ZOOL 110 lecture exam 2 study guide
1/209
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
Lung
highly vascularized space within the mantle cavity of pulmonate gastropods that functions in gas exchange
Neurohypophysis
the posterior half of the pituitary gland that secretes neurohypophyseal hormones
Chondrocyte
a flagellated collar cell that lines the cavities and canals of sponges
Zooid
an individual member of a colony
Action Potential
a brief change in voltage across the cell membrane of a neuron, involved in passing an impulse along an axon
Digenetic
A parasite that has two hosts
Pharynx
the part of the digestive tract between the mouth and esophagus, involved in digestion and respiration
Flame cell
osmoregulatory cell containing a tuft of flagella, also known as a protonephridium
Dioicous
Having two separate sexes that participate in reproduction
Setae
Chitinous external structures present in polychaetes and oligochaetes
Stinging cell that defines Phylum Cnidaria
Cnidocyte
Muscle that functions to close the shell in Class Bivalvia
what electricity is used for in fishes
Hemoglobin _________ its affinity for oxygen at a low pH (more acidic conditions), and__________ its affinity for oxygen when there is a high partial pressure of O2 in surrounding tissue
Decreases, increases
White matter appears white because it is composed of _________________
Myelinated axons of neurons
Dilation of the pupils, an increased heart rate, and dilation of the bronchioles would be due to what division of what nervous system?
Sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
What is the function of a plasma cell
Produce antibodies
The ctenophore gut is
Complete
The cnidarian group that produces coral reefs is called
Hexacorallia
Nematodes have __________ body wall muscles
only longitudinal
oxytocin
In mammals, acts on mammary glands, induces powerful uterine contractions
Growth hormone
Stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and regeneration
adrenocorticotropic hormone
Stimulates adrenal cortex to produce aldosterone or cortisol
gonadotropins
Promote gamete production, stimulate production of sex hormones
ADH
Increases permeability of the kidney’s collecting duct
Depict the path of an action potential from the stretch receptor in your thigh muscle, through a reflex arc, to its effector
stretch receptor → afferent sensory neuron → efferent motor neuron → leg muscle (effector)
Depict the pathway of air into human lungs
nasal cavities → pharynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli
Depict the pathway of water through a complex sponge (leuconoid, for example).
Ostia → incurrent canal → flagellated chamber of choanocytes → excurrent canal → osculum
What features define Nematoda? How are they different from phyla Platyhelminthes & Nemertea?
The most abundant animals, can be parasitic or free living. Pseudocoelomate
What clade are the nematodes found in? What’s ecdysis?
nematodes are in the Ecdysozoa clade. Ecdysis is the molting of the cuticle.
Why do nematodes thrash back and forth when they move?
They only have longitudinal body wall muscles and a pseudocoel that works like a hydrostatic skeleton
Do nematodes have an incomplete gut or a complete gut?
complete gut
Where do nematodes live and what do they eat?
Nematodes are found in marine, freshwater, and soil environments. They can be parasitic or free living. They eat bacteria, yeasts, fungal hyphae, algae, rotifers, tardigrades, small annelids, or other nematodes
lophophore
a horseshoe shaped feeding appendage
Trochophore
free swimming larva with a “skirt” of cilia
How do we define the clade Lophotrochozoa?
have a lophophore or a trochophore larva (except for Phylum Platyhelminthes)
What is a worm?
Bilateral elongate invertebrate without limbs
Why type of coelom does phylum Platyhelminthes have
Acoelomate (no coelom)
does phylum Platyhelminthes have a complete or incomplete gut
incomplete gut
What is the nervous system of phylum Platyhelminthes
paired anterior ganglia + longitudinal nerve cords
What are the sense organs of phylum Platyhelminthes
statocysts + ocelli
How do Platyhelminthes reproduce
Sexually through internal fertilization (penis fencing) or asexually through fragmentation
What type of cells are Platyhelminthes excretory system
flame cells
is turbellaria monophyletic
no, paraphyletic
class turbellaria belongs to what phylum
Platyhelminthes
How many species are in class turbellaria
4500
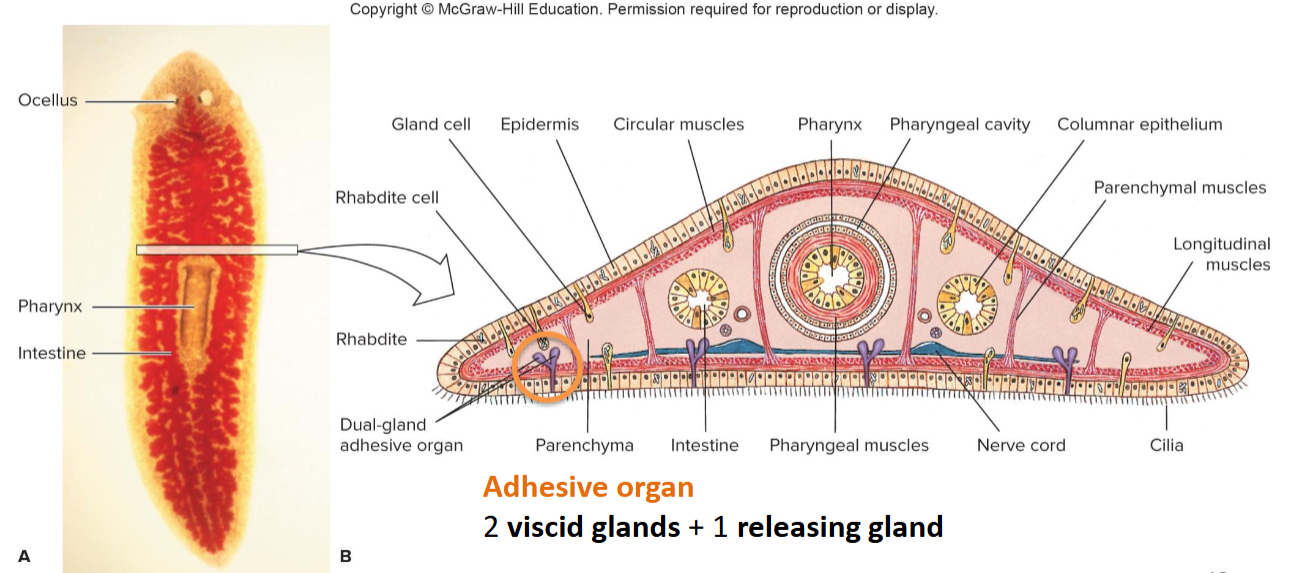
Class turbellaria body plan
Ciliated epidermis w/rhabdites, body wall muscles + muscles around pharynx
What is the only Platyhelminthes class that is not exclusively parasitic
class turbellaria
class Trematoda belongs to what phylum
Platyhelminthes
is class Trematoda monogenetic or digenetic
digenetic
Class Monogea belongs to what phylum
Platyhelminthes
Is class Monogea typically ectoparasites or endoparasites
typically ectoparasites of fish gills
Is class Monogea monogenetic or digenetic
monogenetic
Class Cestoda belongs to what phylum
Platyhelminthes
Cestoda body plan
repeating segments (proglottids) + posterior scolex to attach to the host
what kind of gut does class cestoda have
no gut
What is class cestodas nervous system
Longitudinal nerve cords
how many species are in class termatoda
11,000
how many species are in class monogea
1100
how many species are in class cestoda
4500
what kind of coelom does phylum nemertea have
Eucoelomate (true coelom)
Why clade does phylum Nemertea belong to
Kryptrochozoa
What features define Nemertea
long evertible proboscis, Most < 20 cm long, Outer circular & inner longitudinal muscles, blood-vascular system
does phylum Nemertea have a complete or incomplete gut
complete
How do nemertean worms feed?
Proboscis
Nemertean nervous system
4 lobed brain connected to paired longitudinal nerve trunks
Features shared by all cnidarians
cnidocytes, diploblastic, radial symmetry, intra and extracellular digestion,
Features shared by all ctenophores, and why they are different from cnidarians
diploblastic, bilateral symmetry, no cnidocytes, 8 comb rows
Do cnidarians have true muscles?
no, they have epitheliomuscular cells of epidermis and gastrodermis
What is the cnidarian nervous system like?
nerve net of neurons
In the life cycle of a hydrozoan (Obelia) is the polyp or medusa dominant
The Polyp is dominant
In the life cycle of a scyphozoan (Aurelia) is the polyp or medusa dominant
medusa is dominant
What is coral bleaching?
Corals expel their zooxanthellae. exacerbated by an increase in water temperature & by ocean acidification
What “first” structure is present in Ctenophora?
Anal canal
How do dinoflagellates (algae) & cnidarians work together?
The algae photosynthesize and provide the cnidarian with energy, while the cnidarian provides shelter
What phylum does class Anthozoa belong to
cnidaria
What phylum does class Hydrozoa belong to
Cnidaria
What phylum does class Scyphozoa belong to
Cnidaria
What phylum does class Cubozoa belong to
Cnidaria
What phylum does class Staurozoa belong to
Cnidaria
Class Staurozoa features
obscure cold water forms, no medusa phase
Class Cubozoa (box jellyfish) features
pedalium (base of tentacle), eyes present, velarium (subumbrella)
Class Scyphozoa (true jellyfish) features
oral arms around mouth, tentacles may be long or short
Class Hydrozoa features
most variable, similar to scyphozoans but have velum
Class Anthozoa features
largest class, includes sea anemones, stony corals
Subclass Hexacorallia features
Hard corals, major reef-building organisms, symbiotic dinoflagellate
Subclass Octocorallia features
soft corals, includes gorgonians, sea fans, whip
corals
Is Kingdom Protista monophyletic?
no, paraphyletic
What are the defining features of Phylum Porifera?
Extracellular matrix with collagen signaling molecules, blastula stage of development
How do poriferans feed?
Chondrocytes
How do sponges reproduce?
Asexually (external buds or gemmules) or sexually
How do sponges support their bodies
Spicules made of either spongin (collagen), calcium carbonate, or silica
How many classes of sponges are there?
4: Hexactinellida, Demospongiae, Calcarea, and Homoscleromorpha
Why are placozoans considered animals?
genetic sequencing
Features of Trichoplax adherens
marine, small (2-3 mm), flat sheet of cells
What is the HAM?
hypothetical ancestral mollusc
What features are considered synapomorphies for molluscs?
Head-foot, shell, radula, mantle and mantle cavity
Radula
rasping, protrusible tongue-like organ
Mantle
folds of skin (outgrowths of the body wall)
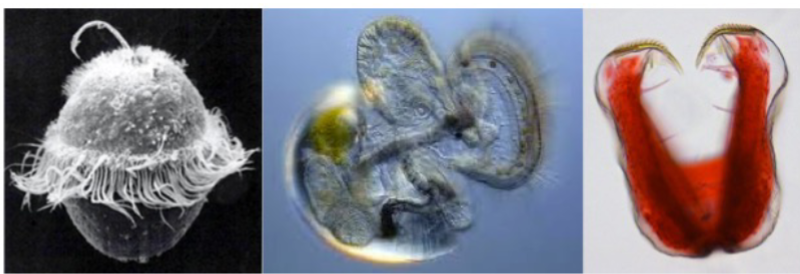
The three types of larvae in molluscs
trochophore, veliger, and glochidium
Class Polyplacophora in is what phylum
Mollusca