L2 Innate Immune System (macrophage)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Primary Lymphatic Organs
Bone marrow, thymus, fetal liver
(main job is develop+create immune cells)
Secondary lymphatic organs
Spleen, lymph nodes, lymph ducts, tonsils, adenoids (specialize and mature)
Lymphatic vessels
part of circulatory system; carry clear fluid (lymph) towards heart, transport immune cells
First Line of Immune Defense
Physical barriers (skin, mucus) and chemical barriers (pH, lipids, enzymes)
Second line defense
Innate immune system, nonspecific response (phagocytic cells, inflammatory response, NK cells, etc.)
Third Line of Immune Defense
Adaptive immune system; specific slower response; improved recognition/immunological memory- faster secondary response (B and T Cells)
Innate Immune System Cells
Phagocytes: monocyte/macrophages, neutrophils
Mast cells, eosinophils, basophils (Granulocytes) (for bacterias, release enzymes to kill)
NK cells, innate lymphoid cells
Adaptive Immunity Cells
Specific Antigen receptors, B Cells (Humoral) (antibodies), T cells (Cell mediated) (Lymphokines), NKT cells
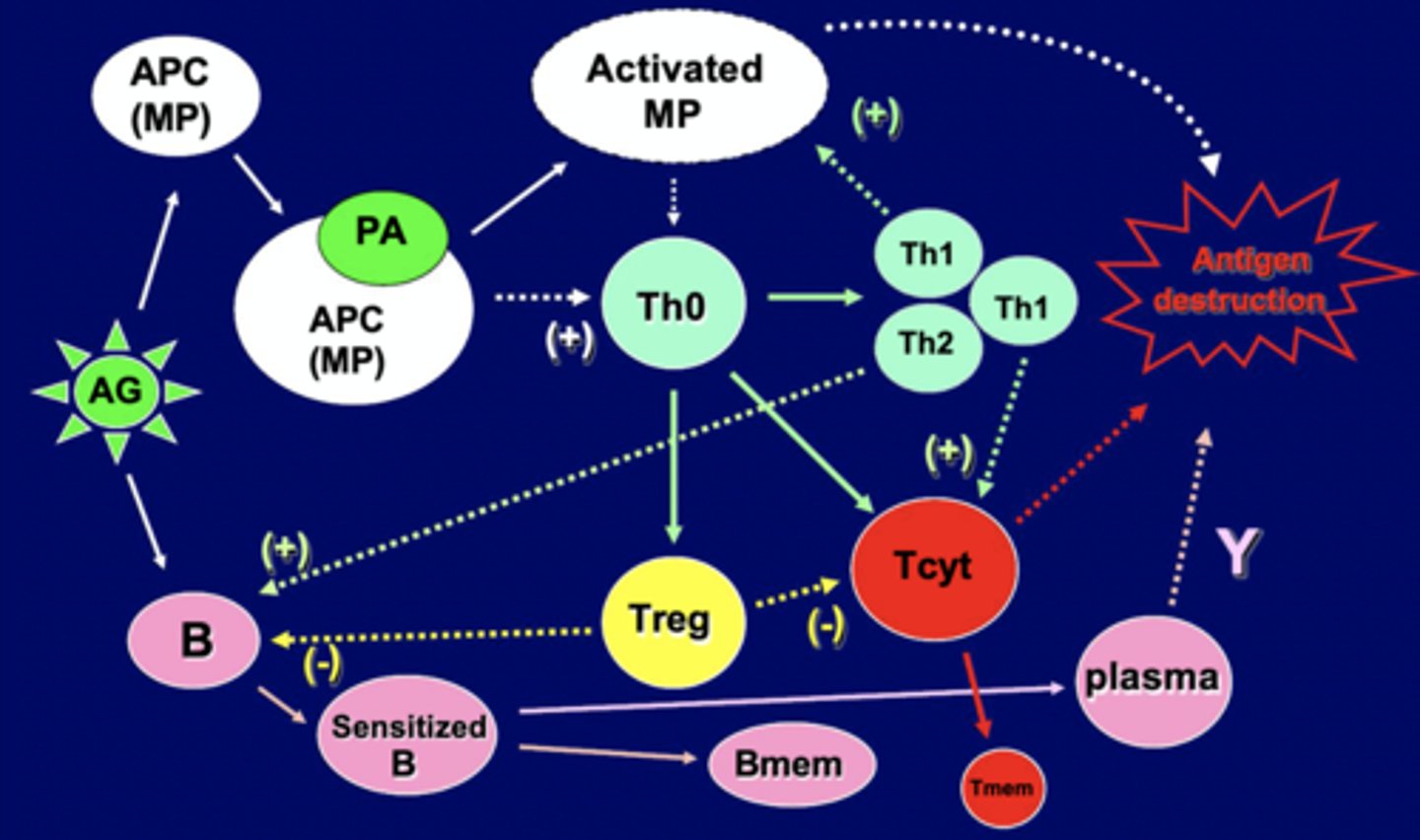
Cell interactions of Immune System
Antigen leads to APC MP, combines with MP, and leads to activated MP. Leads to production/activation of T-helper cells, making TH1 (turn on more macrophage) and Th2 (Turn on B cells). T helpers also help turn on regulatory T or Killer T cells.
B Cells turned on by Th2 and Antigen, leading to sensitized B cells, and memory B cells. Sensitized B cells also turn into plasma cells that secrete antibodies
B cells and killer T cells are regulated.
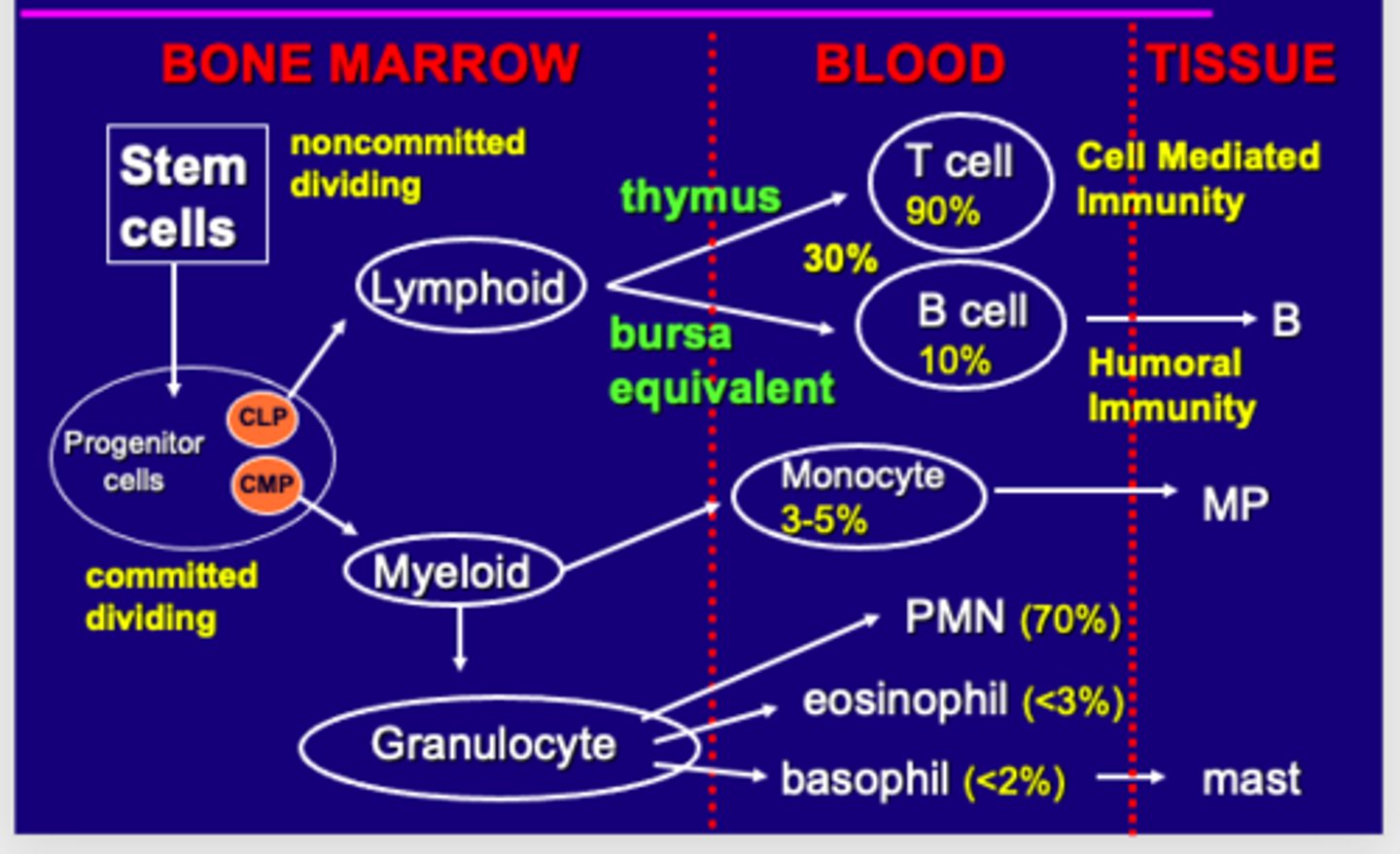
Origin and Development of Immune Cells (Bone Marrow, Blood, Tissue)
In the bone marrow Stem cells turn into progenitor cells (Common lymphoid or Common Myeloid progenitor) that are committed in specialization and dividing
CMP turn to myeloid and then granulocyte in bone marrow while CLP turns into lymphoid in bone marrow.
Through thymus lymphoid cells turn into either T cells (90%) or B cells (10%) live in the blood. Granulocyte specializes in blood into PMN (neutrophils 70), eosinophil (<2), and basophils (<3). Myeloid also turn into monocytes here
T cells go into tissue when cell mediated while B cells turn into B cells living in the tissue for humoral immunity as memory
Basophils turn into mast cells to cause inflammatory reaction.
Monocyte become macrophage in tissue
Innate Immune System Functions
Nonspecific Defense: Doesn't require specific antigen receptors/no prior learning
Provides barriers (physical, mechanical, chemical, cellular)
Identify and eliminate pathogens + other foreign bodies
initiate inflammatory response
Activate specific immune responses (macrophages)
Neutrophils/PMN (Presence, lifespan, functions)
60-70% of WBC, present in tissue at low levels (increase following injury/infection)
9-12 hour life span
First cell at site of infection/injury
Ingest+kill microbes and foreign materials; involves PAMPs (for nonsterile infections) and DAMPs (for sterile inflammatory response) that bind to PRRs
Mononuclear phagocytes (presence, lifespan) +Types of macrophage
1-6 % WBC (MONOCYTES), in tissue is macrophages
Resident macrophage- throughout body, largest population in liver and lung; come from embryonic origins
Inflammatory macrophage: response to injury and infection; come from bone marrow
Life for a very long time
Function of Macrophage
Identify+eliminate pathogens. Has PRR activated by PAMP/DAMP; scavenger receptors; use phagocytosis, pathogen destruction or isolation
Regulate inflammatory response, initiate would healing and promote angiogenesis
Maintain homeostasis; lipid and iron metabolism
Major secretory activity
Activate adaptive immunity (APC+Th Cell activation)
Tumor surveillance and cytotoxicity
Macrophage plascitity
Macrophage modify phenotype/reprogram based on pathophysiologic conditions.
M1-M2 reprogramming help with inflammation resolution and wound repair
Inflammation
response of vasularized tissue to injury/infection, brings defense and healing mechanisms to site of injury
Neutralizes/destroys offending agent, restricts tissue damage to small area, and alerts body to repair/heal
Acute Inflammatory Response (initial+secondary)
Short term response
initial is proinflammatory/cytotoxic caused by neutrophils+m1 macrophage accumulation, release mediators to destroy pathogen+increase inflammatory cells (call in neutrophils)
Secondary: anti/wound repair
M2 macrophage accumulate and release mediators to surpress inflammation + promote wound repair
How to resolve inflammation+wound repair?
Neutrophils undergo apoptosis
Proresolving mediators (lipoxins, resolvins, protectins) released to stimulate M2 efferocytosis/clean up of apoptic dead cells
M2 release mediators to down regulate inflammation (IL1-10, 4, 13)and promote wound repair and angiogenesis (TGFb, EGF, VEGF)
Release chemokines to stimulate fibroblast emigration to inflamed sites, produce ECM proteins
Inflammation Resolution failure
Chronic inflammation, foreign body response, granulomas, cancer
Chemotaxis
Migration to injured/infected site caused by chemotactic factors (Complement, fMLP)
How to remove/localize foreign bodies
Chemotaxis, phagocytosis, metabolic destruction, isolation of foreign body
Foreign Body Reaction
Macrophage wall off body if can't destroy it. Macrophage will fuse into giant cells, recruit other cells like PMN, lymphocytes, eosinophils, fibroblasts, form fibrous capsule around foreign body
FBR depends on size, structure, and surface character of FB.
Granulomas can lead to chronic inflammatory response
Macrophage Secretory Function (3 things)
Release degrading enzymes for ECM proteins (collagenase, elastase)
Release host defense enzymes ROS, RNS, protease, eicosanoids for host defense
Release regulatory proteins like cytokines/chemokines/growth factors/lipids
Immune Function of Macrophage
Antigen processing/presentation
Tumor Cytotoxicity
Tumor surveillance
Macrophage Antigen Processing
Phagocytosis of antigen, degradation/unfolding, bind to MHC II protein on APC, re express processed antigen together with MHC II, present to T-helper cells
NK Cells
Type of cytotoxic lymphocyte part of innate immune system
Apoptosis mediated by granules of perforin+granzyme, comes from CLP
ILC/Innate Lymphoid Cells
Three subsets + interleukins produced
Derived from CLP, is innate, analogous to helper T cells and cytotoxic NK cells (regulate homeostasis and inflammation)
Subsets defined by cytokines:
ILC1: weakly cytotoxi, produce TNFa and IFNg
ILC2: produce IL(interleukin) 4, 5, 9, 13: type 2 cytokines
ILC3: Produce IL 17+22
M1 vs M2 Macrophage
both come from bone marrow m0 macrophage
M1: Cytotoxic/proinflammatory; stimulate immune system (neutrophils)
M2: Anti-inflammatory/wound repair, has four subsets
a: Type II inflammation+Allergy+ killing parasites
b: Th2 Activation (Lead to B cell activation)
c: Immunoregulation, matrix deposition, tissue remodeling
d: cell cycle regulation