forces and motion
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
The velocity of a moving object is similar to its speed, except it also describes the object's direction.



2- it gives everything a weight
3- it keeps planets moons and satellites in their orbit
a force measured in newtons.
measured using a spring balance or newton meters.
measured in kilograms with a mass balance

2- reaction force- acts perpendicular to a surface and away from it.
3- electrostatic force- between two charged objects. like charges repel, opposite charges attract
4- thrust- e.g push or pull due to an object speeding up
5- drag or air resistance or friction- slowing the object down
6- lift- due to an aeroplane wing
7- tension- in a rope or cable
%%2- friction between solid surfaces which are sliding past each other:%%
reduce friction by putting a lubricant like oil or grease between the surface.
friction between solid can often cause wear of the 2 surfaces in contact.
%%3- resistance or drag from fluids:%%
keeping the object streamlined like sport cars.
lorries and caravans have deflectors on them to make them more streamlined and reduce drag.
roof boxes on cards spoil their streamlined shape and slow them down.
AS SPEED INCREASES FRICTION INCREASES
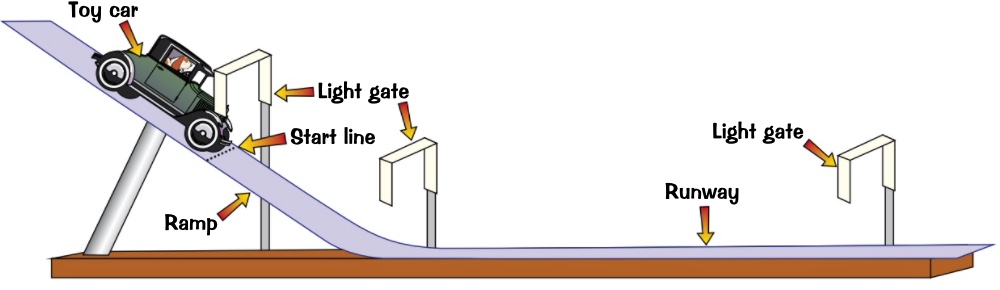
2- measure the distance between each light gate
3- let go of the car just before the light cate so it will start to roll down the slope
4- when the car passes through the light gate a beam of light will show and your time will come on the datalogger
5- repeat the experiment several time to get an average time of how long it takes for the car to reach each light gate
if a stationary object’s resultant force is 0, the object will remain stationary. If a moving object’s resultant force is 0, the object will move in a constant velocity at same speed and direction
newton 1st law
an object’s acceleration is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on it, and inversely proportional to the object’s mass
what is the second law of motion?
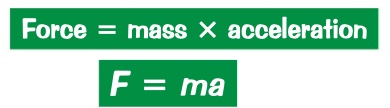
The forces that two objects exert on each other when they interact are equal and opposite
what is the 3rd law of motion?
force
velocity
acceleration
momentum
mass
temperature
time
length
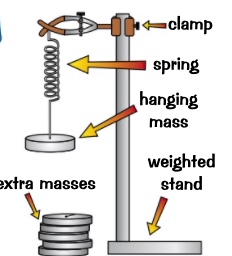
ensure the ruler is vertical and measure the spring at eye level
2- add one mass at a time and allow the spring to come to rest then measure the new length of the spring.
the extension is the change in length from the original length
3- repeat the process until enough measurement
4- plot graph

2- reaction time- affect by things like tiredness drugs alcohol and old age
2- the mass of the vehicle- the larges the mass the longer it takes to stop
3- how good your brakes are- all brakes must be checked
4- how good the grip is depends on three things :
road surface
weather conditions
tyres

Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and velocity.
the greater the mass of an object and the greater its velocity the more momentum the object has
momentum is a vector quantity
what is momentum and formula?

\
a faster change of momentum and so a greater acceleration
a larger force means?
longer it takes for a change in momentum, the smaller the force less sever
how are cars designed to slow people down over a longer time when they crash?
crumple on impact, increasing the time taken for the car to stop.
what do crumple zones do?
stretch slightly, increasing the time taken for person to stop.
reduces force acting on chest
what do seat belts do?
slows you down more gradually
what does air bag do?

a moment is the turning effect of a force about the pivot
what is a moment?/ formula
the force on the spanner causes a turning effect or moment on the nut.
a larger force would mean a larger nut
the force on the spanner causes what?
if the total anticlockwise moments do not equal the total clockwise moments, there will be a resultant moment .
object will turn
what happened in the moments are not equal?