Essentials of Biology Exam 1 Study Guide
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What is the scientific method?
The process of objectively establishing facts through testing and experimentation.
What is a hypothesis?
A testable statement
What is a conclusion for an experiment?
A judgement based on the information obtained
What is a control group?
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group.
What is an observation?
the action or process of observing something or someone carefully or in order to gain information.

What is a prediction?
A logical statement about what will happen if the hypothesis is correct. (If...then...)
What are the three components of an atom?
Protons, neutrons and electrons.
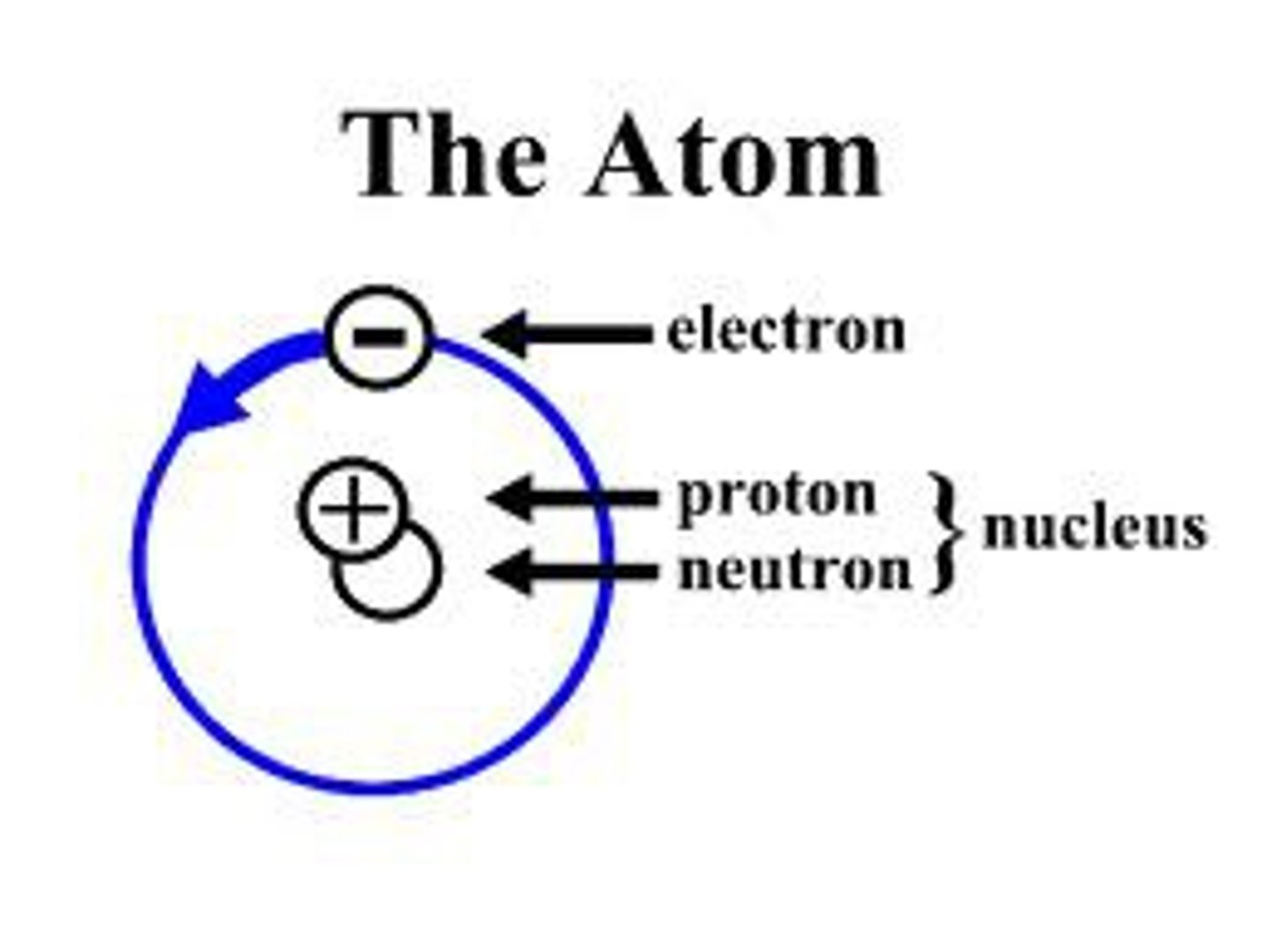
Where are is a proton located and what is the charge?
Located in the center of an atom. Protons have a positive charge.

Where is a neutron located and what is the charge?
Located in the center. Neutrons have no charge. (Neutral)
Where is an electron located and what is the charge?
Located in the outermost shell/region. Electrons have a negative charge.
What is an element?
A chemical substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions.
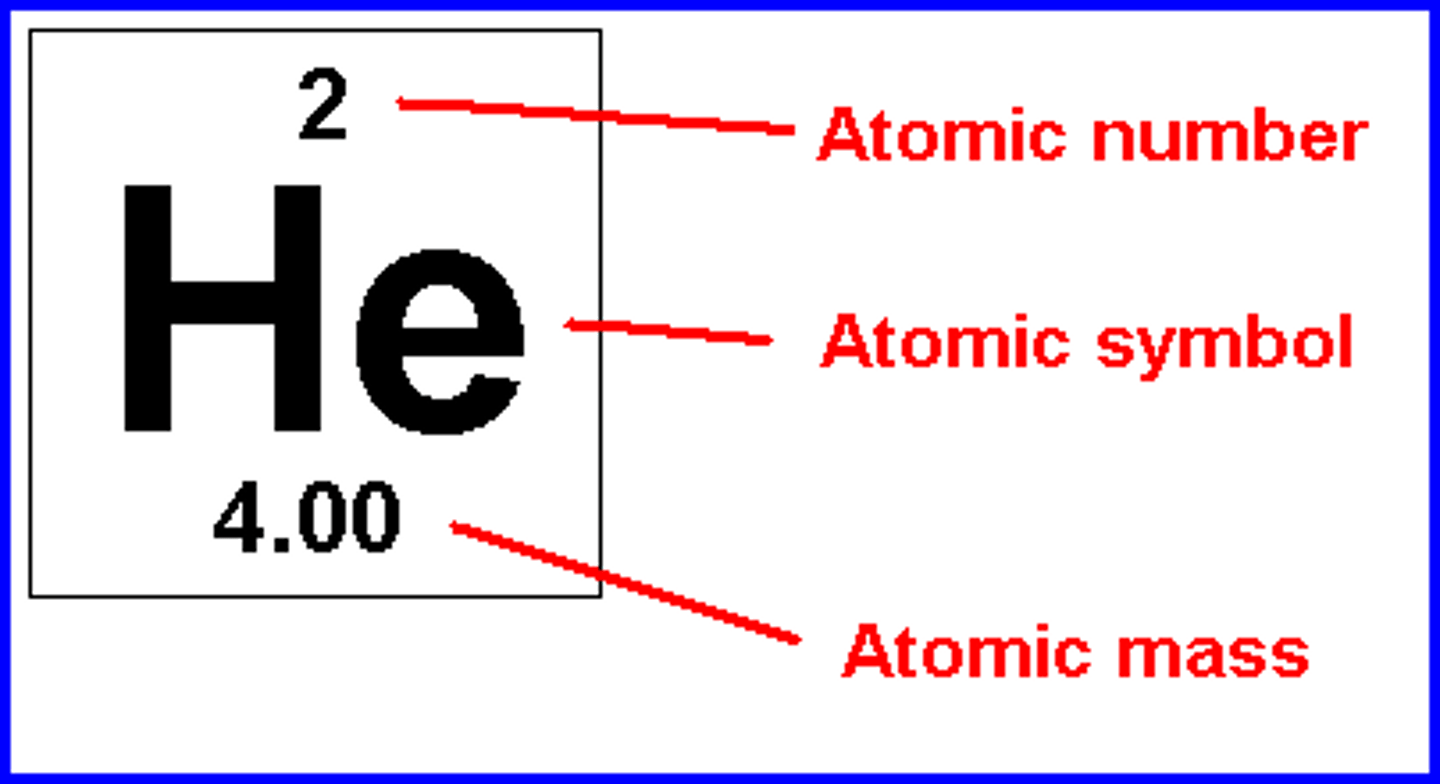
How are elements defined?
Elements are defined by the number of protons in the nucleus.
Why is carbon significant in an element?
Carbon gives the ability to form stable bonds with many other elements.

What is an isotope?
An isotope is a nuclear species with the same atomic number and position. (Different number of neurtrons)
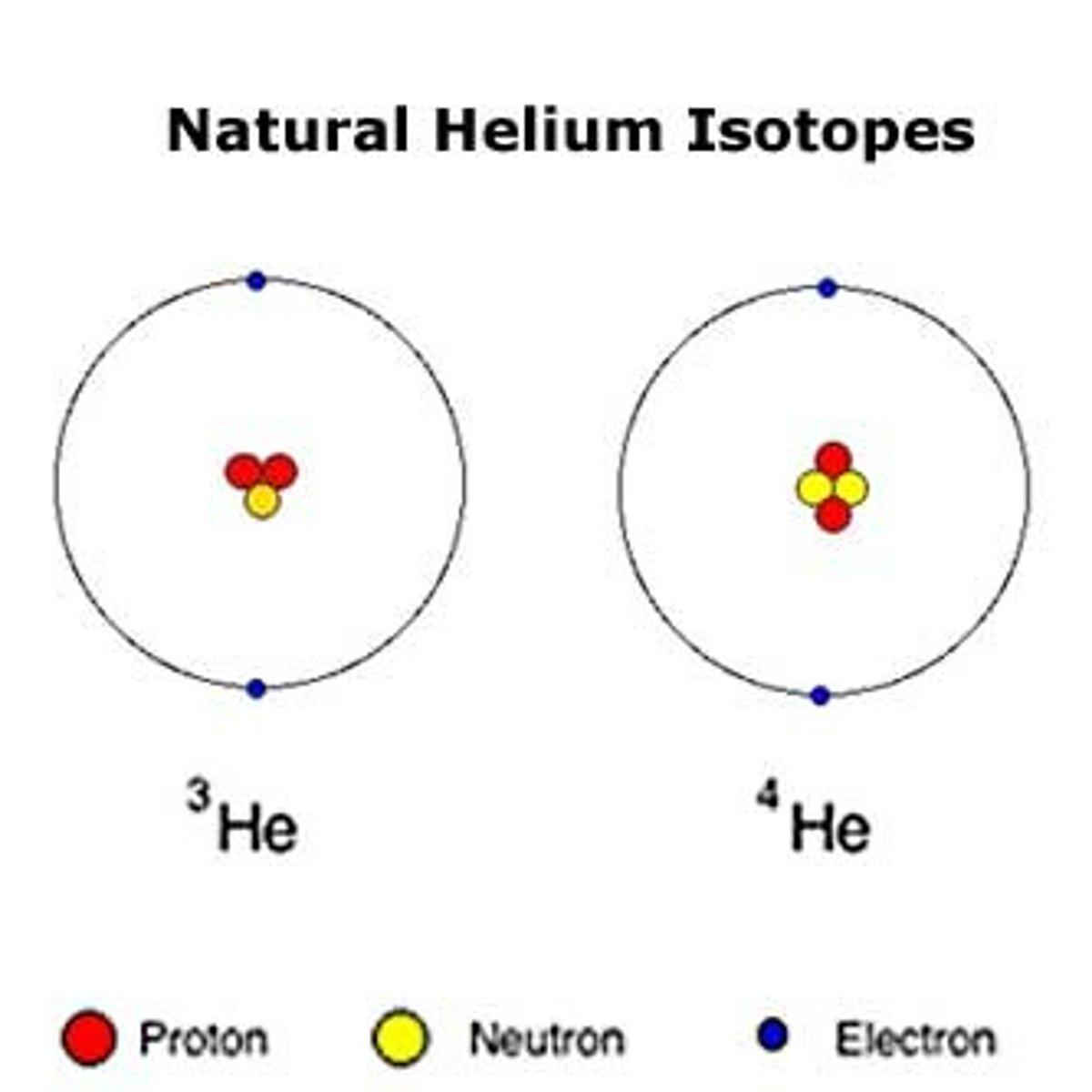
How can isotopes be used in medical research?
Isotopes can be used to diagnose and treat diseases.
How do you determine the number of electrons in an atom?
The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in an atom. (The atomic number)
What makes a stable atom?
A stable atom is based on the balance of the nucleus.
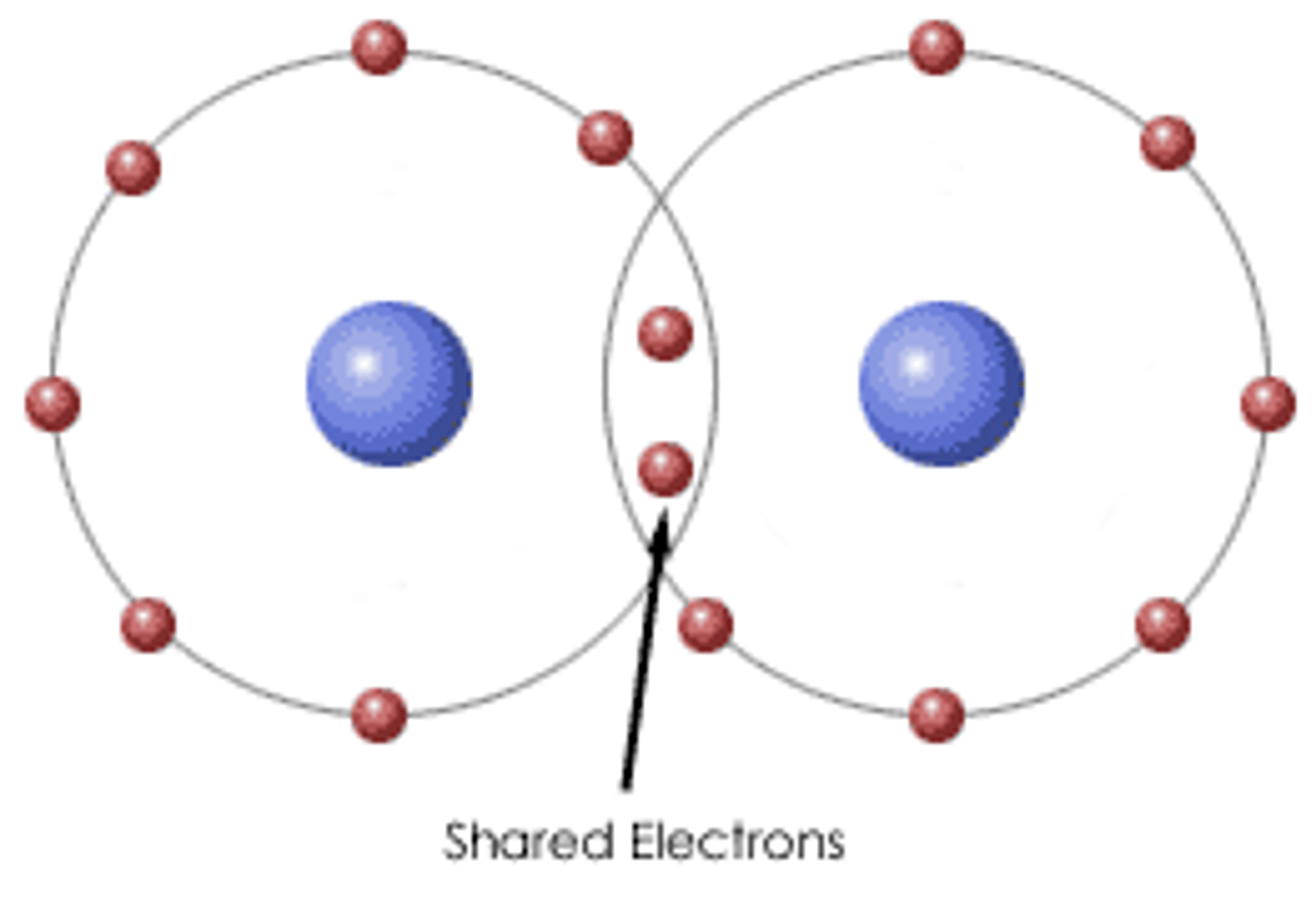
What is a chemical bond?
A chemical bond is the attraction between two atoms.
How are covalent bonds formed?
Covalent bonds are formed through the sharing of electrons.
What is the difference between a single double and triple covalent bond?
A single bond is when two atoms share one pair of electrons. A double bond is when two atoms share two pairs of electrons. (Four electrons) A triple covalent bond is when two atoms are sharing three electron pairs. (Six electrons) So the electrons shared is the difference.
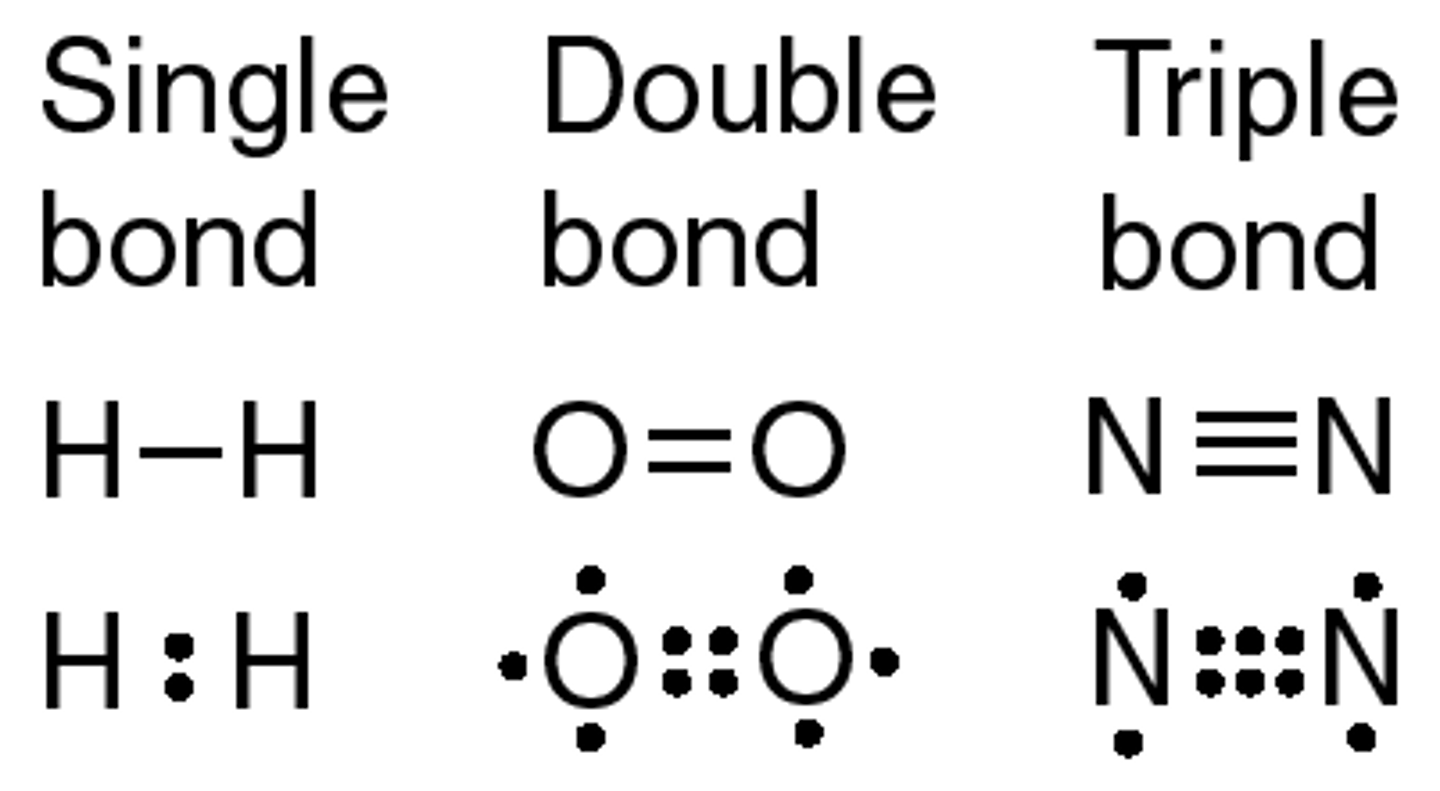
What does it mean when a molecule is polar/nonpolar?
Polar= an unequal distribution of charges/electrons
Nonpolar= an equal distribution (Symmentrical)
What are some examples of polar and nonpolar molecules?
Polar= water
Nonopolar= oil
How are ions formed? Why?
Ions are formed by the addition or removal of electrons from the outermost energy shell. Ions are formed to create stable atoms.
Why does salt dissolve in water?
Water can dissolve salt because the positive part of water molecules attracts the negative chloride ions and the negative part of water molecules attracts the positive sodium ions.
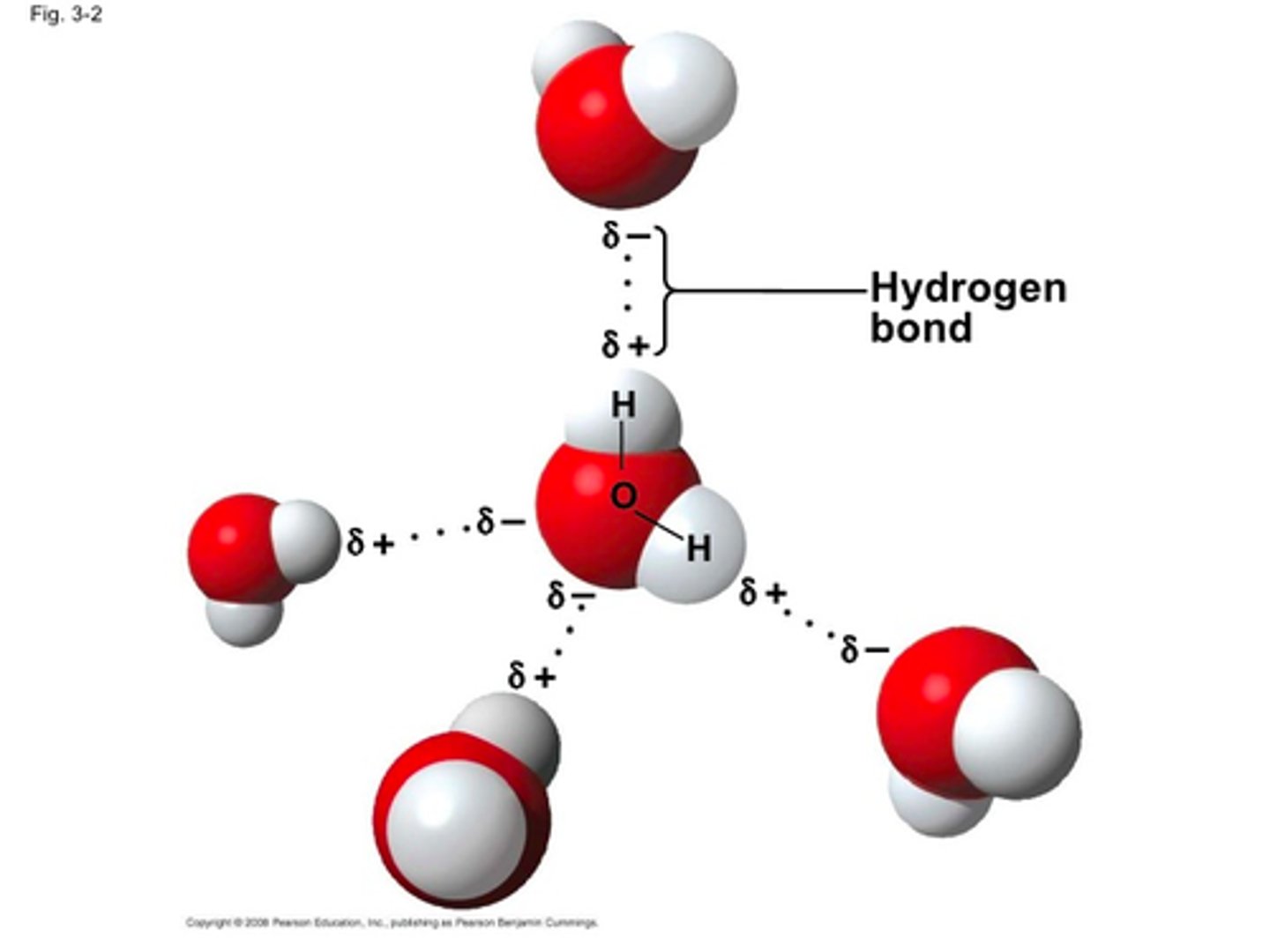
How do hydrogen bonds form?
Hydrogen bonds form when hydrogen atoms covalently bond to nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine.
How do Vander Waals interactions form?
Vander Waals interactions form from fleeting interactions between nonpolar molecules.
What happens in a chemical reaction?
Making and breaking of chemical bonds. Energy is used or released in the process.
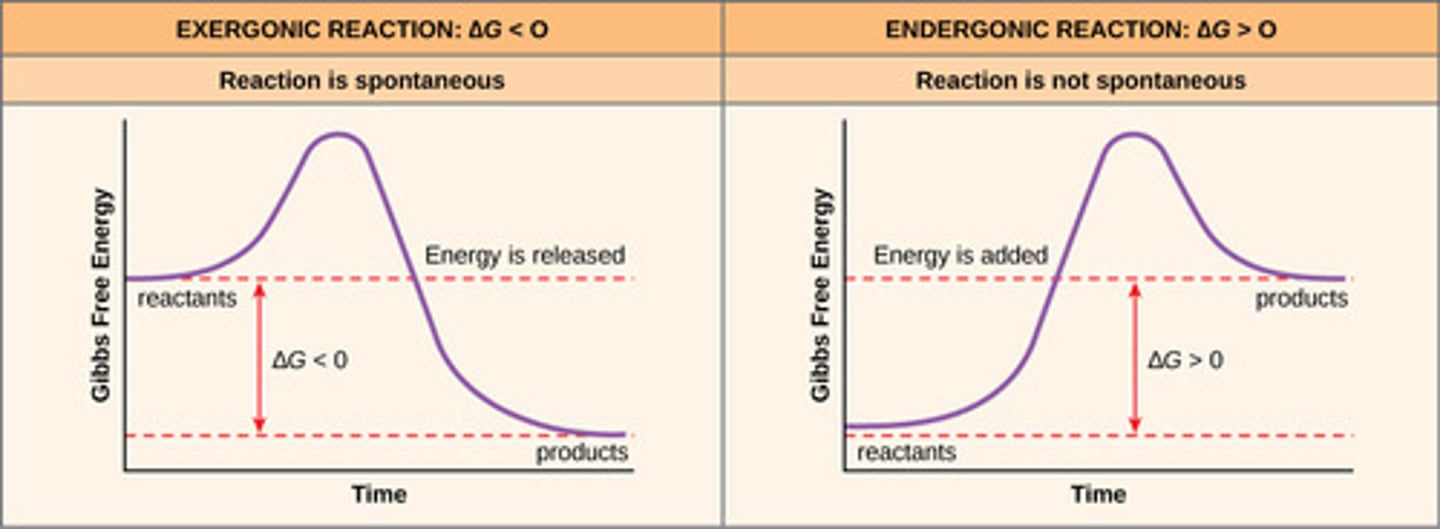
What is difference between an exergonic and endergonic reaction?
Exergonic Reaction= Free energy of reactants is greater/more than the free energy of products.
Endergonic Reaction= Free energy of the reactants is lower/less than the free energy of the products.
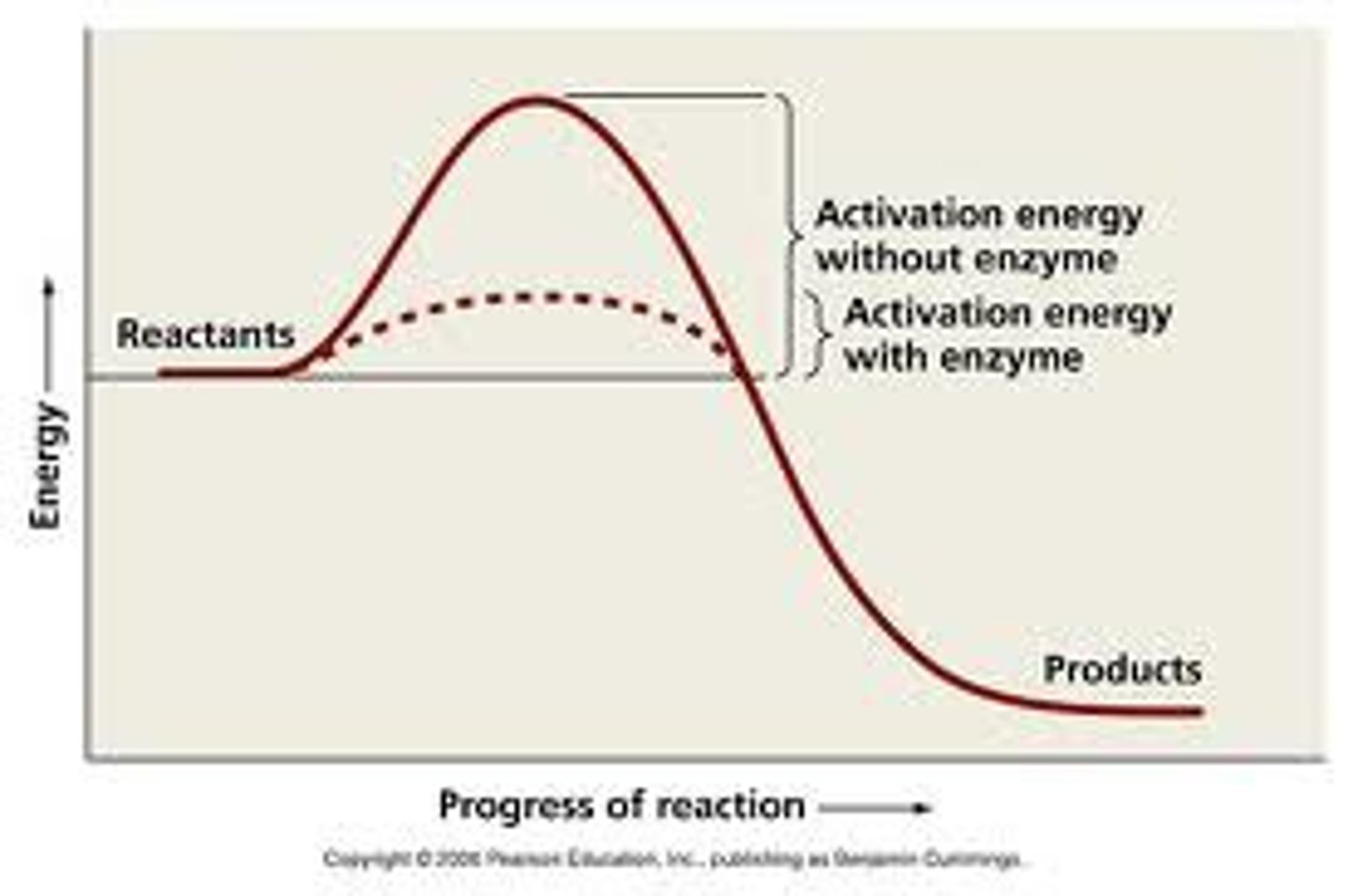
What is activation energy?
The minimum amount of energy that is required to activate atoms or molecules to a condition in which they can undergo chemical transformation or physical transport.
What is free energy?
A measure of the capacity of the system to do work.
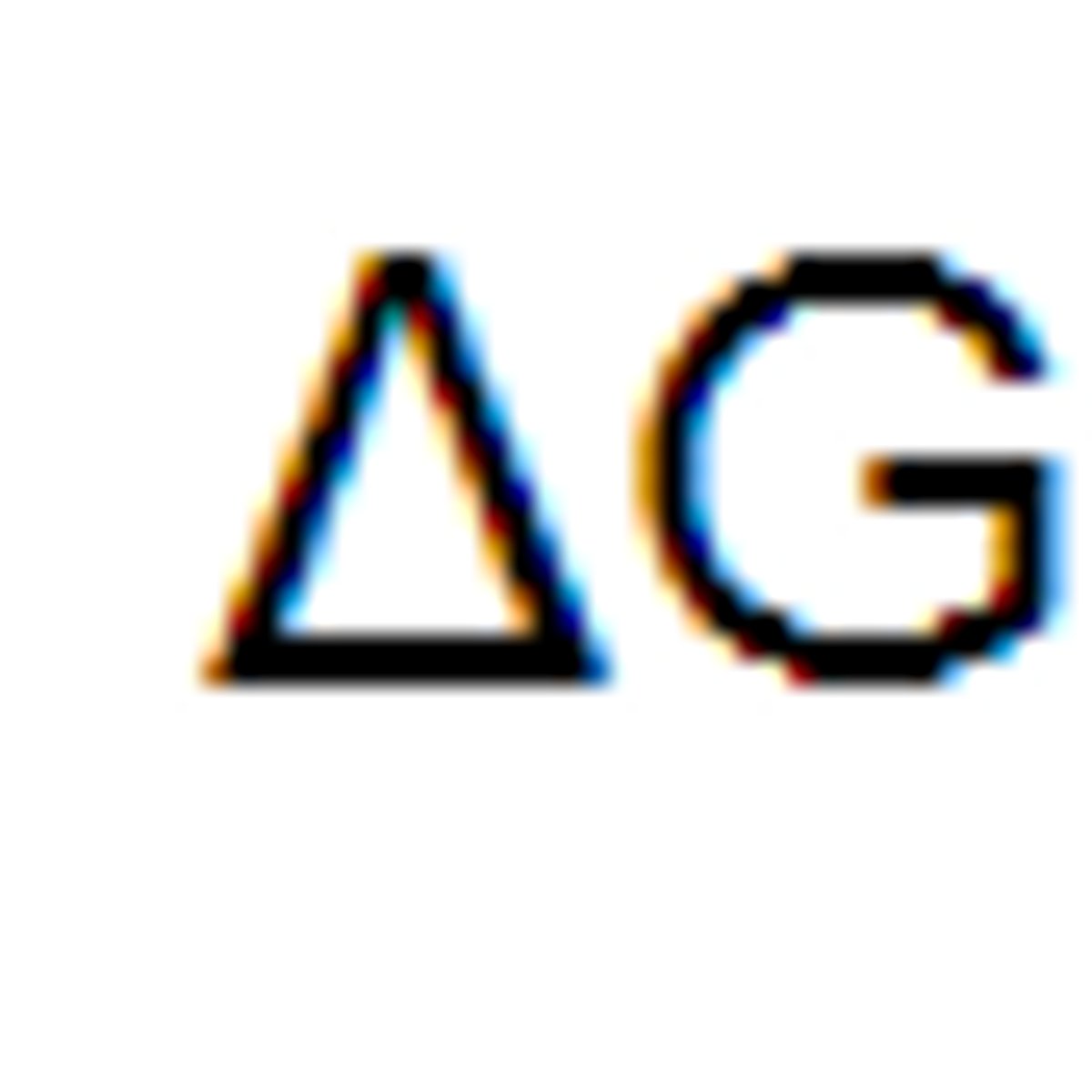
What are the major types of molecules in living organisms?
Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids.
What are the four major reactions?
Hydrolysis, condensation, neutralization and oxidation-reduction.
Describe condensation and hydrolysis reactions.
Condensation= A reaction in which two or ore molecules combine to form a larger molecule.
Hydrolysis= A larger molecule forms two (or more) smaller molecules and water is consumed as a reactant.
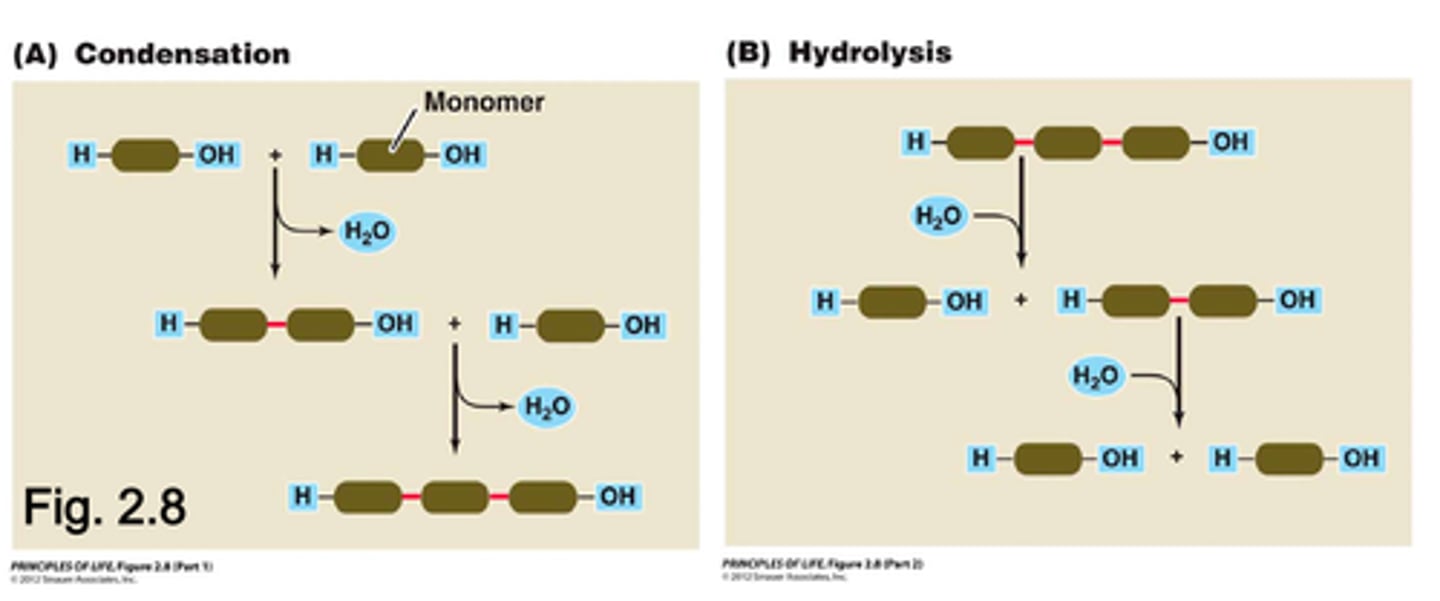
What is the purpose of condensation and hydrolysis reactions?
Condensation reactions are important in building up large molecules, while hydrolysis reactions are used to break down large molecules into smaller molecules. (Such as proteins, polysaccharides, fats and nucleic acids)
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA= double-stranded
RNA= single-stranded
Sugar in DNA is deoxyribose while RNA contains ribose.
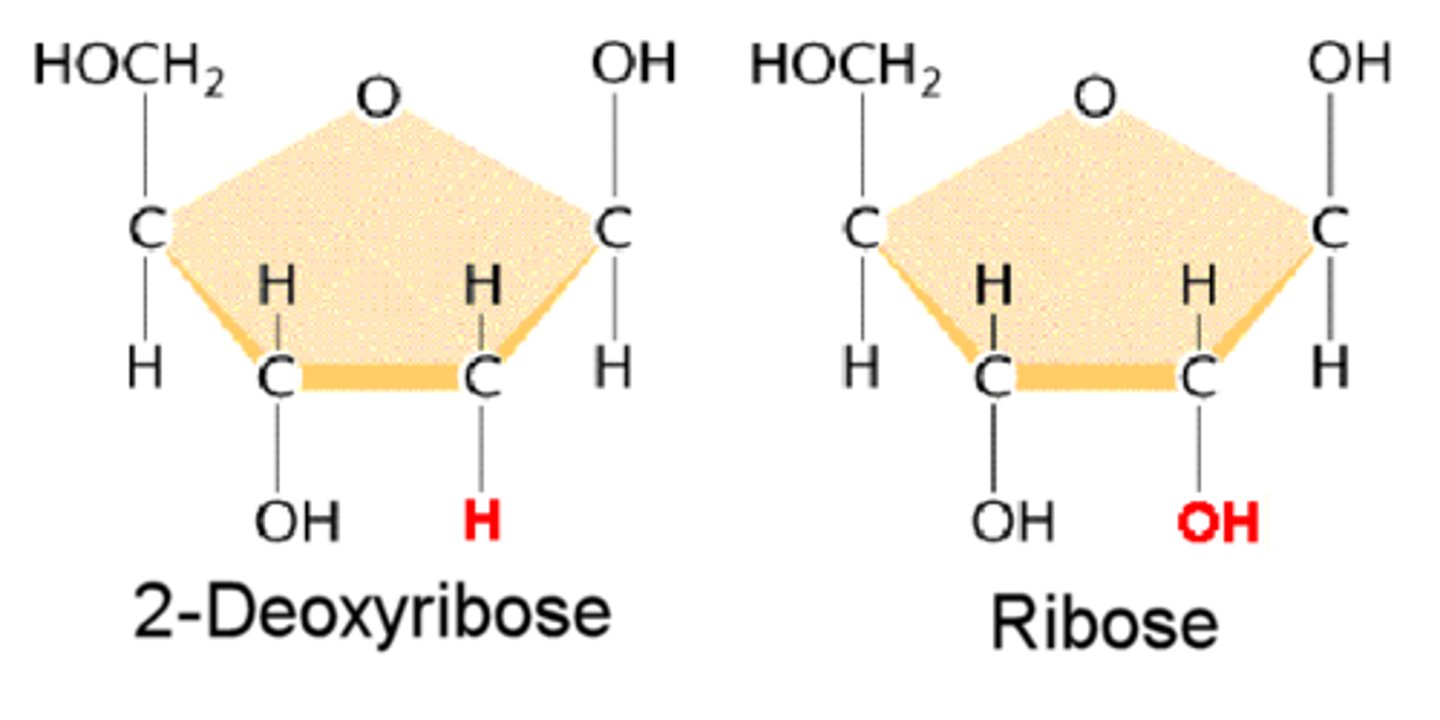
What are the components of DNA and RNA?
Both contain five carbon sugar backbone, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base.
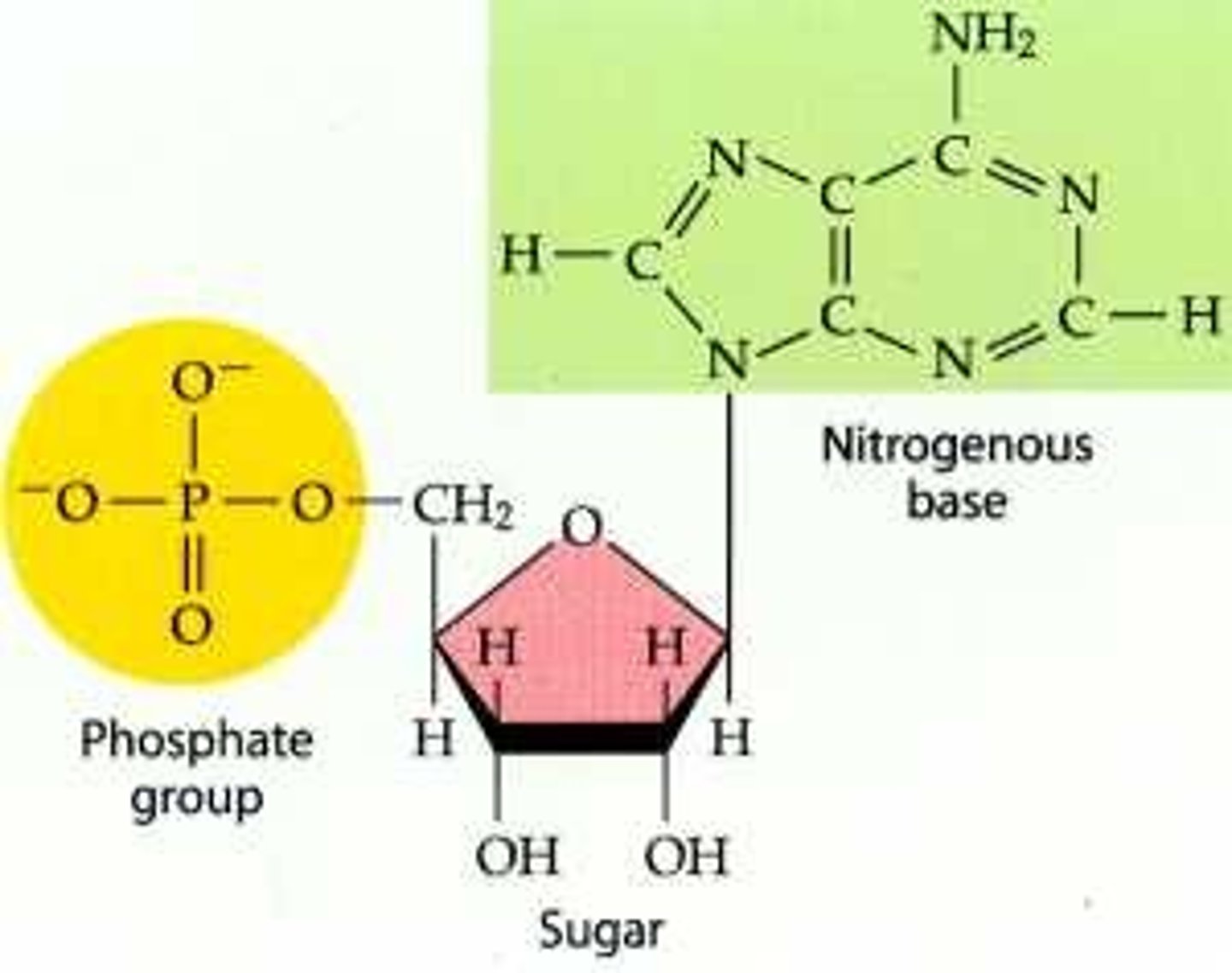
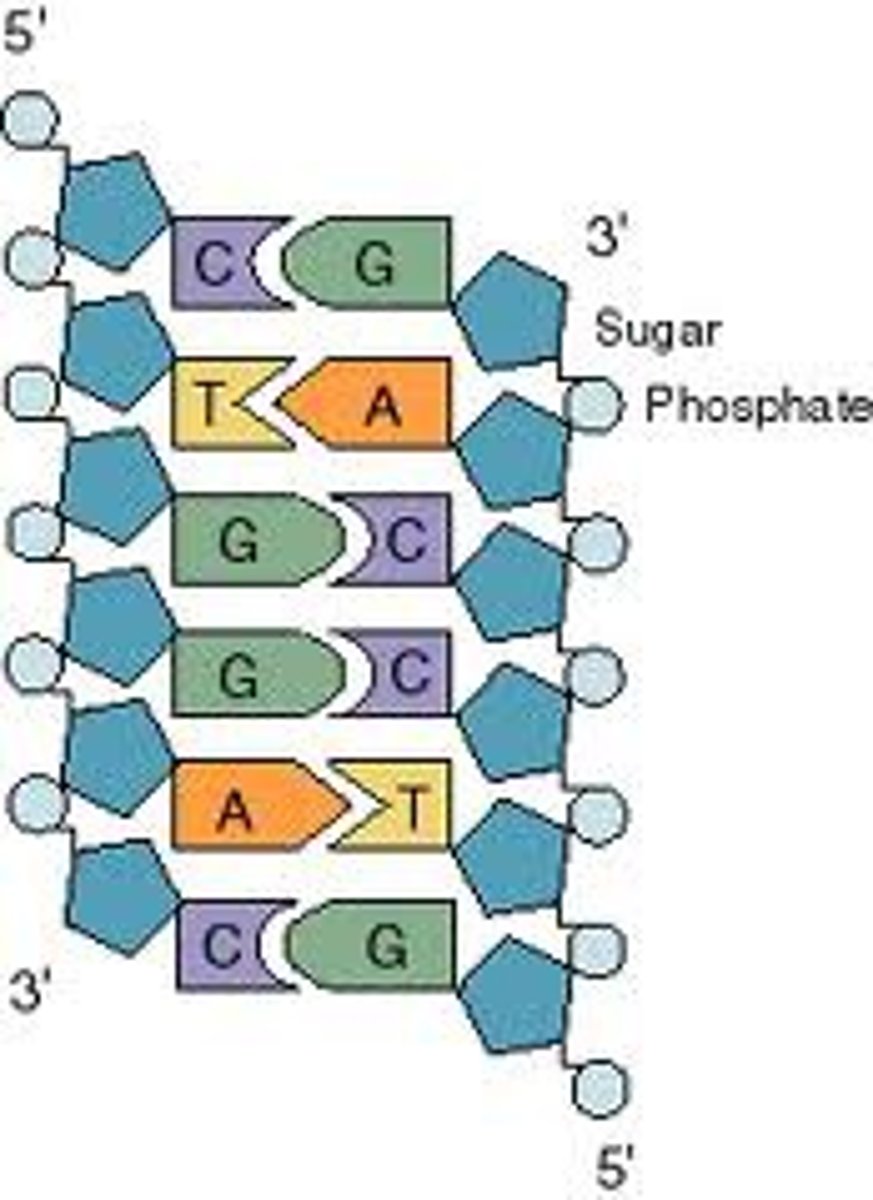
Describe the directionality of DNA sequences.
5'-3' direction
What are the complementary strand letters?
A=T
C=G
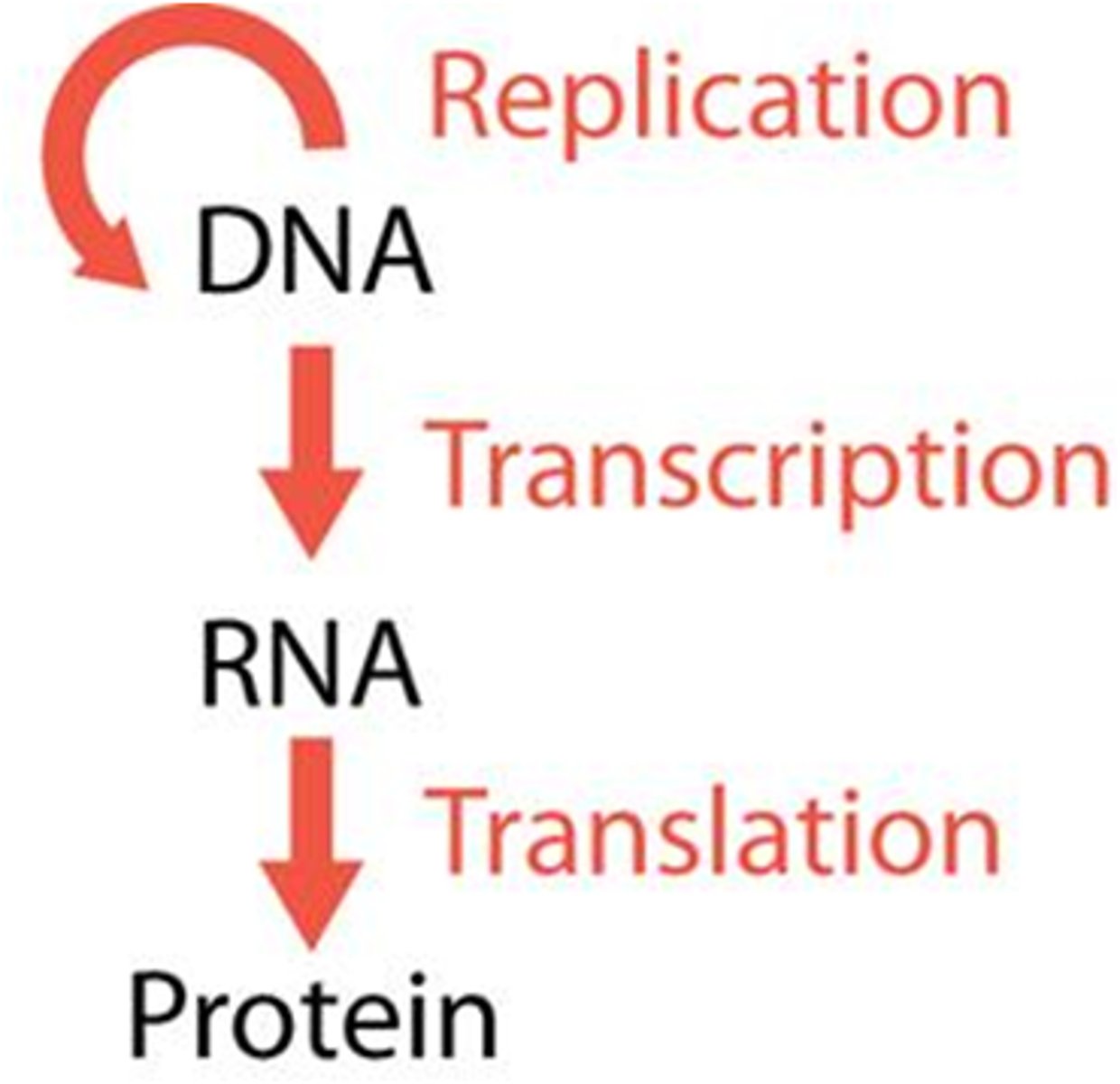
Describe the central dogma of biology.
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
It is a theory stating that genetic information flows only one direction.
What is the function on DNA?
DNA stores and transmits important genetic information to develop, survive and reproduce.
What is the function of RNA?
RNA creates proteins via translation.
What is the function of proteins?
Structural support, enzymes , building blocks and initiators of cellular death.
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
nucleotides
What are the monomers of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides
How are nucleic acid and carbohydrate monomers linked together to form the polymer?
Through condensation reactions.
What are the characteristics of lipids?
Hydrophobic, small molecules, organic compounds containing hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen atoms.
How does the structure of phospholipids lead to the formation of a bilayer?
Their fatty acid tails are poorly soluble in water.
What are some functions of lipids and other living organisms?
They help with moving and storing of energy, absorbing vitamins and making hormones.
What are carbohydrates?
Any group of organic compounds that include sugars, starch and cellulose.
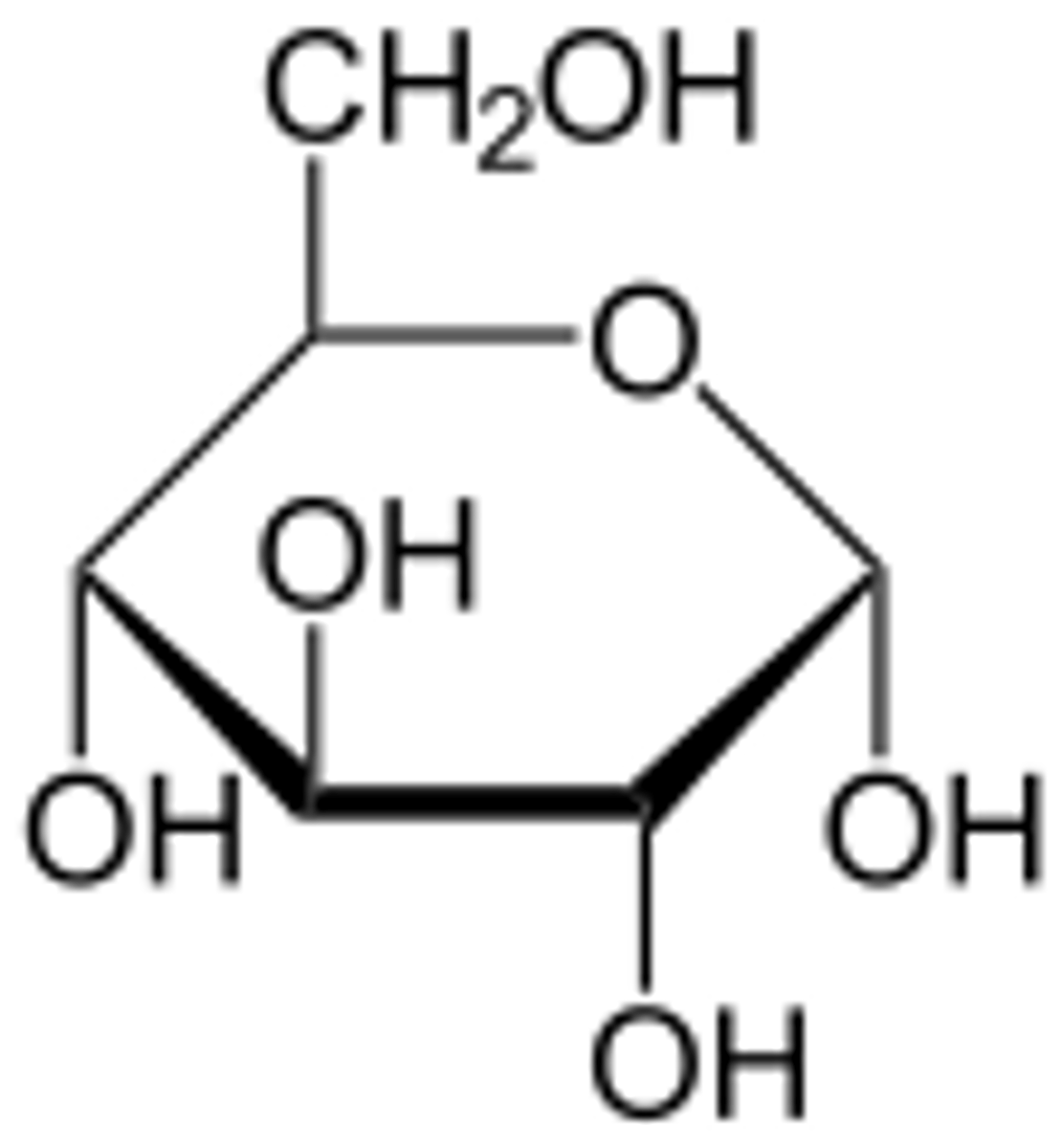
What are carbohydrates general chemical structures and how are they organized into larger molecules?
A long chain or ring of carbon atoms with multiple hydrogen atoms or hydroxyl groups attached and form larger macromolecules through condensation reactions.
What are some functions of carbohydrates in living organisms?
Providing energy, storing energy, building macromolecules and spare protein/fat for other uses.
What is a monosaccharide?
The simplest form of carbohydrate and is composed of a single molecule.
What is a disaccharide?
Composed of two monosaccharides linked together. (Di=two)
What is a polysaccharide?
Composed of three or more monosaccharides linked together. (Poly=multiple)
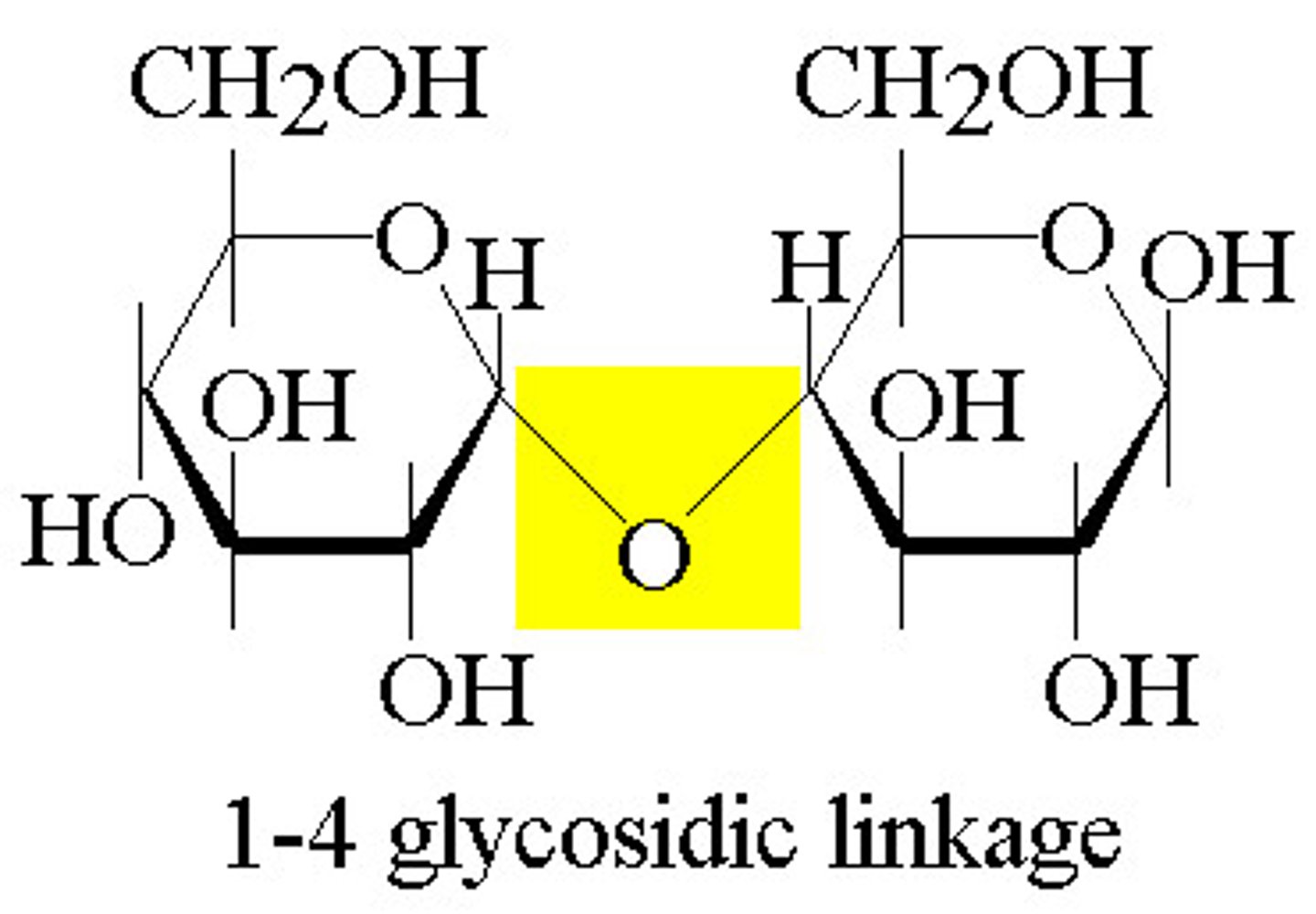
What is a glycosidic linkage?
A glycoside linkage is a covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
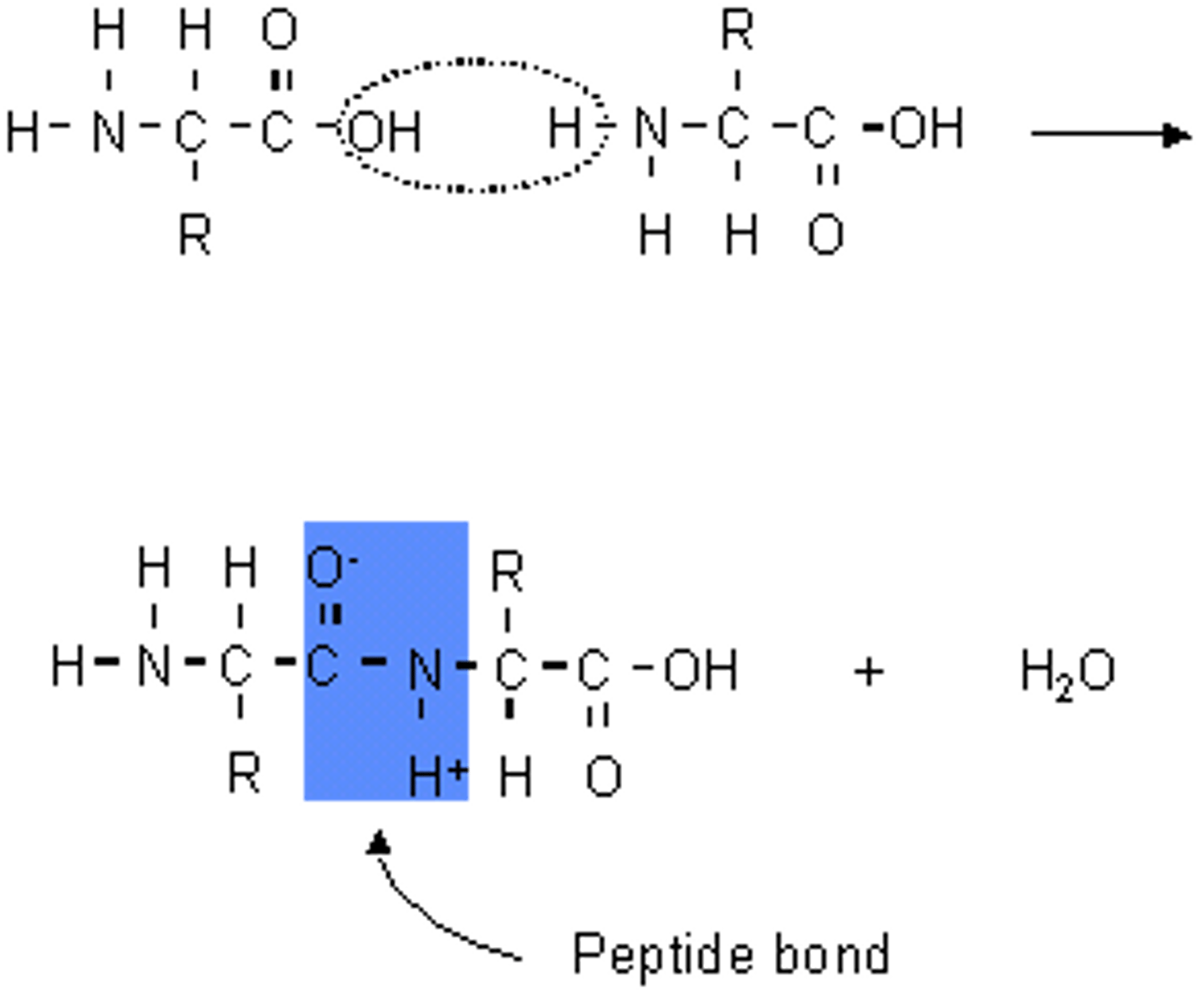
What is a peptide bond?
A peptide bond is a covalent bond between two amino acids.
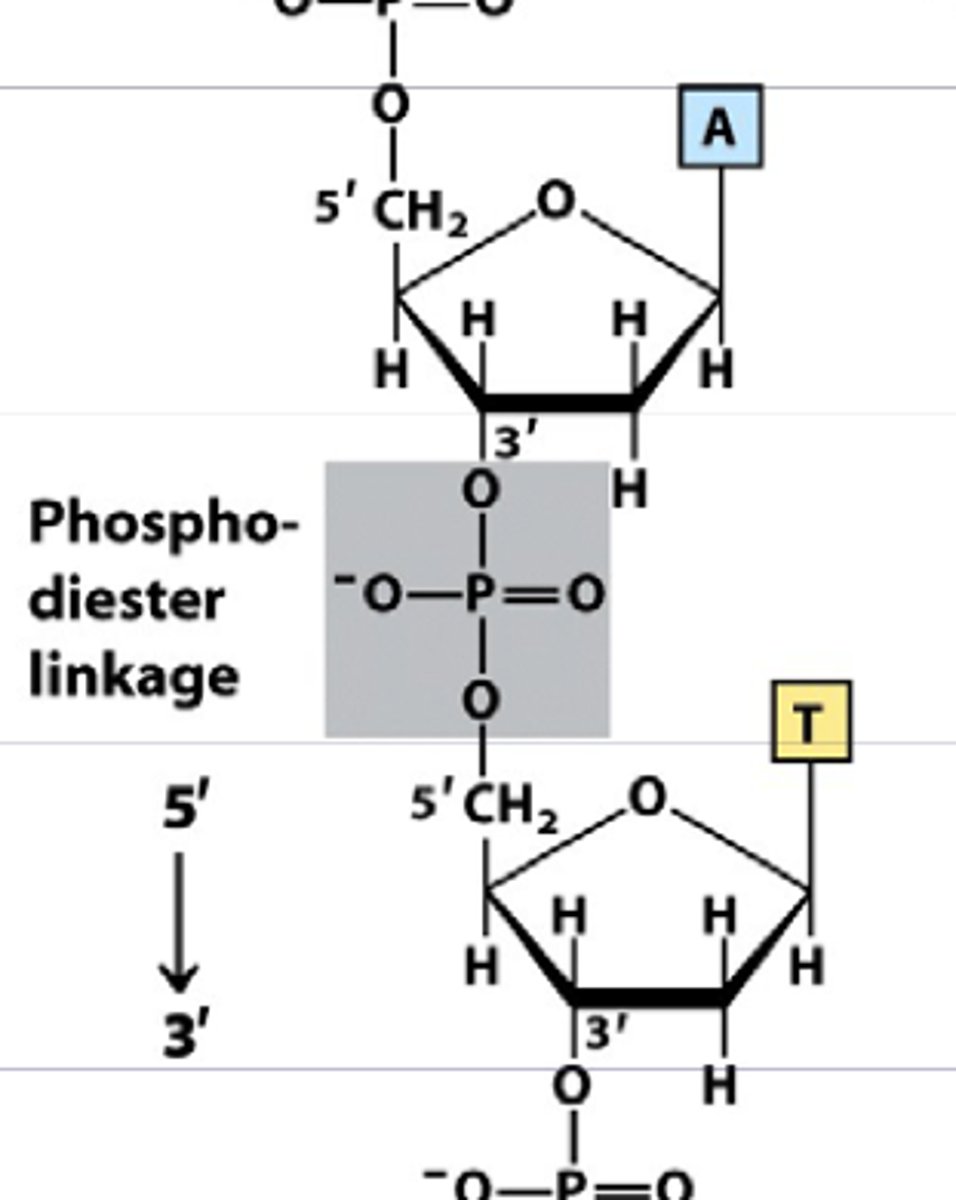
What is a phosphodiester bond?
A phosphodiester bond is a covalent bond that forms the backbone of DNA and RNA molecules.
What are proteins made of?
Amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
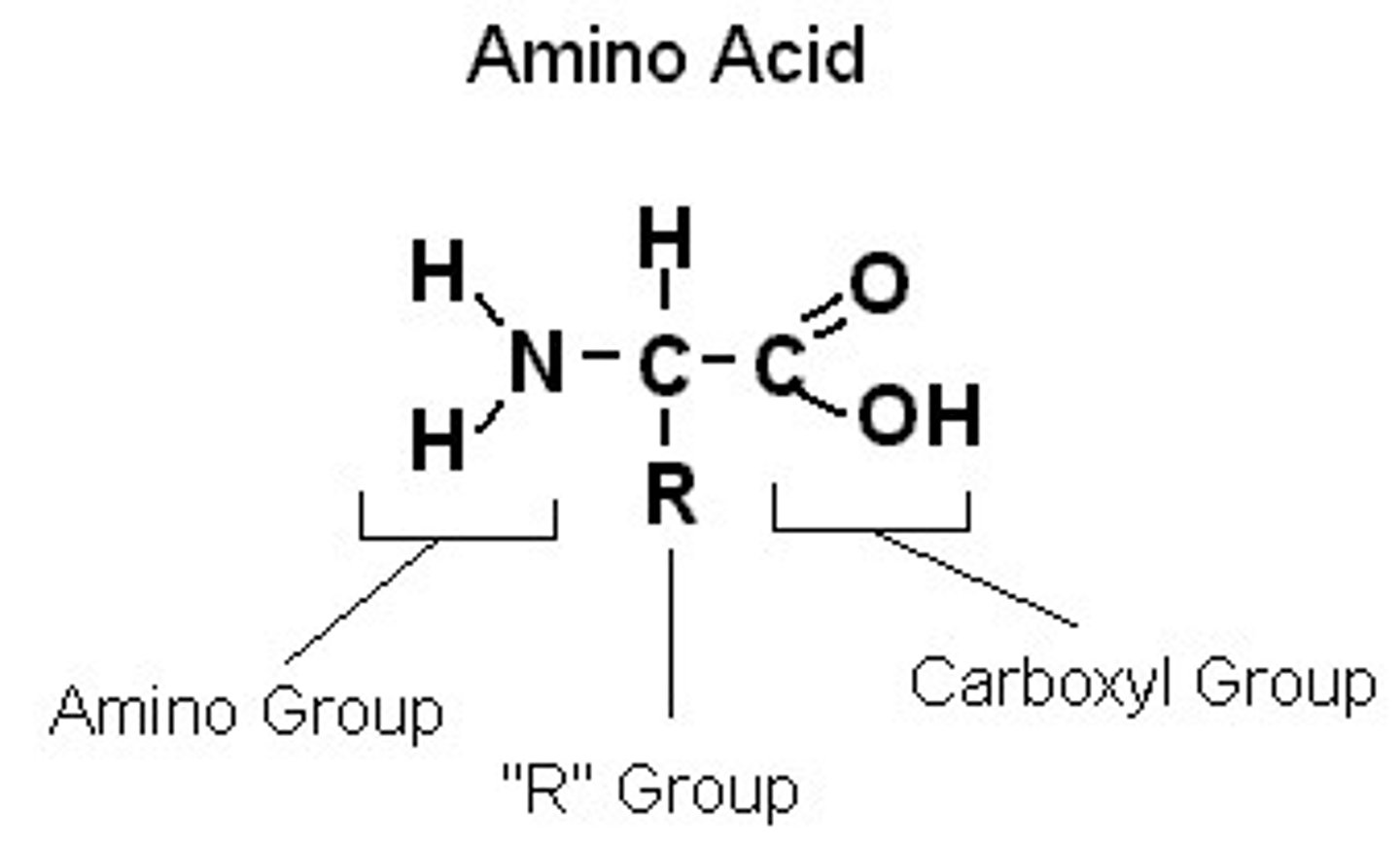
How are proteins assembled?
By linking together amino acids.
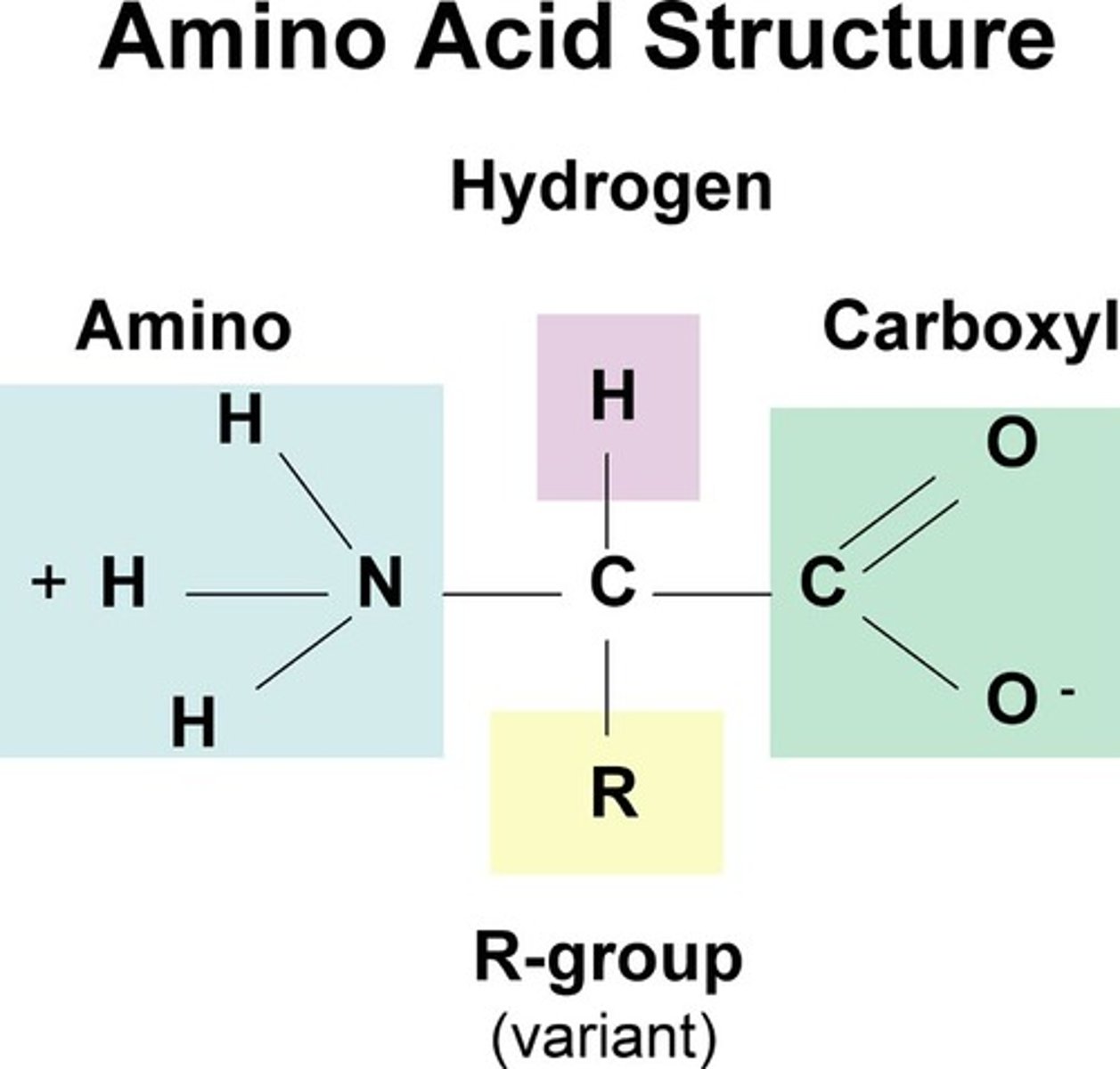
What are the different levels of organization/structure within a protein?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quarternary structures
What is a primary structure of a protein?
sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. (Pleated Sheets)
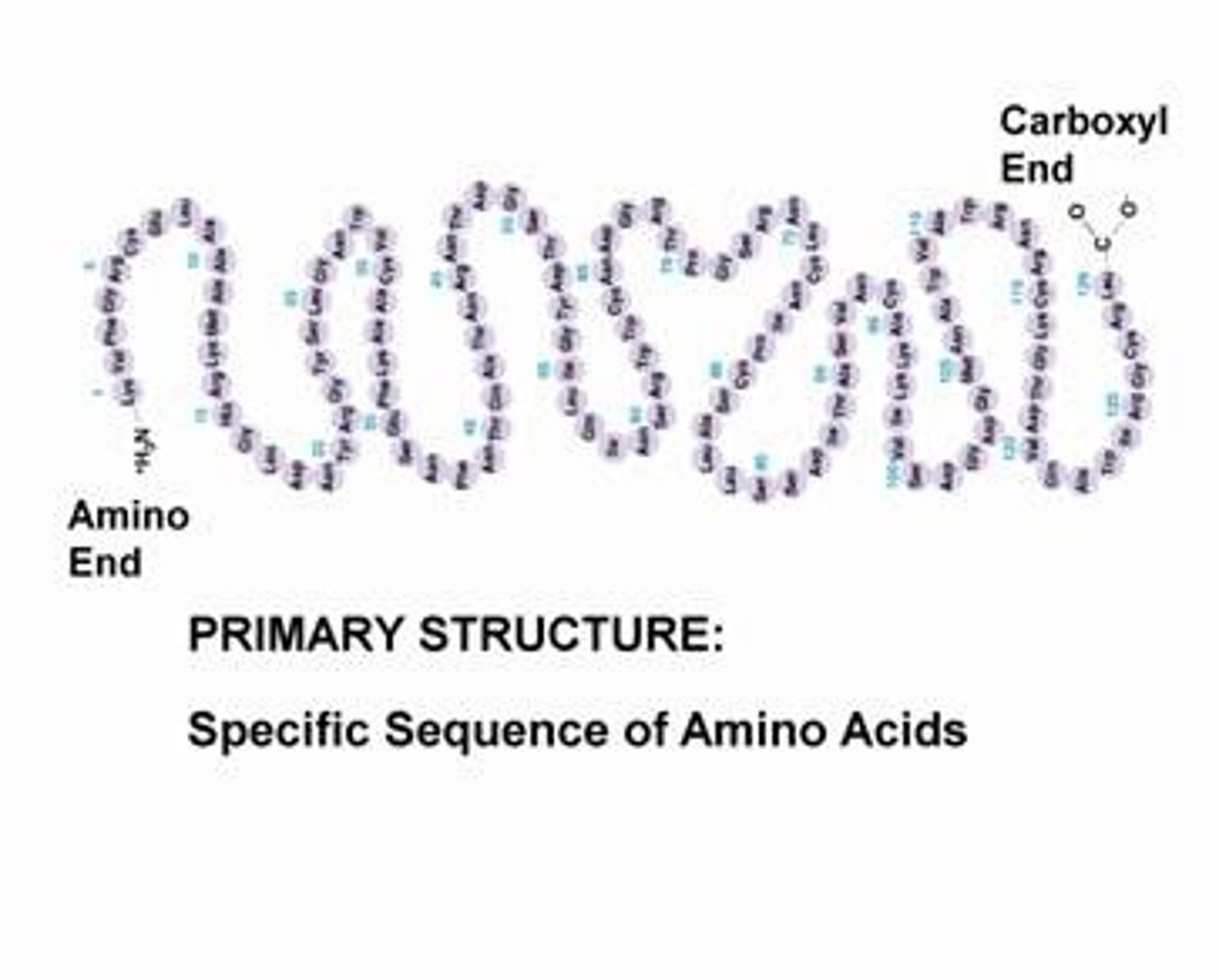
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
forms structural proteins - helix and pleated sheets
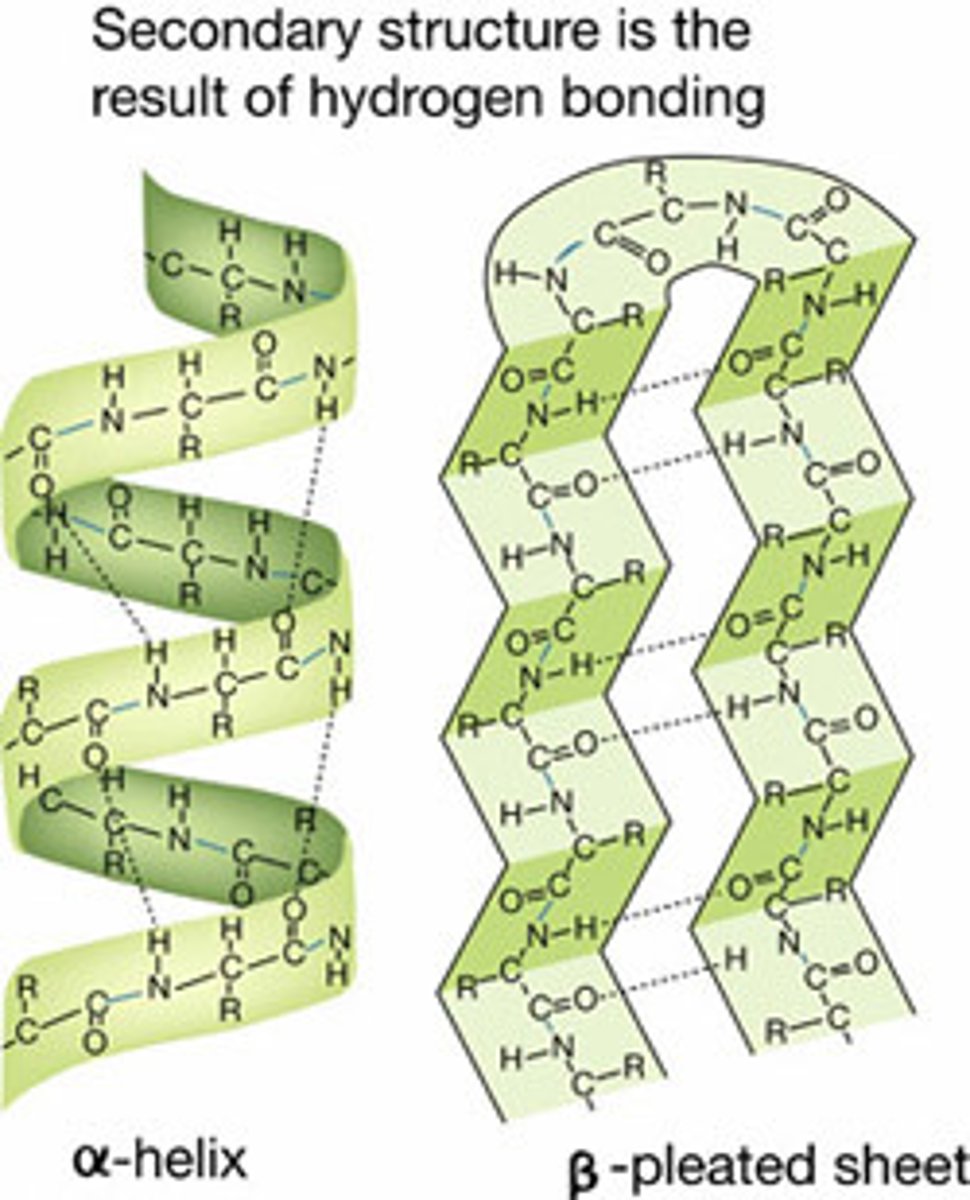
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
3D structure including folding of a polypeptide chain due to interactions between side chains of amino acids that lie in different regions of the primary sequence.
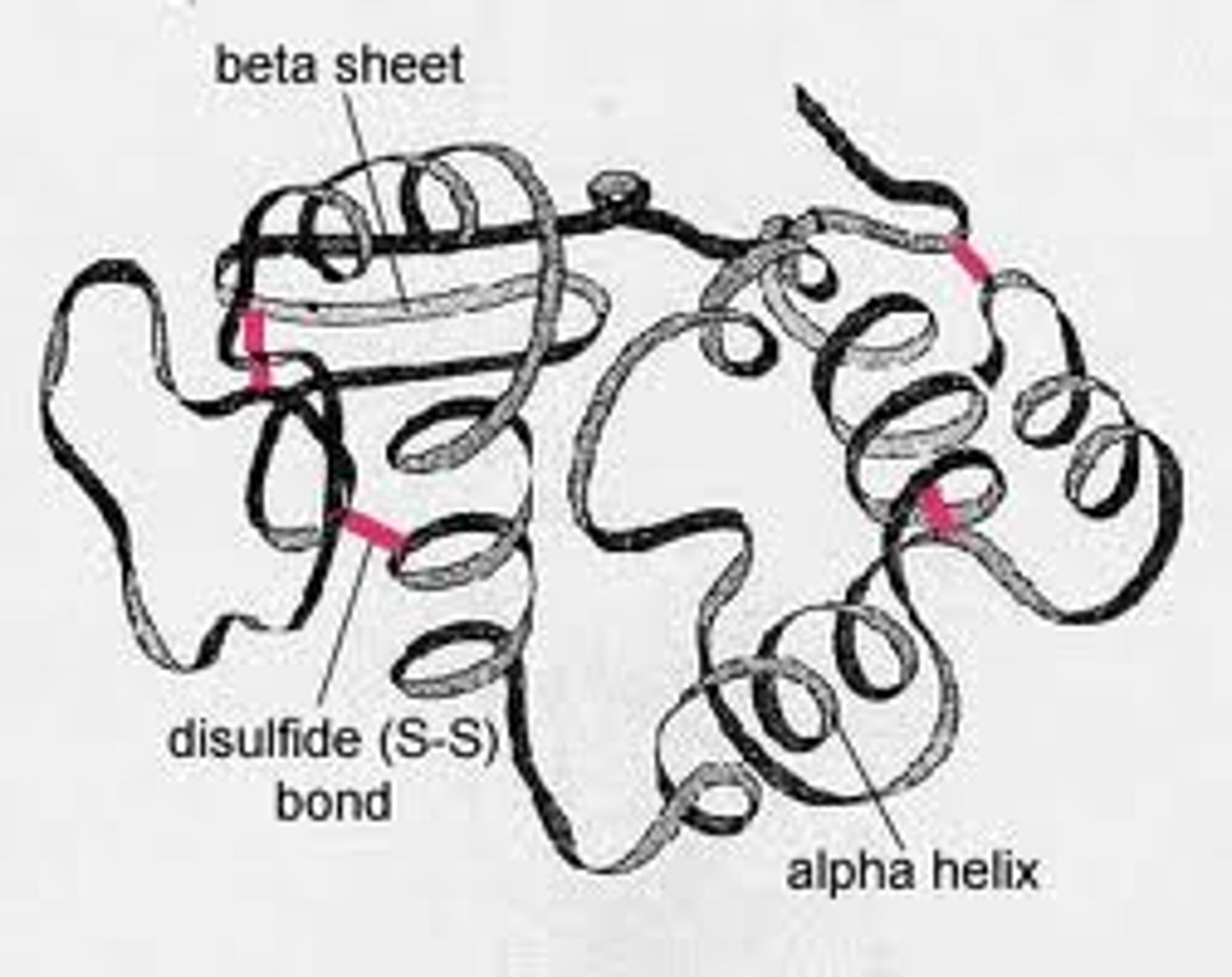
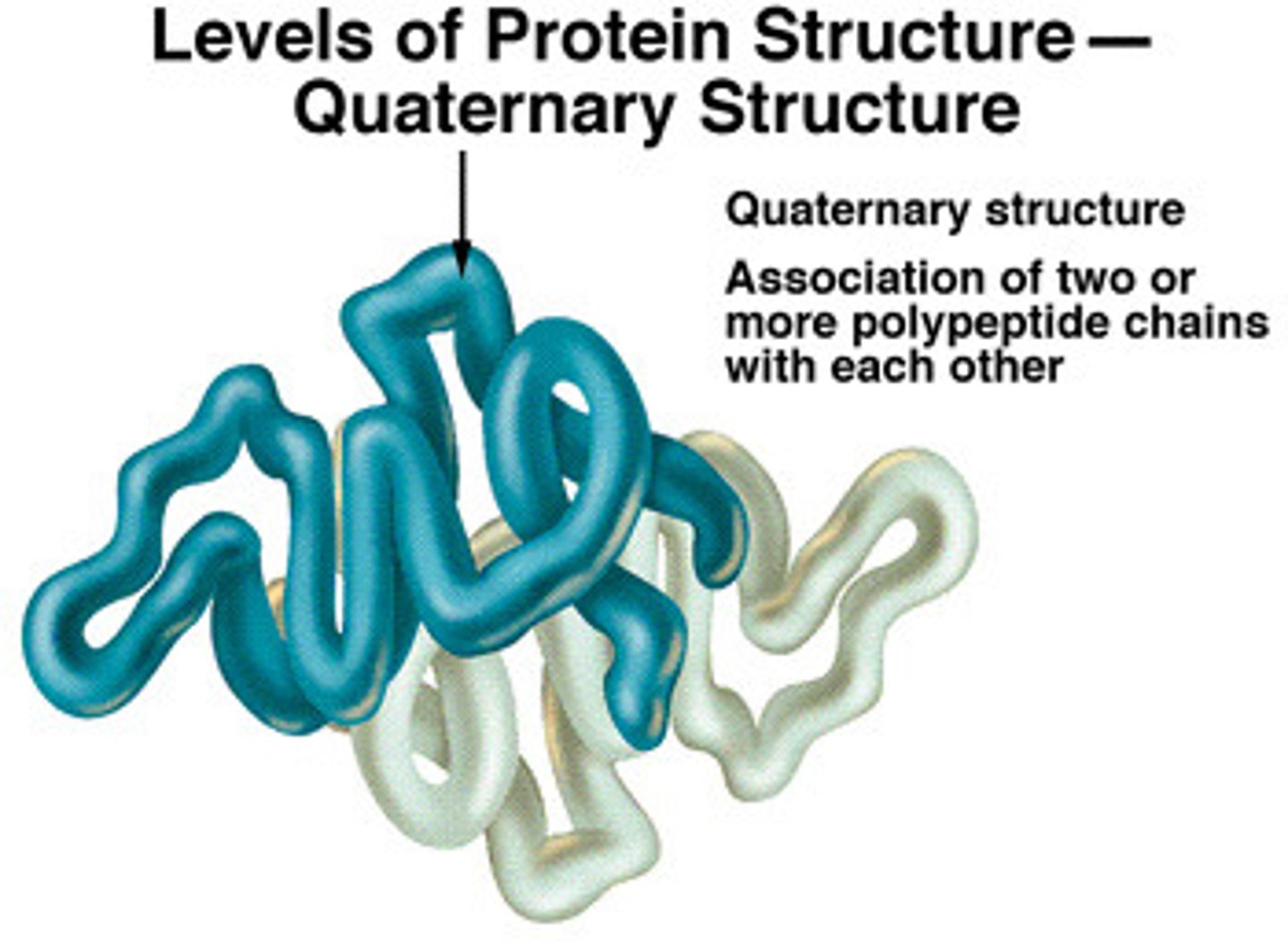
What is the quarternary structure of a protein?
When 2 or more polypeptide chains are linked together.
What factors affect protein folding?
Temperature, pH, salt concentration and hydrophobicity of amino acids.
How do different amino acid side chains play a role in the folding and function of a protein?
Side chains can bond with one another to hold a length of protein in a certain shape or conformation.
What can be a consequence of denaturation or misfolding of proteins?
Loss of biological activities or change in shape of protein and functions.
What kind of molecules can help proteins fold properly?
Molecular chaperones
What affects the rate at which a chemical reaction proceeds?
Reactant concentration, enzymes, Ea, and number of collisions over time.
What is an enzyme?
A biological catalyst for chemical reactions.
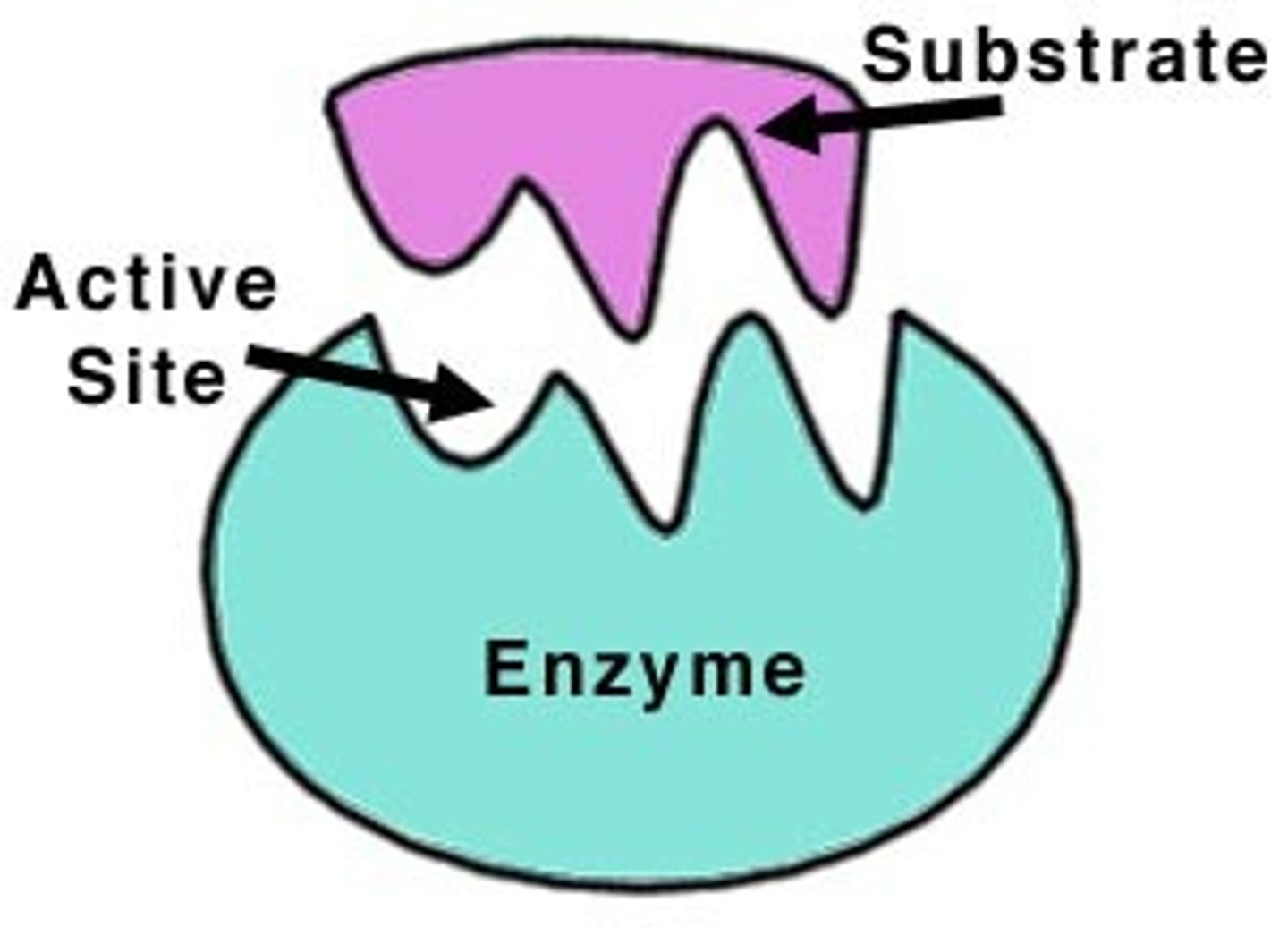
How does an enzyme catalyze a chemical reaction?
An enzyme catalyzes a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy of the reaction, thereby increasing the rate of reaction.
What kinds of modifications change protein structure and function?
Ligand bonding (ligand should be bound to the protein to activate.)
How are enzymes regulated?
Inhibition, activation and feedback inhibition.
Why is enzyme regulation necessary?
If reactions occurred randomly, it would be difficult to maintain homeostasis, allowing cells to respond in controlled ways to changes in both internal and external conditions.
What is feedback inhibition?
The end product of a metabolic pathway shuts down the pathway.
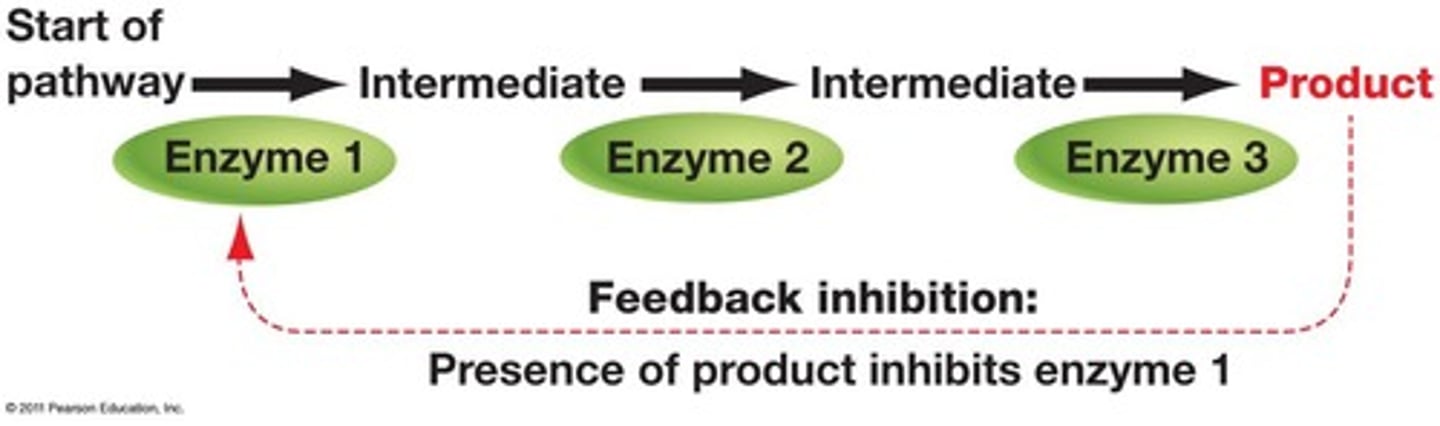
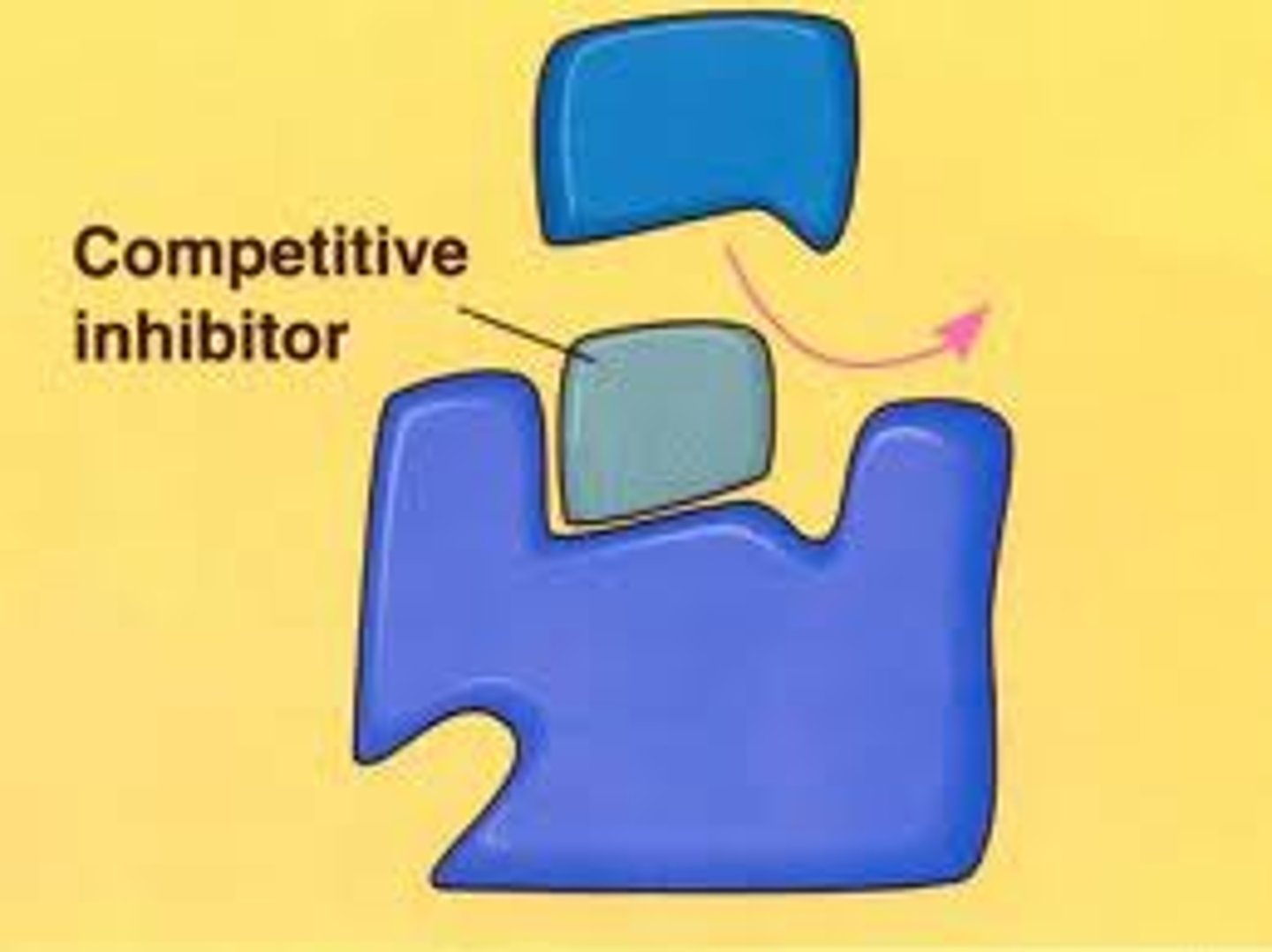
What is a competitive inhibitor?
An inhibitor which works by binding to the active site of the enzyme because it has a similar shape to the substrate.

What is a non-competitive inhibitor?
An inhibitor which works by binding to the enzyme at a site away from the active site which causes the active site to change shape.
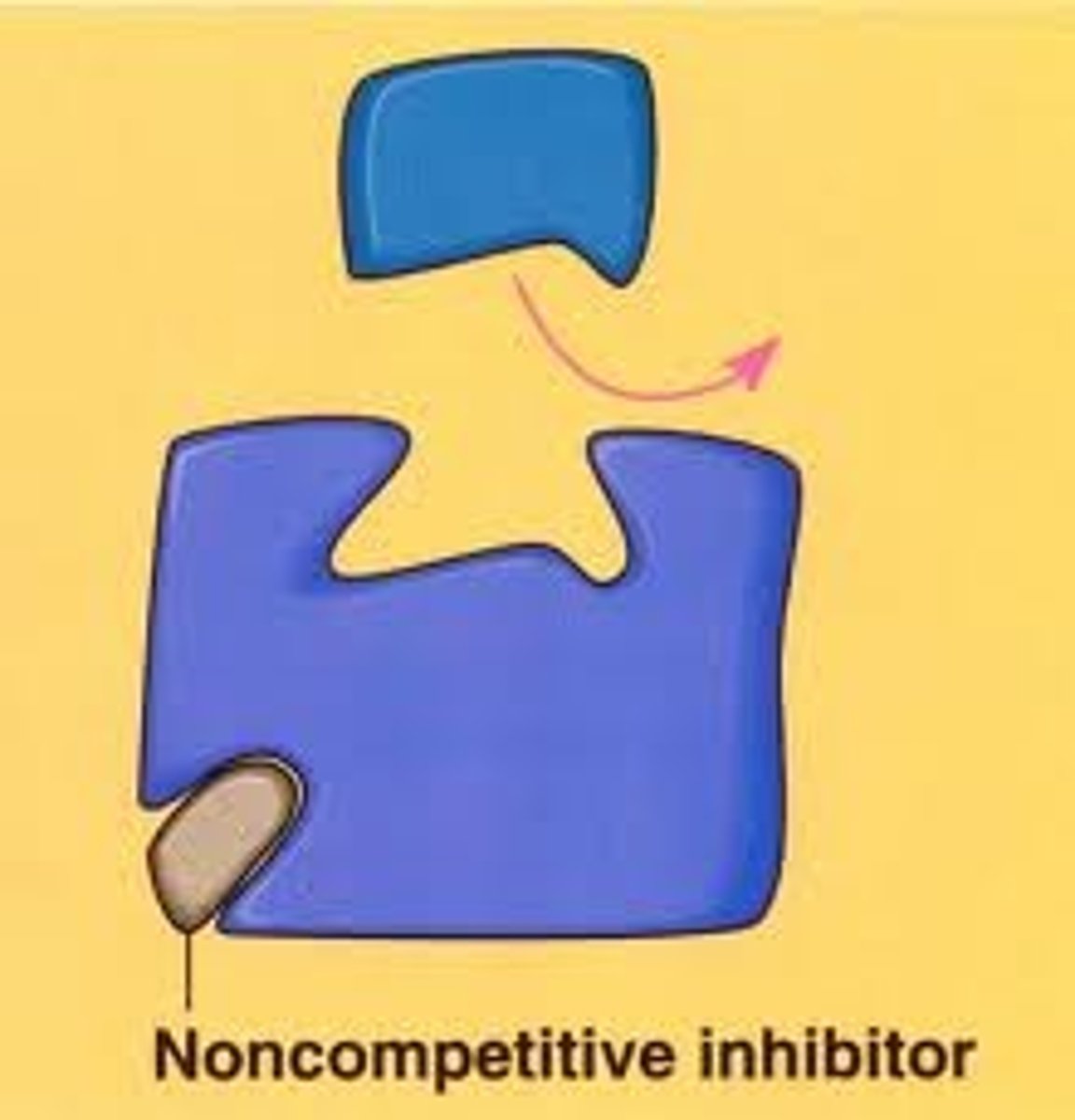
What is a reversible inhibitor?
A substance that binds to an enzyme to inhibit it, but can be released.
What is an irreversible inhibitor?
covalently bonds to the enzyme and permanently inhibits it, has long lasting effects until organism generates more enzyme and the inhibitor is outnumbered by enzyme.
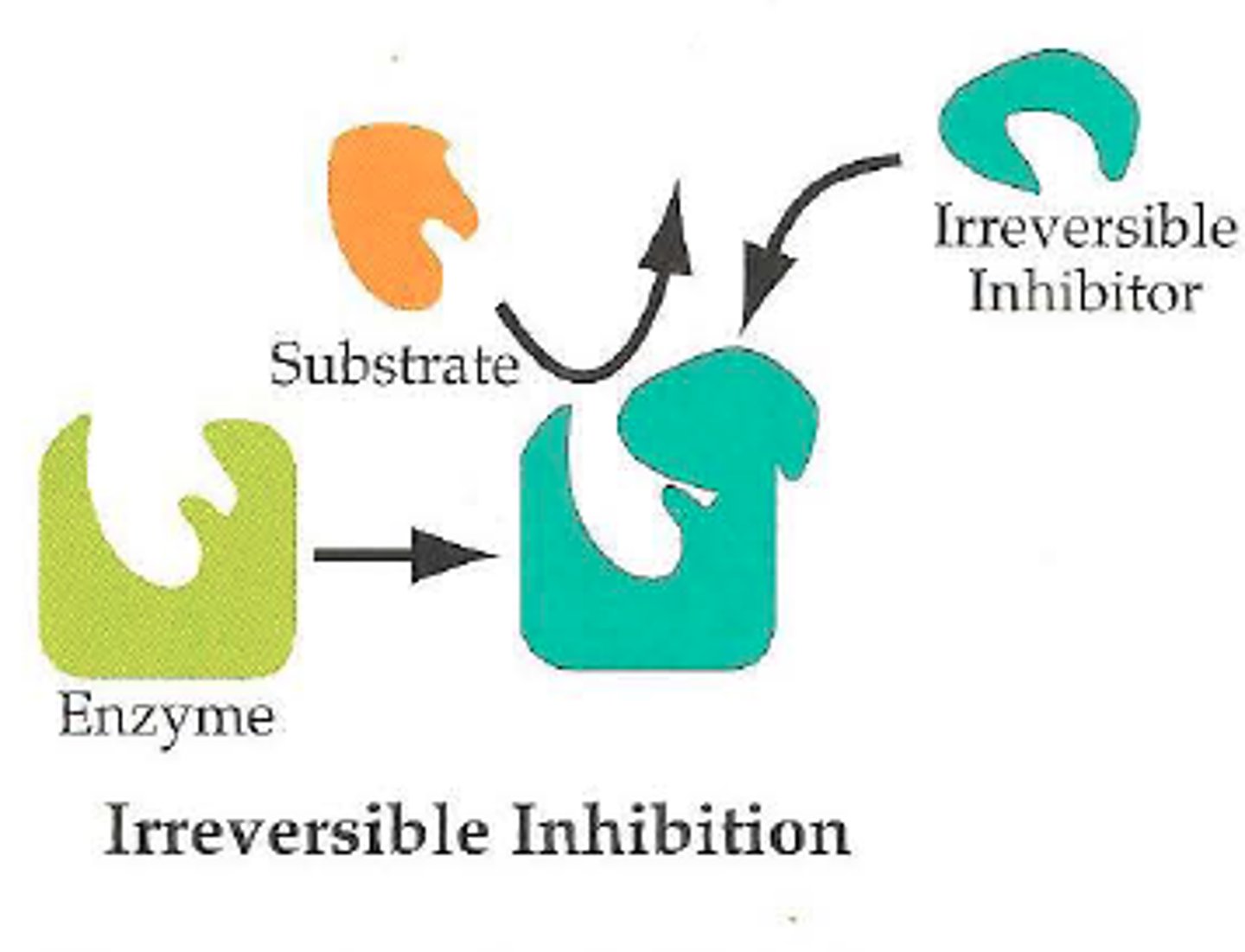
What other factors can affect enzyme activity?
Temperature, pH, inhibitors, enzyme concentration and substrate concentration.
What is allostery?
Allostery is a change in enzyme shape in response to a binding event at a distal site. It can be used to inhibit or activate enzymes.
How does allostery work for enzyme inhibition or activation?
Allostery inhibitors modify the active site of the enzyme so that the substrate binding is reduced or prevented.