SBI4U - Unit 1 Biochemistry
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry Intro Quiz - 1-27 | Carbs & Lipids Quiz - 28-83
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
List: Four Elements that make up 96% of our body
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
Ionic Bond
Chemical bond formed when one atom gives up electrons, while the other gains them, creating oppositely charged ions that attract each other.
Covalent Bond
A chemical bond where two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
Polar Covalent Bond
A covalent bond where electrons are shared unequally, creating slight positive and negative charges on the atoms.
Polarity
A property of a molecule where one end is slightly positive and the other end is slightly negative due to unequal sharing of electrons.
Bonding Capacity
The number of chemical bonds an atom can form
Electronegativty
The strength of the hold an atom has on electrons
Dipole
A separation of electrical charge in a molecule due to an uneven sharing of electrons, resulting in a partial positive & partial negative.
VSEPR theory
Theory that predicts the shape of a molecule based on: Valence Shell, Electron Pairs, Repulsion.
Cohesion
The attraction between like molecules that holds them together.
Adhesion
The attraction between molecules of different substances that causes them to stick together
Hydrophobic
Repels water, refers to non-polar molecules
Hydrophilic
Attracts water, refers to polar molecules
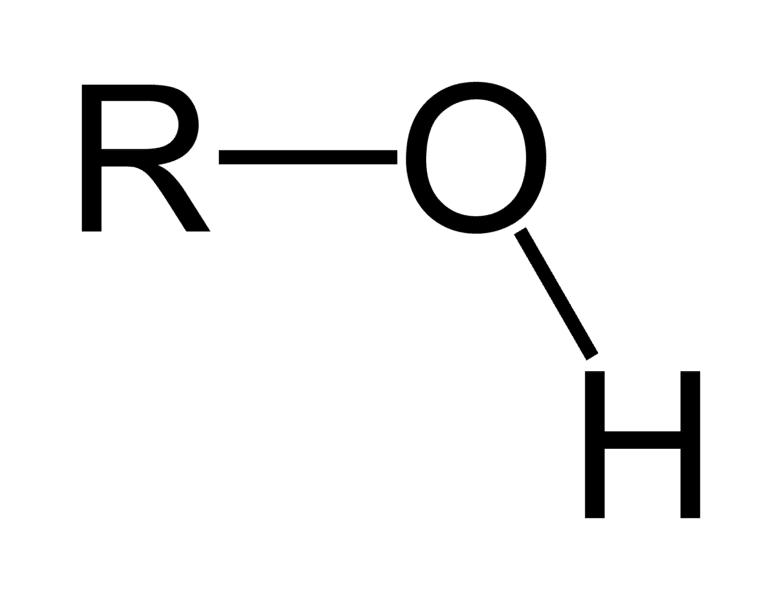
Hydroxyl Group
Functional group with the chemical formula -OH. Referred to as alcohols and they are polar due to electronegativity difference between O and H.
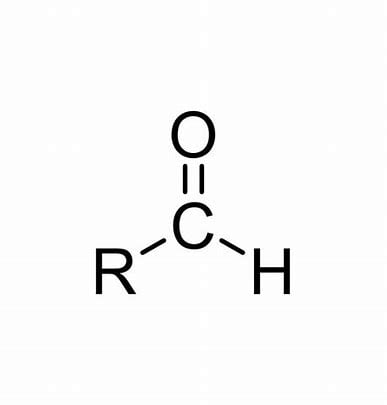
Carbonyl Group (Aldehydes)
Functional group with the chemical formula -COH, where C=O (double bond). Referred to as aldehydes and they are polar.
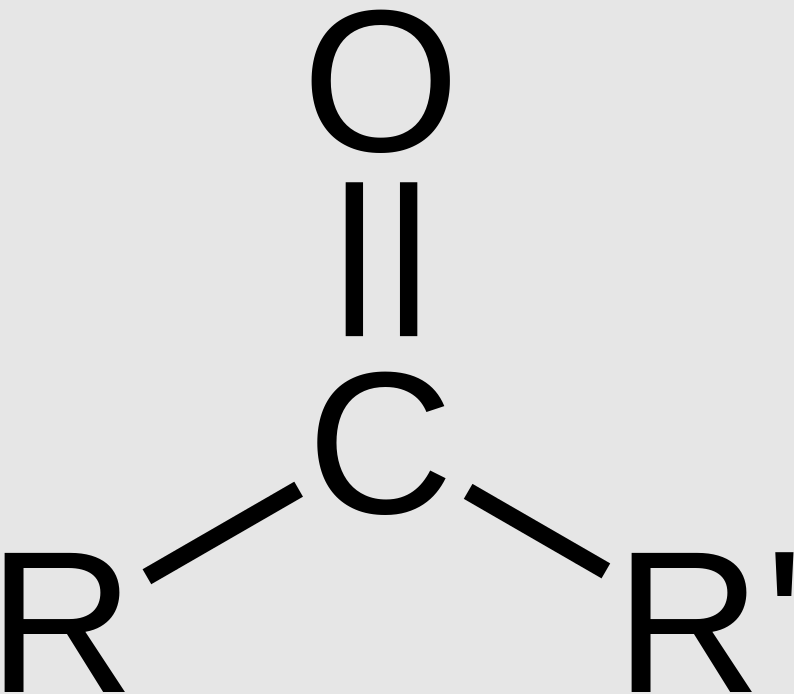
Carbonyl Group (Ketones)
Functional group with the chemical formula -CO-, where C=O (double bond). Referred to as ketones and are polar.
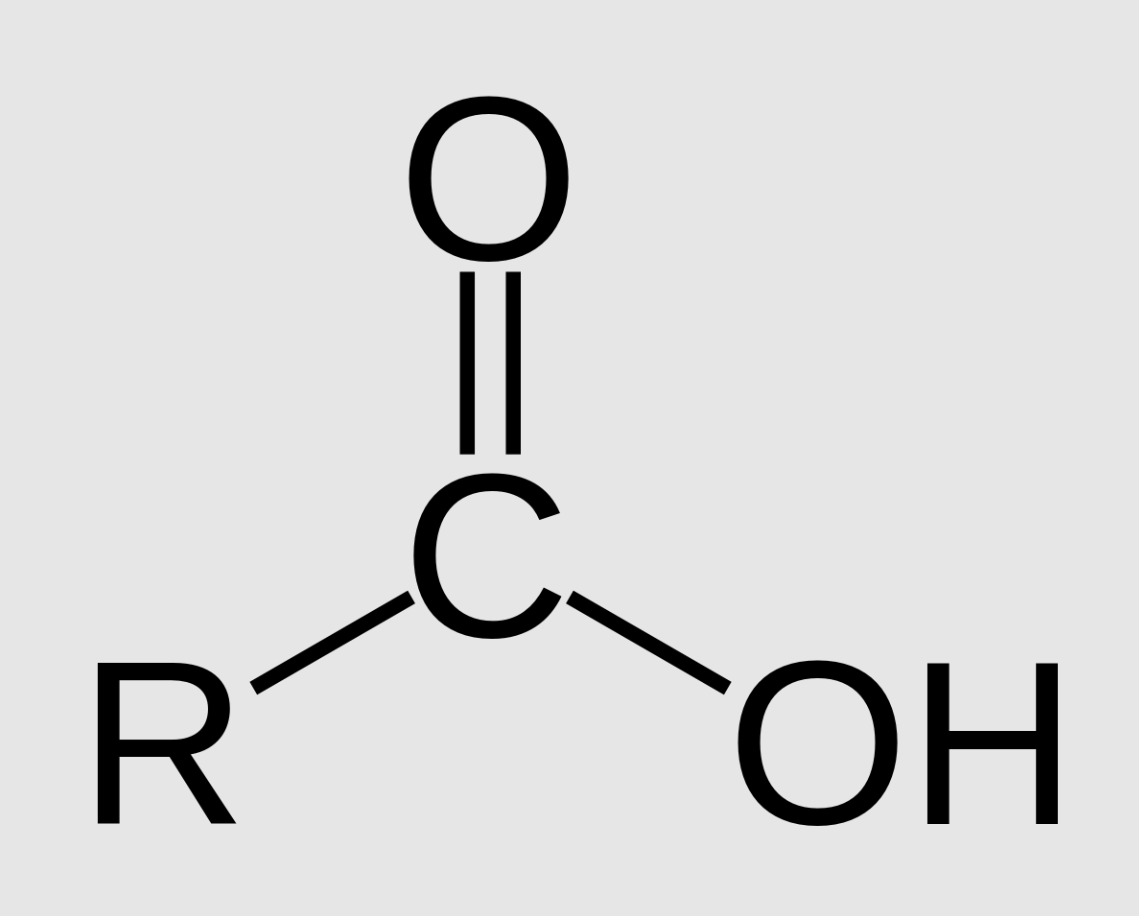
Carboxyl Group
Functional group with the chemical formula -COOH, where C=O (double bond). Referred to as carboxylic acids and are polar.
Amino Group
Functional group with the chemical formula -NH2. Referred to as amines and are polar.
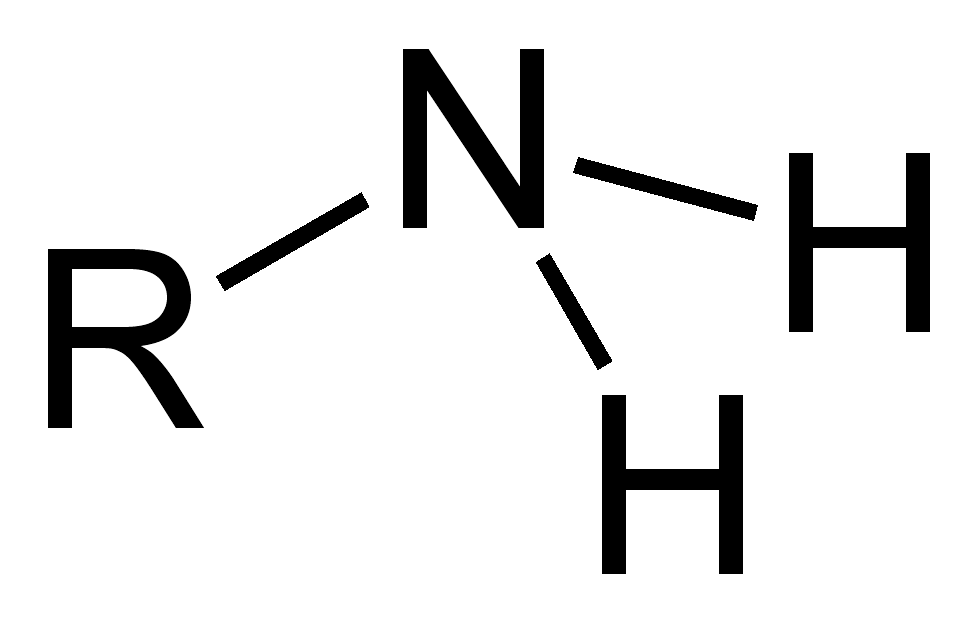
Sulfhydryl Group
Functional group with the chemical formula -SH. Referred to as thiols and are slightly polar.
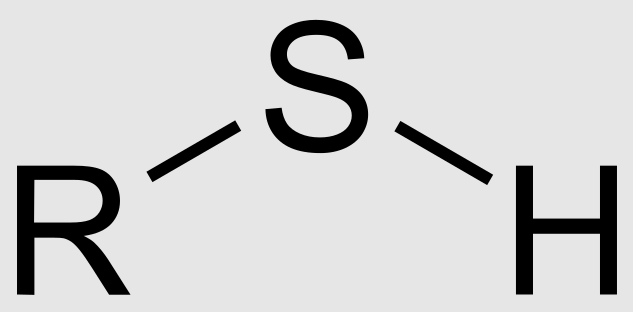
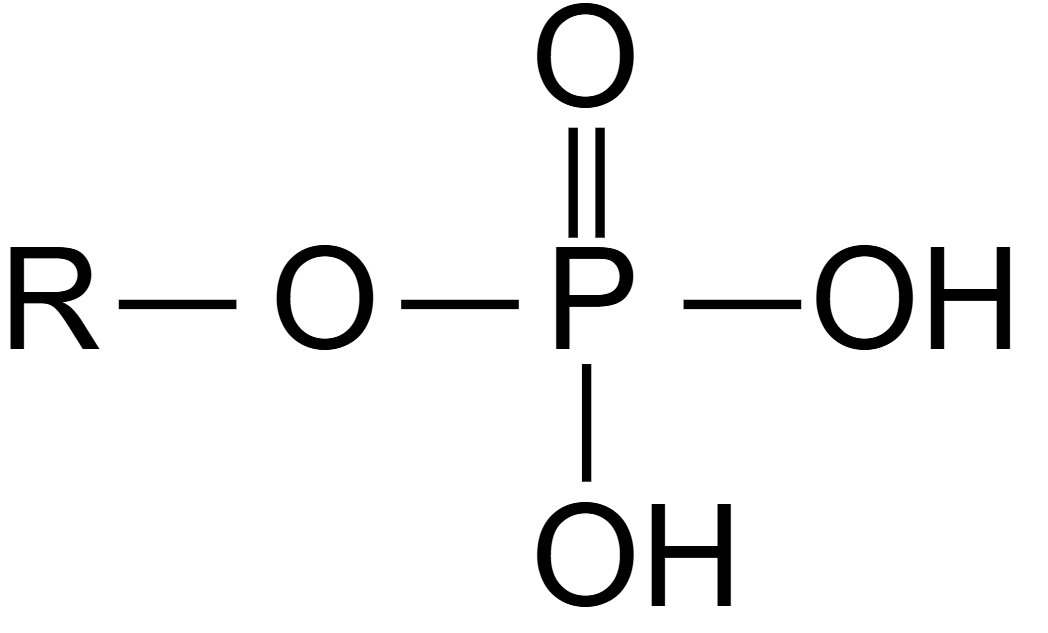
Phosphate Group
Functional group with the chemical formula -PO4. Referred to as organic phosphates and are polar.
London Dispersion Forces
Weak and non-polar intermolecular force created by temporary attraction of electrons from one molecule to the nucleus of another nearby molecule. This is present in all molecules.
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Weak but polar intermolecular force between a positive dipole of one molecule and a negative dipole of another molecule. Present in two polar molecules.
Hydrogen Bonds (THE FORCE)
A special strong type of dipole-dipole force that occurs when a hydrogen atom bonds to a highly electronegative atom (N, O or F).
Bent Molecular Geometry
The shape of a polar molecule where a central atom is bonded to two other atoms and has one or more lone pairs.
Linear Molecular Geometry
The shape of a non-polar molecule where the central atom is bonded to two other atoms with no lone pairs.
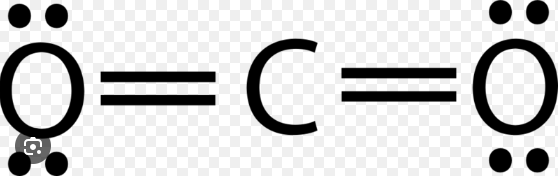
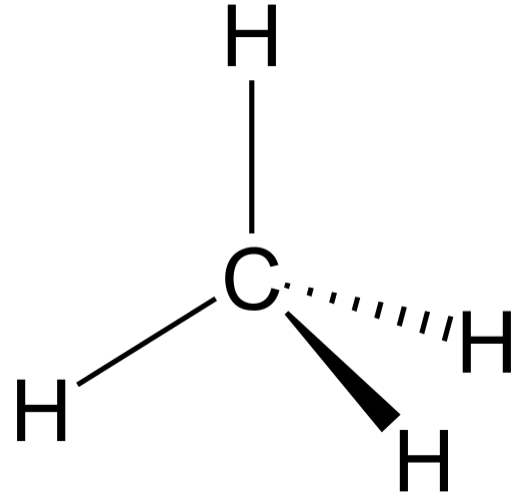
Tetrahedral Molecular Geometry
The shape of a non-polar molecule where a central atom is bonded to four other atoms with no lone pairs.
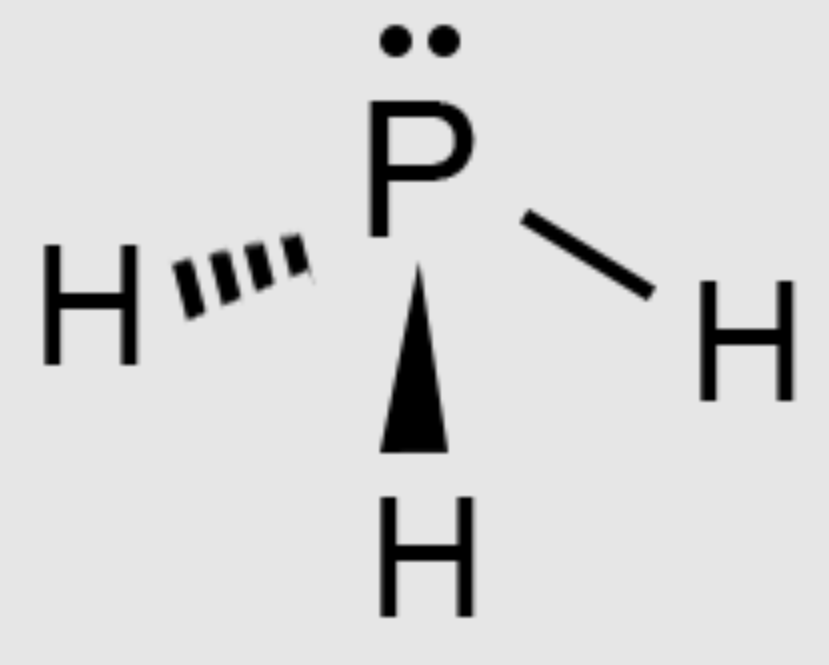
Trigonal Pyramid Molecular Geometry
The shape of a polar molecule where a central atom is bonded to three other atoms and has one lone pair.
Biological Molecules
Macromolecules that are composed of repeating subunits
List: The Four Biological Molecules
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Carbohydrates
A macromolecule that s made up of one or many sugar molecules. They contain C, H & O atoms only and are in a 1:2:1 ratio. They end in -saccharide or -ose.
List: Five Functions of Carbohydrates
Energy Source
Building Materials
Cell-to-cell communication
Blood Glucose Level Regulation
Fibre for waste elimination
Monosaccharide
A carbohydrate referred to as “simple sugars.” They have single chains of C atoms with hydroxyl groups. They can be distinguished by # of C atoms in their backbone and their specific carbonyl group.
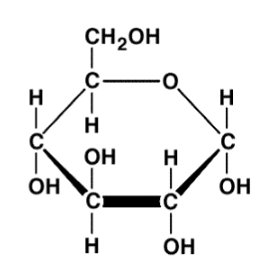
Glucose
An example of a monosaccharide with the chemical formula C6H12O6 and a hexagon ring structure. It is used within cells as energy.
Fructose
An example of a monosaccharide with the chemical formula C6H12O6 and a pentagon ring structure. It is found in fruits.
Monomers
Small, single molecules that join together to form polymers
Polymers
A large molecule made up of many monomers bonded together
Isomers
Molecules with the same chemical formula but with different structural arrangement of atoms
Pentoses
Monosaccharides with five C atoms in the backbone
Hexoses
Monosaccharides with six C atoms in the backbone
Ribose
An example of a pentose found in RNA
Ribulose
An example of a pentose used in photosynthesis
Galactose
An example of a monosaccharide that is found in dairy products.
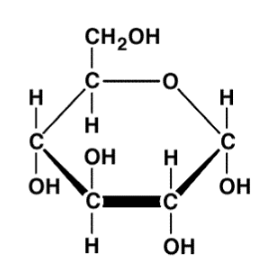
Ring Structure of Monosaccharides
This structure is obtained when the monosaccharide is immersed in water, as the C-5 & C-6 atoms react with the carbonyl group by dissolving to form a closed ring.
Chain Structure of Monosaccharides
This structure is obtained when the monosaccharide is in a dry state
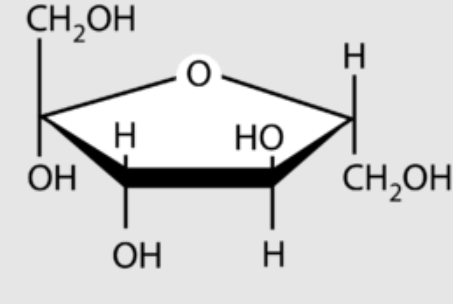
α-glucose
A form of glucose that has the hydroxyl group on C-1 pointing down. It forms starch (in plants) and glycogen (in animals), both of which humans can digest for energy.
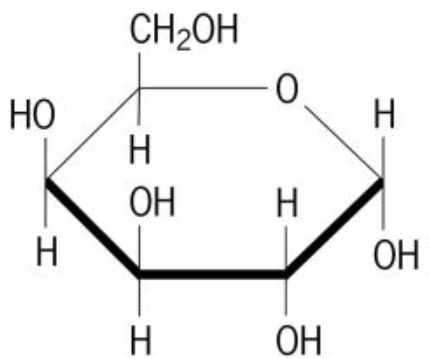
β-glucose
A form of glucose that has the hydroxyl group on C-1 pointing up. It forms cellulose, which humans cannot digest for energy.
Disaccharides
A carbohydrate that consists of two simple sugars (monomers) bonded together.
Dehydration Synthesis
A process in which two monomers bond together to form a polymer by removing a water molecule in the process. Also called a condensation reaction.
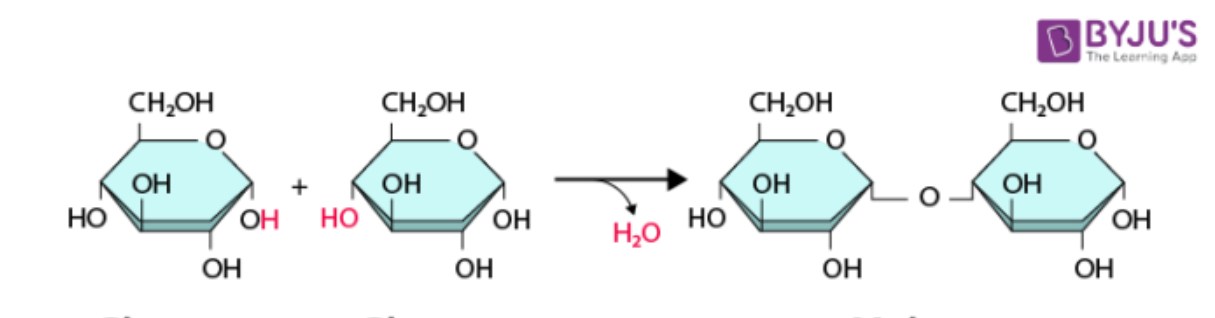
Anabolic Reactions
Reactions that build larger molecules from smaller subunits, requiring energy input
Catabolic Reactions
Reactions that break down larger molecules into smaller subunits, where H2O molecules are used to break covalent bonds, releasing energy output.
Hydrolysis
A process in which a polymer is broken down into two monomers by adding a water molecule.
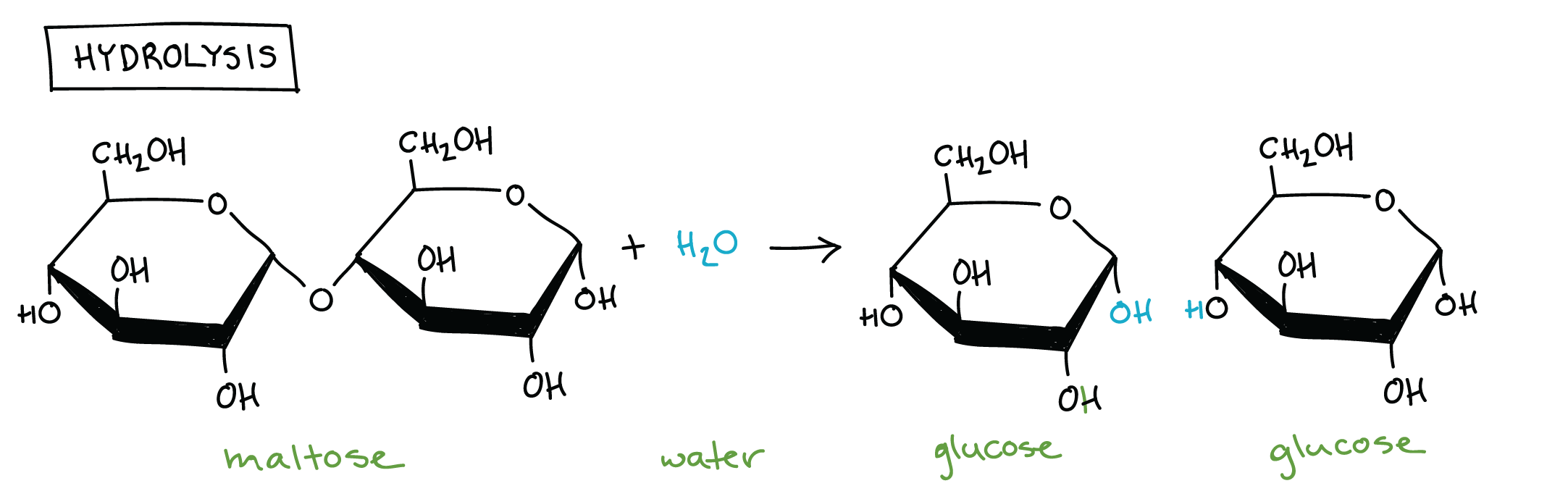
Maltose
An example of a disaccharide that is found in beer. Made up of glucose + glucose.
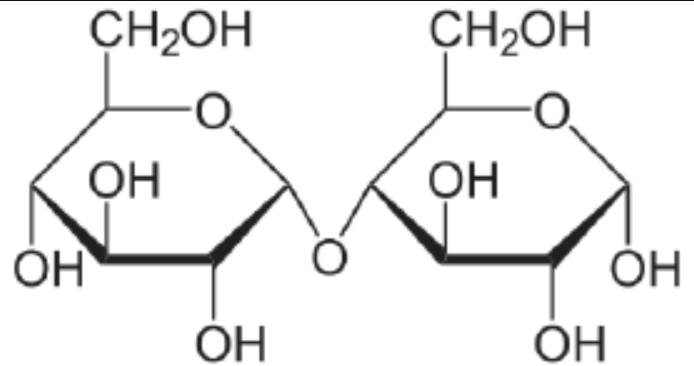
Sucrose
An example of a disaccharide that is found as table sugar. Made up of glucose + fructose.
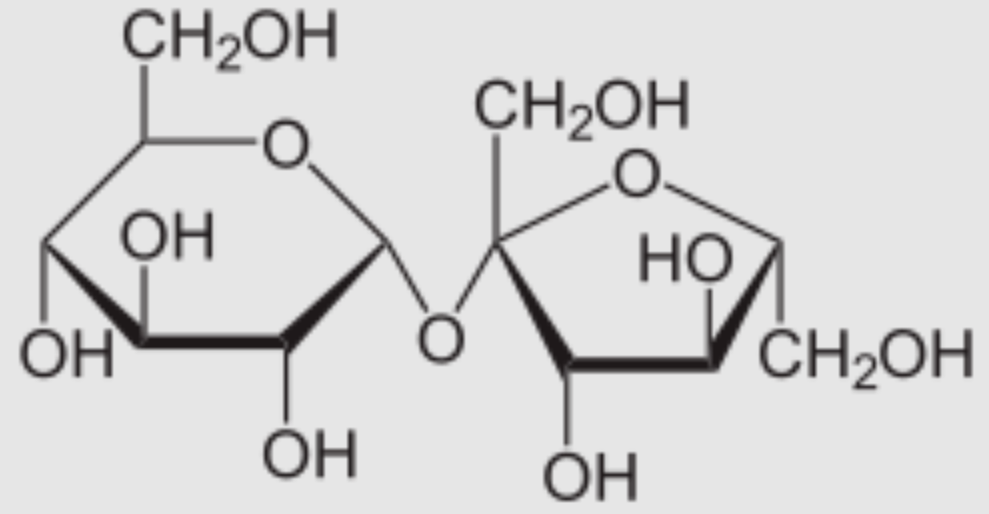
Lactose
An example of a disaccharide that is found in milk. Made up of α or glucose + galactose.
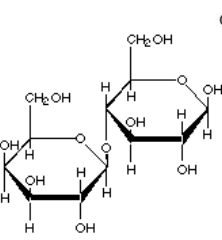
Glycosidic Linkage
A covalent bond that joins two monosaccharides together through an oxygen atom, created by dehydration synthesis.
Polysaccharides
A very complex form of carbohydrate that is made up of 100s or 1000s of subunits held together by glycosidic linkages.
Starch
An example of a polysaccharide that is formed by linking excess α-glucose produced by plants, which they use to store energy. It is made up of amylose and amylopectin.
Amylose
An example of a polysaccharide that makes up starch. They are chains of coiled α-glucose monomers in a straight chain with α1-4 glycosidic linkages.
Amylopectin
An example of a polysaccharide that makes up starch. They are chains of coiled α-glucose monomers with α1-4 glycosidic linkages, AND it has branching α-glucose monomers to the main chain by α1-6 glycosidic linkages.
Glycogen
An example of a polysaccharide that is used by animals to store energy. It is similar to amylopectin, but it has more branches of α-glucose monomers at α1-6. Their stores are depleted after a day of not being used.
Cellulose
An example of a polysaccharide that is a polymer of β-glucose monomers, rather than α-glucose in amylose. The β-glucose monomers are connected by β1-4 glycosidic linkages. It is not coiled, since every second glucose monomer is inverted, creating a straight chain that has no coils. Humans lack the enzyme necessary to break down the linkages of this polysaccharide.
Lipids
A macromolecule that contains mainly C-H bonds. They do not mix well with water, as they are hydrophobic.
List: Four Functions of Lipids
Energy Storage
Insulation
Building cell membranes
Sending cell signals
List: Four Types of Fats
Fats
Phospholipids
Steroids
Waxes
Fats
A type of lipid that is mainly used for energy storage. Excess carbs are converted into fats and stored in adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue
Tissue where excess carbs are converted into fats and stored in
Triglyceride
The most common fat that is made up of a glycerol backbone and three fatty acid chains connected by an ester linkage.
Ester Linkage
A covalent bond formed between a hydroxyl group of glycerol and a carboxyl group of a fatty acid. Used to build triglycerides.
Fatty Acids
Long, hydrocarbon chains with a carboxyl group at the end
Saturated fats
Fsts that only contain single C-C bonds. They are solid at room temperature and mostly found in animals
Unsaturated fats
Fats that contain one C=C bond (monounsaturated) or multiple C=C bonds (polyunsaturated). They are liquid at room temperature and mostly found in plants
Kinks
Refers to the bends in a fatty acid chain caused by double bonded C=C atoms.
“Bad Fats”
Refers to saturated fats since they accumulate in the blood vessels easily, causing plaques and leading to heart disease
Hydrogenation
Process by which H bonds and added, breaking the C=C bonds and creating a solid from a liquid.
Cis Fats
Refers to unsaturated fats where the hydrogen atoms attached to a double C=C bond are on the same side.
Trans Fats
Refers to unsaturated fats where the hydrogen atoms attached to a double C=C bond are on opposite sides.
Phospholipids
A type of lipid that are the main component of cell membranes. They form a bilayer, and have hydrophobic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails facing inward. They are made up of 2 fatty acids, a glycerol molecule, a phosphate and a polar molecule.
Steroids
A type of lipid that are hydrophobic and contain 4 fused rings with functional groups.
Cholesterol
A type of steroid that maintains rigidity & fluidity in the cell membrane. They travel in the bloodstream as lipoproteins.
HDL Cholesterol
A type of cholesterol that is a highly dense lipoprotein. They are the good cholesterol, as they remove excess LDL building up in the body. Cis-unsaturated fats trigger the synthesis of it.
LDL Cholesterol
A type of cholesterol that is a lowly dense lipoprotein. They are the bad cholesterol, as they build plaques in the bloodstream, leading to heart disease. Saturated fats trigger the synthesis of it, and trans fats trigger even more synthesis.
Lipoprotein
A combination of lipids & proteins
Waxes
A type of lipid that are long fatty acid chains with alcohol & carbon rings. They are hydrophobic.
List: Six Functions of Proteins
Cell signaling
Transport
Storage
Biological catalysts
Structure
Movement
Proteins
A type of macromolecule that is made up of an amino acid molecule held together by a peptide bond to for a polypeptide chain.
Peptide Bond
The bond that holds together amino acids, where the carboxyl group of one AA react with the amino group of another AA
Amino Acids
The building blocks of proteins that are made up of an amino group, a carboxyl group and a side chain. There are 20 amino acids.
Essential Amino Acids
8 of the 20 amino acids that humans do not produce, and need to intake as food.
Globular Proteins
Proteins that are described in terms of four different structural levels
Primary Structure
The structural level that refers to the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
Secondary Structure
The structural level that refers to the folding/coiling that occurs as more AA’s are added to a chain. They consist of alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets.
Alpha-Helices
A secondary protein structure that is formed when the O in the carboxyl group (C=O) reacts with the H in the amino group (N-H) in an amino acid that is 4 peptide bonds away
Beta-Pleated Sheets
A Secondary protein structure that is formed when 2 parts of the polypeptide chain lie parallel to each other, allowing H-bonds to form between O atoms in the carboxyl group of one AA to the H atoms in the amino group of another AA.
Tertiary Structure
The structural level that refers to the additional folding occurring between AA’s in a polypeptide due to external environment to create a functional protein. Bonds can affect the tertiary structure.
List: Four Bods that affect tertiary structure
Hydrogen Bonding between polar R groups
Ionic Bonding between acidic/basic R groups
Disulfide bridges (-S-S-) between 2 cysteines
Other Intermolecular Forces
Quaternary Structure
A structural level that refers to when 2 or more polypeptides come together to form a functional protein. This does not always happen.
Protein Denaturation
A process in which the bonds holding a protein in its tertiary structure can break, causing the polypeptide to unravel.
List: Four Causes of Protein Denaturation
Heat
pH
Salinity
Physical Forces