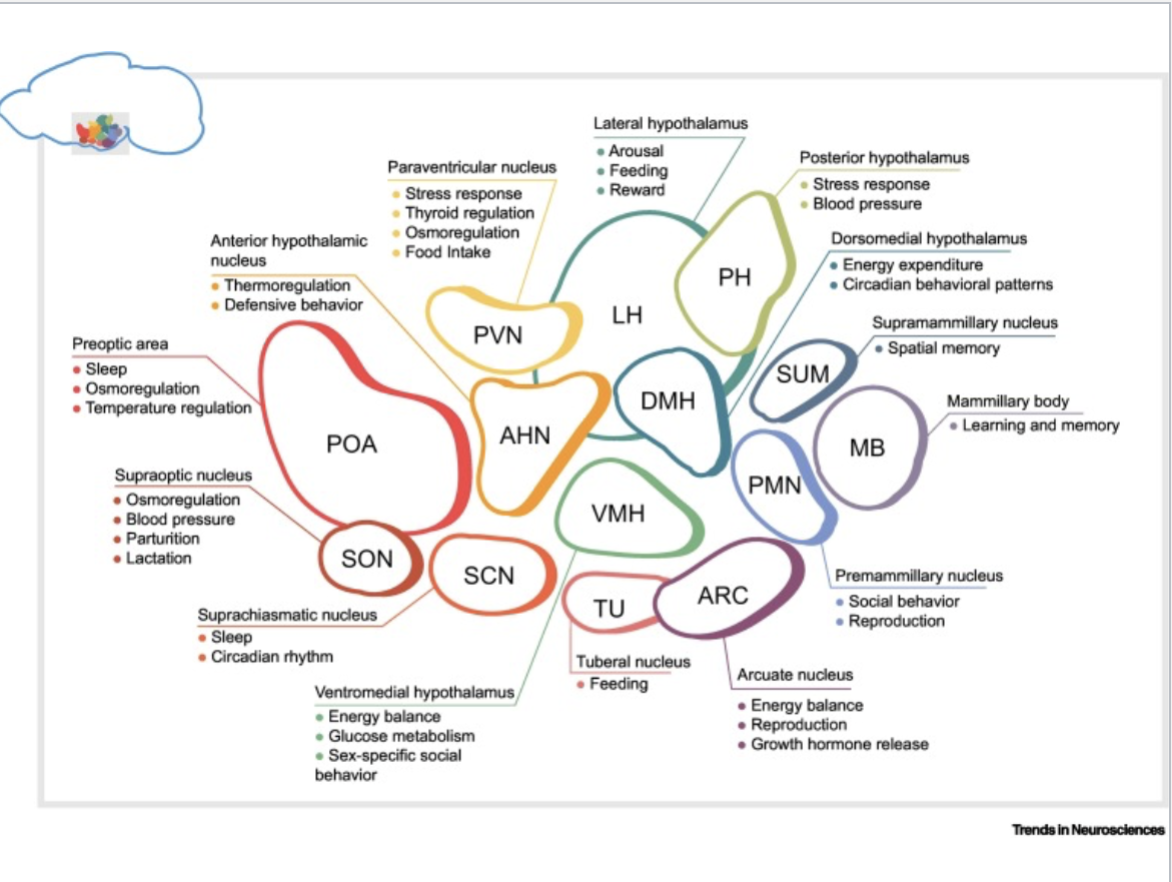
This image shows cellular diversity in the hypothalamus. Just understand that the hypothalamus regulates A LOT.
Got it :p