Algae Test 1
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
CO2 diffusion
critically important factor in phototrophic algal growth that is strongly controlled by the viscosity of water
hardwater
limited free CO2 available, but plenty of HCO3 - (more productive).
softwater
very little available C, as CO2 mostly from overlying air
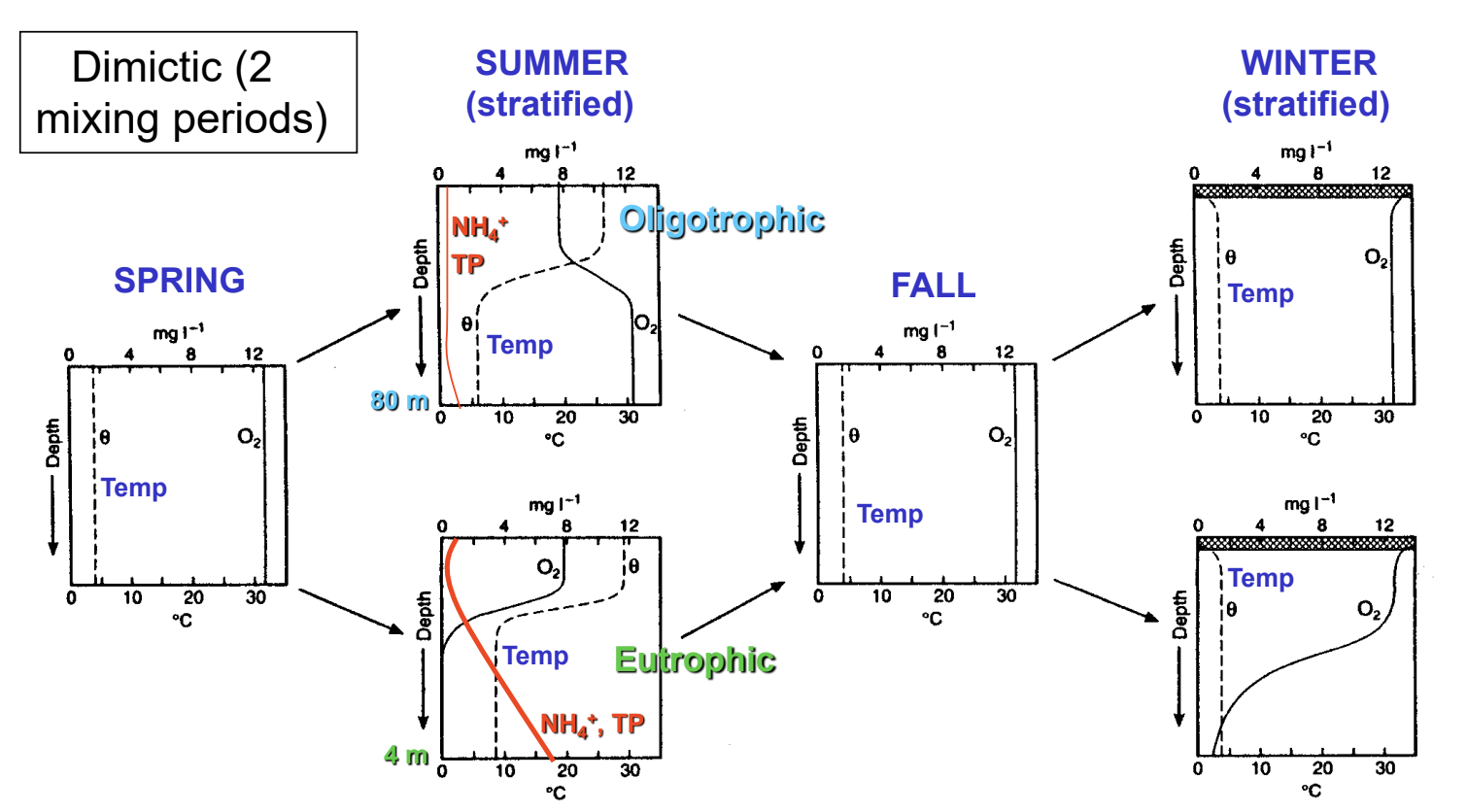
Oligotrophic
deep with steep sides; clear with high light penetration; very low in plant nutrients; oxygen abundant throughout the water column all year; very high species diversity but very low abundance; often with deep-water fishes.
Eutrophic
shallow (depth < 10 meters), low light in growing season(s), high in plant nutrients; surface waters with wide oxygen swings in growing season, little or no oxygen (hypoxic/anoxic) in lower (or more) water column; common - high-biomass “blooms” of a few species (autochthonous production)
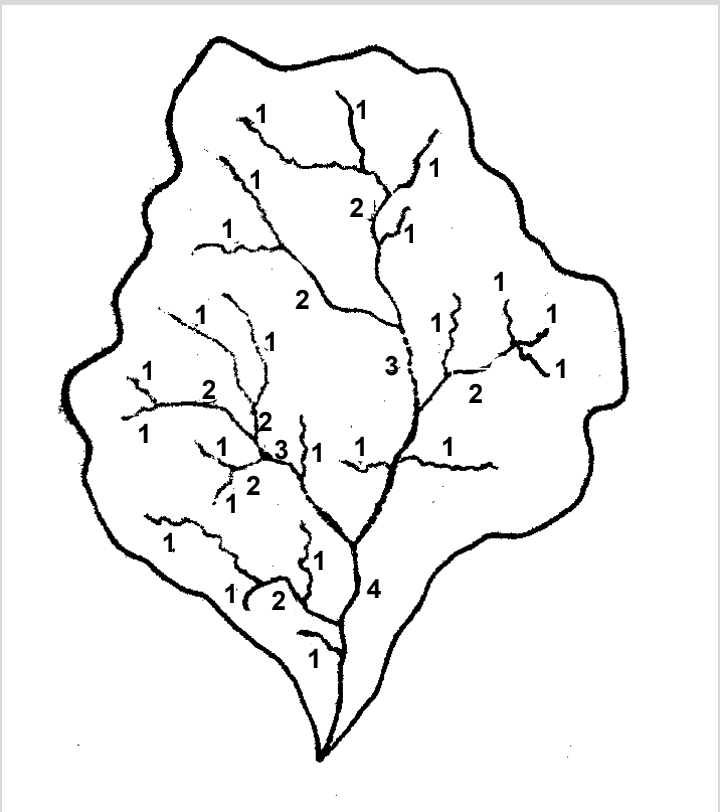
headwaters of lotic systems
(1st to 3rd order segments) – youngest, with no tributaries; heavily shaded, cool, boulder/rock substrata, small, high input of allochthonous (and autochthonous) material; poorly buffered (lower pH); low nutrients, high oxygen.
mid-regions of lotic systems
(4th to 6th order segments) – more light, wider channel, higher volume, increasing sediment load, higher autochthonous input; stone/sand substrata; moderate flow, nutrients.
lower regions of lotic systems
(7th to 12th order segments) – open to light but major sediment load minimizes light availability; also a scouring effect. Large volume, deep channel, wide, slowly flowing; neutral to alkaline pH, lower dissolved oxygen, highest nutrients.
Strahler’s stream ordering system
communication shorthand
factors strongly control algal growth in aquatic systems
Light
Water residence time
Nutrients
two nutrients most strongly control algal growth
N (total nitrogen) / P (total phosphorus)
phototrophy
rely on photosynthesis for their nutrition (have the same photosynthesis as higher plants, including the “universal plant pigment, chlorophyll a);
Mixotrophy
the ability to act both as heterotrophs through consuming other organisms (phagotrophy), and as photosynthetic algae.
How certain are phylogenetic relationships
phylogeneticists are still deciphering and changing relationships
depth profiles for DO, NO3- (same as for DO), NH4+, and TP
How are reservoirs different from natural lakes
reservoirs tend to experience higher algal growth and more frequent blooms due, often having higher nutrient levels and more fluctuating water levels compared to natural lakes, leading to a less stable ecosystem for algae populations
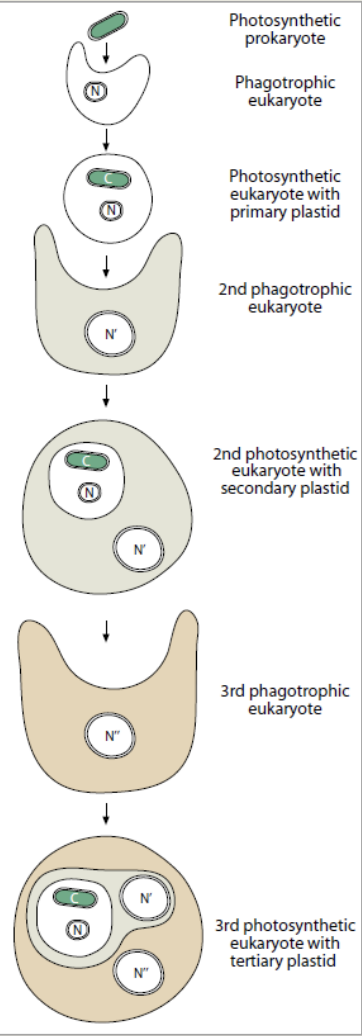
rationale for the hypothesis that much of the adaptive radiation that led to development of major eukaryotic groups occurred in unicellular flagellates
a dinoflagellate cell acquired kleptochloroplasts from cryptomonad prey
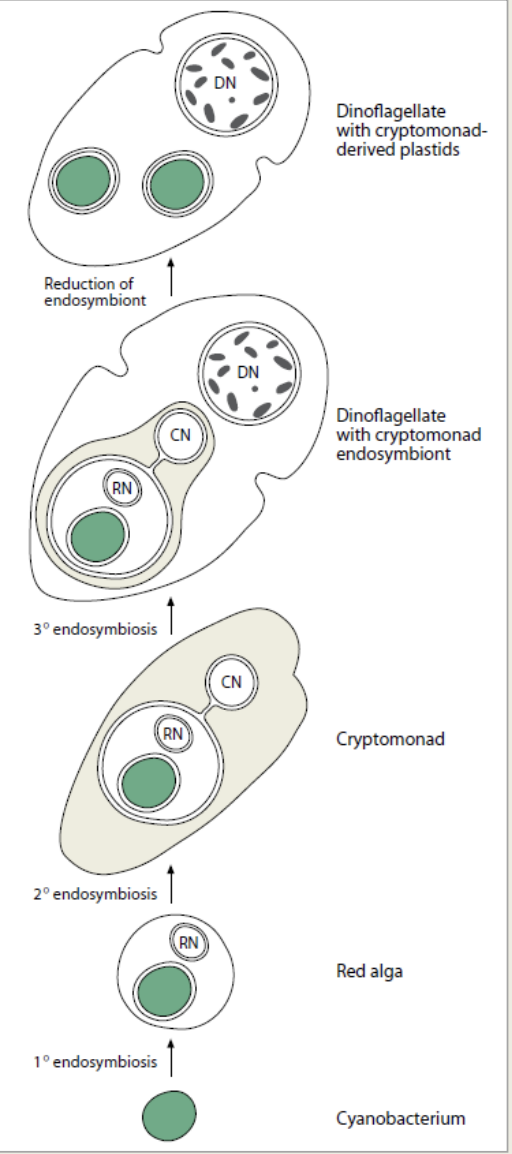
endosymbiont hypothesis for the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts
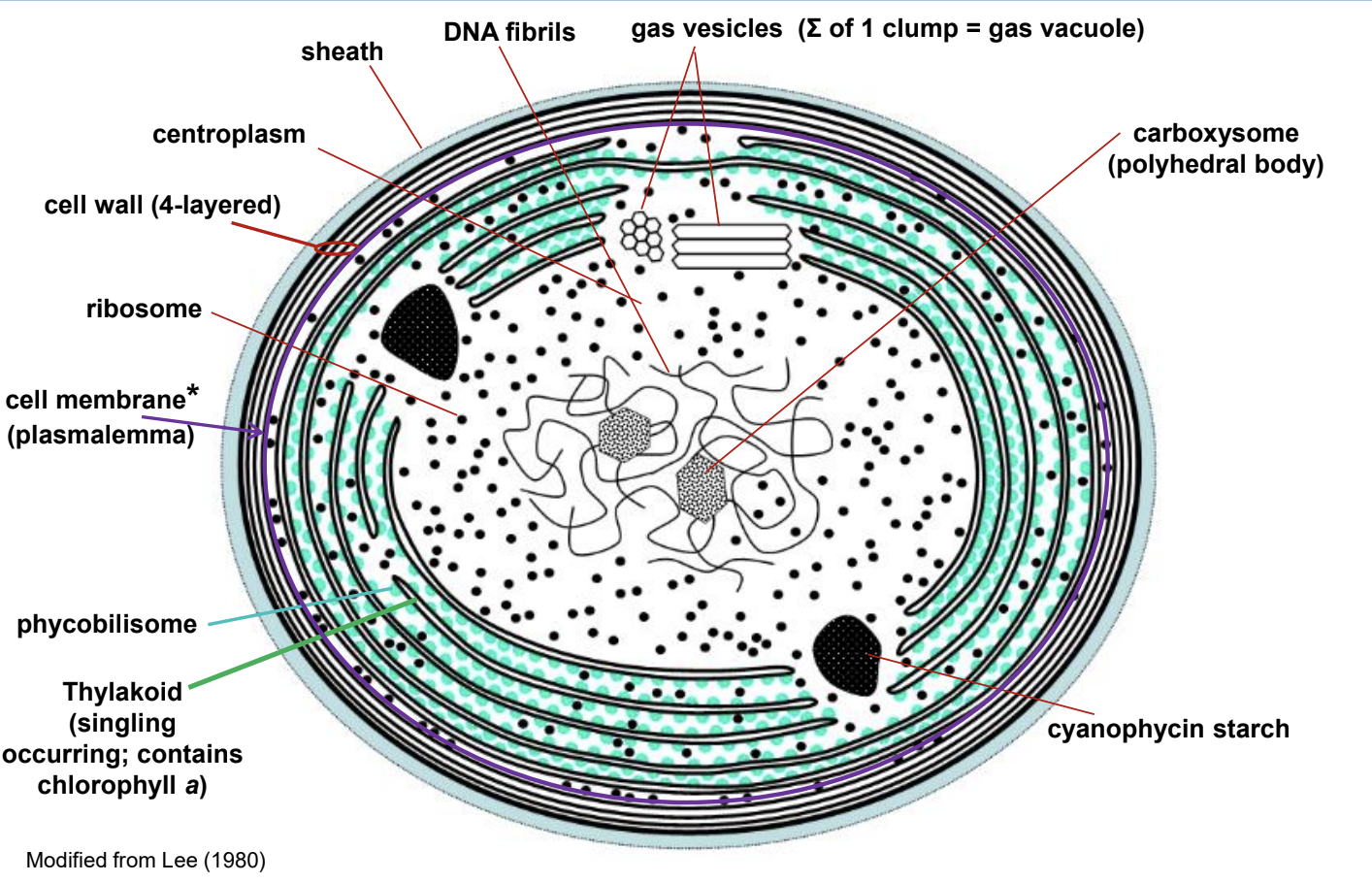
Fine structure (ultrastructure): draw and fully label for a generalized cyanobacteria cell
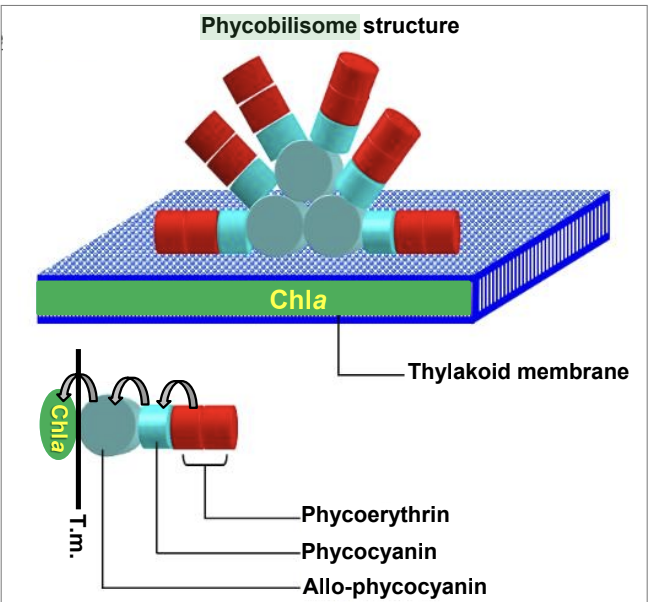
structure of a phycobilisome
pigment absorptive characteristics that make it a great “light antenna”
extremely efficient at harvesting chla, and protects chla. Can capture the entire “green window”
important ecological contribution cyanobacteria
Oxygenated the Earth, primary producers in aquatic food webs
important economic aspects cyanobacteria
N2 fixation, remediation
salient features of nitrogen fixation
nitrogenase enzyme, cannot function in the presence of oxygen, inorganic [“fixed”] nitrogen is added to aquatic and terrestrial food webs
explain “chromatic adaptation” in cyanobacteria
capability of some cyanobacteria to adjust their pigment composition in response to changing light quality (increase PE in green light; increase PC in red light).
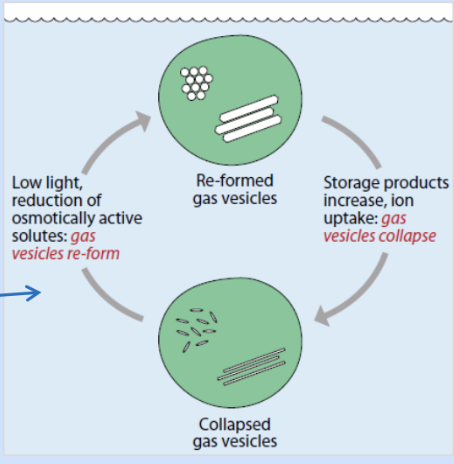
cyanobacteria buoyancy regulation
differ in the fine structure and chlorophylls of “blue” vs. “green” cyanobacteria
green- chla/chlb, eukaryotes, stacked thylakoids
blue- chla, prokaryotes, single thylakoids, anoxygenic photosynthesis
noxious cyanobacteria bloom formers and where
Microcystis in Ohio River, Dolichospermum in Lake Superior
Why are cyanobacteria blooms sometimes described as “Russian roulette” in terms of toxicity?
can’t tell if a bloom is toxic without sampling for toxin but too expensive to sample all cyanotoxins
Why do livestock, wildlife, and pets tend to be the typical victims of acute impacts from toxic cyanobacteria blooms, rather than humans
more likely to consume them
incident of human health impacts from toxic cyanobacteria
Guam Bat People consumed bats that consumed seeds contaminated with Nostoc which produces BMAA (neurotoxin)
BMAA
The “Bat People” of Guam, confirmed in brain tissues of patients who had died of Alzheimer’s disease
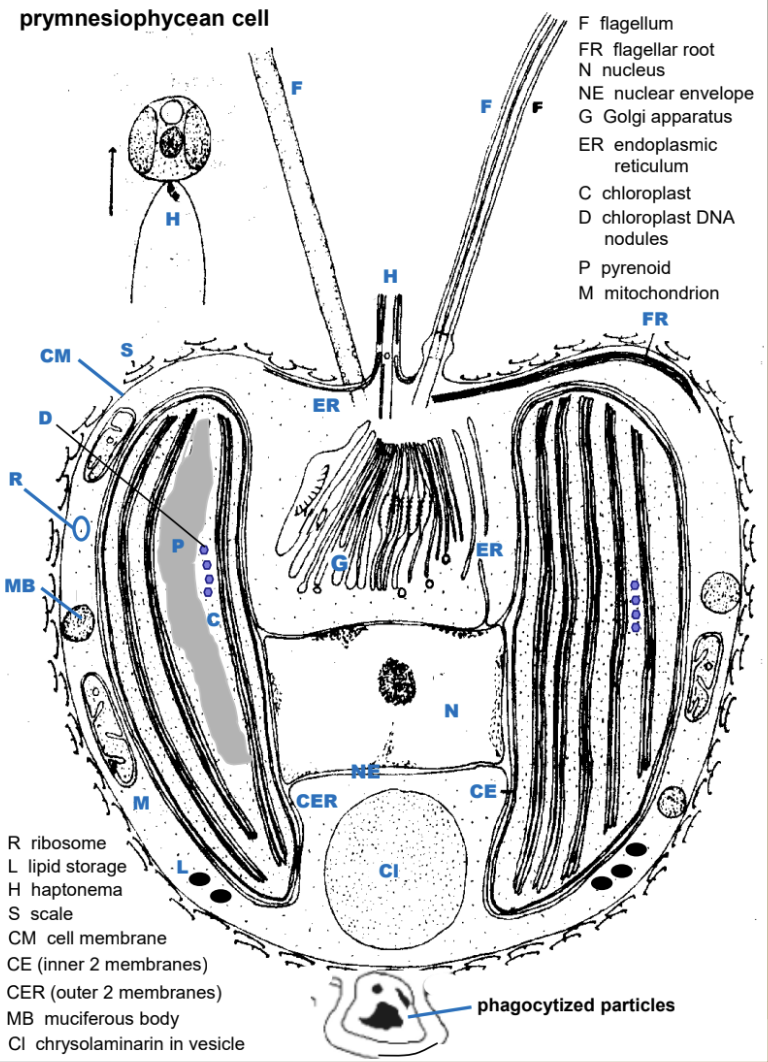
fine structure of a generalized haptophyte cell
three classes of haptophytes (names and 2 differentiating features of each)
Class Pavlovophyceae, 2 unequal flagella, paramylon
Class Rappephyceae, 4 chloroplasts, rhizoplast
Class Prymnesiophyceae, open mitosis, scales
features that collectively distinguish a haptophyte from other algal groups
mostly biflagellate or nonflagellate unicells or colonies with flagellate stages
mixotrophy common
Haptonema
9+2 arrangement of microtubules
no girdling lamella
functions of the haptonema
Used mostly for attachment and prey (bacteria) acquisition (acts like a tentacle). thin filament-like appendage with 3 outer membranes; has 6-7 microtubules in a roughly crescent-shaped array, surrounded by a ring of endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
Do you believe that there are ~300 species of mostly mixotrophic haptophytes
no because there could be polymorphism within one species
present-day serious problem in coccolithophores taxonomy
Emiliania huxleyi wrong name and polyphyletic, now 10 taxa in this species complex so far, including 3 species (2 with type species-subspecies) and 7 other subspecies
importance of mixotrophy in haptophytes, including an example
Their ecologic and evolutionary success, arguably based on mixotrophy, likely has significantly affected the oceanic carbon pump. Prymnesiophyceae have very well developed mixotrophy.
How does the common brackish genus, Pavlova, differ from most haptophytes
stigma often present, inside chloroplast
paramylon food reserve
chlorophyll c1
2 unequal flagella
example of economic importance of haptophytes
Has high levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs = omega-3 fatty acids)
ecological importance of DMS? DMSP?
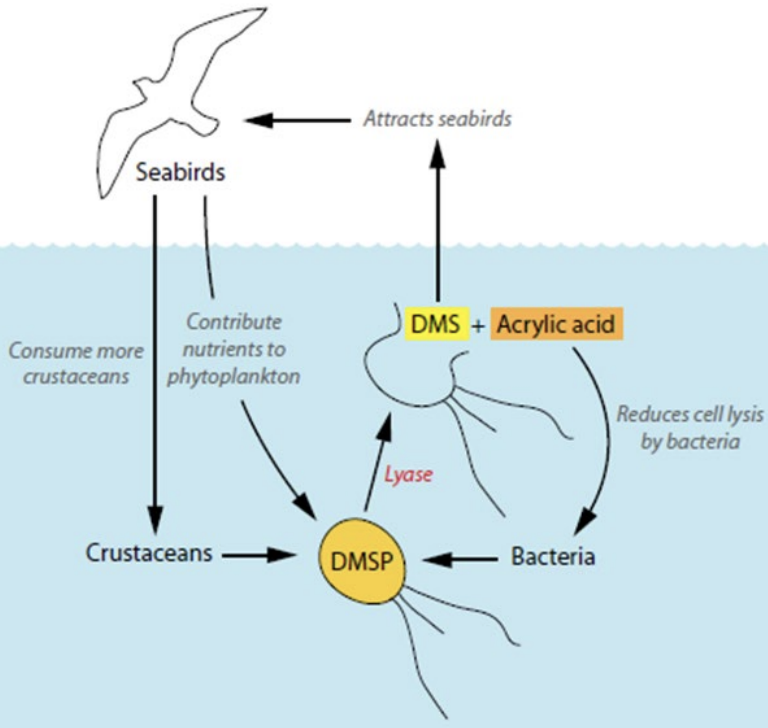
What type(s) of toxin(s) is produced by Prymnesium parvum, and what are two major ecological impacts?
Hemolysins; neurotoxins; fast-acting ichthyotoxins (cycloamines); cytotoxins, hepatotoxins, reactive oxygen species (ROS) H2O2, O2-, OH- ; DMSP; toxic fatty acids; other bioactive substances act on cell membranes loss of selective permeability (reversible); disruption of ion regulation in gills
Describe blooms of Phaeocystis
High-biomass, high mucus production clogs gills, suffocates fish, clogs fishing nets, (very low N:P ratios)
What are three general features of most heterokontophyte/ochrophyte algae?
2 heterokont (9+2) subapically inserted flagellum, fucoxanthin, Chrysolaminarin
Draw and label the fine structure of a “representative” photosynthetic heterokontophyte
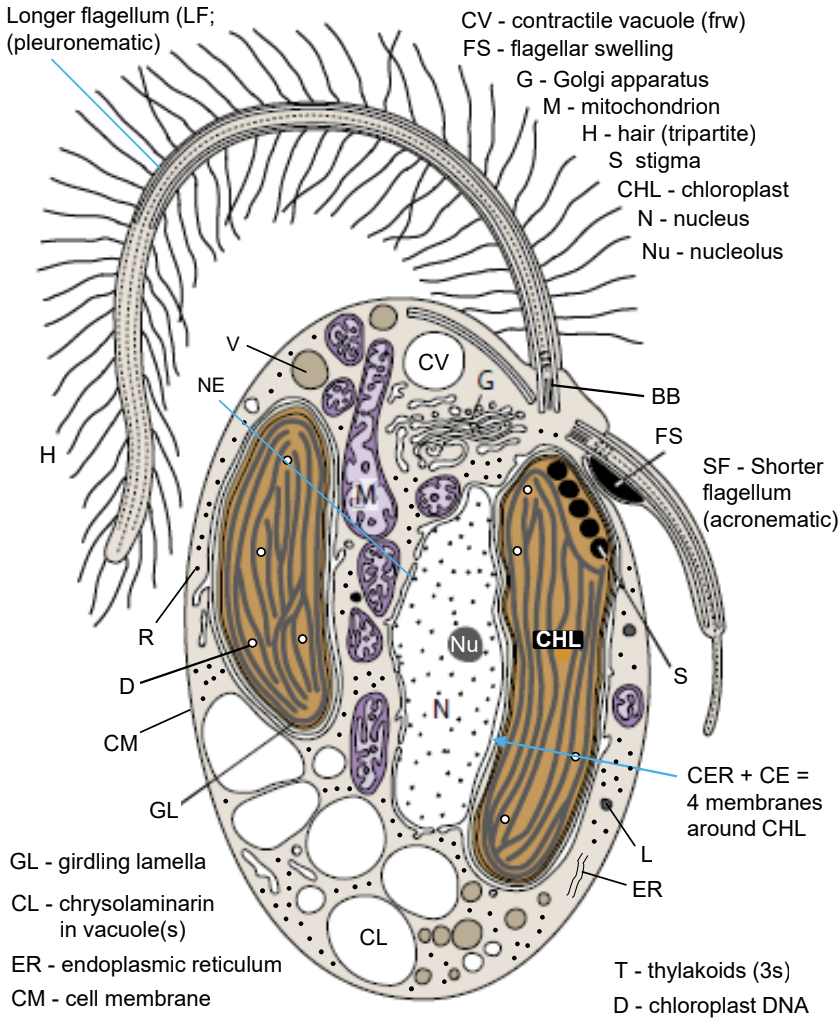
What is believed to have been the common ancestor(s) of mostly-photosynthetic stramenopile chloroplasts?
the common ancestor had a chloroplast derived from a secondary red algal endosymbiont(s) and partially contributed to haptophyte chloroplasts.
The general contribution of diatoms to global net primary production is estimated at ~20-25%. How do you think that might this change given the ongoing/building trend in climate change, and why?
at least a 10% loss in diatoms projected in the Arctic and Antarctic (ongoing thru next few decades) due to increased UV and warming temperatures).
Describe the flagellum: Which diatoms and what stage have it? Is it really a flagellum in your opinion? (general fine structure)
only in centrics’ sperm (9+0 pleuronematic)
What are two major ultrastructural features of diatoms that differ from other heterokontophytes / ochrophytes?
Wall (frustule, 2 pieces), flagellum, LARGE vacuole
Draw / label the process of asexual reproduction in diatoms. What is a consequence of this pattern - for example, what can
one expect to see when viewing a sample of diatom/natural algal assemblages under the light microscope?
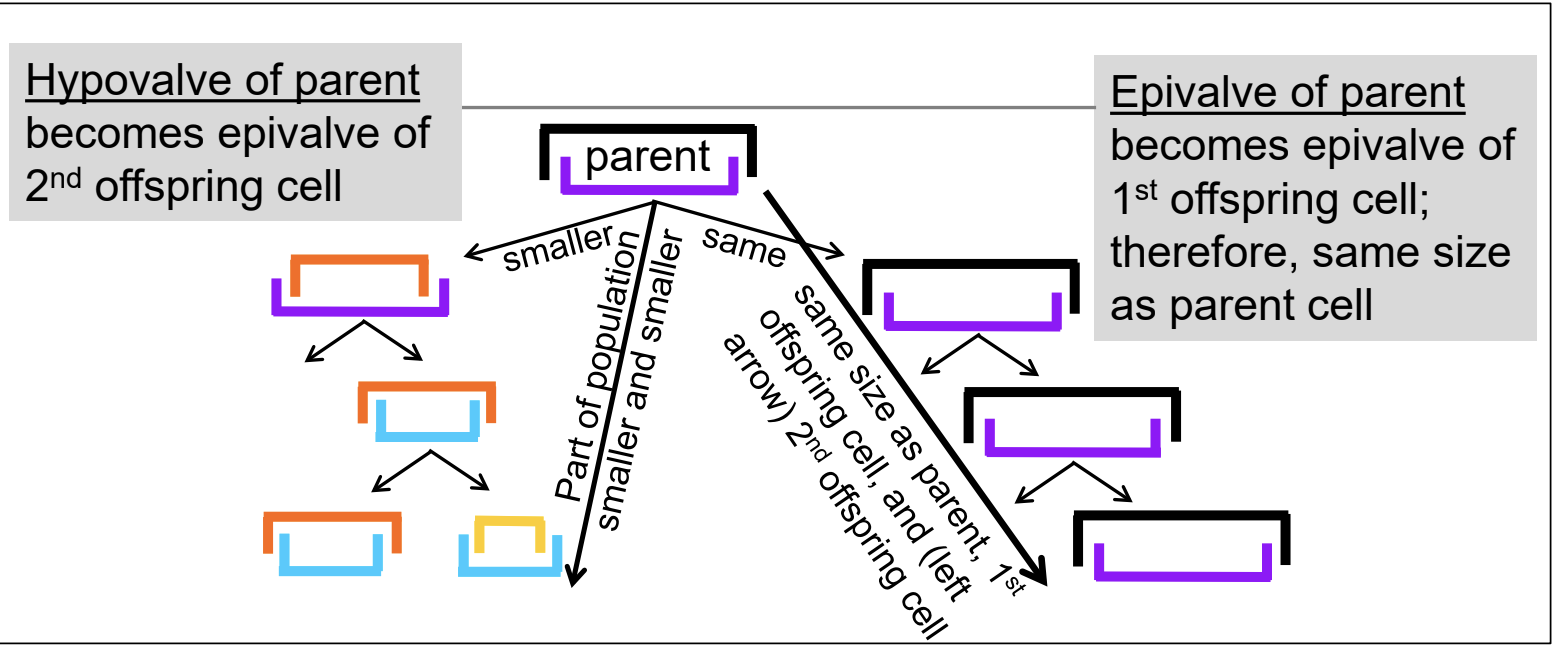
How can diatoms increase their cell size despite the fact that glass walls can’t stretch?
sexual reproduction
Draw and label a motile diatom, showing at least 5 ornamental features in the “top” of the cell wall (valve view).
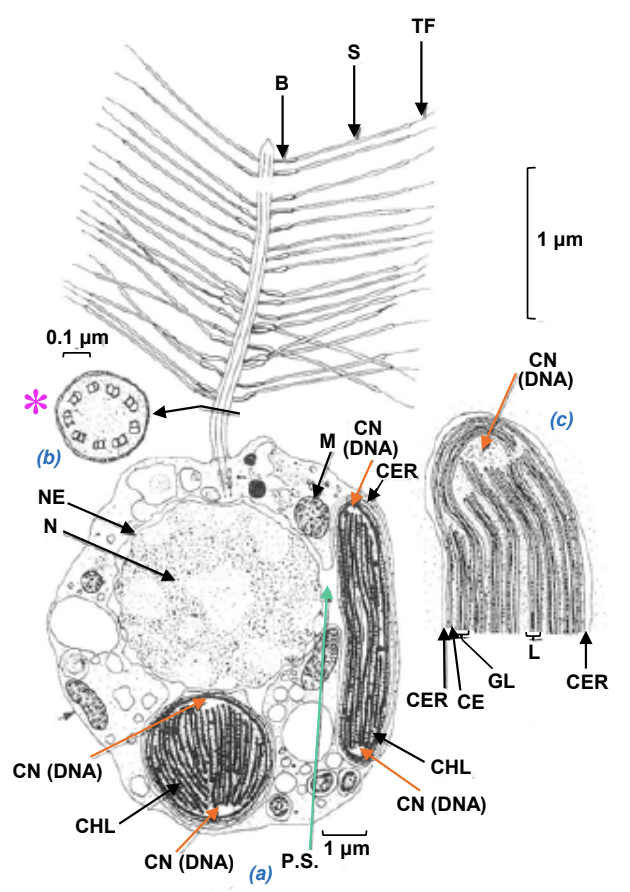
Draw and label the life history (including sexual reproduction) of a centric diatom. Briefly describe how this process differs in pennate diatoms. Life history shorthand?
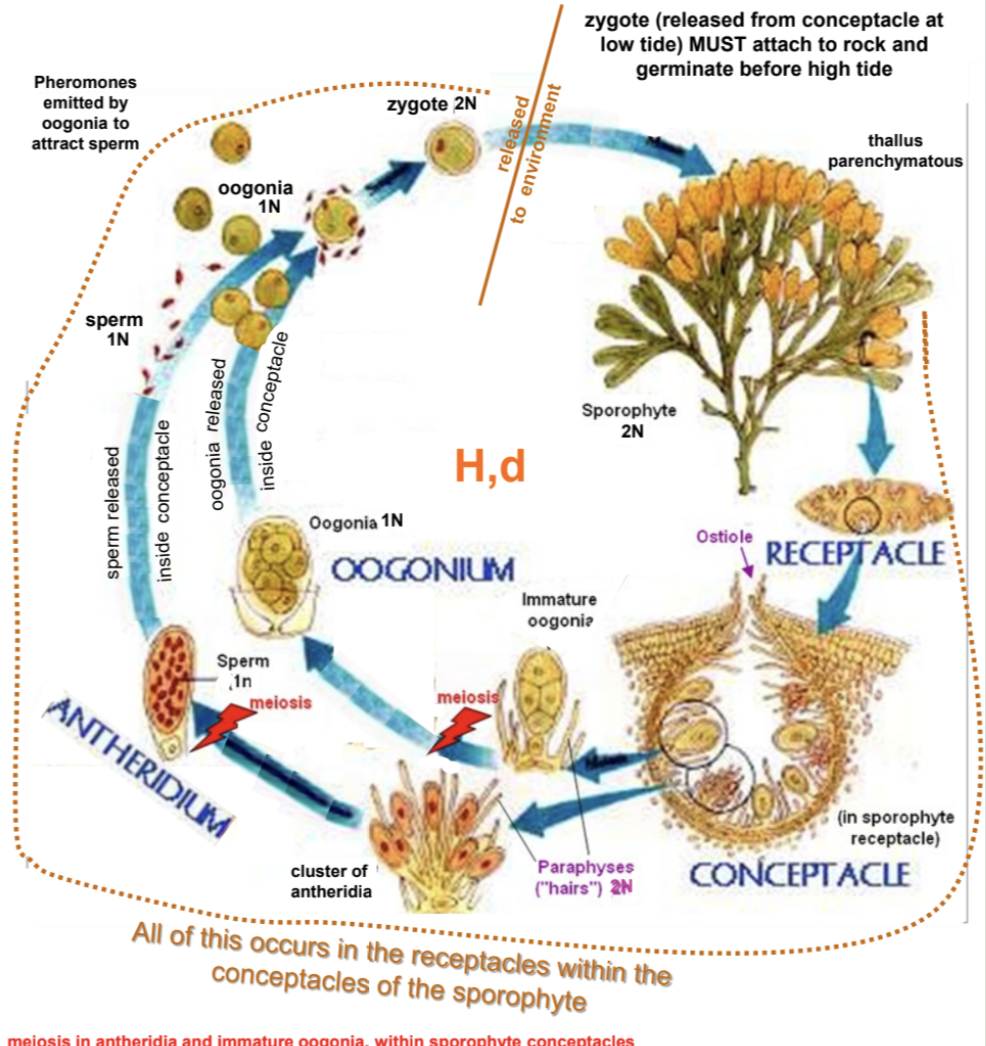
H,d
How are the relative proportions of centric vs. pennate diatoms used as indicators of cultural eutrophication?
microfossils, eutrophication in the paleo sediment record
Name the infamous toxic diatom complex. Habitat? What toxin is produced? What is its main impact on humans in sublethal exposure? (and give the common name). Describe an incident of impacts on wildlife.
Pseudo-nitzschia complex, Nitzschia spp.– ASP, amnesic
shellfish poisoning (sw)

Pelagophyceae Habitat(s)? Basic morphology(s)? Two major distinguishing features?
small coccoid unicells, mostly marine, anterior flagellum sometimes has a paraxonemal rod, perforated theca
Pelagophyceae Describe the ecological importance of brown tides (including where they occur).
massive dieoffs and failures to reproduce everything from fish to plankton, sand-dwelling
Chrysophyceae Major habitat(s)? Two major distinguishing features of this class?
mostly planktonic biflagellate unicells or colonies but VARIABLE; mostly freshwater mildly acidic, stomatocysts, microbial loop
Chrysophyceae Two major beneficial contributions? A negative impact?
stomatocysts, microbial loop
Chrysophyceae What is a special “claim to fame” of Dinobryon? Briefly describe the importance of this discovery across aquatic ecosystems.
microbial loop, phago bacteria
Synurophyceae Major habitat(s)? Two major distinguishing features of this class?
biflagellate cells, solitary or colonial; freshwater, flagella with parallel orientation, directed forward; no flagellar swelling, stomatocysts
Two characteristics distinguishing the closely related chrysophyceans vs. synurophyceans?
Si not essential and no CER-NE connection in synurphyceans
What is a potential economic problem caused by certain synurophyceans?
taste-and-odor problems
Eustigmatophyceae Major habitat? Two distinguishing features?
solitary flagellates or coccoid cells (very small to moderate in size); mostly frw or soil but includes sw, picoplankter Nannochloropsis, stigma, OUTSIDE the chloroplast, NO
girdling lamella
Two differences between eustigmatophyceans and chrysophyceans?
fucoxanthin, pigments
Two similarities between eustigmatos and raphidophyceans?
chla, fucoxanthin absent (only some raphidophyceans)
Raphidophyceae Major habitat? Two distinguishing features? How do frw vs. brw/sw raphidophyceans differ (two ways)?
relatively large flagellates (can also go palmelloid); mostly brackish-marine, no CER-NE connection, NE closed and intact during mitosis
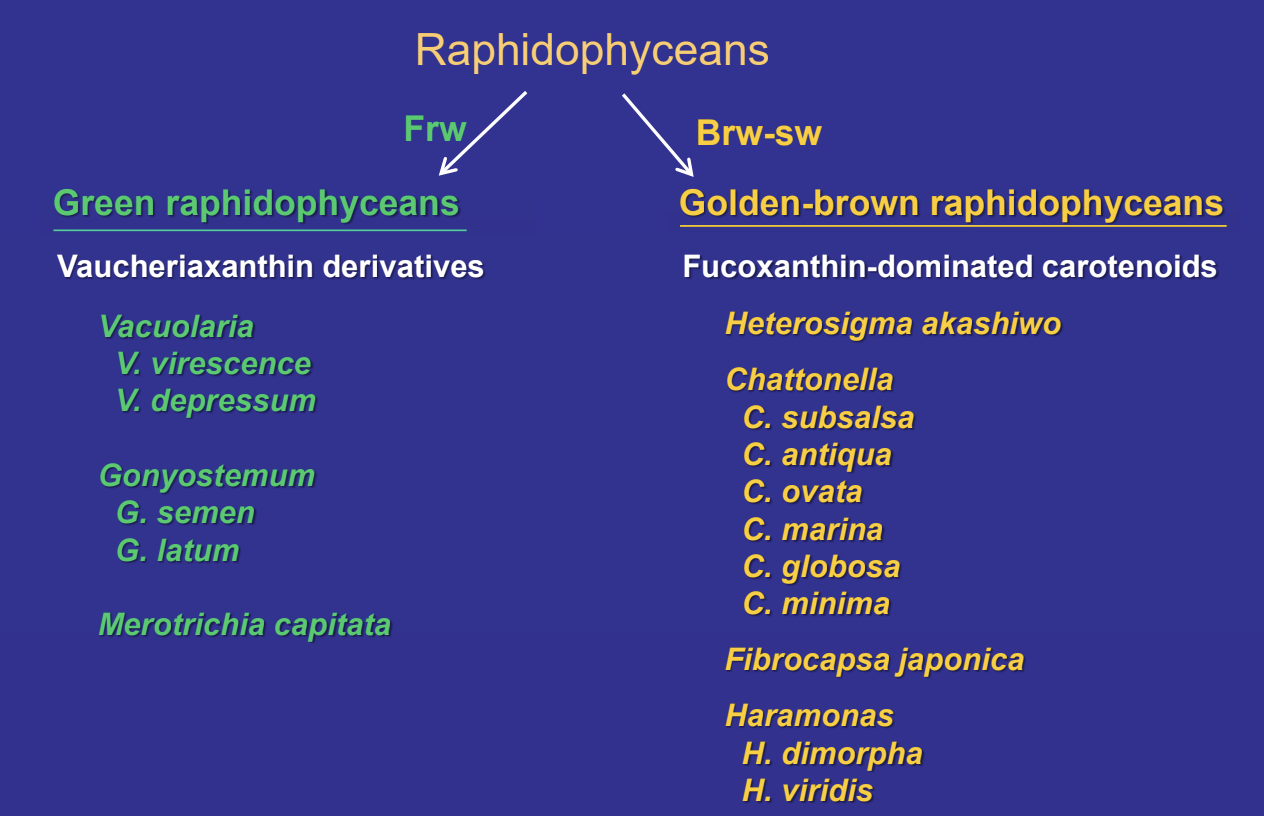
Briefly describe two types of toxins produced by some raphidophyceans [name a genus involved], general impacts, where such problems have occurred, and whether these blooms are exacerbated by nutrient pollution.
Chattonella marina, (ROSs, neurotoxins, hemolytic substances), Massive kills of yellow tail tuna in Japan
Xanthophyceae Major habitat(s)? Most common morphology(s)?
VARIABLE; mostly frw or soil; some brw-sw, synzoospores, chla
Describe the photosynthetic pigments of Xanthophyceae
chla
Phaeophyceae Major habitat(s)? Range in size?
Almost entirely marine, (~20 μm to > 60 m in length)
What are three major food storage products and two economic uses of browns’ phycocolloids?
mannitol, sucrose, and/or glycerol, confer stability, help prevent desiccation, function in ion exchange
Describe famous ecological importance of brown “seaweeds” including a genus / species; and of kelps (including a genus).
Allelopathy Fucus and Sargassum, Macrocystis kelp forests
What brown algal genus has been wreaking havoc in the Atlantic Ocean? Describe what’s happened
Sargassum, above-average sea surface temperatures and high levels of nutrients (N and P)
What are two allelopathic types of compounds produced by brown algae? What is an apparent major ecological function of each?
phlorotannins, polyphenolics, deterring herbivory
Draw and label the basic thallus morphology of a kelp.
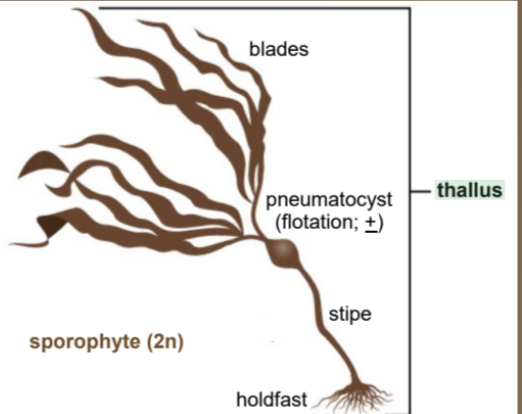
Briefly describe two structural traits shared by certain brown algae and higher (land) plants that “defy” the definition of algae.
Meristematic, Primitive phloem
Briefly describe three basic tissue types in kelps.
Meristoderm of the cortex - outer layer of pigmented cells
Mid-cortex - internal to the meristoderm
Medulla - loose network of longitudinally directed cells
What are three types of meristems found in kelps?
intercalary meristem
meristoderm
basal meristem
Briefly describe phloem and transport rates (of what?) in kelps.
sieve elements + trumpet hyphae or hyphal cells, mannitol transport
What is a natural enemy of kelps, and how have humans helped it?
urchins, we hunt their otter predators for fur
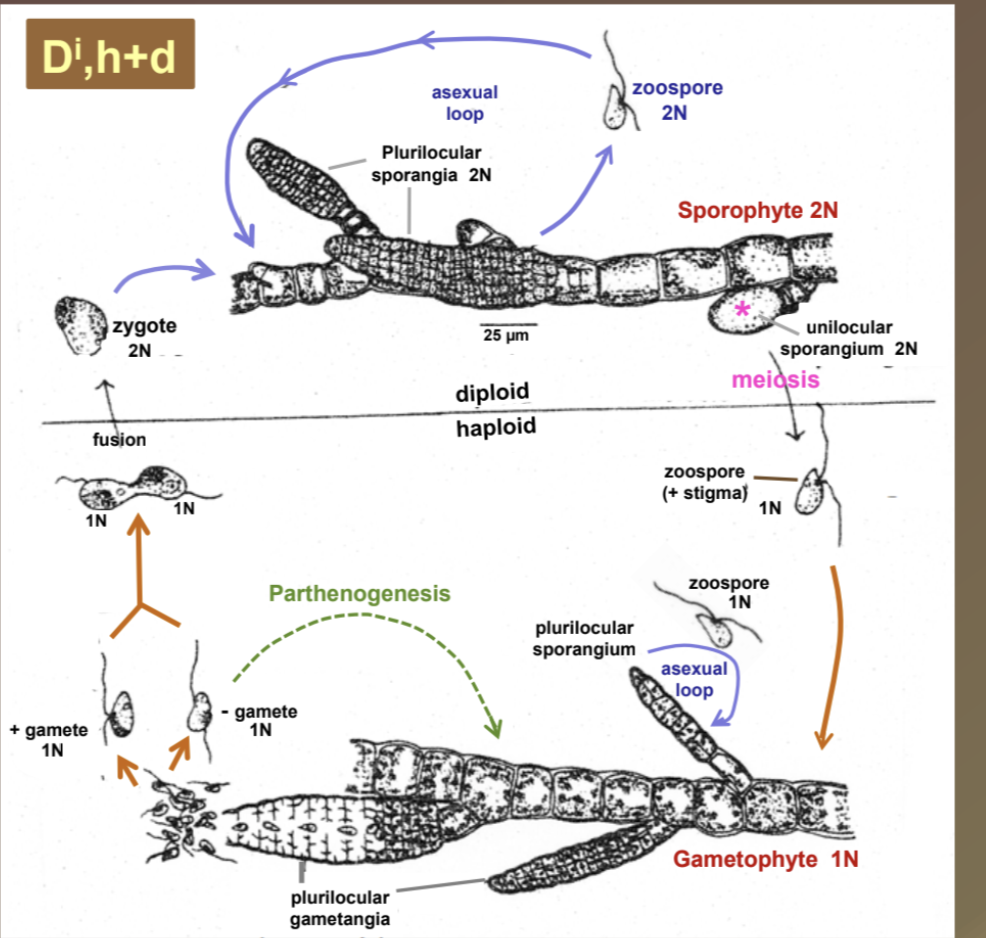
Ectocarpus life history
Di, h+d
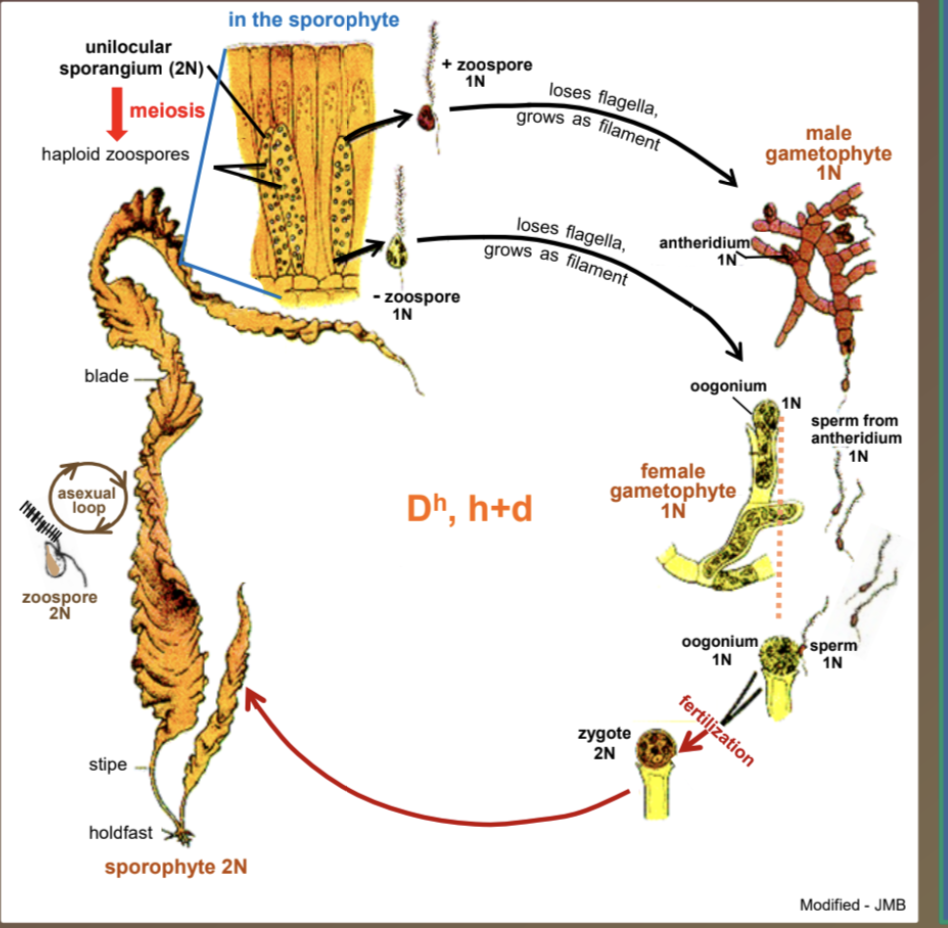
Laminaria life history
Dh, h+d
Fucus life history
H,d