Principles of Life, Ch. 10 Reading
0.0(0)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/77
Last updated 3:08 PM on 10/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
1
New cards
Proteins in the ________ that lack signal sequences for destinations within the endomembrane system are usually secreted from the cell via vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane.
RER
2
New cards
Requires a promoter (special region of DNA to which the ________ binds) to tell ________ where to begin and which of the 2 strands to transcribe.
RNA polymerase
3
New cards
When not active in the ________ the ribosome exists as two separate subunits.
translation of mRNA
4
New cards
________ can technically start synthesizing anywhere, but DNA sequences and certain proteins tell ________ where to stand.
RNA
5
New cards
________ occurs when RNA polymerase catalyzes the formatio nof phosphodiester bonds between added nucleotides and the growing RNA chain, releasing pyrophosphate in the process.
Transcription
6
New cards
________ bind by hydrogen bonds and run antiparallel.
Codon & anticodon
7
New cards
________ A change in a genes sequence that changes the amino acid at that site in the encoded protein; usually causes a single amino acid change in the protein, which may or may not cause a change in function.
Missense mutations
8
New cards
________ read the DNA template in the 3 to 5 direction and synthesize the RNA strand in the 5 to 3 direction.
RNA polymerase
9
New cards
Helps export ________ from nucleus, bind proteins, and makes ________ stable.
mRNA
10
New cards
________ interrupt, but do not scramble, the DNA sequence of a gene.
Introns
11
New cards
TRNAs bind to particular ________.
amino acids
12
New cards
________ spliced out of pre- mRNAl 5 cap and 3 poly A tail added to mRNA.
Introns
13
New cards
When a(n) ________ is encoded by four codons, the first two letters are always the same.
amino acid
14
New cards
There is at least 1 specific tRNA molecule for each of the 20 ________.
amino acids
15
New cards
The synthesis of RNA using one strand of DNA as a template
Transcription
16
New cards
The synthesis of a protein (polypeptide); Takes place on ribosomes, using the information encoded in messenger RNA
Translation
17
New cards
The premise that information flows from DNA to RNA to polypeptide (protein)
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
18
New cards
Most abundant RNA types
mRNA, rRna, and tRNA
19
New cards
Encodes protein information that comes from a template strand of DNA; leaves the nucleous
mRNA
20
New cards
One of the two strands of DNA that for a particular gene specifies the amino acids in a protein; Same base sequence as transcribed RNA but with Ts instead of Us
Coding Strand
21
New cards
The DNA strand that is transcribed to create an RMA transcript; Also refers to a strand of RNA that is used to create a complementary RNA
Template Strand
22
New cards
Several species of RNA that are incorporated into the ribosome; Involved in peptide bond formation
rRNA
23
New cards
A family of folded RNA molecules; each carries a specific amino acid and anticodon that will pair with the complementary codon in mRNA during translation; recognizes which amino acid needs to be added next
tRNA
24
New cards
a protein that binds to RNA polymerase, allowing the complex to bind to and stimulate the transcription of a specific class of genes
Sigma Factors
25
New cards
Proteins that assemble on a eukaryotic chromosome, allowing RNA polymerase II to perform transcription
Transcription Factors
26
New cards
The nucleotide sequences in a gene that directly specify amino acids in a protein
Coding Regions
27
New cards
A portion of a gene within the coding region that is transcribed into pre-mRNA but is spliced out prior to translation
Introns
28
New cards
A portion of a DNA molecule, in eukaryotes, that is present in the mature mRNA and codes for part of a polypeptide
Exons
29
New cards
The initial gene transcript before it is modified to produce functional mRNA; Also known as the primary transcript
Pre-mRNA
30
New cards
introns are removed, and both ends of the pre-mRNA are chemically modified
The primary transcript of a eukaryotic gene is modified in several ways before it leaves the nucleus
31
New cards
The last stage of RNA processing in eukaryotes, in which the transcripts of introns are excised through the action of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNP)
RNA Splicing
32
New cards
Short stretches of DNA that appear, with little variation, in many different genes
Consensus Sequences
33
New cards
A conserved sequence (A followed by several pyrimidines) in the interior of an intron that is used during intron splicing to attach the 5 end of the intron
Branch point
34
New cards
A complex of an enzyme and a small nuclear RNA molecule, functioning in RNA splicing
snRNPs
35
New cards
An RNA-protein complex that splices out introns from eukaryotic pre-mRNAs
Spliceosome
36
New cards
A chemically modified GTP added to the 5 end of mRNA; facilitates binding of mRNA to ribosome and prevents mRNA breakdown
5 Cap
37
New cards
A long sequence of adenine nucleotides (50-250) added after transcription to the 3 end of most eukaryotic cells
Poly A Tail
38
New cards
Three nucleotides in messenger RNA that direct the placement of a particular amino acid into a polypeptide chain
Codons
39
New cards
The set of instructions, in the form of nucleotide triplets, that translates a linear sequence of nucleotides in mRNA into a linear sequence of amino acids in a protein
Genetic Code
40
New cards
A sequence of three nucleotides in an mRNA that encodes a particular amino acid
Sense Codons
41
New cards
The mRNA triplet (AUG) that acts as a signal for the beginning of translation at the ribosome
Start Codon
42
New cards
An organism engineered to contain, and usually express, a gene from another organism
Transgenic organisms
43
New cards
When a DNA substitution alters the codon but does not alter the encoded amino acid; occur because of the degeneracy of the genetic code
Synonymous mutations
44
New cards
A change from a sense codon to a stop (nonsense) codon, causing a premature termination of translation and a shortened protein; usually also loss of function
Nonsense mutations
45
New cards
A change from a stop codon to a sense codon, causing additional amino acids to be added to the end of the protein; effects depend on how many amino acids are added to the end of the protein and how important that part of the protein is to function
Loss-of-stop mutations
46
New cards
The addition or deletion of a single or two adjacent nucleotides in a genes sequence; Results in the misreading of mRNA during translation and the production of a nonfunctional protein
Frame-shift mutations
47
New cards
The three nucleotides in transfer RNA that pair with a complementary triplet (a codon) in messenger RNA
Anticodon
48
New cards
certain bases in the third position of the anticodon are able to pair with more than just their normal partner
Wobble
49
New cards
highly specific enzymes that only bind to one amino acid and one corresponding tRNA, binds using energy
tRNA synthetases
50
New cards
initiation, elongation, termination
Three steps of translation
51
New cards
In protein translation, a combination of a small ribosomal subunit, an mRNA molecule, and the tRNA charged with the first amino acid coded for by the mRNA; formed at the onset of translation
Initiation Complex
52
New cards
The proteins involved in helping to assemble the translation initiation complex
Initiation factors
53
New cards
An RNA molecule with catalyctic activity
Ribozyme
54
New cards
The sequence within a protein that directs the protein to a particular organelle
Signal Sequence
55
New cards
Cutting a polypeptide chain; large polyproteins cannot function unless cut
Proteolysis
56
New cards
Addition of carbohydrates to proteins to form glycoproteins; helps direct some proteins to lysosomes, or help for conformation/regcognition functions at the cell surface
Glycosylation
57
New cards
the additon of phosphate groups to proteins, catalyzed by protein kinases; helps with cell signaling
Phosphorylation
58
New cards
• Used Neurospora (bread mold) to test hypothesis that
specific gene expression → specific enzyme activity.
• All alleles are expressed as phenotypes.
• Wild-type strains have all enzymes to catalyze chemical reactions to make cell constituents.
• They treated wild type Neurospora with mutagens and isolated mutant strains that needed specific nutrient supplements to grow
• For each mutant strain, the addition of just
one compound supported growth.
• Results suggested that each mutation caused a defect in only one enzyme in a metabolic pathway.
specific gene expression → specific enzyme activity.
• All alleles are expressed as phenotypes.
• Wild-type strains have all enzymes to catalyze chemical reactions to make cell constituents.
• They treated wild type Neurospora with mutagens and isolated mutant strains that needed specific nutrient supplements to grow
• For each mutant strain, the addition of just
one compound supported growth.
• Results suggested that each mutation caused a defect in only one enzyme in a metabolic pathway.
Beadle and Tatum
59
New cards
Translation in these species happens because the nuclear envelope separates transcription & translation.
DNA in nucleus, site of
transcription
Ribosomes in cytoplasm (ER), site of translation
mRNA is the intermediate messenger
DNA in nucleus, site of
transcription
Ribosomes in cytoplasm (ER), site of translation
mRNA is the intermediate messenger
Eukaryotes
60
New cards
Translation occurs on growing mRNA for these species.
Prokaryotes
61
New cards
RNA polymerases can only add new nucleotides to the __________ of a growing strand.
3'
62
New cards
Transcription factors only occur in...
Eukaryotes
63
New cards
The template of DNA is TGACT. What is the mRNA (with start location)?
5' ACUGA
64
New cards
The mRNA is the same as the ______ end of _______, just replace T with U.
5', non-template DNA
65
New cards
This is added to the 5' end of pre-mRNA. Protects mRNA from being degraded and facilitates mRNA binding to the ribosome.
G cap
66
New cards
Added to the 3' end while processing ends of eukayotic pre-mRNA. May assist in export from nucleus.
Poly A tail
67
New cards
Start codon that initiaties translation.
AUG
68
New cards
Initiation signal for translation is near which end of mRNA?
5'
69
New cards
Stop codons that stop translation and polypeptide is released.
UAA, UAG, UGA
70
New cards
mRNA consists of...
5' cap, Start codon, exons, stop codon, poly a tail
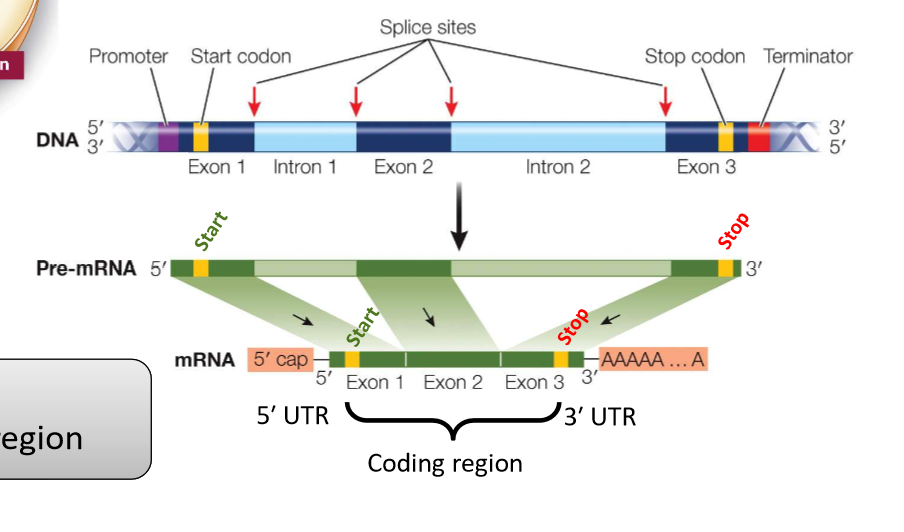
71
New cards
Name for the start codon (AUG)
Methionine
72
New cards
The DNA template for arginine is 3' GCC 5' what is the codon within mRNA?
5' CGG 3'
73
New cards
The DNA template for arginine is 3' GCC 5' what is the anticodon on the tRNA?
3' GCC 5'
74
New cards
Three tRNA binding sites on the large subunit of the ribosome.
A site, P site, E site
75
New cards
During elongation, charged tRNAs enter the _______ site, large subunit acts as peptidyl transferase.
A
76
New cards
During termination, the stop codon enters the _________ site.
Termination
77
New cards
The bond is broken between the tRNA and its amino acid at the _______ site.
P
78
New cards
When the first tRNA has released its methionine, it moves to the ______ site and dissociates from the ribosome.
E