Taxation of Income, Fringe Benefits, and Retirement Plans: Chapters 7-8
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
What happens if an employer pays personal expenses for an employee?
The payment is considered income to the employee.
What are the tax advantages of qualified retirement plans?
Employees recognize no current income for employer contributions or their own contributions, and annual earnings on investments are not taxable.
What happens if contributions exceed the permitted amount in an IRA?
Excess contributions are subject to a 6% excise tax each year until withdrawn.
What is the phaseout range for single taxpayers contributing to a Roth IRA in 2025?
Phaseout begins at a modified AGI of $150,000.
Where are farming expenses reported?
On Schedule F of Form 1040.
When are expenses deducted under the accrual method of accounting?
Expenses are deducted when incurred.
How does the accrual method treat prepaid expenses?
The 12-month rule does not affect the timing of the deduction for prepaid expenses for accrual basis taxpayers.
How do employers report wage and tip income to individuals?
Employers report wages to employees on a Form W-2, which employees include in their income.
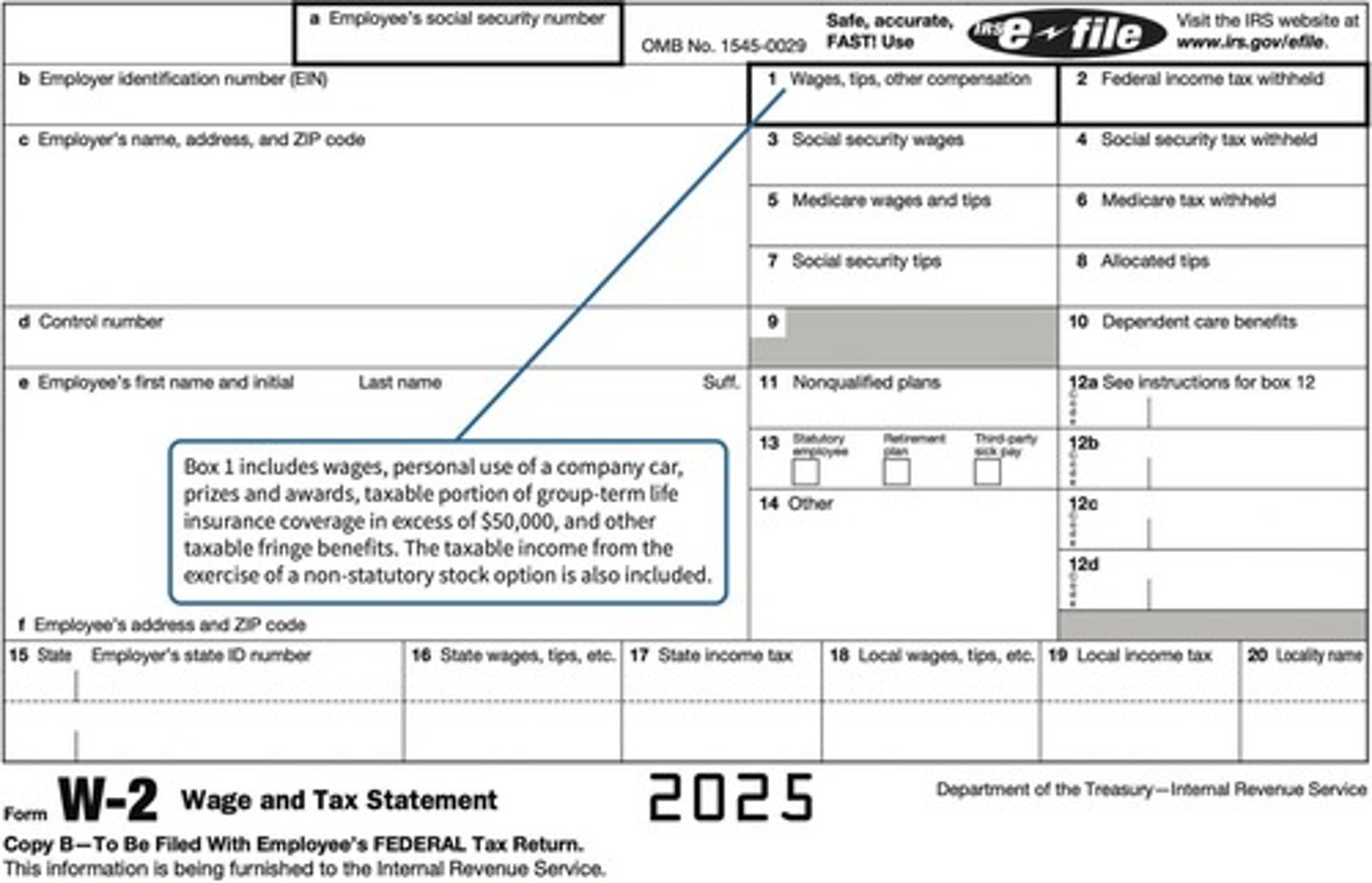
What items should not be included in Box 1 of Form W-2?
Employee elective deferrals to a Section 401(k) or 403(b) plan, and employer-paid health insurance for greater than 2% shareholders in an S corporation.
What is the reporting requirement for employees regarding tip income?
Employees must report all tip income received as income on Form 1040 and report tips of $20 or more for a month to the employer by the 10th day of the following month.
What is a fringe benefit in the context of taxation?
A fringe benefit is an extra benefit supplementing an employee's salary, which must be included in income as wages unless specifically excluded by Congress.
What are the two categories of employees regarding discrimination rules?
Highly compensated employees and nonhighly compensated employees.
What happens if a fringe benefit is deemed discriminatory?
Highly compensated employees are taxed on the fair market value of the benefit, while nonhighly compensated employees are not taxed if the benefit is excludable.
Which fringe benefits are not taxable to any employees?
Health insurance premiums (if not self-insured), working condition fringe benefits, transportation and parking fringe benefits, lodging on employer's premises, and de minimis fringe benefits.
What types of insurance are considered fringe benefits?
Health insurance, disability insurance, and long-term care insurance.
What are the tax implications of employer-provided health and long-term care insurance premiums?
Premiums paid by employers are excluded from employee income and are deductible for employers.
What is the general rule for employer-paid life insurance premiums?
Employees recognize income for premiums paid by the employer, except for group term life insurance coverage up to $50,000.
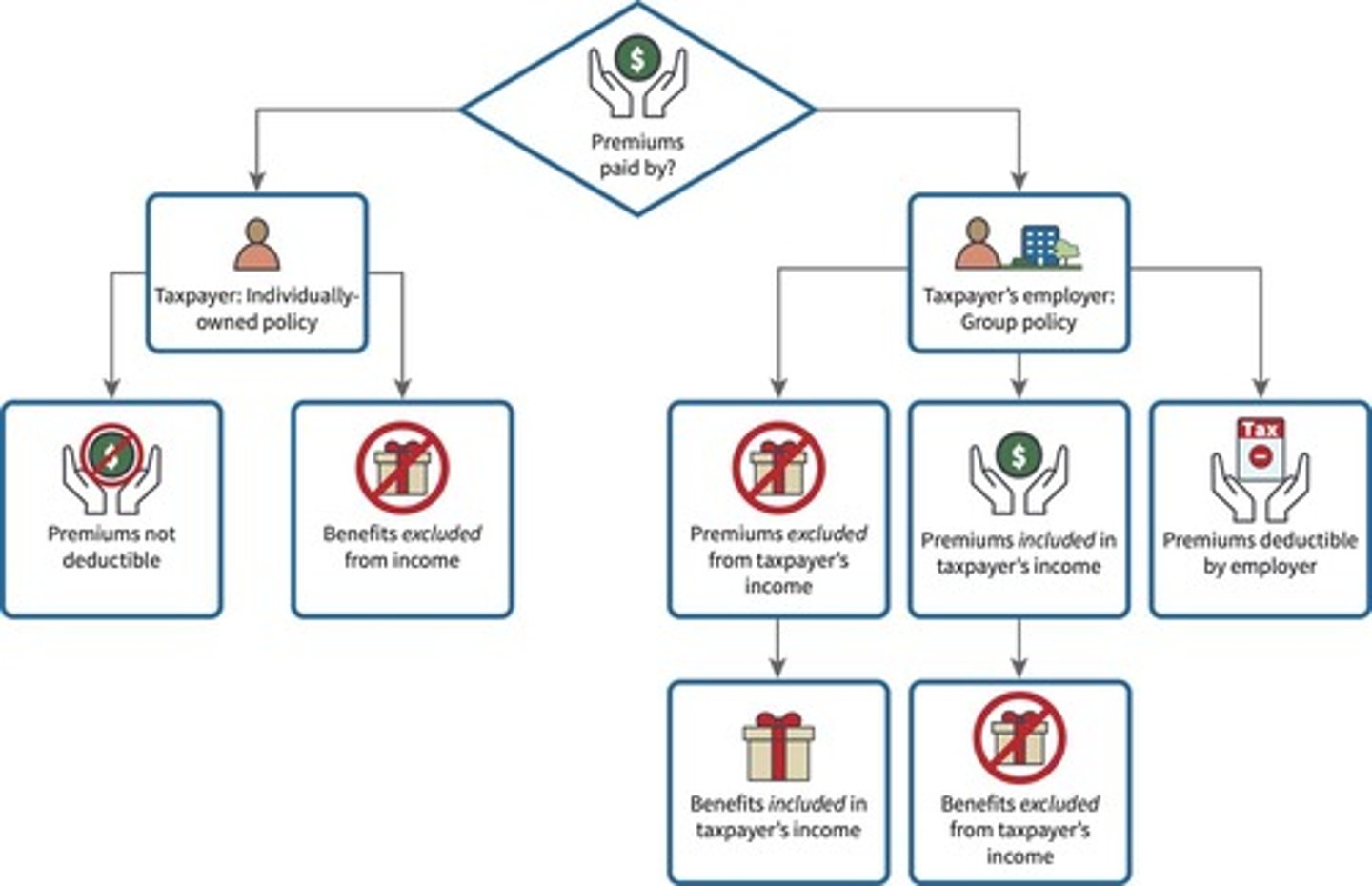
What is Corporate-Owned Life Insurance (COLI)?
A life insurance policy where an employee is insured by an employer that owns the policy, with no tax consequences to the employee.
What are the tax implications of death benefits paid to the family of a deceased employee?
Death benefits are included in income, and it is preferable for employers to provide group-term life insurance.
Can insured individuals exclude benefits from health and disability insurance proceeds?
Yes, if the taxpayer paid the premiums, even if the benefits received are a substitute for lost wages.
What happens if the employer pays the premium for disability insurance?
The employer can deduct the premiums, but the employee must include any benefits received in income.
What are the tax consequences if the employer and employee share the cost of disability insurance?
Tax consequences are determined based on the percentage of the premium paid by each.
What conditions allow employees to exclude health insurance benefits from income?
Benefits are excluded if they cover qualified medical expenses or payments for loss of a body part or permanent disfigurement.
What exclusions apply when a taxpayer receives an insurance benefit?
Members of the armed forces injured during combat duty may not have to include disability payments in income.
What is the significance of qualified medical expenses in health insurance reimbursements?
If reimbursement exceeds qualified medical expenses, the excess is taxable.
What is the treatment of premiums for disability policies paid by the employee?
Individuals cannot deduct premiums for disability policies, but health insurance premiums may be deductible if itemized.
What is the exclusion for employer-provided group term life insurance?
Premiums paid by the employer for up to $50,000 of nondiscriminatory group term life insurance coverage are excluded from income.
What is the daily exclusion limit for long-term care policy benefits in 2025?
$420 per day
What are the categories of fringe benefits that can affect taxable income?
Personal expenses, food and lodging, working condition fringe benefits, de minimis fringe benefits, no additional cost services, employee discounts, nominal gifts, safety and length of service awards, transportation and parking, cafeteria plans.
What must be true for food and lodging provided by an employer to be excluded from income?
It must be provided for the convenience of the employer, on the employer's premises, provided in kind, and required as a condition of employment for lodging.
What defines a working condition fringe benefit?
A benefit that would be deductible as a business expense if paid by a self-employed individual.
What are de minimis fringe benefits?
Fringe benefits that are small in value and infrequent, such as occasional personal use of a copy machine.
What are the requirements for no additional cost services to be tax-free?
They must incur no substantial additional costs and apply only to services provided in the employee's line of business.
What is the limit for excluding employee discounts from income?
20% of the value of services or the average gross profit percentage for merchandise.
What is the maximum value of nominal gifts that can be excluded from income?
Up to $25 per employee, provided they are not cash or cash equivalents.
What conditions must be met for safety and length of service awards to be excluded from income?
The award cannot be cash, must be for length of service or safety, and cannot be similar to an award given in the last five years.
What are the exclusion limits for safety and length of service awards?
Up to $400 under a nonqualified plan and up to $1,600 under a qualified plan.
What is the exclusion limit for employer reimbursements for mass transportation and parking in 2025?
$325 per month for each.
What is the exclusion limit for child and dependent care services provided by an employer?
Up to $5,000, or $2,500 if married filing separately.
What is the exclusion limit for education assistance provided by an employer?
Up to $5,250 for tuition, fees, books, and supplies.
What is the exclusion limit for adoption expenses reimbursed by an employer?
Up to $17,280 in 2025, phased out at AGI levels between $259,190 and $299,190.
When can employer reimbursements for moving expenses be excluded from income?
If the move is related to a military order for a member of the Armed Services.
What benefits can be excluded when using employer-provided athletic facilities?
Use is excluded for the employee, their spouse, dependents, and retirees.
What type of retirement advice can be excluded from an employee's income?
Employer-provided retirement advice.
What are Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs)?
Accounts set up by employers allowing employees to contribute a portion of their salary, which is not taxed, to pay for medical, dependent care, or adoption expenses.
What happens to unused funds in an FSA at the end of the tax year?
Employees forfeit any funds not used by the end of the tax year.
What is a Cafeteria Plan?
A plan where the employer provides cash for fringe benefits, and the employee chooses which benefits to use, with any unspent cash taxed as wages.
What are some qualified benefits that can be offered through a Cafeteria Plan?
Qualified benefits include coverage under accident or health plans, disability coverage, group-term life insurance, dependent care assistance, contributions to 401(k) plans, health savings accounts, and adoption assistance.
What is an accountable plan?
A written plan that allows businesses to reimburse employees for business expenses without the reimbursements being taxable, provided certain conditions are met.
What are the requirements for an accountable plan?
Employees must substantiate all expenses within 60 days and return any excess reimbursements within 120 days.
What does 'substantiated' mean in the context of reimbursements?
It means the employee provides documentation showing the amount, time, place, names of individuals involved, and business purpose of the expense.
What is the tax implication of reimbursements under an accountable plan?
The reimbursement is not taxable, and the employee cannot deduct the expense.
How are reimbursements treated under a nonaccountable plan?
The reimbursement must be included in income, and the employee cannot deduct the expense.
What defines a qualified retirement plan?
It must meet nondiscriminatory, funding, vesting, and participation requirements.
What is a 401(k) plan?
A defined contribution plan where employees contribute pre-tax salary, and they manage the investment of the funds.
What is meant by 'vesting' in retirement plans?
Vesting refers to the employee's right to retain benefits in the plan if they stop working for the employer.
What are the 2025 contribution limits for a 401(k) plan?
Up to $23,500 for voluntary contributions, with catch-up contributions of $7,500 for those age 50 and over, and $11,250 for those age 60-63.
What is a pension plan?
A type of defined benefit plan where the employer promises a retirement benefit based on a formula that includes years of service and salary.
How are pension plans funded?
Through employer contributions and sometimes employee contributions, with no tax on the amounts contributed.
What is a Keogh plan?
A tax-deferred pension plan available to self-employed individuals, typically a defined contribution plan.
What are the contribution limits for a Keogh plan in 2025?
The lesser of $70,000 or 25% of earned income.
What are the two main types of Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)?
Traditional IRA and Roth IRA.
What is the contribution limit for IRAs in 2025?
The lower of $7,000 or earned income for the year, with an additional $1,000 catch-up contribution for those 50 and over.
What happens to earnings on retirement plan assets each year?
Earnings are not taxed until distributions are received.
What triggers a penalty for early withdrawals from qualified retirement plans?
Withdrawals made before age 59½ trigger a penalty in addition to taxation.
What is the maximum contribution limit for married couples to an IRA?
$7,000 per spouse, if there is sufficient compensation.
When can the 6% penalty for excess contributions be avoided?
If the excess contribution is removed before the due date of the tax return for the year of contribution.
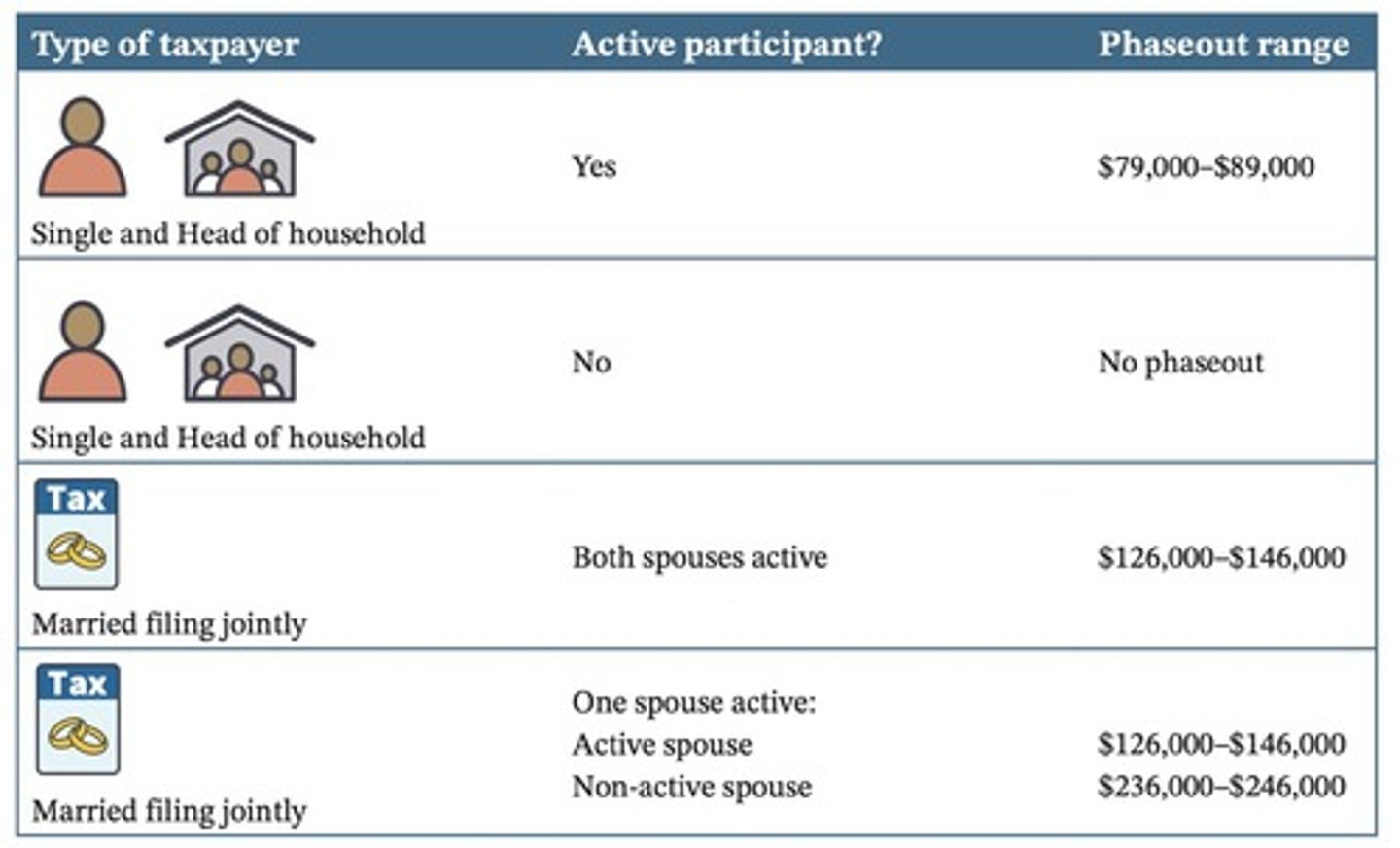
What determines the deduction limits for Traditional IRAs?
Deduction limits depend on whether the taxpayer is an active participant in another qualified retirement plan.
How is an active participant defined for IRA contribution purposes?
An active participant is someone not excluded from an employer-funded defined benefit plan or who contributes to another qualified retirement plan.
What is the deduction phaseout range for active participants in 2025?
The phaseout occurs over a $10,000 range for modified AGI exceeding certain limits.
What is the minimum deduction for Traditional IRAs if not completely phased out?
$200.
What are the contribution limits for Roth IRAs in 2025?
The limit is the same as Traditional IRAs: $7,000 or earned income for the year, plus a $1,000 catch-up contribution for those 50 and over.
Are contributions to Roth IRAs deductible?
No, contributions to Roth IRAs are not deductible.
What happens to distributions from a Roth IRA?
Distributions are not taxable, including both original contributions and earnings.
What is a taxable event when converting a Traditional IRA to a Roth IRA?
The taxpayer must recognize a gain to the extent that the conversion amount exceeds the tax basis in the IRA.
What is the penalty for early withdrawals from a Traditional IRA?
A 10% penalty tax applies unless the taxpayer is at least age 59½ or disabled.
List one exemption from the penalty for early withdrawals from a Traditional IRA.
Withdrawals made for first-time home buyer expenses (limited to $10,000).
What is the requirement for withdrawals from a Traditional IRA starting in 2023?
Withdrawals must begin by April 1 of the year after the taxpayer reaches age 73.
What is the tax-free distribution limit for charitable contributions from an IRA for individuals age 70½ and over?
Up to $108,000 in distributions can be tax-free if contributed to a charitable organization.
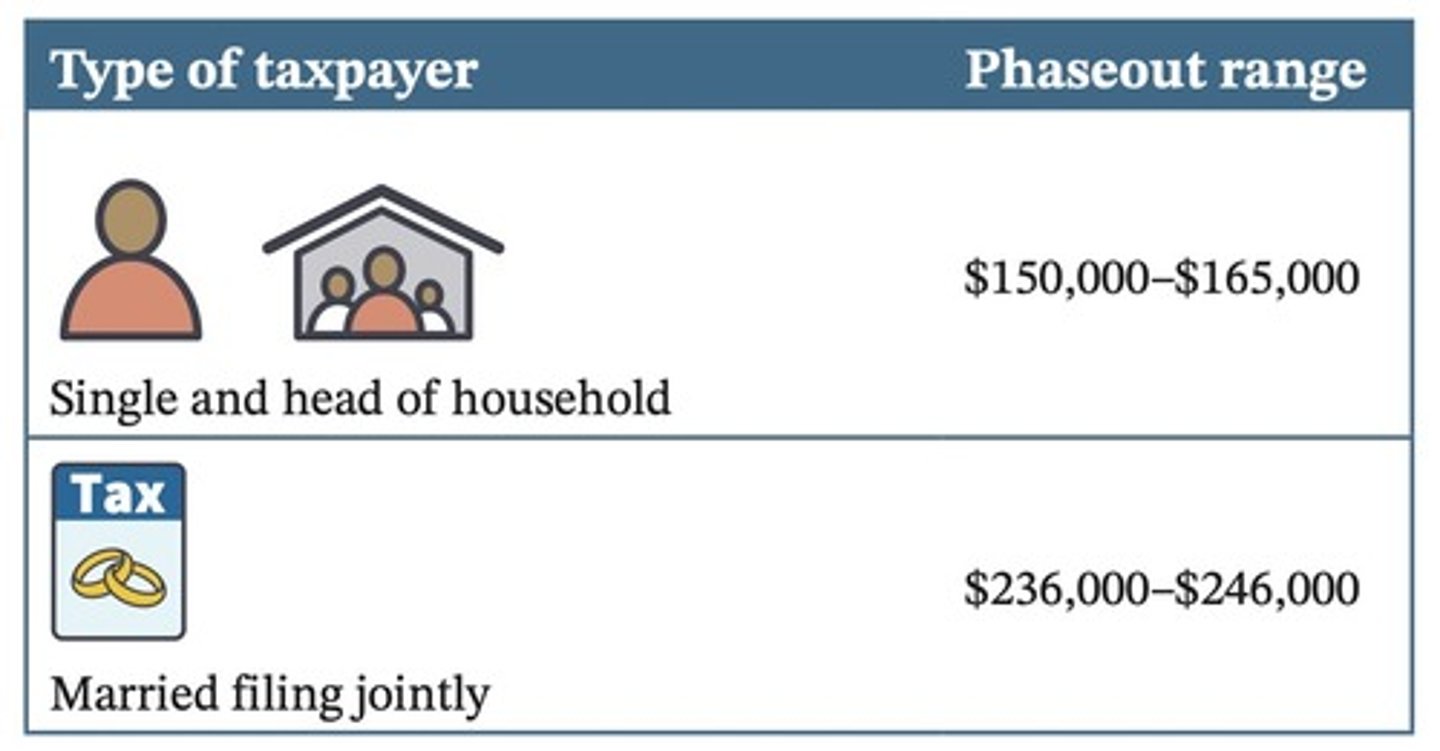
What is the phaseout range for Roth IRA contributions for married filing jointly in 2025?
Phaseout begins at a modified AGI of $236,000.
What is the rule regarding combined contributions to Traditional and Roth IRAs?
Combined contributions cannot exceed the contribution limit.
What happens to distributions from retirement plans if taken early?
Distributions are usually taxable and may incur penalties.
What is the penalty exemption for withdrawals made due to active military duty?
Withdrawals made by individuals called to active military duty are exempt from penalties.
What is the limit on distributions used to pay expenses related to federally declared disaster areas?
Limited to $22,000, and these distributions are included in income over three years.
What is the limit on distributions for expenses incurred during the one-year period after the birth or adoption of a child?
Limited to $5,000.
What conditions allow for tax-free withdrawals from a Roth IRA?
Withdrawals are tax-free if made five years after the initial contribution and after age 59½, due to death or disability, or for first-time home buyer expenses (up to $10,000).
What happens if Roth IRA withdrawal rules are not met?
Distributions are taxable to the extent they exceed contributions and are subject to a 10% penalty.
What is the exception to the 10% penalty for distributions from other qualified plans?
The penalty does not apply to employees aged 55 or older after separation from service.
When must required minimum distributions (RMDs) begin for traditional IRAs?
RMDs must begin by April 1 of the year after reaching age 73 or after retirement.
What is the penalty for not withdrawing the required minimum distribution?
The penalty is 25% of the required distribution not made, reduced to 10% for IRAs if corrected.
What is the rollover process for retirement plans?
Payments can be rolled over by depositing in another plan or IRA within 60 days or through trustee-to-trustee transfers.
What is an annuity in the context of retirement distributions?
An annuity is a fixed sum of money paid annually, usually for the rest of the recipient's life.
What is the tax treatment of distributions from an annuity if there is no basis?
All distributions are taxable if there is no basis in the qualified retirement plans.
What is a single life annuity?
A single life annuity is paid out over the life of the employee who owns the annuity.
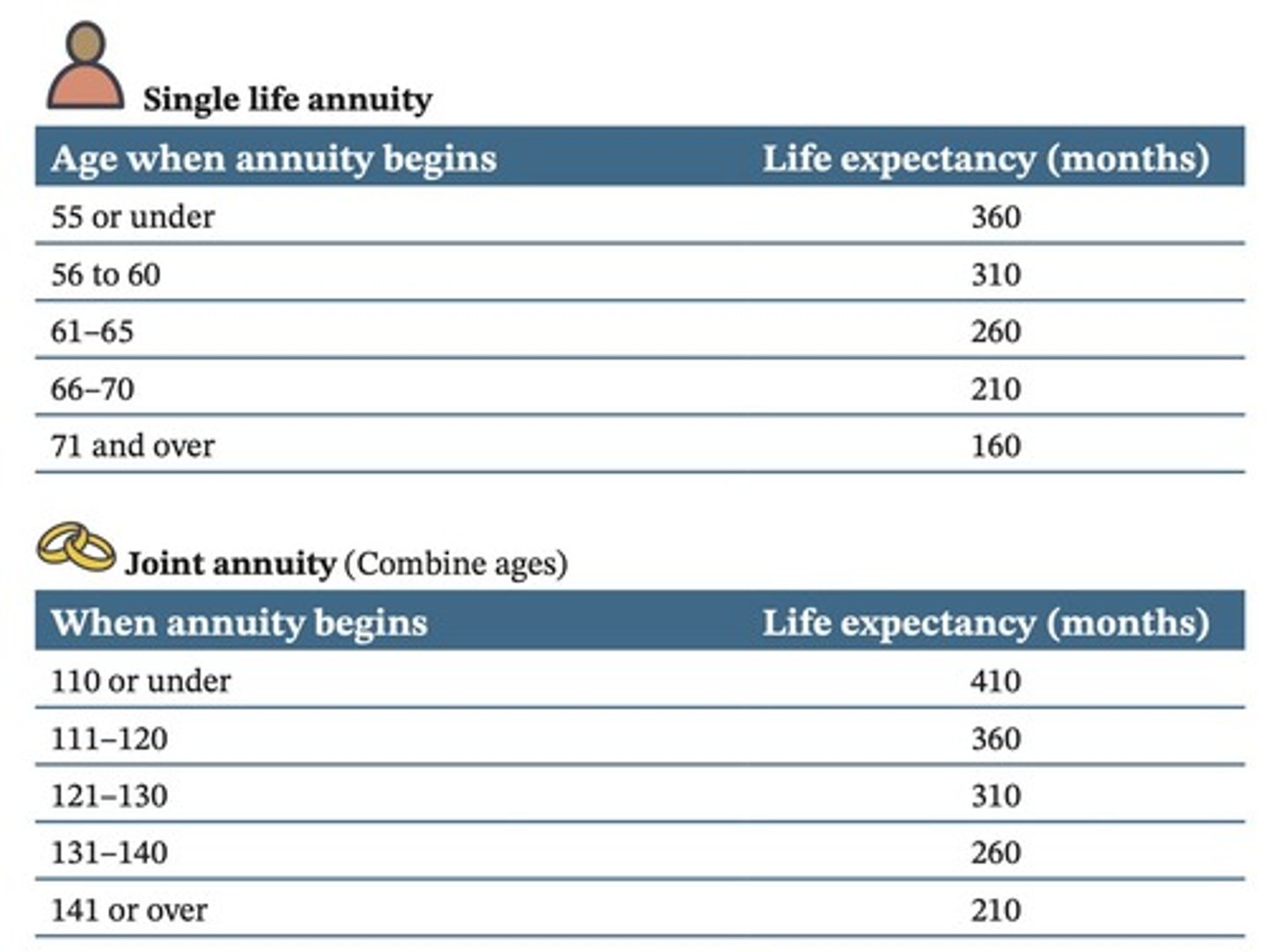
How do you determine the taxable portion of an annuity payment?
Use a four-step process involving reporting the monthly amount, determining life expectancy, calculating expected return, and excluding the return of capital.
What happens to the exclusion ratio of annuity payments after life expectancy is reached?
Payments received after life expectancy are fully taxable.
What is the provisional income (PI) formula for determining taxable Social Security benefits?
PI = AGI (before SSB) + Tax-exempt interest + 50% (SSB).
What are the base amounts used to compute the includible portion of Social Security benefits?
If PI is ≤ BA1, SSB are not taxable; if PI is > BA1 but ≤ BA2, 50% are taxable; if PI is > BA2, 85% are taxable.
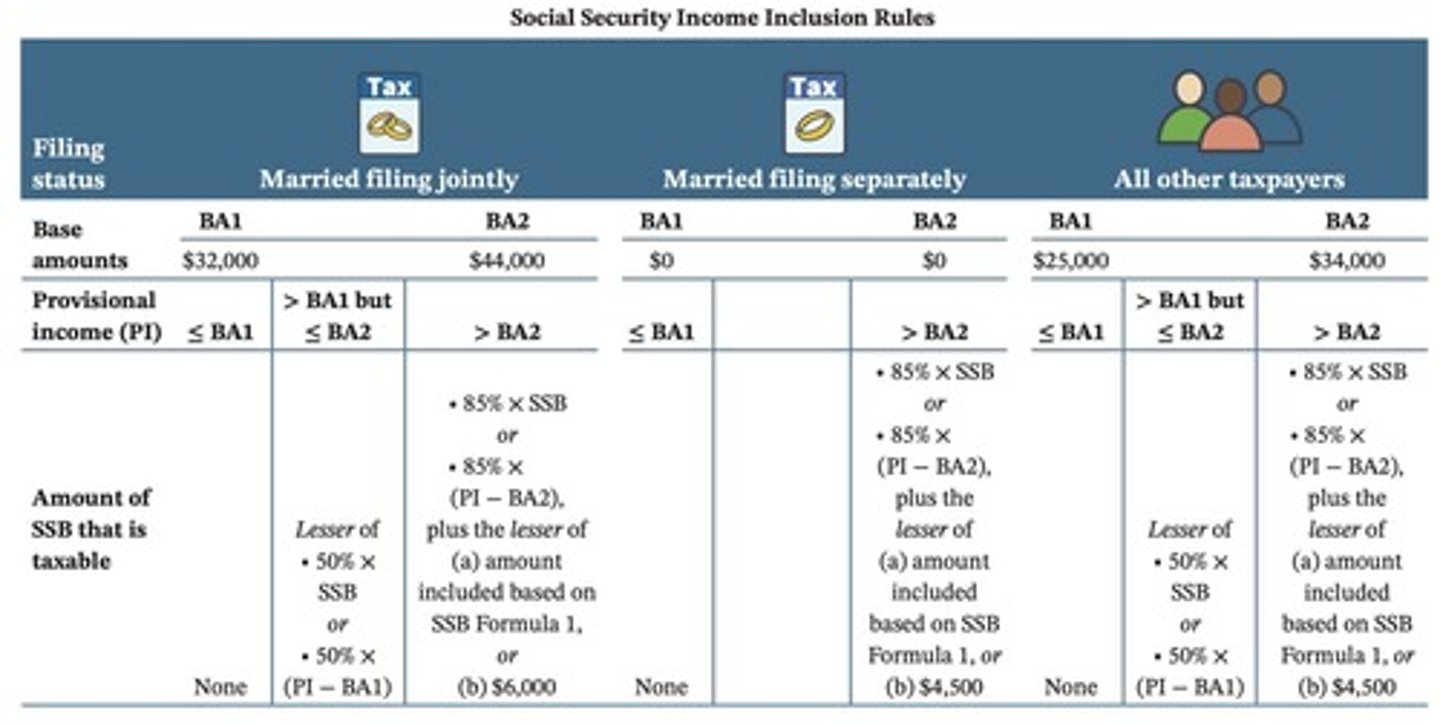
What are the formulas for determining taxable amounts of Social Security benefits?
If PI exceeds BA1 but not BA2, the taxable amount is the lesser of 50% × SSB or 50% × (PI - BA1); if PI exceeds BA2, it's the lesser of 85% × SSB or 85% × (PI - BA2), plus the lesser of the amount from formula 1 or $4,500 ($6,000 if married filing jointly).
What is the foreign-earned income exclusion?
Qualifying individuals can exclude foreign-earned income from personal services, limited to $130,000 in 2025.